Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02518749 2005-09-09
PROTECTIVE DEVICE FOR ARMORED VEHICLES, PARTICULARLY
FOR PROTECTING AGAINST HOLLOW-CHARGE PROJECTILES
The invention relates to a protective device for armored vehicles, in
particular against hollow-charge projectiles, with at least one protective
module that is arranged in front of an exterior side of a wall to be
protected.
Such protective modules are known. They can be formed as passive
or as reactive plating and can be effective as protection against hollow
charge (HL) projectiles or impact (KE) projectiles depending on the
design. Several of the types of designs of these protective modules
are explained, for exa~"~e, ~ EP 0 922 924 B1 and EP 0 379 080 A2,
as well as in DE 41 14 809 C2 and DE 195 09 899 C2.
In particular with protective modules for protection against HL-
projectiles, it is known that the protective effect is greater the greater
the distance between the protective module and the wall to be
protected, since the deflection path of the disrupted penetrator is of
greater significance for efficiency based on the continuing lateral
movement after contact against the protective module. If, however, the
protective modules are disposed at the greatest possible distance from
the wall to be protected, the contour of the vehicle to be protected
1 of 14
Lit Trnsl of PCTlDE2004/000373 Bled Feb. 28, 2005 / Michael Pfennig et al l
Krauss-Maffei
Wegmann GmbH & Co.
CA 02518749 2005-09-09
increases overall, so that the prescribed loading masses no longer can
be adhered to.
The invention is based on the object of constructing a protective device
of the type described above and in the preamble to claim 1 in such a
manner that for defense of the threat, the greatest possible distance of
the protective module from the wall to be protected is achievable; on
the other hand, however, the contour of the vehicle and in particular the
prescribed loading masses are not increased.
The solution of this object takes place according to the present
invention with the features of the characterizing parts of claim 1.
Advantageous embodiments of the invention are described in the
dependent claims. The wording of the patent claims is made by
IS reference to the content of the following description.
The basic idea of the invention is to form the protective module to be
moveable in such a manner that it can be moved from an inoperative
position, in which it is positioned as closely as possible to the wall to be
protected, into an active position, in which it has a substantially greater
distance at least partially from the wall to be protected than in the
inoperative position.
2
CA 02518749 2005-09-09
The movement of the protective module can take place in different
ways depending on its structure and arrangement. As explained
subsequently with reference to the embodiments, here linear
movements, in particular linear motions that take place orthogonally to
the wall to be protected, can be used as well as pivoting motions. The
motions can be produced by means of simple mechanical drive
devices, that is, manual as well as electrical, electromechanical,
hydraulic, or pneumatic drive devices. It is also possible to produce the
motion of the protective module from the inoperative position into the
active position with pyrotechnical means.
The protective modules can be constructed in a known manner in a
sandwich-like manner from multiple, layered plates. However, they
also can be constructed as a buckling sheet louver with a plurality of
inclined layers, for example.
In order to achieve effective protection against HL-projectiles as well as
against KE-projectiles, it was noted to be advantageous when a
second protective module is fixedly disposed between the moveable
first protective module and the wall to be protected, whereby the
structure can be such that the first protective module serves in a first
line for protection against HL-projectiles and the second protective
module serves in a first line for protection against KE-projectiles. It is
3
CA 02518749 2005-09-09
further possible to construct the protective module as a passive plating
as well as an active plating.
Next, embodiments of the protective devices according to the present
invention will be described in greater detail with reference to the
accompanying figures.
In the drawings:
Fig. 1 shows a partial section through an armored vehicle with a first
embodiment of a protective device with a protective module disposed
in the inoperative position;
Fig. 2 shows the protective device according to Fig. 1 with the
moveable protective module in the active position;
Fig. 3 shows a variation of the protective device of Figs. 1 and 2 in an
illustration analogous to Fig. 2, in which the protective module is moved
into a second active position;
Fig. 4 shows a further embodiment of a protective device with a
protective module disposed in the inoperative position in an illustration
analogous to Fig. 1; and
4
CA 02518749 2005-09-09
Fig. 5 shows the protective device of Fig. 4 with the moveable
protective module in the active position.
In Figs. 1 and 2, a first embodiment of a protective device for an
armored vehicle is shown, whereby only the parts that are essential for
illustrating the protective device are shown, namely a part of the
vehicle shell or vehicle body with a roof plate 1 and the side wall 2 to
be protected. On the outer surface of the side wall 2, first a KE-
protective module 6 is fixedly disposed, which can be structured in a
known manner and is not explained in detail below. An Hl_-protective
module is arranged outside of this KE-protective module. This HL_-
protective module is constructed of two plate elements 4.1 and 4.2,
which in a known manner, for example, can comprise two plates that
are separated from one another by air space. The plate element 4.1 is
outwardly pivotable around a pivot axis 5.1 arranged parallel to the side
wall 2 in the area of the roof plate 1. The edge 4.11 of the plate
element 4.1 facing the pivot axis 5.1 is attached to a corresponding
pivot lever 5.11. The plate element 4.2 is outwardly pivotable around a
pivot axis 5.2 running parallel to the side wall 2 and parallel to the pivot
axis 5.1. The pivot axis 5.2 is disposed beneath the pivot axis 5.1 on
the side wall 2. The edge 4.21 faxing this pivot axis 5.2 is attached to a
corresponding pivot lever 5.21.
5
CA 02518749 2005-09-09
In the position shown in Fig. 1, both plate elements 4.1 and 4.2 are
disposed in the inoperative position parallel to one another and parallel
to the side wall 2. In this inoperative position, in which they lie directly
on top of one another in the shown embodiment, they have the least
possible distance to the side wall 2 and lie within a spatially defined
contour 3 of the vehicle.
The plate elements 4.1 and 4.2 are pivotable outwardly into an active
position from the inoperative position shown in Fig. 1 in opposite pivot
motions; the active position is shown in Fig. 2. In this active position,
the edges 4.12 or 4.22 of the plate elements facing away from the pivot
axes 5.1 and 5.2 directly adjoin one another. These edges are
constructed such that they interlock in one another upon reaching the
active position in the manner shown in Fig. 2, and therewith have a
roof-shaped form facing outwardly, comprised of the two plate
elements 4.1 and 4.2. In this position, the protective module projects
outwardly over the contour 3, and as a result of the inclined position of
both plate elements 4.1 and 4.2, an optimal protection against
incoming HL-projectiles is achieved.
With this structure of the protective device, it is therefore possible to
load the vehicle into a transport aircraft, for example, in the inoperative
position of the protective module, in which the prescribed loading mass
is maintained. In use of the vehicle or also first in case of a threat, the
6
CA 02518749 2005-09-09
protective module is moved from the inoperative position into the active
position and can be moved back again into the inoperative position
after termination of the threat or for loading.
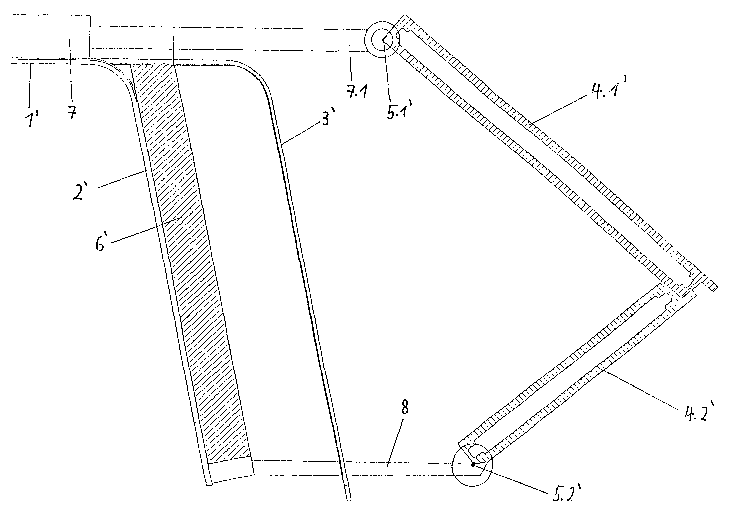
Fig. 3 shows a variation of the protective device according to Figs. 1
and 2, in which a still greater distance of the protective module from the
side wall of the vehicle to be protective is achievable. In Fig. 3,
components which correspond to the embodiment of Figs. 1 and 2 are
provided with the same reference numerals and an apostrophe.
In the inoperative position (not shown) of the protective module, both
plate elements 4.1' and 4.2' lie on top of one another and parallel to the
side wall 2' in front of the outer side of the KE-protective module 6'
within the vehicle contour 3', analogously to the situation of Fig. 1.
Also, the plate elements 4.1' and 4.2' are pivotable about pivot axes
5.1' or 5.2' that run parallel to one another and to the side wall 2', and
the outward pivoting motion takes place by means of a drive device
(not shown). In this manner, analogously to the embodiment of Fig. 1,
both plate elements 4.1' and 4.2' first are pivotable from the inoperative
position into a first active position (likewise not shown), in which they
again adopt a roof-shaped position relative to one another, in which
both outer edges are interlocked in one another. In this first active
position, already a greater distance from the side wall 2' is achieved.
According to Fig. 3, the protective module now can be moved into a
7
CA 02518749 2005-09-09
second active position. In this connection, the pivot axis 5.1' is
disposed on the outer end of the piston rod 7.1 of a piston cylinder
drive 7, and the pivot axis 5.2' is disposed on a guided holding rod 8.
By means of the piston cylinder drive 7, which is disposed above the
roof plate 1', the protective module comprised of the plate elements
4.1' and 4.2' can be displaced outwardly in a displacing motion, which
runs essentially orthogonally to the side wall 2', and therewith the
distance of the protective module to the side wall 2' is increased,
providing a still better protection against incoming HL-projectiles.
Figs. 4 and 5 show another embodiment of a protective device for an
armored vehicle, of which only the roof plate 11 and the side wall 12 to
be protected are shown, analogously to Fig. 1. Again, a KE-protective
module 16 is fixedly mounted in front of the side wall 12, and outside
of the KE-protective module, the moveable HL-protective module 14 is
disposed, which in this case is constructed as an individual, fixedly
assembled component in the form of a buckling sheet louver with a
plurality of sheets 19 running at an angle to the side wall 12. The
sheets 19 are arranged with an intermediate air space. In the
inoperative position shown in Fig. 4, the protective module 14 is
disposed substantially within the vehicle contour 13. The protective
module 14 is moveable from this inoperative position, in a direction that
runs essentially orthogonally to the side wall 12, into an active position,
which is shown in Fig. 5. In this active position, it lies with an
8
CA 02518749 2005-09-09
essentially greater distance to the side wall 12 outside of the vehicle
contour 13. To achieve the motion, the protective module 14 is
connected on the upper side shown in Fig. 4 via a swivel joint 15.1 with
the piston rod 17.1 of a piston cylinder drive 17, which is disposed
above the roof plate 11. On the lower side shown in Fig. 4, the
protective module 14 is guided via a roller 15.2 on a linear guide 18. In
this manner, upon deployment of the piston rod 17.1, the protective
module 14 moves from the inoperative position of Fig. 4 into the active
position of Fig. 5 and if necessary, back into the inoperative position.
In the active position of Fig. 5, a substantially improved protection
against incoming HL-projectiles is achieved as a result of the greater
distance from the side wall 12. In the inoperative position, in contrast,
the vehicle can be loaded into a transport aircraft, for example, as a
result of the reduced vehicle contour.
9