Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02550750 2006-06-21
ATTORNEY DOCKET NO.: 25.0333 UTILITY PATENT
COILED TUBING OVERBALANCE STIMULATION SYSTEM
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
[0001] The present invention relates in general to stimulating a well to
increase the rate of flow
into or out of the surrounding formation and more particularly to a method and
apparatus for
extreme overbalance stimulation of the formation surrounding a well utilizing
coiled tubing.
BACKGROUND
[0002] Well stimulation refers to techniques used for increasing the
productivity of the
formations surrounding the well. For production wells, it is important to
increase the rate at
which fluid flows from the formation into the wellbore. For injection wells,
it is often important
to increase the rate of injection of fluid into the surrounding formation.
[0003] The region of the formation proximate the wellbore is very often the
most significant
restriction to the well's productivity. This region is frequently damaged
during the drilling of the
wellbore creating resistance to fluid flow through the region. The resistance
to fluid flow near
the wellbore is defined by "skin factor." Skin factors are measured by
measuring bottom hole
pressures in a well under differing flow conditions. A positive skin factor
indicates that the
region near the wellbore is more resistive to flow than the formation farther
away from the
wellbore. A negative skin factor indicates that the region near the wellbore
is less resistive to
fluid flow than the formation farther away from the wellbore. The resistance
to fluid flow can be
reduced by stimulation.
1
CA 02550750 2006-06-21
ATTORNEY DOCKET NO.: 25.0333 UTILITY PATENT
[0004] The two primary methods for treating these damaged regions or zones to
stimulate
productivity, include chemical stimulation and fracturing. In chemical
stimulation, fluids such as
acids or other chemicals are injected into the formation to interact with the
rock matrix to
increase the permeability of the formation. In hydraulic fracturing, a fluid
under a pressure
greater than the stress of the formation is injected forming fractures in the
rock matrix.
Typically, proppant is included in the fracturing fluid so as to be lodged in
the fractures to
maintain the created permeability to fluid when the fracturing pressure
ceases. It is desired at
times to combine chemical stimulation with fracturing, for example with acid
fracturing. In
certain circumstances fractures may be created extending hundreds of feet from
the wellbore.
[0005] It is more economical, and at times only necessary, to create fractures
near the wellbore.
One method of creating these near-wellbore fractures is by overbalance
stimulation, wherein
pressure greater than the formation's fracture pressure is suddenly released
proximate the
formation. Prior art methods have been utilized, however, these methods are
expensive and
often uneconomical and thus not feasible for multi-formation wells. The prior
art systems fail to
provide a mechanism for selectively treating formation zones in uncompleted,
open hole,
wellbores or slotted liner completions.
[0006] Therefore, it is a desire to provide an extreme overbalance stimulation
method that
addresses the shortcomings of the prior art devices. It is a still further
desire to provide a
overbalance stimulation method that utilizes coiled tubing as the main
treatment string.
2
CA 02550750 2006-06-21
ATTORNEY DOCKET NO.: 25.0333 UTILITY PATENT
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0007] In view of the foregoing and other considerations, the present
invention relates to an
extreme overbalance stimulation method utilizing coiled tubing as the main
treatment string.
[00081 Accordingly, an extreme overbalance stimulation system and method is
provided. An
embodiment of the overbalance stimulation method includes positioning an
assembly connected
to coiled tubing adjacent a target formation zone and sealing between the
coiled tubing and the
formation to isolate the target formation zone from the rest of the wellbore.
A desired pressure is
accumulated in the coiled tubing with a treatment fluid. The desired pressure
is at least equal to
the fracture pressure of the target formation zone. The accumulated pressure
is substantially
instantaneously released through the assembly at the target formation zone.
[0009] In another embodiment, the extreme overbalance stimulation method
includes positioning
an assembly connected to coiled tubing adjacent a target formation zone,
wherein the assembly
includes a perforating gun. A desired pressure is accumulated in the coiled
tubing with a
treatment fluid. The desired pressure is at least equal to the fracture
pressure of the target
formation zone. Upon detonating the perforating gun the accumulated pressure
is substantially
instantaneously released through the assembly at the target formation zone.
Creating a
temporary path of least resistance, ensuring preferential flow toward the
targeted zone in open
hole and slotted liner completions.
[0010] The system may include a coiled tubing unit having coiled tubing
adapted for disposing
in a wellbore and a pump (or several pumps) for providing a pressurized
treatment fluid in the
coiled tubing. A pressure release device is in fluid connection with the
coiled tubing, the
3
CA 02550750 2008-05-28
79628-57(S)
pressure release device being connected to a port
positionable proximate a targeted formation zone. The
pressure release device is operatable between a closed
position for maintaining the pressurized treatment fluid
within the coiled tubing, and an open position for
substantially instantaneously discharging the pressurized
treatment fluid through the port. The system may further
include a top sealing element adapted for sealing between
the coiled tubing and the formation, and a bottom sealing
element adapted for sealing between the coiled tubing and
the formation, wherein the bottom sealing element is spaced
from the top sealing element sufficient to isolate the
targeted formation zone from the rest of the wellbore.
[0011] The foregoing has outlined the features and
technical advantages of the present invention in order that
the detailed description of the invention that follows may
be better understood. Additional features and advantages of
the invention will be described hereinafter which form the
subject of the claims of the invention.
[0011A] According to one aspect of the present invention,
there is provided a method of selectively stimulating a
targeted formation zone from a wellbore surrounded by a
formation utilizing coiled tubing as the conduit for the
stimulation, the method comprising the steps of: positioning
an assembly connected to coiled tubing adjacent a target
formation zone; sealing between the coiled tubing and the
formation to isolate the target formation zone from the rest
of the wellbore; accumulating a desired pressure in the
coiled tubing with a treatment fluid, the desired pressure
at least equal to the fracture pressure of the target
formation zone; releasing substantially instantaneously the
accumulated pressure through the assembly at the target
formation zone; releasing the sealing isolating the target
4
CA 02550750 2008-05-28
79628-57(S)
formation zone; repositioning the assembly adjacent a
subsequent target formation zone; sealing between the coiled
tubing and the formation to isolate the subsequent target
formation zone from the rest of the wellbore; accumulating
pressure in the coiled tubing at least equal to the fracture
pressure of the subsequent target formation zone; and
releasing substantially instantaneously the accumulated
pressure through the assembly at the subsequent target
formation zone.
[0011B] According to another aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a method of selectively
stimulating a targeted formation zone from a wellbore
utilizing coiled tubing as the conduit for the stimulation,
the method comprising the steps of: positioning an assembly
connected to coiled tubing adjacent a target formation zone,
the assembly including a perforating gun; accumulating a
desired pressure in the coiled tubing with a treatment
fluid, the desired pressure at least equal to the fracture
pressure of the target formation zone; detonating the
perforating gun; releasing substantially instantaneously the
accumulated pressure through the assembly at the target
formation zone; wherein the step of accumulating comprises:
injecting a first treatment fluid into the coiled tubing;
and pressurizing the first treatment fluid by a second
treatment fluid in the coiled tubing.
[OO11C] According to still another aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a method of selectively
stimulating a targeted formation zone from an uncased
portion of a wellbore utilizing coiled tubing as the conduit
for the stimulation, the method comprising the steps of:
positioning an assembly connected to coiled tubing adjacent
a target formation zone; accumulating a desired pressure in
the coiled tubing with a treatment fluid including an acid,
4a
CA 02550750 2008-05-28
79628-57(S)
the desired pressure at least equal to the fracture pressure
of the target formation zone; and releasing substantially
instantaneously the accumulated pressure through the
assembly at the target formation zone.
5[0011D] According to yet another aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a method of selectively
stimulating a targeted formation zone from a wellbore
surrounded by a formation utilizing coiled tubing as the
conduit for the stimulation, the method comprising the steps
of: positioning an assembly connected to coiled tubing
adjacent a target formation zone; sealing between the coiled
tubing and the formation to isolate the target formation
zone from the rest of the wellbore; accumulating a desired
pressure in the coiled tubing with a treatment fluid, the
desired pressure at least equal to the fracture pressure of
the target formation zone, the desired pressure is
accumulated by injecting a first treatment fluid into the
coiled tubing and pressurizing the first treatment fluid by
a second treatment fluid in the coiled tubing; and releasing
substantially instantaneously the accumulated pressure
through the assembly at the target formation zone.
[0011E] According to a further aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a method of selectively
stimulating a targeted formation zone from an uncased
portion of a wellbore utilizing coiled tubing as the conduit
for the stimulation, the method comprising the steps of:
positioning an assembly connected to coiled tubing adjacent
a target formation zone; accumulating a desired pressure in
the coiled tubing with a treatment fluid including an acid,
the desired pressure at least equal to the fracture pressure
of the target formation zone, the desired pressure is
accumulated by injecting a first fluid into the coiled
tubing and pressurizing the first treatment fluid by a
4b
CA 02550750 2008-05-28
79628-57(S)
second treatment fluid in the coiled tubing; and releasing
substantially instantaneously the accumulated pressure
through the assembly at the target formation zone.
4c
CA 02550750 2006-06-21
ATTORNEY DOCKET NO.: 25.0333 UTILITY PATENT
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0012] The foregoing and other features and aspects of the present invention
will be best
understood with reference to the following detailed description of a specific
embodiment of the
invention, when read in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, wherein:
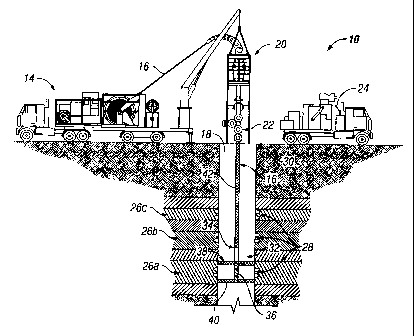
[0013] Figure 1 is an illustration of an embodiment of the overbalance
stimulation system of the
present invention set for stimulating a first formation zone;
[0014] Figure 2 is a schematic illustrating the stimulation of the first
formation zone of Figure 1;
[0015] Figure 3 is an illustration of the overbalance stimulation system set
for stimulating a
subsequent formation zone;
[0016] Figure 4 is a schematic illustrating the stimulation of the second
formation zone;
[0017] Figure 5 is an illustration of another embodiment of the overbalance
stimulation system
of the present invention; and
[0018] Figure 6 is an illustration of the step of stimulating a targeted
formation system of the
embodiment of Figure 5.
CA 02550750 2006-06-21
ATTORNEY DOCKET NO.: 25.0333 UTILITY PATENT
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
[0019] Refer now to the drawings wherein depicted elements are not necessarily
shown to scale
and wherein like or similar elements are designated by the same reference
numeral through the
several views.
[0020] As used herein, the terms "up" and "down"; "upper" and "lower"; and
other like terms
indicating relative positions to a given point or element are utilized to more
clearly describe
some elements of the embodiments of the invention. Commonly, these terms
relate to a
reference point as the surface from which drilling operations are initiated as
being the top point
and the total depth of the well being the lowest point.
[0021] Figure 1 is an illustration of an embodiment of an overbalance
stimulation procedure and
system using coiled tubing, generally denoted by the numeral 10. Overbalance
stimulation
system 10 includes a coiled tubing unit 14 having coiled tubing 16 for
spooling into and out of a
wellbore 18 via an injector head 20 (or other coiled tubing deployment
apparatus) through a
wellhead 22. A pump 24 is in fluid communication with coiled tubing 16 for
providing a
pressurized treatment fluid described in more detail below. As well-known in
the art, pump 24 is
further connected to a treatment fluid reservoir (not shown) as well as a high
pressure treating
line (not shown). The treatment fluid may include, singularly or in
combination, a variety of
fluids, including, but not limited to, gasses, liquids, acids, gels, foams,
and slurries. It should be
further recognized that the treatment fluid may carry a proppant.
[0022] Wellbore 18 may be substantially vertical or at any angle including
horizontal. The earth
surrounding the wellbore includes a formation having one or more formation
zones that are
6
CA 02550750 2006-06-21
ATTORNEY DOCKET NO.: 25.0333 UTILITY PATENT
targeted to produce fluid from or inject fluid into. In the present embodiment
three target zones
26a, 26b, and 26c are illustrated. Zones 26 may include perforations 28, or
perforations may be
created during the process of the present invention. Wellbore 18 may include
casing 30, include
a slotted liner, be an open hole completion, or be a combination of the
aforementioned.
[0023] System 10 further includes a bottom hole assembly (BHA) or treatment
assembly 32 in
functional and fluid connection with coiled tubing 16. Assembly 32 includes a
pressure release
device 34, a discharge port 36 and an upper and lower sealing element 38, 40.
[0024] Sealing elements 38 and 40 may be packers, cups or any other elements
or mechanisms
adapted for isolating a formation zone 26 to be stimulated from the rest of
wellbore 18. Pressure
relief device 34 is adapted for maintaining treatment fluid 42 within coiled
tubing 16 under
pressure until it is desired to discharge fluid 42 through port 36. Pressure
relief device 34 may
be, but is not limited to, valves or frangible discs. Port 36 is positioned
between sealing elements
3 8, 40.
[0025] Figure 1 illustrates the system set in wellbore 18 for stimulating
first formation zone 26a.
Although first formation zone 26a is illustrated as the lower formation zone,
the first formation
zone may be any zone desired to be treated. Coiled tubing 16 is spooled
through injector head
20 and wellhead 22 into wellbore 18 positioning BHA 32 proximate first zone
26a. Sealing
elements 38 and 40 are set between coiled tubing 16 and formation 26,
substantially sealing zone
26a from communication with the remaining portion of wellbore 18. Port 36 is
positioned
proximate first formation zone 26a and pressure release device 34 is in the
closed position,
preventing fluid flow between coiled tubing 16 and wellbore 18 through port
36.
7
CA 02550750 2006-06-21
ATTORNEY DOCKET NO.: 25.0333 UTILITY PATENT
[0026] With port 36 of pressure release device 34 in the closed position,
pressure is accumulated
in coiled tubing 16. The desired pressure accumulated is at least equal to and
preferably greater
than the fracturing pressure for the targeted zone 26, shown as zone 26a in
Figure 1. The
fracture pressure of the zone varies with its depth and its geological
characteristics. Often, an
initial breakdown pressure greater than the fracture pressure is required to
initiate the fractures.
This higher initial breakdown pressure is due in part to the necessity of
overcoming the tensile
strength of the rock. Thus, the desired pressure accumulated may be equal to
or greater than the
initial breakdown of the formation of interest.
[0027] The pressure is accumulated by pumping treatment fluid 42 into coiled
tubing 16 via
pump 24. As described, treatment fluid 42 may be any fluid necessary and
adapted for the
fracturing the formation zone of interest. For example, it may be desired to
utilize nitrogen in a
coal seam well. Additionally, it may be desired to include proppant in
treatment fluid 42 to
maintain the fractures when the pressure is released, or follow the initial
extreme overbalance
stimulation with a fluid carrying proppant or other treatment substances.
[0028] Figure 2 illustrates the step of fracturing zone 26a utilizing extreme
overbalance
stimulation. Once the desired stimulation pressure is accumulated in coiled
tubing 16, pressure
release device 34 is activated to the open position in a manner to
substantially instantaneously
release the accumulated pressure through port 36 to act on formation 26a.
Pressure release
device 34 may be activated by any suitable means. For example, the release
device 34 may be a
frangible disc activated by a dropped bar or ball. Similarly, the release
device 34 may be a valve
8
CA 02550750 2006-06-21
ATTORNEY DOCKET NO.: 25.0333 UTILITY PATENT
activated electrically, hydraulically or optically. Any means capable of
activating the pressure
release device 34 should be considered to be within the scope of the present
invention.
[0029] The sudden, substantially instantaneous, release of the accumulated
pressure equal to or
greater than the fracturing pressure causes fractures 44 to be formed in zone
26a. Seals 38, 40
isolates treatment fluid 42 and the accumulated pressure at zone 26a. Further
pumping of
treatment fluid 42 or a subsequent treating fluid may be pumped after the
shock treatment. The
overbalance treatment may be repeated numerous times if a series of shocks are
needed or
desired.
[0030] With reference to Figures 2 and 3, once stimulation of zone 26a is
completed seals 38, 40
are released. Coiled tubing 16 is then spooled positioning port 36 of pressure
release device 34
adjacent to the next formation zone targeted for stimulation, shown as 26b
herein. Seals 38, 40
are set substantially isolating zone 26b from the rest of wellbore 18 and
formation 26. With
pressure release device 34 in the closed position, the pressure, via treatment
fluid 42 and pump
24, is accumulated in coiled tubing 16 at a pressure equal to or greater than
the fracture pressure
of formation zone 26b.
[0031] Once the desired pressure is accumulated, pressure release device 34 is
activated
substantially instantaneously releasing treatment fluid 42 and the accumulated
pressure through
port 36 at zone 26b, as shown in Figure 4. This sudden release of treatment
fluid 42 under
pressure creates fractures 44, or stimulates pre-existing natural fractures,
cleats or other naturally
occurring or man-made pathways in zone 26b. After stimulation of zone 26b, the
extreme
overbalance stimulation may be conducted on subsequent formation zones 26
without requiring
9
CA 02550750 2006-06-21
ATTORNEY DOCKET NO.: 25.0333 UTILITY PATENT
the removal of coiled tubing 16 or assembly 32 from wellbore 18. Additionally,
the stimulation
of multiple zones does not require the making or breaking of a jointed tubing
string. The present
invention utilizes coiled tubing 16 as the conduit for the stimulation.
[0032] Figures 5 and 6 are illustrations of another embodiment of the
stimulation system of the
present invention, generally denoted by the numeral 10. Illustrated is a
horizontal wellbore 18,
having an open hole section 46, in a carbonate formation. A portion of
wellbore 18 is cased 30
and the well may include jointed tubing 50. The well is designated for
stimulation of the
targeted formation zone 26a. Open hole section 46 may have only one pay zone
26a of interest,
or multiple zones. The prior art stimulation systems require large amounts of
costly treatment
fluids and a may require higher horsepower to stimulate the target zone as
well as the formation
surrounding the uncompleted portion of wellbore 18 that is not of interest.
[0033] Overbalance stimulation system 10 of the present invention provides a
cost effective
method for selectively stimulating zone 26a. Bottom hole assembly 32 includes
a pressure
release device 34 and a perforating gun 48. Assembly 32 is functionally
connected and carried
by coiled tubing 16. Assembly 32 is positioned adjacent to the target zone 26a
with the pressure
release device 34 in the closed position maintaining fluid and pressure within
coiled tubing 16.
[0034] Pressure is accumulated in coiled tubing 16. The pressure may be
accumulated by first
injecting a volume of a first treatment fluid 42a, such as acid, into coiled
tubing 16. Desirably
first treatment fluid is a liquid. A second treatment fluid 42b, is pumped
into coiled tubing 16 to
pressurize the treatment fluid. Desirably, the second treatment fluid is a gas
such as, but not
CA 02550750 2006-06-21
ATTORNEY DOCKET NO.: 25.0333 UTILITY PATENT
limited to, nitrogen. The desired pressure of treatment fluid 42 may be equal
to, or greater than,
the fracture pressure of formation 26a.
[0035] Once the desired pressure of treatment fluid 42 is achieved, zone 26a
may be stimulated.
Perforating gun 32 is detonated. The detonation of gun 32 initiates fractures
44 by creating
perforations. Substantially simultaneous with the detonation of gun 32,
treatment fluid 42 is
substantially instantaneously released under pressure at formation 26a,
illustrated by the arrows
in Figure 6. The extreme overbalance release of treatment fluid 42 extends
fractures 44
connected to the wellbore through the perforation tunnels.
[0036] From the foregoing detailed description of specific embodiments of the
invention, it
should be apparent that a method and system for overbalance stimulation with
coiled tubing that
is novel and unobvious has been disclosed. Although specific embodiments of
the invention
have been disclosed herein in some detail, this has been done solely for the
purposes of
describing various features and aspects of the invention, and is not intended
to be limiting with
respect to the scope of the invention. It is contemplated that various
substitutions, alterations,
and/or modifications, including but not limited to those implementation
variations which may
have been suggested herein, may be made to the disclosed embodiments without
departing from
the spirit and scope of the invention as defined by the appended claims which
follow.
11