Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02493656 2005-O1-19
-1-
PORTABLE SYSTEM FOR DETECTION
AND MANAGEMENT OF ROAD TRAFFIC AND
ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS
CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATION
This patent application claims priority on
Canadian Patent Application No. 2,454,508, filed on
January 19, 2004, by the present applicant.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
1. Field of the Invention
The present invention relates to road surveillance
for vehicle speed derogations and, more particularly, to a
portable detection system and apparatus for road traffic and
environmental conditions.
2. Background Art
Due to the cost of maintaining adequate road
surveillance staffing, many road segments are without
surveillance. There are various problems associated with a
lack of speed derogation/infraction prevention, such as
repeatability of derogations.
It has been observed that the simulation of
surveillance causes the vehicle drivers to slow down to the
speed limit, to avoid being caught speeding (and avoid
associated penalties, such as fines and notices in police
records) .
In order to prevent accidents, for instance on
road construction sites, and in order to reduce the speed of
drivers, police patrols and electronic speed displays are
often used. Police patrols often cannot be used for 24-hour
period, as this represents a costly solution.
As for electronic speed display devices, the
drivers often do not have sufficient time to observe the
display. Moreover, such display devices have become
CA 02493656 2005-O1-19
-2-
commonplace, whereby they have little influence on the
behavior of the drivers.
SUMMARY OF INZTENTION
It is therefore an aim of the present invention to
provide a novel portable detection system and apparatus for
road traffic surveillance.
It is a further aim of the present invention that
the novel detection system be used to collect environmental
conditions and other surrounding information.
l0 It is a still further feature of the present
invention to provide a method for simulating road
surveillance in response to the detection of speed
derogations.
Therefore, in accordance with the present
invention, there is provided a method for signaling speed
de rogations to a vehicle driver in road traffic, comprising
the steps of: i) monitoring a road to detect movement caused
by a vehicle; ii) measuring a speed of the vehicle detected
in step i); and iii) signaling a warning if the speed is
above a given value.
Further in accordance with the present invention,
there is provided a system for detecting road traffic
conditions and environmental conditions, comprising: at
least one detection apparatus comprising sensors for
detecting any one of road traffic conditions and
environmental conditions, the at least one detection
apparatus being adapted to be located at a surveillance
site, the at least one detection apparatus having a
processing unit so as to interpret information collected by
any one of the sensors; a telecommunications device
connected to the apparatus so as to transmit data
interpreted by the at least one detection apparatus to a
remote server; and the remote server for receiving said data
from the at least one detection apparatus, the remote server
CA 02493656 2005-O1-19
-3-
being accessible to provide the data collected by the at
least detection apparatus.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Having thus generally described the nature of the
invention, reference will now be made to the accompanying
drawings, showing by way of illustration a preferred
embodiment thereof and in which:
Fig. 1 is a perspective view of a detection
apparatus in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the
present invention, with a door thereof closed;
Fig. 2 is a perspective view of the detection
apparatus of Fig. 1, with a door open to show the interior
of the detection apparatus;
Fig. 3 is a block diagram illustrating a detection
system in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the
present invention;
Fig. 4 is a flowchart illustrating a method for
signaling a speed derogation in accordance with the
preferred embodiment of the present invention;
Fig. 5 is a flowchart illustrating an image-taking
method in accordance with the present invention;
Fig. 6 is a flowchart illustrating a method for
taking environmental condition measurements in accordance
with the present invention;
Fig. 7 is a flowchart illustrating a method for
transferring data to the server with the detection system of
the present invention;
Fig. 8 is a schematic view of a web page
representing a map upon which are positioned detection
apparatuses in accordance with the present invention; and
Figs. 9 to 11 are schematic views illustrating web
pages presenting data collected using the detection system
of the present invention.
CA 02493656 2005-O1-19
-4-
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
Referring to the drawings, and more particularly
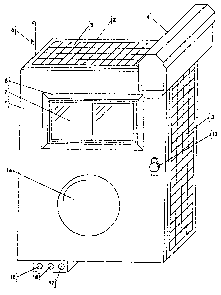
to Figs. 1 and 2, a detection apparatus in accordance with a
preferred embodiment of the present invention is generally
shown at A. The detection apparatus A has a casing 2 which
accommodates various components of the detection apparatus
A. A door 1 conceals in a waterproof way the components
within the casing 2. In Fig. 1, the door 1 is shown closed,
whereas in Fig. 2 an interior of the casing 2 is shown with
the door 1 being open.
The casing 2 is typically of a metallic material
that i.s sealed in a waterproof manner so as to resist
atmospheric conditions. A lock 13 is provided so as to lock
the door 1, and substantially prevent tampering of the
components within the casing 2.
A plurality of components are provided on an
exposed surface of the casing 2. For instance, solar panels
3, a radar 4, an antenna 5, a strobe light 7 and its support
6, as well as a surveillance camera 14, are all on an outer
surface of the casing 2. Moreover, various types of
sensors , such as a temperature sensor 15 , a humidity sensor
16, and a gas sensor 17, are also provided on an outer
surface of the casing 2.
The components within the casing 2 are as follows.
A power supply regulator 8 is provided within the casing 2
and is connected to the strobe light 7 so as to supply the
strobe light 7 with the appropriate power. A modem 9 is
conner_ted to the antenna 5 (e. g., for cellular
communications), and is wired to a processing unit 12 of the
casing 2. A battery charger and/or voltage regulator for
local power supply is shown at 10, and is connected to
batteries 11. The detection apparatus A is powered by the
batteries 11 or by the local supply by way of the voltage
regulator 10, so as to provide suitable voltage to the
various components of the detection apparatus A. The
batteries 11 are recharged by the solar panels 3. It is
pointed out that the solar panels 3 are preferably
CA 02493656 2005-O1-19
-5-
positioned on the sides and the top of the detection
apparatus A (but could be separated from the casing 2) so as
to maximize the exposure to light and increase the
possibility of orientation of the detection apparatus A.
Accordingly, the detection apparatus A may be autonomous
with regard to power consumption if no local power port is
available.
Referring to Fig. 3, the detection system in
accordance with the present invention is generally shown at
B. The detection system A has the detection apparatus A.
A processor unit 12 is used to control the
operation of the detection apparatus A. The processor unit
12 has suitable ports so as to be connected to the various
components within the detection apparatus A, such as the
radar 4 (e.g., a hyper frequency radar, laser radar or the
like), the strobe light 7 through the power supply regulator
8, the modem 9, as well as the temperature sensor 15, the
humidity sensor 16 and the gas sensor 17. Moreover, the
detection apparatus A may also be provided with a sound
level sensor 18, so as to provide additional information
pertaining to the sound level in the surroundings of the
detection apparatus A. This is advantageously used to
measure the sound level of freight carriers.
The processing unit 12 of the detection apparatus
A is connected to the radar 4, so as to obtain data from the
radar 4. Therefore, the radar 4 can be used to detect speed
derogations, by the processing unit 12 interpreting the data
from the radar 4.
The processing unit 12 is also connected to the
strobe light 7 by way of the power supply regulator 8, such
that a speed derogation detected by the processing unit 12
(from the scan data provided by the radar 4), can be
signaled as a derogation signal through the light 7.
Alternatively, a rotating light, also simulating a
derogation signal, can be used to warn the driver of the
derogation.
CA 02493656 2005-O1-19
-6-
The processing unit 12 is also connected to other
components, as described previously. For instance, the
surveillance camera 14 is provided in the detection
apparatus A, so as to visually record the surroundings of
the system B. For instance, road conditions (e. g., presence
of snow, ice or the like on the pavement) and other
associated visual information, as well as statistical data
is recorded by the surveillance camera 14. Moreover, the
vehicle identification can be recorded in response to a
speed derogation detection by the processing unit 12. The
power supply regulator 8 is typically wired to the
processing unit 12 via the digital port of the interface
card. The surveillance camera 14 is typically connected to
the processing unit 12 by way of a video port, integrated to
the mother board. The various sensors, such as the
temperature sensor 15, the humidity sensor 16, and the gas
sensor 17, are typically connected to the conversion
interface 20 by way of digital ports.
Referring to Figs. 1, 2 and 3, the environmental
conditions sensors (i.e., temperature sensor 15, humidity
sensor 16 and gas sensor 17) are connected to the processing
unit 12 via the conversion interface 20 so as to provide the
processing unit 12 with environmental conditions. For
instance, levels of noxious gases are monitored by way of
the gas sensor 17, and high levels of such gases can be
detected by the processing unit 12.
Therefore, the processing unit 12 gathers various
types of information, which can prompt on site intervention
from the detection apparatus A (e.g., derogation signal by
the strobe light 7 to simulate police presence).
Alternatively, the information gathered by the detection
apparatus A may be transmitted to an off site server C, by
way of the Internet D, as will be explained hereinafter. It
is contemplated to provide the detection apparatus A with
cellular communication, by adapting the detection apparatus
A to local cellular networks.
CA 02493656 2005-O1-19
-7-
Alternatively, it is contemplated to use the
detection apparatus A to communicate the collected data to
nearby surveillance personnel. More specifically, the modem
9 can transfer the data to a hand-held wireless device 19,
such that a surveillance officer standing near to the
detection apparatus A can intervene in response to readings
obtained by the hand-held wireless device 19 if there are
infractions or derogations in the measured values (e. g.,
speed limit derogations, significantly high sound levels
l0 measured). It is contemplated to used a RF modem and RF
communications between the detection apparatus A and the
hand-held wireless device 19.
Referring to Fig. 4, a method used by the
detection system B of the present invention is generally
shown at 50.
In Step 52, the road is scanned for the presence
of vehicles if the vehicle detection function is enabled for
the processing unit 12 of the detection apparatus A. More
specifically, the vehicle detection function is performed
jointly by the radar 4 and the processing unit 12, with the
radar 4 detecting the presence of any vehicle on the road
that is scanned, and transmitting the scan data to the
processing unit 12.
In Decision 54, a vehicle detected will bring the
detection apparatus A to Step 56. Otherwise, the detection
apparatus A will keep on scanning the road until a vehicle
is detected, or until the vehicle detection function is
disabled.
In Step 56, once the radar signals the presence of
a vehicle to the processing unit 12, vehicle speed data and
other information are obtained. Moreover, the vehicle speed
is calculated and the information is recorded along with
statistical data. For instance, in addition to the vehicle
speed, the time and images of the vehicle are gathered. The
size (i.e., length) of the vehicle may also be calculated
from the scanned data of the radar 4. An average speed for
the last few vehicles may also be calculated.
CA 02493656 2005-O1-19
_$-
In Decision 58, the calculated vehicle speed is
compared to the speed limit or other suitable speed
parameter (such as an average speed). If the calculated
speed is above the speed limit, the method goes to Step 60.
Otherwise, the method will go to Step 62.
In Step 60, if the calculated speed is above the
speed limit, the derogation is signaled to the vehicle
driver. This is performed by the use of the strobe light 7
or other suitable lighting source. In order to try to cause
l0 the vehicle driver to slow down, the detection apparatus A
and its strobe light 7 are turned on when the vehicle is
still at a substantial distance from the detection apparatus
A, so as to simulate the presence of a police vehicle. By
simulating the presence of a police vehicle, the vehicle
driver will have a tendency to slow down.
In Step 62, the detection apparatus A is reset for
a subsequent vehicle.
In Fig. 5, a method for regulating the image
taking picture of the detection apparatus A is generally
illustrated at 60.
In Fig. 6, a function for activating the periodic
environmental condition measurement function for detection
apparatus A is generally illustrated at 70.
In Fig. 7, a method for transferring information
collected by the detection apparatus A to a server is
generally illustrated at 80.
In addition to preventing and diminishing the risk
of accidents due to speed, the detection system B in
accordance with the present invention will, by way of its
data acquisition configuration and its mobility, allow a
better understanding of the road behavior of drivers. The
collection of data (the number of vehicles, types of
vehicles, the speed, the time values, and other factors) and
management of this data are performed remotely towards a
server in an efficient and low-cost way. Moreover, this can
be performed continuously over 24 hours.
CA 02493656 2005-O1-19
_g_
All information gathered by the detection system B
of the present invention may be posted on a website, such
that clients may remotely consult the website to obtain
information pertaining to the detection points. Moreover,
in view of the available information, road traffic
controllers can suggest different courses to a fleet of
drivers to avoid bad road conditions. For instance, in
Fig. 8, a web page illustrating a map upon which are
positioned detection apparatuses is generally shown at 90.
Upon clicking on some of the points representing apparatus
sites, information web pages, such as those illustrated in
Figs. 9 to 11, are reached.
The multiple functions and data-gathering
components of the detection system of the present invention
will enable road traffic controllers to know, in a short
amount of time, the road conditions at many points by way of
the collection of data from the detection system B. It is
pointed out that a plurality of the detection apparatus A
may be used over a territory to provide multiple data
collection points.