Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02519800 2005-09-20
WO 2004/094280 PCT/US2003/008848
METHOD AND APPARATUS
FOR TRANSFERRING SUBSTRATES
Cross Reference to Related Application
This application is a continuation-in-part of U.S. Patent Application Serial
No. 09/967,414, filed on September 28, 2001, entitled "Systems, Methods and
Apparatuses for Manufacturing Dosage Forms" (MCP0295), and incorporated herein
by
reference.
1o Field of the Invention
This invention relates generally to methods and apparatuses for transferring
substrates, such as tablets, from one location to another.
Background of the Invention
15 Double-sided tablet presses are commonly used in the pharmaceutical
industry for making tablets. Their configuration is well known. Typically,
they comprise
a rotor having dies located along its periphery. The rotor rotates through
first and second
compression zones. In each compression zone, powder is fed to dies, optionally
the
powder is precompressed and then compressed within the dies, and finally
finished tablets
2o are ejected from the press. Because double-sided tablet presses contain two
compression
zones, with each revolution of the rotor two sets of tablets are made. The
tablets are
ejected from opposite sides of the press at first and second tablet ejection
zones. The
ejected tablets are conventionally transferred away in bulk by an ejection
chute leading to
a collection container such as a drum or hopper.
25 Commonly assigned, copending U.S. Patent Application Serial No.
09/967,414, the disclosure of which is incorporated herein by reference,
discloses a
transfer device capable of handling substrates such as tablets having a high
degree of
friability and softness. It is a rotating device comprising a plurality of
transfer units
attached to a flexible conveying means, such as a belt. It is preferably used
for
3o transferring substrates within a continuous process from one operating unit
to another, for
example from a compression apparatus to a coating apparatus. The flexible
conveying
means follows a path from the first operating unit to the second operating
unit. The
velocity and positions of the transfer units are synchronized with the
operating units to
which it is coupled, so that substrates can be smoothly captured from the
first operating
CA 02519800 2005-09-20
WO 2004/094280 PCT/US2003/008848
unit and released to the second operating unit. The transfer units comprise
retainers for
holding the substrates. The retainers are preferably flexible and constructed
from an
elastomeric material. In a preferred embodiment, the retainers are circular
and comprise
segmented fingers of elastomeric material.
Applicants have now designed a transfer device having transfer units
comprising inner and outer, side by side retainers that sequentially rather
than
simultaneously capture substrates. The device may be used to transfer tablets
or other
substrates, preferably from a rotary, double-sided tablet press to a second
location. The
transfer units are mounted on a flexible conveying means that travels along a
path
coincident with those portions of the tablet press where tablets are ejected.
In one
embodiment, the transfer units are adapted to receive first tablets at a first
substrate
receiving station of the apparatus located proximal to the first tablet
ejection zone of the
tablet press, and adapted to receive second tablets at a second substrate
receiving station
located proximal to the second tablet ejection zone of the tablet press.
Summary Of The Invention
The invention provides an apparatus for transfernng substrates, comprising: a)
a
flexible conveying means; b) a plurality of transfer units mounted to said
conveying
means, each transfer unit adapted to hold first and second substrates; c) a
cam track
2o defining a path from a first substrate receiving station, passing through a
second substrate
receiving station, and then to a substrate transfer station; and d) means for
driving said
conveying means along said cam track.
The invention also provides an apparatus for transfernng tablets from a double
sided tablet press comprising first and second tablet ejection zones to a
second location,
said apparatus comprising a plurality of transfer units mounted to a flexible
conveying
means, each transfer unit adapted to hold first and second tablets, a cam
track defining a
path from a first substrate receiving station located proximal to the first
tablet ejection
zone, passing through a second substrate receiving station located proximal to
the second
tablet ejection zone, and then to a substrate transfer station located at the
second location;
and means for driving said conveying means along said cam track.
Brief Description of the Drawings
Figure 1 depicts a conventional double-sided tablet press.
CA 02519800 2005-09-20
WO 2004/094280 PCT/US2003/008848
Figure 2 depicts a transfer apparatus according to the invention coupled with
the
tablet press of Figure 1.
Figure 3 is a cross-sectional view of a transfer apparatus according to the
invention.
Figures 4- 8 illustrate a preferred embodiment of a transfer unit.
Detailed Description of the Invention
Figure 1 depicts a conventional, double-sided tablet press 1. The tablet press
1
comprises a rotor 2 having a plurality of dies 3 around its periphery. Figure
1 depicts 12
dies. Accordingly, each revolution of this tablet press produces 24 tablets.
Tablet press 1 comprises first and second powder feeders 4a, 4b, first and
second
precompression rollers Sa, 5b (which are optional), and first and second main
compression
rollers 6a, 6b. First powder feeder 4a is located on the opposite side of
rotor 2 from
second powder feeder 4b. First precompression roller Sa is located on the
opposite side of
rotor 2 from second precompression roller 5b. Likewise, first main compression
roller 6a
is located on the opposite side of rotor 2 from second main compression roller
6b. A first
compression zone 11 a comprises first powder feeder 4a, first precompression
roller 5a and
first main compression roller 6a. A second compression zone l 1b comprises
second
powder feeder 4b, second precompression roller 5b and second main compression
roller
5b. Tablets 10a, l Ob are ejected from opposite sides of tablet press 1 at a
first tablet
ejection zone 7a and a second tablet ejection zone 7b.
The tablet press operates as follows. Powder is fed from the first powder
feeder 4a
to dies 3 passing thereunder as rotor 2 rotates in the direction shown by
arrows a. This
powder is optionally precompressed by the first precompression roller 5a, and
compressed
by the first main compression roller 6a into tablets 10a. Tablets 10a are
ejected from the
dies 3 at first tablet ejection zone 7a. Empty dies 3 next pass underneath the
second
powder feeder 4b and new powder is fed to the dies 3. The new powder is
optionally
precompressed by the second precompression roller 5b, and compressed by second
main
compression roller 6b into tablets 10b. Tablets lOb are ejected from the dies
3 at the
second tablet ejection zone 7b.
The apparatus for transfernng substrates (also referred to herein as the
transfer
apparatus) may be coupled with a double-sided tablet press as described above,
as shown
for example in Figure 2. In particular, the transfer apparatus may be used to
retrieve
tablets from a double-sided tablet press and transfer them to a second
location for further
3
CA 02519800 2005-09-20
WO 2004/094280 PCT/US2003/008848
processing, for example coating. Advantagously, the transfer apparatus
transfers the
tablets on a continuous basis.
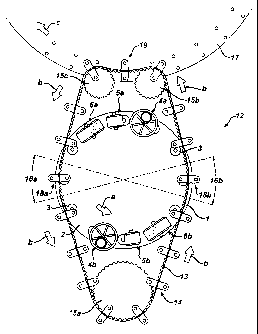
Refernng to Figure 2, the transfer apparatus 12 comprises a flexible
conveying means 13, shown here as a belt, to which a plurality of transfer
units 14 are
attached. The flexible conveying means may be made of any suitable material,
one
example of which is a composite consisting of a polyurethane toothed belt with
reinforcing
cords of polyester or poly-paraphenylene terephthalamide (Kevlai , E.I. duPont
de
Nemours and Company, Wilmington, DE). Other flexible materials, such as
chains, linked
belts, metal belts, and the like can be used as the flexible conveying means.
The transfer apparatus can be driven by any suitable power source such as an
electric motor. In one embodiment, the transfer apparatus is linked to the
tablet press and
driven by mechanical means through a gearbox (not shown) that is connected to
a main
drive motor (not shown). In this configuration the velocity and positions of
the individual
transfer units of the transfer apparatus can be synchronized with the dies of
the tablet
press.
In one embodiment of the invention, as shown in Figure 3, the transfer
apparatus
includes a drive pulley 20 and an idler pulley 21. A drive shaft 22 connects
drive pulley
to a main drive train (not shown). Drive shaft 22 drives drive pulley 20 to
rotate. Drive
pulley 20 has teeth that engage teeth 23 disposed on the interior of flexible
conveying
2o means 13, which in turn moves the transfer apparatus in the direction of
arrows b shown in
Figure 2. Idler pulley 21 has teeth that engage flexible conveying means 13 as
well, which
causes the idler to rotate with flexible conveying means 13.
The transfer apparatus further comprises a cam track 24 that precisely
determines
the path for the flexible conveying means 13. The path of cam track 24, the
pitch distance
between the transfer units 14, the pitch of the flexible conveying means 13,
and the gear
ratio between the driving means of the transfer apparatus and the driving
means of the
tablet press (as well as the driving means of other operating units to which
the transfer
apparatus is coupled) are all selected such that the transfer apparatus is
precisely aligned
with the tablet press and any other operating units linked to it. As each
operating unit
rotates, the transfer apparatus remains synchronized and phased with each,
such that a
precise and controlled transfer from one operating unit to another is
achieved.
The velocity and positions of the transfer units 14 are matched to the
velocity and
positions of the dies 3 in the tablet press along two portions of the path
defined by the cam
4
CA 02519800 2005-09-20
WO 2004/094280 PCT/US2003/008848
track 24. As shown in Figure 2, the path travels through a first substrate
receiving station
18a, a second substrate receiving station 18b, and a substrate transfer
location 19.
Substrate transfer location 19 may be located for example at a second location
remote
from the tablet press, for instance proximal to another operating unit 17.
First portion 16a of the path defined by the cam track is an arc coincident
with
tablet press rotor 2 when it passes through the first tablet ejection zone 7a
of the tablet
press. Second portion 16b of the path is an arc coincident with the tablet
press rotor 2
when it passes through the second tablet ejection zone 7b. Substrates are
received along
these two arc lengths.
to A preferred transfer unit 14 is depicted in Figure 4. Each transfer unit is
adapted to
hold first and second substrates in a side-by-side fashion. Each transfer unit
14 generally
includes a pair of plunger shafts 25, one or preferably more than one cam
follower 26, a
plurality of bearings 27 to retain the plunger shafts 25, a spring 28, a plate
29 that secures
the plunger shafts 25 to cam follower 26 thereby controlling their movement,
first retainer
15 30a and second retainer 30b. Preferably, each transfer unit 14 is attached
to flexible
conveying means 13 in a cantilever configuration so that retainers 30a, 30b
are
cantilevered over the path of the substrates.
Retainers 30a, 30b are preferably flexible and constructed from an elastomeric
material. Retainers 30a, 30b flex upward as shown in Figures 6-8 to grasp
substrates,
2o shown as tablets 100, therein. Substrates are ejected from the retainers
30a, 30b by
pushing down on them, thereby flexing the retainers. Once released, the
retainers 30a, 30b
flex back to their original positions to receive further substrates. In a
preferred
embodiment, the retainers 30a, 30b are circular and include segmented fingers
of
elastomeric material as shown in Figure 5, but need not be so constructed. The
retainers
25 30a, 30b need only be flexible enough to flex, hold a substrate, and
release the substrate.
First and second retainers 30a and 30b are disposed side-by-side within each
transfer unit. In one embodiment of the invention, each transfer unit is
attached to the
center of the flexible conveying means as shown in Figure 2, such that the
first and second
retainers 30a and 30b are disposed on either side of the flexible conveying
means. Viewed
3o from the perspective of forward movement of the flexible conveying means
along the path,
the first retainer 30a is located on the outside of each transfer unit, while
second retainer
30b is located on the inside of each transfer unit, i.e., closer to the center
of the transfer
apparatus. This inner/outer configuration, coupled with the path followed by
the cam
track, allows the transfer unit to pick up one substrate at a time, as
described below.
CA 02519800 2005-09-20
WO 2004/094280 PCT/US2003/008848
Referring to Figure 4, riding in cam track 24, cam follower 26 is mounted so
that it
can move up and down as shown in Figures 4-8. Plate 29 is coupled to cam
follower 26.
Spring 28 biases the plate 29 and cam follower 26 to an upper position. Plate
29 is also
coupled to each plunger shaft 25, so that movement of the plate 29 will cause
movement of
the plunger shafts 25. Each plunger shaft 25 is mounted within a transfer unit
14 by a
plurality of bearings 27 that permit vertical movement of the plunger shafts
25. The
plunger shafts 25 are mounted so that one end of each plunger shaft 25 can
move into the
respective space in which a substrate is retained to eject it from the
associated retainer, as
shown in Figure 8. The plunger shafts 25 and bearings 27 may be made of any
suitable
material.
The transfer apparatus operates as follows. As shown in Figure 2, flexible
conveying means 13 is moved along the path defined by the cam track 24 and
wheels 15a,
15b, 15c in the direction of arrows b. This directs each transfer unit 14 in
series to the first
substrate receiving station 16a. Here, a transfer unit 14 comes into proximity
with a die 3
containing a first tablet in the first tablet ejection zone7a of the tablet
press. The first
retainer 30a of the transfer unit 14 aligns with the die 3. The first tablet
is ejected from the
die 3 by the punches of the tablet press and into the retainer 30a as shown in
Figures 6-8.
Retainer 30b remains empty.
Further rotation of the transfer apparatus by the drive pulley causes the
flexible
2o conveying means 13 and its attached transfer units 14 to travel farther
along the path
shown by arrows b. Retainer 30a continues to hold a first tablet therein. When
the
transfer unit 14 reaches the second substrate receiving station 16b it comes
into proximity
with a die 3 containing a second tablet in the second tablet ejection zone 7b
of the tablet
press. The second tablet is ejected from the die 3 and into retainer 30b. Now,
retainers
30a and 30b contain first and second tablets, side-by-side in the transfer
unit.
As each full transfer unit 14 reaches substrate transfer location 19, cam
track 24
pushes on the cam follower 26, which pushes on plate 29. Plate 29 moves the
plunger
shafts 25, which in turn move down and contact the retained substrates. The
substrates are
pushed past the elastomeric collets and ejected from the retainers. Plunger
shafts 25 return
to their original upward position.
The transfer device may alternatively comprise rotatable transfer units, as
described in commonly assigned, copending U.S. Patent Application Serial No.
09/967,414, particularly as shown in Figures 77-81 therein. This is useful for
example
with elongated dosage forms, i.e., caplets that are compressed horizontally
but then must
6
CA 02519800 2005-09-20
WO 2004/094280 PCT/US2003/008848
be coated in a vertical position. As shown in Figure 80 of the '027
application, each
transfer unit 602 comprises of a dosage form holder 608 rotatably mounted in a
housing.
Each dosage form holder comprises two sets of flexible retainers 630, 630B,
one for entry
of a substrate 630 and one for exit of a substrate 630B. During transit along
path defined
by the cam track 606, the dosage form holder rotates 90 degrees due to motion
of a cam
follower 626 within the cam track 606. An ejector pin assembly 612 enters
through holes
608A in the dosage form holder 608 to eject the substrate. The dosage form
holder 608
rotates 90 degrees again, returning to its horizontal position to begin the
cycle over again.
1o The following non-limiting example further illustrates the claimed
invention.
Example
Acetaminophen-containing tablets are compressed in a double-sided tablet
press,
Fette model 3090. The press operates at 2000 tablets per minute per side, or
4000 tablets
15 per minute total. The tablet press is coupled to a coating apparatus via a
transfer device
according to the invention. The transfer device, tablet press and coating
apparatus are all
driven by a common motor, and are synchronized. The transfer device comprises
transfer
units, each with first and second retainers, and receives acetaminophen
tablets from both
sides of the tablet press. The first retainer receives first tablets from one
side of the tablet
20 press, and the second retainer receives second tablets from the other side
of the tablet
press. The transfer units proceed to a coating apparatus, where they are
ejected and coated
with gelatin.