Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02549711 2006-06-08
NOISE DAMPENER FOR A GARAGE DOOR OPENER
Field of the Invention
This invention relates to the field of garage door openers, and in particular
to
=
noise dampening systems for garage door openers.
Background of the Invention
Garage door openers are characteristically comprised of two primary
components, namely a motor and a chain. The motor is mounted in a housing. The
housing is
suspended from the garage ceiling, set back from the garage door. Typically a
long piece of
metal channel extends from the housing to the garage wall above the door. The
chain runs in
or on the channel. The distal end of the channel is rigidly affixed to the
wall above the garage
door. Ordinarily the chain is a heavy gauge endless or circular chain. An arm
extends from the
chain to the top of the garage door. The chain turns around, and is driven by,
a drive sprocket
extending from the motor. The chain also turns around an idler sprocket or the
like at the
opposite end of the channel adjacent the wall above the garage door.
When engaged, the motor turns the drive sprocket. The drive sprocket turns the
chain thereby causing the arm and, consequently, the garage door to move
either toward or
away from the motor. The motor is attached to the garage ceiling by means of
two or more
metal bars or struts, the upper ends of which are ordinarily rigidly mounted
to the wood trusses
above the ceiling.
As garage doors are heavy, the garage door opener motor must be sufficiently
powerful in order for it to lift the door by pulling the arm along the
channel. The supports
= attaching the motor housing to the ceiling must be sufficiently strong to
bear the static weight
1
CA 02549711 2006-06-08
of the motor as well as the additional strain created when the motor is
running and the chain
and garage door are in motion.
When operating, the running of the motor, and in particular, the action of the
sprocket and chain, create significant vibration. This vibration is evidenced
by significant
noise in the garage and by the generation of acoustic frequency vibration
transmitted to the
structure of the building via the struts which are rigidly attached to the
ceiling and thus
through to the ceiling joists above. The vibration is also transmitted through
the end of the
channel where it is rigidly mounted to the wall above the garage door. The
struts and chain
channel, being both rigid, are good conduits of the acoustic frequency
vibration. The vibration
generated by the motor and chain operation is transmitted through the struts,
and to a lesser
degree through the chain channel, into the structure of the building resulting
in noise being
heard inside the building. Although Applicant does not wish to be bound by any
particular
theory of operation, it is postulated that the acoustic frequency vibration
created by the motor
and chain is transmitted into the structural framework of the building. Thus,
being of a dense
mass, the framework effectively transmits the acoustic frequency vibration to
other parts of the
building. In addition, the space between the walls of the building each
covered, for example,
by drywall, may act to amplify the sound. In the case in many multi-unit
buildings where the
framework of the building is concrete or steel, the structure makes an
excellent transmitter of
sound.
Hence, there is a need for, and it is one object of the present invention to
provide a means to attenuate the structure-borne acoustic vibration created by
the operation of
a conventional garage door opener.
2
CA 02549711 2006-06-08
Summary of the Invention
The invention described here is for use with a garage door motor as is found
in
conventional garage door openers. wherein a motor-driven chain functions to
raise and lower
the garage door.
The present invention replaces, in whole or in part, the conventional use of
rigid
metal struts attaching the motor to the ceiling and building frame. The struts
are replaced in
whole or in part with resilient hangers comprised of a resilient material such
as rubber. To
mount the motor to the ceiling, one end of each of the resilient hangers is
attached to the motor
housing or struts. The other ends of the resilient hangers are attached to a
rigid mounting bar.
The mounting bar is rigidly mounted to the garage, advantageously so as to
perpendicular the
direction of the garage trusses. Orienting the mounting bar across the trusses
makes it easier to
mount the mounting bar to both the garage ceiling and the garage trusses. This
is because the
mounting bar may be provided with holes along its length, and the installer
may thus simply
use whichever holes in the mounting bar align with the garage trusses so as to
bolt the
mounting bar directly into the bottom of the trusses. Quite often this
orientation of the
mounting bar means that the motor must be mounted perpendicular to the
mounting bar. This
orientation is also advantageous in that the position of the motor may be
easily adjusted along
the mounting bar so as to align with the center of the garage door even though
the motor does
not align directly under one or more of the trusses.
The use of at least two resilient hangers, one on each side of the motor
housing,
equalizes the distribution to the mounting bar of the weight of the motor,
housing, channel,
chain, etc. and helps maintain the motor level. The ability to retrofit the
resilient hangers to a
variety of makes and models of conventional garage door openers adds utility
to the present
invention.
3
CA 02549711 2006-06-08
In summary, the noise dampener for a garage door opener of the present
invention may be characterized in one aspect as including a pair of resilient
members, each
resilient member of the pair of resilient members having first and second
opposite ends. The
first ends are adapted for mounting to a garage ceiling mounting bracket. The
second ends are
adapted for mounting to motor mounts mounted to an upper side of a motor
housing of the
garage door opener. The first and second ends of the resilient members are
mountable to the
ceiling mounting bracket and the motor mounts respectively by fastening means
through
apertures in the first and second ends. A vibration dampening pad is provided
for mounting
between the garage wall adjacent the garage door and a chain channel support
extending from
the motor housing.
The first and second ends are wide so as to provide a widened bearing surface
for distributing the weight load from the garage door opener to the ceiling.
The second ends
are widened so as to distribute the weight load when the second ends are
mounted to the motor
IS mounts.
In one embodiment the pair of resilient elongate members are each
substantially
rectangular so as to provide the bearing surfaces on each of the first and
second ends, the first
and second ends have a plurality of apertures therein for journaling fasteners
therethrough.
A centre portion of each elongate member may include an elongate aperture so
that the centre portion comprises a substantially parallel spaced apart array
of elongate resilient
struts extending between the first and second ends.
4
CA 02549711 2006-06-08
Brief Description of the Drawings
Figure I is, in right side perspective view, a conventional garage door
opener.
Figure 2 is, in right side perspective view, one embodiment of the noise
dampener for a garage door opener according to the present invention.
Figure 3 is, in right side perspective view, a further embodiment of the noise
dampener for a garage door opener according to the present invention.
Figure 3a is, in plan view, a resilient dampener according to the embodiment
of
Figure 3.
Figure 4 is, in perspective view, a pair of the dampeners of Figure 3a mounted
to a strut and ceiling mounting bar.
Figure 5 is, in perspective view, one embodiment of a dampener mounted
between the distal end of a chain supporting channel and a garage wall above a
garage door.
Figure 6 is, in perspective view, a further embodiment of the dampener
mounted between the distal end of the chain supporting channel and the garage
wall above the
garage door.
Figure 7 is, in perspective view, the dampener of Figure 6.
Figure 8 is, in plan view, one of the rigid guides of the dampener of Figure
7.
Figure 9 is, in plan view, one of the compression absorbers of the dampener of
Figure 7.
5
CA 02549711 2006-06-08
Detailed Description of Embodiments of the Invention
Figure 1 depicts a conventional garage door opener motor housing 10, chain
channel 12, chain 14, motor housing mounting rails 16, metal struts 18 and
ceiling mounting
bar 20. Chain 14 is an endless chain which slides carriage 22 in direction A
along channel 12
thereby drawing the garage door along by means of connecting arm 24.
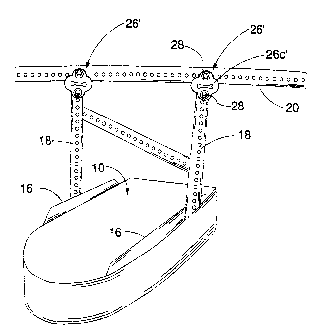
In the present invention metal struts 18 are replaced in whole or in part with
resilient hangers 26 as shown in Figure 2. Without intending to be limiting,
two embodiments
of resilient hangers are depicted; namely, resilient hangers 26, and resilient
hangers 26' as
shown in Figures 3, 3a and 4.
Any suitable means may be used to attach the resilient hangers 26 or 26' so as
to be suspended between motor mounting rails 16 and ceiling mounting bar 20.
Without
intending to be limiting, Figure 2 illustrates an embodiment wherein two
resilient mounting
hangers 26 are bolted to corresponding motor mounting rails 16 and to the
ceiling mounting
bar 20. At the lower ends of each hanger 26, bolts 28 are inserted through
holes in the
corresponding hanger 26 and then through corresponding holes in motor mounting
rail 16.
Nuts secure the bolts in place. The upper ends of hangers 26 are bolted to
ceiling mounting
bar 20. Advantageously, bar 20 is mounted perpendicular to the long axis of
channel 12 so
that bar 20 crosses perpendicularly under the garage trusses (not shown) for a
mounting of bar
20 thereto. Consequently, bar 20 is also perpendicular to rails 16. Each
hanger 26 allows for a
90 degree twist between its upper and lower ends so that wide flange 26a of
the upper end of
the hanger may be mounted securely along bar 20, and wide flange 26b at the
lower end of the
hanger may be mounted securely along a corresponding rail 16. Because hangers
26 are
resilient they allow for twisting torsion without compromising weight-bearing,
that is, tensile
strength.
6
CA 02549711 2006-06-08
In the embodiment of Figure 2, two resilient hangers 26 are mounted on either
side of motor housing 10. The use of two or more hangers 26 reduces the
tensile load on each
hanger and may improve attenuation of the vibration resulting from the
operation of the motor
and chain drive moving the garage door. In addition, the aperture, in this
embodiment an
elongate aperture 26c, along the centerline of each hanger is thought to
further spread out, and
thereby reduce on individual loading points, the static and dynamic loading on
each hanger
while at the same time further increasing the attenuation of vibration which
causes noise.
As the static and dynamic loading on the resilient mounting hangers will cause
stress concentration at, and strain of, the holes where bangers 26 are
attached to rails 16 and
will cause stress and strain of hangers 26 themselves, the resilient material
selected for the
hangers should be made of a resilient material which is tear resistant such
as, without
intending to be limiting, heavy rubber.
In another embodiment, in order to retrofit the resilient mounting hangers to
garage door openers presently in use, three or four mounting hangers around
the periphery of
the motor housing, each hanger made of resilient material, may be utilized.
This may result in
increased stability, reduced static and dynamic weight-bearing load on each
hanger and may
increase attenuation of vibration.
In another embodiment of the present invention as seen in Figures 3, 3a and 4,
resilient hangers 26' are mounted between the upper ends of struts 18 and bar
20. Without
intending to be limiting, Figure 3 illustrates two resilient hangers 26'
bolted between metal
struts 18 and ceiling mounting bar 20. Each resilient hanger 26' may be
cloverleaf in shape so
as to define four arcuate protrusions extending from between four
corresponding notches or
indentations 26a'. The upper and lower arcuate protrusions contain mounting
holes 26b' for
joumaling of bolts 28 therethrough. Each hanger 26' has an elongate aperture
26c' along an
axis approximately perpendicular to the vertical load, that is horizontal when
installed. The
indentations 26a' are contoured into an approximately 90 degree corner angle
to fit over, that is
7
CA 02549711 2006-06-08
conform to, the upper end of the L-shape of each strut 18 as seen in Figure 4
such that each
hanger 26' may be attached to a corresponding strut. Any suitable means may be
used to
mount resilient hangers 26' to struts 18 at one end, and to mounting bar 20 at
the other end
Conventionally, bar 20 is mounted perpendicular to the long axis of channel 12
so that bar 20
crosses under the garage trusses (not shown) for a mounting of bar 20 thereto.
Consequently,
bar 20 is also perpendicular to rails 16. As best seen in Figure 4,
utilization of two hangers 26'
on each side of each strut 18 and on each side of mounting bar 20 reduces the
weight-bearing
tensile load on each hanger 26' thereby reducing the risk that bolts 28 will
pull through the
holes or otherwise tear the hangers 26'. The elongate aperture 26c' along the
centerline of each
hanger 26' is thought to further spread the static and dynamic loading on each
hanger while at
the same time, through the absorption by each hanger of the shock and
vibration caused by the
operation of the garage door opener, further increasing the attenuation of
vibration which
causes noise. Each hanger 26 or 26' serves as a vibration attenuating buffer
between struts 18
and bar 20.
In another embodiment, in order to retrofit the resilient mounting hangers to
garage door openers presently in use, three or four mounting hangers, each
made of resilient
materials, may be utilized. This may result in increased stability, reduced
static and dynamic
weight-bearing load on each hanger and increased attenuation of vibration.
In a further aspect of the invention, a resilient dampener 30 is mounted
between
the end of channel 12 opposite the motor and the garage wall 32 over the
garage door opening.
Without intending to be limiting, Figures 5 and 6 illustrate two embodiments
of
a resilient dampener mounted between the end of channel 12 and the garage door
wall 32.
Any suitable means may be used to attach the resilient dampener 30 between a
mounting
bracket 34 and the garage door wall 32. The dampener is made of a resilient
material.
Cavities, such as elongate passageways or ducts 36 in dampener 30 (ducts 36
shown partly in
dotted outline in Figure 5) extend in parallel array through dampener 30.
Screws or the like
8
CA 02549711 2006-06-08
are inserted through holes in mounting bracket 34 and through corresponding
holes (not
shown) in dampener 30 so as to mount into garage door wall 32. Passageways or
ducts 36
serve as further shock absorbers, that is, they assist in absorbing or
attenuating vibration
transmitted from channel 12 into dampener 30.
In a further embodiment of the invention seen in Figures 6 to 9, mounting
bracket 34 and dampener 30 are replaced with a shock absorber assembly 38. The
end 12a of
channel 12 is attached to garage door wall 32 by means of shock absorber
assembly 38.
Assembly 38 includes a U-shaped mounting bracket 40, two rigid extension
limiter guides 42,
two resilient compression absorbers 44, and bolts 46a and 46b for mounting the
two extension
limiter guides 42 and the two compression absorbers 44 between the U-shaped
bracket 40 and
end 12a of channel 12. Compression absorbers 44 are oblong in shape with
mounting holes
44a located at each longitudinal end. An elongate, hour-glass shaped cavity
44b is formed so
as to extend through each absorber 44 and perpendicular to the longitudinal
axis bisecting the
mounting holes 44a. The extension limiter guides 42 have an elongate aperture
42a in one end
and a mounting hole 42b at the other end.
In use, the mounting bracket 40 is bolted to the wall 32 through holes 40a.
The
extension limiter guides 42 and compression absorbers 44 are attached to the U-
shaped
mounting bracket with bolts 46a and 46b journalled through holes 42a, 42b in
guides 42 and
holes 44a in absorbers 44. Nuts 46a secure bolts 46a and 46b in place.
When the garage door is in the closed position, the compression absorbers 44
and extension limiter guides 42 are closely parallel and proximate at one end
to garage door
wall 32. When the garage door opener is engaged, thereby causing the door to
be raised, the
compression absorbers 44 and the extension limiter guides 42 rotate in
direction A on the axis
of rotation about the two bolts 46a and 46b. The elongated apertures 42a of
the extension
limiter guides 42 allow bolt 46 mounted therein to slide forward and backwards
in direction B
with the movement in direction C of channel 12 caused by the operation of the
garage door
9
CA 02549711 2014-04-08
opener, taking with it the compression absorbers 44, being resilient, allow
channel 12 to move
toward and away from garage door wall 32. The forward and backward movement of
channel
12 caused by the operation of the garage door opener creates pressure on bolt
46a, the pressure
is transmitted to bolt 46b through absorber 44. As bolt 46b has limited
mobility being
constrained within hole 42a, and thus acts as a stop for the compression of
absorbers 44 as
channel 12 moves towards the wall 32. The compression absorbers 44 compress to
absorb some
or all of the forward movement of channel 12 toward the wall 32 and stretch to
allow the
backward movement of channel 12 away from wall 32. The movement of the channel
is thereby
cushioned or absorbed by the compression absorbers 44 to attenuate the
vibration which, it is
thought, causes noise.
As will be apparent to those skilled in the art in the light of the foregoing
disclosure, many
alterations and modifications are possible in the practice of this invention
without departing
from the spirit or scope thereof.