Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02494504 2005-02-O1
WO 2004/013546 PCT/GB2003/003366
-1-
Cooler Structure for Surface Coolina
The present inventi on relates to a cooler structure for
cooling a surface and more particularly to .a cooler
structure suitable for cooling a vehicle windscreen.
In hot ambient conditions (particularly in climates having
strong sunshine) vehicle windscreens can reach high
temperatures frequently in excess of 50°C and on occasions
up to 90°C plus. In such high temperature conditions it is
a known problem that small windscreen breaks or cracks can
become elongated (or result in shattering of the
windscreen) when stresses are applied to the windscreen.
This phenomenon is known in the art as 'cracking off'.
Cracking off may occur when pressure or stresses are
applied by crack or break repair devices which are mounted
to the vehicle windscreen to repair a crack or,break in
such hot ambient conditions. Such a device is disclosed in
WO-A-0134373.
An improved apparatus and technique have now been devised
for such situations. According to the invention, there is
provided a cooler structure for use in cooling a surface,
the cooler structure comprising a backing panel and,
supported on the backing panel, cooling medium in heat
transfer relationship with the backing panel.
The cooler structure beneficially has a zone (access zone)
CA 02494504 2005-02-O1
WO 2004/013546 PCT/GB2003/003366
-2-
within its periphery through which a target zone of the
surface (such as a zone of a windscreen having a crack or
break) may be accessed. This zone of the structure (the
accessible zone) is beneficially bounded by a cooling zone
of the structure having the cooling medium supported on the
structure. The target zone is beneficial 1y accessed by a
removable (or at least partially displace able) portion of
the cooler structure, such as a fold-back flap or the like
which may be cut through the backing panel of the cooler
structure. Beneficially the removable or displaceable
portion carries cooling medium such that when the relevant
portion is in place adjacent and contact ing the surface
(windscreen) the target zone is also directly cooled.
The removable or displaceable portion may be removed or
displaced to permit the target zone to be accessed (and the
repair process conducted) whilst the remainder of the
structure remains in cooling contact with the surface
(windscreen). The access zone is benefic i ally dimensioned
to permit windscreen repair apparatus t o be placed on a
vehicle windscreen whilst the cooler structure is in place.
The cooling medium is beneficially present over an area of
the cooler structure corresponding to substantially 600 or
more (more preferably 70 0, more preferably ~ still 80%) of
the backing panel.
The backing panel is beneficially subs tantially liquid
impermeable and preferably comprises a p1 antics or rubber ,
material such as for example PVC. Beneficially the backing
CA 02494504 2005-02-O1
WO 2004/013546 PCT/GB2003/003366
-3-
panel comprises a flexible sheet material which is
conformable to the shape of the surface (for example the
curvature of a vehicle windscreen).
It is preferred that the cooling medium comprises a
material to be hydrated (or an already hydrated material).
The cooling medium beneficially comprises an absorbent
polymer material, preferably a superabsorbent polymer
material such as for example a polymer obtainable under the
trade name Hysorb M 7055 (BASF). Beneficially the cooling
medium is in granular, particulate or hydrogel form.
The cooling medium is beneficially contained within pockets
deffined and formed on the structure. Discrete pockets
effective 1y permanently retaining dosed quantities of the
cooling medium.
The pockets beneficially have a front panel portion,
beneficia 11y comprising liquid permeable material. The
backing panel preferably defines the opposite panel of the
relevant pocket. The pockets are preferably formed by weld
seams along face adjacent face sheets comprising the
pockets .
Beneficially the structure is provided with mounting means
for securing the structure in position on the surface. In
one embodiment the mounting means may comprise one or more
sucker cups, preferably provided along an upper portion of
the cools r structure.
CA 02494504 2005-02-O1
WO 2004/013546 PCT/GB2003/003366
-4-
According to a second aspect, the invention provides a
method of cooling a surface (particularly a vehicle
windscreen), the method comprising positioning a cooler
structure as defined herein, in position with the backing
panel of the cooler structure adjacent the
surface/windscreen.
According to a further aspect, the invention provides a
method of repairing a flaw (such as a crack or break) in a
vehicle windscreen, the method comprising positioning a
cooler structure in position with a backing panel of the
cooler structure in contact with the windscreen; permitting
a period of time to elapse; and carrying out a repair
process on the flaw.
Beneficially the cooler structure has a zone within the
periphery of the cooler structure which zone is positioned
over the flaw in the windscreen and through which zone the
flaw of the windscreen may be accessed. Beneficially the
repair process is carried out on the flaw whilst the cooler
is in situ, positioned on the windscreen.
Beneficially the cooler structure includes temperature
indicating means arranged to indicate the local temperature
of the surface (e. g. windscreen).
According to a further aspect, the invention provides a
method of manufacturing a cooler structure, the method
comprising welding a liquid permeable sheet material to a
liquid impermeable backing along weld lines to form a
CA 02494504 2005-02-O1
WO 2004/013546 PCT/GB2003/003366
_5 _
series of pockets containing a cooling medium retained in
the pockets.
According to still a further aspect, the invention provides
a kit comprising a cooler structure as defined herein and
a carrier container for cont a fining the cooler structure,
typically in the hydrated st ate. Beneficially the kit
further includes a container for dispensing hydrating
liquid to hydrate the cooler structure. The container for
the cooler structure may also contain the hydrating liquid
container.
The invention will now be further described in specific
embodiment by way of example only and with reference to the
accompanying drawings, in which:
Figure 1 is a schematic plan view of a cooler according to
the invention;
Figure 2 is a schematic sectional view along Z-Z in Figure
l;
Figure 3 is an enlarged view of detail Y in Figure 1; and
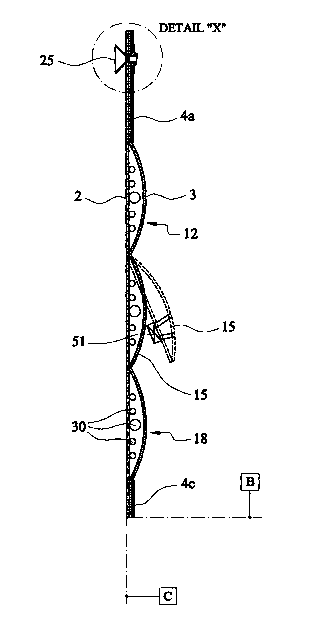
Figure 4 is an enlarged view of detail X in Figure Z.
Referring to the drawings, a cooler 1 particularly suited
for cooling a zone of a vehicle windscreen, comprises a
flexible PVC backing layer 2 and a top sheet 3 of a non-
woven polyester material overt aying the backing. A second
CA 02494504 2005-02-O1
WO 2004/013546 PCT/GB2003/003366
-6-
PVC layer sheet comprising marginal portions 4a, 4b, 4c and
4d and having a square central opening is laid over the
non-woven polyester sheet 3. The layer structure is then
welded using high frequency welding along a peripheral weld
line 5 (extending around the entire perimeter of the cooler
and along the internal edges of the marginal portions 4a,
4b, 4c to produce a peripheral weld line 6 defining a
square boundary with the polyester top sheet 3. High
frequency welding is also used to weld the polyester top
sheet 3 to the backing layer 2 along parallel top to bottom
weld lines 7, 8 and side to side parallel weld lines 9, 10.
The polyester top sheet 3 is liquid permeable and is not
stretched tightly across the backing layer 2 prior to
welding in order to ensure the top sheet 3 can separate or
pull away from the backing layer 2. In this way, when
welded as described, the top sheet 3 together with the
backing layer 2 forms a series of discrete pockets 11, 12,
13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19 into which liquid may pas s via
the top sheet 3. Prior to the welding stage granules 30 of
a superabsorbent polymer gel material are placed in the
zone of the pockets 15 to 19 intermediate the backing PVC
layer 2 and the polyester top sheet 3. Typically, the
polymer gel granules 30 are contained within soluble
packets for ease of manufacturing. V~lhen the pockets are
created by the welding process, the polymer gel granules 30
are effectively constrained within respective pockets 11 to
19.
When welding the top sheet 3 to the PVC backing layer 2 ,
three lengths of over-wide weld line 7a, 8a, 10 a are
CA 02494504 2005-02-O1
WO 2004/013546 PCT/GB2003/003366
_7_
produced. Centrally of the over-wide weld line lengths 7a,
8a, 10a a continuous cut line 20 is formed extending from
a first cut-li<ne end 21 to a second cut-line end 22. Cut
line ends 21 and 22 are defined by small circular apertures
cut through the welded portion of the cooler. A flap or
opening pocket 15 is thereby defined which may be folded
back along welded seam 9 to reveal an aperture extending
completely through the welded layer arrangement of the
cooler. The facility to fold back flap pocket 15 is shown
most clearly in Figure 2 where the folding back pocket 15
is shown in dashed lines. The purpose of the folding
pocket is explained in detail below. It should be noted
that the fold back pocket is surrounded by other pockets.
The top triangular peripheral zone of the cooler 1 is
provided with three plastic suckers 24, 26, 27 enabling the
structure 1 to be mounted to the windscreen surface to be
cooled with the backing layer 2 in contact with the
windscreen surface. The suckers are mounted through
respective apertures with a push fit stank 28.
The purpose of the cooler structure is to enable a
windscreen to be cooled from a high ambient temperature
condition to a' cooler condition for apertures such as
windscreen crack repair. As previously mentioned, in hot
or sunny climates or ambient conditions, vehicle
windscreens can reach high temperatures, frequently in
excess of 50°C and on occasions up to 90°C and above. In
such high temperature conditions, it is a known problem
that small windscreen breaks or cracks can become elongated
when stresses are applied to the windscreen. Such
CA 02494504 2005-02-O1
WO 2004/013546 PCT/GB2003/003366
-g_
occurrences are referred to as 'cracking off'. Such
cracking off can occur when crack or break repair devices
are mounted on the windscreen to repair a crack or break.
WO-A-0134373 discloses device for use in repairing
windscreen cracks or breaks by infilling with resin. The
device rests on the surface and applies vacuum pressure to
the crack or break. In so doing, the stress applied to the
windscreen can result in 'cracking off' in hot ambient
conditions. The repair of what should have been a minor
1 O windscreen crack or break is therefore transformed into a
more major repair job or even replacement of the screen.
This is a technically more difficult, time consuming and
expensive procedure. The cooler structure of the present
invention enables 'cracking off' situations to be avoided
1 5 even in very hot ambient conditions.
The cooler structure 1 is first either completely immersed
in water to hydrate the superabsorbent polymer granules 30
in the pockets 11 to 19. The hydrated granules 30 expand
2 0 to pad out the relevant pockets. The granules are manually
spread out evenly through the relevant individual pockets.
Following immersion in water, top up water may be added to
maintain the hydration of the granules present in the
pockets. The non-woven top sheet 3 material is water
2 5 permeable. The PVC backing layer 2 is water impermeable.
Next the surface of the PVC backing layer is wiped dry. It
is important to keep moisture away from the break or crack
zone of the windscreen. The cooler structure is then place
30 on the vehicle windscreen with the surface of the backing
CA 02494504 2005-02-O1
WO 2004/013546 PCT/GB2003/003366
-9-
layer 2 in contact with the screen. The fold back pocket
15 is centered over the crack or break zone of the
windscreen. Folding back~the pocket 15 enables t he crack
to be observed whilst positioning the cooler structure 1 on
the windscreen. The suckers 25, 26, 27 hol d the structure
in place on the screen. With the cooler structure in place
on the screen, the central fold back pocket is folded to
its closed position and the structure left in pl ace for a
fixed period (typically 5 - 10 minutes or so) to 1 ower the
temperature of the windscreen. The fold back pocket 15
carries an LED thermometer 51 which is visible from
externally of the structure in order to provide indication
of the local surface temperature of the windscreen.
In trials, the cooler structure 1 has been shown to reduce
the screen temperature by up to 35°C in 6 minutes,
depending upon the screen start temperature . The mechanism
for cooling is heat transfer from the screen vi a the PVC
backing.layer 2 to the wet gel material 30, which is at a
lower temperature than the screen. Additionally, the
ambient hot conditions cause the water held by the gel
material 30 to evaporate producing an added cooling effect
on the gel material due to evaporation. The gel material
in the pockets can have water added as required by sinking
through the top sheet layer 3.
Following cooling, the central fold back pocket 15 is
folded back and the break is repaired. For example, a
vacuum resin repair apparatus as disclosed in WO-A-0134373
can be applied to the windscreen to repaid the crack or
CA 02494504 2005-02-O1
WO 2004/013546 PCT/GB2003/003366
-10-
break. The pockets surrounding the folded back central
pocket 15 remain in cooling contact with the winds Green
during the repair process.
Following the successful completion of the repair, the
cooler structure is removed from the screen, folded for
storage in a sealed plastics carry case. The sealed carry
case is useful for storing the structure in a damp o r wet
condition, keeping the polymer gel material in an at 1 east
partially hydrated condition.
In cooling from very hot conditions (screen temperature of
80°C or more) it has been found that with pocket 1 5 in
place cooling the screen slight, slight extension o f the
crack can sometimes occur. The provision of a small
aperture 30 (sealed at a weld seam) through the centre of
the pocket 15 has been found to ameliorate this problem and
aid positioning of the device, the crack or break being
centered on aperture 30.
The invention has primarily been described in relat i on to
cooling vehicle windscreens. Those skilled in the art
appreciate however that the invention has application in
other situations where cooling of a surface or structure
may be required. Furthermore, the invention may also be of
use in situations when temperature modification by heating
may be required. The structure may in such circums t antes
be used to hold a heating material at higher temperature
than the temperature of the surface to be heated. The
pockets 15 may in such circumstances hold a material
CA 02494504 2005-02-O1
WO 2004/013546 PCT/GB2003/003366
-11-
arranged to selectively undergo an exothermic reaction to
cause a heating effect.