Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-l3-01
Page 2
s METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR ADAPTIVE DISTRIBUTION OF
MATERIALS IN RAILWAY MAINTENANCE AND OTHER APPLICATIONS
This invention relates generally to railway maintenance logistics, and more
particularly
relates to a GFS-based system for use in the distribution of railroad ties or
similar
to materials along railroad tracks in railroad maintenance applications.
BACKGROUND
is Railroads in North America typically consist of a network of railroad
tracks. Each of
these railroad tracks is typically formed by placing wooden or concrete
crossties on top of
a bed of gravel ballast, and then attaching a pair of steel rails to the top
of those ties.
Variations in specific construction methods occur in special function areas
such as road
and bridge crossings, yards or the like.
ao
One of the major railroad maintenance activities which is undertaken on an
ongoing and
regular basis is the monitoring and replacement of the cxossties beneath the
tracks, in
order to maintain the integrity and safety of these railroad tracks. While
many railroad
maintenance tasks have become highly automated over the last number of years,
tie
is replacement is still a task which while being mechanically assisted, is
somewhat more
labour and logistic intensive in nature at the present time. For example,
while there are
machines which can be used to in relatively automated or streamlined fashion
withdraw
and replace individual railroad ties under a track, the actual movement,
supply and
placement of the ties to be put in place beneath the track remains the
difficult portion of
3o the task.
Onc of the issues which still remains is that there is no efficient or fluid
method for the
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 3
s placement of variable numbers of replacement railroad ties in approximate
proper
position along the railroad right of way for use in replacement activities.
In determining which railroad ties might need to be replaced, a machine can lx
driven
along the track which would exercise some type of mechanical test on each
railroad tie or
~o otherwise calctelate which tie or ties needed to be replaced and mark them
as such. The
second method, which is still widely used as well, consists of a track
maintenance
employee physically walking along the railroad track and, based on visual
inspection,
marking individual railroad ties that need to be replaced with a paint marking
or the like.
Once the ties have been marked for replacement, a track gang can then replace
the
is necessary ties in the course of performing maintenance on the track.
Beyond the oldest method of simply walking along or moving along the track
with a
complete set of equipment, replacing each tie directly as it is inspected,
there is not a
quick and efficient use of the equipment and crews necessary in these
circumstances or
io applications. As indicated above the most difficult portion of the task of
railroad tie
replacement in terms of logistics is the distribution of the replacement ties
along the
railroad right of way so that they can be properly installed by the
maintenance crew.
Automatic tic replacement machines can carry very few if any supplies of
replacement
zs ties. The majority of those machines are designed to basically replace a
tie under the
track with a new tie which is picked up from the ground beside the track and
installed in
position. In certain cases what might have been done in the past to distribute
the proper
number of replacement ties would be to effectively bring along a truckload or
a train load
of replacement ties behind the tie replacement machine and use a tractor or
the like to
so drop the ties into approximate position before the tie replacement machine
was there to
make that particular replacement. However, this makes the actual tie
replacement
process take longer than if the replacement ties are already in place on the
ground beside
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-01
Page 4
s the track and can simply be picked up in the appropriate position and
installed.
One of the methods of distribution of replacement ties rather than bringing
along an
entire train Ioad of replacement ties with the tie replacement machine has in
the past been
to effectively come along the track after the ties have been marked for
replacement and
to drop ties in approximate position where they will be used by the following
maintenance
equipment or tie replacement machine. A distribution crew working separately
from the
actually tie replacement crew can work more efficiently, as can the
replacement crew, if
the two jobs are not directly combined or done at the same time.
is In circumstances where a large number of ties is required in an area for
replacement, that
number of ties needs to be dttrnped beside the track for use by the crew,
whereas in other
circumstances where fewer ties are required a smaller number of ties might
need to be
dumped for use, or on a section of track where no tie replacement was required
to be
done at all, then no replacement ties would be needed for a distance.
zo
Beyond simply dumping replacement ties in approximately the right numbers and
approximately the right places, another method which has been practised in the
past is to
drop a predefined batch or number of ties, or a banded quantity of ties, along
the railroad.
For example, it is known that certain railinad maintenance companies have
banded
xs replacement ties together in groups of 15 (or some other predetermined
number), and
then they simply count their way along the replacement markings on the track
and drop
those banded batches of ties along the track in approximately the right place
so that they
are in position when they are required for use. However, the cost of preparing
these
banded groupings of ties is significant, and when the replacement ties are
banded into
3o these predefined Iots they also present somewhat of a limitation insofar as
limiting where
and how many batches of ties can be distributed, since they can only be
distributed in
multiples of 15 or whatever the predetermined number is which is in each
banded group.
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 5
s This banding approach does save significantly on the time and labour
involved in the
actual tie distribution process, however the cost of the banding step is
significant.
Something which has been done in the past to enhance the banding method is to
effectively capture GPS coordinates for each tie which needs to be replaced,
and then
io generating a signal or somehow marking for action the dropping of one of
these
predefined batches or numbers of ties as necessary. For example, if the ties
were hatched
in units of 15, a marking or location is captured or marked every 15th
replacement tie
being required, and then a banded number of ties is dropped at that point.
However, the
ties will be dropped in a large batch at either the beginning or end of a
replacement
is section, and in a particular section of track where not a large number of
replacement ties
were required, the lSth tie might be a long ways from the first tie needing to
be replaced
and as such the problem of needing to move the replacement ties around a fair
bit for
installation then resurfaces.
ao It is also known that in certain circumstances where this banded approach
has been used,
the marking crew who are responsible for marking the locations for the
dropping of
various items and replacement ties need to work in very close physical
proximity to the
tie distribution crew. This is a significant rate limiting step for the
marking crew, since
they would not typically spend nearly as much time on a particular section of
track
zs testing or identifying ties for replacement as would the maintenance crew
who were
actually undertaking the job of distribution or replacement. In addition to
trying to
eliminate the banding system, if it were possible to come up with a method by
which the
marking crew could work at their own speed independently from the maintenance
crews,
this would also minimise the cost of the railroad tie replacement task.
Because railroads typically are required to maintain hundreds or thousands of
miles of
railroad tracks on a recurring basis, tie replacement is a major component of
track
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
FBcK 1490-13-01
Page 6
s maintenance. Anything that can be done to streamline the tie replacement
process in
terms of equipment, materials, traffic control, labour and management would
enhance
profitability of railroads since tracks would be down for shorter periods of
time for
maintenance and less cost potentially would be involved in the actual
maintenance step.
It is contemplated that any type of system which could be created which would
enhance
io the tie replacement function by allowing for the distribution of variable
predetermined
numbers of replacement ties in close to the right locations along a railroad
right of way
would be welcome as an optimisation of the tie replacement function of
railroad
maintenance.
~s
SUN»IARY OF THE INVENTION
It is the object of the present invention to provide a method and apparatus
for the adaptive
distribution of random quantities of railroad ties at randomly spaced
locations along a
2o railroad right of way with a minimum of labour or cost.
It is a further object of the present invention to provide a method or
apparatus by which
these variable quantities of reptacement railroad ties can be placed at non-
standard or
calculated locations where they are optimally located in relation to their
eventual use in
zs maintenance or replacement tasks.
It is the further object of the present invention to provide a method and
apparatus for the
adaptive distribution of railroad ties in railway maintenance applications
which will allow
for the marking or acquisition of the use location data with respect to these
ties, to take
so place in a separate site inspection pass in advance of the equipment for
distributing or
replacing the railroad ties.
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-0!
Page 7
s A method for the adaptive distribution of materials and railway maintenance
and other
applications, and more specifically for the distribution of replacement
railroad ties in the
present case, accomplishes its objectives as follows. The method of the
present invention
is "adaptive" insofar as it can automatically and correctly calculate and
adjust the right
number of replacement ties to be placed at particular spots along a railroad
right-of way
io for eventual replacement, such that not only the number of ties distributed
at individual
drop locations will vary, but also the specific locations for the dropping of
those materials
will be adjusted based upon the proximity or use requirements for the
materials in
question.
~s The invention includes a method of distribution of materials along a
railroad track, the
first step in which is, with respect to a section of railroad track,
identifying at least one
use location in proximity to the railroad track at which a quantity of
materials is required
to be used. The use location or locations might be anywhere that a quantity of
materials
would need to be placed for subsequent use.
zo
The use location or locations would be identified using at least one drop
location
detection module capable of communicating with a central location database and
capable
of determining the location of the drop location detection module in relation
to the
railroad track, determining and capturing the coordinates of each use location
in relation
zs to the railroad track. The use location capture module or modules would
capture the
coordinates of each use location, along with potentially the quantity of
materials required
at that location or any other optional desirable data, for storage to a
central location
database. The connection of the use location capture modules to the central
location
database might be real-time and 'always on', or the modules could from time to
time be
3o uploaded to the central location database.
Next a location selection software component would be used to determine the
proper
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K I49t1-13-01
Page 8
s siting of drop locations for the materials in question, based upon the use
location
coordinates stored within the central database as well as a profile of rules
relating to the
optimized distribution of the materials in question. The location selection
software
component, which might be resident upon the use location capture module, the
drop
location detection module or modules, or a central computer added for this or
other
io purposes, would select at least one drop location at which materials can be
placed in
proximity to the railroad track, wherein each drop location corresponds to at
least one use
location from the central database in relation to the railroad track in
question and wherein
each use location from the central database in relation to the railroad track
in question
corresponds to a drop location. The coordinates in relation to the railroad
track for each
is drop location, being drop location coordinates, would be determined as
would be the
appropriate quantity of materials to be placed at each drop location, being
the drop
location quantity, wherein the drop location quantity for a particular drop
location
denotes a sufficient quantity of material to meet the requirements at each use
location to
which the drop location in question corresponds.
Next the materials could actually be distributed, using materials distribution
equipment
equipped with a drop location detection module capable of communicating with
the
central location database, and capable of determining the location of the drop
location
detection module in relation to the railroad track. While moving the materials
zs distribution equipment along the railroad track, the drop location
detection module would
monitor the location of the drop location detection module in relation to the
railroad track
and compare the location of the drop location detection module to the drop
location
coordinates in respect of drop locations along the railroad track selected by
the location
selection software component. When it is determined that the drop location
detection
3o module has reached a drop location, the placement of the drop location
quantity of
materials at the drop location could take place.
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-fll
Page 9
s The drop location coordinates and drop location quantities could be stored
in the central
location database along with the use location coordinates or other data, or
could be
calculated in memory and used by the drop location detection module or modules
and
discarded rather than retained in the central location database. While the
obvious utility
for historical purposes of retaining the drop location information will be
understood,
~o either such implementation of the method of the present invention is
contemplated within
the scope hereof.
The location selection software component might be resident upon and the drop
location
coordinates and drop location quantities calculated by the device on which the
central
is location database is resident. The central location database could be
resident on the drop
location detection module, and the drop location detection module capable of
communicating with the drop location detection module to access data from the
central
location database. Alternatively the central location database could be
resident on the
drop location detection module, and the drop location detection module capable
of
xo communicating with the drop location detection module to access data from
the central
location database. The central location database could also be resident on a
central
computer, wherein both the drop location detection modules and drop location
detection
modules are capable of communicating with the central computer for the purpose
of
communicating with the central location database.
zs
The drop locations could be selected and the drop location coordinates and
drop location
quantities saved to the centre! location database in advance of the actual
materials
distribution step, or alternatively they could be computed in real time as the
materials
distribution equipment moves down the railroad track.
The use location capture module could be equipped with a GPS receiver, so that
the
coordinates of a use location would effectively be a GPS fix at the time the
use location
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-01
Page 10
s coordinates were captured. Alternately as is outlined herein there are other
methods of
measurement or determination of the location of a use location in relation to
the railroad
track, including measuring the distance along the track from a fixed point, or
counting a
repetitive track feature, which could also be used.
to Similarly once drop locations are selected, the drop location coordinates
could be
generated in whatever format would be usable by the drop location detection
modules.
For example if the location detection modules had a GPS receiver in them the
drop
location coordinates might be a set of GPS coordinates. Alternatively if the
drop location
detection module were equipped to measure the distance along the track from a
fixed
is point to determine the location of the module, then the drop location
coordinates could be
generated for this type of a measurement method.
It is even foreseeable that multiple measurement methods mix&t be used and the
location
selection software component could be used to translate between the two. For
example,
ie GPS use location coordinates could be used to select the drop locations,
the drop location
coordinates of which could be determined or calculated for detection by
measurement
along the track or using some other method.
The method could also be used to distribute more than one type of materials -
the use
a location capture module could be modified to allow for the marking of
particular use
locations for the distribution of one or more specific types of materials and
this again
could be incorporated into the selection of the appropriate drop locations.
If the materials being distributed were railroad ties, the materials
distribution equipment
3o could include a picker arm for removal of such replacement ties from a
transport railcar
for placement at use locations. There might also be a load cell on the picker
arm capable
of measuring the number of ties removed from the railcars at one time.
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 11
The materials being distributed could either be dropped automatically by the
materials
distribution equipment upon the determination by the drop location detection
module that
the equipment has reached a drop location, or alternatively the materials
could be
distributed manually upon the arrival of the materials distribution equipment
at a drop
io location. In a manual distribution, the operator of the materials
distribution equipment
could be notified when the drop location detection module has determined that
the
materials distribution equipment has reached a drop location.
Where the materials distribution equipment comprised a longer supply train or
the like,
is the drop location detection module could also include a slave display on
the power unit of
the distribution equipment, to advise the operator of the power unit when the
distribution
equipment is in position at a drop location in addition to advising the
operator of the
distribution equipment.
zo The use location capture module could be adapted to allow the operator to
specifically
choose some drop locations if they wished to do so., or alternately to specify
places
which should not be used as drop locations.
There is also disclosed a system for use in the adaptive distribution of
variable quantities
as of materials along a railroad track, comprising firstly a central location
database capable
of storing the coordinates in relation to the railroad track of use locations
at which
materials are required for use. The system also includes at least one drop
location
detection module which is able to determine its coordinates in relation to the
railroad
track and capture said coordinates as use location coordinates corresponding
to a use
30 location, and wherein said drop location detection module is capable of
communicating
with the central location database for the purpose of storing use location
coordinates
therein.
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 12
A location selection software component which will select drop locations in
proximity to
the railroad track at which materials are to placed and will determine the
coordinates of
such drop locations in relation to the railroad track, being drop location
coordinates,
along with determining the quantity of materials to be placed at each drop
location, being
~o drop location quantities, is used in the system to determine precisely
where quantities of
materials should be placed. At least one piece of materials distribution
equipment
equipped with a drop location detection module capable of communicating with
the
central location database to access location coordinates stored thereon as
well as being
capable of determining its own position in relation to the railroad track,
will be moved
is along the track and as it determines that a drop location has been reached
it will either
notify the operator for a manual material drop or automatically dispense the
materials
required in other embodiments.
In operation of the system, use location coordinates of use locations in
relation to the
zo railroad track will be captured to the central location database by the at
least one drop
location detection module. The location selection software component will
select drop
locations and generate the drop location coordinates and drop location
quantities
corresponding thereto based upon use location coordinates and a profile of
rules
pertaining to the optimal distribution of the materials in question and the
drop location
zs detection module on the materials distribution equipment will access the
drop location
coordinates and drop location quantities in respect of the railroad track and
monitor or
compare the location of the drop location detection module in relation to the
railroad
track against the drop location coordinates as the materials distribution
equipment is
moved along the railroad track, and upon determining that a drop location has
been
so reached the materials distribution equipment will place the required drop
location
quantity of materials at that drop location.
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-D1
Page 13
s The system might also include a central computer in which the central
location database
is resident, said central computer being capable of communicating with the at
least one
drop location detection module as well as with the at least one drop location
detection
module.
io As outlined with respect to the method above, the system of the present
invention could
use GPS or track measurement methods to determine the location of either the
use
location capture module or the drop location detection module in relation to
the railroad
track and to capture the coordinates or measurements re same.
is Also included in the invention is a location selection software component,
which is a
computer program capable of applying a set of predetermined rules in either a
static or
fuzzy context to a list of use location coordinates and data stored within a
central location
database, to yield properly selected drop locations in proximity to the
railroad track along
with the necessary coordinates to detect or locate them using a drop location
detection
Zo module.
Also within the scope of the present invention is the use location capture
module itself
which is any device capable of capturing the measurement or location of a use
location in
relation to the railroad track and storing it for subsequent upload to a
central location
as database or other use in accordance with the method of the present
invention.
Also within the scope of the present invention is any drop location detection
module
capable of locating drop locations for quantities of materials along or in
proximity to a
railroad track as the module is moved along the railroad track, in accordance
with drop
30 locations and their drop location coordinates and drop location quantities
determined by
the location selection software program of the present invention.
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-I3-01
Page 14
s In addition to the overall method of acquiring the data related to the use
locations,
selecting the appropriate drop locations and subsequently locating the drop
locations and
dropping or distributing an appropriate amount of materials at cach drop
location, the
invention also comprises a computer program for the actual generation of drop
location
co-ordinates based upon an assessment or analysis of a plurality of use
location co-
to ordinates. Specifically, it is intended that a computer program which can
take a plurality
or use location co-ordinates along with the general route information and
other GIS or
business factors into account and, an that basis, properly select the most
convenient or
efficient drop locations for materials be used, and generate the appropriate
drop location
co-ordinates therefor, is contemplated within the scope of the present
invention as well.
is
The use location capture module in its most basic embodiments will be any
device or
apparatus capable of effectively marking and caching to memory sets of GPS co-
ordinates which relate to individual use locations for replacement ties. These
use location
co-ordinates can subsequently either be manipulated within the memory of the
use
w location capture module or uploaded either to a central computer or directly
to a drop
location detection module on a distribution machine for subsequent
manipulation or use
in the location of appropriate drop location co-ordinates and the subsequent
distribution
of materials thereto.
is A central computer could be used to house all of the use location co-
ordinates captured
by the one or more use location capture modules of the method of the present
invention.
Basically, the use location capture modules could upload to the memory of a
central
computer, and more specifically into a location database stored therein, the
use location
co-ordinates which had been captured by use of the use location capture
modules) and
so then subsequently those use location co-ordinates could be used by the
central computer,
or more directly by a drop location detection module on a tie distribution
machine, to
properly calculate or locate drop locations and assist operators of the tie
distribution
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-01
Page 15
equipment in the distribution of appropriate numbers of replacement ties or
other
materials at each such location.
The method of the present invention could either use a central computer or the
use
location co-ordinates could be stored directly in the use location capture
module or the
m drop location detection module. Por example, while one of the elements of
the present
invention is that use location capture module and drop location detection
module are
physically separate equipment so that the operator of the use location capture
module
does not have to operate in close proximity to the distribution equipment and
drop
location detection module attached thereto, it may be the case that in certain
~s circumstances it is decided to implement the method of the present
invention using either
a use location capture module or drop location detection module which itself
had the
appropriate memory and computational characteristics to maintain a database of
some
type of all of the necessary use location co-ordinates and be able to
calculate the proper
location or co-ordinates of drop locations based thereon. I will be understood
that either
zo the use of a central computer to house and receive this information from
use location
capture modules and subsequently download that information to the drop
location
detection modules of one or more sets of distribution equipment, or
alternatively the
housing of that data directly on the use location capture module or the drop
location
detection module with the removal of the central computer from the method or
apparatus,
zs are both contemplated within the scope of the present invention_
Data stored in the location database in addition to the use location co-
ordinates for
individual replacement ties could be used for unrelated data analysis or
historical
purposes. As outlined above, the necessary software components to analyze the
contents
30 of the location database for the purpose of properly locating and
calculating the co-
ordinates of drop locations for varying quantities of railroad ties or other
materials are
also specifically contemplated within the scope of the present invention, both
in terms of
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 16
s their overall method and apparatus as well as a separate business method or
software
embodiment.
The actual methodology used to determine the appropriate location of
individual drop
locations could take one of at least three forms. In the most basic
embodimcnt, drop
io locations could be selected based on individual sets of use location co-
ordinates, such that
there was an individual drop location and set of drop location co-ordinates
created to
correspond to each individual use location and its related use location co-
ordinates. The
second method which could also be used would be to effectively select drog
locations at
which to drop multiple quantities of railroad ties based on comparison of the
individual
is use location co-ordinates of the ties needing to be replaced such that the
optimum
location for dropping of multiple ties could be selected. For example, if a
number of
close or adjacent co-ordinates were held in the location database it may be
the case that it
was optimal to generate a single drop location and set of drop location co-
ordinates in the
centre of the are of those particular use location co-ordinates and basically
indicate to the
xo operator of the distribution equipment the proper number of ties, equipment
or material to
be dropped at that location.
The third and most adaptive method of selection of drop locations would likely
be some
combination of the two outlined above, wherein individual ties that were
further apart
as could be equated to individual drop locations of their own, and locations
where there
were a multiplicity or plurality of adjacent locations would result in the
generation of a
single set of drop location co-ordinates at which a multiple number of ties
could be
dropped.
3o Various types of user interfaces can be contemplated for a drop location
detection
module, with varying degrees of complexity.
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-01
Page 17
s The tie distribution equipment or machinery itself may be further equipped
with a load
cell or some other method of counting the ties which have actually been
distributed, in
order to provide comparative data to the operator of the machine and/or
provide
effectively a method of counting the ties which have been distributed for
comparison to
the required numbers.
io
It is also contemplated that either a slave display or a more elaborate
secondary drop
location detection module could be used in the power unit or locomotive of the
train or
equipment used to distribute the replacement ties and, effectively, what the
slave display
or the secondary drop location detection module would do would be to identify
to the
is operator of the locomotive, who would in all likelihood be a second
operator from that of
the distribution equipment, when the distribution equipment was properly
located at the
co-ordinates of a drop location so that the train could be stopped in the
appropriate place
for the operator of the actual distribution equipment to drop the required
number of ties.
Either the use of a simple secondary display slaved to the primary marking
module used
zo in the distribution equipment could be contemplated, or a separate GPS
enabled
secondary drop location detection module which would either, based on
communication
with the primary drop location detection module or alternatively by virtue of
some
manual setting, apply the appropriate distance offset to the co-ordinates in
question could
also be used to properly locate the train in relation to the distribution
equipment at the
zs drop locations.
The equipment of the present invention could either be built into new railroad
maintenance equipment or could be built in such a fashion that it could be
retrofitted to
existing equipment. With respect to the use location capture module, for
example, that
3o could be built into some type of a track evaluation device or some other
device or vehicle
which is used by a track maintenance employee to assess and identify ties to
be replaced.
Alternatively, that could be built as some sort of a portable or handheld
module where
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-0!
Page 18
s track employees still walked along the track to identify ties to be
replaced.
Similarly, the drop location detection module to be used in the tie
distribution equipment
could either be built into the cab electronics of the equipment in question or
could
alternatively be built in a retrofittable fashion.
io
DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS:
While the invention is claimed in the concluding portions hereof, preferred
embodiments
is are provided in the accompanying detailed description which may best be
understood in
conjunction with the accompanying diagrams, where like parts in each of the
several
diagrams are labelled with like numbers, and where:
Figure 1 is a diagram showing the profile of a section of railroad track in
which a
zo plurality of railroad ties require replacement;
Figure 2 is a system diagram showing one overall embodiment of the system of
the present invention;
zs Figure 3 is a flow diagram demonstrating the general steps of the method of
the
present invention;
Figure 4 is a block diagram of one embodiment of a data capture module of the
system of the present invention;
Figure 5 is a block diagram of one embodiment of a central computer of the
system of the present invention;
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-01
Page 19
Figure 6 is a block diagram of one embodiment of the distribution equipment of
the system of the present invention;
Figure 7 is a block diagram of one embodiment of the location distribution
to monitoring hardware on the distribution equipment of the system of the
present
invention;
Figures 8A and 8B show two sample embodiments of an operator interface of the
drop location detection module of one embodiment of the system of the present
is invention; and
Figure 9 is a system diagram showing one embodiment of the system of the
present invention demonstrating the integrated control of distribution
equipment
using a plurality of drop location detection modules.
zo
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE ILLUSTRATED EMBODIMENTS:
As required, detailed embodiments of the present invention are disclosed
herein;
a however, is to be understood that the disclosed embodiments are merely
exemplary of the
invention, which may be embodied in various forms. Therefore, specific
structural and
functional details disclosed herein are not to be interpreted as limiting, but
merely as a
basis for the claims and as a representative basis for teaching one skilled in
the art to
variously employ the present invention in virtually any appropriately detailed
structure or
3o method.
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 20
s Prior art:
The method which has been used in the prior art in terms of replacement of
ties
constitutes a three-pass approach. Firstly, a marking crew or a sighting crew
comes along
the track and marks particular railroad ties which are to be replaced -
typically with a
to splash of paint or the like. In a second pass, another crew comes along the
track behind
them and, using the marks that the marking crew has generated, drops the
appropriate
numbers of ties in position. They are then followed in a third pass by the
actual tie
replacement equipment which will actually take the new ties which are staged
in position
along the railroad right-of way and replacement in the proper places under the
rails where
to the ties are marked for replacement. Subsequently, another crew may follow
along
directly behind or in a fourth pass and pick up the spent or used railroad
ties which are in
position by the track on the opposite side of the right-of-way.
The limitation of the prior art which is addressed by the present invention is
that the
zo present system and method overcomes the limitations of, for example, a
banding-type
method for distribution of replacement ties or materials where predetermined
set
quantities of ties or materials were required to be distributed at the
appropriate
determined locations.
zs The collection of the used railroad ties is not directly relevant to the
method of the
present invention, although the use location data which would be maintained by
the
system of the present invention could also be used by a following crew picking
up the
used ties to more quickly speed between locations where ties to be picked up
from the
right-of-way as well would be found.
GPI:,
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 21
The system of the present invention 1 in many embodiments is contemplated to
use a
satellite based global positioning system (GPS) 2 to record or identify the
geographical
coordinates of certain locations. The GPS 2 includes a satellite constellation
3
comprising a number of individual satellites whose positions are continuously
monitored.
io The satellites transmit signals, including positioning data, which can be
received by either
fixed position differential GPS stations or by GPS receivers such as a mobile
GPS
receiver.
It will be understood that the specifics of the GP5 receiver used in the
method of the
zs present invention will not affect the operation of the present invention
and insofar as this
is the case it is intended that any and all such variants on a GPS system to
be used are
contemplated within the scope of the present invention.
It is also contemplated that a different type of a GIS system altogether from
GPS could be
zo used to capture or define location data for the replacement of ties or
other materials in
accordance with the method of the present invention and that the use of any
other such
GIS type system in place of GPS positioning will also be contemplated within
the scope
of the present invention.
zs The other GIS or mapping systems and methods which are contemplated as
practicable in
terms of locating or identifying certain locations on or in proximity to a
portion of
railroad include the use of a system which can measure the location in
relation to a fixed
point on the track itself - for example, a measuring module could be 'zeroed'
or
calibrated to a certain reference point on the railroad and locations could
then be
3o identified by measuring, mechanically or otherwise, the distance of travel
of the
measuring module along the tracks. For example, one or more reference points
could be
selected along the relevant portion of railroad track and the coordinates for
certain
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-01
Page 22
s locations could then be captured or expressed in, for example, feet or
metres from the
reference point, rather than in specific geographically referenced GPS
coordinates. It will
be understood that the alternate method of measuring and marking locations
along a
section of railroad track comprising measuring the distance of a particular
point or
location along the distance and direction of travel on the railroad track from
a
to predetermined reference point, and any and all necessary and attendant
modifications to
the remainder of the system and method of the present invention, as would be
obvious to
one skilled in the art, are contemplated within the scope of the present
invention.
Yet another method of measurement or location of certain points in relation to
the
is railroad would be to measure the locations in some other way than by the
measurement
along the track itself from a fixed reference point. For example it is
contemplated that
another method of identifying certain locations might be to count the number
of ties for
example, from a calibrated or selected reference point along the railroad
track, and the
locations could be selected or identified in this fashion. Again it will be
understood that
Zo the alternate method of measuring and marking locations along a section of
railroad track
comprising counting the number of ties or another similar repetitive and
'countable' track
feature along the distance and direction of travel on the railroad track from
a
prodetetmined reference point, and any and all necessary and attendant
modifications to
the remainder of the system and method of the present invention, as would be
obvious to
zs one skilled in the art, are contemplated within the scope of the present
invention.
Other methods of determining the location of certain use or drop locations, as
will be
further described herein, might also be selected by one skilled in the art.
Insofar as such
other methods of measurement or identification of particular locations on or
in proximity
3o to a railroad track result in the ability to capture a set of coordinates
or measurements
which will allow for the subsequent relocation of a particular spot, any and
all such
measurement methods and attendant modifications to the method of the present
invention
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
FBr.K 1490-13-01
Page 23
are also contemplated within the scope hereof.
Overall, one of the main advantages to the method of the present invention is
that one or
more operators of location capture devices will be able to work separately,
independently
and at their own speed both from each other as well as from the actual
following
io distribution or maintenance equipment which is distributing the ties or
other materials in
question. In a networked implementation of the method of the present
invention, it will
be understood that, for example, numerous crews in charge of simply
identifying ties or
materials to be replaced could each have a use location capture module and
could go
along their way marking use locations and the use location co-ordinates
captured by the
is one or more use location capture modules could then be uploaded to a single
central
database. From the central database, one or more drop location detection
modules or
distribution equipment equipped with location marking capabilities as outlined
herein
could download subsets of information from the central database and follow
again along
at their own speed performing their respective individual maintenance
functions.
w
Materials to be distributed in accordance with the method of the present
inyention:
As will be outlined in further detail elsewhere herein, the system and method
of the
zs present invention is designed to be used to distribute various materials
along a section of
railroad track, including railroad ties or other replacement materials.
It is particularly contemplated that the method of the present invention will
be useful in
railroad maintenance applications and specifically in the distribution of
replacement
so railroad ties along the railroad right of way for subsequent installation.
However, it is
also contemplated that there could be found other similarly useful ways to
employ the
system and method of the present invention with the attendant modifications
primarily to
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-01
Page 24
s the distribution equipment. For example, ballast might be placed at
locations along the
right of way for subsequent use, or other types of materials even including
rail sections or
the like could all be distributed in accordance with the method of the present
invention.
io Use and drop location overview:
For the sake of illustration of the method of the present invention, it is
posited that the
method will be used to distribute replacement railroad ties along a section of
railroad
track for subsequent replacement. As outlined elsewhere herein, railroad tie
replacement
is equipment which is used in such maintenance applications typically does not
have
storage for large numbers of replacement ties and as such it is typically
desired to place
the ties to be used in replacement applications along the railroad right of
way in advance
of the arrival of the track and tie maintenance equipment so as to have all of
the
necessary quantities of materials in place where and when they are needed.
zo
Figure 1 demonstrates a section of railroad track in which railroad ties
require
replacement. This figure is intended to provide the ability to demonstrate
both flexibility
of the present invention as well as the limitations of the prior art.
zs For the sake of description herein and throughout, the location of a
particular railroad tie
to be replaced 28 is a use location 25. At each point that one or more
railroad ties is
required for use or replacement purposes, that would constitute a use location
25. For
example, if five railroad ties are needed to be replaced, there would
effectively be five
use locations, either in close or not so close proximity depending on how
close those ties
3o needing to be replaced were to one another. If the materials being
distributed for use
were something other than railroad ties it will be understood that the
location at which
they will be used is still referred to as a use location.
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 25
A use location 25 could correspond to a single tie or quantity of material to
be
distributed, or could alternatively correspond to a multiple quantity of ties
or materials.
This might depend on the proximity of the places in which the ties or
materials need to be
used - for example if five ties in row needed to be replaced, a single use
location 25
io might defined at which a multiple quantity of five ties were to be placed,
or alternatively
each tie to be replaced could me marked as a single use location in which case
five use
locations 25 would be defined, at each of which a singular quantity or
singular tie was
required.
is The second piece of location-specific terminology which is required for the
description of
the method and system of the present invention is the concept of the drop
locations 26,
which are also shown in Figure I. A drop location 26 is a location at which
the necessary
ties or materials for one or more use locations 25 are to be dropped. Three
drop locations
26, more specifically lettered 26A, 26B and 26C, are shown in Figure 1. The
drop
20 locations 26, as will be understood further below, might correspond each
directly to a
single use location 25. However, as will be understood from the further detail
below, a
drop location 26 could also correspond to more than one use location 25 -
where for
examplc six adjacent railroad ties needed to be replaced and had each been
marked as
single use locations, it would be potentially more convenient, within the
reach of the tie
is replacement equipment itself, to simply drop six replacement ties at a
single drop location
26 rather than dropping them at six more specific adjacent drop locations 26,
which
would in effect be side by side in any event.
There is shown in Figure 1 a railroad track 27 which is comprised of a pair of
rails with a
3o plurality of ties placed in ballast thereunder. As a railroad maintenance
task, from time to
time certain of the ties need to be replaced. In this particular case, the
track demonstrated
in Figure 1 has been marked with a number of ties requiring replacement, using
the
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-01
Page 26
numeral 28 for ties to be replaced, for the sake of demonstrating the concept
of the
present invention and the limitations in the prior art.
It can be seen, for example, in the track section 27 that the ties to be
replaced 28 are not
evenly spaced and, for example, there is at least one section where five or
six ties in close
io proximity all need to be replaced, and other sections, spaced apart by the
divisions shown
in the track section for demonstrative purposes, where only one tie at a time
may need to
be replaced. The limitation of the banding method in the prior art described
above in the
background of the invention was that the railroad ties, even though they could
be mapped
for distribution to particular locations, needed to be distributed in preset
batches such as
~s the number of fifteen or the like, banded together in one large batch. This
is not optimal
in terms of distributing the right number of ties in a situation either where
only a very few
ties are required or where a large number that is not a multiple of the number
in the
batches is required. Referring again to Figure 1, the use of a batch of ties
banded for
example in groups of five, would be only partially useful at drop location
26A, since six
zo replacement ties are required at that location. Dropping ties in multiples
of five would
result in either one too few or four too many ties being at that location if
either one or two
bundles of five ties each were dropped at location 26A, Conversely and
similarly, at
location 26B only two replacement ties are required. As such, if a banded
group of five
ties were dropped there, there would be three too many ties.
The system and method of the present invention is intended to allow for the
adaptive
selection of drop locations 26 and the appropriate quantity of ties and/or
other materials
to be dropped at each drop location 26. As is shown in Figure 1, there are ten
ties to be
replaced 28. One of these ties corresponds to each of the use locations 25A
through 25J
3o respectively.
The next item which is shown in Figure 1 for reference purposes is the
grouping of the
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-OI
Page 27
s tics to be replaced. In this particular case, there are four drop locations
26A through 26D,
which are lettered in the figure. Drop location 26A corresponds to six
adjacent railroad
ties requiring replacement, whereas drop location 26B corresponds to two
railroad ties
which are close or adjacent to each other requiring replacement, and locations
26C and
26D each correspond to single railroad ties requiring replacement at varying
positions
io along the track section 27.
Use location coordinates:
is For the operation of the method of the present invention, each use location
at which ties
or other materials are eventually required for use must be able to be located,
either
geographically or in relation to the railroad track. The specific location of
the use
location as would be captured and used by the remainder of the system of the
present
invention is referred to herein as a set of use location coordinates. The use
location
Zo coordinates corresponding to a particular use location might, in the case
of a GPS enabled
system in accordance with the invention, be a set of GPS coordinates at which
the capture
of a use location was triggered in accordance with the system of the present
invention.
In other embodiments of the invention where other types of measurement or
location of
is use locations are used, such as the two methods outlined in summary fashion
above
where a use location is located by measuring the distance of travel along a
particular
railroad track from a predetermined reference point, or where a location is
determined by
for example mechanically counting the number of ties or some other track
feature to
determine the location of a use location so that the search for that location
could later be
3o replicated based on the measurement, which would be captured as a use
location
coordinate. In either case, any type of a mapping or measurement solution that
results in
the pinpointing of a use location on or in proximity to the railroad track is
contemplated
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-01
Page 28
s within the scope of the present invention.
Drop location coordinates:
to Each drop location at which ties or other materials are to be deposited by
the distribution
eduipment must be able to be located, either geographically or in relation to
the railroad
track. The specific location of the drop location as would be calculated and
used by the
remainder of the system of the present invention is referred to herein as a
set of drop
location coordinates. The drop location coordinates corresponding to a
particular drop
is location might, in the case of a GPS enabled system in accordance with the
invention, be
a set of GPS coordinates.
In other embodiments of the invention where other types of measurement or
location of
drop locations are used, such as the two methods outlined in summary fashion
above
zo where a drop location is located by measuring the distance of travel along
a particular
railroad track from a predetermined reference point, or where a location is
determined by
for example mechanically counting the number of ties or some other track
feature to
determine the location of a drop location so that the search for that location
could later be
replicated based on the measurement, which would be captured as a drop
location
is coordinate. In either case, any type of a mapping or measurement solution
that results in
the pinpointing of a drop location on or in proximity to the railroad track is
contemplated
within the scope of the present invention. Drop locations will typically be
calculated
rather than captured, in accordance with the present invention, but could also
from time
to time be marked or captured as well by the use location capture module.
so
Overview of system components and orreration:
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O 1
Page 29
Figure 2 demonstrates the essential components of the system 1 of the present
invention.
The system 1 of the present invention is basically a railroad tie distribution
system which
allows for the adaptive distribution of varying quantities of railroad ties or
other materials
at varying locations along a railroad right of way for use in subsequent
railroad
io maintenance applications.
A GPS-enabled use location capture module 4 is used to mark or otherwise
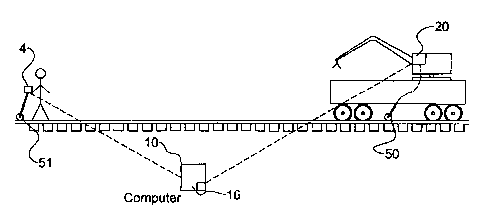
capture the
coordinates of specific railroad ties requiring replacement and to capture the
coordinates
of these ties requiring replacement on the use location capture module 4. The
location of
is each of these ties or groups of ties needing replacement are use locations,
as that term is
described elsewhere herein, and the coordinate of each of the use locations
are use
location coordinates, as described elsewhere herein.
As will be discussed in further detail below, the use location capture module
4 is
zo effectively contemplated to be a portable or handheld size device with a
GPS receiver
which can, upon pressing a button or some other user intervention, capture a
GPS fix, the
GPS coordinates captured being the use location coordinates corresponding to a
particular use location 25 as outlined in Figure 1 above. As the use location
capture
module 4 is used to capture multiple sets of use location coordinates those
use location
a coordinates are cached in the memory of the use location capture module 4
until they can
be uploaded to a central location database.
In the embodiment show in Figure 2, the central location database in which the
use
location coordinates are uploaded or stored is shown resident on a central
computer 10.
3o The central computer 10 which contains a location database lb is used to
store the
location data captured by the use location capture module 4 and can also be
used to
compute or determine the appropriate drop locations for quantities of railroad
ties.
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-01
Page 30
Also shown is the tie distribution equipment 17 which will include a drop
location
detection module 20 {also known as a location marking module) which contains
the drop
location coordinates and drop location quantities for the dropping of various
quantities of
railroad ties or materials. As shown the distribution equipment 17 will also
be GPS
io enabled so that fhe GPS location of the distribution equipment 17 can be
related to the
various drop location coordinates stored on the drop location detection module
20 and the
operator of the equipment 17 can be notified at the appropriate time when a
drop location
is reached to drop the requisite number of railroad ties on the right of way
at that location
so they will be closely located to their eventual use locations when the
following
is maintenance equipment shows up.
Figure 2A demonstrates another alternate embodiment of the system of the
present
invention which shows how a different method of measurement of the location of
use
locations and drop locations could be accomplished. Rather than a GPS-based
system
so shown in Figure 2, Figure 2A shows a use location capture module which has
a
measurement wheel attached thereto, which as the individual or for that matter
equipment
to which the locations capture module 4 is attached moves along the track, the
measurement wheel can measure the distance travelled by the wheel from some
particular
fixed point on the railroad. The fixed point on the railroad is now shown
here, but could
Zs be any sort of a milepost, landmark or otherwise. As the measuring wheel
rolls along the
track, and it was desired to mark the position of the use location, the
measuring wheel
distance travelled would be recorded by the remainder of the use location
capture module
4. The measuring wheel is shown at 51.
3a In the embodiment shown in Figure ZA, again the use location coordinates
are uploaded
to a central computer 10 with a database 16 therein. Again, as will be
outlined elsewhere
herein, there are other system typologies which could be contemplated which
would
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490- l 3-O 1
Page 31
s eliminate the need for a central computer 10 and rely upon direct
communication
between the use location capture module 4 and the drop location detection
module 20.
Continuing on with Figure 2A, however, the second portion of the track
measurement
method which is contemplated is demonstrated where the distribution equipment
shown
io in Figure 2A, in addition to the drop location detection module 20,
includes a
measurement wheel 50 attached to the equipment and operatively connected to
the drop
location detection module 20 such that again the distance along the track from
a fixed
point can be measured and documented or accessed or used by the drop location
detection
module 20, and on that basis the use locations previously marked using the use
location
is capture module 4 can be replicated or identified again simply by measuring
along the
same track the same distance from the same reference point. It will be
understood that
various changes to some of the remainder of the method of the present
invention would
be required to practice a measurement method such as this for the capture of
use location
coordinates, rather than using a GFS receiver and capturing fixed GFS fixes
with respect
so to use locations, but all such necessary changes to implement this would be
obvious to
one skilled in the art and are contemplated within the scope of the present
invention.
Referring to Figure 3, there is a shown a flow diagram of the method of the
present
invention for the adaptive distribution of railroad ties or other materials in
railroad
is maintenance applications. Effectively, the method capturing use location
coordinates for
uploading to a central storage location and subsequent download to a
distribution
machine. Drop locations for quantities of ties or materials are determined by
the software
of the system of the present invention to optimize the placement of various
quantities of
materials or ties along the railroad right of way. The distribution equipment
can then in
so turn use the drop location data generated to properly distribute the proper
quantities of
materials.
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 32
s Reviewing the flow chart of Figure 3 in further detail, the following can be
seen. The
first step in the process is to capture the co-ordinates of each use location
25. These are
use location coordinates 37. At the most detailed level each tie requiring
replacement is a
separate use location 25 having its own coordinates 37. Where the coordinates
of two
adjacent ties to be replaced overlap, then the two use locations 25 might
constitute a
io single use location 25 at which two ties were required to be dropped. This
overlap or
possibility is also accommodated by the method of the present invention.
As will be outlined further herein, with respect to the equipment and
apparatus of the
present invention it is contemplated that the capture of the use location data
at Step 32
is will be done using some type of a use location capture module 4 which
includes a GPS
receiver 5 which can effectively generate the necessary co-ordinates for each
use location
25 for storage in the memory of the use location capture module 4. The use
location
capture module 4 could be any type of a device with the proper instrumentation
to
measure or capture the coordinates of a use location upon the triggering of
such a capture
zo by the operator.
The interface of the use location capture module 4 might also allow for manual
overndes
or the like from the operator so that the operator could somehow tag along
with the co-
ordinates of a particular use location 25 for example that three ties rather
than one needed
as to be dropped at that location. This is a logical extension of the use
location data and the
method of the present invention and any necessary changes to the method,
apparatus or
software of the present invention which would be required to accomplish this
will be
understood by one skilled in the art to be contemplated within the scope
hereof.
so One of the other limitations of the prior art, even where GPS has been used
in the past to
effectively tag the drop zones for banded quantities of railroad ties is that
the equipment
used to do the tagging has also been required to be physically present at the
dropping of
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-01
Page 33
s the material. Basically, a data capture module is used in those prior art
methods which
can tag in its own memory a particular set of GPS co-ordinates, but it was
then necessary
for that device to be physically present on the distribution train, for
example, and it would
effectively beep back or otherwise notify the operator when it reached again
in its display
mode the same co-ordinates that had previously been tagged in its memory. One
of the
io limitations to this, of course, is that the marking crew or the data
capture or acquisition
crew who are marking the drop locations for their predetermined numbers of
ties is
required to only work as fast as the speed of the actual distribution train
following along
behind. This is a significant time and cost problem since the data capture
crew may, in
all likelihood, be able to work fairly quickly and may be able to effectively
travel over an
is entire railroad and accomplish their data capture function or tie marking
function in the
same amount of time which is taken by the tie replacement crew or the
distribution crew
to do a much lesser number of miles or kilometres of the overall maintenance
requirement. This is another issue which is intended to be addressed by the
system of the
present invention.
Referring to Figure 3 the second stage which is shown in that flow chart after
the capture
of the use location data, including the use location co-ordinates 37 for each
location at
which ties are required to be used shown at Step 32 again in Figure 3, is to
upload that
use location data 37 from the use location capture module 4 to a central
computer 10 for
2s storage in a location database 16. It will be understood that any number of
different
methods of communication between the use location capture module 4 and the
central
computer 10 which would result in the uploading of use location co-ordinates
37 and any
other related data from the use location capture module 4 to the location
database 1G
stored within the central computer 10 will be contemplated within the scope of
the
3o present invention.
It is also contemplated that in certain embodiments of the system of the
present invention
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 34
s the necessity for a central computer might be eliminated by having the use
location
capture module 4 and the drop location detection module, to be discussed
forthwith,
communicate directly with each other. The central location database of use
location
coordinates could for example be stored in the use location capture module 4
and be
accessed directly by the drop location detection module when the download of
certain
to subsets of use location data were required. Alternately or conversely, the
central location
database could be stored on the drop location detection module and the use
location
coordinates captured by the Location capture device 4 could be uploaded for
storage to the
central location database on the drop location detection module on either an
offline or
real-time basis. In either such circumstance, the software for the generation
of drop
is locations and drop location coordinates could be resident upon either the
use location
capture module 4 or the drop location detection module, rather than on the
central
computer, and all such configuration and communication changes as would be
necessary
to implement this change in the system of the present invention are
contemplated within
the scope hereof.
The next step in the process which is shown at Step 34 is the computation of
the drop
locations 26 based upon the use location co-ordinates 37 for each of the use
locations 25.
This could either be done in the central computer 10, or could also be done in
the use
location capture module 4 in advance of uploading the information or
alternatively could
as also be done by the drop location detection module 20 on distribution of
the ties. In any
event, as is shown at Step 34 in Figure 3, the appropriate location of the
drop locations 26
is computed. It will be understood that the necessary geographical information
both with
respect to the individual use Location co-ordinates 37 acquired by the use
location capture
module 4 as well as any other background geographical information such as
track layout
so or other general GPS or mapping information which might be required would
also be
contained within the location database 16 or elsewhere such that the
appropriate
calculations could be made to determine the appropriate drop location co-
ordinates 38 for
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 35
individual drop locations 26.
The key to the method of the present invention is that the numbers of ties or
materials to
be dropped at a particular drop location, as well as the spacing or location
of the drop
locations themselves, is flexible so that the materials to be distributed can
be placed in
to optimal positions along the railroad right of way for their subsequent use.
Depending
even upon the type of materials being distributed it may be the case that
there were
different preferences or rules applicable to the distribution of such
materials, and that the
incorporation of these local preferences or rules into the software
determining the
appropriate drop locations would also be contemplated within the scope of the
present
is invention and would certainly enhance the accuracy and utility of the
system to the end
user.
In the simplest embodiment of the location marking method of the present
invention,
each use location 25 would correspond to a drop location 26, so that
effectively each set
zo of use location co-ordinates 37 would be rendered into a corresponding set
of drop
location co-ordinates 38 for download and use by the drop location detection
module 20
in due course alongside the remainder of the distribution equipment 17.
Effectively, a
single tie location would be a single drop location, and ties would be dropped
individually at each required location.
is
In a more elaborate calculation methodology, however, the central computer 10
and its
attendant software components could use the use location co-ordinates 37
stared in the
location database 16 along with whatever remaining information or formulas
were
required to identify optimal drop locations 26 based upon the proximity of
different sets
so of use location co-ordinates 37. For example, referring to the sample
section of track in
Figure 1, the computer could calculate that of the railroad ties to be
replaced, the first six
lettered 25A through 25F were located in such close proximity to each other
based on the
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-01
Page 36
s individual use location co-ordinates 37, that a single drop location 26
could be used and,
as such, the drop location co-ordinates 38 for that drop location could be
calculated to be
in proximity to all six of those ties and the drop location co-ordinates 38
would then
simply also include the additional data for the distribution team that six
ties rather than
one were to be dropped at that particular drop location 26A.
io
Once the drop locations 26 had been computed by the central computer 10,
either in the
more elaborate method outlined above or alternatively even by simply
transposing the use
location data 37 where ties were to be distributed at drop locations on a one-
to-one basis
with use locations 25, that information would be stored in the location
database 16 until
is required by the distribution equipment 17 at which point it could be
downloaded. The
downloading of drop location data or co-ordinates 38 to the distribution
equipment 17 is
shown at Step 35 in the flow chart of Figure 3. Again, as was the case with
the use
location capture module 4 and its upload capability to the central computer
10, it is
similarly contemplated that the drop location detection module 20 or related
electronic
zo equipment used in association with the distribution equipment 17 could
similarly
download drop location co-ordinates and data 38 from the location database 16
in the
central computer 10 via some type of an interface, whether that be by
telephone,
hardwire, Internet or the like. All such methods of communication are
contemplated
within the scope of the present invention. It could even by the case that the
distribution
z,s equipment 17 and the drop location detection module 20 contained some type
of a
cellular telephone or some other type of wireless capability so that on an
ongoing basis
the distribution equipment 17 could remain in contact or communication with
the location
database 16 on a more up to date basis.
3o With the drop location co-ordinates 38 downloaded to the drop location
detection module
20 the only task remaining, as shown at Step 36 in the flow chart of Figure 3,
is the actual
distribution of replacement ties or materials. Effectively, the drop location
detection
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-0I
Page 37
s module 20 is contemplated to include a GPS receiver 21 which would allow the
operator
of the distribution equipment 17 to know when a particular set of drop
location co-
ordinates 38 were reached which corresponded to a drop location 26 and at
which one or
more railroad ties or other materials were to be dropped.
ie It will also be understood that while the method of the present invention
is disclosed
herein in relation to the use of manual labour or supervision in the
distribution of the
railroad ties - for example, there still needs to be an operator of the train
or of the tie
distribution machine 19 to distribute the ties to the railroad right-of way -
it will also be
understood that this could be employed in an entirely automated circumstance
and any
i5 such additional modifications to the method of the present invention are
contemplated
within the scope hereof.
In any event, to relate the distribution Step 36 again to the fictitious or
sample track
section shown in Figure l, as the distribution equipment 17 moves down the
track 27, at
za each drop location 26A through 26D the appropriate number of ties would be
notified to
the operator and dropped at that location. This adaptive and flexible method
of
distribution of railroad ties or other materials is able to enhance the
efficiency of the tie
distribution process and overcome many limitations both in terms of cost and
time effort
expended in this process in the prior art.
zs
Identifvine ase locations:
Figure 4 shows one embodiment of the use location capture module 4 of the
present
3o system and method. The essential components of a use location capture
module 4 are a
GPS receiver 5 which is capable of receiving GPS co-ordinate information from
the GPS
system 2. Another component of the use location capture module 4, in addition
to the
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 38
GPS receiver 5, is a memory 8 which is capable of storing particular use
location co-
ordinates 37. Beyond the memory 8 and the GPS receiver 5, there is an upload
interface
9 from which the use location capture module 4 can upload use location co-
ordinates 37
from the memory 8 to the central computer 10. As is discussed in more detail
herein, the
central computer 10 can be equipped to communicate with the use location
capture
to module 4 in any type of physical fashions or using a number of different
protocols, and
any method which accomplishes the objective of transferring the use location
co-
ordinates 37 from the memory 8 of the use location capture module 4 to the
central
computer 10 is contemplated within the scope of the present invention.
is The use location capture module 4 also has a user interface 7 of some type,
which would
be used by an operator of the device 4 to instigate the capture of a
particular set of use
location co-ordinates 37. The user interface 7 of the use location capture
module 4 might
be something as simple as a button on the face of the device which, when
pressed by the
operator, would cache the GPS co-ordinates at that present time as a set of
use location
zo co-ordinates 37. The interface 7 might be more elaborate than this as well,
allowing for
example the operator to manually override or increase the number of ties to be
provided
at a particular use location 25 or the interface 7 could also allow for
additional
information to be stored by the user or displayed to the user, for example
information as
to track condition or other types of information which could be used in other
applications
Zs to either view or assess track condition information or to distribute other
types of
materials. While the use location co-ordinates 37 for the sake of tie
distribution will
basically consist of a set of GPS co-ordinates, on the assumption that each
time a co-
ordinate is stored it corresponds to a single tie needing to be replaced, it
will be
understood that other extensions of the equipment could be conceived which
would or
3o would not be directly relevant to the method of the present invention, but
could in any
event enhance the overall functionality of the maintenance function again and
might be
desirable by railroads on this basis.
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 39
The use location capture module 4 could be directly integrated into some type
of a tie
marking module or vehicle. As has been indicated herein, typically what has
been done
in the past is the ties that are to be replaced 28 are marked in some visual
fashion,
typically with a splash of paint or the like, for the tie replacement
equipment to follow on
to to know which ties to replace. It might be the case that a simple machine
could be
developed which would, at the same time as applying this marking to the tie,
capture the
use location co-ordinates 37 corresponding thereto.
Any embodiment of a use location capture module 4 which accomplishes the goal
of
is capturing and caching the GPS coordinates of use locations for use in the
method of the
present invention will, it is understood, be within the scope of the claimed
invention.
If a method other than GPS marking was used to locate use locations, such as
the
methods of measurement of locations along the track outlined herein, the
necessary
zo changes could be made to the general type of use location capture module 4
outlined
herein to accommodate any such different measuring or capture method and all
such
changes are contemplated within the scope of the present invention. For
example another
method of marking use locations as has been described herein would be to
effectively
measure the distance of particular use locations along the track from a fixed
or
zs predetermined base point or 'zero point' - for example, a particular
crossing or marking
on a train track could be chosen as the fixed base point, and the use location
capture
module 4 could then be attached to a measuring device which would travel along
the train
track as the user or operator of the module 4 moved along the tracks {perhaps
on a track
speeder or the like) - it is contemplated that such a mechanical or electronic
sensor or
3o measurement device could then provide to the remainder of the use location
capture
module 4 the accurate measurement of distance from the fixed base point to a
particular
use location along the train track. To later find the same location, a drop
location
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-01
Page 40
s detection module and distribution equipment could travel along the same
track and
measure the same distance from the fixed base point to locate the use location
or
locations in question. It will be understood that any necessary modifications
to the
system or method of the present invention to accommodate this means of
selecting or
measuring use locations by measuring the distance to a use location along the
track from
io a fixed base point is specifically contemplated within the scope of the
present invention.
In such an embodiment, the measurement of distance along the track from the
fixed base
point to the use location would constitute the use location coordinates in
respect of that
particular use location.
a
It is also contemplated that the use location capture module 4 might allow for
the user to
manually designate a particular drop location - while it is contemplated that
the method
of the present invention would typically include the step of optimally
selecting the drop
locations on an automated basis based on the use locations and other rules or
formulae
zo within the system of the present invention, the use location capture module
4 could allow
for the designation of a specific drop location. In an embodiment of the
present invention
it is specifically contemplated that such a use location capture module might
be a PDA or
other portable electronic device with a more intricate user interface, in
which case the
software in that device could allow for the designation of a particular drop
location or
zs locations by the user, and the system could automatically match up a
selection of use
locations to this predetermined or specified drop location, or the interface
of the use
location capture module 4 could also provide for the ability to have the user
match up a
specifically marked drop location to one or more specific use locations. Where
a PDA or
the like was used for a use location capture module 4, the PDA or other unit
would
3o simply need to have a GPS receiver attached thereto or be otherwise
instrumented to
allow for the measurement or location of use locations and the capture of the
coordinates
of such locations as outlined otherwise herein.
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-01
Page 41
Centr$1 computer:
Figure 5 is a block diagram of one preferred embodiment of the central
computer 10 of
~o the present invention. The central computer 10 includes a CPU 11 and a
memory system
12. The use of a CPU 11 in conjunction with ROM, RAM, disk-based storage
devices
and the like and a clock circuit is well know to those skilled in the art of
CPU-based
electronic circuit design. The central computer IO as referred to herein means
the
combination of memory and storage devices used to retain data within the
computer 10.
is
The central computer 10 also includes one or more communication ports, two
being
shown here at 13 and 14, which are used to communicate with devices outside of
the
computer I0. Specifically, a location capture upload interface or port 13
could be used to
communicate with one or more use location capture modules 4 in order to upload
use
zo location co-ordinates 37 from the use location capture modules 4 to the
location database
16 hosted by the central computer 10 in its memory 12. Secondly and similarly,
a
distribution download interface 14 can be used to communicate with one or more
drop
location detection modules 20 on various tie distribution equipment 17 to
download from
the central computer 10 and the location database 16 hosted therein the
necessary drop
2s location co-ordinates 38 to instruct the distribution equipment 17 properly
in location of
drop locations 26 for the distribution of railroad ties or other materials in
accordance with
the present invention.
It will be understood that the use location capture module 4 and the drop
location
so detection module 20 might also be equipped with the same protocol such that
a single
communications port rather than the two ports 13 and 14 which are shown could
also be
used. In particular, the ports 13 and 14 might be modems, network connections
or some
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 42
s other method or apparatus allowing for the transmission and receipt of data
by the
computer 10 with or from an external device.
As indicated, the central computer 10 hosts a location database 16, and in
addition it
would also potentially include processor instructions 15 which can be read and
executed
to by the CPU 11 where necessary to complete the storage of use location co-
ordinates 37
received from a use location capture module 4 or to otherwise compute the
location of
drop locations 26 and/or communicate drop location co-ordinates 38 which have
been
computed and/or stored in the location database lb to the drop location
detection module
20 on one or more sets of distribution equipment 17.
is
The central computer 10 would have, in addition to the data stored in the
location
database 16, which would be the use location co-ordinates 37 and drop location
co-
ordinates 38, the necessary software components or processor instructions to
allow fox
the proper computation or location of drop locations 26 and drop location co-
ordinates 38
ao upon receipt of use location co-ordinates 37 from one or more use location
capture
modules 4
It will also be understood that the central computer 10 could be removed from
the method
or system of the present invention without departing from the scope yr
intention hereof.
zs The benefit of having a separate central computer 10 containing the
location database 16
is that for example more than one use location capture module 4 and more than
one
distribution system I7 could be used an a network-wide basis by a railroad.
For example,
there could be more than one data. capture team out marking the use locations
25 with
more than one use location capture module 4, and there could be more than one
set of
3o distribution equipment 17 working on the railroad, and each of those sets
of distribution
equipment 17 could download the necessary size of batches of work to do at one
time,
and on this basis the use of a central computer 10 to host a location database
16 can be
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 43
s seen to be desirable. However, it could be the case that the use location
capture module 4
actually had the necessary software and hardware capabilities therein to, on
its own,
calculate the appropriate drop location co-ordinates 38 and/or could either
store the
location database 16 itself until it was accessed directly by the drop
location detection
modules) 20 to download information, or alternatively and conversely the use
location
io capture module 4 could communicate directly with the drop location
detection module 20
and upload the use location co-ordinates 37 from the memory 8 of the use
location
capture module 4 to a location database 16 hosted directly by the drop
location detection
module 20 in the place of the central computer 10.
is It will be understood that the direct interface of the use location capture
module 4 with
the distribution equipment 17 and its necessary marking module 20 is
contemplated
within the scope of the present invention, as is the addition of the central
computer 10 to
the present invention for the purposes of centrally maintaining all of the
necessary
information so that multiple units of either the acquisition type or
distribution type could
zo be used in varying locations or at varying speeds.
Location database:
Zs The location database 16 would be used to record the use location co-
ordinates 37 of
various use locations 25 identified by the user of one or more use location
capture
modules 4 interfaced with a central computer 10. As well as storing the use
location co-
ordinates 37, which might include not only GPS co-ordinates but also
quantities of
materials required at a particular use location 25 or other non-related
information, the
so location database 16 would also hold in a separate table or elsewhere in
its data structure
the calculated drop location co-ordinates 38 for each drop location 26 at
which materials
were to be distributed. The drop location co-ordinates 38 could be calculated
or prepared
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-01
Page 44
s by a software component resident in the central computer 10 upon receipt of
use location
co-ordinates 37 from a use location capture module 4.
Storage of the use location data such as the use location co-ordinates 37 or
the drop
location co-ordinates 38 in the location database 16 for later historical
analysis of
io maintenance requirements, ongoing maintenance tasks or the like is also
contemplated
herein.
The type of information stored in the location database 16 with respect to use
locations
25 or drop locations 26 could again vary in levels of complexity. At its most
basic level,
rs where each use location 25 was made to correspond to a single drop location
26, the only
information which might be maintained in the location database 16 would be the
use
location co-ordinates 37, which would be equated in the software to individual
drop
locations 2b and, as such, the use location co-ordinates 37 would also be used
by the
distribution equipment as the drop location co-ordinates 38_ As indicated,
there could be
zo other information stored with respect to each use location 25 or drog
location 26 in
addition to the GPS co-ordinates of that particular location such as
modifications or
numbers or quantities of materials required at an individual location or other
data
checking fields in the data structure or the like.
as As has been outlined above, the software components of the central computer
10, or in
the case that the use location capture module 4 or the drop location detection
module 20
is hosting the location database 16, then the software components resident in
and
exercising upon those particular machines, would be capable in the more
elaborate
adaptive method of the present invention of aggregating or calculating the
location of the
3o drop locations 26 by aggregating the use locations 25 that were in close or
adjacent
proximity. The software components that did this could, for example, identify
from
looking at multiple sets of use location co-ordinates 37 that they were in
close enough
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 45
s proximity that it would be more efficient to simply drop all of the ties or
materials
required at those number of locations at one drop location 26 and, as such,
one single set
of drop location co-ordinates 38 could be generated, rather than a plurality
of drop
location co-ordinates, and the drop location co-ordinates or date 38 could
simply include
the necessary information for the distribution equipment via the marking
module 20 tv
io know the particular proper number of ties ox materials to drop at that
location.
The method of calculation of these drop locations 26 where certain use
locations 25 were
going to be aggregated for batched or grouped material distribution could be
such that as
the use locations 25 got further apart the system would automatically laiow,
determine or
is ascertain based on the proximity of those use location co-ordinates 37,
using some type
of GIS system or formulas in place therein, that in those cases it was more
efficient to
drop the ties or materials individuaIiy at individual use locations 25 rather
than
aggregating the material for central distribution at an aggregated drop
location 26.
zo It will be understood that the precise nature or structure of the location
database 16 could
be any structure that could be properly managed by the central computer 10,
use location
capture module 4 or drop location detection module 20, wherever the database
was
resident in the system of the present invention.
zs It is specifically intended that the software and business methodology
outlined herein and
the program resulting therefrom, i.e. a program which can based upon a series
of map
coordinates of use locations for tie replacement, along with the related route
information
necessary being stored in the system, properly allocate or locate the
appropriate drop
locations for distribution of varying quantities of railroad ties or other
materials is
3o specifically claimed and covered.
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 4b
s Determining drop locations:
There are two different extreme material distribution methods which are
contemplated to
be workable within the scope of the present invention, and the combination of
these two
methods would also be workable and in fact may be the most desirable.
~o
The system could be used to either drop individual replacement ties or
quantities of other
materials at or very near to their individual use locations, since the data
which can be
captured can obviously be stored on an individual railway tie basis. As such
that
necessary information could be generated by the central computer and with the
is appropriate modifications to the distribution device itself or the user
interface thereof, the
tie distribution equipment I7 could simply move along the track and at each
individual
location where a tie was to be replaced, individual ties could be dropped.
The second method which could also be used or practised using the method and
apparatus
ao of the present invention would be to effectively select the appropriate
locations at which
to drop multiple quantities of railroad ties based on again the individual GPS
coordinates
of the ties needing to be replaced having been captured and stored in the
central computer
such that the optimal location for dropping of multiple ties could be
selected.
23 The method of selection of locations for distribution of railroad ties or
other materials
could also be effectively a combination of the method of dropping single ties
where
required, and the distribution of larger batches of varying sizes. An adaptive
distribution
model could be used where any number of required ties as was determined to be
most
efficiently or effectively placed or located could be used - i.e. single ties
could be
so distributed where optimal, and if there was a crossing or some other
location where a
larger number was required then the method could create or indicate to the
operator a
particular distribution location at which to distribute a larger number of
ties. It will be
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 47
s understood that this adaptive potential - i.e. the predetermined location of
distribution
locations for varying numbers of ties - could be changed in non-substantial
ways obvious
to one skilled in the art, and that all such variations on the method are also
contemplated
within the scope of the present invention.
io The central computer could determinc the optimal distribution locations and
numbers of
ties to be distributed at each location based upon whatever distribution
profile were
loaded therein, and the distribution locations could then be downloaded into
the drop
location detection module 20 on the distribution equipment 17 for use in the
distribution
of ties to the selected distribution locations. Factors ranging from the reach
or nature of
is the specific tie distribution equipment to be used, grade of the track or
right of way, speed
with which the equipment should reach the replacement ties etc. could all be
written into
the algorithms uscd to determine the optimal placement of drop Locations.
ao Commuter software:
One element of the system of the present invention is a computer software
component
which can be used to select the proper location or sites for drop locations 26
in
accordance with the method of the present invention.
zs
It is specifically contemplated with respect to the majority of the
embodiments
demonstrated in the figures herewith that the central location database 16
would be
located on a central server computer 10 which central server computer 10 would
be
capable of communicating with both the use location capture modules 4 and the
drop
30 location detection modules 20 of the broader system of the present
invention. Each of
those modules would be able to communicate with the central server computer 10
for the
sake of either uploading use location coordinates and data to the central
location database
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 48
s or alternatively for the sake of downloading drop location coordinates,
quantities and
other data from the central location database. It will, however, be understood
that overall
the method of the present invention could also be practised in the absence of
the central
server computer 10, whereby the central location database could be resident
either in the
use location capture module 4 or the drop location detection module 20 and the
necessary
io changes to the communication protocols between those two modules directly
could be
made so as to allow for the seamless operation of the method of the present
invention in
the absence of the central server computer.
In any event, it is contemplated that the Location selector software component
52 of the
~s system of the present invention will be a software component which, as
demonstrated,
would be resident upon the central server computer 10. The location selection
software
component 52 would choose the location or sites for drop locations 26 along
the portion
of railroad in question based upon the use location coordinates 37 stored
within the
central location database. Effectively, the location selector software
component 52
zo would access the central location database X and, based upon the use
location coordinates
37 stored therein, as well as the remainder of a profile saved within the
memory of that
software component or elsewhere in the central server computer, would select
the proper
locations alongside or in proximity to the railroad, being drop locations 26
at which
materials should be deposited. A drop location would be selected in respect of
each use
is location which was stored within the database. It rnay, as outlined
elsewhere herein, be
the case that each single use location was made Lo correspond to a separate
and single
drop location, or alternatively depending upon the settings in the profile on
the central
server computer and the proximity of the use location coordinates in respect
of each use
location to each other, the location selector software component 52 might also
in certain
3o cases choose to site one drop location 26 which would correspond to
multiple use
locations 25 and at which drop location 2b then a multiple quantity of
materials such as
railroad ties or the like would be dropped.
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 49
The location selector software component 52 could be resident on the same
processor or
computer unit as the central location database 16. For example, the central
server
computer 10 in the embodiments shown might not only be a host to the central
location
database 16, but also host or store and execute the location selector software
processor
to instructions 15 as well. It will also be understood, however, that the
location selector
software component and processor instructions could be resident upon either
the use
location capture module 4 or the drop location detection module 20 and that
the
calculation or determination of appropriate drop locations 26 could be
conducted by
either of those modules at their appropriate point of engagement in the method
of the
is present invention. For example, if the location selector software component
52 were
resident upon the use location capture module 4, the use location capture
module 4 upon
execution of these location selection processor instructions 15 and the
attendant profile
data used therewith, could determine the proper locations for drop locations
26 in
advance of storing all of the use location data as well as the drop location
data to the
zo central location database. In fact, in a situation where the use location
capture module 4
was determining the location of drop locations 26, it may not even be
necessary for the
central location database 16 to retain the use location data, since the only
information
which might in a very basic embodiment be important to the materials
distribution
equipment 17 would be the location of the drop locations 26 and presumably the
work
as crew which came along after the fact woe~ld know where the use locations 25
were that
corresponded to each drop location. It is contemplated that this could simply
be an
optional approach, however, and by and large both the use location data 37 as
well as the
drop location data 38 would likely be retained in the central location
database 16, both for
operational as well as historical purposes.
so
The location selection software component 52 could be located on the use
location
capture module 4, but could also alternatively be resident upon and executed
by the drop
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-01
Page 50
s location detection module 20. If the location selection software component
52 were
resident on the drop location detection module 20, the central location
database 16 might
also be located on the drop location detection module 20 or could still also
be stored on a
central server 10 or on the use location capture module 4. Again, it will be
understood
that so long as the location selection software component 52 were capable,
through the
zo particular module or computer on which it was resident, of accessing the
central location
database 16 on the module or computer on which it were resident, that the
method of the
present invention could be practised.
The location selection software component 52 of the present invention could
have a fixed
zs profile built into it which would basically consist of a fixed number of
formulas or
algorithms which could be applied to the various use location coordinates 37
and data
contained within the central location database 16 for the purpose of
determining the
proper locations for drop locations 26 and subsequently generating the drop
location
coordinates 38 and drop location quantities for use in the depositing of
materials at those
ao drop locations 26. It might also be the case, however, that the profile
itself which
determined the location of the sites would be customizable, either
automatically or
manually. For example, it might be the case that if the location selection
software
component 52 detected or determined that the use location coordinates 37
related to use
locations that were on average further apart rather than closer together, the
weighting of
zs the formulas in the equation which determined the location of drop
locations 26 could be
adjusted. It will be understood that this is only one type of an obvious
modification to a
static calculation or model for the location of drop locations 26 in
accordance with the
method of the present invention and any such similar formula adjustments or
the like
which would accomplish the result of adjusting the basis on which the location
selection
3o software component 52 of the present invention would determine the location
of drop
locations 26 and their attendant drop location coordinates 38 and drop
location quantities
are contemplated within the scope of the present invention.
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 51
Distribution ectuinment:
The next element of the system of the present invention is the actual supply
distribution
equipment 17. Normally what the distribution equipment 17 will comprise is a
train used
to to carry and subsequently drop or distribute railway ties or other
materials to their
appropriate locations along the railroad right-of way. This distribution
equipment 17
which is shown in Figure 6 consists of a work train containing one or more
gondola or
other railcars 18 for the carriage of replacement railway ties. Effectively,
either a road
rail power unit or a locomotive could be used to push or pull one or more such
tie
is transport cars 18 along the railway and the ties could then be removed from
these cars as
needed and dropped at their required drop locations 26.
In this particular case what is shown is a tie distribution machine 19 which
is capable of
effectively crawling along the top of a train and removing materials from the
cars for
zo placement along the trackside. Alternatively, this equipment could also be
used for other
railroad maintenance applications, but in this particular case it is
contemplated that this
type of car top crawling device would be of utility in the distribution of
railroad ties or
similar maintenance materials such as this. There are various other types of
equipment
which could be used to haul or drop ties at their required locations and all
such prior art
zs equipment or machinery is contemplated within the scope of that element of
the present
invention.
Drou location detection module:
While the use location capture module 4 is responsible for the acquisition of
the use
location co-ordinates 37, it is the drop location detection module 20 which,
when used in
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 52
association with the tie distribution machine i9, is responsible for the
indication to the
operator andlor for the distribution of the railway ties or other materials at
their
appropriate drop locations 26.
The drop location detection module 20 and its related user interface or
information
io display would be located in the cab or at the controls of the distribution
machine 19. As
is discussed further herein, the drop location detection module 20 is
effectively a device
which can either be built into new equipment or retrofitted to existing
equipment that
comprises a GPS receiver 21, a memory 39, a download interface 40, and some
type of
an operator display or interface 23. In circumstances where the locations of
use locations
n have been captured in a non-GPS method - i.e. such as measurement along the
track as
outlined elsewhere herein - the drop location detection module 20 could have
the
necessary instrumentation or sensor to make these types of measurements and
that
equipment and its appropriate interface to the remainder of the module 20
could take the
place of the GPS receiver 21.
zo
The drop location detection module 20 via the download interface 40 will
acquire from
the central computer 10 and the location database 16 stored therein the drop
location co-
ordinates 38 and related data and information which are required to properly
distribute
the railroad ties or other materials contemplated or calculated by the
location database 16.
zs The module 20 can basically download the necessary drop location co-
ordinates 38 for a
particular section of track on which the distribution equipment 17 are
currently working
and, in this fashion, more than one set of distribution equipment 17 can be
used with one
central computer IO and database 16.
so In any event, a quantity of drop location co-ordinate data 38 will be
downloaded from the
location database 16 into the memory 39 of the marking module 20. The
circuitry of the
marking module 20 would then basically monitor the current location of the
distribution
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-01
Page 53
s machine 19 in relation to the sets of drop location co-ordinates 38 stored
within the
memory 23. As a particular drop location 26 is reached, the display or user
interface 23
will alert the operator of the tie distribution machine or picker arm 19 to
the fact that they
are located at a drop location 26 and that one or more ties or quantities of
material need to
be dropped at that location. Once the requisite quantity of material is
dropped at that
io drop location 26, that particular set of drop location co-ordinates 36
would be dropped
from the memory of the module 20 or otherwise skipped such that the next
approaching
set of drop location co-ordinates 38 would be monitored for their proximity to
the
machine 19 and again the operator could be advised when that next location 26
were
reached and the next quantity of material could be dropped.
is
As outlined above, there is a circumstance contemplated in which the drop
location
detection module 20 may actually host the location database 16, in an
embodiment of the
system of the present invention where the central computer 10 is removed. In
that case,
the additional circuitry and storage involved in storing and maintaining the
location
io database 16 would be added to the construction of the drop location
detection module 20
and such changes or modifications will be obvious to one skilled in the art
and are also
contemplated within the scope of the present invention.
The user interface 23 of the drop location detection module 20 might be as
simple as an
is indicator light which would illuminate or otherwise notify the operator
each time a single
tie needed to be distributed. This would lend itself best to the circumstance
or situation
outlined herein in which each use location 25 and its attendant set of co-
ordinates 37
corresponds to a separate and singly calculated or located drop location 26
with its
corresponding co-ordinates 38. An indicator light which would illuminate when
3o individual ties were to be dropped would be a very simple user interface
which could be
enhanced for added functionality, but demonstrates the basic utility and
simplicity of the
method and model of the present invention. A single indicator light could also
be used in
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-01
Page 54
a method where more than one tie was to be dropped at individual drop
locations 26,
since basically what could happen would be the light could remain illuminated
until the
proper number of ties had been dropped. (This would require the automatic
counting or
keying into the module 20 somehow of the count of the number of ties dropped -
a load
cell on the picker arm or distribution arm might be incorporated for this
purpose).
~o
One aspect of the actual tie distribution machine 19 of the present invention
which is
contemplated, particularly in the case of the train top distributors 19 as
shown which use
a picker arm of some kind yr another to distribute individual or more than one
tie at a
time, would be to incorporate a load cell into that picker arm which would
effectively
is allow the distribution equipment 17 and specifically the tie distribution
machine or arm
19 to count the number of ties which were distributed or taken off the train
in a particular
arm motion and it could then basically count or compare this number of ties
against the
number of ties required to be distributed at an individual location. This
would be of
particular benefit in situations where potentially more than one tie was to be
distributed at
zo an individual location. The use of a load cell on a picker arm or the use
of any other type
of method of counting the number of ties distributed at a particular drop
location 26 for
the purpose of comparing that against the calculated number of required ties
is
contemplated within the scope of the present invention as well.
zs Beyond the basic single indicator light user interface 23 outlined so far,
Figures SA and
8B show two other alternate types of user interface 23 which could potentially
work with
the marking module 20 on the tie distribution machine 19. Figures 8A and 8B
show only
two particular types of a user interface which it is contemplated can be used
with a drop
location detection module 20 of the present invention. It will be understood
that other
3o types of interfaces could also be conceived without departing from the
intended scope of
the invention as claimed and outlined herein.
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-01
Page 55
s Figure 8A shows one type of a user interface which it is contemplated could
be
effectively mounted in the cab of a picker arm or tie distribution machine 19.
There is
shown basically a set of three indicator lights 41 which are marked "forward",
"stop" and
"backward". It is contemplated on the basis of the proximity of the module 20
and its
associated GPS receiver 21 to the next drop location 26, the circuitry of the
user interface
to box 23 could basically indicate to the operator whether or not the next
drop location 26
was forward or back from the present location and, by illuminating one of
those two
lights, could direct the operator of the machine in terms of moving forwards
or back to
the next location. The "stop" indicator light could for example tell the
person that they
are at the location and that would be the location to stop and drop the next
quantity of ties
is or materials.
The next item which is also shown on the interface box 23 in Figure 8A, in
addition to
the indicator lights 4I, is a digital counter 42 which could effectively
display from the
memory 39 of the device the number of ties or quantity of materials to be
distributed at
za that particular location. For example, if that particular drop location 26
required the
dropping of five ties, the number "5" could be displayed by a digital counter
in this
fashion. That is what is shown here with the digital counter being at "5" and
then> in
conjunction with a load cell or in some other fashion, that counter could be
reduced with
each tie or quantity of material that was dropped at the drop location 26
until it came
as down to zero, at which point one of the indicator lights 41 for forward or
backward could
come on and the machine could move on to the next drop location 26. It will be
understood that this is just one very simple embodiment of a user interface 23
which
could be used with the drop location detection module 24 in accordance with
the present
invention to help the operator of the distribution equipment 17 to properly
locate and
so distribute the railroad ties or other materials at their appropriate drop
locations 26.
Figure 8B shows a somewhat more elaborate user interface box 23 which again
could be
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 56
integral with or a part of or connected to the drop location detection module
20 of the
present invention. In the interface of Figure 8B there is again shown a set of
indicator
lights 41 for the directions of forward and reverse as well as a stop
indicator light. Again
there is also shown a digital counter 42 which could indicate the quantity of
ties or
materials to be dropped at a particular drop location 26 when it was reached.
to
Also present in the interface of Figure 8B however are two cumulative
counters, one of
which 43 shows a cumulative total of the number of ties or quantity of
materials that,
based on a count of the information or data stored in the memory that the
distribution
equipment 17 should have dropped to that point, and the second counter 44
shows the
~s actual count of the number of ties or quantity of materials that have been
dropped.
Basically, the goal of the operator of the equipment 17 would be to keep the
values of
these two counters 43 and 44 as close as possible. The digital counter 42
could in one
embodiment, in addition to showing the number of ties that needed to be
dropped to make
the counters equal, also show a negative number if, in some circumstance, more
ties had
ao been dropped than should have been, and this would again allow the operator
to keep the
numbers as close as possible and to be aware of the overage at any point in
time.
These interfaces shown in the modules of Figures 8A and 8B are not in any way
intended
to be at all demonstrative of the total scope of different interfaces which
could be
zs contemplated within the scope of the present invention. In the case of a
drop location
detection module 20 or location marking functionality being built in to a new
piece of
equipment, it is even foreseeable that the user interface 23 could be a part
of the
dashboard or cab electronics or in some other fashion integrated into the
machine and that
any type of an indicator or user interface which generates an indication of
the location at
so which a tie or some material is to be dropped will be within the scope of
the present
invention as it is intended to be claimed.
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-Ol
Page 57
s As indicated in further detail above, it is contemplated that the tie
distribution machine 19
itself could include a load cell of some type of a counting mechanism by which
the
distribution quantities which had to that point been distributed could be
counted and
properly tracked by the system. It will be understood that the use of such a
load cell or
some type of counting mechanism could obviously be integrated with the user
interface
io 23 of whatever type of a primary drop location detection module 20 were
used in the
machinery.
Integrated eauiument operation using multiple drop location detection modules:
a
It is also contemplated that the use of a secondary drop location detection
module 46 in
accordance with the general principles of the present invention could further
enhance the
operation of the distribution equipment 17.
zo As outlined above, the distribution equipment 17 would typically be pushed
or pulled by
either a road rail unit or a locomotive at the head or tail end of a string of
gondola cars 18
on which a crawler unit or the like 19 could move or endeavour to unload
railroad ties at
their desired locations. It is foreseen that the drop location detection
module 20 would be
used by the operator of the actual tie distribution machine in order to make
sure that they
zs know exactly where and how many ties need to be dropped. Figure 9
demonstrates the
use of a secondary drop location detection module 46 installed in the
locomotive 45.
It is contemplated that the primary drop location detection module 20 on the
tie
distribution equipment and the secondary drop location detection module 46
installed in
3o the power unit 45 could communicate directly with each other for the
purpose of
exchanging their respective individual actual GPS co-ordinate locations. In
this fashion,
effectively the secondary drop location detection module 4b could locate the
drop
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-OI
Page 58
s locations 26 by seeking out the same drop location co-ordinates 38 as the
primary drop
location detection module 20, but could apply to the calculation for location
purposes an
offset of the distance between the two modules (the distance from the power
unit to the
tie distribution machine 18). For example, if the distribution machine 19 was
working at
the far end of a train, 250 feet from the locomotive, the secondary drop
location detection
io module 46 located in the locomotive 45 could basically move the
distribution equipment
17 and more specifically the tie distribution machine 19 to the precise drop
location co-
ordinates 38 of a particular drop location 26 by applying effectively a 250
foot offset to
the drop location co-ordinates 38 stored in the memory of the secondary drop
location
detection module 46.
~s
Beyond storing the co-ordinates separately, it may even be the case that the
secondary
drop location detection module 46 did not contain a separate memory or GPS
receiver
and was basically a slave to the memory of the primary drop location detection
module
20 and simply somehow received its information, wirelessly or in some other
zo communicative fashion, from the primary module 20.
Effectively, then, in such a circumstance as the crawler machine 18 was moved
down the
top of the train and certain cars full of ties were exhausted, the primary
drop location
detection module 20 and the secondary drop location detection module 46 could,
by
as virtue of their continued communication, automaticahy adjust the offset
distance between
the locomotive power unit 45 and the tie distribution machine 18. The obvious
advantage
to the offset functionality of using two drop location detection modules is
that basically
the driver of the power unit 45 would have their own relatively accurate
readout of the
proper location for a stop of the train while ties were to be distributed. In
the absence of
3o a separate readout in the power unit 45, the tie distribution machine 19
would somehow
need to have direct control of the movement of the entire tie distribution
train, while
alternatively the operators and tie distribution machine and the locomotive
would all need
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-O1
Page 59
s to be in constant radio contact.
If a secondary drop location detection module 46 of the type outlined herein
were present
or available in the power unit 45, then the operator of the power unit 45
could basically
know as they drove the train down the tracks the right places to stop at a
particular drop
io location 26, and by stopping the train ai what their secondary drop
location detection
module 46 indicated was a drop location 26, the remainder of the distribution
equipment
17, including the tie distribution machine 19 should be, at that point in
time, located in
relatively close proximity to the actual precise co-ordinates 38 of the drop
location 26 at
which the ties were to be dropped. yt addition, communication between those
two
is modules could include the fact that the locomotive or driver of the train
would know how
many more ties were to be dropped at a particular location or would somehow
have their
own indication of when tie distribution tasks were finished and it was safe to
move
forward to the next location.
zo Basically the secondary drop location detection module 46 could basically
be a secondary
readout driven by the primary module 20 on the actual distribution machine 19,
or could
be a separately equipped GPS enabled unit that could exercise more elaborate
offset
calculations and independent, location of the drop locations 26 for the
operator of the
power unit.
zs
Retrofitting the system of the present invention to existing eQUil mp ent:
It is contemplated that the system of the present invention could either be
built into
3o railway maintenance equipment or alternatively could be retrofetted to
existing
equipment.
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K l 490-13-d 1
Page 60
s For example, with respect to the use location capture module 4, it will be
understood that
the device 4 could be built into some type of a track inspection vehicle or
the like or even
a tie marking module as discussed under the heading of "Use location capture
module"
above, and on that basis the use location capture module 4 could be integrated
into one or
more track inspection units by a particular railroad or railway maintenance
company.
to Alternatively, it may also be the case that the use location capture module
4 is a handheld
device which could be effectively used by one or more individual track
inspectors,
manually or otherwise inspecting a railway. Effectively the handheld device
would be
easily accomplished give the size of GPS electronics which are available on
the market
today, and all that would need to be done would be to take a mobile GPS
receiver and
is combine with it the necessary additional electronics to accomplish some
type of a basic
user interface to trigger the capture of use location co-ordinates 37 as well
as a memory 8
to store these co-ordinates 37 for eventual upload to the central computer 10.
Practically
speaking, it is foreseen that either a handheld unit or a backpack unit or
something along
these lines could quite easily be created for use in situations where it was
desired to have
zo a handheld or manual unit available for use as the use location capture
module 4.
It will be understood that both the building in of the use location capture
module 4 into
some type of a track inspection or tie marking module or vehicle is
contemplated within
the scope of the present invention, as well as the creation of a handheld or
otherwise
as portable unit which could be used by one or more individuals in the use
location marking
aspect of the method of the present invention.
The use location capture module 4 then can be rendered either portable or
retrofitted to an
existing or new track inspection vehicle. The second item which can also be
retrofitted to
3o existing equipment or built into new equipment would be the drop location
detection
module 20, which would effectively be responsible for the download of the drop
location
co-ordinates 38 and other remaining or related data from the central computer
10 and the
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-)3-01
Page 61
s database 16 hosted therein. The drop location detection module 20 and any
associated
user interface could be built into a new tie distribution unit or materials
distribution train
or unit for use by a railway, or alternatively could be again designed in such
a fashion as
to be retrofitted onto existing equipment. Insofar as the module 20 itself
again consists of
a basic user interface and a GPS receiver, it is easily foreseeable that
something in either
so a handheld or briefcase size or style could be designed which could be
retrofitted into
existing tie distribution equipment.
Conch~sion:
is
While the description herein has been directed to explaining the adaptive
distribution
system and method of the present invention in relation to the distribution of
railroad
maintenance applications, it will be understood that the system and method of
the present
invention could also be used with attendant modifications to the data capture
function or
zo the distribution equipment to distribute materials other than railroad ties
in similar
applications. It will be understood that any such modifications and resulting
embodiments are also contemplated within the scope of the present invention.
Distribution of any material in varying amounts along a roughly predetermined
course
zs that can be followed by both a data capture unit as well as the subsequent
distribe~tion
equipment and/or personnel would lend itself to the use of the present
invention. For
example, beyond railroad maintenance tasks which are obviously an ideal
candidate for
the use of such a method another similar application might be the use of the
system and
method of the present invention in road maintenance applications. Again the
data capture
so unit could be taken along a particular stretch of road and used to capture
location and
quantity information for materials to be distributed, and then a distribution
unit could
follow at a later time down the same piece of road and drop the right required
quantities
CA 02521978 2005-09-28
F&K 1490-13-01
Page 62
s of materials in their use locations. Again it will be understood that this
type of a use for
the method of the present invention is also contemplated within the scope of
the present
invention, as would any attendant required modifications - for example, the
distribution
equipment would become truck mounted rather than train mounted, in all
likelihood, but
could still function equivalently beyond these modifications.
~o
Thus it can be seen that the invention accomplishes all of its stated
objectives. The
foregoing is considered as illustrative only of the principles of the
invention. Further,
since numerous changes and modifications will readily occur to those skilled
in the art, it
is not desired to limit the invention to the exact constmction and operation
shown and
is described, and accordingly, ail such suitable changes or modifications in
structure or
operation which may be resorted to are intended to fall within the scope of
the claimed
invention.