Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02510694 2005-06-27
WEB CAMERA IDENTIFICATION SYSTEM AND METHOD
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
1. Field of the Invention
The present invention relates to a web camera identification system and
method, and especially relates to a web camera storing an application.
2. Description of Related Art
People desire to communicate visually through computers and the
Internet. On the current market, there are two prevalent ways to install a
video
communication application in a computer. One is installing by a setup disc and
the other is installing by a remote setup application through the Internet.
However, most people are not familiar with an installation process because
they never learn computer skills or installation methods. Even for
professional
computer engineers, many complicated steps are necessary to finish the
installation of avideo communication application.
SLJIVINIARY OF THE INVENTION
The main aspect of the present invention is to provide a web camera
identification system and method. The web camera of the present invention
stores an application to simplify the installation process.
To achieve the above aspect, the present invention provides a web
camera identification system including a server website, a client computer,
and
a web camera. The server website has an authentication module and a function
module. The web camera connects to the client computer and has a non-
volatile memory for storing an authentication password and a connection
activation password. The client computer connects to the server website by
1
CA 02510694 2005-06-27
using the connection activation password and then downloads a communication
application for installation. The authentication module of the server website
checks the authentication password of the web camera to determine whether the
web camera is allowed to obtain services provided by the function module.
To achieve the above aspect, the present invention provides a web
camera identification system including a server website, a client computer,
and
a web camera. The server website has an authentication module and a function
module. The web camera connects to the client computer and has a non-
volatile memory for storing an authentication password and a video
communication application. The client computer connects to the server website
to execute video communication data transmission after the installation of the
video communication application from the web camera. The authentication
module of the server website checks the authentication password of the web
camera to determine whether the ~ web camera is allowed to obtain services
provided by the function module.
To achieve the above aspect, the present invention provides a web
camera identification method, which includes the following steps. An
authentication password is stored in a web camera. The web camera connects
to a server website via a client computer. The server website authenticates
availability of the web camera by checking the authentication password. The
web camera obtains services provided by the server website after passing the
authentication.
2
CA 02510694 2005-06-27
It is noted that the drawings are expected for the purpose of reference
and illustration but not expected for the purpose of restricting the scope of
the
present invention.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
The foregoing aspects and many of the attendant advantages of this
invention will be more readily appreciated as the same becomes better
understood by reference to the following detailed description, when taken in
conjunction with the accompanying drawings, wherein:
FIG. 1 illustrates a preferred embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 2 illustrates a preferred embodiment of a web camera of the present
invention;
FIG. 3 illustrates a preferred embodiment of another web camera of the
present invention;
FIG. 4 illustrates a preferred embodiment of a server website of the
present invention; and
FIG. 5 illustrates a flow chart of a preferred embodiment of the present
invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
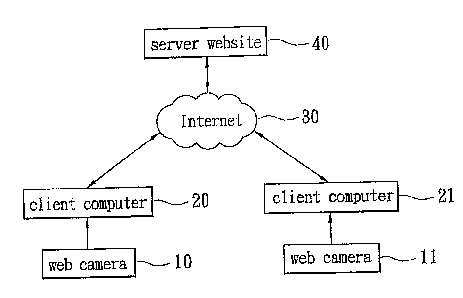
FIG. 1 shows a preferred embodiment of the present invention. It is a
web camera identification system, adapted for a master-slave network, which
includes a web camera 10, a client computer 20, and a server website 40. The
web camera 10 stores an application and connects to the client computer 20
through a USB interface. The client computer 20 connects to the server
website 40 through the Internet 30. The server website 40 identifies the web
3
CA 02510694 2005-06-27
camera 10 to determine availability of the web camera 10 and to determine
whether the web camera 10 is allowed to obtain services, such as video
communication transmissions or video related applications, provided by the
server website 40.
There are two implementations for the web camera of the present
invention as shown in FIG. 2 and FIG. 3. Referring to FIG. 2 first, the web
camera 10 includes a non-volatile memory 12 configured to store the
information of an authentication password 121 and a connection activation
password 122. The authentication password 121 is used for the server website
40 to determine availability of the web camera 10. The connection activation
password 122 is used for the client computer 20 to connect to the server
website 40 automatically and to download a video communication application
for installation.
Referring to FIG. 3, the web camera 11 also includes a non-volatile
memory 12 configured to store the information of the authentication password
121 and a video communication application 123. The authentication password
121 is used for the server website 40 to determine availability of the web
camera 11. 'The video communication application 123 is installed into a client
computer 21. Therefore, the client computer 21 does not have to connect to the
server website 40 to download a video communication application as shown in
FIG. 2.
Accordingly, the installation of a video communication application of
the present invention may be either like the web camera 10 of FIG. 2
connecting to the server website 40 to download a video communication or like
4
CA 02510694 2005-06-27
the web camera 11 of FIG. 3, installing the video communication application
123 by itself.
FIG. 4 shows a preferred embodiment of the server website of the
present invention. The server website 40 includes an authentication module 41,
a function module 42, and a database 43. The authentication module 41 checks
the authentication password 121 of the web camera 10 or 11. Once the web
camera 10 or 11 passes the check, the web camera 10 or 11 is allowed to obtain
services provided by the server website 40. The function module 42 of the
server website 40 responds to the operations of the installed video
communication application. The function module 42 also can provide the
download service of the video communication application to the web camera
10 of FIG. 2. The database 43 is configured to store data associated with the
operation history of the web camera 10 or 11.
FIG. 5 shows a flow chart of a preferred embodiment of the present
invention. First, the web camera identification method determines whether the
web camera connecting to the client computer has a video communication
application stored therein (5501). If not, the web camera has the structure
shown in FIG. 2 or the web camera is just a web camera of the prior art
without
an authentication password, which needs the client computer to connect to a
server website by using a connection activation password or by a manual input
to download a video communication application (S513). If yes, the web
camera has the structure shown in FIG. 3. The client computer can obtain a
video communication application from the web camera. When the client
computer connects to the server website through the installed video
5
CA 02510694 2005-06-27
communication application, the server website will check availability of the
web camera; i.e., the authentication module of the server website checks the
authentication password of the web camera (5503). If the web camera passes
the check, the web camera is allowed to execute the services provided by the
server website (5505). If the web camera does not pass the check, the user may
input a password manually so a web camera without an authentication
password may execute the services provided by the server website as well
(5507). Then the password input by the user is checked (5509). If the check is
passed, the method goes to S505. If the check is not passed, the web camera
cannot obtain the services provided by the server website (S511).
Referring back to FIG. 1, when the web cameras 10 and 11 respectively
connect to the client computers 20 and 21, both of the web cameras 10 and 11
pass the check, and the client computers 20 and 21 have a video
communication application installed therein, the client computers 20 and 21
may transmit communication data to each other by using the web cameras 10
and 11 through the Internet 30.
Based on the above description, the web camera identification system
and method of the present invention have the following advantages:
1. The web camera storing an application can reduce the process of
application installation and quicken the installation speed. This makes
operations easier.
2. The web camera having an authentication password can connect to any
computer and can make the computer to upgrade as a video communication
6
CA 02510694 2005-06-27
computer by accessing the information stored in the web camera instantly
through a master-slave network.
The above description of the preferred embodiments is expected to
clearly expound the characteristics of the present invention but not expected
to
restrict the scope of the present invention. Those skilled in the art will
readily
observe that numerous modifications and alterations may be made while
retaining the teaching of the invention. Accordingly, the above disclosure
should be construed as limited only by the bounds of the claims.
7