Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02555606 2006-08-04
1
FLOOR COVERINGS WITH WOODEN FLOORS ON A SUBSTRATE, METHOD FOR
THE COVERING OF A SUBSTRATE AND USE OF STUDDED PLATES
Area of the Invention
The present invention concerns floor coverings with wooden
floors on a substrate, for example of concrete. The invention
also concerns a method for the covering of a substrate with a
_
floor covering and the use of a studded plate for such
flooring.
Technical Background
It is known to use studded plates as supporting plates. They
may be used as ordinary supporting plates, drainage plates,
decoupling plates, or plaster plates for plastering or support
for adhesive for tiles, for example when flooring with ceramic
tiles.
All concrete floors which are laid directly on the ground
contain moisture. Therefore, floor coverings such as wooden
floors may not be placed directly on the concrete. Many years
may be needed to dry out a concrete floor which is a slab on
ground construction. The floor may also be affected by rising
damp. Initially, all concrete floors contain residual moisture
and the above problem therefore concerns cellars, basement
floors, slab on ground floors and floors between different
storeys of different types of concrete, including for example
floors made of light expanded clay aggregate concrete and
lightweight concrete, plaster based floors, floating floors,
floating floors screed or flooring substitute, generally all
floors which have the feature of curing or hardening by using
water. The moisture in the concrete is often invisible and
difficult to detect. This results in an unawareness of the
risks such as rot, moisture damage etc. Without an effective
damp proof membrane with sufficient performance
characteristics, moisture from the concrete will for example
attack wood materials from underneath. The same problem also
CA 02555606 2006-08-04
2
concerns tiled floors wherein the filled joints will allow
passage of moisture.
The result is damaged floors with swelling, mould and rot. In
addition, hazardous mould spores, bad smell and a poor indoor
environment may result.
Studded plates are used to prevent problems related to
moisture in floors. To solve such problems, "passive" venting
may be provided towards the room. The studded plates often
comprise hollow studs with rounded, square or other cross-
sections, i.e. the form of the circumference of the studs,
with a diameter or transversal length from 5 to 55 mm and a
height from 1 to 10 mm. The studs are often distributed in a
diamond pattern or a check pattern providing adequate
distribution of the loading as well as venting. The studs can
advantageously be distributed over the plate with a distance
between the studs from 1 to 10 mm. The studded plates are
placed with the top of the studs facing downwards toward the
base floor to obtain an air gap on the underside of the plate,
between the studs.
The plates may be joined by sealing tape on the topside of the
plates to obtain a sealed floor. In case of severe problems
with moisture, smell or other emissions, the air gap beneath
the studded plates may be ventilated mechanically in order to
provide air flow over the concrete surface or substrate and
create a negative pressure in relation to the room. A
ventilated air gap may also contribute to the drying out of
the concrete.
It is furthermore known to use studded plates as a membrane
between a concrete substrate and tiles laid on such substrate.
The concrete substrate is covered with studded plates. The
studded plate is thereafter covered by a bonding adhesive on
which the tiles are laid.
CA 02555606 2006-08-04
3
However, wooden floors are also used instead of tiles in
living rooms etc. Some wooden floors may be laid "floating"
without bonding to the substrate. Others need to be bonded. It
is therefore desirable to find a method for covering a
substrate where the dampness from the concrete substrate is
not affecting wooden floors which require to be bonded to the
substrate.
With a "substrate" or "concrete substrate" it is here meant
floors made of light expanded clay aggregate concrete and
lightweight concrete, plaster based floors, floating floors,
floating floors screed or flooring substitute, generally all
floors which have the feature of curing or hardening by using
water.
Different types of primer or adhesive are commonly used to
bond wooden floors to concrete substrates. However, it has
been seen that this may result in problems.
The object of the present invention is therefore to present a
method for covering of a substrate with wooden floor coverings
bonded to the substrate where the wooden floor or parquet or
parquet strips are not in contact with or affected by humidity
in the concrete floor underneath.
This is done by covering the substrate with a bonding
adhesive. The substrate is covered with a layer of flexible
bonding adhesive. The adhesive can be a 1 or 2 component
adhesive based on cement, polymer, polyurethane, epoxy or
other. A studded plate is then laid on the adhesive layer. The
plates are laid in the adhesive with adjacent plates edge to
edge or with a flat overlapping edge laid over the previous
plate. The joints in the plates are then sealed by using a
suitable sealing tape.
The studded plate may have a material such as a non-woven, a
fine net or a fabric, laminated or adhered to the protruding
part of the studs facing the substrate surface, so that the
CA 02555606 2006-08-04
4
material bonds to the substrate surface. The material is
preferably of low permeability preventing the air gap between
the studs from being filled.
The studded plates are covered with an adhesive to which
parquet strips or other wooden floor types can be adhered. The
adhesive can be a 1 or 2 component adhesive based on polymer,
polyurethane, epoxy or other. The adhesive is laid on the
studded plates in such a way that the upper inside of the
studs are filled with the adhesive. The wooden floor, parquet
or parquet strips can then be fixed to the adhesive.
The walls of the studs may preferably comprise undercut
cavities and/or overhangs. Undercuts may be obtained by
shaping the studs with inclined walls with a dovetailed shaped
section, such as by inverted truncated pyramids or cones, as
described in EP 1 068 413 to Isola AS. Overhangs may be
obtained by lips extending from the edges of the opening of
the studs, such as described in EP 1 073 813 to Schluter
Systems KG. The mentioned shapes of the studs limits the area
of the opening of the studs is in relation to the area of the
top of the studs and thereby provide improved anchoring of the
adhesive filled into the studs, and hence improved fixing of
the wooden floor.
Alternatively or in addition, the openings of the studs may be
covered by a permeable material, such as a non-woven, a net or
a loose fabric laminated or adhered to the plate, to achieve
the same effect. The adhesive will fill the studs and the
permeable material will reinforce the adherence of the
adhesive fixing the wooden floor to the plate.
A gap can be left between the edge of the floor and the
surrounding walls. Dampness from the substrate can then easily
escape from the floor. A skirting board is arranged on the
lower part of the wall in such a way that it covers the edge
of the floor. The skirting board is arranged so that a space
is left between the wall surface and the rear surface of the
CA 02555606 2012-07-19
. 5
board. Dampness from the floor is thus free to pass
through vents in the board and diffuse into the room.
It is also possible to arrange a studded plate with a fold
line adjacent to the wall in such a way that the studded
plates cover the lower part of the wall surrounding the
substrate floor. Such an arrangement is described in EP
1586721. The floor will then mainly be produced as
described below, but without leaving a gap between the
adhesive layers and the adjacent walls. The gap may thus
be formed by the studded plate with fold line.
The method according to the invention produces a floor
which is well protected against humidity from underneath,
and tolerates changes in surrounding air humidity in the
room.
Certain exemplary embodiments can provide a floor covering
on a substrate with wooden floors comprising: a substrate
covered with a bonding adhesive; the substrate and bonding
adhesive covered with studded plates having hollow studs
with openings facing away from said substrate, the openings
of the studs being covered by a permeable material; and
the studded plates covered with an adhesive, such that the
adhesive fills up the hollow studs, on which a wooden floor
is fixed.
Certain exemplary embodiments can provide a method for
covering a substrate with a wooden floor comprising:
covering the substrate with a bonding adhesive; covering
CA 02555606 2013-02-13
6
the bonding adhesive with studded plates; laying a second
layer of a bonding adhesive on the studded plates; and
fixing a wooden floor on at least a part of the studded
plates covered with the adhesive, wherein the studded
plates include a permeable material layer.
Certain exemplary embodiments can provide the use of
studded plates for covering of a substrate with a wooden
floor, comprising the studded plates being adhered to the
substrate, and the wooden floor being adhered to the
studded plates, wherein the studded plates include a
permeable material layer.
The invention will now be further described by an example
which is not limiting the scope of the invention which is
defined by the attached claims.
In the figures:
Fig. 1 shows a substrate partly covered with a wooden
floor according to the invention;
Fig. 2 shows a cross sectional side view of a floor
according to the invention;
Fig. 3 shows a cross sectional side view of a floor
having undercuts and overhangs; and
Fig. 4 shows a cross sectional side view of a floor
according to the invention having sealing tape sealing
joints.
CA 02555606 2012-07-19
. 7
Figure 1 shows a wooden floor in the process of being laid.
On a substrate 1, a first adhesive layer 2 is spread to
cover the substrate 1. One or more studded plates 3 are
laid on the adhesive layer 2. A second adhesive layer 4 is
laid on the one or more studded plates, mainly filling the
upper cavities in the studded plates. A wooden floor 5 is
subsequently laid on the second adhesive layer 4.
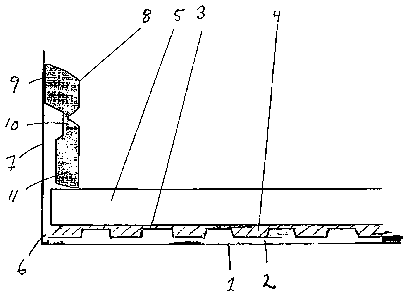
Figure 2 shows a cross sectional view of the floor
according to the invention. The first adhesive layer 2 is
spread on the base substrate 1. However, a small
gap 6 is left between the edge of the adhesive layer 2 on
the substrate 1 and the adjacent walls 7. The gap 6 is
maintained as the studded plate(s) 3, the second adhesive
layer 4 and the wooden floor 5 are subsequently laid on the
substrate.
As shown in Figures 2 and 3, the shape of the studs may
vary. The interior walls of the studs may contain
narrowing walls from the opening towards the top of the
stud, straight walls perpendicular to the plane of the
plate, narrowing walls from the top and towards the opening
of the stud producing undercuts 12, or straight walls with
overhangs 13 as mentioned above, or combinations thereof.
Undercut walls 12 or walls with an overhang 13 are
preferable in obtaining a good adhesion between the wooden
floor 5 and the studded plate 3. The openings of the studs
are covered by a permeable material 14.
CA 02555606 2013-02-13
8
A skirting board 8 can thereafter be arranged on the
wooden floor 5 abutting the adjacent walls 7. The
skirting board 8 preferably has cross-section comprising
an upper part 9, a middle section 10 and a lower part 11.
A recess is preferably provided in the middle section 10
on the side of the board facing the wall 7. The
backwards surface of the lower part is preferably offset
with regard to the backwards surface of the upper part.
Thereby, a cavity is obtained between the wall 7 and the
middle section and lower part of the skirting board 8,
while the upper part of the board 8 abuts the wall 7 such
cavity improves aeration of the substrate.
Fig. 4 shows a cross sectional side view of the floor
where the plates 3 are joined by sealing tape 15 on the
topside of the plates to obtain a sealed floor.