Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02498654 2008-04-24
DEVICE FOR THE PRECISE POSITIONAL COUPLING OF TWO MATERIAL WEBS
The invention relates to an arrangement for the precise
positional joining of a first material web which includes
elements of sections having a section length divided by
separation locations and a second material web which is prqvided
with marks having a predetermined distance which corresponds to
the section length, except possibly for a certain difference.
The 'arrangement includes a first device by which the two
materzal-webs are joined, a transport.device, by which the two
material webs are advanced, stepwise, by the predetermined
distance, and a second device by which an element is applied-to
the first material web when, after the advancing step of the two
material webs by a section length, the length of the first
material web between the first device and the second device
corresponds to a predetermined multiple of the section length
plus.an offset length which is adjustable by an offset device,
and a transport arrangement by which the two material webs can
be advanced by the predetermined distance.
With such an arrangement.fdr example so-called bl'ister
packages are produced by iahich for example tablets are distrib-
uted and sold. A blister package consists generally of a deep
1
CA 02498654 2005-03-10
drawing film of plastic or paper includi.ng indentations in
which the tablets are disposed and which are sealed by a cover
foil. The cover foil is generally provided with imprints which
genGrally include information concerning the tablets such as
data when and which tablets should be taken. It is therefore
very important that this information is applied to the cover
foil accurately positioned according to the position of the
tablets and consequently the indentations.
Although with modern printing techniques a tiiyh accuracy
can hP achieved, the position-accurate coordination of the im-
print on the cover foil with respect to the deep drawing web is
highly problemaLic since any deviations present may be added
up. In time, the position of an imprint could deviate from the
required position by an intolerable amount. Therefore, print-
ing arrangements have been developed by which the position ac-
curacy of the imprint on the cover foil has been substantially
improved. DE 195 25 713 Cl, for example, discloses an arrange-
ment for a position-accurate imprinting of an endless foil
without markings, by which imprints of a first predetermined
length are applied to a metal foil and, after being imprinted,
the foil is cut into sections of a certain predetermined length
by a cutting device so that the imprints must be applied to the
foil accurately between the cuts.
The known arrangement includes a printer which has an in-
put for initiating a position-accurate printing procedure.
Furthermore, there is a sensor which provides at its output a
signal when the length of the foil between the cutting device
and the location corresponding to the beginning of a section to
be imprinted is a predeterma.n,ed multiple of the second prede-
termined length.
2
CA 02498654 2005-03-10
Since the output of the sensor is connected to the output
of the printer the beginning of a foil section to be imprinted
is always newly determined. With the constant new determina-
tion of the begi.nning of the section to be imprinted errors
possible present cannot be added up. Consequently, even rela-
tively large devidLions are generally harmless since errors
present in one section do not influence the beginning of the
next section to be imprinted. _
Furthermore, DE 198 50 275 discloses diiother arrangement
for the position-accurate imprinting of an unmarked endless
foil, which operates according to the same principle as the
printing arrangement described above. The main difference from
the above printing arrangcmcnt resides in that the endless foil
is transported in the earlier mentioned printing arrangement
discontinuously whereas in the further printing arrangement the
endless foil is continuously transporLed. However, the printer
is also activated whenever the length of the endless foil be-
tween the section limit formed by the last cutting and the
printing arrangement is a predetermined multiple of the second
predeterminccl length.
Although these known arrangements provide for excellent
results, it still has beeri found that, as a result of external
influences, the imprint may be displaced with respect to the
location of the indentatzons. Particularly after a stand-still
of the arrangement, deviations sometimes occur, which are no
longer tolerable.
US 5,964,970 discloses an arrangement for the position-
accuraLe jo.ining of a first foil, on which elements of an ab-
sorbing material are disposed, with a second foil, to which im-
print images are applied which include a reference mark. The
imprints must correspond to the absorbing elements. The absorb-
3
CA 02498654 2007-07-13
ing elements are applied to the first foil which advances at a
constant speed, whereby the absorbing elements are disposed on
the first foil at a distance from one another which can easily
vary. The reference marks or, respectively, the associated im-
prints are disposed on the second foil at a constant distance
from one another, which corresponds to the constant distance at
which the absorbing elements of the first foil are arranged.
Before the two foils are joined the second foil is riffled
in an apparatus whereby it is shortened. After the second foil
has become shorter, it passes though a device in which it can
again be stretched. The stretching depends on the position of
the absorbing elements disposed on the first foil. With a re-
duced distance of the subsequent absorbing elements, less
stretching takes place than when the elemerits are arranged at
larger distances from one another. With the different stretch-
ing of the second foil consequently position displacements of
the absorbing elements on the second foil can be corrected.
It is the object of the present invention to provide an
arrangement of the type disclosed above in such a way that the
position displacements of the elements disposed on the first
material web with respect to the marks disposed on the second
material web can be reduced.
The solution to this object is obtained by a sensor by
which the difference can be determined and the offset is
adjusted dependent on the difference.
In accordance with the invention, an arrangement for a po-
sition accurate joining of a first material web, which com-
prises elements in a section length separated by separating lo-
cations, with a second material web which is provided with
marks arranged at a predetermined distance from each other cor-
4
CA 02498654 2005-03-10
responding to the section length - except for a possibly cer-
tain deviation. The arrangement includes a first device by
which the two material webs are joined, a transport device by
which the two material webs are moved stepwise by the predeter-
S mined-distance, and a second device by which an element applied
to the first material web when after movement of the two mate-
rial webs by a section length, the length of the material web
between the first device and the 5econd device corresponds to a
predetermined multiple of the section length plus an offset
which is adjusLable by an offset device, and a transport device
by which the two material webs can be moved section-stepwise,
characterized in that a sensor is provided by which the differ-
ence is determined and the offset is adjusted depending on the
difference,
Since a sensor is provided by which the differences are
d.etermined, any position displacements of the elements applied
to the first material web relative to the marlcs on the second
material web are recognized. By the adjustment of the offset
depending on the difference the position displacements can be
corrected.
That means that, with any change in the predetermined dis-
tance between the marks of the second material web, also the
transport length changes by which the second material web is
advanced by a section and, since the first material web is
joined to the second material web, also the respective trans-
port length of the first material web. Sirrce the elements, af-
ter the advance of the two material webs by a section length,
are applied to the material web always when the length of the
first material web between the first device and the second de-
vice is a multiple of the section length, the elements are dis-
placed relative to the separation locations which are newly de-
fined on the basis of the changed transport length. By the ad-
5
CA 02498654 2005-03-10
justment of the offset depending on the difference the dis-
placement can be compensated for. Consequently, the position
of the elements on the first material web are corrected even if
the transport length of the first material web changes, for ex-
ample, by a change of the di;stance of the marks present on the
second material web.
The arrangement according to the invention is particularly
advantageous for the position-accurate joining of an aluminum
foil provided with an imprint and a plastic: foil whic:h includes
indentations.
A pd1'l:icular embodiment of the invention has been found to
especially advantageous wherein the sensor is so arranged that
the length of the second material web between the sensor. and
the first device corresponds to the length of the second mate-
rial web between the first device and Lhe second device when
the application of the element is initiated. in this way, the
sensor detects the sum of the differences up to the sensor po-
sition. Furthermore, the correction of the position of the
element on the first material web with respect to the first de-
vice occurs at the same place where the difference of the sec-
tion length is determined. This has the advantageous result
that the position of the element on the first material web can
be corrected in a simple manner. For the correction of the po--
sition of the element on the first material web essentially no
special measures are required.
If the offset corresponds to the difference as it is pro-
vided for in another particular embodiment of the invention, an
almosL 100% correction is achieved so that an error is not even
noticeable.
6
CA 02498654 2005-03-10
In another embodiment of the invention, the difference de-
tected by the sensor is divided by the number of marks of the
second material web which are disposed between the sensor and
the first device when the application of the elements is initi-
ated and the offset corresponds to the product of the result of
the division and the predetermined multiple of the section
length. Such an embodiment of the invention is particularly
advantageous if the sensor cannot be arranged at the location
where the length of the second material web between the sensor
and the first device corresponds to the length of the firsL ma-
terial web between the first device and the second device when
the application of the element is initiated. If the sensor
cannot be arranged in such a way that the length of the second
material web between the sensor and first device corresponds to
the length of the first material web between the first device
and the second device when the application of the element is
initiated, it is necessary to calculate the offset.
By dividing the sum of the differences by the number of
markings of the part of the second material web present between
the sensor and the first dcvice when the application of the
element is initiated, the difference per marking is determined.
If this difference is multiplied by the predetermined multiple
of a section length which corresponds to the length of the
first material web between the first device and the second de-
vice at the time of initiation of the application of the ele-
ment, a difference is obtained which would be present at the
location if the length of the second material web between the
sensor and the first device would correspond to the length of
the first material web between the first device and the second
device at the time of iniLial:ion of the application of the ele-
ment. If the offset is adjusted in accordance with the differ-
ence calculated in this way, the error is very well corrected.
7
CA 02498654 2005-03-10
With the arrangement, according to the invention it js
pc53ible, particularly after a shut-down of a blister packaging
machine becausc of a uniform deviation of the position of the
print image B with respect to the recesses, to re-establish the
position accuracy of the print B in a very short time.
Further details, features and advantages of the invcntion
will become apparent from the following description of a par-
ticular embodiment with reference to the accompanying drawings:
It is shown in:
Fig. 1 a schematic represental:ion of the arrangement ac-
cording to the invention,
Fig. 2 a schematic representation of two joined webs
wherein the predetermined distance corresponds to the section
length,
Fig. 3 a schematic representation of two joined webs,
wherein the predetermined distance of the markings is smaller
than the section length, and
Fig. 4 a schematic representation of two joined webs,
wherein the predetermined distance of the markings is larger
than the section length.
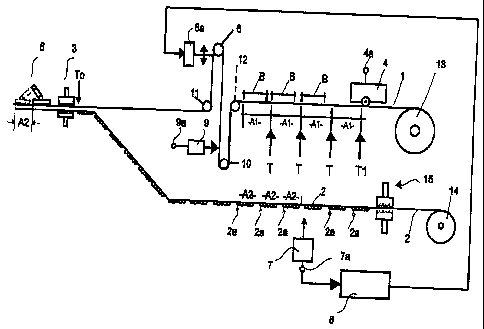
As apparent from Fig. 1, a first material web 1 in the
form of an aluminum foil is joined in accordance with the in-
vention in a first device 3, which is a sealing station, with a
second material web 2, which is a plastic foil. The plastic
foil 2 incl,udes indentations (so-called yards), Several inden~
tations are combined in groups of which - in travel direction -
the front edge of the first indentation represents a mark 2a.
The marks 2a are disposed at a predetermined distance A2 from
one another.
8
CA 02498654 2005-03-10
The indentations are stamped, by a stamping tool 15, into
the plastic foil 2 which is unwound from a roll 14.
In a filling station which is not shown in Fig. 1, tablets
are placed into the indentatioiis. After the tablets are depos-
ited in the indentations, the indentations are covered and
sealed by the aluminum foil 1.in the sealing station 3. In
this way, a so-called blister package is formed. Since such
blister packages must generally include informatioci, an image S
is imprinted onto the aluminum foil 1 which has to be accu-
rately positioned over the respective indentations after com-
pletion of the package.
For imprinting the aluminum foil 1 which is unwound from a
roll 13, the aluminum fozl is moved continuously through a
printer 4 in which the aluminum foil is imprinted. For i.niti-
ati.ng a printing procedure the printer has an input 4a. In the
transport direction after the printer 4, the aluminum foil
passes over a reversing roller 12 and then extends in an S-
shaped pattern over a compensating roller 10 and an offset
roller 6. The compensating roller 10 and the offset roller 6
are arranged each in the bottom of opposite loops which are
formed by the course of the aluminum foil 1. After the offset
roller 6, the aluminum foil 1 passes over another reversing
roller 11. After the second reversing roller 11, there is a
transport device 5 by which the aluminum i'oil 1 is advanced
stepwise by the length Al of a section in which the imprinted
image B must be accurately positioned. Between the sections,
there is a theoretical separation location T.
Ahead of the transport device 5, the sealing device 3 is
arranged wherein the aluminum foil 1 is joined with the plastic
9
CA 02498654 2005-03-10
foil. 2. Consequently, by means of the transport device 5, also
'the plastic foil 2 is advanced.
The two foils 1, 2 are advanced by the transport device 5
until the mark 2a formed by the front edge of a first indenta-
tion has arrived at a L':ixed point TO of the sealing station 3.
That is, the two foils 1, 2 are advanced until the front edge
2a of the first indentation of the next group of indentation of
indentations has arrived at the fixed point TO. Since the
front edges 2a are disposed at a predetermined distance A2 from
one anothPr both foils 1, 2 are advanced by the predetermined
distance A2.
The compensating roller 10 and the offset roller 6 are so
arranged that they can be moved toward, and away from, one an-
other. While the offset roller can be fixed in position and is
movable only by an adjustment unit 6a Lhe compensating roller
10 is freely movable.
In the lower area of the loop of the aluminum foil 1 ex-
tending around the compensating roller 10, a compensating
roller sensor 9 is arranged. The compensating roller sensor 9
is designed as a photoelectric barrier and includes an output
9a_ At the output 9a of Lhe compensating roller sensor 9, a
signal is provided when the compensating roller 9 is in a par-
ticular position in front of the compensating roller sensor 9.
The output 9a of the compensating roller sensor 9 is connected
to the input 4a of the printer 4.
During the period in which the foils 1, 2 are at a stand-
sLill, the part of the aluminuttt foil 4 which is disposed be-
tween fixed point TO and the printer 4 becomes longer as the
aluminum foil 1 is moved continuously through the printer 4.
As a result, the compensating roller 10 moves downwardly. The
CA 02498654 2005-03-10
compensating roller 10 moves downwardly until the two foils 1,
2 are advanced by the transport device 5. The representation
in Fig. 1 corresponds aboiut to the point in time when the
transport device 5 begins to again advance the two foils 7, 2.
During the advance of the two foils 1, 2 which occurs at a
speed which is a multiple of the speed at which the aluminum
foil 1 is moved through the printer 4, the length of the alumi-
nurri foil 1 between the fixed point TO and the printer 4 is
shortened. By thc shortening of the length, the compensation
roller 10 is moved upwardly so that it is disposPd above the
compensation roller sensor 9.
When the advancement of the two foils 1, 2 by the trans-
port device 5 has ended arnd the two foils 1, 2 are again at
rest, the compensation roller 10 moves again downwardly by the
continuous movement of the aluminum foil 1 through the printer
4. At the instance when the compensation roller 10 reaches the
position in which the compensation roller sensor 9 supplies,
via its output. 9A, a signal to the input 4A of the printer, the
length of the aluminum foil 1 between the fixed point TO and
the location T corresponding to beginning of a section to be
imprinted is for example twelve times the length Al of a sec-
tion. since the printer receives a printing signal exactly at
that moment, an imprint is applied exactly at the beginning T
of a section to be imprinted.
As long as the length Al of a section to be imprinted cor-
responds to the predetermined distance A2 at which the marks 2a
are arranged relative to one another, an imprint 13 is accu-
rately positioned within the section to be imprinted. Flowever,
since the predetermined distance A2 can change for example as a
result of outside influences so that it no longer corresponds
to the section length Al but the section length differs by a
11
CA 02498654 2005-03-10
difference D which is added or subtracted, the two foils 1, 2
and, consequently, the aluminum foil 1 are advanced by a sec-
tion length Al plus, or respectively, minus the difference D.
But since the image is imprinted onto the aluminum foil inde-
pendently of the advance amount of the aluminum foil 1, the im-
print B is displaced with respect to the indentations of the
aluminum foil.
The arrangemenl, i:herefore includes an edge sensor 7 by
means of which it can be determincd by which distance the posi-
tion of a front edge 2a of the first indentation of a group has
been displaced. If in the groups of indentations which are
disposed between the edge sensor 7 and the fixed point TO the
predetermined distance A2 of the front edge of the first inden-
tation of a group indentation from the front edge 2a of the
firsl-, indentation of the next group of indentations has noL
changed, the edge scnsor 7 provides a signal corresponding to a
correct distance.
If in the groups of .in,dentatioiYs which are disposed be-
tween the edge sensor 7 and the fixed point TO, the predeter-
mined distance A2 between the front edge 2a of the first indeh-
tation of a group of indentations and the front edge 2a of the
first indentation of the next group of indentations is short-
ened, the edge sensor 7 provides a signal which corresponds to
the sum of the individual reductions of the distances A2 be-
tween front edges 2a of.the indentation groups.
If, in the groups of indentations, which are disposed be-
tween the edge sensor 7 and the fixed point TO, the predeter-
mined distance A2 between the front edge 2a of the first inden-
tation of a group of indentation and the first indentation of
the next group of identities has become larger, the edge sensor
7 provides a signal which corresponds to the sum of the indi--
12
CA 02498654 2005-03-10
viclual increases of the distance A2 between the front edges 2a
of the first indentations.
In a control device 8, which is connected to the edge sen-
sor 7, from the signal of the edge sensor 7 the decrease or,
respectively, increase of the distance A2 between the front
edge 2a of the first indentation of two adjacent groups of in-
dentations is determined. This occurs in that the sum of all
the displacements is divided by the number of groups of inden-
tations which are disposed between the edge sensor 7 and the
fixed point TO. This value is then multiplied in the control
unit 8 by the multiple of the section length A1 which is based
on the length of the part of the aluminum foil (1) between the
fixed point TO and the printer 4. By this value then the off-
set roller 6 is displaced by the adjustment device 6a. In this
way, a correction of the position of the imprint 13 on the alu-
minum foil is achieved.
The correction procedure described above will be described
below on the basis of Figs. 2 to 4.
In the state as shown in Fig. 2, the section length Al of
the aluminum foil ]. in which an imprint B is arranged corre-
sponds to the predetermined distance A2 of the plastic foil 2,
at which the front edges 2a of the first indentations of two
adjacent groups of indentations are disposed. The front edge
2a of the first indentaLion in front of the edge sensor 1 is
disposed in the center of an area 7b which can be surveyed by
the edge sensor 7. The offset roller 6 is in its basic posi--
tion. That means it is so adjusted that the printer 4 applies
the image B to the aluminum foil 1 in such a way that it begins
at the separation location T between two adjacent sections.
13
CA 02498654 2005-03-10
In the state as shown in Fig. 3, the predetermined dis-
tance A2 at which the front edges 2a of the front indentations
of two subsequent groups of indentations are arranged, has de-
creased as it may happen for example by shrinking of the plas-
tic foil 2. The predetermined distance A2 consequently does
not equal any more the section length Al of the aluminum foil
1. It has become smaller by a difference D-. Therefore, the
aluminum foil 1 is no longer advanced by the section length Al
but by a predetermined length A2 which is smaller by the dif-
ference D- so that the imprinted image B would start with re-
spect to the preceding separation location T already in preced-
ing section. With a correction of the position of the offset
roller 6, the position of the printing image B is moved back
until it is disposed at the corresponding new separation line
T- corresponding to the advance of the aluminum foil by the
section lengCh Al minus the difference D-.
With this reduction of the predetermined distance A2, the
front edge 2a of the first indentation ahead of the edge sensor
7 is no longer in the center of Lhe area 7b covered by the edge
sensor 7 but at the right edge thereof. The front edge 2a of
the first indentation has moved to the right by the amount F-,
which corresponds to the sum of the differences D- of the
groups of indentations disposed between the fixed point TO and
the edge sensor 7. The output signal of the edge sensor 7,
which has changed therefore, is used for the correction of the
offsets by the offset roller 6. This means that the position
of the offset roller b is changed such that the imprint image B
is disposed at the new separation line T-.
In the state as shown in Fig. 4, the predetermined dis-
tance A2 has become larger. The predetermined distance A2
therefore no longer corresponds to the section length Al of the
aluminum foil 1. It has become larger by a distance D+. Con-
14
CA 02498654 2005-03-10
sequently, the aluminum foil is no longer advanced by the sec-
l.ion lengL-h Al but by the predetermined distance A2 which is
greater by the differcncc D+. As a result, the imprinted image
B would start at a distance from the separation location T with
regard to the earlier separation location 7. By a correction
of the position of the offset roller 6 the position of the im-
printed image B is moved until it is disposed at the new sepa-
ration location T+ corresponding to the advancement of the alu-
minum foil 1 by the section length A plus the difference D+_
By the reduction of the decrease of predetermined distance
A2, the front edge 2a of the first indentations which is in
front of the edge sensor 7 is no longer in the center of the
area 7b covered by the edge sensor 7, but at the left edge
t5 thereof. The front edqe 2a of the first indentation has moved
to the left by the amount F+ which corresponds to the sum of
the differences D+ of the groups of indentations disposed be-
tween the fixed point TO and the edge sensor 7. The output
signal of the edge sensor 7 which is changed as a result
thereof is used for the correction of the offset adjusted by
the offset roller 6. That is, the position of the offset
roller 6 is changed such that the imprinted image B is at the
new separation location T+.
Although for the description of the present invention a
printing apparatus as known from DE 195 25 713 Cl has been used
the application of the invention is not limited to this par-
ticular printing apparatus. Although the two material webs are
described as being two foils to be joined, wherein the im-
printed ilnage is applied to one foil, the image may be applied
with any type of printer particularly with a so-called plate
printer, flexa-printer or screen printer.
CA 02498654 2005-03-10
Furthermore, it is not necessary that the sections of the
two mat2rial webs are advanced discontinuously. Ttle invention
may as well be used in an arrangement wherein the material webs
are continuously advanced as for example in accordance with bE
196 50 275 Al.
16