Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~
CA 02456902 2004-02-10
a
1
METHOD, DATA CARRIER, COMPUTER SYSTEM AND COMPUTER
PROGRAMME FOR THE IDENTIFICATION AND DEFENCE OF ATTACKS ON
SERVER SYSTEMS OF NETWORK SERVICE PROVIDERS AND OPERATORS
The invention relates to a method for the recognition
of and defense against attacks on server systems of
network service providers and carriers by an electronic
device that has to be integrated into a computer
network and contains a computer software and to a data
medium containing a computer software which performs
this technique. Furthermore the invention relates to a
computer system which is connected to a network like
Internet, intranet and the like, containing one or more
computers which are configured as server computers or
client computers and to a computer software product
containing computer software codes for the recognition
of and defense against attacks on server systems of
network service providers and carriers by an electronic
device that has to be integrated into a computer
network and contains this computer software.
The worldwide networking grows with high speed. An
ever-growing number of companies increasingly trusts in
the apparently unlimited chances in the fields of
online marketing and e-Business. But also increasing
are the dangers for the servers of well-known companies
and institutions being blocked by attacks from the
Internet.
CA 02456902 2004-02-10
2
The significance of the Internet as electronic
marketplace for the e-commerce activities of many
companies is growing more and more. Nevertheless the
threat on company networks by DoS and DDoS attacks
(Denial of Service and Distributed Denial of Service =
blocking access or utilization of a computer or the
service process running on it) is also growing
excessively. Frequently considerable financial damage
is done quite easily even without actual intrusion of
hackers into the secure system environment of a company
but only by successfully blocking the online business
(e-commerce / e-business?. Many approaches mastering
the solution for this problem fell far behind the
expectations. One of the reasons is that so far there
has been no real method of detection for this kind of
attack which is principally the only chance of defense
in a system environment affected by attacks. Another
problem is the nature of the Internet and the almost
hopeless situation of only being able to prevent the
cause of such attacks if absolutely all of the
worldwide network providers would establish uniform
restrictive measures for stopping such hacker attacks.
Among other things this is the reason for all national
attempts to prevent DoS or DDoS attacks being
unsuccessful or having only less success so far.
As is generally known the Internet is an international
network of technical components e.g. switches, routers
and transmission components with multiple routing etc.
Therefore often it is easily possible for hackers to
paralyze single servers or complete networks or network
regions. Local or national measures hardly promise an
~
CA 02456902 2004-02-10
c
3
effective prevention because the international network
of routers, network providers and the fancied call-by-
call connections makes it quite easy for the hackers to
find a way for a feasible attack strategy. Even if
there are no direct damages by loss or manipulation of
data or unauthorized copying of data, the loss of
reputation affects the company severely.
Programs which help executing such attacks are
available in the world wide web (WWW) for free. They
may be downloaded by hackers at any time. Most of these
feared attacks take advantage of technical flaws in the
data transmission protocols which are the basis of the
communication in the Internet. Mostly the affected
computers are stressed with such a huge number of
pretended requests so that serious requests can be
processed no longer. As a result the affected computer
seems to be inactive to the real customer.
Exemplary some well-known measures for protecting or
preventing DoS and DDoS attacks are named.
In the local environment of the network carriers and
providers measures making DoS and DDoS attacks more
difficult could be taken by active blocking of faked IP
addresses. That is because many DoS attacks use faked
IP sender addresses (IP spoofing) to prevent detection
of the hacker or at least make detection difficult. By
means of appropriate technical rules in the networking
infrastructure of the network carriers the network
providers can reduce this way significantly so that
faked IP packets from the own service environment are
~
CA 02456902 2004-02-10
4
no longer passed on to the Internet. Each organization
that is connected to a network provider has to its
disposal a specific range of IP addresses. Each IP
packet which is sent from this organization into the
Internet must have a sender address from this range. If
not it is almost certainly a faked address and the IP
packet should not be passed on by the network carrier,
i.e. a packet filtering mechanism regarding the sender
addresses should be performed while passing the packets
to the Internet. IP spoofing within the permitted
address range of the organization is still possible but
the range of possible sources is limited to the
organization. In addition to this the operation of so-
called "anonymous hosts" should be revised worldwide
and restricted or prohibited as far as possible. But
this is extremely costly concerning organization, time,
law and money.
So far the servers have often very limited abilities to
resist against the practiced DoS and DDoS attacks. Some
systems can withstand these attacks a little longer,
some systems only very shortly. But by now longer
lasting attacks are virtually always successful.
Unfortunately conventionally used packet filtering
solutions often don't help against DoS and DDoS attacks
or they are affected so much themselves that they lose
their protective effect quite soon, at least with
lasting attacks. Also numerous attack detection systems
stand far back because often they only detect the high
network traffic and issue warnings which mostly lead to
reactions much too late.
~
CA 02456902 2004-02-10
In case of a successful attack the possibility of
quickly reacting is of substantial relevance. Only by
that means it is possible to take effective measures,
maybe to identify the aggressor and to return to normal
service as soon as possible. In an emergency plan a
practical escalation procedure must be established.
Necessary data are among other things contact person,
responsible person, alternative communication paths,
action directives and storage place of probably needed
resources and backup media.
The servers of the carriers may be misused as agents of
a DoS attack. To accomplish this the attacker installs
harmful software taking advantage of well-known weak
points. Therefore the carriers have to configure their
servers in a careful and safe manner. Network services
which are not necessary should be deactivated and those
which are necessary should be secured. Adequate
password and access security as well as timely changes
of (especially default) passwords must be assured.
Many WWW pages in the Internet by now are only usable
with browser options that are questionable under
security aspects because they may be misused by an
attacker.
Many content providers make programs and documents
available in the Internet. If an attacker succeeds in
installing a Trojan Horse he can anticipate wide
distribution within a short time. This tactic is
tempting attackers especially with DDoS attacks because
CA 02456902 2004-02-10
6
a huge amount of hosts is necessary for an efficient
attack.
Hosts of end users are usually not targets of DoS
attacks. On the other hand these hosts may be used by
attackers to install software which later enables
remotely controlled DoS attacks at arbitrary hosts.
Hosts of end users may be misused as agents for
attacks. These agents can be installed on individual
hosts most simply via viruses, Trojan Horses or active
contents. Therefore a reliable and current virus
protection as well as the switching off of active
contents in the browser is absolutely required. If
necessary the use of utilities for online protection of
the clients (e. g. PC-firewalls) may be thought about.
However often computer viruses (esp. new ones) are not
detected and eliminated adequately.
Time and again new weak points which are relevant to
security are discovered in operating systems and server
software and are fixed by the manufacturers a little
later by updates or patches. For reacting as quickly as
possible it is necessary to constantly watch software
manufacturers for updates. The relevant updates must be
installed as quickly as possible so that the recognized
weak points are fixed.
To protect a host from risks and dangers considerable
know-how is necessary for implementing an efficient IT-
security configuration. Therefore administrators have
to be trained sufficiently and extensively.
~
CA 02456902 2004-02-10
7
Certainly the measures for blocking IP-spoofing are not
implemented quickly wold wide and uniformly by the
numerous network carriers and providers but with the
other protection measures described above, quite
effective success against DoS and DDoS attacks can be
reached. Nevertheless it is not possible by now to
reach a satisfactory result with the recognized
methods.
HUNT Ray, ~~Internet/Intranet firewall security-policy,
architecture and transaction services", COMPUTER
COMMUNICATIONS, BUTTERWORTHS & CO. PUBLISHERS LTD, GB,
Bd. 21, Nr. 13, 1. September 1998 /1998-09-O1), pages
1107-1123, XP004146571 ISSN 0140-3664 shows an overview
of firewall architectures.
WO 99/48303 discloses a method for blocking denial of
service and address spoofing attacks on a private
network.
The purpose of the invention is to create means for the
recognition of and defense against attacks on server
systems of network service providers and carriers of
the kind mentioned earlier. With these methods DoS and
DDoS attacks can be recognized and eliminated directly
so that a high degree of security and protection
against DoS and DDoS attacks is attained and the
computer or the computer system is kept in a stable and
efficient state continuously.
In the case of the invention in question, this purpose
is achieved methodically by the components and steps
AMENDED SHEET
CA 02456902 2004-02-10
8
- defense against DoS and DDoS attacks (flood attacks)
whereas
- each IP SYN (IP connection request) is registered
and answered with a SYN ACK for preservation of
time restrictions (timeouts) defined in the IP
protocol while the registered SYN packet is checked
for validity and available services in the target
system and
- the connection to the target system is initialized
and the received data packet is forwarded to the
target system for further processing if the
verification was successful and the expected ACK as
well as a consecutively following valid data packet
was received from the requesting external system in
the meantime, and
- link level security whereas the data packets which
have to be checked are received directly from the OSI
layer 2 (link level), and
- examination of valid IP headers whereas the structure
of each IP packet is checked for validity before it
is forwarded to the target system and each invalid
packet is rejected, and
- examination of the IP packet by especially checking
the length and the checksum for conformity of the
values in the TCP or IP header with the structure of
the IP packet and
- TCP/IP fingerprint protection whereas the answering
outgoing data traffic from the secured systems to the
requesting external systems is neutralized by using
default protocol identifiers, and
- blocking of each UDP network packet for avoiding
attacks at the secured systems via the network
AMENDED SHEET
CA 02456902 2004-02-10
9
protocol UDP (user datagram protocol), by selectively
registering and unblocking services required to be
reached via UDP whereas for these UDP ports messages
are explicitly admitted and the other UDP ports stay
closed, and
- length restrictions of ICMP packets (Internet control
message protocol) whereas only ICMP messages with a
predefined maximal length are identified as valid
data and others are rejected, and
- exclusion of specific external IP addresses from the
communication with the target system, and
- packet-level firewall function whereas incoming and
outgoing IP packets are examined by freely definable
rules and because of these rules are rejected or
forwarded to the target system, and
- protection of reachable services of the target system
by exclusion of specific services and users and
redirection of service requests to other servers.
Relating to the invention the purpose is also achieved
by a data medium containing a computer software for the
recognition of and defense against attacks on server
systems of network service providers and carriers for
the use in an electronic device that has to be
integrated into a computer network and contains the
program steps
- defense against DoS and DDoS attacks (flood attacks)
whereas
- each IP SYN (IP connection request) is registered
and answered with a SYN ACK for preservation of
time restrictions (timeouts) defined in the IP
protocol while the registered SYN packet is checked
AMENDED SHEET
CA 02456902 2004-02-10
1~
for validity and available services in the target
system and
- the connection to the target system is initialized
and the received data packet is forwarded to the
target system for further processing if the
verification was successful and the expected ACK as
well as a consecutively following valid data packet
was received from the requesting external system in
the meantime, and
- link level security whereas the data packets which
have to be checked are received directly from the OSI
layer 2 (link level), and
- examination of valid IP headers whereas the structure
of each IP packet is checked for validity before it
is forwarded to the target system and each invalid
packet is rejected, and
- examination of the IP packet by especially checking
the length and the checksum for conformity of the
values in the TCP or IP header with the structure of
the IP packet and
- TCP/IP fingerprint protection whereas the answering
outgoing data traffic from the secured systems to the
requesting external systems is neutralized by using
default protocol identifiers, and
- blocking of each UDP network packet for avoiding
attacks at the secured systems via the network
protocol UDP (user datagram protocol), by selectively
registering and unblocking services required to be
reached via UDP whereas for these UDP ports messages
are explicitly admitted and the other UDP ports stay
closed, and
AMENDED SHEET
CA 02456902 2004-02-10
11
- length restrictions of ICMP packets (Internet control
message protocol) whereas only ICMP messages with a
predefined maximal length are identified as valid
data and others are rejected, and
- exclusion of specific external IP addresses from the
communication with the target system, and
- packet-level firewall function whereas incoming and
outgoing IP packets are examined by freely definable
rules and because of these rules are rejected or
forwarded to the target system, and
- protection of reachable services of the target system
by exclusion of specific services and users and
redirection of service requests to other servers.
Preferably the data medium is represented by an EPROM
and is a component of an electronic device. This
electronic device may be a slot device for use in a
computer or a separate device box.
Alternatively the purpose is also achieved by a
computer system which is connected to a network like
Internet, intranet and the like, containing one or more
computers which are configured as server computers or
client computers. Inserted into a data line which has
to be protected and which connects~the network and the
server or client computers is an electronic device
which is provided with a data medium containing a
computer software which contains the program steps
- defense against DoS and DDoS attacks (flood attacks)
whereas
- each IP SYN (IP connection request) is registered
and answered with a SYN ACK for preservation of
AMENDED SHEET
" CA 02456902 2004-02-10
12
time restrictions (timeouts) defined in the IP
protocol while the registered SYN packet is checked
for validity and available services in the target
system and
- the connection to the target system is initialized
and the received data packet is forwarded to the
target system for further processing if the
verification was successful and the expected ACK as
well as a consecutively following valid data packet
was received from the requesting external system in
the meantime, and
- link level security whereas the data packets which
have to be checked are received directly from the OSI
layer 2 (link level) , and
- examination of valid IP headers whereas the structure
of each IP packet is checked for validity before it
is forwarded to the target system and each invalid
packet is rejected, and
- examination of the IP packet by especially checking
the length and the checksum fox conformity of the
values in the TCP or IP header with the structure of
the IP packet and
- TCP/IP fingerprint protection whereas the answering
outgoing data traffic from the secured systems to the
requesting external systems is~neutralized by using
default protocol identifiers, and
- blocking of each UDP network packet for avoiding
attacks at the secured systems via the network
protocol UDP (user datagram protocol), by selectively
registering and unblocking services required to be
reached via UDP whereas for these UDP ports messages
AMENDED SHEET
' CA 02456902 2004-02-10
13
are explicitly admitted and the other UDP ports stay
closed, and
- length restrictions of ICMP packets (Internet control
message protocol) whereas only ICMP messages with a
predefined maximal length are identified as valid
data and others are rejected, and
- exclusion of specific external IP addresses from the
communication with the target system, and
- packet-level firewall function whereas incoming and
outgoing IP packets are examined by freely definable
rules and because of these rules are rejected or
forwarded to the target system, and
- protection of reachable services of the target system
by exclusion of specific services and users and
redirection of service requests to other servers.
Furthermore the solution of the purpose relating to the
invention is achieved by computer software product
containing computer program codes for the recognition
of and defense against attacks on server systems of
network service providers and carriers by an electronic
device that has to be integrated into a computer
network and contains this computer software product.
The computer software product contains the program
steps
- defense against DoS and DDoS attacks (flood attacks)
whereas
- each TP SYN (IP connection request) is registered
and answered with a SYN ACK for preservation of
time restrictions (timeouts) defined in the IP
protocol while the registered SYN packet is checked
AMENDED SHEET
" CA 02456902 2004-02-10
14
for validity and available services in the target
system and
- the connection to the target system is initialized
and the received data packet is forwarded to the
target system for further processing if the
verification was successful and the expected ACK as
well as a consecutively following valid data packet
was received from the requesting external system in
the meantime, and
- link level security whereas the data packets which
have to be checked are received directly from the OSI
layer 2 (link level), and
- examination of valid IP headers whereas the structure
of each IP packet is checked for validity before it
is forwarded to the target system and each invalid
packet is rejected, and
- examination of the IP packet by especially checking
the length and the checksum for conformity of the
values in the TCP or IP header with the structure of
the IP packet and
- TCP/IP fingerprint protection whereas the answering
outgoing data traffic from the secured systems to the
requesting external systems is neutralized by using
default protocol identifiers, and
- blocking of each UDP network packet for avoiding
attacks at the secured systems via the network
protocol UDP (user datagram protocol), by selectively
registering and unblocking services required to be
reached via UDP whereas for these UDP ports messages
are explicitly admitted and the other UDP ports stay
closed, and
AMENDED SHEET
" CA 02456902 2004-02-10
- length restrictions of ICMP packets (Internet control
message protocol) whereas only ICMP messages with a
predefined maximal length are identified as valid
data and others are rejected, and
- exclusion of specific external IP addresses from the
communication with the target system, and
- packet-level firewall function whereas incoming and
outgoin IP packets are examined by freely definable
rules and because of these rules are rejected or
forwarded to the target system, and
- protection of reachable services of the target system
by exclusion of specific services and users and
redirection of service requests to other servers.
A special advantage of the solution relating to the
invention is that not only each of the secured systems
are protected against DoS and DDoS attacks but also the
computer software itself that performs the method of
recognition of and defense against attacks on server
systems of network service providers and carriers.
AMENDED SHEET
CA 02456902 2004-02-10
15a
The protection against DoS and DDoS attacks makes up
the kernel of the method relating to the invention. The
goal of these attacks is to stop the target computer or
computers i.e. to crash them by a flood of connection
request packets. As a result the attacked systems are
no longer able to react to communication requests. By
means of an intelligent set of rules each of the
secured systems are protected against attempts to
attack via DoS and DDoS attacks. Special treatment of
the incoming packets is assured by letting only
authorized requests pass the secured data line so that
the target systems e.g. world-wide-web (WWW) or email
servers are not crashed by mass attacks.
An own IP address is not necessary because the packets
to be checked are taken directly from the OSI layer 2
in the link level security module. As a result
configuration changes of the existing network
environment regarding logical addressing (IP routing)
are riot required. The hardware performing the method is
AMENDED SHEET
CA 02456902 2004-02-10
16
not an addressable network component so neither an
aimed attack nor spying out is possible.
Many TCP/IP implementations react incorrectly if the
structure of an IP header is invalid. If each IP
packet"s structure is checked for validity before it is
forwarded to the target system, it is assured that only
IP packets with correct structure get to the target
systems.
For successful attacks on computer systems knowledge of
the running operating system is important because aimed
attacks base on the knowledge of the operating system
of the target computer. TCP/IP fingerprint routines
examine the behavior of the TCP/IP implementations of
the target system and are able to derive information
about the operating system. The invention by its
functionality assures that the attacker cannot make
conclusions on the operating system by analysis of the
returned packets.
There are different methods or attacking computers in a
TCP/IP network. One of these methods is the sending of
ICMP messages with an inappropriately high packet
length. The function for restriction of the ICMP packet
length which is integrated into the invention helps to
fight this problem.
The possibility to exclude specific external IP
addresses increases the total security of the own
systems. For example if it is detected that a computer
from outside of the network checks which ports of the
CA 02456902 2004-02-10
17
system are open and thus able to be attacked, it is
possible to order to reject all the packets originating
from that computer. The list of blocked computers
(blacklist) can later be modified so that old entries
can be deleted again.
Additional to the packet level firewall function on the
IP packet layer the invention is extended by security
mechanisms relating to the reachable services which are
reached via the IP protocols HTTP, FTP, NNTP, POP,
IMAP, SMTP, X, LDAP, LPR, Socks or SSL. The exclusion
of specific services or users or the redirection of
service requests to other servers is assured by this
functionality. Easy configuration of this component is
enabled by an administration user interface for setting
these restrictions.
With the method relating to the invention, the software
and the device containing the computer software every
incoming and outgoing message is checked. When an
attack is detected the solution relating to the
invention intervenes specifically and selectively
blocks the suspicious data packets without influence on
the regular data traffic. All regular data is forwarded
with hardly any delay~so the operation of the solution
relating to the invention causes no disruption of work
or communication to the user. This is valid also with
high speed (and high data volume) Internet connections
(100 Mbit/s) of the server.
CA 02456902 2004-02-10
18
Further measures and arrangements of the method
relating to the invention result from the sub claims 2
to 6.
With one arrangement of the method relating to the
invention the length restriction of ICMP packets the
invalid length of packets is reduced to a valid one.
Beside the length restriction of ICMP packets specific
ICMP message types may be blocked completely.
With another arrangement of the packet-level firewall
function the appropriate rules are defined on the basis
of special criteria of the IP packet especially
referring to exclusions, restrictions and logging.
Subsequently the administration software creates a
configuration file for the firewall.
With an advantageous arrangement of the invention
administrative actions are done only from a console or
via secured network connections so that controlled
configuration and flawless operation are ensured.
Furthermore the access to the target system may be
restricted in detail by adjustable time configurations.
The entirety of this invention consequently is a
specially configured hardware, based on PC technology,
integrated microchips with additional specially
developed microcode. Further on a specially developed
software, based on the system- link level, which
contains a unique interdisciplinary method to react to
the miscellaneous problems by different system
CA 02456902 2004-02-10
19
routines. The invention also assures that the data
stream in total for the OSI-layer 3 up to the OSI-layer
7 is already selected on the link-level (OSI-layer 2)
and at that level deeply examined against security
related contents in all upper layers. An essential
feature of the invention is consequently, the proactive
extention for a the low level data line (which is
normally passive) with the active intelligence to
detect attack relevant contents in the whole data
stream. Because of the objective fact, that the
implemented methods of detection are able to detect
also "flood-attacks" and another attacks for the "IP-
stack" and for various "operating systems", there are
additional unique characteristics implemented. The
invention (hard- and software combined) protects itself
and all correctly connected systems behind against the
various attacks. The combined solution should be
installed between the screening router and the normally
to that router connected systems. With the implemented
different methods, which can be set in as a whole or
restricted, because of the modularity of the invention,
the various attacks in the whole IP data stream (incl.
the Internet protocol itself) will be detected and
defended. The data is independent of the IP-header or
IP-address directly from the link-level selected and
will be checked by a kind of "neutral instance", which
means the invention, for attack related contents. The
system where this "neutral instance" is running needs
no IP-address. Therefore it can't be attacked on the
IP-level, which is also a differentiator of this
invention. For all active network components this
system is hidden and unreachable.
CA 02456902 2004-02-10
One essential element of this invention is the active
detection of DoS- and DDoS-attacks, which are via this
combined hard- and software solution now possible. On
the side of server provider implemented, the server
systems can be protected against DoS- and DDoS-attacks.
On the side of network provider implemented, the lines
can be protected against the still possible line
flooding. Important: Using this functionality of the
invention only, the existing firewalls are not to be
replaced, but used as essential extension of the
security model.
It goes without saying that the aforementioned and
following characteristics are not mutually exclusive
but can be utilised in other combinations or on their
own. This would not exceed the scope of the present
invention.
The basic approach of the invention is shown in the
following description with some implementation examples
described in the figures. The figures show:
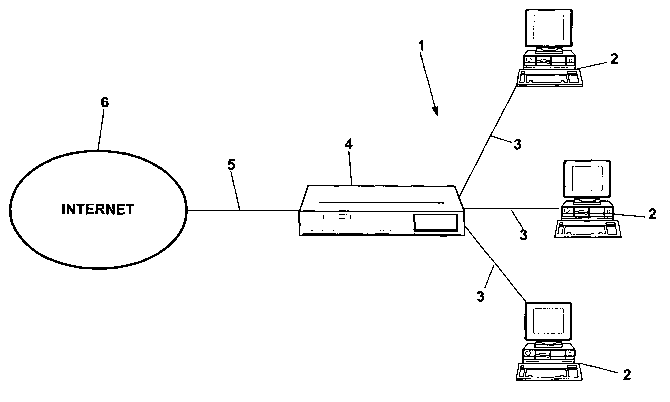
Fig. 1 a schematic description of a computer system
corresponding to the invention which is
connected to the Internet in a small network
environment;
Fig. 2 a schematic description of a computer system
corresponding to the invention which is
connected to the Internet in a medium-sized
network environment;
" CA 02456902 2004-02-10
21
Fig. 3 a schematic description of a computer system
corresponding to the invention which is
connected to the Internet in a large network
environment;
Fig. 4 a schematic description of a procedure
corresponding to the invention establishing a
connection with the authorized use of a
protocol;
Fig. 5 a schematic description of a procedure
corresponding to the invention building up a
connection with the non-authorized use of a
protocol;
Fig. 6 a schematic description of a procedure
corresponding to the invention failing to
establish a connection;
Fig. 7 a schematic description of a procedure
corresponding to the invention after
establishing a connection with authorized flow
of data;
Fig. 8 a schematic description of a procedure
corresponding to the invention after
establishing a connection with non-authorized
flow of data;
Fig. 9 a schematic description of the protocol levels
protected through an electronic device;
CA 02456902 2004-02-10
22
Fig. 10 a description of the examination of valid IP
headers;
Fig. 11 a description of the examination of a IP
packet;
Fig. 12 a description of the examination of adjustable
UDP connections and
Fig. 13 a description of the length limitations of
ICMP packets.
The computer system 1 according to figures 1 to 3
consists of several server computers 2 which are
possibly mutually connected through further data lines.
Those are not described in further details. The server
computers are connected to an electronic device 4 via a
data line 3 each. This device shows a data carrier
instructed as EPROM , which is not described in further
details, which implements a computer program to
recognize and to refuse the attacks on server systems
of network providers and operators.
The electronic device 4 is connected to the Internet
via an ISDN data line 5 according to figure 1. The
electronic device serves as protection of DOS and DDOS
attacks and as an enhanced functionality as Internet
gateway via ISDN. In addition to this, the electronic
device 4 is equipped with an Ethernet and an ISDN
adapter. Beside the protection of the systems in the
Local Area Network (LAN) against DOS and DDOS attacks,
the electronic device 4 is used as router for the
CA 02456902 2004-02-10
23
access on services of the Internet. The establishing of
the ISDN connection is, as a standard, effected
whenever a communication access to an external network
is requested. The establishing of a connection is
effected automatically if the computer program
contained in the EPROM within the electronic device 4
does not transfer any further network packets after a
certain time frame. One can modify this standard
attribute trough a corresponding configuration.
The electronic device 4 is, for instance, connected to
the Internet 6 via an ISDN/Ethernet data line 7
according to figure 2. In addition to this, the
electronic device 4 integrates a non-visible firewall-
function-module. Thus it can be used as integrated
firewall roister, possibly via a further dedicated
roister. The server computers 2 or personal computers,
respectively of the internal network use the electronic
device 4 with the EPROM including the computer program
protecting and refusing attacks on servers systems of
network service providers and operators as transition
into the Internet via Ethernet or ISDN. Moreover, the
electronic device 4 protects the internal systems
against DOS and DDOS attacks. With this incoming and
outgoing IP packets are forwarded or aborted by means
of defined rules. The access to the services open to
the public is approved or denied according to defined
rules on the locals systems.
The rules necessary for the individual functions are
established and modified through a configuration
program being able to establish a readable
CA 02456902 2004-02-10
24
configuration set according to simplified inputs of
users as well. The functions offered by the electronic
device 4 including the computer program for recognizing
and refusing attacks on server systems of network
service providers and operators may be configured
freely to a large extent. Thus they can be adopted for
the use within the own network in an optimal way.
The way of describing the invention according to figure
3 shows the firewall-function-module 9 being separate
that is to say switched separately between the server
computers 2 and the electronic device 4 including the
computer program for recognizing and refusing attacks
on server systems of network service providers and
operators. The electronic device 4 is connected to the
Internet 6 via an Ethernet data line 8 and offers the
protection necessary against DOS and DDOS attacks
(flood attacks). Only those network packets will be
forwarded to the firewall for further handling which do
not cause any harm to the target system concerned.
After that the decision whether to accept or deny
forwarding the network packets is taken on the
firewall.
Figure 4 shows a schematic description of the procedure
when establishing a connection with authorized use of
protocol whereas figure 5 shows the procedure when
establishing a connection with non-authorized use of
protocol.
Figure 6 shows the procedure corresponding to the
invention with the failing of completely establishing a
CA 02456902 2004-02-10
connection. Figure 7 schematically simulates the
procedure after establishing a connection with
authorized flow of data and figure 8 simulates the
procedure after establishing a connection with non-
authorized data flow.
Figure 9 show a schematic description of the protocol
levels being protected through an electronic device
with the EPROM including the computer program
protecting and refusing attacks on servers systems of
network service providers and operators.
Figure 10 describes the examination of valid IP
headers. Figure 11 describes the examination of a IP
packet. Figure 12 describes the examination of
adjustable UDP connections and figure 13 describes the
length limitations of TCMP packets.
' CA 02456902 2004-02-10
26
List of signs of reference
1 computer system
2 server computer
3 data line
4 Electronic device
ISDN data line
6 Internet
7 ISDN/Ethernet data line
8 Ethernet data line