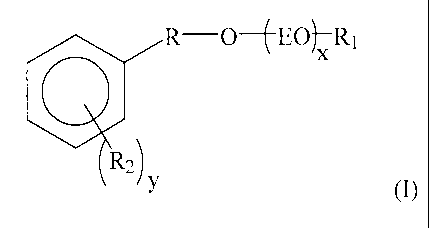Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02532032 2006-01-10
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
CLEANING CONCENTRATE
Background of the Invention
The invention relates to cleaner/degreaser compositions and, more
particularly, to stable cleaner/degreaser compositions that include a
surfactant with an HLB less than 10, and an aryl ethoxylate.
While not wishing to be held to any theory as to the nature of the
cleaning and degreasing action of presently available compositions, it is
believed that highly or infinitely water soluble organic solvents presently
used in both retail as well as industrial and institutional cleaner/degreaser
compositions are too hydrophilic in nature to function effectively in
removing hydrophobic "oleophilic" soilants, especially in the presence of
diluting water. As the level of the latter is increased to bring conventional
compositions to ready to use strength, the solvating action of the organic
solvent is drastically reduced with a consequent and marked reduction in
the cleaning/degreasing action required for effective cleaning and oily
soilant removal.
There remains a need, therefore, for cleaning, degreaser
compositions with improved cleaning and degreasing capabilities without
the other deficiencies of presently available cleaner/degreaser
compositions.
1
CA 02532032 2006-01-10
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
Summary of the Invention
Generally, the present invention relates to low HLB and aryl
ethoxylate based cleaning compositions that are stable in concentrate and
dilute use solution form.
One embodiment of the invention includes a composition including:
a surfactant having an HLB value from 1 to 10; and a compound of formula
(I):
R-O-~EOj-R1
qx
R2)
y (I)
where; x is an integer from 2 to 6, y is an integer from 0 to 5, R is a bond
or
(Ci-C4)alkylene, Ri is a hydrogen, halo, aryl, (Ci-C4)alkyl, heteroaryl,
cycloalkyl, or heterocycyl, R2 is independently selected from hydrogen,
halo, (Ci-C4)alkyl, (Ci-C4)alkoxy, (C2-C4) alkenylene.
Another embodiment of the invention includes a method of forming
a stable cleaning composition that includes combining: a surfactant having
an HLB value from 1 to 10, (b) a compound of formula (I):
R-O EO- 1
R2
y (I)
where; x is an integer from 2 to 6, y is an integer from 0 to 5, R is a bond
or
(Ci-C4)alkylene, Ri is hydrogen, halo, aryl, (Ci-C4)alkyl, heteroaryl,
2
CA 02532032 2011-11-29
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
cycloalkyl, or heterocycyl, R2 is independently selected from hydrogen,
halo, (Cf-C4)alkyl, (C1-C4)alkoxy, (C2-C4) alkenylene, and a second
surfactant having an HLB value greater than 10 foaming a stable non-
aqueous cleaning concentrate or water forming an aqueous cleaning
concentrate.
The above summary of the present invention is not intended to
describe each disclosed embodiment or every implementation of the present
invention. The Detailed Description and Examples which follow more
particularly exemplify these embodiments
Detailed Description
While the invention is amenable to various modifications and
alternative forms, specifics thereof have been shown by way of the
Example and will be described in detail.
For the following defined terms, these definitions shall be applied,
unless a different definition is given in the claims or elsewhere in this
specification.
All numeric values are herein assumed to be modified by the term
"about," whether or not explicitly indicated. The term "about" generally
refers to a range of numbers that one of skill in the art would consider
3
CA 02532032 2006-01-10
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
equivalent to the recited value (i.e., having the same function or result). In
many instances, the terms "about" may include numbers that are rounded to
the nearest significant figure.
Weight percent, percent by weight, % by weight, and the like are
synonyms that refer to the concentration of a substance as the weight of that
substance divided by the weight of the composition and multiplied by 100.
The recitation of numerical ranges by endpoints includes all
numbers subsumed within that range (e.g. 1 to 5 includes 1, 1.5, 2, 2.75, 3,
3.80, 4, and 5).
As used in this specification and the appended claims, the singular
forms "a", "an", and "the" include plural referents unless the content
clearly dictates otherwise. Thus, for example, reference to a composition
containing "a compound" includes a mixture of two or more compounds.
As used in this specification and the appended claims, the term "or" is
generally employed in its sense including "and/or" unless the content
clearly dictates otherwise.
The term "alkyl" refers to a straight or branched chain monovalent
hydrocarbon radical having a specified number of carbon atoms. Alkyl
groups may be unsubstituted or substituted with substituents that do not
interfere with the specified function of the composition and may be
substituted once or twice with the same or different group. Substituents
may include alkoxy, hydroxy, mercapto, amino, alkyl substituted amino,
nitro, carboxy, carbanoyl, carbanoyloxy, cyano, methylsulfonylamino, or
halo, for example. Examples of "alkyl" include, but are not limited to,
4
CA 02532032 2006-01-10
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, s-butyl, t-butyl, n-pentyl, n-
hexyl, 3-methylpentyl, and the like.
As used herein, the term "alkylene" refers to a straight or branched
chain divalent hydrocarbon radical having a specified number of carbon
atoms. Alkylene groups include those with one to twenty carbon atoms.
Alkylene groups may be unsubstituted or substituted with those substituents
that do not interfere with the specified function of the composition.
Substituents include alkoxy, hydroxy, mercapto, amino, alkyl substituted
amino, or halo, for example. Examples of "alkylene" as used herein
include, but are not limited to, methylene, ethylene, propane- 1,3-diyl,
propane-l,2-diyl and the like.
The term "alkoxy" refers to refers to a straight or branched chain
monovalent hydrocarbon radical having a specified number of carbon
atoms and a carbon-oxygen-carbon bond, may be unsubstituted or
substituted with substituents that do not interfere with the specified
function of the composition and may be substituted once or twice with the
same or different group. Substituents may include alkoxy, hydroxy,
mercapto, amino, alkyl substituted amino, nitro, carboxy, carbanoyl,
carbanoyloxy, cyano, methylsulfonylamino, or halo, for example.
Examples include, methoxy, ethoxy, propoxy, t-butoxy, and the like.
The term "alkenyl" or "alkenylene" refers to a straight or branched
chain divalent hydrocarbon radical having a specified number of carbon
atoms and one or more carbon--carbon double bonds. Alkenylene groups
may be unsubstituted or substituted with substituents that do not interfere
5
CA 02532032 2006-01-10
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
with the specified function of the composition and may be substituted once
or twice with the same or different group. Substituents may include
alkoxy, hydroxy, mercapto, amino, alkyl substituted amino, nitro, carboxy,
carbanoyl, carbanoyloxy, cyano, methylsulfonylamino, or halo, for
example. Examples of "alkenyl" or "alkenylene" include, but are not
limited to, ethene-1,2-diyl, propene-1,3-diyl, and the like.
The term "cycloalkyl" refers to an alicyclic hydrocarbon group
having a specified number of carbon atoms. Cycloalkyl groups include
those with one to twelve carbon atoms. Cycloalkyl groups may be
saturated or unsaturated, unsubstituted or substituted with those substituents
that do not interfere with the specified function of the composition.
Cycloalkyl may be substituted by halo, C1-C6 alkyl, C1-C6 alkoxy, C2-C6
alkenyl, substituted C1-C6 alkyl, C1-C6 substituted alkoxy, substituted C2-C6
alkenyl, substituted alkoxy, amino, nitro, cyano, carboxy, hydroxymethyl,
aminomethyl, carboxymethyl, C1-C4 alkylthio, hydroxy, C1-C4
alkanoyloxy, carbamoyl, or halo-substituted C1-C6 alkyl and may be
substituted once or more with the same or different group. Such a
cycloalkyl ring may be optionally fused to one or more of another
heteroaryl ring(s), aryl ring(s), or cycloalkyl rings. Examples of
"cycloalkyl" include, but are not limited to, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl,
cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, cycloheptyl, or cyclooctyl, and the like.
The term "heterocyclic" or "heterocyclyl" refers to a monovalent
three to twelve-membered non-aromatic ring containing one or more
heteroatomic substitutions independently selected from S, 0, or N and
6
CA 02532032 2006-01-10
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
having zero to five degrees of unsaturation. Heterocyclyl groups may be
unsubstituted or substituted with those substituents that do not interfere
with the specified function of the composition. Heterocyclyl may be
substituted by halo, C1-C6 alkyl, C1-C6 alkoxy, C2-C6 alkenyl, substituted
C1-C6 alkyl, C1-C6 substituted alkoxy, substituted C2-C6 alkenyl, substituted
alkoxy, amino, nitro, cyano, carboxy, hydroxymethyl, aminomethyl,
carboxymethyl, C1-C4 alkylthio, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkanoyloxy, carbamoyl,
or halo-substituted C1-C6 alkyl and may be substituted once or more with
the same or different group. Such a heterocyclic ring may be optionally
fused to one or more of another heterocyclic ring(s), heteroaryl ring(s), aryl
ring(s), or cycloalkyl rings. Examples of "heterocyclic" include, but are
not limited to, tetrahydrofuryl, pyranyl, 1,4-dioxanyl, 1,3-dioxanyl,
piperidinyl, pyrrolidinyl, morpholinyl, tetrahydrothiopyranyl,
tetrahydrothiophenyl, and the like.
The term "aryl" refers to monovalent unsaturated aromatic
carbocyclic radicals having a single ring, such as phenyl, or multiple
condensed rings, such as naphthyl or anthryl. Aryl groups may be
unsubstituted or substituted with those substituents that do not interfere
with the specified function of the composition. Aryl may be substituted by
halo, C1-C6 alkyl, C1-C6 alkoxy, C2-C6 alkenyl, substituted C1-C6 alkyl, C1-
C6 substituted alkoxy, substituted C2-C6 alkenyl, substituted alkoxy, amino,
nitro, cyano, carboxy, hydroxymethyl, aminomethyl, carboxymethyl, C1-C4
alkylthio, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkanoyloxy, carbamoyl, or halo-substituted Ci-
C6 alkyl and may be substituted once or more with the same or different
7
CA 02532032 2006-01-10
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
group. Such an aryl ring may be optionally fused to one or more of another
heterocyclic ring(s), heteroaryl ring(s), aryl ring(s), or cycloalkyl rings.
Examples of "aryl" include, but are not limited to, phenyl, 2-naphthyl, 1-
naphthyl, biphenyl, 2-hydroxyphenyl, 2-aminophenyl, 2-methoxyphenyl
and the like.
The term "heteroaryl" refers to a monovalent five to seven
membered aromatic ring radical containing one or more heteroatoms
independently selected from S, 0, or N. Heteroaryl groups may be
unsubstituted or substituted with those substituents that do not interfere
with the specified function of the composition. Heteroaryl may be
substituted by halo, C1-C6 alkyl, C1-C6 alkoxy, C2-C6 alkenyl, substituted
C1-C6 alkyl, C1-C6 substituted alkoxy, substituted C2-C6 alkenyl, substituted
alkoxy, amino, nitro, cyano, carboxy, hydroxymethyl, aminomethyl,
carboxymethyl, C1-C4 alkylthio, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkanoyloxy, carbamoyl,
or halo-substituted C1-C6 alkyl and may be substituted once or more with
the same or different group. Such a "heteroaryl" ring may be optionally
fused to one or more of another heterocyclic ring(s), heteroaryl ring(s), aryl
ring(s), or cycloalkyl rings. Examples of "heteroaryl" include, but are not
limited to, furyl, thiophenyl, pyrrolyl, imidazolyl, pyrazolyl, triazolyl,
tetrazolyl, thiazolyl, oxazolyl, isoxazolyl, oxadiazolyl, thiadiazolyl,
isothiazolyl, pyridinyl, pyridazinyl, pyrazinyl, pyrimidinyl, quinolinyl,
isoquinolinyl, benzofuryl, benzothiophenyl, indolyl, and indazolyl, and the
like.
The term "halo" and "halogen" refer to chloro, bromo, fluoro, and
8
CA 02532032 2006-01-10
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
iodo.
The term "EO" refers to ethylene oxide.
The term "PO" refers to propylene oxide.
The term "Hydrophilic Lipophilic Balance (HLB)" refers to a
surfactant's solubility in water. An HLB scale was derived as a means for
comparing the relative hydrophilicity of amphiphilic molecules. Molecules
with an HLB value of 10 or greater indicate that the molecule is hydrophilic
and soluble in water. Molecules with an HLB value less than 10 indicate
that the molecule is hydrophobic and insoluble in water. The HLB system
is well known to skilled surfactant chemists and is explained in the
literature such as in the publication, "The HLB System," ICI Americas
(1987).
The term "surfactant" or "surface active agent" refers to an organic
chemical that when added to a liquid changes the properties of that liquid at
a surface.
Compositions
The compositions of the invention include a surfactant with an HLB
less than 10, an aryl ethoxylate and optionally with a surfactant with an
HLB greater than 10 or water. The composition forms a stable cleaning
concentrate and remains stable when diluted to a use solution. The stable
cleaning concentrate may be a stable single phase solution or a stable micro
emulsion.
9
CA 02532032 2006-01-10
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
One embodiment of the invention includes a composition including:
a surfactant having an HLB value from 1 to 10; and a compound of formula
(I):
R-O-(-EO)-RI
x
qR2)
Y (I)
where; x is an integer from 2 to 6, y is an integer from 0 to 5, R is a bond
or
(C1-C4)alkYlene, Rl is a hydrogen, halo, aryl, (C1-C4)alkY1, heteroaryl,
cycloalkyl, or heterocycyl, R2 is independently selected from hydrogen,
halo, (C1-C4)alkyl, (C1-C4)alkoxy, (C2-C4) alkenylene.
Another embodiment includes a method of forming a stable
cleaning composition that includes combining: a surfactant having an HLB
value from 1 to 10, a compound of formula (I):
R-O EO- 1
R2
s y (I)
where; x is an integer from 2 to 6, y is an integer from 0 to 5, R is a bond
or
(C1-C4)alkylene, Rl is hydrogen, halo, aryl, (C1-C4)alkyl, heteroaryl,
cycloalkyl, or heterocycyl, R2 is independently selected from hydrogen,
halo, (C1-C4)alkyl, (C1-C4)alkoxy, (C2-C4) alkenylene, and a second
surfactant having an HLB value greater than 10 forming a stable non-
CA 02532032 2006-01-10
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
aqueous cleaning concentrate or water forming an aqueous cleaning
concentrate.
The composition can include 10 to 90 wt% of a surfactant having an
HLB value from 1 to 10 based on the total weight of surfactant having an
HLB value from 1 to 10 and aryl ethoxylate. The composition can include
25 to 75 wt% of aryl ethoxylate based on the total weight of surfactant
having an HLB value from 1 to 10 and aryl ethoxylate. The composition
can have a weight ratio of aryl ethoxylate to surfactant having an HLB
value from 1 to 10 of 1:3 to 3:1. The composition can be diluted with a
solvent or water from 1-99% wt% aryl ethoxylate and surfactant having an
HLB value from 1 to 10.
Surfactant
A surfactant may be present in the composition of the invention.
The surfactant or surfactant admixture can be selected from water soluble
or water dispersible nonionic, semi-polar nonionic, anionic, cationic,
amphoteric, or zwitterionic surface-active agents; or any combination
thereof. The surfactant can be a specified combination of surfactants such
as, for example, a anionic and nonionic surfactant, a anionic and two or
more nonionic surfactants, or a anionic and a hydrophobic nonionic and a
hydrophilic nonionic surfactant. The particular surfactant or surfactant
mixture chosen for use in the process and products of this invention can
depend on the conditions of final utility, including method of manufacture,
physical product form, use pH, use temperature, foam control, and soil
11
CA 02532032 2006-01-10
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
type.
Anionic surfactants may include, for example, carboxylates such as
alkylcarboxylates (carboxylic acid salts) and polyalkoxycarboxylates,
alcohol ethoxylate carboxylates, nonylphenol ethoxylate carboxylates, and
the like; sulfonates such as alkylsulfonates, alkylbenzenesulfonates,
alkylarylsulfonates, sulfonated fatty acid esters, and the like; sulfates such
as sulfated alcohols, sulfated alcohol ethoxylates, sulfated alkylphenols,
alkylsulfates, sulfosuccinates, alkylether sulfates, and the like; and
phosphate esters such as alkylphosphate esters, and the like.
Nonionic surfactants may include those having a polyalkylene oxide
polymer as a portion of the surfactant molecule. Such nonionic surfactants
include, for example, chlorine-, benzyl-, methyl-, ethyl-, propyl-, butyl- and
other like alkyl-capped polyethylene glycol ethers of fatty alcohols;
polyalkylene oxide free nonionics such as alkyl polyglycosides; sorbitan
and sucrose esters and their ethoxylates; alkoxylated ethylene diamine;
alcohol alkoxylates such as alcohol ethoxylate propoxylates, alcohol
propoxylates, alcohol propoxylate ethoxylate propoxylates, alcohol
ethoxylate butoxylates, and the like; nonylphenol ethoxylate,
polyoxyethylene glycol ethers and the like; carboxylic acid esters such as
glycerol esters, polyoxyethylene esters, ethoxylated and glycol esters of
fatty acids, and the like; carboxylic amides such as diethanolamine
condensates, monoalkanolamine condensates, polyoxyethylene fatty acid
amides, and the like; and polyalkylene oxide block copolymers including
an ethylene oxide/propylene oxide block copolymer such as those
12
CA 02532032 2006-01-10
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
commercially available under the trademark PLURONICTM (BASF-
Wyandotte), and the like; and other like nonionic compounds. Silicone
surfactants such as the ABILTM B8852 can also be used.
Cationic surfactants useful for inclusion in a cleaning composition
for sanitizing or fabric softening, include amines such as primary,
secondary and tertiary monoamines with C18 alkyl or alkenyl chains,
ethoxylated alkylamines, alkoxylates of ethylenediamine, imidazoles such
as a 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-imidazoline, a 2-alkyl-l-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-
imidazoline, and the like; and quaternary ammonium salts, as for example,
alkylquatemary ammonium chloride surfactants such as n-alkyl(C12-
C18)dimethylbenzyl ammonium chloride, n-tetradecyl
dimethylbenzylammonium chloride monohydrate, a naphthylene-
substituted quaternary ammonium chloride such as dimethyl- l -
naphthylmethylammonium chloride, and the like; and other like cationic
surfactants.
Surfactants may also be categorized as hydrophobic or hydrophilic
surfactants. Hydrophobic surfactants posses an HLB value of less than 10.
Hydrophilic surfactants possess an HLB value of 10 or greater. Surfactants
with an HLB value from 1 to 10 may include, for example, primary alcohol
ethoxylate, secondary alcohol ethoxylate, ternary alcohol ethoxylate,
primary amine ethoxylate, and secondary amine ethoxylate. Surfactants
with an HLB value from 1 to 10 further include, for example alkyl
polysaccharides, alkylamine ethoxylates, block copolymers, castor oil
ethoxylates, ceto-oleyl alcohol ethoxylates, ceto-stearyl alcohol
13
CA 02532032 2011-11-29
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
ethoxylates, decyl alcohol ethoxylates, end-capped ethoxylates, ethoxylated
alkanolamides, fatty alcohol alkoxylates, lauryl alcohol ethoxylates, mono-
branched alcohol ethoxylates, random copolymer alkoxylates, sorbitan ester
ethoxylates, stearic acid ethoxylates, synthetic alcohol ethoxylates, tall oil
fatty acid ethoxylates, tallow amine ethoxylates. All of these surfactants
have low HLB species and are widely commercially available from, for
example, Huntsman Chemical Company (Houston, TX).
A hydrophobic surfactant may have a formula (II):
R' 0--*O)a(PO) b R" (II)
where a is an integer from 1 to 10 or 1 to5, b is an integer from 0 to 5 or 0,
R' is (C6-C22 or C8-C16)alkyl, (C6-C22)alkoxy, (C6-C22) alkenylene with the
proviso that when R' is C6 alkyl, C6 alkoxy, or C6 alkenylene, a is at least 1
and b is at least 1, and R" is a hydrogen, halo, aryl, (C1-C4)alkyl,
heteroaryl, cycloalkyl, or heterocycyl.
Exemplary hydrophobic surfactants include TomadolTM 1-3 (HLB
8.7), Tomadol 25-3 (HLB 7.5), Tomadol 91-2.5 (HLB 8.5), Tomado123-1
(HLB 3.7), SurfonicTML24-2 (HBL 6.2), Surfonic L24.-1.3 (HLB 4.5), and
Condea VistaTM 6-1EO-1PO (HLB 4.3). Tomadols are commercially
available from Tomah Products Inc. (Milton, Wisconsin). Surfonics are
commercially available from Huntsman Chemical (Houston, TX). Condea
Vistas are commercially available from Condea Vista Inc., (Houston, TX).
As will be apparent to those skilled in the art, the above-listed
hydrophobic surfactants are merely illustrative and various other
14
CA 02532032 2006-01-10
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
hydrophobic surfactants meeting the criteria set out above may also be used
in the practice of the invention. The hydrophobic surfactants may be
present in the composition from 1 wt%, 10 to 90 wt % or 25 to 75 wt%
based on the total weight of hydrophobic surfactant, and aryl ethoxylate.
Surfactants with an HLB value greater than 10 may be added to the
composition and may include, for example, hydrophilic anionic surfactants
such as, dodecylbenzene-sulfonic acid, sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate,
potassium dodecylbenzene sulfonate, triethanolamine dodecylbenzene
sulfonate, morpholinium dodecylbenzene sulfonate, ammonium
dodecylbenzene sulfonate, isopropylamine dodecylbenzene sulfonate,
sodium tridecylbenzene sulfonate, sodium dinonylbenzene sulfonate,
potassium didodecylbenzene sulfonate, dodecyl diphenyloxide disulfonic
acid, sodium dodecyl diphenyloxide disulfonate, isopropylamine
decyldiphenyloxide disulfonate, sodium hexadecyloxy-poly(ethyleneoxy)
(10)ethyl sulfonate, potassium octylphenoxy poly(ethyleneoxy)(9)ethyl
sulfonate, sodium C12_14 olefin sulfonate, sodium hexadecane-1 sulfonate,
sodium ethyl oleate sulfonate, potassium octadecenylsuccinate, sodium
oleate, potassium laurate, triethanolamine myristate, morpholinium tallate,
potassium tallate, sodium lauryl sulfate, diethanolamine lauryl sulfate,
sodium laureth (3) sulfate, ammonium laureth (2) sulfate, sodium
nonylphenoxypoly(ethyleneoxy)(4) sulfate, sodium
diisobutylsulfosuccinate, disodium laurylsulfosuccinate, tetrasodium N-
laurylsulfosuccinimate, sodium
decyloxypoly(ethyleneoxy(5)methyl)carboxylate, sodium octylphenoxy
CA 02532032 2006-01-10
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
poly(ethyleneoxy(8)methyl) carboxylate, sodium mono decyloxy
poly(ethyleneoxy)(4)phosphate, sodium didecyloxy poly(ethyleneoxy)(6)
phosphate, and potassium mono/di octylphenoxy
poly(ethyleneoxy)(9)phosphate. Useful hydrophilic nonionic surfactants
include, for example, octylphenoxy poly(ethylene-oxy)-(11)ethanol,
nonyiphenoxy poly(ethyleneoxy)(13)ethanol, dodecylphenoxy
poly(ethyleneoxy)(10)ethanol, polyoxyethylene (12) lauryl alcohols
polyoxyethylene (14) tridecyl alcohol, lauryloxy poly(ethyleneoxy) (10)
ethyl methyl ether, undecyl thiopoly(ethyleneoxy) (12) ethanol, methoxy
poly(oxy-etyhylene-(10)/oxypropylene(20))2-propanol block copolymer,
nonyloxy poly(propyleneoxy) (4)/(ethyleneoxy) (16)ethanol, dodecyl
polyglycoside, polyoxyethylene (9) monolaurate, polyoxyethylene (8)
monoundecanoate, polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan monostearate,
polyoxyethylene (18) sorbitol monotallate, sucrose monolaurate,
lauryldimethylamine oxide, myristyldimethylamine oxide,
lauramidopropyl-N,N-dimethylamine oxide, 1:1 lauric diethanolamide, 1:1
coconut diethanolamide, 1:1 mixed fatty acid diethanolamide,
polyoxyethylene(6)lauramide, 1:1 soya diethanolamido poly-
(ethyleneoxy)(8)ethanol, coconut diethanolamide, "modified"; and coconut
diethanolamide, "long chain modified". Useful hydrophilic cationic
surfactants include, for example, a mixture of n-alkyl (C12 50%, C14 30%,
C16 17%, C18 3%) dimethyl ethylbenzyl ammonium chlorides,
hexadecyltrimethyl-ammonium methosulfate, didecyldimethylammonium
bromide and a mixture of n-alkyl (68% C12, 32% C14) dimethyl benzyl
16
CA 02532032 2006-01-10
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
ammonium chlorides. Useful hydrophilic amphoteric surfactants include
cocamidopropyl betaine, sodium palmityloamphopropionate, N-coco beta-
aminopropionic acid, disodium N-lauryliminodipropionate, sodium coco
imidazoline amphoglycinate and coco betaine.
As will be apparent to those skilled in the art, the above-listed
hydrophilic surfactants are merely illustrative and various other hydrophilic
surfactants meeting the criteria set out above may also be used in the
practice of the invention. Hydrophilic surfactants are not needed in the
compositions of the invention to form stable concentrates and diluted use
solutions. The hydrophilic surfactants may be present in the composition
from 1 wt% or 5 to 90 wt% based on the total weight of hydrophobic
surfactant, hydrophilic surfactant, and aryl ethoxylate.
17
CA 02532032 2011-11-29
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
Aryl Ethoxylate
An aryl ethoxylate may have the general formula (1):
R-O--{-EO-RI
R2) y
(1)
where x is an integer from 2 to 6; y is an integer from 0 to 5; R is a
bond or (Ci-C4)alkylene; Rl is a hydrogen, halo, aryl, (Ci-C4)alkyl,
heteroaryl, cycloalkyl, or heterocycyl; and R2 is independently selected
from hydrogen, halo, (Ci-C4)alkyl, (C1-C4)alkoxy, (C2-C4) alkenylene.
Preferred ethoxylates are those derived from phenol itself and benzyl
alcohol and those containing 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, or 15
ethoxylate groupings. Especially preferred is "Ethylan HB4TM" which is a
phenol ethoxylate containing around 4 ethoxylate units.
The aryl ethoxylate is surprisingly useful in coupling the
hydrophobic surfactant into water or hydrophilic surfactant to form a stable
concentrate and in coupling the hydrophobic surfactant into the hydrophilic
surfactant or water upon dilution to a use solution. Thus, the aqueous
and/or non-aqueous concentrate and aqueous use solution version of the
inventive composition remains stable as, for example, a single phase or
micro emulsion.
Ethoxylated aryl alcohol may be produced by reacting a desired
alcohol with a desired number of ethoxylate moles at standard reaction
18
CA 02532032 2006-01-10
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
conditions such as, 30 - 40 psi pressure, 300 -360 degree F, with 0.2-0.5
wt% catalyst neutralized with acid. The reaction can be illustrated by the
following:
/O\ catalyst
ROH + nCH2 CH2 > RO(CH2CH2O)õH
As will be apparent to those skilled in the art, the above-listed aryl
ethoxylates are merely illustrative and various other aryl ethoxylates
meeting the criteria set out above may also be used in the practice of the
invention. The aryl ethoxylate may be present in the composition from 1
wt%, 10 to 90 wt % or 25 to 75 wt% based on the total weight of
hydrophobic surfactant, and aryl ethoxylate.
The compositions may further include hydrotopes, enzymes,
enzyme stabilizing system, chelating agents, sequestering agents, bleaching
agents, an alkaline or acid source, secondary hardening agent or solubility
modifier, detergent filler, defoamer, anti-redeposition agent, a threshold
agent or system, aesthetic enhancing agent (i.e. dye, perfume, ect.) and the
like. Adjuvant and other additive ingredients will vary according to the
type of composition being manufactured and can be included in the
compositions in any amount.
The above processes can be used to produce a product having a
stable solution. The compositions can be diluted with aqueous and/or non
aqueous materials to form a use solution of any strength depending on the
application. The compositions and diluted use solutions may be useful as,
19
CA 02532032 2011-11-29
for example, detergents for laundry, warewashing, vehicle care, sanitizing,
and the like.
EXAMPLES
All of the following compositions were formed at ambient pressure
and temperature. A formulation was created by combining the components
in the amounts listed in the tables below.
FORMULATION A
Component Wt%
Tomadol 1-3 22.5
Ethylan HB4 7.5
TEA 29
LAS 27
Barlox 12 14
Tomadol 1-3 is an a lcohol ethoxylate nonionic surfactant made
from linear C11 alcohol with 3 moles (average) of ethylene oxide with has
an HLB of 8.7 and is commercially available from Tomah Products Inc.
(Milton, Wisconsin). Ethylan HB4 is an ethylene glycol phenol ether
(EPH) with 4 moles of ethylene oxide and is commercially available from
Akzo Nobel N.V., (Arnhem, Netherlands). TEA (triethanol amine) is
commercially available from Huntsman Chemical (Houston, TX). LAS
(Linear Dodecyl Benzene Sulfonic Acid) is commercially available from
Stepan Chemical (Northfield, IL). Barlox 12 is a cocamine oxide (CAS#
CA 02532032 2006-01-10
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
61788-90-7) commercially available from the Lonza Inc. (Switzerland) and
is 30% active.
FORMULATION B
Component Wt%
Tomadol 1-3 15
Ethylan HB4 15
TEA 29
LAS 27
Barlox 12 14
Formulation A and Formulation B above provide a cleaning
solution that can be used as a dilutable cleaner/degreaser for both food soils
and greasy soils and is compatible with stainless steel, aluminum and other
hard surfaces, and the like. Formulation A and Formulation B also exhibits
stability in the above concentrate form and when diluted to a use solution.
The exemplary formulations can be used as an all purpose cleaner, floor
cleaner, glass and stainless steel cleaner, manual pot and pan cleaner,
degreaser, and the like.
Formulations C and D below have a varying amount of water and
can be classified as either a concentrate or ready-to-use composition.
These compositions form stable solutions and may be further diluted with
water or solvent to any desired strength depending on end use. Formulation
21
CA 02532032 2006-01-10
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
C is an example of a 50% dilution. Formulation D is an example of a 5%
dilution.
FORMULATION C
Component Wt%
Tomadol 1-3 11.25
Ethylan HB4 3.75
TEA 14.5
LAS 13.5
Barlox 12 7
Water 50
FORMULATION D
Component Wt%
Tomadol 1-3 1.125
Ethylan HB4 0.375
TEA 1.45
LAS 1.35
Barlox 12 0.7
Water 95
Formulation E below is another example of a stable cleaning
concentrate in accordance with the invention.
22
CA 02532032 2011-11-29
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
FORMULATION E
Component Wt%
Tomadol 1-3 15
Ethylan HB4 15
TEA 29
Tall Oil Fatty acid 27
Barlox 12 14
Formulation F below is another example of a stable cleaning
concentrate in accordance with the invention.
FORMULATION F
Component Wt%
HetoxolTM L 02 15
Ethylan HB4 15
TEA 29
LAS 27
Barlox 12 14
Hetoxol L 02 (POE-2 Lauryl Ether - CAS# 9002-92-0) is a nonionic Cis
alkyl with 2 moles of EO with an HLB of 6.1 and is commercially available
from Heterene Inc.
Formulation G below is another example of a stable cleaning
composition in accordance with the invention.
23
CA 02532032 2006-01-10
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
FORMULATION G
Component Wt%
Tomadol 1-3 15
Ethylan HB4 15
TEA 6
LAS 4
Barlox 12 2.5
Water 57.5
As illustrated in the chart below, Ethylan HB4 and Tomadol 1-3
were combined to form a mixture in the specified amounts and then were
diluted with water and visually observed to determine is the solution
remained stable. Microemulsions and clear solutions indicate that the
solution was stable.
Ethylan Tomadol % mixture in water
HB4 1-3
5 10 15 20
50 50 Milky Milky Milky Clear
55 45 Milky Milky Microemulsion Clear
60 40 Milky Microemulsion Clear Clear
65 35 Microemulsion Clear Clear Clear
24
CA 02532032 2006-01-10
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
As illustrated in the chart below, Ethylan HB4 and Surfonic L24-1.3
were combined to form a mixture in the specified amounts and then were
diluted with water and visually observed to determine is the solution
remained stable. Microemulsions and clear solutions indicate that the
solution was stable.
Ethylan Surfonic % mixture in water
HB4 L24-1.3
5 10 15 20
50 50 Milky Milky Milky Milky
55 45 Milky Milky Milky Milky
60 40 Milky Milky Clear Microemulsion
65 35 Milky Clear Microemulsion Clear
70 30 Milky Microemulsion Clear Clear
75 25 Microemulsion Clear Clear Clear
Ethylan Surfonic L24- % mixture in water
HB4 1.3
25 30
50 50 Milky Clear
55 45 Microemulsion Clear
60 40 Clear Clear
65 35 Clear Clear
70 30 Clear Clear
75 25 Clear Clear
As in the above tables, stable aqueous dilutions of hydrophobic surfactant
and aryl ethoxylate can be formed in the absence of any other substance.
CA 02532032 2011-11-29
WO 2005/019399 PCT/US2004/024827
The present invention should not be considered limited to the
particular examples described above, but rather should be understood to
cover all aspects of the invention as fairly set out in the attached claims.
26