Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02442140 2003-09-23
1
DESCRIPTION
BODY FRAME CORRECTOR
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a body frame corrector for correcting a
frame or a body of an automobile which has been deformed by a traffic accident
or the like.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
As a device for correcting a frame or a body of an automobile deformed by
a traffic accident or the like, some examples of frame correctors are
disclosed in
Unexamined Japanese Patent Publications Nos. S47-14850, S50-37143,
S51-118235, S54-17238 and S55-55221.
The frame correctors described in the above publications have structures to
fix the frames or the bodies using chains or dedicated supporting members.
Accordingly, these devices require a large working space as well as
considerable
labor and time for the operations of fixing the automobiles onto the devices
and
removing them after correction.
In addition, when the deformed portions are pressed during the correcting
operations, a springback farce has to be taken into account, which requires
that
the operators be highly skilled for accurate correction and, moreover, has
sometimes damaged the frames due to an overload or caused unnecessary
deformation of undesired portions. Furthermore, the chains pulling the frames
or
the like may come off or be damaged by an overload, which would lead to
serious
CA 02442140 2003-09-23
2
accidents.
To solve the above problem, the present inventor has developed a body
frame corrector that is capable of correcting a body frame or the like within
a
short time and in an accurate and safe manner and also realizes an efficient
use of
a space, which has been disclosed in Unexamined Japanese Patent Publication
No.
2000-203395.
In the body frame corrector disclosed in the above publication, while the
pressing devices disposed on the inner side surfaces of the frame-shaped body
are
movable in the directions along the inner surfaces, the pressing directions
are still
1o limited. Therefore, when correcting the frames or the like that have been
complicatedly deformed, it tends to be difficult to apply pressure onto the
portion
to be pressed in an accurate direction, which deteriorates workability.
In addition, the body frame corrector described above has a limit in
moving the pressing devices disposed on the ceiling surface within a front-
half
portion of the frame-shaped body. Thus, when correcting a long frame or the
like, the correcting operations often have to be divided into several steps by
moving the frame. This causes the working efficiency to be lowered.
The present invention relates to an improvement of the above-described
body frame corrector, which provides a body frame corrector capable of
2o efficiently correcting a complicatedly deformed frame or the like with
excellent
workability.
DISCLOSURE OF THE INVENTION
The body frame corrector of the present invention comprises a
frame-shaped body for installing a body frame therein, a plurality of pressing
devices for correcting the body frame, said pressing devices being disposed on
a
CA 02442140 2003-09-23
3
ceiling surface, a floor surface and inner side surfaces of the frame-shaped
body
and movable to directions along each of the respective surfaces, and a tilting
mechanism for changing pressing directions of the pressing devices, the
tilting
mechanism being disposed on the inner side surfaces of the frame-shaped body.
Employing the above structure, the pressing devices on the inner surfaces
of the flame-shaped body can be tilted against the body frame installed within
the
frame-shaped body when pressing, thereby efficiently correcting even
complicatedly deformed frames or the like and enhancing the workability.
The tilting mechanism described above may comprise a hinge member
to which moves up and down along a pillar which is mounted on a side of the
frame-shaped body and movable in a horizontal direction, a pressing device
mounting member provided on the hinge member, and a detachable fixing
member to keep the pressing device mounting member in a predetermined posture.
By this structure, the pressing device mounted to the pressing device mounting
member is movable in both horizontal and vertical directions along the inner
side
surfaces of the frame-shaped body and can be fixed in a tilted position, which
enables the pressing operations in tilted directions to be accurate and safe.
The above body frame corrector may further comprise a moving
mechanism which moves the pressing device disposed on the ceiling surface of
2o the frame-shaped body throughout an entire area of the ceiling surface.
Thus, it
is possible to press from any position on the ceiling surface to enlarge the
operable area, which enhances workability when correcting a comparatively
large-sized body frame.
The above moving mechanism may comprise a rail member disposed on
the ceiling surface of the frame-shaped body, a beam member disposed in a
direction perpendicular to the rail member and movable along the rail member,
and a pressing device mounting member which is movable along the beam
CA 02442140 2003-09-23
4
member. By this structure, the pressing device can be positioned at any place
on
the ceiling surface to securely support a reaction force of the pressing
device
during the pressing operation, which further improves workability and
efficiency
of the operation.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Fig. 1 is a side view showing a body frame corrector of an embodiment of
the present invention;
Fig. 2 is a partially omitted plan view showing the body frame corrector of
Fig. 1;
Fig. 3 is a sectional view taken along the line A-A of Fig. 1;
Fig. 4 is a front view of the body frame corrector shown in Fig. 1;
Fig. 5 is a rear view of the body frame corrector shown in Fig. 1;
Fig. 6 is a sectional view taken along the line B-B of Fig. 2;
Fig. 7 is a front view of a side cylinder tilting mechanism shown in Fig. 6;
Fig. 8 is a sectional view taken along the line C-C of Fig. 7;
Fig. 9 is a sectional view taken along the line D-D of Fig. 7;
Fig. 10 is an explanatory perspective view illustrating a correcting
operation using the body frame corrector of Fig. 1;
Fig. 11 is an explanatory plan view illustrating a correcting operation
using the body frame corrector of Fig. 1;
Fig. 12 is a sectional view taken along the line E-E of Fig. 11,
Fig. 13 is an explanatory plan view illustrating another correcting
operation using the body frame corrector of Fig. 1;
Fig. 14 is a sectional view taken along the line F-F of Fig. 13; and
Fig. 15 is an explanatory side view illustrating further another correcting
CA 02442140 2003-09-23
operation using the body frame corrector of Fig. 1.
BEST MODE FOR CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION
5 Figs. 1 to 9 show a body frame corrector of an embodiment of the present
invention. As shown in Figs. 1 to 5, a body frame corrector 1 of the present
embodiment comprises a frame-shaped body 2 formed by a combination of steel
materials, frame lifting devices 3 for lifting a body frame installed within
the
frame-shaped body 2, an operation box 3a of the frame lifting devices 3,
wheels 4
1o and 5 disposed at four positions in front/rear and right/left of the frame-
shaped
body 2, wheel lifting cylinders 4a and Sa, a steering cylinder 4b for the
wheels 4,
driving motors Sb for the wheels 5, a plurality of ceiling cylinders 7 and
suspending cylinders 8 disposed on a ceiling surface to press the body frame
installed within the frame-shaped body 2, a plurality of side cylinders 9
disposed
on right and left inner side surfaces, and a plurality of floor cylinders 10
disposed
on a floor surface.
In a front part of the right and left inner side surfaces of the frame-shaped
body 2, reaction force supporting members 12 which are movable up and down by
lifting cylinders 11 are disposed. A hydraulic power generator 13, which is
2o disposed for driving the frame lifting devices 3, wheel lifting cylinders
4a and Sa,
the steering cylinder 4b, the ceiling cylinders 7, the suspending cylinders 8,
the
side cylinders 9, the floor cylinders 10 and the lifting cylinders 11, is
attachable to
and detachable from the frame-shaped body 2. In the present embodiment, all of
the cylinders mean hydraulic cylinders as pressing devices.
On the right and left sides of the ceiling surface, two ceiling rails 14 are
disposed in a longitudinal direction. Perpendicular to the ceiling rails 14,
four
beam members 15 which are movable in front and rear directions along the
ceiling
CA 02442140 2003-09-23
6
rails 14 are disposed. Sliding members 16 are mounted to each of the four beam
members 15, which are movable in a longitudinal direction of the beam members
15. Each of the ceiling cylinders 7 and the suspending cylinders 8, mounted to
each of the sliding members 16, is movable in front/rear and right/left
directions
throughout the entire area of the ceiling surface.
The suspending cylinders 8 are mounted to the sliding members 16 via
lifting cylinders 17 having universal joints (not shown) on top and bottom
ends
thereof. Therefore, the suspending cylinders 8 can freely move in up-and-down,
rotating, swinging and tilting directions, which allows the pressing position
and
to direction of the suspending cylinder 8 to be optionally determined.
Accordingly,
as further explained below, when correcting a deformed body frame, the frame
can be pressed at a desired position from an optimal direction depending on
size,
form and deformed condition of the frame, thereby realizing an accurate
correction.
In a front portion of the ceiling surface of the frame-shaped body 2,
disposed are two horizontal rails 18 in a lateral direction and two sliding
rails 19
which are perpendicular to and movable along the horizontal rails 18. A
sliding
member 20 which is movable in a longitudinal direction of the sliding rails 19
is
mounted on each bottom surface of the sliding rails 19. The sliding member 20,
2o similar to the sliding member 16, functions as a mounting member of the
pressing
cylinder or the like.
The beam members 15, the sliding rails 19, and the sliding members 16
and 20 are freely movable when the ceiling cylinders 7, the suspending
cylinders
8 and others are not in use. However, when a reaction force is applied
upwardly
due to extension of the ceiling cylinders 7, for example, these members are
automatically fixed at their present positions with a lock mechanism.
Therefore,
the members do not move inadvertently during the operation, but become
CA 02442140 2003-09-23
7
movable again after the upward reaction force is released.
As shown in Fig. 3, a horizontal supporting member 21 is detachably
mounted on the floor surface of the frame-shaped body 2 to be movable along
the
floor surface. Also on the upper surface of the horizontal supporting member
21,
auxiliary cylinders 10a, which have a similar function as the floor cylinders
10,
are mounted, which allows the same supporting and pressing operations as the
floor cylinders 10. The auxiliary cylinders 10a, which are movable in a
longitudinal direction of the horizontal supporting member 21, also enable
supporting and pressing operations out of the moving range of the floor
cylinders
l0 10.
The side cylinders 9, as shown in Fig. 6, are mounted to be movable up
and down along a pillar 22 made of H-shaped steel, which is movable in a
horizontal direction. Four of the pillars 22 are each provided on both right
and
left side surfaces of the frame-shaped body 2. The pillar 22 is disposed
between
two side rails 29 arranged at different heights and side members 30. To allow
a
smooth movement of the pillar 22 in a horizontal direction, casters 31
rotating
along top surfaces of the side rails 29 are provided on outer side surface of
the
pillar 22.
As shown in Figs. 7 to 9, a hinge member 23 is mounted to the pillar 22 to
be movable up and down in a longitudinal direction. A pair of supporting
plates
and 26 are fixed to the pillar 22 at two positions with different heights in a
manner that the supporting plates 25 and 26 sandwich the pillar 22. On a
surface
facing each other of each of the supporting plates 25 and 26, a guide rail 32
is
disposed, and sliding member 23s fixed to an upper plate 23a of the hinge
25 member 23 is slidably engaged with a gap between the pillar 22 and the
guide rail
32. To a lower plate 23b of the hinge member 23 which can be tilted toward a
center of the frame-shaped body 2, a cylinder mounting member 24 is fixed.
CA 02442140 2003-09-23
8
By inserting a fixing pin 28 into one of a plurality of fixing holes 27
mounted to the supporting plates 25 and 26 to support a lower surface of the
cylinder mounting member 24, as shown in Fig. 6, the cylinder mounting member
24 can be kept in a horizontal or tilted posture. Thus, a pressing direction
of the
side cylinder 9 which is mounted coaxially with the cylinder mounting member
24
can be determined in a horizontal or tilted posture.
The floor cylinders 10 are, as shown in Figs. 3 to 5, disposed on the floor
surface of the frame-shaped body 2, and mounted to six floor rails 33 which
are
movable in right and left directions along the floor surface via sliding
members 34,
1o respectively, which allows the floor cylinders 10 to be movable in
frontlrear and
righr/left directions on the floor surface. Furthermore, the floor cylinders
10,
which are fixed to the sliding members 34 by engaging an internal screw
portion
formed on each lower end of the floor cylinders 10 with an external screw
portion
formed in each of the sliding members 34, can be detachable from the sliding
members 34. Thus, only the floor cylinders 10 can be replaced. The floor rails
33 and the sliding members 34 are freely movable when the floor cylinders 10
are
not in use. However, when a reaction force is applied downwardly due to
extension of the floor cylinders 10, for example, these members are
automatically
fixed at their present positions with a lock mechanism. Therefore, the members
2o do not move inadvertently during the operation, but become movable again
after
the downward reaction force is released.
As shown in Fig. l, as auxiliary members for fixing a chain 37 explained
below, a plurality of fixing members 36 are mounted to pillars 35 standing on
the
side surface of the frame-shaped body 2. The fixing members 36 are movable up
and down along the pillars 35 and can be fixed to any position on the pillars
35
using a fixing screw 42.
As shown in Figs. 1 and 5, on supporting posts 38 disposed at both right
CA 02442140 2003-09-23
9
and left ends of the rear side of the frame-shaped body 2, a plurality of
engaging
holes 38a are formed at various heights, one of which is chosen to detachably
mount a horizontal bar 39 made of H-shaped steel. To the horizontal bar 39,
mounted are a plurality of fixing members 46 for fixing the chain 37, which
are
movable in a longitudinal direction of the horizontal bar 39. The horizontal
bar
39 and the fixing members 46 function, similarly to the above-described
pillars 35
and the fixing members 36, as fixing means for the chain 37.
The members such as the ceiling cylinders 7, the suspending cylinders 8,
and the side cylinders 9 and the floor cylinders 10 are provided with oil
cylinders
to inside which are operated by a hydraulic power generator 13 and screw
portions at
their tip ends to which various forms of engaging attachments that fit
different
portions of a body frame to be corrected can be mounted.
The lifting cylinders 17 to lift up and put down the suspending cylinders 8
and the lifting cylinders 11 to lift up and put down the reaction force
supporting
members 12, which are also oil cylinders operated by the hydraulic power
generator 13, have a larger moving stroke compared to the oil cylinders
operating
the ceiling cylinders 7 and other members and thus can lift up and put down
the
suspending cylinders 8 and the reaction force supporting members 12 in a wider
range. The body frame corrector 1 can be operated by an operation box 13a of
2o the hydraulic power generator 13.
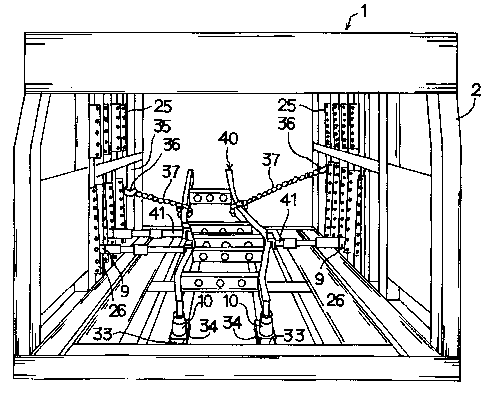
Next, referring to Figs. 10 to 12, a correcting operation using the body
frame corrector 1 will be explained below. As shown in Fig. 10, a body frame
40 which has been deformed by a traffic accident or the like is inserted into
the
frame-shaped body 2 from the front side or the rear side thereof. A front
portion
of the body frame 40 is laid on the floor cylinders 10 while right and left
sides of
the rear portion are supported by the chains 37 which are fixed by the fixing
members 36. Then, tip ends of engaging attachments 41 mounted to three of the
CA 02442140 2003-09-23
side cylinders 9 projecting from the inner side surface are put on the
deformed
portion of the body frame 40. Thus, the body frame 40, the floor cylinders 10,
the side cylinders 9, the chains 37 and other members are arranged in the
state
shown in Figs. 11 and 12.
5 In the above arrangement, the three side cylinders 9 are correlatively
operated to gradually press the deformed portion of the frame body 40 at three
points and elastically transform the deformed portion, thereby restoring the
original form of the body frame 40 which has been deformed. After completing
the correction of the body frame 40, the side cylinders 9, the chains 37 and
others
1o are removed to take out the body frame 40 from the frame-shaped body 2.
According to the correcting operation using the body frame corrector 1,
three different points on the body frame 40 are simultaneously pressed to
constantly apply a pressure in a stable condition without rattling or shaking
during
the correcting operation, thereby completing the operation with high accuracy
in a
short period of time. Furthermore, as a deformed portion of the body frame 40
along with the proximity of the portion are directly pressed to be corrected,
the
spring back force is extremely small, which enables an operator without an
advanced skill to conduct accurate correction. In addition, all of the
correcting
operations can be carried out within the frame-shaped body 2, prompting more
2o effective use of the working space.
The floor cylinders 10, the side cylinders 9, the fixing members 36 of the
chains 37 and others, which are independently movable, can be disposed at
optimal positions according to the size of the body frame 40 and the deformed
condition, making the correcting operation more appropriate. The pressing
position and direction of the side cylinders 9 are alterable by inserting the
fixing
pin 28 into one selected from the plurality of the fixing holes 27 of the
supporting
plates 25 and 26. Thus, the body frame 40 complicatedly deformed, which needs
CA 02442140 2003-09-23
11
to be pressed from the slanting directions, can also be corrected with
accuracy,
which leads to excellent workability and an efficient operation.
Next, referring to Figs. 13 to 15, another correcting operation using the
body frame corrector 1 will be explained below. When correcting a body frame
43 which has been complicatedly deformed over a relatively wide range, the
suspending cylinders 8, in addition to the side cylinders 9, are used for the
correcting operation. As shown in Fig. 13, depending on the deformed condition
of the body frame 43, the side cylinders 9 and the suspending cylinders 8 are
moved to suitable positions respectively, to which the engaging attachments 41
to and others are mounted, and the distal ends thereof are put on the deformed
portion and their proximity of the body frame 43. Here, base end portions of
the
suspending cylinders 8 are made to touch the reacting force supporting members
12 in order to support the reaction force of the suspending cylinders 17 which
are
disposed at the up front position.
Keeping the above arrangement, the deformed portion and others are
gradually pressed by operating the side cylinders 9 and the suspending
cylinders 8
to restore the original form of the body frame 43. Also in this case, rather
than
operating all of the side cylinders 9 and the suspending cylinders 8 at the
same
time, it is preferable that each single step to press three different points
of the
2o body frame 43 is conducted in turn. If there is concern that the body frame
43
might be dented inwardly by pressure, such deformation can be prevented by
disposing one of the suspending cylinders 8 inside the body frame 43 to
support
the body frame 43 from the inside using an extension attachment 44 having an
appropriate length.
Referring to Fig. 15, further another correcting operation using the body
frame corrector 1 will be explained below. When correcting a body frame 45
which has been deformed in a vertical direction, the body frame 45 installed
CA 02442140 2003-09-23
12
within the frame-shaped body 2 is placed on the floor cylinders 10 with the
deformed portion positioned between two of the floor cylinders 10. The
deformed portion is pressed with the ceiling cylinder 7 to restore the
original form.
Also in this operation, as three different points of the body frame are
simultaneously pressed, without rattling nor shaking during the correcting
operation, the pressure can be applied in a constantly stable state, leading
to an
accurate and safe correcting operation completed in a short period of time.
In the body frame corrector in the above embodiment, the hydraulic power
generator 13, which is attachable to and detachable from the frame-shaped body
2,
to can be separated from the frame-shaped body 2 and used in combination with
other pressing devices having oil cylinder systems.
The whole body of the body frame corrector 1 can be driven in any desired
directions by moving the wheels 4 and 5 down onto the ground using the wheel
lifting cylinders 4a and Sa and spacing the frame-shaped body 2 from the
ground,
followed by rotating the wheels 5 with the driving motors Sb and steering the
wheels 4 with the steering cylinder 4b. Accordingly, it is easy to transfer
the
body frame corrector 1 to a working site, to carry it in a workshop, to
install a
body frame within the frame-shaped body 2, and to return the body frame
corrector 1 to a storehouse after an operation. After stopping the body frame
2o corrector 1, by lifting the wheels 4 and 5 using the wheel lifting
cylinders 4a and
Sa, the frame-shaped body 2 is landed on the ground and the wheels 4 and 5 are
stored inside the frame-shaped body 2.
INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY
The body frame corrector according to the present invention is suitable for
correcting a frame or a body of an automobile complicatedly deformed by a
traffic
CA 02442140 2003-09-23
13
accident or the like by directly applying a pressure onto the frame or the
body.