Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02441668 2003-09-24
Method for weaving an airbag
The invention relates to a method for broad loom machine
weaving an at least two-ply, one-piece airbag.
One-piece woven (OPW) airbags are known which find application
in the fabrication of vehicular airbag systems. For inflation
of such one-piece woven airbags a gas lance is inserted
thereinto. Experience has shown tears materializing in the
regions of the airbag in which gas is jetted into the airbag
from the gas lance. Gas lances often feature a train of slots,
so-called gills, oriented roughly transversely to the gas flow,
through which the gas is jetted into the airbag at several
locations. The aforementioned tears in the airbag may
materialize e.g. because of differences in the design of the
inflator, causing it to be more or less aggressive, termed
dispersion within and between inflator jets. Tears in the
airbag may also be influenced by the positioning of the jet
gills relative to the airbag chamber. In addition, airbag tears
more frequently occur in borderline situations as regards
inflator aggressiveness as well as the ambient temperature at
which the airbag is put to use.
21192222.1
CA 02441668 2008-01-23
2
The object of the invention is to propose a method for weaving
an at least two-ply, one-piece airbag in which the drawbacks as
known from prior art, particularly the incidence of tears in the
fabric occurring in the region impacted by the gas flow jetted
into the airbag, may be eliminated, alleviated or at least
reduced.
According to a first broad aspect of the present invention,
there is provided a method for machine weaving an at least two-
ply, one-piece airbag or air tube comprising weft threads of
differing dtex woven in at least one ply, wherein at least a
portion of the weft threads are picked only in defined warp
thread length regions.
According to a second broad aspect of the present invention,
there is provided a method for machine weaving an at least two-
ply, one-piece airbag or air tube comprising: weaving weft
threads of differing dtex in at least one ply, picking said weft
threads only in predetermined warp thread length regions, and
interweaving part of said weft threads only in predetermined and
non-overlapping width regions of the airbag.
According to a third broad aspect of the present invention,
there is provided a method for manufacturing an inflatable
safety device, the method comprising: (a) weaving threads of a
lower dtex value in a first area; (b) weaving threads of a
higher dtex value in a second area; and (c) weaving threads of
the higher dtex value in a third area, wherein the first area is
located between the second and third areas, the second and third
areas not overlapping each other.
According to a fourth broad aspect of the present invention,
there is provided a method for manufacturing an airbag or
passenger restraint air tube, the method comprising: (a) weaving
a first reinforced area at a first gas inflation location; (b)
weaving a second reinforced area at a second gas inflation
location, the first and second locations being in fluid
communication with each other, and (c) weaving a non-reinforced
area between the inflation locations.
According to a fifth broad aspect of the present invention,
there is provided an inflatable safety device comprising: (a)
threads of a lower dtex value in a first area; (b) threads of a
higher dtex value in a second area; and (c) threads of the
higher dtex value in a third area; wherein the first area is
CA 02441668 2008-01-23
2a
located between the second and third areas, the second and third
areas not overlapping each other, wherein the material is more
easily folded in the first area as compared to the second and
third areas.
The available fabric mass in the one-piece woven airbag as
tailorized by the method, now makes it possible to reinforce the
airbag fabric individually oriented. Thus, at a high stress
location formerly exhibiting airbag tears, a fabric quality is
now available of enhanced resistance, achieved among other
CA 02441668 2003-09-24
3
things by an increase in the thermal capacity in the neuralgic
locations of the airbag where namely the jet lances feature
their so-called jet gill zone. Now, by increasing the fabric
mass to advantage in desired airbag positions in the fabric, a
higher strength both mechanically and also thermally is
available in preventing tears in the airbag.
In one aspect of the invention a weft yarn is employed in the
desired region which as compared to standard yarn has an at
least 25% higher dtex. The invention will now be detailled with
reference to the drawing for a better understanding, in which:
Fig. 1 is a greatly diagrammatic illustration of an
airbag which in this case is a vehicular side
airbag extending over the side windows of the
right-hand front and rear seat of the vehicle.
Fig. la is a diagrammatic arrangement of a vehicular
airbag.
Fig. 2 is again a greatly diagrammatic illustration of
part of a fabric in which two airbags are
evident one alongside the other fully woven on
the machine.
Fig. 3 is a greatly diagrammatic illustration of a
cross-section through one ply of an airbag in
which weft threads of differing dtex are woven.
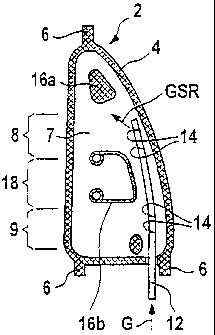
Referring now to Fig. 1 there is illustrated diagrammatically,
by way of example, an airbag 2 shown from the side. The
location of this airbag 2 in a motor vehicle may be imagined
for the right-hand side windows of a vehicle shown on the move
in the upper part (Fig. la) of the drawing. The airbag 2 is
framed by a single-ply woven edge 4 shown shaded in the
drawing. In accordance with its location in the vehicle, tabs 6
arranged "front" and "rear" serve to secure the airbag 2 in
place (not shown). The position of the airbag 2 in a vehicle 3
is indicated diagrammatically in Fig. la. The airbag 2 is
divided into various regions, namely a front seat region 8 and
a rear seat region 9 in which, in case of a collision, the head
of a vehicle occupant could impact the side window of the
21192184.1
CA 02441668 2003-09-24
4
vehicle. This is why the airbag 2 needs to be inflated at the
earliest in the cited regions 8 and 9. For inflating the airbag
a gas lance 12 is inserted into the interior 7 of the airbag 2,
the gas lance 12 comprising jet orifices 14 in the regions 8
and 9. The gas is jetted into the cited regions roughly in the
direction of an arrow GSR and is then distributed in the
airbag. The shaded edge 4 of the airbag 2 is, as just said,
woven single-ply whilst the interior 7 framed by the edge 4 is
woven two-ply in this example. Some regions within the airbag 2
serving particularly to shape the airbag 2 or orient the flow
of gas into the airbag 2 are included in the weave single-ply
woven as connecting regions in the form of surface areas 16a or
webs 16b. Thus, for example, in the vicinity of the so-called
A-pillar (not shown) and B-pillar (likewise not shown) of the
vehicle a region 16a and a webbed region 16b respectively are
woven single-ply. In these regions 16a, 16b upper and lower
fabric plies are joined to each other.
The fabric as is usually configured rather fine for an airbag
is subjected to exceptionally heavy stress in the region of the
jet orifices 14 of the gas lance 12 unlike other regions of the
airbag 2. The shock of the hot gas jet stresses the surface or
fabric of the airbag exceptionally in the corresponding
regions.
Referring now to Fig. 2 there is illustrated part of a fabric
20 in which two inwoven airbags I and II are evident. In this
case the airbags I and II are shown not yet parted from the
fabric 20. Indicated in airbag I is an inserted jet lance 12'
depicted by the dotted line which analog to the jet lance 12 as
shown in Fig. 1 comprises jet orifices arranged in the regions
8 and 9. The fabric 20 in the example as shown in this case is
basically woven single-ply in the non-shaded region located
outside of the airbags I and II. The requirement in this case
is substantially a woven structure and thus there is no need to
go into detail as regards the connections. What is particularly
of interest in the fabric 20 as shown in Fig. 2 is the special
use made of weft threads differing in dtex. A weft thread in
the direction of the arrow S transversely to the warps running
in the direction of the arrow K is picked, for example, over
the full width of the fabric 20 as shown here merely
sectionwise. To attain higher strength in the wall of the
airbag 2 in the regions 8 and 9 as cited above, regions of the
airbag offering greater resistance are created in accordance
with the invention (Fig. 2) in the regions 28 and 29 by
21192184.1
CA 02441668 2003-09-24
employing a yarn VS in the cited regions in the weft direction
S and which as compared to weft threads used in other regions
of the fabric 20 has a 25% higher dtex, for instance. This so-
called reinforcement weft yarn VS is picked, for example. with
no change in the weft set, into the fabric 20 so that in the
regions 28 and 29 a corresponding increase in the fabric mass
and thus the desired fabric strength is achieved. This
inventive approach attains, on the one hand, the desired
reinforcement where it is wanted within a ply of the airbag,
but, on the other hand, the reinforcement effect is also
achieved elsewhere in the airbag where not required. This may
result in the stiffness of the airbag as well as the pack
volume of airbag being unfavorable in some assembly conditions.
This situation can be improved by selecting in the
reinforcement regions 28 and 29 a weft sequence in which
reinforcement weft yarns VS differing in dtex, for example by
alternating 470 with 350 dtex reinforcement weft threads in a
predefined sequence. This permits reducing the stiffness and
thus also the pack volume of the airbag as compared to that of
an airbag woven with just one reinforcement weft thread dtex.
On top of this, any surfeit in the regions of the fabric (i.e.
the fabric may form advance cloth, indeed even folds, in
approaching the absolute limit to the fabric density that can
be accommodated, when only a single reinforcement weft thread
dtex with no change in the weft set is employed) is reduced.
In optimizing the procedure as just described in which the
reinforcement weft yarn VS reinforcing the full width of the
fabric in the regions 28 and 29 is picked, the reinforcement
weft yarn VS is picked only in defined regions transversely in
the fabric. To prevent the reinforcement regions from extending
over the full width of the fabric, i.e. over the full "height"
of the airbag, the reinforcement wefts VS are activated only in
defined regions (identified by the reference numeral 38 in Fig.
2) in which the inflow of gas is actually anticipated through
the jet orifices 14 of the gas lance 12 on inflation of the
airbag.
Referring now to Fig. 3 there is illustrated how, in this
procedure a reinforcement weft thread VS (depicted merely
diagrammatically) is picked in the fabric only in the region 38
whilst outside thereof it is present as a floating
reinforcement weft also outside of the fabric. Analogous to the
location of the reinforcement weft VS a basic weft thread BS
21192184.1
CA 02441668 2003-09-24
6
runs in the region 38 floating outside of the fabric 20, whilst
in the remaining regions of the fabric it is interwoven into
the plies of the fabric conventionally.
Evident likewise from Fig. 3, shown in section, are the warp
threads KF which together with the basic weft thread BS and
reinforcement weft thread VS form a ply of the airbag 2. It
will be understood that the illustration as shown in Fig. 3 is
merely diagrammatic and not at all true to scale. The person
skilled in the art will recognize from the diagrammatic
illustration the various principles and weaves of different
weft and warp threads involved. In the regions 40 the
reinforcement thread VS is located floating, whilst in the
region 38 the basic weft thread is located floating outside of
the fabric. To advantage the reinforcement weft threads VS may
furthermore be parted on the machine in the floating regions so
that they actually remain only in the desired regions 38 of the
fabric 20. This procedure has many advantages. The fabric is
reinforced only in the regions in which stress is anticipated
whilst the pack volume is reduced practically to that of the
standard fabric. Likewise, the stiffness of the airbag is
minimized.
The method in accordance with the invention also covers, of
course, a method for weaving an air tube for a so-called
airbelt, in other words an inflatable seat belt. It is of
advantage with such air tubes when particularly elastic weft
threads, e.g. monofil threads, are picked in regions of the
fabric desired to be particularly elastic. Thus, regions in the
fabric required to have "only" an airbag function in the
finished airbelt, may be woven with very fine, soft weft
threads whilst other regions having "also" an airbelt function
are woven at least in part with monofil threads in thus making
for enhanced cost effectiveness and more function-specific
airbelt fabrication.
It will be understood that the above description gives no
details as to how the remaining regions of the airbag (single-
ply region, two-ply region, etc) are woven in kind, since these
basics are known to the person skilled in the art. Also,
implementing the method in accordance with the invention by
ways and means as described above is intended merely to be
appreciated as an example. Employing a Jacquard weaving machine
permits discrete localized interweaving of reinforcement weft
threads in making use of the "picked weft technology" as just
21192184.1
CA 02441668 2003-09-24
7
described with all of its advantages as likewise described.
Just as possible too, is the arrangement of further juxtaposed
airbags in a fabric web.
21192184.1