Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02521155 2005-09-26
RAILWAY TRUCK PEDESTAL BEARING ADAPTER
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a railway freight car truck and, more
particularly, to a
pedestal bearing adapter for use in the pedestal jaw opening of the sideframe
of a railway freight
car truck.
In a railway freight car truck, two axles are held in a pair of laterally
spaced sideframes,
with a bolster extending laterally between and supported on each sideframe.
The wheels are
press fit on the axles, with the ends of the axles also fitted with a roller
bearing assembly. The
roller bearing assembly itself is fit into a bearing adapter that is fit into
a pedestal jaw opening at
the longitudinal end of each sideframe. The ends of the bolsters are
themselves supported on
spring groups, which are supported on the lower portion of the center openings
of the
sideframes.
US Patent Number 5,562.045 discloses a adapter and pad assembly useful in the
fitting of
the bearing assembly into the pedestal jaw opening of each sideframe. The
bearing adapter,
which is itself fit on top of the bearing assembly, is comprised of a unitary
cast steel piece. This
piece includes shoulders that are laterally spaced to form a receiving opening
at each longitudinal
edge of the bearing adapter. An elastomeric adapter pad is fitted on top of
the bearing adapter.
The adapter pad itself is disclosed to be comprised of an injection molded
polymer or a castable
polyurethane. The adapter pad itself includes depending legs which extend from
opposite
longitudinal edges of the adapter pad. The depending legs are spaced laterally
at each
longitudinal edge of the adapter pad such that the depending legs are received
in openings
between the laterally spaced shoulders of the bearing adapter. One problem
with this assembly is
the tendency of the adapter pad to move longitudinally across the top of the
bearing adapter.
CA 02521155 2005-09-26
This movement is exacerbated by the slight steering movement of the wheel
axles in the pedestal
25 jaw openings, such that the movement of the adapter pad completely off the
bearing adapter
occurs. This is an undesirable situation leading to poor performance of the
railway freight car
truck.
Accordingly, it is an object of the present invention to provide an improved
bearing
adapter and pad assembly.
30 It is another object of the present invention to provide an improved
bearing adapter and
pad assembly that eliminates the tendency of the adapter pad to move
longitudinally across the
top of the bearing adapter.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
A railway freight car truck of the so-called three piece standard design, is
comprised of
35 two laterally spaced, unitary cast steel sideframes and a laterally
extending bolster, also of a
unitary cast steel structure. The ends of the bolster are received and
supported on spring groups
that themselves are supported on the bottom section of a bolster opening in
each sideframe.
The wheel axle assemblies themselves are received in openings, commonly
referred to as
pedestal jaw openings. at longitudinal ends of each sideframe. The wheel axle
assemblies
40 themselves extend laterally between the sideframes, and hence, also
laterally between the two
spaced railway tracks. For improved performance of the railway freight car
truck, it is desirable
to receive the bearings press fit on each axle end into a bearing adapter
assembly. The improved
bearing adapter assembly of the present invention is comprised of a cast
steel, unitary bearing
adapter. This bearing adapter includes lateral edges themselves having arcuate
cutouts to be
45 placed over the bearing assembly. The bearing adapter further comprises
depending shoulders
that extend from each longitudinal edge of the bearing adapter. The shoulders
at each
CA 02521155 2005-09-26
longitudinal edge of the bearing adapter themselves are laterally spaced to
form an opening there
between. Further, the bearing adapter includes depressions that extend
laterally and are spaced
longitudinally across the top section of the bearing adapter. It should be
understood that the top
50 section of such bearing adapter is generally rectangular in structure, such
that the depressions are
near each longitudinal edge of the bearing adapter. These depressions can be
of a general v-
shape, formed by acute angle cuts into the top section of the bearing adaptex,
or they could be of
an arcuate nature as well.
The improved adapter pad in accordance with the present invention is comprised
of an
SS improved elastomer or polymer, usually a polyurethane. Such improved
adapter pad is usually
formed in a casting operation, although recent improvements have allowed the
improved adapter
pad to also be formed in an injection molding operation. The adapter pad
itself is seen to be
comprised of a generally rectangular top section, with depending legs
extending from each
longitudinal edge thereof. The depending legs are spaced laterally on each
longitudinal edge.
60 Such depending legs are fit downwardly into the opening in the bearing
adapter and abut the
shoulders of the bearing adapter to provide lateral support for the adapter
pad. Further lateral
support is provided by raised projections extending from the top of the
bearing adapter that abut
lateral edges of the adapter pad. Further, the adapter pad includes laterally
extending projections
extending downwardly from the top section of the adapter pad. Such projections
are received in
65 the complementary depressions in the top section of the bearing adapter
itself. These projections
will correspond to the depressions in the bearing adapter, so it is seen that
such projections may
be of a general v-shape, formed by two wall sections extending downwardly at
an acute angle
from the lower surface of the top section. It is also seen that such
projections could be of an
~3~
CA 02521155 2005-09-26
arcuate nature, extending into complementary arcuate depressions in the top
section of the
70 bearing adapter.
The bearing adaptex of the present invention has the legs extending around the
thrust
lugs. In addition to this the new design pad has the additional interlock on
the bottom side of the
adapter pad, which allows the pad to function in shear. With the proper
relationship between
cross section and hardness of the pad, a spring rate is designed into the
elastomer material of the
75 pad. The elastomer then allows the railway truck wheel-sets to move from a
high warp stiffness
position to that of radial steering position when the truck passes through
curves. Once through
the curve the elastomer acts as a spring to re-center the adapter to a neutral
position.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
In the drawings,
80 Fig. 1 is a partial perspective view of a sideframe and bolster and bearing
adapter and
adapter pad;
Fig. 2 is a top view of a first embodiment of a bearing adapter in accordance
with the
present invention;
Fig. 3 is an end view of the first embodiment of a bearing adapter in
accordance with the
85 present invention;
Fig. 4 is a side view of the first embodiment of a bearing adapter in
accordance with the
present invention;
Fig. 5 is a top view of a second embodiment of a bearing adapter in accordance
with the
present invention;
90 Fig. 6 is an end view of the second embodiment of a bearing adapter in
accordance with
the present invention;
CA 02521155 2005-09-26
Fig. 7 is a side view of the second embodiment of a bearing adapter in
accordance with
the present invention;
Fig. 8 is a top view of an adapter pad in accordance with the present
invention;
95 Fig. 9 is an end view of an adapter pad in accordance with the present
invention, and
Fig. 10 is a side view of an adapter pad in accordance with the present
invention.
Fig. 11 is a perspective view of a third embodiment of a bearing adapter and
an adapter
pad in accordance with the present invention, and
Fig. 12 is a perspective view of a fourth embodiment of a bearing adapter and
adapter pad
100 in accordance with the present invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
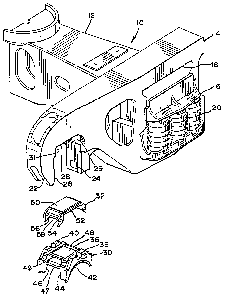
Referring now to Figure 1 of the drawings, the lateral end of each sideframe
14 is seen to
be comprised of a downwardly extending pedestal jaw 22. The inside wall 26 of
pedestal jaw
22, along with roof section 28 and vertical face 24 are seen to combine to
form the pedestal j aw
105 opening. At the interface between vertical face 24 and roof section 28,
there is seen to be an
inner thrust lug 29. Inner thrust lug 29 is seen to comprise an angled section
that extends from
an upper section of vertical face 24 to an inward section of roof section 28.
Similarly, but not
entirely seen in this perspective view of Figure 1, outer thrust lug 31 is
seen to comprise an
angled section extending from an upper portion of inside wall 26 extending to
an inner portion of
110 roof section 28.
Another part of the present invention includes bearing adapter 30, which is
seen to be a
generally rectangular structure having depending legs extending therefrom.
Bearing adapter 30
is usually comprised of a unitary cast steel structure. Adapter pad 32 is also
seen to be a
generally rectangular structure with depending legs extending therefrom.
Adapter pad 32 is
CA 02521155 2005-09-26
115 usually comprised of a cast or injection molded polymer or elastomer,
which will be further
described.
Bearing adapter 30 is seen to be comprised of a unitary, cast steel structure
that is
generally rectangular in shape. Bearing adapter 30 is comprised of a generally
rectangular top
section 36, which is seen to be generally flat. Two raised edge supports 38
are seen to extend
20 upwardly from the lateral edges of bearing adapter 30, as are similar
raised edge supports 40
from the opposite lateral edge of bearing adapter 30. The combined raised edge
supports 38 and
40 form a receiving surface and pocket for adapter pad 32. Bearing adapter 30
is also seen to
comprise an arcuate opening 42 on each lower lateral edge; this arcuate
opening 42 is adapted to
seat against a bearing, which is not shown in this view. Bearing adapter 30 is
also seen to
125 comprise four depending shoulders, of which 44 and 46 are shown in this
view. Depending
shoulders 44 and 46 are seen to be laterally spaced, forming an opening for
the adapter pad
structure.
Adapter pad 32 is usually comprised of a cast polymer or elastomeric material
and is of
unitary structure. It is also possible to construct adapter pad 32 with a
blown injection method,
130 but casting is the preferred method of forming adapter pad 32. Adapter pad
32 is comprised of a
generally rectangular and flat top section 50, with lateral edges, of which
lateral edge 52 is
shown. Four depending legs, of which depending leg 54 and 56 are shown in this
view, are seen
to extend downwardly, and form a thrust lug opening 58 there between. A
similar thrust lug
opening is formed on the other longitudinal edge of adapter pad 32. In
assembling adapter pad
135 32 onto the top of bearing adapter 30, it can be seen that depending legs
54 and 56 project
downwardly and are supported laterally against depending shoulders 44 and 46,
respectively, of
bearing adapter 30.
~6~
CA 02521155 2005-09-26
Referring now to Fig. l, the partial perspective view of the main components
of a railway
freight car truck are shown generally at 10. Such components include bolster
12, which is
140 generally a cast steel unitary structure, that extends laterally between
two sideframes 14.
Sideframes 14 are also unitary cast steel structures. Sideframes 14 are seen
to extend
longitudinally and parallel with the railway tracks. Each sideframe 14
includes a bolster opening
18 through which end 16 of bolster 12 extends. End 16 of bolster 12 is
supported on spring
group 20, with damping devices known as friction shoes, which are not shown in
this view.
145 Referring now to Figs. 2-4, the detailed view of bearing adapter 30 shown
in Figure 1 is
provided. This bearing adapter is used in a 6.5 x 12 size arrangement. Bearing
adapter 30, as
described above in Figure l, is seen to include a generalw rectangular top
section 36, with raised
edge supports 38 and 40, extending upwardly from the lateral edges of bearing
adapter 30.
Arcuate opening 42 is also seen to be formed in lateral edges of bearing
adapter 30 to allow
150 fitting of bearing adapter 30 on top of a bearing assembly. Depending
shoulders 44 and 46 are
seen to extend downwardly from opposite longitudinal ends of bearing adapter
30, and
depending shoulders 44 and 46 are seen to be spaced laterally from each other,
forming opening
47. As shown in Fig. 1, and Figs. 2 and 4, depressions 48 and 49 are spaced
longitudinally and
extend laterally across top section 36 of bearing adapter 30. Each of
depressions 48 and 49 is
155 seen to be comprised of a wall section extending downwardly from top
section 36 at an acute
angle therefrom. Depressions 48 and 49 are seen to extend across top section
36 to an
intermediate support 60 and 62, respectively. Intermediate supports 60 and 62
are seen to extend
longitudinally across top section 36 of bearing adapter 30, and are located
inwardly from raised
edge supports 38 and 40, respectively.
~7~
CA 02521155 2005-09-26
160 Referring now to Figs. 5-7, and another embodiment of bearing adapter is
shown at 130.
This bearing adapter is used in 6.5 x 9 size applications. Bearing adapter
130, as described
above in Figure 1, is seen to include a generally rectangular top section 136,
with raised edge
supports 138 and 140, extending upwardly from the lateral edges of bearing
adapter 130.
Arcuate opening 142 is also seen to be formed in lateral edges of bearing
adapter 130 to allow
165 fitting of bearing adapter 130 on top of a bearing assembly. Depending
shoulders 144 and 146
are seen to extend downwardly from opposite longitudinal ends of bearing
adapter 130, and
depending shoulders 144 and 146 are seen to be spaced laterally from each
other, forming
opening 147. Depressions 148 and 149 are spaced longitudinally and extend
laterally across top
section I 36 of bearing adapter I 3G. Each of depressions 148 and 149 is seen
to be comprised of
170 a wall section extending downwardly from top section 136 at an acute angle
therefrom.
Depressions 148 and 149 are seen to extend across top section 136 to an
intermediate support
160 and 162, respectively. Intermediate supports 160 and 162 are seen to
extend longitudinally
across top section 136 of bearing adapter 130, and are located inwardly from a
raised edge
supports 140 and 138, respectively.
175 Referring now to Figs. 8-10, a detailed view of adapter pad 32 is
provided. Adapter pad
32 is seen to be comprised of a generally rectangular top section 50. Top
section 50 includes
lateral edges 52 and 53. Legs 54 and 56. extend downwardly from each
longitudinal edge of
adapter pad 32. Legs 54 and 56 are seen to be spaced laterally so as to form
thrust lug opening
58 there between. Thrust lug opening 58 and its counterpart at the other
longitudinal edge of
.80 adapter pad 32 is seen to receive one of inner thrust lug 29 or outer
thrust lug 31, when adapter
pad 32 is fit up into roof section 28 of pedestal jaw 22.
~g~
CA 02521155 2005-09-26
Bearing adapter pad 32 is also seen to comprise depending protrusions 64 and
66, that
extend downwardly from the bottom surface of top section 50. Protrusions 64
and 66 are seen to
extend laterally across the width of adapter pad 32. extending to, or nearly
to, lateral edges 52
~ 85 and 53. Protrusions 64 and 66 are designed to be fit into depressions 48
and 49 in top section 36
of bearing adapter 30. Such fitting provides lateral and longitudinal
stability for adapter pad 32
when fit against bearing adapter 30. Lateral stability is also provided with
edges 52 and 53 of
adapter pad 32 abutting raised edge supports 38 and 40, respectively, of
bearing adapter 30.
Adapter pad 32 is comprised of a cast elastomer of a durometer hardness
between 90A
190 and 58D. It should be understood that it is preferred to have adapter pad
32 formed in a casting
operation to obtain the desired hardness ratings, but other forming operations
are possible so
long as the preferred hardness ratings of adapter pad 32 are provided.
Referring now to Fig. 11. and another embodiment of bearing adapter is shown
at 230.
This bearing adapter is used in 6.5 x 9 size applications. Bearing adapter 230
is seen to include a
195 generally rectangular top section 236, with raised edge supports 238 and
240, extending
upwardly from the lateral edges of bearing adapter 230. Generally arcuate
opening 242 is also
seen to be formed in lateral edges of bearing adapter 230 to allow fitting of
bearing adapter 230
on top of a bearing assembly. Depending shoulders 244 and 246 are seen to
extend downwardly
from opposite longitudinal ends of bearing adapter 230, and depending
shoulders 244 and 246
200 are seen to be spaced laterally from each other, forming opening 247.
Depressions 248 and 249
are spaced laterally and extend longitudinally across top section 236 of
bearing adapter 230.
Each of depressions 248 and 249 is seen to be comprised of a wall section
extending
downwardly from top section 236 at an acute angle therefrom. Depressions 248
and 249 are seen
to extend across top section 236 adjacent and parallel to an intermediate
support 260 and 262.
CA 02521155 2005-09-26
205 respectively. Intermediate supports 260 and 262 are seen to extend
laterally across top section
236 of bearing adapter 230, and are located inwardly from a raised edge
supports 240 and 238,
respectively.
Refernng now to Fig. 11, a detailed view of adapter pad 232 is provided.
Adapter pad
232 is seen to be comprised of a generally rectangular top section 250. Top
section 250 includes
210 lateral edges 252 and 253. Legs 254 and 256, extend downwardly from each
longitudinal edge
of adapter pad 232. Legs 254 and 256 are seen to be spaced laterally so as to
form thrust lug
opening 258 there between. Thrust lug opening 258 and its counterpart at the
other longitudinal
edge of adapter pad 232 is seen to receive one of inner thrust lug 29 or outer
thrust lug 31, when
adapter pad 32 is fit up into roof section 28 of pedestal jaw 22.
215 Bearing adapter pad 232 is also seen to comprise depending protrusions 264
and 266, that
extend downwardly from the bottom surface of top section 250. Protru2sions 264
and 266 are
seen to extend longitudinally across the length of adapter pad 232, extending
nearly to the
longitudinal edges 272 and 273. Protrusions 264 and 266 are designed to be fit
into depressions
248 and 249 in top section 236 of bearing adapter 230. Such fitting provides
lateral and
220 longitudinal stability for adapter pad 232 when fit against bearing
adapter 230. Lateral stability
is also provided with edges 252 and 253 of adapter pad 232 abutting raised
edge supports 240
and 238, respectively, of bearing adapter 230.
Adapter pad 232 is comprised of a cast elastomer of a durometer hardness
between 90A
and 58D. It should be understood that it is preferred to have adapter pad 232
formed in a casting
X25 operation to obtain the desired hardness ratings, but other forming
operations are possible so
long as the preferred hardness ratings of adapter pad 232 are provided.
10~
CA 02521155 2005-09-26
Referring now to Fig. 12, and another embodiment of bearing adapter is shown
at 330.
This bearing adapter is used in 6.5 x 9 size applications. Bearing adapter 330
is seen to include a
generally rectangular top section 336, with raised edge supports 338 and 340,
extending
X30 upwardly from the lateral edges of bearing adapter 330. Arcuate opening
342 is also seen to be
formed in lateral edges of bearing adapter 330 to allow fitting of bearing
adapter 330 on top of a
bearing assembly. Depending shoulders 344 and 346 are seen to extend
downwardly from
opposite longitudinal ends of bearing adapter 330, and depending shoulders 344
and 346 are seen .
to be spaced laterally from each other, forming opening 347. A plurality of
generally square
235 shaped depressions 349 are spaced longitudinally and extend laterally
across top section 336 of
bearing adapter 330. Each of depressions 349 is seen to be comprised of wall
sections extending
downwardly from top section 336 at an acute angle therefrom. Depressions 349
are seen to be
patterned across top section 336. Depression 349 could also be comprised of
rounded openings
or other outer shapes. Intermediate supports 360 and 362 are seen to extend
longitudinally
240 across top section 336 of bearing adapter 330, and are located inwardly
from a raised edge
supports 340 and 338, respectively.
Referring now to Fig. 12, a detailed view of adapter pad 332 is provided.
Adapter pad
332 is seen to be comprised of a generally rectangular top section 350. Top
section 350 includes
lateral edges 352 and 353. Legs 354 and 356, extend downwardly from each
longitudinal edge
245 of adapter pad 332. Legs 354 and 356 are seen to be spaced laterally so as
to form thrust lug
opening 358 there between. Thrust lug opening 358 and its counterpart at the
other longitudinal
edge of adapter pad 332 is seen to receive one of inner thrust lug 29 or outer
thrust lug 31, when
adapter pad 332 is fit up into roof section 28 of pedestal jaw 22.
~11~
CA 02521155 2005-09-26
.1
Bearing adapter pad 332 is also seen to comprise a plurality of depending
protrusions
250 366, that extend downwardly from the bottom surface of top section 350.
Protrusions 366 are
spaced and extend laterally across the width of adapter pad 332. Protrusions
366 are designed to
be fit into depressions 349 in top section 336 of bearing adapter 330. Such
fitting provides
lateral and longitudinal stability for adapter pad 332 when fit against
bearing adapter 330.
Lateral stability is also provided with edges 352 and 353 of adapter pad 332
abutting raised edge
255 supports 340 and 338, respectively, of bearing adapter 330. .
Adapter pad 332 is comprised of a cast elastomer of a durometer hardness
between 90A
and 58D. It should be understood that it is preferred to have adapter pad 332
formed in a casting
operation to obtain the desired hardness rari~ys. but other forming operations
are possible so
long as the preferred hardness ratings of adapter pad 332 are provided.
260
~12~