Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02487825 2004-11-29
WO 03/102828 PCT/EP03/05258
SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR SELECTING AND RETRIEVING
INFORMATION FROM AN AUDIO-VISUAL PRESENTATION
Field of the invention
The present invention relates to techniques for integrating, in audio-visual
presentations, means for accessing sources of information, and more
particularly to
a system and a method for enabling an auditor, during the course of a
presentation,
to select one or several topics drawing his attention or interest, and,
immediately
after said presentation or at a later time, to easily access information
related to the
topics previously selected.
Background of the invention
Presentation systems allow to create electronic foils, slides or pages and to
assemble them to form a presentation that can be displayed. Presentation
systems
are used, during the course of a presentation, to select and display
electronic foils to
an audience, for illustrating and completing the speaker's explanations. In
particular,
presentation systems allow to advance to the next foil, to return to the
previous foil
or to go to any other foil within the presentation using a graphical user
interface or a
keyboard. The speaker also has the possibility to navigate from one foil to
another,
for instance to skip some foils, to present the more relevant foils of the
presentation,
or to present foils requested by some auditors.
A presentation system can generate or reference a sequence of HTML files
stored on one or a plurality of Web servers, each HTML file being accessible
by
activating an hyperlink from the presentation system, said hyperlink
comprising an
address for locating the HTML file in the network (for instance an Uniform
Resource
Locator (URL) in the Internet network). During the presentation, the speaker
can
present all or a subset of the HTML foils depending on the timing of the
presentation, the interest shown by the auditors, or any other factor.
Therefore, the
presentation of foils and related topics can flow sequentially or in any other
i
CA 02487825 2004-11-29
WO 03/102828 PCT/EP03/05258
convenient order, depending on the course that the presentation takes and the
amount of time spent for each topic (i.e., to each chart or slide of the
presentation).
Usually, the auditor of a presentation is interested in some particular
topics,
and not particularly interested in topics considered as being irrelevant or
already
known to him. Thus, very frequently, the auditor wants to select, during the
course of
the presentation, not all the foils that are presented by the speaker, but
merely a few
foils, related to the topics that have drawn his interest or attention, so
that he can
directly and immediately access and review, once the presentation is over, the
selected foils.
Accordingly, a system and method is needed for recording information in a
transparent way for the speaker while keeping the audience's attention on
particular
topics without needing to take notes. The selection of foils by the audience
for a
subsequent display should be as simple as pressing a button, and sufficiently
flexible to deal with the dynamic content provided by presentation systems.
Objects of the invention
It is an object of the invention to enable an auditor of an audio-visual
presentation to select one or several topics drawing his attention in the
course of the
presentation, and immediately, or at a later time, to access, retrieve and
display
information related to said selected topics.
It is another object of the invention to enable an auditor of an audio-visual
presentation to select foils drawing his attention in the course of the
presentation,
and to immediately, or at a later time, access, retrieve and display the
selected foils
or information related to the selected foils.
It is a further object of the invention to enable an auditor of a presentation
to
select foils with a minimum effort and involvement from his side.
2
CA 02487825 2004-11-29
WO 03/102828 PCT/EP03/05258
Summary of the invention
The present invention is directed to a system, method and computer program,
as defined in independent claims, for enabling an auditor in the course of a
presentation, to select one or several topics drawing his attention or
interest, and,
immediately after said presentation or at a later time, to easily access
information
related to the selected topics.
The system is based on a synchronization of a speaker device with several
auditor devices (e.g., workstations, portable computers, wearable computers,
Personal Digital Assistants - PDAs, WAP enabled mobile phones, smart phones or
any other type of hand-held computing devices), according to a same universal
time,
so that the times at which topics are selected by auditors can be correlated
with the
time intervals during which the corresponding presentation foils are presented
by the
speaker. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the synchronization
between
the speaker device and the auditor device is done referring to an universal
time such
as the Global Positioning System Time (GPS-time), the Global Orbiting
Navigational
Satellite System (GLONASS) time or another suitable universal time based on a
satellite system. A GPS or GLONASS receiver is integrated or connected to the
speaker device. A GPS or GLONASS receiver is integrated or connected to each
auditor device. Each auditor device is independent and separate from the
speaker
workstation.
The system is also based on a plurality of hyperlinked HTLM documents
located on one or several servers accessible from the speaker workstation
through a
network. The foils are selected by the speaker during universal time intervals
that
are recorded. Depending on the interest on the presented topics, one or
several foils
can be selected by each auditor during the course of the presentation.
More particularly, the present invention discloses a system, method and
computer program for generating from a speaker device, a Presentation Time
Table
during the presentation of one or a plurality of foils, said Presentation Time
table
being accessible by one or a plurality of auditors. The method comprises the
steps
of:
3
CA 02487825 2004-11-29
WO 03/102828 PCT/EP03/05258
~ locating and accessing a Presentation Hyperlink Table comprising
~ means for identifying one or a plurality of foils;
~ means for locating and accessing information related to each of said one or
plurality of foils;
~ means for locating and accessing a Presentation Time Table;
~ locating and accessing the Presentation Time Table using the Presentation
Hyperlink Table;
and, for each presented foil
~ identifying the presented foil in the Presentation Hyperlink Table;
~ determining an universal-time interval corresponding to the presentation of
the
foil;
~ creating a new record on the Presentation Time Table;
~ copying into said new record
~ the universal-time interval corresponding to the presented foil;
~ means, retrieved from the Presentation Hyperlink Table, for identifying the
presented foil;
~ means, retrieved from the Presentation Hyperlink Table, for locating and
accessing information related to the presented foil.
The present invention further discloses a system, method and computer
program for selecting from an auditor device, one or a plurality of foils in a
presentation of one or more foils, and for accessing at a later time,
information
related to each of said one or plurality selected foils, comprising the steps
of:
~ each time a selection command is received for selecting a foil currently
presented:
~ determining the current universal-time;
~ recording the current universal-time in a Selections Time Table ;
~ accessing a Presentation Time Table, said Presentation Time Table accessible
by one or a plurality of auditor devices, comprising for each presented foil:
~ an universal-time interval corresponding to the presentation of the foil;
4
CA 02487825 2004-11-29
WO 03/102828 PCT/EP03/05258
~ means for identifying the presented foil;
~ means for locating and accessing information related to the presented foil;
for each universal-time recorded in the Selections Time Table
~ identifying in the Presentation Time Table, the foil selected at the
recorded
universal-time;
~ retrieving from the Presentation Time Table, said means for identifying the
selected foil and for locating and accessing information related to said
selected
foil;
~ storing the retrieved means for identifying the selected foil and for
locating and
accessing the information related to said selected foil into the Selections
Time
Table.
Further embodiments of the invention are provided in the appended
dependent claims.
The foregoing, together with other objects, features, and advantages of this
invention can be better appreciated with reference to the following
specification,
claims and drawings.
Brief description of the drawings
The novel and inventive features believed characteristics of the invention are
set forth in the appended claims. The invention itself, however, as well as a
preferred mode of use, further objects and advantages thereof, will best be
understood by reference to the following detailed description of an
illustrative
detailed embodiment when read in conjunction with the accompanying drawings,
wherein:
~ Figure 1 shows how auditors of a presentation perceive topics of interest
when
listening to the speaker and viewing the presentation foils.
s
CA 02487825 2004-11-29
WO 03/102828 PCT/EP03/05258
~ Figure 2 illustrates the principle of the invention based on the
synchronization of
the speaker workstation and the auditor workstations according to a same
universal-time, such as, for example, the Global Positioning System (GPS)
time.
~ Figure 3 shows a presentation according to the present invention, said
presentation comprising a sequence of HTML foils referenced in a Presentation
Hyperlink Table.
~ Figure 4 shows how the speaker workstation uses the Presentation Hyperlink
Table to select HTML foils, how these HTML foils are retrieved and presented,
and how the universal times corresponding to the presentation of these HTML
foils by the speaker are stored in a Presentation Time Table according to the
present invention.
~ Figure 5 shows an example of Presentation Time Table generated during a
presentation and stored on a Presentation Server according to the present
invention.
~ Figure 6 shows how, during a presentation, an auditor selects a topic by
pressing a key on his workstation according to the present invention.
~ Figure 7 shows how the universal times, at which topics are selected by the
auditor, are stored in a Selections Time Table located in the auditor
workstation
according to the present invention.
~ Figure 8 shows how, when the presentation ends, the auditor updates the
Selections Time Table located in his workstation from the Presentation Time
Table stored in the Presentation Server.
~ Figure 9 shows how names and URLs of HTML foils that have been presented
by the speaker and selected by the auditor, are identified and retrieved from
the
Presentation Time Table located in the Presentation Server and how the
6
CA 02487825 2004-11-29
WO 03/102828 PCT/EP03/05258
Selections Time Table located in the auditor workstation is updated according
to
the present invention.
~ Figure 10 shows how from the updated Selections Time Table, the auditor
activates an hyperlink to a selected HTML foil according to the present
invention.
~ Figure 11 shows how the presentation HTML foil that corresponds to the
selected item is received from the Web server and is displayed on the auditor
device.
~ Figure 12 shows how the foils presented by the speaker and the selections
made by the auditors are correlated using a same universal-timing system .
~ Figure 13 shows the steps of the method for creating a Presentation
Hyperlink
Table on the speaker workstation according to the present invention.
~ Figure 14 shows the steps of the method for generating, during a
presentation,
a Presentation Time Table on a Presentation Server, according to the present
invention.
~ Figure 15 shows the steps of the method for selecting one or several topics
of
interest during a presentation, according to the present invention.
~ Figure 16 shows the steps of the method for accessing information related to
topics that have been selected during a presentation, according to the present
invention.
Preferred embodiment of the invention
As shown in Figure 1, each auditor (100) attending a presentation has one or
several particular topics of interest. At some moments, this auditor is
particularly
interested from what the speaker (102) is saying (103) or from what is being
shown
on the presentation screen (104), and while at other moments, this auditor may
CA 02487825 2004-11-29
WO 03/102828 PCT/EP03/05258
consider that the presented topics are already known, lack of interest or are
irrelevant. Under these circumstances there is a need to provide a simple
mechanism to enable an auditor (100) to exclusively select the topics that
draw his
interest in the course of the presentation (e.g., exclusively the information
related to
the "Pomerol'; "Medoc" and "Burgogne" wines during a long presentation about
"French Red VI/ines'~ and to access, at a later time, information related to
the
selected topics, in particular the information comprised in the foils that
have been
presented by the speaker and which concerns the selected topics.
The principle of the invention as illustrated by Figure 2, is based on the
synchronization of the speaker workstation (202) (i.e., the computing system
under
the control of the speaker (201) which is connected to the presentation screen
(203))
with the auditor devices (204) (e.g., a PDA, a hand-held computer, a wearable
computer, a smart phone) to the same universal time. In a preferred embodiment
of
the invention, speaker workstation (202) and auditor's devices (204) are
synchronized according to an universal time system (205), such as the Global
Positioning System Time (GPS-time), the Global Orbiting Navigational Satellite
System (GLONASS) time or another suitable universal time based on a satellite
system. A GPS or GLONASS receiver (207) is integrated or connected to the
speaker workstation (202). On the auditor's side, GPS or GLONASS receivers
(208)
can be integrated or connected to the auditor (200) devices (204), (e.g.,
wearable
computers, Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs), smart phones or any other
hand-held computing device). The auditor devices (204) are independent and are
not connected nor in communication with the speaker workstation (202).
Figure 12 also shows how events (1202) generated by an auditor (600) (such
as the universal times Ta, Tb corresponding to the selection by the auditor of
a first
and a second topic), can be correlated with events (1201) generated by the
speaker
(602) (such as the universal time intervals (T1,T2), (T3, T4) corresponding to
the
presentation by the speaker of Foil 1 and Foil 3). This correlation of
independent
wants is based on the synchronization of the speaker workstation (202) with
the
auditors devices (204) according to an universal time (205). This correlation
allows
she identification of the foils that have been selected by the auditor during
the course
of the presentation.
s
CA 02487825 2004-11-29
WO 03/102828 PCT/EP03/05258
Universal Timing Systems
Timing sequences, independent of locations of transmitters and receivers,
can be derived from an absolute timing reference such as, for example, the
Global
Positioning System (GPS) time or the Universal Time Co-ordinated (UTC) time
(also
known today as GMT and ZULU time).
To transmit precise timing signals, the GPS uses 24 satellites in 55°
inclined
orbits 10,000 miles above the earth. These timing signals are used by any GPS
receiver anywhere on the earth to determine its position. A 1575 MHz
transmission
carries a 1-MHz bandwidth phase-modulated signal named the clear acquisition
(C/A) code. When a GPS receiver receives this signal from at least three GPS
satellites, it can determine its own latitude and longitude with an accuracy
of about
30 meters. Apart the determination of geographical positions, the GPS is today
widely used for distributing Precise Time and Time Interval (PTTI). The system
uses
time of arrival (TOA) measurements for determining a position. A precisely
timed
clock is not essential for the user because time is obtained in addition to
position by
the measurement of the TOA of four satellites simultaneously in view. If the
altitude
over sea level is known, three satellites are sufficient. If the user is
stationary at a
known position then, in principle, the time can be obtained by the observation
of a
single satellite. Information about the GPS time service is supplied by the
"Time
Service Department", U.S. Naval Observatory, Washington, DC, at
http:!ltycho.usno.navy.mill
GPS is today the world's principal supplier of accurate time. It is used
extensively both as a source of time and as a means of transferring time from
one
location to another. Three kinds of time are available from GPS: GPS time, UTC
as
estimated and produced by the United States Naval Observatory, and the times
from
each free-running GPS satellite's atomic clock. The Master Control Station
(MCS) at
Falcon Air Force Base near Colorado Springs, Colorado, gathers the GPS
satellites'
data from five monitor stations around the world. A Kalman filter software
program
estimates the time error, frequency error, frequency drift and Keplerian orbit
9
CA 02487825 2004-11-29
WO 03/102828 PCT/EP03/05258
parameters for each of the satellites and its operating clock. This
information is
uploaded to each satellite so that it can be broadcasted in real time. This
process
provides GPS time consistency across the constellation to within a small
number of
nanoseconds and accurate position determination of the satellites to within a
few
meters.
The second universal time standard, Universal Time Co-ordinated (UTC),
introduces leap seconds to remain synchronized with the rotation of the earth.
In
order to provide an estimate of UTC time derivable from a GPS signal, a set of
UTC
corrections is also provided as part of the GPS broadcast signal. This
broadcast
message includes the time difference in whole seconds between GPS time and
UTC. This complicates software that deals with the smooth flow of data streams
or
calculates the times between data samples. GPS Time is preferred in this
invention
as this system avoids the introduction of leap seconds and is easily related
to UTC.
Information about UTC (GMT) time service can be found on:
http:lltime.greenwich2000. coml
GPS Receivers
A Direct-to-Digital GPS Receiver is described in the following Web site
http:llw3.research.ibm.comlpresentlgto200038.htm
This is an example of a tiny low cost chip which can integrate GPS into
anything
(e.g., a PDA, a mobile phone, a wearable computer, a video camera) . This
receiver
has been jointly developed between IBM and Leica. The high speed analog
capabilities of Site technology, when integrated with the CMOS technology,
allows
the integration of this single chip directly to a digital GPS (Global
Positioning
System) receiver. GPS derived position information is finding a multitude of
diverse
applications: from mapping and surveying to vehicle tracking to 911 cell phone
caller
location to automated farm equipment to even robotics golf carts... This
receiver chip
reduces the radio dimensions and complexity. There are no analog mixer stages,
nor costly discrete components (such as high quality filters) that
conventional two
stage analog down conversion would have required. Instead, the incoming GPS
signal is literally digitized right at the antenna, then filtered digitally in
a CMOS based
io
CA 02487825 2004-11-29
WO 03/102828 PCT/EP03/05258
chip. This direct digitization is made possible by the ability of Site
technology to run
at high speed on very little power, and the core of this technology is a Site
based
Analog to Digital Data Converter.
According to the present invention GPS or GLONASS receivers must be
integrated or connected to the speaker workstation (202) (e.g., a Personal
Computer), and to auditor devices (204) (e.g., wearable computers, Personal
Digital
Assistants (PDAs), smart phones, WAP enabled phones, games consoles). The
universal timing signals that are received from GPS or GLONASS satellites, are
used to initialize and synchronize the internal electronic clocking systems
according
to the same universal time. During the periods on which GPS or GLONASS
satellites
are out of sight (e.g., when user's devices are inside buildings or not
connected to
an external antenna), and no timing signals are thus received from those
satellites,
timing information must be continuously derived from the autonomous electronic
clocking systems of those devices. Depending on the drift of the clocking
systems
set up in the devices, and to keep enough timing precision and to be sure that
auditor devices and speaker workstation are synchronized at the same
universal-time, a more or less frequent periodic reception of satellite
signals must be
performed. In practice,
~ if the user device is a portable satellite signals will be received when the
user is
out of doors or is traveling.
~ If the user device is fixed or installed in a house or building during long
periods,
the user device must be connected to an outdoors installed GPS or GLONASS
antenna, (e.g., antenna installed on the roof of the building).
Presentation Hyperlink Table
As illustrated in Figure 3, a presentation, according to a preferred
embodiment of the present invention, is structured as a set of HTML foils
stored on
one or a plurality Web servers. These Web servers are referenced in a
Presentation
Hyperlink Table (300) preferably stored on the speaker workstation (202). For
each
presentation foil, the Presentation Hyperlink Table encodes
m
CA 02487825 2004-11-29
WO 03/102828 PCT/EP03/05258
~ A foil number (301 ),
~ A foil name or short title (302), and
~ A network address (i.e., the URL) (303) where the HTML foil (or information
related to the foil) can be found on the Internet network.
Figure 3 shows an example of a Presentation Hyperlink Table (300) for a
presentation entitled "French Red Wines", presented by a speaker called
"Robert
Durand". During the presentation, the sepuence of the foils that are presented
by
the speaker, is stored on a Presentation Time Table, located on a Presentation
Server, at the URL (304):
Http:llwww.directbuyer.comlpresentation-0173.html
For instance, when the speaker selects the foil number "14" (301), named
"Bourgogne" (302), the hyperlink to the URL address (303):
http:llw~nrw.french-wines.comlbourgogne.htm
Is activated. The HTML foil is retrieved from this network address and shown
to the
audience.
PRESENTATION: SPEAKER: PRESENTATION TIME TABLE URL:
French Red WinesRobert Durandhtt ://www.directbu er.com/ resentation-0173.htm/
FOIL NUMBER FOIL NAME FOIL URL
1 French red http://www.french-wines.com/red%20wine.htm
wines
2 Bordeaux htt ://www.french-wines.com/bordeaux.htm
3 Pomerol http://www.french-wines.com/pomerol.htm
4 St Emilion http://www.french-wines.com/st%20emilion.htm
St Este he htt ://www.french-wines.com/st%20este
he.htm
6 St Julien http://www.french-wines.comlst%20'ulien.htm
7 Pauillac http://www.french-wines.com/pauillac.htm
8 Moulis htt ://www.french-wines.comlmoulis.htm
9 Medoc http://www.french-wines.com/medoc.htm
Mar eaux http://www.french-wines.com/mar eaux.htm
11 Haut Medoc htt ://www.french-wines.com/haut%20medoc.htm
12 Beau'olais http://www.french-wines.com/beau'olai.htm
13 Beaune http://www.french-wines.com/beaune.htm
14 Bour o ne htt :l/www.french-wines.com/bour o
ne.htm
Brouill htt :/lwww.french-wines.com/brouill
.htm
16 Fronsac http://www.french-wines.com/fronsac.htm
17 Cote de Castillonhtt ://www.french-
wines.com/coteIo20castillon.htm
18 Cote de Bour http://www.french-wines.com/cote%20bour
.htm
19 Cotes de Bla http://www.french-wines.com/cotes%20b1a
a e.htm
12
CA 02487825 2004-11-29
WO 03/102828 PCT/EP03/05258
Method for Creating a Presentation Hyperlink Table on a Speaker Workstation
As shown in Figure 13 , the present invention discloses a method for creating
a Presentation Hyperlink Table (300) for a presentation (like the presentation
entitled
"French Red IIVines" described in the previous example) and for defining, in
this
Presentation Hyperlink Table, hyperlinks (303) to one or a plurality of
servers (403)
(i.e., Web servers) connected to a network (404) (i.e., to the Internet
Network) where
foils can be accessed. These hyperlinks can be used by the auditor (301) to
access
the foils (i.e., Web pages, HTML foils) of the presentation on the servers.
The method of creating a Presentation Hyperlink Table in a speaker device
and for defining, in said Presentation Hyperlink Table, hyperlinks to one or a
plurality
of servers where foils can be accessed, comprises the steps of:
~ (1301 ) creating a new Presentation Hyperlink Table (300), said Presentation
Hyperlink Table comprising a header (305);
~. assigning to said Presentation Hyperlink Table means for locating and
accessing
address (for instance an URL within the network) (304) a Presentation Time
Table on a Presentation Server;
~ copying said locating and accessing means in the Presentation Hyperlink
Table,
preferably in the header (305);
and, for each new created foil of a presentation:
~ (1302) creating a new record in the Presentation Hyperlink Table;
~ (1303) assigning means (302) for identifying the foil (a name (302) andlor a
short
description);
~ copying said identifying means in said record;
~ (1304) assigning means for locating and accessing the foil, preferably a
destination address (303) (for instance an URL within the network) where said
foil can be accessed;
~ copying said locating and accessing means (303) in said record.
13
CA 02487825 2004-11-29
WO 03/102828 PCT/EP03/05258
Method for Generating a Presentation Time Table on a Presentation Server
As shown in Figure 4 the present invention also discloses a method for
generating during a presentation, a Presentation Time Table (408) on a
Presentation
Server (407). The speaker (400) selects the HTML foils using a presentation
software application running on his workstation (402). Each time the speaker
selects
(401) a new foil (e.g., the HTML foil number "~4'; named "Bourgogne'~, the URL
corresponding to the selected HTML foil
(e.g.,http:llwwHr.french-inrines.comlbourgogne.htm) is retrieved from the
Presentation Hyperlink Table (300). The hyperlink associated with the selected
HTML foil is then activated using a browser program on the speaker
workstation.
The selected HTML foil (405) is then accessed and retrieved from the Web
server
(403) through the network (404) and is presented to the auditors on a
presentation
screen (406).
Figure 4 also shows how, each time the speaker selects (401 ) a new HTML
foil, the universal-time interval (409) corresponding to this selection, is
determined
using the GPS receiver connected to the speaker workstation (402). The name
(302)
and the URL (303) of the selected HTML foil are then retrieved from the
Presentation Hyperlink Table (300) and transmitted, with the corresponding
universal-time interval (409), to a Presentation Server (407) and copied into
a
Presentation Time Table (408) located on said Presentation Server. The URL of
the
Presentation Time Table (408) is retrieved (304) using the presentation
software
application, from the header of the Presentation Hyperlink Table (300). fn the
present example, the URL:
http:llwwvv.direcfbuyer.comlpresentation-0173.html is the network address of
the Presentation Time Table (presentation-0~73.htm) stored on the Presentation
Server (www.direcfbuyer.com). The speaker must provide the audience, the URL
of the Presentation Time Table (304) before the presentation.
More particularly, as illustrated in Figure 14, the method, for generating
from
a speaker device (402), a Presentation Time Table (408) on a Presentation
Server
(407) during the presentation of one or a plurality of foils, comprises the
steps of:
14
CA 02487825 2004-11-29
WO 03/102828 PCT/EP03/05258
~ locating and accessing a Presentation Hyperlink Table (300), said
Presentation
Hyperlink Table, preferably located in the speaker device (402), comprising
~ means for identifying (302) one or a plurality of foils (each foil being
preferably identified by a name (302) andlor a short description);
~ means for locating and accessing (303) said one or plurality of foils
(preferably a destination address (303), for instance an URL within the
network);
~ means for locating and accessing (304) a Presentation Time Table (408) on a
Presentation Server (407);
~ (1401) locating and accessing the Presentation Time Table (408) on the
Presentation Server (407);
and, for each presented foil
~ (1402) identifying (401) the presented foil in the Presentation Hyperlink
Table;
~ (1403) determining an universal-time interval (409) corresponding to the
presentation of the foil by means of an universal-time device (e.g., a GPS
receiver);
~ (1404) creating a new record on the Presentation Time Table (408) located on
the Presentation Server (407);
~ (1405) copying into said new record
~ the universal-time interval (501) corresponding to the presented foil;
~ means, retrieved from the Presentation Hyperlink Table, for identifying
(502)
the presented foil;
~ means, retrieved from the Presentation Hyperlink Table, for locating and
accessing (303) the presented foil.
Figure 5 shows an example (also shown in the next table) of Presentation
Time Table (500) stored on a Presentation Server (407) at the end of a
presentation.
PRESENTATION: SPEAKER: PRESENTATION TIME TABLE URL:
French Red Wines yRobert Durand- Ihttp://www.directbuyer.com/presentation-
0173.html II
CA 02487825 2004-11-29
WO 03/102828 PCT/EP03/05258
SELECT. TIME FOIL NAME FOIL URL
12/05/2001 14:21:52French red http://www.french-wines.com/redI20wine.htm
wines
12/0512001 14:23:18Bordeaux http://www.french-wines.com/bordeaux.htm
12!05/2001 14:25:07Pomerol htt ://www.french-wines.com/ omerol.htm
12105/2001 14:27:18St Emilion http://www.french-wines.com/st%20emilion.htm
12!05/2001 14:30:12St Estephe htt ;//www.french-wines.com/st%20estephe.htm
12/05/2001 14:31:11St Julien htt ;//www.french-wines.com/st%20~ulien.htm
12/0512001 14:35:15Pauillac http:/lwww.french-wines.com/pauillac.htm
12/05/2001 14:38:43Moulis http://www.french-wines.com/moulis.htm
12/05/2001 15:05:21Medoc htt ://www.french-wines.com/medoc.htm
12/05/2001 15:07:44Mar eaux htt ://www.french-wines.comlmar eaux.htm
12105/2001 15:08:56Haut Medoc http:/lwww.french-wines.com/haut%20medoc.htm
12/0512001 15:11:16Beaujolais htt ://www.french-wines.com/beau~olai.htm
12/05/2001 15:15:29Beaune http://www.french-wines.com/beaune.htm
12105/2001 15:22:38Bour o ne http://www.french-wines.com/bour o
ne.htm
1210512001 15:25:58Brouill htt ://www.french-wines.com/brouill
.htm
12/0512001 15:28:09Fronsac htt ://www.french-wines.com/fronsac.htm
12/05/2001 15:32:24Cote de Castillonhttp://www.french-
wines.com/cote%20castillon.htm
12/05/2001 15:35:56Cote de Bour htt ://www.french-wines.com/cote%20bour
.htm
1210512001 15:38:13Cotes de Blayehttp://www.french-wines.com/cotes%20blaye.htm
The header section (504) of this Presentation Time Table is the same and is
directly copied from the header (305) of the Presentation Hyperlink Table
(300)
located on the speaker workstation. Each row of the table corresponds to a
foil of
the presentation (300) selected by the speaker. For each selected foil, the
three
columns of the Presentation Time Table corresponds respectively to:
~ (501) the universal-time interval at which the HTML foil has been selected
by
the speaker;
~ (502) the title (or short name, or short description) of the selected HTML
foil;
~ (503) the address or URL of the selected HTML foil.
Method for Selecting Topics of Interest
In the example illustrated by Figure 6, during the course of the presentation
(for example, the presentation entitled "French Red INines'~, the auditor
(600) uses
a portable workstation (601 ) in stand-alone mode (i.e., isolated, not
connected to a
network). In the particular embodiment shown in this figure, each time the
auditor
(600) perceives (603) during the presentation done by the speaker (602), an
interesting topic (604), he selects this topic simply by pressing (605) a
reserved key
16
CA 02487825 2004-11-29
WO 03/102828 PCT/EP03/05258
on his portable workstation (601 ). Universal times (606) at which interesting
topics
are selected by the auditor, are locally stored on a Selections Time Table on
the
auditor workstation (601 ).
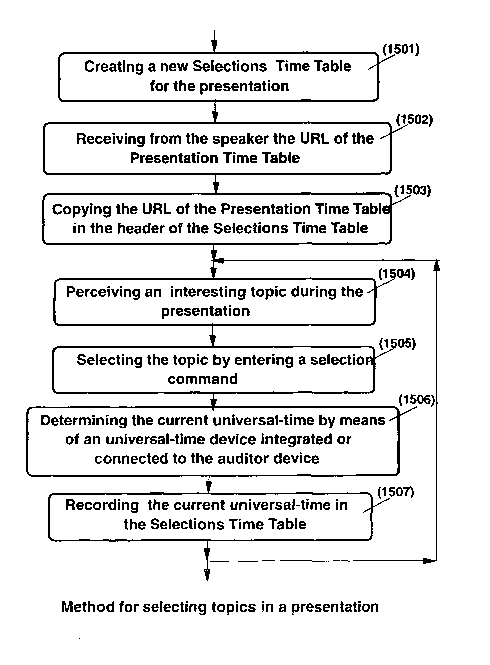
Figure 15 shows the steps of the method for selecting in a presentation, one
or a plurality of foils corresponding to one or a plurality of interesting
topics, and for
accessing at a later time said selected foils. To select particular topics of
interest,
the auditor (600) of a presentation:
~ (1501 ) creates on his workstation (601 ), a Selections Time Table for the
presentation;
~ (1502) receives from the speaker device (602), means for locating and
accessing
(304) a Presentation Time Table (500) on a Presentation Server (407),
preferably
a destination address (for instance an URL within the network);
~ (1503) stores on his workstation (601) said means (304) for locating and
accessing the Presentation Time Table (500);
~ (1504) perceives (listens or views) during the presentation a topic of
interest
(604) for which he desires to review the corresponding foil at a later time;
~ (1505) selects the foil corresponding to the topic of interest by entering a
selection command (605) on his workstation (601 );
~ (1506) determines the current universal-time (606) by means of an universal-
time
device (for instance a GPS receiver) integrated or connected to his
workstation;
~ (1507) records the current universal-time in the Selections Time Table .
The following table, also shown in Figure 7, is an example of Selections Time
Table created on an auditor workstation (601) during the course of a
presentation
(for instance, the presentation about "French Red II1/ines'~. Each row of this
table
corresponds to a selection by the auditor, of a foil presented by the speaker
at the
universal-time recorded in the first column. In the header section of this
table, the
auditor has copied the URL (701) of the Presentation Time Table (e.g.,
http:llwv~w.direct~buyer.comlpresentation-0173.html ). This URL is provided by
the speaker to the auditors in advance, before the presentation.
m
CA 02487825 2004-11-29
WO 03/102828 PCT/EP03/05258
PRESENTATION: SPEAKER: PRESENTATION TIME TABLE URL:
French Red WinesRobert Durandhtt :llwww.directbu er.com/ resentation-0173.htm/
SELECTION TIME FOIL NAME FOIL URL
12/05/2001 14:26:33
12/05/2001 15:07:18
1210512001 15:23:51
i
Method for Accessing and Displaying Selected Foils
Once the auditor (600) has selected one or a plurality of topics of interest
(604) during a presentation (for example in the presentation entitled "French
Red
INines'~, and once the universal-times (606) corresponding to these selected
topics
have been stored or recorded in the Selections Time Table (700) on the auditor
workstation (601), by means of the method described in Figure 16, the auditor
or
viewer can retrieve from the Presentation Server (803) the names and URLs
associated with the selected foils. The retrieved names and URLs are locally
stored
in the Selections Time Table (700) on the auditor workstation (601 ). From the
updated Selections Time Table, the auditor can select, retrieve and display
anyone
of said foils. The method for an auditor of a presentation, of accessing and
displaying selected foils from a workstation, comprises the steps of:
~ (1601) accessing from the workstation (800), the Presentation Time Table
(802)
on the Presentation Server (803);
~ (1602) sending to the Presentation Server (803), the universal-times of the
selections recorded on the Selections Time Table (700) located on the
workstation (800);
~ (1603) searching in the Presentation Time Table, for the foils that were
presented at these universal-times;
~ (1604) retrieving from the Presentation Server (803), the means for
identifying
the selected foils (names or descriptions) (502) and the associated URLs
(503);
~ (1605) storing the retrieved foil names and URLs into the Selections Time
Table
(902).
The method includes the further steps of:
is
CA 02487825 2004-11-29
WO 03/102828 PCT/EP03/05258
~ (1606) selecting a foil (1001) from the Selections Time Table (1002) ;
~ (1607) activating the hyperlink (1003) from the workstation using a browser
program;
~ (1608) accessing the foil on a server (1102) (preferably a Web server)
through
the network (1103) (preferably the Internet network);
~ (1609) retrieving from the network (1101) and displaying the foil (1104) on
the
workstation using a browser program (1100).
Figures 8, 9, 10 and 11 illustrate the different steps according to the
present
method. As illustrated in Figure 8, when the presentation ends (for instance,
the
presentation of "French Red IlVines'~, the auditor connects his workstation
(800) to
a communications network (e.g., the Internet network (801)). By means of a
software
application running on his workstation, the Presentation Time Table (802) on
the
Presentation Server (803) is accessed and the Selections Time Table (804),
which is
locally stored on his workstation (800), is updated.
Figure 9 illustrates the process of updating the Selections Time Table (900)
on the auditor workstation (800) using the information stored in the
Presentation
Time Table (901 ) located on the Presentation Server (803). Basically, for
each
universal-time recorded in the Selections Time Table (900), the name and the
URL
of the HTML foil that was being presented by the speaker at that time, are
identified
on the Presentation Time Table (901 ) and are copied into the Selections Time
Table
(902). The following table shows a Selections Time Table, updated by means of
this
process:
PRESENTATION: SPEAKER: PRESENTATION TIME TABLE URL:
French Red WinesRobert Durandhtt :l/www.directbu er.com/ resentation-0173.htm/
SELECTION TIME FOIL NAME FOIL URL
12/05/2001 14:26:33pomerol http://www.french-wines.com/pomerol.htm
12105/2001 15:07:18Medoc htt ://www.french-wines.com/medoc.htm
12/0512001 15:23:51gour o ne http://www.french-wines.com/bour o
ne.htm
Figure 10 illustrates how the auditor selects and accesses, from his
workstation, (1000) HTML foils previously selected during the presentation.
19
CA 02487825 2004-11-29
WO 03/102828 PCT/EP03/05258
Basically, the auditor points to and selects an HTML foil (1001) on the
updated
Selections Time Table (1002). By means of a software application located on
his
workstation (1001), he activates the hyperlink (1003) pointing to the URL of
the
selected item. In the example shown in Figure 10, the auditor selects the
topic of
interest "Medoc" (1001) (in fact a denomination of French red wine) and
activates
the hyperlink (1003) pointing to the URL:
http;llwwwr,french-wines.comlmedoc.htm
Finally, Figure 11 shows how an HTML foil (1101 ) (e.g., medoc.htm)
associated with the item selected (1001) in the Selections Time Table, (e.g.,
"Medoc'~, is received from a Web server (1002) (e.g., www.french-wines.com)
through the network (1103) and is finally displayed (1104) on the auditor
workstation
(1100).
!n the previous examples, it has been shown that the auditor can access after
the presentation to the foils previously selected during the course of the
presentation. In fact when the auditor selects a topic of interest during a
presentation
(e.g., while the speaker is presenting the foil "Bourgogne wines"), the
information
related with the selected topic ("Bourgogne wines"), that can be retrieved by
the
auditor when the presentation is over, can be
~ the HTML foil that have been presented when the selection was made.
~ a long (HTML) document comprising a description concerning La Bourgogne
(geography, history, economy, agriculture) and the wines from this region.
~ even a list of references (hyperlinks) to several Web documents or
multimedia
concerning "Les vins de la Bourgogne".
While the invention has been particularly shown and described with reference
to a preferred embodiment, it will be understood that various changes in form
and
detail may be made therein without departing from the spirit, and scope of the
invention.