Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02451305 2003-12-19
WO 03/002819 PCT/EPO1/07346
1
METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANUFACTURING PAVING
AND/OR PANELLING MODULES
Technical Field
The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus for
s manufacturing paving and/or panelling modules.
Background Art
Paving by means of blocks or tesserae in a mosaic-like pattern is
currently generally performed by manually laying a single block or tessera
at a time on a sand or cement bed.
to The manner in which the individual blocks are arranged creates, as a
whole, ornamental patterns which reproduce geometric shapes, e.g. an arc, a
circle or a compound fan, which are repeated identically a number of times
depending upon on the dimensions of the surface to be covered.
The- workers assigned to laying the blocks must then be expert in the
is trade, since carrying out these geometric shapes requires long working
experience and a special skill in placing the individual blocks in order to
obtain the best overall results, at a fair laying speed.
A drawback of current block laying methods is therefore the fact that
since they must be performed necessarily on site and by specialized
ao personnel, they entail long production_times _and rather high labor costs.
Another drawback of paving and/or panelling with current laying
techniques is that any detachment of a single block and/or mosaic tessera
leaves space for the adjacent elements to move and, in a relatively short
time, detach, thereby compromising the integrity of the composition.
Zs Disclosure of the Invention
The main object of the present invention is to provide a new method for
paving and/or panelling by means of blocks or tesserae which does not
necessarily involve the use of specialized labor, thereby significantly
xeducing its implementation costs.
so Another obj ect of the present invention is to provide an apparatus for the
CA 02451305 2003-12-19
WO 03/002819 PCT/EPO1/07346
2
mass-production of modules for street paving and/or panelling by means of
which it is possible to cover larger surfaces in less time, while making the
laying operation simpler and above all faster.
Another object of the present invention is to allow mass production of a
s plurality of variously shaped modules which can be mutually assembled and
are suitable for producing multiple ornamental patterns also for panelling
sloping surfaces and vertical walls.
Another object of the present invention is to provide modules which
adapt themselves to the uneveness of the surface to be covered and ensure
to integrity of the finished work, thereby preventing detachment of single
blocks, which would cause movement and gradual separation of adjacent
blocks.
Another object of the present invention is to provide modules which,
once laid, are durable and ensure particularly extended resistance to
is mechanical stresses and atmospheric agents.
Another object of the present invention is to provide a paving system
which is permeable to, and capable of draining rainwater while preventing
washing out of the sand from the bed.
Another object of the present invention is to provide modules which can
~o be easily lifted and carried by one operator.
According to a first aspect of the present invention, there is provided a
method for manufacturing paving and/or panelling modules which
comprises,the following operating steps:
-- arranging a plurality of blocks or tesserae in a suitable template,
2s according to a predetermined layout defined by a locating grid delimiting a
.
module;
-- cutting a piece of a layer of flexible material having through openings
so as to match the configuration of said module and being of larger
dimensions than said module;
30 -- securing, by means of permanent securing means said layer of flexible
CA 02451305 2003-12-19
WO 03/002819 PCT/EPO1/07346
3
material to each one of said blocks or tesserae forming said module, so that
they are held together by said piece of flexible material with the possibility
of changing their mutual inclination.
Advantageously, said method, before rigidly coupling said layer to the
s bottom of said blocks, includes an operation of spraying and drying a primer
onto the bottom of said blocks in order to promote adhesion of said coupling
means.
According to another aspect of the present invention there is provided an
apparatus for performing the above method, which has a supporting frame, a
to plurality of workstations arranged sequentially and a conveyor which
extends sequentially through said workstations, and is characterized in that
it comprises at least one moving unit designed to be arranged on said
conveyor to convey a module through each one of said workstations, and in
that one of said workstations comprises a device for applying permanent
is coupling means, 'thereby coupling a piece of flexible material to the
bottom
of said module.
Advantageously, said moving unit comprises a movable transfer tray
which is designed to be arranged on said conveyor, a template supporting
tray arranged to be located on said movable transfer tray, at least one
ao reference template to be fitted. on said template supporting tray and a
locking cover which is designed to fix the or each reference template on
said template supporting tray.
According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided at
least one module for street paving and/or panelling which comprises at least
as one block or tessera, characterized in that it comprises a layer of
flexible
material which has through openings and permanent securing means for
rigidly coupling said layer of flexible material to the or each block.
Advantageously, said layer of flexible material provided with through
openings comprises a meshed net.
3o Conveniently, said module comprises two or more of said blocks or
CA 02451305 2003-12-19
WO 03/002819 PCT/EPO1/07346
4
tesserae arranged according to a predetermined composition and held
together by said net.
Brief Description of the Drawings
Further aspects and advantages of the present invention will become
s better apparent from the following detailed description of some currently
preferred embodiments thereof, given merely by way of non-limitative
example with reference to the accompanying drawings, wherein:
Figure 1 is a plan view of an apparatus for producing a prefabricated
module according to the present invention;
so Figure 2 is an axonometric view of a movable transfer tray;
Figure 3 is an axonometric view of a template supporting tray;
Figure 4 is an axonometric view of a locking cover;
Figure 5 is an axonometric view of a detail of the locking cover of Figure
4;
1s Figure 6 is a plan view of a composition shaped like a contrasting arc;
Figure 7 is a plan view-of a left module of the composition of Figure 6;
Figure 8 is a plan view of a reference template for producing the module
of Figure 7;
Figure 9 is a plan view of a right module of the composition of Figure 6;
ao Figure 10 is a plan view of a left initial module of the composition of
Figure 6;
Figure 11 is a plan view of a right initial module of the composition of
Figure 6;
Figure 12 is a plan view of a left final module of the composition of
as Figure 6;
Figure 13 is a plan view of a right final module of the composition of
Figure 6;
Figure 14 is a plan view of a lateral closure module of the composition of
Figure 6;
so Figure 15 is a plan view of a circular composition;
CA 02451305 2003-12-19
WO 03/002819 PCT/EPO1/07346
s
Figure 16 is a plan view of a module of the composition of Figure 15;
Figure 17 is a plan view of a module with corner frame of the
composition of Figure 25;
Figure 18 is a plan view of a module with left frame of the composition
s of Figure 15;
Figure 19 is a plan view of a module with right frame of the composition
of Figure 15;
Figure 20 is a plan view of a composition shaped like a compound fan;
Figure 21 is a plan view of a left module of the composition of Figure
l0 20;
Figure 22 is a plan view of a right module of the composition of Figure
20;
Figure 23 is a plan view of a central module of the composition of Figure
20;
is Figure 24 is a plan view of a left half central module of the composition
of Figure 20;
Figure 25 is a plan view of a right half central module of the composition
of Figure 20;
Figure 26. is a plan view of a left module of the composition of Figure 20
2o according to another embodiment;
Figure 27 is a plan view of a right module which can be coupled to the
module of Figure 26;
Figure 28 is a plan view of a left final module of the composition of
Figure 20;
as Figure 29 is a plan view of a right final module of the composition of
Figure 20;
Figure 30 is a plan view of a left lateral closure module of the
composition of Figure 20; and
Figure 31 is a plan view of a right lateral closure module of the
so composition of Figure 20.
CA 02451305 2003-12-19
WO 03/002819 PCT/EPO1/07346
6
Ways of carrying out the Invention
In the accompanying drawings, identical or similar parts or components
have been designated by the same reference numerals.
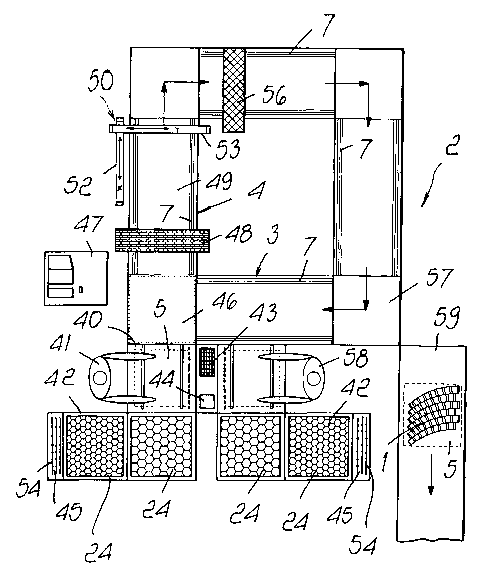
Initially with reference to Figures 1 to 8, reference numeral 1 indicates a
s generic module, the method for producing a module 1 requiring an
apparatus ~ 2 comprising a frame 3 which supports an uninterrupted conveyor
4 arranged to move a series of movable units 5.
Each movable unit 5 comprises a movable transfer tray , 6, shown in
Figure 2, which is designed to slide along guides 7 of the conveyor 4 and to
to support a template supporting tray 8, as shown in Figure 3.
The movable transfer tray 6 can be constituted by a square platform 9
which has two straight and parallel raised guides 11 on its upper surface 10
and a vertical locating pin 12 at each one of its four corners.
Each locating pin 12 has a rack-shaped side or front 13 and is orientated
is so that its rack-shaped side is directed toward the rack-shaped front of
the
pin located in the adjacent corner and on the same side with respect to the
guides 11.
The template supporting tray 8, shown in Figure 3, has on its lower
surface 14 two straight and parallel grooves 15 which are designed to slide,
ao in_use,._along the guides 11 of the transfer tray 6..
The template supporting plate 8 also has, at its upper surface, a
peripheral rim 16 which delimits a recessed inner surface 17.
A reference template 18, e.g. shaped as shown in Figure 8, is arranged, in
use, on the recessed surface 17.
2s The reference template 18, which can be made of aluminum, steel or
plastics, has an external supporting. frame 19, which is common to all kinds
of template, and a locating grid 20 which instead varies according to the
shape to be given to the module 1.
In the specific case shown in Figure 8, the locating grid 20 has a series
30 of ribs 21 which reproduce the shape of a left module 22, shown in Figure
7,
CA 02451305 2003-12-19
WO 03/002819 PCT/EPO1/07346
7
of a composition shaped like a contrasting arc 60, shown in Figure 6,
thereby delimiting spaces 23 within which the blocks or tesserae 24, shown
in Figure 1, are to be arranged.
Figure 4 illustrates a locking cover 25 which is constituted by an outer
s border 26 delimiting a central opening 27 which is smaller than the recessed
surface 17 of the template supporting tray 8.
The outer border 26 has, at its four corners, wider regions 28 at which
there are provided through openings 29 arranged to act as female elements
in coupling with the locating pins 12 when the locking cover 25 is
to superimposed, in use, on the transfer tray 6.
On each shoulder 30 and 31 of the border 26 there is a locking device 32
of the type shown in Figure 5, which is constituted by a pair of rods 33 and
34 which are aligned and fitted on a respective shoulder by means of
brackets 35 and free to perform small straight strokes lengthwise.
is The rods 33 and 34 are connected, at their ends, by a spring 36 which has
a central supporting cylinder 37 which is designed to keep them at a
predefined distance. .
In order to use the locking device 32 it is necessary to move the rods 33
and 34 mutually closer, thus overcoming the urge of the spring 36 and, once
ao the locking cover 25 has been placed on the template supporting tray 8,
release them so that the outward ends 38 of the two wedge-shaped rods 33
and 34 interact with the rack-shaped front 13 of the respective facing
locating pins 12, thereby preventing any upward movement of the cover 25.
As shown in Figure 1, a movable unit 5 is prepared in the workstation 40
Zs of the apparatus 2 and is initially constituted only by the transfer tray 6
and
the template supporting tray 8.
An operator 41 can thus arrange on the template supporting tray 8 a
reference template 18 which is suitable for providing a module such as the
module 22 of Figure 7.
so The same operator 41 can deposit the blocks 24, available in containers
CA 02451305 2003-12-19
WO 03/002819 PCT/EPO1/07346
8
42 located in the vicinity of the workstation 40, inside the grid 20, by
placing them with their bottom upward and trying to completely fill the
spaces 23 delimited by the ribs 21 that constitute the grid 20.
After blocks 24 have been placed on the template 18, the operator 41 can
s also be given the task of cleaning the bottom of the blocks 24 of any
impurities that might be present. For cleaning the blocks 24 it is possible to
use a rotating brush with steel bristles 43, which is located near the
workstation 40 within reach of the operator 41.
Alternatively, the same cleaning operation can be performed by
to subjecting the blocks 24 to a jet of water under pressure; in this case it
is
necessary to perform a subsequent drying step, . e.g. by employing j ets of
hot
air; this solution is not shown in Figure 1.
While the movable unit 5 is still located in the workstation 40, a primer
44 is advantageously sprayed onto it; said primer includes for example a
is petroleum resin and/or rosin applied in a solvent phase and is designed to
increase bonding of an adhesive material on the bottom of the blocks 24.
This operation, too, can be performed manually by the operator 41 or by a
suitable primer dispensing device (not shown in Figure 1).
The operator 41 then places on the template 18, and therefore on the
ao blocks 24 arranged therein, a piece of net 45 cut beforehand so as to have
the same configuration as that of the module being produced and larger
dimensions than said module, so as to protrude from its contour to a
predetermined extent.
In order to complete the preparation of the movable unit 5, the locking
a_s cover 25 is arranged on the template supporting tray 8, by inserting the
pins
12 of the transfer tray 6 inside the through openings 29 of the cover 25. In
this manner, the frame 26 of the locking cover 25 locks the template 18 on
the template supporting tray 8 owing to the two locking devices 32.
Once the preparation of the movable unit 5 has been completed, the
30 operator 41 arranges it on the initial station 46 of the conveyor 4, which
by
CA 02451305 2003-12-19
WO 03/002819 PCT/EPO1/07346
9
being controlled by a control unit 47 transfers it sequentially through a
series of workstations according to a predefined production cycle.
Preferably, the conveyor 4, controlled by a control unit 47, causes a
given module 1 being produced to pass through a drying device 48 provided
s with hot air j ets, not shown in Figure 1, so as to ensure full drying of
the
primer 44 and heating of the material to the temperature suitable for the
subsequent glueing step.
Once the drying step is terminated, the control unit 47 sends a control
signal for the advancement of the movable unit 5 to the workstation 49.
to Once the movable unit 5 has reached the workstation 49, a device 50 for
applying permanent securing means is energized in order to rigidly secure
the net 45 to the bottom of the blocks 24.
Preferably, a dispenser 50 of an adhesive material is used which is
equipped with a metering device (not shown) and is mounted on suitable
is mechanical arms 52 and 53 which can freely move, upon control, along two
perpendicular directions X and Y.
In this manner, adhesive material, which can be for example of the hot-
melt type including EVA (Ethyl Vinyl Acetate) and synthetic resins or
synthetic adhesives, is deposited at preset points upon control of the control
ao unit 47 and are usually distributed so as to secure the net 4S at its nodes
54
to the bottom of the blocks 24.
Advantageously, a step is provided for drying the freshly deposited
adhesive material; in this case, the module 1~ being produced is forwarded to
another drying device 56 e.g. provided with a series of hot air jets (not
2s shown).
The production cycle at this points provides for the advancement of the
movable unit 5 to the workstation 57, where an operator 5S has the task of
checking the quality of the finished product and, should the module 1 meet
predefined characteristics, transferring it to a conveyor belt 59 which
3o discharges into a store.
CA 02451305 2003-12-19
WO 03/002819 PCT/EPO1/07346
Transfer of the finished module 1 from the workstation 57 to the
conveyor 59 can be performed manually by the operator 58, who can
overturn it in order to prepare it for the subsequent step of packaging or
storage.
s As shown in Figure 7 and in Figures 9 to 23, a generic module 1 can be
composed of blocks or tesserae 24 made of porphyry, granite or other stone-
like or artificial materials.
In the specific case of module 22 in Figure 7, which illustrates the left
module of a composition shaped like a contrasting arc 60 shown in Figure 6,
1o it will be noted that the blocks 61 that are designed to occupy, in use,
positions at the center of the composition 60 are larger than the lateral ones
62.
Moreover, module 22 of Figure 7 and modules shown in Figures 9 to 14
have a step-shaped side 63 which is designed to delimit, in use, one of the
is two lateral edges of the contrasting arc composition 60; two adj scent
modules which belong to two nearby arcs 60 are thus coupled by arranging
the corresponding lateral edges 63 side by side, thereby penetrating each
other so as to ensure a self-locking effect in addition to uniformity of the
finished work.
~o So far as the module 22 of Figure 7 and to those of Figures 9 to 13 are
concerned, the lateral saw-tooth edge 64 which is opposite to the step-
shaped edge 63 is constituted by an alternation of recesses 65 and
protrusions 67 which is studied so as to allow to combine them by
interlocking in pairs, i.e., the left module 22 with the right one 68, the
left
as initial module 69 with the right one 68, the right initial module 70 with
the
left one 22, the left final module 71 with the right one 68, and the right
final
module 72 with the left one 22. The lateral module 95 of Figure 14 instead
has a straight lateral edge 96 which is opposite to the step-shaped one 63,
since it acts as an element for defining the border of the surface to be
3o covered.
CA 02451305 2003-12-19
WO 03/002819 PCT/EPO1/07346
11
If the composition is circular, like the composition 73 shown in Figure
15, the module 74 of Figure 16 is a single one and represents a quarter of a
circle. The module 74 is constituted by a sequence of concentric circular
arcs 75 formed by blocks 24 whose dimensions decrease towards the center
s of the circle. There is also an angular module 76 and two lateral modules, a
left one 78 and a right one 79, as shown respectively in Figures 17, 18 and
19.
The composition shaped like a compound fan 80 of Figure 20 is
composed of two lateral modules, a left one 81 as in Figure 21 and a right
one 82 as in Figure 22, and a central module 83 of Figure 23.
The standard central module 83 shown in Figure 23 can in turn be
constituted by two modules which represent, respectively, its left half 84,
shown in Figure 24, and its right half 85, shown in Figure 25.
A second embodiment of the fan-shaped composition 80 is constituted
1s only by two modules, a left one 86 and a right one 87, shown respectively
in
Figures 26 and 27, each of which already includes the left half 84 and the
right half 85 of the central module 83, respectively.
The left and right final prefabricated modules 89 and 90 and the left and
right lateral closure modules 91 and 92, shown respectively in Figures 28,
29, 30 and 31, are common to both of the embodiments of the fan-shaped
composition 80.
The method and the apparatus for producing prefabricated modules for
paving and/or panelling are susceptible of numerous modifications and
variations within the scope of the protection defined by the content of the
2s appended claims.