Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
, CA 02505366 2012-06-29
25771-1056
- 1 -
Dry Powder Inhaler
The invention relates to an inhaler for inhaling powdered pharmaceutical
compositions from capsules which are inserted in a capsule holder provided in
the
inhaler before use. After the capsule has been inserted in the capsule holder
the
patient can press an actuating member which can be moved out of a resting
position,
thereby cooperating with at least one pin which can stick into the capsule
holder. The
capsule is pierced by the minimum of one pin and the pharmaceutical
composition is
released.
An inhaler of this kind is described for example in EP 0703800 B1 or EP
0911047 Al.
The inhaler known from the above mentioned specifications has a dish-shaped
lower part and an equally dish-shaped lid which fits it, these two parts being
capable
of being flipped apart for use, about a joint provided in the edge portion.
Between the
lower part and the lid, a mouthpiece which can also be flipped open and a
plate
below it with a capsule holder provided underneath also act on the joint.
After the
individual assemblies have been flipped open the patient can insert a drug-
filled
capsule in the capsule holder, pivot the plate and capsule holder and the
mouthpiece
into the lower part and pierce the capsule by means of a spring loaded
actuating
member projecting laterally from the lower part. The patient being treated
then draws
the pharmaceutical composition into his airway by sucking on the mouthpiece.
The intention is to improve the known inhalers still further in terms of their
handling.
This aim is achieved according to the invention with an inhaler according to a
first embodiment, wherein the actuating member is constructed as a double
function
actuating member by means of which, in a first actuation, the closure element
for
pivoting the lid can be detached from the lower part, and by means of which,
in a
second actuation, the procedure for piercing the capsule as described above
can be
carried out. More particularly, the invention relates to an inhaler for
inhaling a
powdered pharmaceutical composition from a capsule, comprising a lower part, a
. CA 02505366 2012-06-29
25771-1056
- 1a -
plate which can be latched to the lower part and with which the lower part can
be
closed off, and a capsule holder for receiving the capsules, this holder being
adapted
to be lowered into the lower part, a mouthpiece latchable to the plate, a lid
which
covers the mouthpiece in a closed position and latches it by means of a
closure
element, the lower part, the plate, the mouthpiece and the lid being hinged
together
by means of a single joint, and an actuating member which can be moved out of
a
resting position and thereby interact with at least one pin which can be made
to
pierce the capsule holder wherein the actuating member is constructed as a
double
function actuating member by means of which, in a first actuation, the closure
element can be released from the lower part in order to swivel the lid, and
with which,
in a second actuation, the capsule is pierced. The dosage form may be used for
delivering tiotropium bromide or a hydrate thereof from a capsule.
The essential advantage of the invention is that the forces needed to release
the lid
from the mechanical latching are not introduced directly through the lid but
instead
through the double function actuating member. This ensures quick and reliable
opening of the lid with a clockwork-type mechanism, to make the inhaler ready
for
use.
, , , CA 02505366 2005-04-26
,
- 2 -
In order to allow the lid to be released from the lower part by a clockwork-
type
mechanism, the double function actuating member has on its upper side a recess
which is
inclined so as to form a sliding surface for the closure element in the form
of a tilting plane
and to release the lid from the lower part as the double function actuating
member is
actuated and hence moved forward. The recess may vary in size. The minimum
size
must be sufficient to enable the lid to be released from the lower part by a
clockwork type
mechanism. The maximum size depends on the upper surface of the double
function
actuating member. The actual opening movement of the lid can then be carried
out as
previously by actuation of the lid by the patient, opening it fully.
The mouthpiece, which can also be flipped aside, is provided according to the
invention
with a gripping aid which ensures quick and reliable opening of the
mouthpiece. The
gripping aid is arranged so that the contact with the mouthpiece is outside
the area of the
mouthpiece which the patient has to place in his mouth when sucking. The
contact
surface for opening and the contact surface for sucking are clearly separated
from one
another thanks to the shape and appearance of the mouthpiece. Consequently,
the
mouthpiece has an appearance which is improved both optically and practically,
which
enables the user to handle it intuitively and at the same time ensures optimum
hygiene.
This is particularly important in the region of the mouthpiece as this
component is placed
in the mouth when the inhaler is used.
The clockwork-like opening mechanism for the lid according to the invention
and the
gripping aid on the mouthpiece according to the invention are of great
importance,
particularly at the start of an asthma attack, as they provide a secure grip
and an effective
arrangement for patients who would otherwise find it difficult to use the
inhaler, possibly
because they were suffering from arthritis or had some other restriction to
the mobility of
their fingers.
In a preferred embodiment, in addition to the spring element between the
double function
actuating member and the capsule holder for assisting the return of the double
function
actuating member, at least one other spring element may be provided between
the plate
and lower part, to assist the opening movement, this additional spring element
allowing
the lid and/or the mouthpiece to spring open, if the dimensions are suitably
selected,
thereby completing the clockwork-like opening mechanism.
i
CA 02505366 2005-04-26
- 3 -
Preferably, the double function actuating member is movably mounted on the
plate or on
the capsule holder. The plate and/or capsule holder thus form or forms an
abutment for
the double function actuating member which slides along the plate when moved
from the
resting position into the functional position and is guided thereby, for
example by means of
a guide rail.
In a favourable embodiment, the double function actuating member is spring-
loaded. The
restoring force which is present even in the resting position ensures that
after the double
function actuating member has been used it is returned to the resting position
and thus
the inhaling process can be started or continued.
Advantageously, the double function actuating member comprises a main body and
two
parallel guide arms engaging thereon. The guide arms project into the lower
part and,
together with corresponding inserts, e.g. with guide sleeves provided on the
outside of the
capsule holder, serve to guide the double function actuating member as it
moves from the
resting position into the various operating positions and back to the resting
position.
The guide arms may have end stops at their end remote from the main body,
these end
stops abutting on the guide sleeves in the resting position. This creates a
spring bias on
the double function actuating member.
In a preferred embodiment the main body of the double function actuating
member has an
upper rifled surface and at least one lateral rifled surface. These rifled
surfaces are both
design elements and help to provide optimum grip during actuation. They are on
the main
body of the double function actuating member outside the inhalation area and
consequently do not come into contact with the patient's mouth area. Moreover,
the rifled
surfaces may be smaller in area than the rifling of the overall surface and
still provide a
guarantee of safe and rapid use of the inhaler.
Expediently, the upper rifle surface in the resting position is formed, in its
area nearest the
lid, with a recess to accommodate the closure element of the lid. Inside the
recess the
side wall directed towards the lateral rifled surface is inclined so that when
the main body
is inserted it forms a sliding surface for the closure element and in this way
the closure
element together with the lid is raised out of the latched position.
CA 02505366 2005-04-26
- 4 -
Advantageously, the plate latched to the lower part can be detached from the
lower part
such that the plate can be swivelled away from the lower part. This swivel
function makes
the inhaler easier to clean. The latching between the plate and lower part can
be
achieved by means of projecting retaining lugs.
It is also possible to construct all the embodiments of the inhaler such that
the double
function actuating member with the minimum of one pin that can be stuck into
the capsule
holder is attached to the plate so that it can be detached from the lower part
and swung
away, together with the plate latched to the lower part.
To make the invention easier to understand it will now be described more fully
with
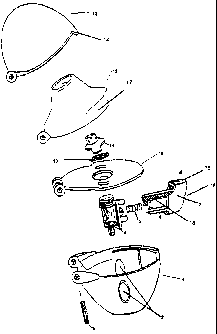
reference to the drawing that follows (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 shows an exploded view with a double function actuating member and
mouthpiece
with gripping aid.
Fig. 1 shows the inhaler in exploded view. The essential components are the
lower part 1
which accommodates the plate 9 and is covered by the latter, the mouthpiece 12
with
gripping aid 17, said mouthpiece being latchable to the lower part 1 by means
of the
retaining lugs of the screen holder 11 and the lid 13 which is shaped so as to
complement
the lower part 1.
In the closed state of the inhaler the closure element 14 on the lid 13 acts
on the plate 9
and is held there by frictional engagement. It is also possible to achieve
interlocking
engagement by the provision of bead-like structures on the closure element 14.
For the
closure element 14 on the lid 13 to act on the plate 9, the main body of the
double function
actuating member 7 comprises a recess 8 into which the closure element 14 is
lowered as
it closes. The recess 8 has an inclined side wall and is located in the area
of the upper
rifled surface 15 nearest the lid. For particularly reliable operation the
double function
actuating member 7 is also provided with at least one lateral rifled surface
16.
In order to open the lid 13, first of all the double function actuating member
7 is moved or
pressed towards the inhaler. The closure element 14 on the lid 13 makes
contact with the
inclined side wall of the recess 8 which acts a sliding surface as the main
body 7
continues to move forward, and releases the lid 13.
CA 02505366 2005-04-26, =
- 5 -
The lower part 1 is cup-shaped and accommodates the entire capsule holder 4
which is
mounted on the underside of the plate 9. In order to be able to place a drug
filled capsule
(not shown) in the capsule holder 4, the mouthpiece 12 also has to be flipped
open. In the
embodiment shown in Fig. 1 this is done by acting on the gripping aid 17
shown.
In this opened position of the lid 13 and mouthpiece 12 the capsule can be
placed in the
capsule holder 4 through an opening in the plate 9. Then the mouthpiece 12 is
swivelled
back again and closed again by the latching of the retaining lugs of the
screen holder 11
in the plate 9. In order to release the active substance, at least one pin,
but preferably two
perpendicularly offset, parallel pins 6 are mounted on the main body of the
double function
actuating member 7, moving continuously towards the capsule (not shown) as the
double
function actuating member 7 is pushed in, so as to perforate said capsule. The
perforating process can be observed through an inspection window 2.
In the capsule holder 4 there is one or at least two tubular pin guides which
is or are
directed axially in accordance with the direction of movement of the pin or
pins 6. This
ensures accurate targeting of the pin or pins on the capsule (not shown) and
also provides
additional guiding for the double function actuating member 7. However, the
essential
guiding is achieved by means of two laterally mounted guide arms 18. The guide
arms 18
also have the task of holding the double function actuating member 7 under pre-
tension.
For this, the guide arms 18 are provided, at their ends remote from the main
body, with
end stops which abut on the guide sleeves of the capsule holder 4 in the
resting position
of the double function actuating member 7. The guide sleeves are provided on
the
outside of the capsule holder 4. Between the guide arms 18 is a helical spring
5 which in
the axial direction extends parallel to the pin or pins 6, the helical spring
5 being matched
to the length of the guide arms 18 such that the double function actuating
member 7 is still
biased in the resting position.
The individual assemblies of lower part 1, plate 9, mouthpiece 12 and lid 13
are joined
together by means of joint sockets and a joint bolt 3 and are all movable or
pivotable
about this bolt, relative to one another.
The pharmaceutical compositions used for inhalation may be all of kinds of
powdered
pharmaceuticals which it is therapeutically advisable to administer by
inhalation.
Particularly preferred in this context are pharmaceutical compositions
selected from
CA 02505366 2005-04-26
- 6 -
among the anticholinergics, beta-2-agonists, steroids, PDE IV-inhibitors, LTD4-
antagonists and EGFR-kinase inhibitors.
Anticholinergics for use are preferably selected from among tiotropium
bromide,
oxitropium bromide, flutropium bromide, ipratropium bromide, glycopyrronium
salts,
trospium chloride, tolterodine, tropenol 2,2-diphenylpropionate methobromide,
scopine
2,2-diphenylpropionate methobromide, scopine 2-fluoro-2,2-diphenylacetate
methobromide, tropenol 2-fluoro-2,2-diphenylacetate methobromide, tropenol
3,3',4,4'-
tetrafluorobenzilate methobromide, scopine 3,3',4,4'-tetrafluorobenzilate
methobromide,
tropenol 4 ,4'-difluorobenzilate methobromide, scopine 4,4'-difluoroben zilate
methobromide, tropenol 3,3'-difluorobenzilate m ethobromide, scopine 3,3'-
difluorobenzilate methobromide, tropenol 9-hydroxy-fluorene-9-carboxylate
methobromide, tropenol 9-fluoro-fluorene-9-carboxylate methobromide, scopine 9-
hydroxy-fluorene-9-carboxylate methobromide, scopine 9-fluoro-fluorene-9-
carboxylate
methobromide, tropenol 9-methyl-fluorene-9-carboxylate methobromide, scopine 9-
methyl-fluorene-9-carboxylate methobromide, cyclopropyltropine benzilate
methobromide,
2,2-diphenylpropionate cyclopropyltropine methobromide, cyclopropyltropine 9-
hydroxy-
xanthene-9-carboxylate methobromide, cyclopropyltropine 9-methyl-fluorene-9-
carboxylate methobromide, cyclopropyltropine 9-methyl-xanthene-9-carboxylate
methobromide, cyclopropyltropine 9-hydroxy-fluorene-9-carboxylate
methobromide,
methyl 4,4'-difluorobenzilate cyclopropyltropine methobromide, tropenol 9-
hydroxy-
xanthene-9-carboxylate methobromide, scopine 9-hydroxy-xanthene-9-carboxylate
methobromide, tropenol 9-methyl-xanthene-9-carboxylate methobromide, scopine 9-
methyl-xanthene-9-carboxylate methobromide, tropenol 9-ethyl-xanthene-9-
carboxylate
methobromide, tropenol 9-difluoromethyl-xanthene-9-carboxylate methobromide
and
scopine 9-hydroxymethyl-xanthene-9-carboxylate methobromide, optionally in the
form of
the racemates, enantiomers or diastereomers thereof and optionally in the form
of the
solvates and/or hydrates thereof.
Beta-2-agonists used are preferably selected from among albuterol, bambuterol,
bitolterol,
broxaterol, carbuterol, clenbuterol, fenoterol, formoterol, hexoprenaline,
ibuterol,
isoetharine, isoprenaline, levosalbutamol, mabuterol, meluadrine,
metaproterenol,
orciprenaline, pirbuterol, procaterol, reproterol, rim iterol, ritodrine,
salmeterol, salmefamol,
soterenot, sulphonterol, tiaramide, terbutaline, tolubuterol, CHF-1035, HOKU-
81, KUL-
1248, 3-(4-{642-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3-hydroxymethyl-phenyl)ethylaminoi-
hexyloxy}-
butyl)-benzenesulphona mide, 5-[2-(5,6-diethyl-indan-2-ylam ino)-1-hydroxy-
ethyI]-8-
CA 02505366 2005-04-26
- 7 -
hydroxy-1H-quinolin-2-one, 4-hydroxy-742-{[2-([3-(2-
phenylethoxy)propyl]sulphonyllethyl]-
aminolethyl]-2(3H)-benzothiazolone, 1-(2-fluoro-4-hydroxypheny1)-244-(1-
benzimidazoly1)-
2-methy1-2-butylamino]ethanol, 143-(4-methoxybenzyl-amino)-4-hydroxypheny1]-
244-(1-
benzimidazoly1)-2-methy1-2-butylamino]ethanol, 1-[2H-5-hydroxy-3-oxo-4H-1,4-
benzoxazin-8-y1]-2-[3-(4-N,N-dimethylaminopheny1)-2-methy1-2-
propylamino]ethanol, 1-
[2H-5-hydroxy-3-oxo-4H-1,4-benzoxazin-8-y1]-2-[3-(4-methoxypheny1)-2-methy1-2-
propylamino]ethanol, 1-[2H-5-hydroxy-3-oxo-4H-1,4-benzoxazin-8-y1]-2-[3-(4-n-
butyloxypheny1)-2-methy1-2-propylamino]ethanol, 142H-5-hydroxy-3-oxo-4H-1,4-
benzoxazin-8-y1]-2-{443-(4-methoxypheny1)-1,2,4-triazol-3-y1]-2-methy1-2-
butylaminolethanol, 5-hydroxy-8-(1-hydroxy-2-isopropylaminobuty1)-2H-1,4-
benzoxazin-3-
(4H)-one, 1-(4-amino-3-chloro-5-trifluoromethylphenyI)-2-tert.-
butylamino)ethanol and 1-
(4-ethoxycarbonylamino-3-cyano-5-fluorophenyI)-2-(tert.-butylamino)ethanol,
optionally in
the form of the racemates, enantiomers or diastereomers thereof and optionally
in the
form of ihrer pharmacologically acceptable acid addition salts, solvates
and/or hydrates
thereof.
The steroids used are preferably selected from among prednisolone, prednisone,
butixocortpropionate, RPR-106541, flunisolide, beclomethasone, triamcinolone,
budesonide, flu ticasone, mometasone, ciclesonide, rofleponide, ST-126,
dexamethasone,
(S)-fluoromethyl 6a,9a-difluoro-17a-[(2-furanylcarbonyl)oxy]-110-hydroxy-16a-
methyl-3-
oxo-androsta-1,4-diene-1713-carbothionate, (S)-(2-oxo-tetrahydro-furan-3S-y1)
6a,9a-
difluoro-11[3-hydroxy-16a-methy1-3-oxo-17a-propion yloxy-androsta-1,4-diene-
170-
carbothionate and etiprednol-dichloroacetate (BNP-166), optionally in the form
of the
racemates, enantiomers or diastereomers thereof and optionally in the form of
the salts
and derivatives thereof, the solvates and/or hydrates thereof.
PDE IV inhibitors used are preferably selected from among enprofyllin,
theophyllin,
roflumilast, ariflo (cilomilast), CP-325,366, BY343, D-4396 (Sch-351591), AWD-
12-281
(GW-842470), N-(3,5-dichloro-1-oxo-pyridin-4-yI)-4-difluoromethoxy-3-
cyclopropylmethoxybenzamide, NCS-613, pumafentine, (-)p-[(4aR*,10bS*)-9-ethoxy-
1,2,3,4,4a,10b-hexahydro-8-methoxy-2-methylbenzo[s][1,6]naphthyridin-6-y1]-N,N-
diisopropylbenzamide, (R)-(+)-1-(4-bromobenzy1)-4-[(3-cyclopentyloxy)-4-
methoxyphenyl]-
2-pyrrolidone, 3-(cyclopentyloxy-4-methoxypheny1)-1-(4-N'4N-2-cyano-S-methyl-
isothioureidolbenzyl)-2-pyrrolidone, cis[4-cyano-4-(3-cyclopentyloxy-4-
methoxyphenyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid], 2-carbomethoxy-4-cyano-4-(3-
cyclopropylmethoxy-4-difluoromethoxyphenyl)cyclohexan-1-one, cis[4-cyano-4-(3-
4
CA 02505366 2005-04-26
- 8 -
cyclopropylmethoxy-4-difluoromethoxyphenyl)cyclohexan-1-01], (R)-(+)-ethyl[4-
(3-
cyclopentyloxy-4-methoxyphenyl)pyrrolidin-2-ylidene]acetate, (S)-(-)-ethyl[4-
(3-
cyclopentyloxy-4-methoxyphenyl)pyrrolidin-2-ylidene]acetate, CDP840, Bay-
198004, D-
4418, PD-168787, T-440, T-2585, arofyllin, atizoram, V-11294A, CI-1018, CDC-
801,
CDC-3052, D-22888, YM-58997, Z-15370, 9-cyclopenty1-5,6-dihydro-7-ethy1-3-(2-
thienyI)-
9H-pyrazolo[3,4-c]-1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-a]pyridine and 9-cyclopenty1-5,6-dihydro-
7-ethy1-3-
(tert-buty1)-9H-pyrazolo[3,4-c]-1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-a]pyridine, optionally in
the form of the
racemates, enantiomers or diastereomers thereof and optionally in the form of
the
pharmacologically acceptable acid addition salts thereof, solvates and/or
hydrates thereof.
LTD4-antagonists used are preferably selected from among montelukast, 1-(((R)-
(3-(2-
(6,7-difluoro-2-quinolinyl)ethenyl)pheny1)-3-(2-(2- hydroxy-2-
propyl)phenyl)thio)methylcyclopropane-acetic acid, 1-(((1(R)-3(3-(2-(2,3-
dichlorothieno[3,2-b]pyridin-5-y1)-(E)-ethenyl)phe nyI)-3-(2-(1-hydroxy-1-
methylethyl)phenyl)propyl)thio)methyl)cyclopropanacetic acid, pranlukast,
zafirlukast, [2-
[[2-(4-tert-buty1-2-thiazoly1)-5-benzofuranyl]oxymethyliphenyliacetic acid,
MCC-847 (ZD-
3523), MN-001, MEN-91507 (LM-1507), VUF-5078, VUF-K-8707 and L-733321,
optionally
in the form of the racemates, enantiomers or diastereomers thereof, optionally
in the form
of the pharmacologically acceptable acid addition salts thereof as well as
optionally in the
form of the salts and derivatives thereof, the solvates and/or hydrates
thereof.
EGFR-kinase inhibitors used are preferably selected from among cetuximab,
trastuzumab, ABX-EGF, Mab ICR-62, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)amino]-6-([4-
(morpholin-
4-y1)-1-oxo-2-buten-1-yl]amino}-7-cyclopropylmethoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(R)-(1-
phenyl-
ethyl)amino]-6-([4-(morpholin-4-y1)-1-oxo-2-buten-1-yl]amino}-7-cyclopentyloxy-
quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-6-{[44(R)-6-methy1-2-oxo-
morpholin-4-y1)-
1-oxo-2-buten-1-yllamino}-7-[(S)-(tetrahydrofuran-3-yl)oxy]-quinazoline, 4-[(3-
chloro-4-
fluoro-phenyl)amino]-6424(S)-6-methyl-2-oxo-morpholin-4-y1)-ethoxy]-7-methoxy-
quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)a mino]-6-({44N-(2-methoxy-ethyl)-N-
methyl-
amino]-1-oxo-2-buten-1-yl}amino)-7-cyclopropylmethoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(R)-(1-
phenyl-
ethyl)amino]-6-({44N-(tetrahydropyran-4-y1)-N-methyl-amino]-1-oxo-2-buten-1-
yl}amino)-
7-cyclopropylmethoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)amino]-6-({44N-
(2-
methoxy-ethyl)-N-methyl-amino]-1-oxo-2-buten-1-yl}amino)-7-cyclopentyloxy-
quinazoline,
4-[(3-chloro-4-fluorophenypaminol-6-{[4-(N,N-dimethylamino)-1-oxo-2-buten-1-
yl]amino}-
7-[(R)-(tetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methoxy]-quinazoline, 4-[(3-ethynyl-phenyl)amino]-
6,7-bis-(2-
methoxy-ethoxy)-quinazoline, 4-[(R)-(1-phenyl-ethyl)amino]-6-(4-hydroxy-
pheny1)-7H-
= . CA 02505366 2005-04-26
- 9 -
pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine, 3-cyano-4-[(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)amino]-6-([4-
(N,N-
dimethylamino)-1-oxo-2-buten-1-yl]amino}-7-ethoxy-quinoline, 4-[(R)-(1-phenyl-
ethyl)amino]-6-{[44(R)-6-methy1-2-oxo-morpholin-4-y1)-1-oxo-2-buten-1-
yl]amino}-7-
methoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)amino]-6-([4-(morpholin-4-y1)-
1-oxo-2-
buten-1-yl]amino}-7-[(tetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methoxy]-quinazoline, 4-[(3-ethynyl-
phenyl)amino]-6-{[4-(5,5-dimethy1-2-oxo-morpholin-4-y1)-1-oxo-2-buten-1-
yl]amino}-
quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-6-{214-(2-oxo-morpholin-4-y1)-
piperidin-1-
y1]-ethoxy}-7-methoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenypamino]-6-(trans-
4-amino-
cyclohexan-1-yloxy)-7-methoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-
6-(trans-
4-methanesulphonylamino-cyclohexan-1-yloxy)-7-methoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-
chloro-4-
fluoro-phenyl)amino]-6-(tetrahydropyran-3-yloxy)-7-methoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-
chloro-4-
fluoro-phenyl)amino]-6-{1-[(morpholin-4-yl)carbonyl]-piperidin-4-yloxy}-7-
methoxy-
quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-6-(piperidin-3-yloxy)-7-
methoxy-
quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-6-[1-(2-acetylamino-ethyl)-
piperidin-4-
yloxy]-7-methoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-6-
(tetrahydropyran-4-
yloxy)-7-ethoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-6-{trans-4-
Rmorpholin-4-
y1)carbonylaminoFcyclohexan-1-yloxy}-7-methoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-
fluoro-
phenypamino]-6-{1-[(piperidin-1-y1)carbonyl]-piperidin-4-yloxy}-7-methoxy-
quinazoline, 4-
[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-6-(cis-4-{N-Rmorpholin-4-yl)carbon yli-N-
methyl-amino}-
cyclohexan-1-yloxy)-7-methoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-
6-(trans-
4-ethansulphonylamino-cyclohexan-1-yloxy)-7-methoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-
4-fluoro-
phenyl)amino]-6-(1-methanesulphonyl-piperidin-4-yloxy)-7-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-
quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-641-(2-methoxy-acetyl)-
piperidin-4-
yloxy]-7-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-quinazoline, 4-[(3-ethynyl-phen yl)amino]-6-
(tetrahydropyran-
4-yloxy]-7-methoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-6-(cis-4-
{N-
Rpiperidin-1-yl)carbony1FN-methyl-amino}-cyclohexan-1-yloxy)-7-methoxy-
quinazoline, 4-
[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-6-{cis-4-[(morpholin-4-yOcarbonylamino]-
cyclohexan-1-
yloxy}-7-methoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-6-{1-[2-(2-
oxopyrrolidin-
1-ypethyl]-piperidin-4-yloxy}-7-methoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-ethynyl-
phenyl)amino]-6-(1-
acetyl-piperidin-4-yloxy)-7-methoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-ethynyl-phenypamino]-6-
(1-methyl-
piperidin-4-yloxy)-7-methoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-ethynyl-phenyl)amino]-6-(1-
methanesulphonyl-piperidin-4-yloxy)-7-methoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-
fluoro-
phenyl)amino]-6-(1-methyl-piperidin-4-yloxy)-7(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-quinazoline,
44(3-
ethynyl-phenyl)amino]-6-{1-[(morpholin-4-y1)carbonyl]-piperidin-4-yloxy}-7-
methoxy-
quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-6-{1-[(N-methyl-N-2-
methoxyethyl-
amino)carbonyl]-piperidin-4-yloxy}-7-methoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-
fluoro-
i
CA 02505366 2005-04-26
- 10 -
phenyl)amino]-6-(1-ethyl-piperidin-4-yloxy)-7-methoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-
chloro-4-fluoro-
phenyl)amino]-6-[cis-4-(N-methanesulphonyl-N-methyl-amino)-cyclohexan-1-yloxy]-
7-
methoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-6-[cis-4-(N-acetyl-N-
methyl-
am ino)-cyclohexan-1-yloxy]-7-methoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-
phenyl)amino]-6-
(trans-4-methylamino-cyclohexan-1-yloxy)-7-methoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-
fluoro-
phenyl)amino)-6-Brans-4-(N-methanesulphonyl-N-methyl-amino)-cyclohexan-1-
yloxyl-7-
methoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-6-(trans-4-
dimethylamino-
cyclohexan-1-yloxy)-7-methoxy-quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-
6-(trans-
4-{N-Rmorpholin-4-yOcarbonyli-N-methyl-amino)-cyclohexan-1-yloxy)-7-methoxy-
quinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-642-(2,2-dimethy1-6-oxo-
morpholin-4-y1)-
ethoxy]-7-[(S)-(tetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methoxyFquinazoline, 4-[(3-chloro-4-
fluoro-
phenyl)amino]-6-(1-methanesulphonyl-piperidin-4-yloxy)-7-methoxy-quinazoline,
4-[(3-
chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-6-(1-cyano-piperidin-4-yloxy)-7-methoxy-
quinazoline, and 4-
[(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)amino]-641-[(2-methoxyethyl)carbonyll-piperidin-4-
yloxy}-7-
methoxy-quinazoline, optionally in the form of the racemates, enantiomers or
diastereomers thereof, optionally in the form of the pharmacologically
acceptable acid
addition salts thereof, the solvates and/or hydrates thereof.
Examples of acid addition salts with pharmacologically acceptable acids which
the
compounds may be capable of forming include salts selected from among the
hydrochloride, hydrobromide, hydroiodide, hydrosulphate, hydrophosphate,
hydromethanesulphonate, hydronitrate, hydromaleate, hydroacetate,
hydrobenzoate,
hydrocitrate, hydrofumarate, hydrotartrate, hydrooxalate, hydrosuccinate,
hydrobenzoate
and hydro-p-toluenesulphonate, preferably hydrochloride, hydrobromide,
hydrosulphate,
hydrophosphate, hydrofumarate and hydromethanesulphonate.
Inhalation is an option for powdered pharmaceutical compositions containing
the above-
mentioned active substances as well as the salts thereof, esters and
combinations of
these active substances, salts and esters.
CA 02505366 2005-04-26
- 11 -
List of reference numerals
1 lower part
2 inspection window
3 articulation bolt
4 capsule holder
5 helical spring
6 pin
7 double function actuating member (main body)
8 recess with sloping side wall as sliding surface
9 plate
10 screen
11 screen holder with retaining lugs
12 mouthpiece with gripping aid
13 lid
14 closure element
15 upper rifled surface of 7
16 lateral rifled surface of 7
17 gripping aid
18 guide arms