Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~
- . ' c ~ CA 02445766 2003-10-28
' Case 1/1208-fft BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM PHARMA KG
77965fft.206
Improved process for preparing zolpidem
The invention relates to a process which can be used for preparing zolpidem on
an
s industrial scale.
Background to the invention
Zolpidem is a known sedative which has the following structure:
io
"y
N-
EP 0 251 859 describes a process for preparing zolpidem. The six-step
synthesis
starting with a bromoacetophenone is a generally laborious method.
A process for preparing compounds analogous to zolpidem in which
is 2-aminopyridines and corresponding bromoketoamides are reacted is described
in
the literature (J. of Med. Chem.,1999, Vol. 42, No.19,3934-3941).
The problem of the present invention is therefore to provide an improved,
economical
process for preparing zolpidem which can be used on an industrial scale.
Detailed description of the invention
The present invention solves the problem outlined above by the method of
synthesis
described hereinafter.
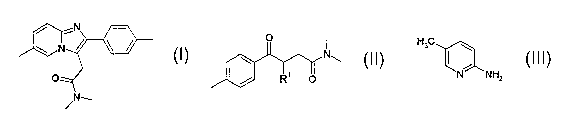
The invention thus relates to a process for preparing a compound of formula
(I)
' ,' 'y . CA 02445766 2003-10-28
2
\ /
0
N--_
wherein
a compound of formula (II)
0
w Nw
,, ..
R O
s (I I>
wherein
R' denotes chlorine, bromine, iodine, -O-COCH3 , tosylate or mesylate,
io is reacted with a compound of formula (III),
H3C
i
N NHZ
(III)
optionally in a suitable diluent andlor in the presence of a suitable added
reagent or
is catalyst,
characterised in that the reaction is carried out in a temperature range from
20 to
80°C.
In a particularly preferred process a diluent is used which is selected from
among
ao acetonitrile, N-methylpyrrolidinone, tetrahydrofuran, acetone, ethanol and
dichloromethane.
In another preferred process, acetonitrile is used as the diluent.
CA 02445766 2003-10-28
3
According to the invention, a process in which the reaction is carried out at
a
temperature of about 60 to 75 °C, preferably 70°C, is
particularly important.
Also preferred is a process in which the compound of formula (II) is used in a
molar
ratio of 1:1 to 1:3 to the compound of formula (III),
Particularly preferred is a process in which the compound of formula (II) is
used in a
molar ratio of about 1:1.3 to the compound of formula (III).
to Most particularly preferred is a process in which an added reagent andlor
catalyst is
used which is selected from among p-toluenesulphonic acid monohydrate, sodium
hydrogen carbonate, sodium acetate, pyridine, dimethylaminopyridine, magnesium
sulphate, triethylamine, trimethylorthoformate and tetrabutylammonium bromide.
i5 The invention further relates to the compound of formula (II)
0
N~
R' O
2o wherein
R' denotes bromine.
The present invention also relates to a process for preparing a compound of
formula
(11), wherein a compound of formula (IV)
N~
O
(IV)
'.. CA 02445766 2003-10-28
4
is reacted with elemental bromine in a diluent, preferably dichloromethane.
The reaction of a compound of formula (IV) with elemental bromine is generally
carried out at a temperature of 10 to 50 °C, preferably 15 to 35
°C, more preferably
s 18 to 30 °C, most preferably about 20 or 25 °C.
The compound of formula IV is generally used in a molar ratio of 1.5 :1 to
1:1.5,
preferably about 1:1.2, to elemental bromine.
io The invention also relates to the use of compounds of formula (I I) for
preparing
pharmaceutically active compounds.
Preferably, the compound of formula (II) is used to prepare zolpidem.
is The invention further relates to a process for preparing a compound of
formula (I),
this process comprising the following steps:
a) reacting the compound of formula (IV) in an organic diluent at a
temperature of 30
to 50 °C, preferably about 40 °C, with elemental bromine.
b) washing the reaction mixture with water,
2o c) after phase separation, concentrating the organic phase by evaporation
and
optionally diluting it with another organic diluent , and
d) reacting the concentrated organic phase of a) to c) with the compound of
formula
' (III) at 20 to 80 °C, preferably 60 to 75 °C, preferably about
70 °C, without isolating
the intermediate product.
The present invention further relates to the use of the compound of formula
(I) for
preparing the pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
The compound of formula (I ) is preferably used to prepare zolpidem
semitartrate.
Acids suitable for forming a salt of the compounds according to the invention
include,
for example, hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, sulphuric acid, phosphoric
acid,
nitric acid, oxalic acid, malonic acid, fumaric acid, malefic acid, tartaric
acid, citric acid,
ascorbic acid and methanesulphonic acid, particularly tartaric acid.
CA 02445766 2003-10-28
In a preferred embodiment of the process according to the invention for
preparing the
compound of formula II, one equivalent of the compound of formula IV is
dissolved in
a diluent, preferably glacial acetic acid, ethyl acetate, n-butyl acetate or
diethylether,
s most preferably ethyl acetate. A solution of usually 1 to 1.5 equivalents,
preferably
one equivalent, of bromine is added dropwise in a diluent, preferably ethyl
acetate, at
a temperature of 40 to 70 °C, preferably about 45 °C, and
stirred for 2 to 24 h,
preferably 5 to 15 h, most preferably 12 h, at a temperature of 10 to 50
°C, preferably
to 35 °C, more preferably 18 to 30 °C, most preferably about 20
or 25 °C. The
io suspension obtained is filtered, the residue is added to a little water and
stirred for
about 0.5 to 2 h, preferably about 1 h. The suspension is filtered again and
the
residue is washed with water. The crystals obtained are dried, preferably in a
vacuum drying cupboard at 40 to 80 °C, preferably at about 70
°C.
is In a preferred embodiment of the process according to the invention for
preparing the
compound of formula I , about 1 equivalent of the compound of formula (II) is
placed
in a diluent, for example acetonitrile, and a solution of generally 2
equivalents of the
compound of general formula (III) and a diluent, for example acetonitrile, is
added
dropwise at 20 to 80 °C, more preferably at 40 to 75°C, most
preferably at a
2o temperature of about 70 °C within 0.5 to 3 h, preferably 1 to 2 h,
more preferably
about 1.5 or 1.75 h. After it has all been added, the mixture is stirred for 2
to 6 h ,
preferably 2 to 5 h, more preferably about 2.5 to 3 h.
The reaction mixture is then diluted with a diluent, preferably
dichloromethane, and
2s washed one to five times, preferably three times, with water. The organic
phase is
extracted one to five times with hydrochloric acid, preferably 2 N
hydrochloric acid.
The combined acid phases are adjusted to a pH of between about 7 and 9,
preferably to a pH of about 8, using a base, preferably sodium hydroxide
solution,
more preferably 20% sodium hydroxide solution. After the reaction mixture has
been
3o cooled it is extracted one to five times with an organic diluent , selected
from among
dichloromethane, toluene, ethyl acetate, n-butyl acetate and methyl-tert.-
butylether,
preferably dichloromethane and ethyl acetate, more preferably ethyl acetate.
The
combined organic phases are dried, preferably with magnesium sulphate, and
concentrated by evaporation. The product which crystallises out is mixed with
a little
's , CA 02445766 2003-10-28
6
water and stirred for 5 to 20 h, preferably 15 h, and the crystals are
filtered off,
washed with water and dried, preferably at 30 to 80 °C, preferably at
60 °C, for 1 to
h, preferably 5 h.
s In a preferred embodiment of the process according to the invention for
preparing the
semitartrate salt of the compound of general formula I, generally 2
equivalents of the
compound of formula I are placed in a diluent, preferably methanol, ethyl
acetate,
Isopropanol or ethanol, more preferably methanol, and a solution of 1
equivalent of
(2R, 3R)-(+)-tartaric acid in a diluent, preferably methanol, ethanol or
isopropanol,
io more preferably methanol, is added.
A precipitation agent, preferably tert.butylmethylether, an
isopropanol/methanol-
mixture or a methanol/ether mixture, preferably tert.butylmethylether, is
optionally
added. The mixture is stirred for 1 to 24 h, preferably 12 h, at a temperature
of 15 to
is 30 °C, preferably at about 20 or 25 °C. The suspension formed
is stirred for a further
0.5 to 3 h, preferably about 1 hour at a temperature of 0 to 20 °C,
preferably 3 to
10°C, most preferably at about 5°C. The crystals obtained are
filtered, optionally
washed with a solvent, preferably with tert.butylmethylether, and the crystals
are
dried, preferably for 1 to 10 h, more preferably for 5 hours at a temperature
of 20 to
70°C, preferably about 50°C.
In a particularly preferred embodiment of the process according to the
invention,
about 1 equivalent of the compound of formula (IV) is placed in a diluent, for
example
ethyl acetate, butyl acetate or dichloromethane, preferably dichloromethane,
and
2s heated to 30 to 50 °C, preferably 40 °C. Preferably,
catalytic amounts, preferably 5 to
6 mol%, of HBr are added to the reaction mixture. Then 1.2 equivalents of
bromine
are added dropwise. The reaction mixture is stirred for another 60 min,
preferably 30
min. The mixture is cooled to about 20 to 25 °C and extracted with
water. The
organic phase is evaporated down to about 10% (vlv) and then diluted with
another
so diluent, preferably tetrahydrofuran, N-methylpyrrolidinone or acetonitrile,
preferably
acetonitrile. The mixture is added dropwise to a solution of 1.3 equivalents
of 6-
amino-3-picoline and a diluent, preferably tetrahydrofuran, N-
methylpyrrolidinone or
acetonitrile, preferably acetonitrile. The resulting mixture is then stirred
for about 2 h
at 50 to 80 °C, preferably 70 °C. The reaction mixture is
combined with an organic
CA 02445766 2003-10-28
7
diluent, preferably toluene, extracted with an aqueous solution, for example
2N
hydrochloric acid, and the organic phase is discarded. The aqueous phase is
again
mixed with an organic diluent, adjusted to a pH of about 4, and the organic
phase is
discarded again. The extraction step is repeated at a pH of about 8 to 9.
After the
s aqueous phase has been separated off the organic phase is evaporated down to
about 10%. The residue is combined with diisopropylether, diethylether or
methyl-
tert.butylether, preferably methyl-tert.butylether, and stirred for about 30
to 60
minutes at about 0 to 15°C, preferably 5 °C. The crystals formed
are washed and
dried.
to
The procedure according to the invention leads to an economical process with a
high
space-time yield with regard to the compound of formula I or the
pharmacologically
acceptable salts thereof and a high yield and purity of the intermediate
product of
formula II, which can be further processed without being isolated or purified
by
is chromatography.
The Examples that follow serve to illustrate the processes for preparing the
compound of formula I. carried out by way of example. They are to be
understood as
examples of possible procedures without restricting the invention to their
contents.
Example 1
3-(4-methyl-benzoyl)-2-bromo-propyl-dimethylam ide
,l
18.6 g (84.8 mmol) of 3-(4-methyl-benzoyl)-propyl-dimethylamide are dissolved
2s in 50 ml of glacial acetic acid. A solution of 13.55 g (84.8 mmol) of
bromine and 45 ml
of glacial acetic acid is added dropwise within 50 minutes at ambient
temperature
and the mixture is then stirred overnight. The suspension formed is filtered
and
washed with 30 ml of glacial acetic acid. The filter residue is added to 200
ml of
distilled water, triturated thoroughly and stirred for 1 hour. The product is
filtered
3o again and washed with another 200 ml of water. The crystals obtained (21.16
g) are
dried for 6 hours in a vacuum drying cupboard at 70°C.
Yield 18.18 g of white crystals (71.9 % of theory)
Melting point: 119 - 121 °C
CA 02445766 2003-10-28
8
Example 2
N,N-6-Trimethyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-acetamide
50 g (167.7 mmol) of 3-(4-methyl-benzoyl)-2-bromo-propyl-dimethylamide are
placed
s in 500 ml of acetonitrile. A solution of 36.27 g (335.4 mmol) of 6-amino-3-
picoline and
350 ml of acetonitrile is added dropwise at 60°C within 1.75 hours and
once the
solution has all been added the mixture is stirred for another 4 hours. The
resulting
solution is diluted with 1000 ml of dichloromethane and washed three times
with
2000 ml of distilled water. Then the organic phase is extracted three times
with 1000
io ml of 2N hydrochloric acid. The combined acid phases are adjusted to pH 8
with
20 % sodium hydroxide solution and, after being cooled, extracted three times
with 1
litre of dichloromethane. These organic phases are combined, dried with
magnesium
sulphate and concentrated by evaporation. The crystals obtained are triturated
with
500 ml~of distilled water, stirred overnight, filtered off, washed again with
50 ml of
is distilled water and the residue is dried in a vacuum drying cupboard for 5
hours at
60°C.
Yield: 17.94 g of light-brown crystals (45.7 % of theoretical).
Example 3
2o N,N-6-Trimethyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-acetamide
10.0 g (33.5 mmol) of 3-(4-methyl-benzoyl)-2-bromo-propyl-dimethylamide and
7.25
g (67.0 mmol) of 6-amino-3-picoline are dissolved in 170 ml of 1,3-dimethyl-2-
imidazolidinone and stirred for 3 hours at 60°C. The reaction mixture
is cooled and
diluted with 100 ml of dichloromethane. It is then washed five times with 150
ml of
2s distilled water. The organic phase is washed twice with 150 ml of 2N
hydrochloric
acid. The combined acid phases are adjusted to pH 8 with 2N sodium hydroxide
solution. The mixture is extracted twice with 150 ml of dichloromethane, the
organic
phases are dried with MgSOa and concentrated by evaporation. The brown oil
obtained is mixed with 50 ml of n-heptane and stirred for 30 minutes. The
so supernatant diluent is decanted off from the precipitated product which is
then
washed twice with 10 ml of n-heptane. The residue is evaporated down again,
combined with 200 ml of distilled water and stirred for 30 minutes. The
product is
filtered off, washed with 50 ml of distilled water and dried.
Yield: 2.38 g of beige crystals (23.1 % of theoretical.)
CA 02445766 2003-10-28
9
Melting point: 194 -195°C
Example 4
N N-6-Trimethyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)imidazo~1,2-alpyridine-3-acetamide
semitartrate
17.94 g (94 %) (54.9 mmol) of N,N-6-trimethyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)imidazo[1,2-
a]pyridine-3-acetamide are placed in 90 ml of methanol. A solution of 4.13 g
(27.5
mmol) of (2R, 3R)-(+)-tartaric acid and 125 ml of methanol are added, followed
by 28
ml of methyl-tert.-butyl-ether (MTBE) within 30 seconds. The mixture is
stirred for 15
io h at ambient temperature. The light-brown suspension formed is stirred for
another 1
hour at 5°C, filtered off, the residue is washed with 50 ml of MTBE,
and the crystals
are dried for 5 hours in a vacuum drying cupboard at 50°C.
Yield: 18.3 g crystals ( 87.2 % of theoretical.)
is Example 5
N,N-6-Trimethyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)imidazof 1,2-alpyridine-3-acetamide
100 g (0.456 mol) of 3-(4-methyl-benzoyl)-propyl-dimethylamide are dissolved
in 400 ml of dichloromethane. 2 g (0.025 mol) of hydrogen bromide are piped
into the
2o solution which is then refluxed. Then 86.1 g (0.539 mol) of bromine is
added
dropwise within 45 minutes and the mixture is stirred for 30 min. It is then
cooled to
ambient temperature and washed with 600 ml of distilled water. The aqueous
phase
is discarded. The organic phase is evaporated down to about 10 % (v/v) and
then
diluted with 300 ml of acetonitrile. This solution is added dropwise within 45
min to a
2s solution of 66.62 g (0.616 mol) of 6-amino-3-picoline in 150 ml of
acetonitrile at 70 °C
and stirred for 1.5 h. Then 400 ml of toluene are added at 20-30 °C and
the mixture is
then extracted with 500 ml of 2N hydrochloric acid. The toluene phase is
discarded,
the aqueous phase is again combined with 400 ml of toluene and adjusted to pH
4
with 20% sodium hydroxide solution. The toluene phase is discarded, the
aqueous
3o phase is combined with 400 ml of toluene and adjusted to pH 8.5 with 20%
sodium
hydroxide solution. The toluene phase is separated off and evaporated down to
10
(v/v). The residue is combined with MTBE and stirred for 2 h at 5°C.
The crystals
obtained are suction filtered, washed with MTBE and dried.
Yield: 43 g of zolpidem (30.7 %).