Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02448300 2003-11-25
WO 02/096860 PCT/FI02/00466
1
PROCESS FOR PREPARING SERTRALINE INTERMEDIATES
The present invention relates to a novel method for the production of
sertraline. The present invention also relates to a novel process for the
preparation of
a pharmaceutical intermediate, N-[4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1(2H)-
naphtalenylidene]methanamine.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
N-[4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1 (2H)-naphtalenylidene]-
methanamine of formula I
/CH3
N
I
CI
CI
is a well known pharmaceutical intermediate which can be used e.g. in the
preparation of sertraline, (1S-cis)-4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-
N-
methyl-1-naphthalenamine, which has a structure of formula II
/CH3
HN
/ I I
~CI
CI
CA 02448300 2003-11-25
WO 02/096860 PCT/FI02/00466
2
Sertraline is marketed in the form of its hydrochloride for the treatment of
depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder and panic disorder.
The synthesis of sertraline is described in U.S. Patent no. 4,536,518. The
process described includes a condensation reaction of 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-
3,4-
dihydro-1(2H)-naphtalenone of formula III
O
III
-CI
CI
with monomethylamine, which is catalyzed by titanium tetrachloride yielding N-
[4-
(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1(2H)-naphtalenylidene]methanamine. The
reaction is an equilibrium reaction, where the equilibrium has to be shifted.
This can
be done e.g. by using titanium tetrachloride to remove water from the reaction
mixture. Titanium tetrachloride, however, is extremely reactive with water and
side
products formed are hazardous, and therefore other dehydrating agents have
been
considered.
Another route to N-4-[3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1 (2H)-
naphtalenylidene]methanamine is described in U.S. Patent No. 4,855,500,
wherein
the dehydration characteristics of appropriate mesh molecular sieves are
employed to
remove water from the reaction mixture to promote the condensation reaction
between 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1(2H)-naphtalenone and
monomethylamine. Molecular sieves are expensive and they must typically be
regenerated if they are to be reused.
In a process described in EP 1 059 287 (+) enantiomer of sertraline is
prepared by either of the processes described above using (+) enantiomer of 4-
(3,4-
dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1(2H)-naphtalenone as a starting material, so that
no
resolution of the final product is needed.
CA 02448300 2003-11-25
WO 02/096860 PCT/FI02/00466
3
Still another route to to N-4-[3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1(2H)-
naphtalenylidene]methanamine is described in the patent application WO
99/36394.
In the process described the condensation reaction of 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-
3,4-
dihydro-1(2H)-naphtalenone with monomethylamine is performed in an alcohol
solvent. The solubility of the reaction product to the solvent is such that
the
equilibrium is favorably enhanced towards the product. No catalysts or
dehydrating
agents are needed. However, monomethylamine is easily vaporized in reaction
temperatures (about 50 deg C or above) and therefore a suitable pressure rated
vessel
is needed and the reaction is carried out under pressure.
Sertraline hydrochloride is produced by further hydrogenating the N-4-[3,4-
dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1(2H)-naphtalenylidene]methanamine resulted from
processes above and resolving the racemic mixture and finally crystallizing
sertraline
hydrochloride.
Now we have surprisingly found, that if the solvent for the imination process
is selected from the solvents of the invention, the reaction can be performed
in
atmospheric pressure and ambient temperature. Also the amount of the solvent
needed is low, impurities are not formed and the yield is good. Water removal
agents
like titanium tetrachloride or molecular sieves are not needed.
Another aspect of this invention relates to the process wherein the imine
product formed in the process of the invention is hydrogenated to form
sertraline
which is further resolved by e.g. mandelic acid and finally crystallized as
(1S-cis)-4-
(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-N-methyl-1-naphthalenamine
hydrochloride
or some other pharmaceutically suitable salt.
Still another aspect of the invention is a pharmaceutical composition
comprising (1S-cis)-4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-N-methyl-1-
naphthalenamine or its hydrochloride or some other pharmaceutically suitable
salt
prepared by the process of the invention.
CA 02448300 2003-11-25
WO 02/096860 PCT/FI02/00466
4
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
In a first embodiment, the present invention provides a process for producing
N-[4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1(2H)-naphthalenylidene]methanamine, by
reacting 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1-(2H)-naphthalenone with
monomethylamine in a solvent selected from the a group consisting of amide
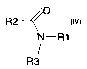
solvents of general formula IV:
R2~0
IV
N-R1
R3
wherein R1 and R3 are independently hydrogen or C1_6 alkyl, which can be
substituted, and R2 is hydrogen.
In another embodiment, the present invention provides a process wherein the
N-[4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1(2H)-naphthalenylidene]methanamine so
formed in the process of the invention is hydrogenated to form sertraline
which may
be further resolved by the use of, e.g., mandelic acid and finally
crystallized as ( 1 S-
cis)-4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-N-methyl-1-naphthalenamine
hydrochloride or some other pharmaceutically suitable salt.
In still another embodiment, the present invention provides a pharmaceutical
composition comprising (1S-cis)-4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-N-
methyl-1-naphthalenamine or its hydrochloride or some other pharmaceutically
suitable salt prepared by the process of the invention.
In a preferred embodiment of the present invention the solvent used in the
imination step is dimethylformamide or methylformamide, most preferably, the
solvent is dimethylformamide.
CA 02448300 2003-11-25
WO 02/096860 PCT/FI02/00466
The imination of 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1-(2H)-naphthalenone
with monomethylamine may be performed in the presence of acid catalyst, which
can
be any suitable organic or inorganic acid, e.g., formic acid, acetic acid,
sulfonic acid,
or hydrochloric acid. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, formic acid
or
5 acetic acid is used as the acid catalyst.
The solubility of the product in the solvent of the invention is low, so that
the
product is slowly crystallizing out of the reaction mixture and it can be
isolated
easily by, e.g., filtration. The process has also considerable purification
capacity.
The reaction can be performed under atmospheric pressure and is typically
carried
out at a temperature in the range of from about 0 °C to about 50
°C, preferably at
ambient temperature, i.e., from about 15 °C to. about 25 °C. Of
course, the imination
may also be carried out under a slight positive pressure of an inert
atmosphere, such
as nitrogen gas or argon gas.
Suitably, the 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1-(2H)-naphthalenone is
added to the solvent in an amount of about 300 g to about 400 g per liter of
solvent,
preferably about 320 g to about 350 g per liter of solvent. The methylamine is
added
in an amount of about 4 mole to about 6 mole per mole of 4-(3,4-
dichlorophenyl)-
3,4-dihydro-1-(2H)-naphthalenone, preferably about 4.8 mole to about 5.2 mole
per
mole of 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1-(2H)-naphthalenone. When used,
the
acid catalyst is typically added to the mixture in an amount of about 0.1 mole
to
about 2.0 mole per mole of 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1-(2H)-
naphthalenone, preferably about 0.4 mole to about 0.6 mole per mole of 4-(3,4-
dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1-(2H)-naphthalenone.
The present method is not constrained to any particular order of addition, and
the reaction may be conveniently performed by charging all of the components
into a
suitable-size vessel at 0 °C and then allowing the reaction mixture to
rise to ambient
temperature. The reaction mixture is then stirred at ambient temperature for a
time
of about 10 to about 30 hours, preferably about 20 to about 24 hours. If
desired, the
progress of the reaction may be monitored by any suitable technique, including
chromatography, especially high-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) or thin-
layer chromatography (TLC).
CA 02448300 2003-11-25
WO 02/096860 PCT/FI02/00466
6
The resulting imine compound, N-[4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-
I(2H)-naphthalenylidene]methanamine is insoluble in the reaction solvent and
exists
as a solid precipitate in the reaction mixture at the completion of the
reaction. The
resulting imine compound, N-[4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-I (2H)-
naphthalenylidene]methanamine may then be isolated from the reaction mixture
by
any suitable solid-liquid separation technique, such as filtration,
centrifugation, or
decantation.
The resulting imine compound, N-[4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-
1(2H)-naphthalenylidene]methanamine may be further hydrogenated to form cis-
(1S)(1R)- 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-N-methyl-1-naphthalenamine
which may then be optically resolved with, e.g., mandelic acid and finally
crystallized to afford (1S-cis)-4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-N-
methyl-1-
naphthalenamine hydrochloride or some other pharmaceutically suitable salt.
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising ( 1 S-cis)-4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-
1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-N-methyl-1-naphthalenamine or its pharmaceutically suitable
salt
prepared by the method of the invention can be prepared by methods well-known
in
the art.
The following examples are used to illustrate 'but by no means to limit the
scope of the invention, which is defined in the claims.
EXAMPLE 1.
Preparation of N-[4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1-(2H)-
naphthalenylidene]-methanamine
4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1-(2H)-naphtalenone (100 g), N,N-
dimethylformamide (300 ml) and formic acid (6.5 ml) are charged. Methylamine
(56.0 g) is added at about 0 °C. The mixture is stirred~for~ 20 hours
at room
temperature. The mixture is cooled to 10 °C and stirred for I hour. The
crystalline
compound is filtered and washed with methanol.,The yield is 97.7 g (93.5 %) as
dried.
CA 02448300 2003-11-25
WO 02/096860 PCT/FI02/00466
7
The same process was performed using N-methylformamide as a solvent in
the imination step. Yield was 90.1 %.
EXAMPLE 2.
Preparation of (1S-cis)-4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-N-methyl-
1-naphthalenamine hydrochloride (sertraline hydrochloride)
N-[4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1 (2H)-naphthalenylidene]-
methanamine (50 g) is hydrogenated over palladium on charcoal to yield cis-
(1S)(1R)- 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-N-methyl-1-
naphthalenamine.
The rasemic compound is resolved by mandelic acid and finally crystallized as
sertraline hydrochloride. The total yield from 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3,4-
dihydro-1-
(2H)-naphtalenone is 67 % (of the theoretical (+)-enantiomer).