Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02473856 2004-07-13
WO 03/061423 PCT/US03/00242
Embeddingly Installed-Type Fastener
Field of the Invention
The present invention relates to a fastener that is installed integrally to an
article
by means of an embedding section provided on a back surface of a strip-shaped
base.
Background of the Invention
In an article like a seat on a vehicle, an office chair, a home chair, or a
mattress,
etc. there are used a core member having a cushion core member made of a
molded
product like a foamed resin material, and a flexible covering member made of
cloth or
leather for covering the surface of the core member. In such an article, it
has been
known that an inter-engagement type fastener (what is called a plane fastener)
having a
plurality of engaging elements disposed on one plane of a base, that is, on a
major
surface, is used for fixing the covering member to the core member.
Particularly, users
expect a high level of comfort from the articles like seats and chairs. In
order to meet
such user's needs, there has been an increasing trend that a flexible strip-
shaped fastener
that can be disposed in a slender groove recessed on the surface of the core
member
along the seam of the covering member is used as fixing means for fixing the
covering
member to the core member(as disclosed, for example, in Japanese Unexamined
Patent
Publication (Kokai) No. 11-127915). In such a form of application, the strip-
shaped
fastener fixes the covering member to the core member with the engaging
elements being
detachably engaged with its counterpart, that is, engaging elements such as
fiber loops
provided on the covering member.
In order to fixedly install the strip-shaped fastener at a desired position of
the
2 5 surface of the core member with the engaging elements exposed, an insert-
molding
method can be applied advantageously. This is a method in which the fastener
is
disposed within a mold of the core member as the molded body and is fixed to
the core
member simultaneously with molding of the core member. According to this
insert-
molding method, an elongated rail-shaped guide for holding the fastener in a
3 0 predetermined posture is provided within the mold of the molded body. The
guide
usually has an elongated groove capable of accommodating the base of the
fastener and
the engaging elements. The fastener is installed on the guide by inserting the
engaging
CA 02473856 2004-07-13
WO 03/061423 PCT/US03/00242
elements and the base into the groove in a state that a back surface (the
surface opposite
to a major surface) of the base is exposed.
An embedding section which is to be fixedly embedded into the molded body by
means of the insert-molding process, is provided on the back surface of the
base of the
fastener. Thus, the fastener is integrally installed to the molded body using
the
embedding section. Conventionally, the embedding section has been composed so
as to
comprise a plurality of posts erected upright to the back surface of the base
and thin
plate-shaped anchors formed at the end of each post and extending generally
parallel to
the back surface. Each anchor has an elliptical profile of koban-like shape
that does not
project out in the width direction on the back surface of the base. The molded
body is
formed adjacent to the back surface of the base so as to surround the
plurality of posts
and anchors. Each anchor is thus bound as if it bites into the molded body,
whereby the
fastener is securely fixed to the molded body.
Summary of the Invention
In the conventional strip-shaped fastener as described above, it is necessary
not
only to ensure that the engaging elements exhibit desired level of adhering
force for
adhering to the counterpart engaging elements, but also to ensure that
sufficient strength
be obtained in the installation of the fastener to the article (or the molded
body) via the
2 0 embedding section. Especially, when the manner in which the fastener is
used in the
above-described seats or chairs as fixing means for fixing the covering member
to the
core member is taken into account, it is required that the strength of the
installation
exhibited by the embedding section should be larger than the adhering force
exhibited by
the engaging elements, in order to prevent the destruction of the
interconnection between
2 5 the fastener and the core member, when, for example, tension is
intermittently applied to
the covering member by frequent and rapid movement of the center of gravity of
the
seated person, or when the covering member is intentionally separated from the
core
member for the purpose of replacement or the like. From this view-point, it is
required
in the conventional strip-shaped fastener to improve the installation strength
for installing
3 0 it to an article via the embedding section as much as possible without
impairing the
inherent flexibility of such a construction.
2
CA 02473856 2004-07-13
WO 03/061423 PCT/US03/00242
One object of the present invention can be to provide a fastener which is
integrally installed to an article by means of an embedding section provided
on a back
surface of a strip-shaped base, and which is capable of improving the strength
of
installation to the article by means of the embedding section as much as
possible without
impairing the inherent flexibility of such a construction.
In one aspect of the present invention, a fastener is provided that comprises
a
strip-shaped base having a major surface and a back surface opposite to the
major
surface, an engaging section provided on the major surface of the base, and an
embedding section provided on the back surface of the base, being adapted to
be
integrally installed to an article via the embedding section, characterized in
that the
embedding section comprises a plurality of projecting elements which are
discretely
arranged spaced apart from each other in the longitudinal direction of the
base, and each
of which extends outward from the base substantially in the width direction of
the base.
The projecting elements can be formed integrally with the base. The projecting
elements can be provided detachably on the base. The plurality of projecting
elements
can be arranged at regular intervals in the longitudinal direction of the
base, and the
projecting elements project symmetrically on both lateral sides of the base.
Each of the
projecting elements can have generally flat outer surface extending in
parallel to the
back surface of the base on the side away from the back surface of the base.
Brief Description of the Drawings
Fig. 1. An enlarged perspective view showing a portion of a fastener according
to a first embodiment of the present embodiment.
Fig. 2. A plan view showing a portion of the fastener of Fig. 1.
2 5 Fig. 3. A bottom plan view showing a portion of the fastener of Fig. 1.
Fig. 4. A schematic perspective view showing a guide for installing the
fastener
of Fig. 1 together with the fastener.
Fig. 5. A view showing an article equipped with the fastener of Fig. 1.
Fig. 6. A cross-sectional view showing the fastener installing portion of the
3 0 article of Fig. 5 when the fastener is inoperative.
Fig. 7. A cross-sectional view showing the fastener installing portion of the
article of Fig. 5 when the fastener is operative.
3
CA 02473856 2004-07-13
WO 03/061423 PCT/US03/00242
Fig. 8. (a) a plan view, and (b) a side view, of a good example of the
projecting
elements of the fastener of Fig. 1.
Fig. 9. (a) a plan view, and (b) a side view, of a modification of the
projecting
elements of the fastener of Fig. 1.
Fig. 10. (a) a plan view, and (b) a side view, of another modification of the
projecting elements of the fastener of Fig. 1.
Fig. 11. (a) a plan view, and (b) a side view, of still another modification
of the
projecting elements of the fastener of Fig. 1.
Fig. 12. An enlarged, partially cut-out plan view showing a portion of a
fastener
according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 13. (a) a plan view, and (b) a front view, of an anchor member having
projecting elements of the fastener of Fig. 12.
Fig. 14. (a) a plan view, and (b) a front view, of a modification of the
anchor
member having projecting elements of the fastener of Fig. 12.
Detailed Description of the Invention
Embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below with
reference to the attached drawings. In the drawings, identical or similar
constituent
elements will be denoted by common reference symbols.
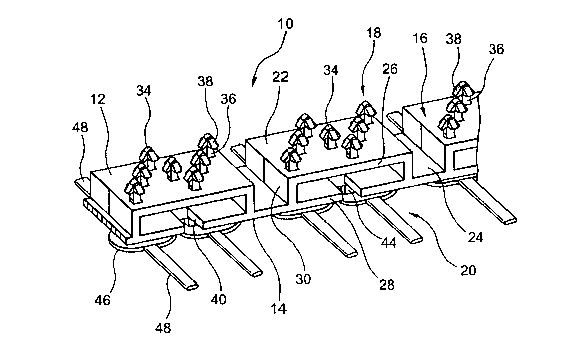
2 0 Figs. 1 to 4 are views showing a fastener 10 according to a first
embodiment of
the present invention. The fastener 10 is an inter-engagement type fastener
having
flexibility in multiple directions, and is comprised of a strip-shaped base 16
having a
major surface 12 and a back surface 14 opposite to the major surface 12, an
engaging
section 18 provided on the major surface 12 of the base 16, and an embedding
section 20
2 5 provided on the back surface 14 of the base 16.
The base 16 is constructed of a plurality of box-shaped parts 22 arranged in
spaced-apart relationship with each other in the longitudinal direction, and a
plurality of
connecting parts 24 for mutually connecting the box-shaped parts 22 into one
unit. Each
of the box-shaped parts 22 has a substantially hollow structure consisting of
a plane
3 0 upper plate 26 and a plane lower plate 28 extending approximately in
parallel, a pair of
side plates 30 for connecting between the upper and lower plates 26 and 28,
and a
partition plate 32 extending in the longitudinal direction between the plates
26, 28,
4
CA 02473856 2004-07-13
WO 03/061423 PCT/US03/00242
and 30. The major surface 12 of the base 16 is constructed of the upper plates
26 of the
plurality of the box-shaped parts 22, and the back surface 14 of the base 16
is constructed
of the lower plates 28 of the plurality of the box-shaped parts 22 in
cooperation with the
plurality of the connecting parts 24.
The engaging section 18 comprises a plurality of engaging elements 34 erected
at
regular spacing on the major surface 12 of the base 16. Those engaging
elements 34 are
provided on each upper plate 26 of the plurality of box-shaped parts 22
forming the
base 16, in the same number (seven in the Figures) and in the same layout.
Each
engaging element 34 comprises a leg 36 stretching generally upright from the
upper
plate 26 of each box-shaped part 22, and a plurality of (four in the Figures)
engaging
pieces 38 projecting sideways near the front end of the leg 36. The fastener
10 is
detachably fixed to other article by having the plurality of engaging elements
34 of the
engaging section 18 frictionally engaged by means of the respective engaging
pieces 38
with corresponding engaging section provided on the other article. The
engaging
elements 34 may be omitted on desired box-shaped parts 22 (at both ends in the
longitudinal direction in the Figures).
The lower plate 28 of each box-shaped part 22 has a slit 40 formed so as to
extend in a crossing direction at approximately the center in the longitudinal
direction of
the box-shaped part 22. Further, the lower plate 28 has one rib 42 extending
in the
2 0 longitudinal direction crossing the slit 40 provided to project on the
back surface 14
along the whole length of the base 16. The rib 42 has two posts 44 for each
box-shaped
part 22 extending in the shape of thin plate along the rib 42, provided
perpendicularly to
the back surface 14. An anchor 46 in the shape of a thin plate extending
generally in
parallel with the back surface 14 is formed on the front end of each post 44.
Each
2 5 anchor 46 has a profile of koban-like shape which does not bulge out in
the width
direction on the back surface 14 of the base 16. These plurality of posts 44
and
anchors 46 serve as an embedding section 20 for fixedly installing the
fastener 10 to a
desired article.
In the fastener 10 having above-described construction, owing to the stress
3 0 dispersion effect at each box-shaped part 22 having the hollow structure,
the base 16 can
be bent as a whole relatively easily in a horizontal direction, that is, in a
direction
generally parallel to the major surface 12 and the back surface 14. Further,
owing to the
5
CA 02473856 2004-07-13
WO 03/061423 PCT/US03/00242
hinge effect of each thin connecting part 24, the base 16 can be bent
relatively easily also
in a vertical direction, that is, in a direction generally orthogonal to the
major surface 12
and the back surface 14. Since the fastener 10 has the base 16 that can be
easily bent
both in horizontal and in vertical directions, it is possible to install the
base 16 on any
desired surface portion of an article having a variety of three-dimensional
surface by
accurately following the surface three-dimensionally. Preferably, the fastener
10 is
integrally formed with a resin material like nylon, polypropylene, etc.
As a specific feature of the construction of the fastener 10 according to the
present invention, the embedding section 20 further comprises a plurality of
projecting
elements 48 arranged discretely so as to be spaced apart from each other in
the
longitudinal direction of the base 16. In the embodiment shown in the Figures,
each of
the projecting elements 48 has a bar-shaped form and is integrally connected
at one
longitudinal end thereof to a periphery of the anchor 46 provided on the back
surface 14
of the base 16, so as to extend generally in parallel with the back surface 14
substantially
in the width direction of the base 16. Each projecting element 48 has, at the
free end
area thereof, a dimension projecting over a specified length laterally from
the base 16.
In the embodiment as shown in Figs. 1 to 3, the plurality of projecting
elements 48 are formed with two elements being connected to each of the
plurality of
anchors 46 provided at generally equal spacing in the longitudinal direction
on the back
2 0 surface 14 of the base 16 so as to project from both side edges of the
anchor 46 laterally
on both sides of the base 16. As a result, these projecting elements 48 are
arranged at
equal spacing in the longitudinal direction of the base 16, and symmetrically
with each
other on both sides of the base 16. With this construction, when the fastener
10 is
installed to an article by means of the embedding section 20 as described
later, the
2 5 plurality of projecting elements 48 exhibit an installation strength
uniformly in
equilibrium over the entire length of the fastener 10.
Alternatively, as shown in Fig. 4, the projecting elements may be provided
only
on desired anchors 46 among the plurality of anchors 46 provided on the back
surface 14
of the base 16. In such a case, the installation strength of the base 16 to an
article
3 0 exhibited by the embedding section 20 can be locally increased at the
position
corresponding to the anchors 46 at which the projecting elements 48 are
formed. Only
one projecting element 48 may be formed for each anchor 46, provided that the
6
CA 02473856 2004-07-13
WO 03/061423 PCT/US03/00242
equilibrium of the installation strength in the width direction of the base 16
is not
significantly impaired.
The fastener 10 is, by means of an insert-molding process using a guide 50 as
shown in Fig. 4 to be described later, integrally installed to a molded body
of desired
shape.
The guide 50 is a rail-shaped block unit for supporting the fastener 10 over a
desired length, and is comprised of a bottom wall 52, and a pair of side walls
54
integrally erected from the bottom wall 52 along both edges of the bottom wall
52
extending in the longitudinal direction. The bottom wall 52 and the pair of
side walls 54
form one stream of a groove 56 capable of accommodating the base 16 of the
fastener 10
and the plurality of engaging elements 34 along the whole length of the guide
50. Both
side walls 54 have inner surfaces 54a respectively facing each other with a
uniform
spacing therebetween over the entire length of the guide 50. The bottom wall
52 has a
pair of sealing surfaces 52a orthogonal to the inner surfaces 54a of both side
walls 54 at
both ends in the longitudinal direction of the guide 50, and a pair of
auxiliary supporting
surfaces 52b extensively provided in the longitudinal direction of the guide
50 adjacent to
the inner surface 54a of each side wall 54. The groove 56 is divided into two
parts in
function; a first part 56a capable of accommodating the base 16 of the
fastener 10
between the inner surfaces 54a of both side walls 54 above the sealing surface
52a and
2 0 the auxiliary supporting surface 52b; and a second part 56b capable of
accommodating
the plurality of engaging elements 34 of the fastener 10 below the sealing
surface 52a
and the auxiliary supporting surface 52b.
The spacing between the inner surfaces 54a of both side walls 54 is made to
have
a size approximately identical to the size of the base 16 of the fastener 10
in the width
2 5 direction as an object to be supported. Therefore, when the fastener 10 is
properly
accommodated into the groove 56 of the guide 50, the inner surfaces 54a of the
side
walls 54 are brought into close contact with the side edges extending in the
longitudinal
direction of the base 16 of the fastener 10 accommodated in the first part 56a
of the
groove 56. The pair of sealing surfaces 52a of the bottom wall 52 are brought
into close
3 0 contact with major surface 12 of the box-shaped part 22 (having no
engaging
elements 34) on both ends in the longitudinal direction of the fastener 10.
7
CA 02473856 2004-07-13
WO 03/061423 PCT/US03/00242
In this way, the guide 50 can hold the fastener 10 in a predetermined posture
with
frictional force in a state that the base 16 of the fastener 10 is embedded
into the first
part 56a of the groove 56 while the engaging elements 34 of the engaging
section 18 of
the fastener 10 are accommodated in the second part 56b of the groove 56. As a
result, it
is possible to prevent liquid material from penetrating into the second part
56b of the
groove 56 when forming the molded body in a state that the fastener 10 is
supported by
the guide 50. In a state that the fastener 10 is properly held in the guide
50, the plurality
of projecting elements 48 of the engaging section 20 project at the free end
region thereof
outwards from both side walls 54 of the guide 50. The guide 50 can be
integrally
manufactured by cutting from a metal bar-shaped material like aluminum,
aluminum
alloy, iron, etc.
Fig. 5 exemplifies an article 60 having the fastener 10 integrally installed
on a
molded body 58 by the insert-molding process using the guide 50. In the
example shown
in the drawing, the article 60 is a seat for a vehicle, and the molded body 58
constitutes a
core member made of a foamed resin material like polyurethane. In this
construction, a
plurality of fastener 10 function as fixing means for fixing a covering member
62 made
of cloth or leather to the molded body 58. Each fastener 10 is fixedly
disposed in a
slender recess 64 provided on the surface of the molded body 58 at a desired
position
along a seam 62a of the covering member 62.
2 0 In the insert-molding process, the guides 50 in a number corresponding to
the
number of fasteners 10 to be installed to the article 60 are disposed within a
mold (not
shown) of the molded body 58, in a layout corresponding to the layout of the
fasteners 10
on the surface of the molded body 58. Each guide 50 is fixed on the formed
surface of
the mold by fixing means like putty, bolts, magnets or the like, with the
groove 56
2 5 (Fig. 4) facing to the hollow part of the mold. Each fastener 10 is
installed on the
corresponding guide 50, with the plurality of engaging elements 34 of the
engaging
section 18 inserted into the second part 56b of the groove 56 of the guide 50,
and with
the plurality of box-shaped parts 22 of the base 16 fit into the first part
56a of the
groove 56 of the guide 50. Thus, the back surface 14 of the base 16 of each
fastener 10,
3 0 and the rib 42 and the embedding section 20 (the plurality of posts 44,
anchors 46 and
projecting elements 48) projectingly provided on the back surface 14, are
disposed in an
exposed state in the hollow part of the mold.
8
CA 02473856 2004-07-13
WO 03/061423 PCT/US03/00242
In this state, a liquid foam resin material of the molded body 58 is supplied
to the
hollow part of the mold. As described before, the base 16 of the fastener 10
is brought
into close contact with the pair of inner surfaces 54a, the sealing surface
52a and the
auxiliary supporting surface 52b of the guide 50, thereby to prevent the
liquid resin
material from penetrating into the second part 56b of the groove 56 of the
guide 50.
Thereafter, when the liquid resin material is foamed and solidified to form
the molded
body 58, each recess 64 is formed on the surface of the molded body 58 at a
position
corresponding to the space occupied by each guide 50 within the hollow part of
the mold.
As shown in an enlarged view in Fig. 6, in each recess 64, the fastener 10 is
fixed
to the molded body 58 with the base 16 (except the major surface 12) and the
embedding
section (the plurality of posts 44, anchors 46 and projecting elements 48)
embedded in
the molded body 58, and thereby with the plurality of engaging elements 34 of
the
engaging section 18 exposed in the inner space of each recess 64. In this
state, each
fastener 10 has its plurality of engaging elements 34 exposed in each recess
so that these
engaging elements 34 may be detachably engaged with corresponding engaging
elements 66 such as fiber loops formed on the back surface of the seam 62a of
the
covering member 62, thereby fixing the covering member 62 to the surface of
the molded
body 58 (see Fig. 7).
After the insert-molding process as described above, the molded body 58 is
2 0 formed in such a shape that it substantially surrounds the plurality of
posts 44, anchor 46
and projecting elements 48 which together constitute the embedding section 20
of the
fastener 10. At this point, the plurality of projecting elements 48 projecting
sideways on
both sides of the base 16 of the fastener 10 are in a state that they bite
into the molded
part further outside of the recess 64 of the molded body 58 (see Figs. 6 and
7). As a
2 5 result, compared to a conventional fastener that only has the koban-shaped
anchors which
do not project out of the base as an embedding section, the fastener 10
according to the
present invention is fixed to the molded body 58 under sufficiently larger
installation
strength. Therefore, by means of the fastener 10 according to the invention,
destruction
of the interconnecting portion between the fastener 10 and the molded body 58
(the
3 0 portion of molded material surrounding the embedding section 20) can be
reliably
prevented when the fastener 10 is used, for example, in a seat for a vehicle
as described
above, under a tension unintentionally exerted to the covering member 62 due
to frequent
9
CA 02473856 2004-07-13
WO 03/061423 PCT/US03/00242
and rapid movement of the center of gravity of a seated person, or under a
tension
intentionally exerted for the purpose of replacement or the like, thereby
permitting the
covering member 62 to be detached accurately and stably from the fastener 10.
Also,
when the molded body 58 is removed from the mold after the insert-molding
process is
completed, the fastener 10 is smoothly detached from the guide 50, which
advantageously
facilitates the removing operation of the molded body 58.
In the fastener 10, the plurality of projecting elements 48 are discretely
disposed
by being spaced apart from each other in the longitudinal direction of the
base 16 so that
presence of the projecting elements 48 does not impair the three-dimensional
flexibility
of the base 16 as described before. Since individual projecting element 48
enlarges the
size in the width direction of the embedding section 20 disposed on the back
surface 14
of the base 16, even when the fastener 10 is applied to a case where presence
of the
fastener 10 can be recognized by the feeling of touch by a user as in the
above-described
application to a seat for a vehicle, installation strength of the fastener can
be increased as
much as possible by means of the embedding section 20 without impairing the
feeling of
touch. Further, since the plurality of projecting elements 48 can be formed
integrally
with the base 16, for example, by an injection molding process, increase of
the number of
parts can be avoided.
The projecting element provided on the embedding section of the fastener
2 0 according to the present invention may be formed in various forms,
provided that the
required installation strength as described above can be ensured. In
particular, the
construction as shown in Fig. 8 in which projecting elements 48 in the shape
of round bar
(circular or elliptic cylinder) are connected to an anchor 44 having a koban-
shaped
profile, and in which the anchor itself has a generally flat outer surface 44a
extending in
2 5 parallel to the back surface 14 on the side away from the back surface 14
of the base 16,
has following advantageous effect in the mounting of the fastener on the above-
described
guide 50. That is, when an operator mounts the fastener 10 manually on the
above-
described guide S0, the fastener 10 can be smoothly slid on the surface 44a of
the
plurality of anchors 44 arranged adjoiningly in the longitudinal direction of
the
3 0 fastener 10 with a finger or jig abutted to it. By such a smooth sliding
operation, the
base 16 of the fastener 10 can be pushed into the groove 56 of the guide 50
quickly and
progressively.
CA 02473856 2004-07-13
WO 03/061423 PCT/US03/00242
As shown in Fig. 9, the koban-shaped anchor 44 may be omitted, and the whole
anchoring function may be composed of a bar-shaped projecting element 68. Or,
as
shown in Fig. 10, a projecting element 70 of a generally rectangular shape may
be
adopted. Or, as shown in Fig. 11, a plate-like projecting element 72 of a
generally
diamond shape may be adopted.
In the above-described embodiment, the size relation between the base 16 and
the
projecting element 48 for ensuring the required installation strength can be
chosen as
follows. For example, the size relation between the base 16 and the projecting
element 48 in the longitudinal direction of the fastener 10 is such that, when
expressed
with the longitudinal dimension A of a box-shaped part 22 of the base 16 and
the
width B of an individual projecting element 48 (Fig. 2), B/A is preferably
within the
range 0.1 s B/A s 0.4. Also, the size relation between the base 16 and the
projecting
element 48 in the width direction of the fastener 10 is preferably such that,
when
expressed with the width dimension C and the distance D between both ends of a
pair of
projecting elements 48 (Fig. 3), D/C is chosen to be within the range 1 s D/C
s 6.
In the above-described construction, the plurality of projecting elements of
the
fastener according to the present invention are formed integrally with the
base. However,
the present invention is not limited to the above construction, and the
projecting elements
may be detachably provided on the base. Fig. 12 is a view showing a fastener
78
2 0 according to a second embodiment of the present invention which comprises
an anchor
member 76 having such projecting elements 74. Since the fastener 78 has
substantially
the same construction as the above-described fastener 10 except for the
construction of
the projecting element 74, corresponding constituent elements are denoted by
common
reference symbols, and explanation thereof is omitted.
2 5 As shown in Fig. 13, the anchor member 76 is comprised integrally of a
pair of
plate-shaped projecting elements 74 having a profile of generally equilateral
triangle, a
square-bar shaped beam 80 interconnecting the two projecting elements in a
symmetric
layout with the vertices facing opposite to each other, and a plate-shaped
mounting
portion 82 formed between the two projecting elements 74 approximately at the
3 0 longitudinal center of the beam 80. Two sets of anchoring elements 84, 86
projecting
sideways on both sides of the beam 80 are formed on the mounting portion 82.
One set
of anchoring elements 84, 86 are composed of a small-sized anchoring element
84 having
11
CA 02473856 2004-07-13
WO 03/061423 PCT/US03/00242
a profile of generally right-angled triangle and a large-sized anchoring
element 86 having
a profile of generally rectangular shape. The two anchoring elements 84, 86
are disposed
such that an oblique side of the small-sized anchoring element 84 is situated
away from
the large-sized anchoring element 86, and that a gap slightly larger than the
thickness of
the post 44 provided on the back surface 14 of the base 16 of the fastener 78,
is formed
between the two anchoring elements 84 and 86. The two sets of anchoring
elements 84,
86 are disposed symmetrically to each other with respect to the beam 80 as a
centerline.
The anchor member 76 is detachably mounted to the back surface 14 of the
fastener 78 in a relative positioning with the beam 80 facing in a direction
approximately
orthogonal to the rib 42 provided on the base back surface 14 of the fastener
78. Thus,
the beam 80 of the anchor member 76 is inserted between a pair of adjoining
koban-
shaped anchors 46 provided on the base back surface 14 of the fastener 78, and
the
mounting portion 82 formed at approximately the longitudinal center of the
beam 80 is
anchored to a pair of posts 44 supporting the anchors 46 (Fig. 12). Here, with
the
oblique side of the pair of small-sized anchoring elements 84 abutted first to
the two
posts 44, the mounting portion 82 is inserted between the posts 44 under a
pressing force.
Thereby, with accompanying elastic deformation of the two posts 44,
corresponding
post 42 is fit in a snap style into the gap between the anchoring elements 84,
86 of the
respective set. When the anchor member 76 is properly mounted to the base back
2 0 surface 14 of the fastener 78, a pair of projecting elements 74 are
disposed as a whole so
as to project on both sides in the width direction of the base 16.
The fastener 78 having the above-described construction is, by means of the
insert
molding process as described before, integrally installed to the molded body
58 (Fig. 6).
In this state, the plurality of posts 44 and anchors 46 of the fastener 78 are
embedded into
2 5 the molded body 58, and the anchor members 76 mounted on the adjoining
pair of
posts 44, especially two projecting elements 74, bite deeply into the molded
body 58, in
the same manner as the projecting elements 48 shown in Fig. 6. As a result,
compared to
a conventional fastener that only has the koban-shaped anchors which do not
project out
of the base as an embedding section, the fastener 78 is fixed to the molded
body 58 under
3 0 sufficiently larger installation strength. It will be appreciated that, in
this manner, the
same operative effect can be obtained with the fastener 78 as with the above-
described
fastener 10.
12
CA 02473856 2004-07-13
WO 03/061423 PCT/US03/00242
Further, the fastener 78 has the advantage in that it permits desired number
of
anchor members 76 to be selectively mounted at desired positions in the
longitudinal
direction, on the fastener base having conventional construction. With this
construction,
even if the required fastener installation strength varies depending on the
installation
position, when installing the fastener to the molded body of an article to
which the
fastener is applied, the optimal fastener installation strength can be easily
achieved.
The projecting elements of the anchor member mounted on the embedding section
of the fastener according to the present invention may take various forms
provided that
the required installation strength as described above can be ensured. For
example, as
shown in Fig. 14, an anchor member 94 comprising integrally a plate-shaped
projecting
element 88 having a generally rectangular profile, a square-bar shaped beam 90
extending over the entire length in the longitudinal direction of the
projecting element 88,
or a mounting portion 92 formed approximately at the longitudinal center. of
the
projecting element 88, may be adopted. Two sets of anchoring elements 84, 86
projecting laterally on both sides of the projecting element 88, are formed on
the
mounting portion of the anchor member 94, and in the same manner as in the
anchor
member 76, these anchoring elements 84, 86 are anchored to a pair of posts 44
of the
fastener 78. When the anchor member 94 is properly mounted on the base back
surface 14 of the fastener 78, the projecting elements 88 are disposed so as
to project
2 0 laterally on both sides in the width direction of the base 16.
Example
In order to determine the improvement effect on the installation strength of
the
fastener according to the present invention, a separation test was performed
on the
fastener 10 shown in Fig. l, as installed to the molded body. Specifically, a
fastener 10
was prepared with total length of the base 16 of 250 mm, total width of the
base 16 of
8.5 mm, and distance D between both ends of a pair of projecting elements 48
(Fig. 3) of
mm, and by means of an insert-molding process, was installed to the molded
body 58
(or a sitting part of a vehicle seat) shown in Fig. 5 (see Fig. 6). In this
state, a stretching
3 0 force was applied at one longitudinal end of the base 16 of the fastener
10, in a direction
perpendicular to the bottom surface of the recess 64 of the molded body 58,
and the force
at the moment when the embedding section 20 was separated from the molded body
58
13
CA 02473856 2004-07-13
WO 03/061423 PCT/US03/00242
was measured as the installation strength. The measured installation strength
was about
40 N.
As a comparative example, same separation test was performed on a conventional
fastener having koban-shaped anchors which do not project out of the base. The
conventional fastener had identical construction as the above-mentioned tested
fastener 10, except that the projecting elements 48 were not provided. The
installation
strength measured with the conventional fastener was about 20 N.
As is evident from the foregoing explanation, in accordance with the present
invention, with the fastener integrally installed to an article by means of an
embedding
section provided on the back surface of the strip-shaped base, the
installation strength for
installing to an article by means of the embedding section can be improved as
much as
possible without impairing the flexibility inherent in the fastener.
14