Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02479280 2004-08-26
1
POWER TOOL
The present invention relates to power tools, and relates particularly, but
not
exclusively, to power sanders.
Known power tools, such as power drills i n w hich a drill bit is rotated by
an
output shaft which is in turn rotated by means of an electric motor, generate
significant amounts of vibration, which can under certain circumstances limit
the
length of time during which the tool can be used continuously. In addition,
the
housing of such tools is generally made from a durable plastics material on
which it
can be difficult for a user of the tool to maintain a grip when the tool is in
use for a
sustained period. This generally limits the degree of comfort and ease with
which a
user can handle the tool.
Preferred embodiments of the present invention seek to provide a power tool
which is easier and more comfortable to use.
According to the present invention, there is provided a power tool comprising:-
a housing defining at least one handle portion having a graspable surface
having first and second concave portions and a third concave portion between
said
first and second concave portions; and
a motor located in the housing for actuating a working member of the tool.
By providing a housing defining at least one handle portion having a graspable
surface having first and second concave portions and a third concave portion
between said first and second concave portions, this provides the advantage of
making the power tool easier and more comfortable for the user.
The power tool may further comprise a platen mounted to said housing on a
side thereof remote from at least one said handle portion.
The platen may include a narrower portion at a forward end thereof.
P~CA~CS1185
CA 02479280 2004-08-26
2
In the case where the power tool is a sander, this provides the advantage of
enabling more accurate sanding operations to be carried out.
The platen may taper inwardly in a longitudinal direction of the tool.
The graspable surface may be generally saddle shaped.
A majority of the housing as measured in a longitudinal direction may be
disposed in use over the platen.
Approximately two thirds of said housing as measured in said longitudinal
direction may be disposed in use over said platen.
Substantially all of said housing as measured in a direction transverse to
said
longitudinal direction may be disposed in use over said platen.
The housing may f urther define a curved f orward surface, and t he t ool may
further comprise a motor on/off switch disposed on said curved forward
surface.
At least one said first and/or said second concave portion may have a radius
of
curvature of 5mm to 40mm.
At least one said first and/or said second concave portion may have a radius
of
curvature of 5mm to l5mm.
At least one said first and/or said second concave portion may have a radius
of
curvature of 8mm to 12mm.
Said third concave portion may have a radius of curvature of 5mm to 40mm.
Said third concave portion may have a radius of curvature of 15mm to 30mm.
Said third concave portion may have a radius of curvature of 20mm to 25mm.
P-CA-CS1195
CA 02479280 2004-08-26
3
The tool may be a power sander.
According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a
power
tool comprising:-
a housing defining a forvvard surface and an upper surface, and a notch
defined in said upper surface rearwardly of said forward surface;
a platen moveably mounted to said housing; and
a motor located in the housing for causing oscillatory movement of the platen
relative to the housing;
wherein a majority of the housing as measured in a longitudinal direction of
the
tool and a direction transverse to said longitudinal direction is disposed
over said
platen in use.
The upper surface may be curved downwardly in a rearward direction from an
upper edge of said forward surface to define a recessed surface area and then
curved upwardly rearwardly from said recessed surface area to define said
notch.
The forward surface may be curved.
Substantially all of said portion of said housing disposed over said platen in
use
as measured in the longitudinal direction may be also disposed over said
platen in
use as measured in a direction transverse thereto.
At least one said first and/or said second concave portion may have a radius
of
curvature of 5mm to 40mm.
At least one said first and/or said second concave portion may have a radius
of
curvature of 5mm to 15mm.
At least one said first and/or said second concave portion may have a radius
of
curvature of Smm to 12mm.
Said third concave portion may have a radius of curvature of 5mm to 40mm.
P-(:A-CS1185
CA 02479280 2004-08-26
4
Said third concave portion may have a radius of curvature of 15mm to 30mm.
Said third concave portion may have a radius of curvature of 20mm to 25mm.
The~tool may be a power sander.
According to a further aspect of the present invention, there is provided a
power tool comprising:-
a housing having side surfaces below an upper surtace to form a graspable
handle portion;
a platen mounted to said housing, wherein a majority of said housing as
measured in a longitudinal direction of the tool and in a direction transverse
to said
longitudinal direction is disposed over said platen in use;
a motor located in the housing for causing oscillatory movement of said platen
relative to the housing; and
at least one chamber containing at least one gel material protruding from each
said side surface.
The tool may further comprise a third chamber containing a gel material
disposed on said upper surface.
Preferred embodiments of the invention will now be described, by way of
example only and not in any limitative sense, with reference to the
accompanying
drawings, in which:-
Figure 1 is a perspective view of a power sander embodying the present
invention;
Figure 2 is a top view of the sander of Figure 1;
Figure 3 is a rear view of the sander of Figure 1;
Figure 4 is a front view of the sander of Figure 1;
Figure 5 is a left side view of the sander of Figure 1;
Figure 6 is a right side view of the sander of Figure 1;
Figure 7 is a detailed rear view of a top surtace of the sander of Figure 1;
Figure 8 is a detailed side view of the surtace of Figure 7;
P-CA-CS1185
CA 02479280 2004-08-26
Figure 9A is an exploded perspective view of the housing and gripping portion
of the sander of Figure 1 from the right side;
Figure 9B is an exploded perspective view of the housing and gripping portion
of the sander of Figure 1 from the left side;
5 Figure 10 is a side cross sectional view of part of the sander of Figure 1;
Figure 11 is a view, corresponding to Figure 10, of a sander of a second
embodiment of the present invention;
Figure 12 is a perspective view of a mounting platen and sanding shoe of the
sander of Figure 10; and
Figure 13 is a perspective view of the mounting platen and sanding shoe of
Figure 10, showing the attachment side of the mounting platen;
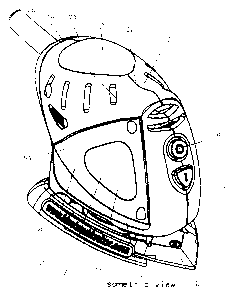
Referring to Figures 1 to 9, a power sander 2 has a housing 4 supporting a
mounting platen 6 for supporting a sanding head 8 (Figure 10) for oscillatory
orbital
motion of the platen 6 and sanding head 8 relative to the housing 4. The
housing 4
has side surfaces 10, 12, a curved front surface 14 containing an on/off
switch 16 for
switching electrical power to a motor 18 (Figure 10) in the housing 4, a
curved upper
surface 20 and a generally saddle shaped graspable surface 22 located between
the
front surface 14 and upper surface 20. The graspable surface 22 has a concave
upper portion 24 and concave side portions 26, 28 arranged on opposite sides
of the
upper portion 24.
For ergonomic handling of the sander by a user, the saddle shaped graspable
surface 22 has a concaved upper portion 24 having a radius of curvature of
about
23mm, and side portions having radii of curvature of about 10mm.
The upper surface 20 of the housing 4 is defined by a blister pack 30,
defining
a gel-containing chamber 32 containing vibration absorbing gel formed from a
semi
solid silicone rubber or polyurethane material and protruding from an aperture
in a
clamping plate 34. Similarly, each side surface 10, 12 is defined by a blister
pack 36,
defining a gel-containing chamber 38 protruding through an aperture in
clamping
plate 4 0. I t c an t herefore b a s een t hat the a xtemal s urface o f the
sander 2 to b a
gripped by a user is defined by the gel-containing chambers 32, 38 of blister
packs
30, 36 respectively, and the clamping plates 34, 40, so that the amount of
vibration
P-CA-CS1785
CA 02479280 2004-08-26
6
transmitted to a user's hand is reduced by means of the gel material contained
in the
blister packs 30, 36.
As shown in greater detail in Figures 9A and 9B, the blister pack 36 forming
part of side surface 10 is formed from a pair of flexible sheets 46 of
polyurethane
material defining gel-containing chamber 38 and sealed together at a
peripheral
portion 48 surrounding the gel-containing chamber 38. The peripheral portion
contains no vibration absorbing gel material and is pierced by a series of
apertures
44 which correspond in position to apertures 42 on the part of housing 4 to
which the
blister pack 36 is to be mounted, and to pins 43 moulded onto the rear surface
of
clamping plate 40. The blister pack 36 is mounted to the housing 4 by passing
the
pins 43 of clamping plate 40 through the corresponding apertures 44 in the
peripheral
portion of blister pack 36, and then inserting the pins 43 into the con-
esponding
apertures 42 on the housing 4. In particular, the blister pack 36 is located
on the pins
43 of clamping plate 40, and the pins of the clamping plate 40 are then
located in the
apertures 42 on the housing. The pins 43 and apertures 42, 44 are irregularly
spaced, which minimises the risk of incorrect location of the clamping plate
40, blister
pack 36 and housing 4 relative to each other.
The pins 43 on clamping plate 40 are of such length that when the blister pack
36 is located on the pins and the clamping plate 40 is mounted to the housing
4 by
locating the pins in apertures 42 on the housing 4, the pins protrude from the
inner
wall of the housing 4 to a depth of approximately 3 mm. The clamping plate 40
is
then sealed to the housing 4 by a technique known to persons skilled in the
art as
"hot staking" in which a heated mandrel is applied to the protruding ends of
the pins,
which melts the protruding ends so that they are widened in a generally
circular
arrangement and fix the pins to the housing 4 in a manner similar to that of a
rivet.
Alternatively, the distal ends of the pins can be heated by means of
ultrasound. The
clamping plate 40 is then sealed to the housing and prevents removal of the
clamping plate 40 from the housing 4, and the gel-containing chamber 38 of
blister
pack 36 protrudes through the aperture 45 of clamping plate 40 to define part
of side
surface 10, while removal of the blister pack 36 is prevented because the pins
pass
through the apertures 44 in the blister pack 36.
P-CA-cSt 185
CA 02479280 2004-08-26
7
Similarly, the blister pack 36 forming part of opposite side surface 12 and
the
blister pack 30 forming part of upper surtace 20 are secured to the housing in
a
similar manner by means of heat or ultrasound.
Figure 10 shows a drive unit including the electric motor 18 and first drive
shaft
50. A fan 52 mounted on shaft 50 is arranged to draw air in from mouth 54 of
the
drive unit as shown by arrow A (Figure11 ), and direct it through extractor
duct 56 to
outlet 58, as shown by arrow B. Bearing 60 is eccentrically located radially
in respect
to shaft 50, and a second drive shaft 62 rotates about the axis of bearing 60.
Mounting platen 6 is fixed to the housing 4 by means of four flexible rubber
legs 64.
The mounting platen 6 is substantially flat, and the legs 64 extend from a
common
major surface of the platen 6 (the upper surface as shown in Figure 10),
directed into
the body of the housing 4. The flexible legs 64 extending from the mounting
platen 6
are permanently fixed at their housing end to the housing 4, i.e. they are not
removable in use by the operator. They are attached to the housing 4 by means
of
clamping flanges 66 of the housing 4. The flexible legs 64 are attached at
their
mounting platen end to the mounting platen 6 by passing through apertures in
hollow
projecting portions 68 that extend in the direction of the f lexible legs 64
from the
upper surface of the mounting platen 6. The flexible legs 64 are provided at
their
mounting platen 6 end with an internally screw threaded hollow recess for
attachment
to a securing screw. The manner in which this securement to the mounting
platen is
effected is described in more detail below with reference to Figure 11.
The m ounting p laten 6 s urrounds t he s econd d rive s haft 6 2, a nd i s s
paced
radially therefrom. This means that the mounting platen 6 itself is not
directly driven
by either of the drive shafts.
In Figure 10 a first sanding platen, which is a random orbit sanding head 8,
is
secured next to the mounting platen 6 onto the drive shaft 62. Securement of
the
random orbit sanding head 8 is achieved by a bolt 70 and washer 72. The bolt
70
passes through an aperture in the sanding head 8, through aperture 74 in the
mounting platen (see Figures 12 and 13), and over the driving spindle of the
second
drive shaft 62. The sanding platen 8 is located in a parallel plane to the
mounting
platen 6, but is spaced from it, so that there is no contact between the
facing
P-(:A-CSt t 85
CA 02479280 2004-08-26
8
surfaces of the mounting platen 6 and the sanding shoe 8. Therefore tree
rotation of
the sanding platen 8 is permitted about the bearing axis 60, and the platen 8
exhibits
a random orbit.
A brake pad 76 is provided on the under-surface of the mounting platen 6. The
brake pad 76 comprises a resilient member 78 in the form of a ring formed from
a
synthetic rubber resilient material, and an abrasion resistant contact layer
80
comprising polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) filed with carbon fibre or glass for
increased abrasion resistance. The arrangement of the layers is such that when
the
sanding platen 8 is secured in place onto the drive 62 then the resilient ring
78 is
under compression so that a resultant load is put by the filled PTFE layer 80
onto a
reaction surface part 82 of the underlying upper surface of the sanding platen
8. The
purpose of this brake 76 is two-fold: first, in use, the brake acts as a speed
limiter,
operating in particular to prevent scratches when the unit is placed on and
taken off
the work surface, and secondly when the unit is switched off, the stop time is
very
much reduced compared to a non-braked tool. In operation the drive shaft 50 is
typically driven at a rotational speed of 12000rpm, which is too fast a speed
for
rotation of the sanding platen 8. The brake pad 76 limits the rotational speed
of the
platen to an acceptable operating speed, typically around 1200 rpm, or 10% of
the
rotational speed of the motor.
Figure 11 shows the drive unit of the hand tool with an orbital sanding platen
84
mounted in place of the random orbit platen of Figure 10. Also Figures 12 and
13 are
perspective views of the mounting platen 8 (which is common to both Figures 10
and
11) and the sanding platen 84 (which is shown in Figure 11, but not in Figure
10).
Figures 12 and 13 show in more detail features of the mounting platen 8, which
remains on the housing when the platens 84 and 8 are interchanged. From these
Figures it can be seen that the mounting platen 8 is generally a blunt shoe
shape,
and is substantially flat, with a peripheral lip 86 extending downwards
towards the
sanding shoe 84. The large central aperture 74, allowing it to be positioned
around
the second drive shaft, radially distant therefrom, so there is no direct
contact
between the mounting platen 6 and the second drive shaft 62, can also be
clearly
seen in these Figures, as can the four hollow right cylindrical portions 88,
integrally
P-CA-CSt 185
CA 02479280 2004-08-26
9
formed with the surface of the mounting platen 8, and projecting into the body
of the
housing 4 i.e. upwards as shown in the Figures. An inner lip 90 extends
downwards
around most of the central aperture 74, and joins to the outer peripheral lip
92 of the
mounting platen 6 at two points 94 on one short side of the mounting platen 8.
In I ine with t he a pwardly d irected p rojections 8 8, a nd p rojecting i n
t he o ther
direction, from the opposite surface of the mounting platen 6 are four hollow,
generally cylindrical pin shaped coupling members 96. The pin-shaped coupling
members 96 are also integrally formed with the mounting platen 8. The
substantially
flat mounting platen with its projecting portions 88 and 96 are preferably
integrally
injection moulded from polymeric material or diecast zinc.
The four coupling pins 96, provided on the opposite surface of the mounting
platen 6 from the flexible legs 64, in corresponding positions, i.e.
vertically aligned
with the legs 64 as shown in Figures 12 and 13 have a dual function; the pins
96
secure the legs 64 in place, and couple with an orbital sanding head 84, in
use, to
prevent free rotation of that sanding head (Figures 11 to 13).
Each coupling pin 96 is an integrally formed part shaped as a hollow cylinder.
The pin member 96 contains a radially directed flange 98 extending partially
into the
hollow of the pin member 96, to act as a stop member for a separate externally
screw
threaded headed bolt member 100 (see Figures 10 and 11 ). The externally screw
threaded bolt member 100 passes through the hollow central pin member 96, and
is
shaped and sized to slide into the hollow pin member until its head abuts the
internal
stop flange 98, and then screw into inner hollow screw threaded cylindrical
recesses
at the mounting platen end of the flexible legs 64. By this screw threaded
bolt
member 100 the flexible legs 64 are therefore secured to the mounting platen.
As best seen in Figure 11, each pin member 96 is located between part of the
peripheral lip 86 and the inner lip 90 of the mounting platen 6. The pin
member 96 of
the coupling means acts to couple to the orbital sanding shoe 84 to prevent
its free
rotation.
P-CA-CS1785
CA 02479280 2004-08-26
As shown in Figure 11, when mounted on the drive unit, the orbital sanding
shoe 84 is secured to the spindle of second drive shaft 62 by means of the
same nut
70 and washer 72 used to secure the random orbit sanding platen 8 of Figure
10.
The orbital sanding shoe 84 is substantially flat, and is provided, on its
upper major
5 surface in the orientation shown in the Figure, with coupling means 92
shaped to co-
operate with the coupling means 96 of the mounting platen 6. The coupling
means
92 each comprise a hollow right-cylindrical stub, projecting upwards from the
surface
of the sanding shoe 84. The hollow right cylindrical projection 92 is shaped
so that it
provides a recess into which the pin member 96 of the mounting platen fits.
One side
10 of the cylindrical projection 92 on the sanding shoe 84 fits between the
peripheral lip
86 of the mounting platen 6 and the outer surface of the pin member 96 of the
mounting platen 6; and the opposite side of the cylindrical projection 92 on
the
sanding shoe 84 fits between the inner lip 90 of the mounting platen 6 and the
opposite outer surface of the pin member 96 of the mounting platen 6.
By means of the co-operating coupling means 96 and 92, the sanding shoe 84
and mounting platen 6 are therefore securely located substantially to prevent
relative
movement between the mounting platen 6 and the sanding shoe 84 in a plane
perpendicular to the axis of the bearing 60. Relative movement parallel to the
axis of
the bearing 60 is, of course, prevented by the nut 70 and washer 72
attachment.
In operation, when the motor is switched on and the drive shafts 50 and 62
tum, since the sanding shoe 84 is prevented from rotation relative to the
mounting
platen 6, and the mounting platen 6 is fixed relative to the housing 4 by
means of
legs 64, then free rotation of the sanding shoe 84 around the bearing 60 axis
is
prevented. The flexibility in the legs 64, however, allows the sanding platen
84 to
follow the rotating motion of the eccentric spindle itself driven by the first
drive shaft
50. Therefore the sanding shoe 84 is allowed to oscillate within a fixed orbit
due to
the flexibility of the legs 64.
In order to ensure that the sanding shoe 84 is always located the correct way
round on the mounting platen 6, the coupling means 96 and 92 are non uniformly
spaced over the surface of the mounting platen 6 and the sanding platen 84,
those
on one lateral side of the platens (the right as shown in Figures 12 and 13)
being
P~CA~CS1185
CA 02479280 2004-08-26
11
further apart from each other than those on the other lateral side of the
platens (the
left as shown in the Figures).
It will be appreciated by persons skilled in the art that the above
embodiments
have been described by way of example only, and not in any limitative sense,
and
that various alterations and modfications are possible without departure from
the
scope of the invention as defined by the appended claims.
P-CA~CS1185