Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02558518 2006-08-30
- 1 -
REINFORCED BICYCLE FRAME
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates generally to a bicycle frame and more
particularly to a
bicycle frame with advantageous stiffness. More particularly, the invention
relates to a bicycle
with increased stiffness in one direction as opposed to another direction of
the bicycle frame,
preferably with tubes forming the frame having reinforced sidewalls to
increase the stiffness in
the sides of the tubes. Furthermore, the tubes are made of composite material.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Conventional bicycle frames are designed with tubular members of the bicycle
frame
having a uniform wall thickness. The uniform walls provide uniform stiffness
in each direction.
Typically, if an increase in stiffness is desired, the thickness of the
uniform thickness wall size is
increased with the disadvantages of increase in weight and inability to
customize the stiffness
directionally.
Conventional bicycle frames are also designed with a uniform wall thickness in
a cross-
section and with differing wall thickness in the longitudinal direction of the
bicycle tubes. In
particular, a cross-section taken at one point compared to a cross-section
taken at a different point
in the longitudinal direction may be different when compared to each other.
When comparing
these different cross-sections, one cross-section may be stiffer because of
stiffer material being
used or one cross-section may be thicker than the other.
CA 02558518 2006-08-30
- 2 -
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
Accordingly, to at least partially overcome the disadvantages of previously
known
devices, the present invention provides a bike frame which is selectively
reinforced over portions
of the frame members, preferably which is reinforced side walls of tubular
members forming the
frame.
An object of the present invention is to provide a bicycle frame designed to
have
advantageous stiffness, as with increased stiffness in one direction without
increasing stiffness in
another direction. In particular, an object of the present invention is to
provide a bicycle frame
designed to have advantageous stiffness in the lateral direction while not
increasing the stiffness
in the vertical direction.
Another object of the invention is to increase the stiffness of a bike frame
without adding
excessive additional weight to the frame.
In accordance with the present invention, a tubular member of a bicycle frame
may be
provided with additional material along their side walls to reinforce the
tubular member. Such
reinforced side walls can be provided in one or more of the tubular members of
the bicycle frame.
In one aspect, the present invention provides a bicycle frame comprising: a
top tube
with a front end and a rear end, a head tube with a top end and a lower end, a
down tube with
a front end and a rear end, a seat tube with a top end and lower end, a pair
of chainstays each
with a front end and rear end, and a pair of seatstays each with a front end
and rear end, the
CA 02558518 2006-08-30
- 3 -
front end of the top tube connected to the top end of the head tube, the front
end of the down
tube connected to the lower end of the head tube, the top tube and down tube
diverging away
from each another as they extend rearwardly from the head tube, the rear end
of the down tube
coupled to the lower end of the seat tube, the rear end of the top tube top
connected to the top
end of the seat tube, the top tube, head tube, down tube and seat tube
substantially forming a
closed main frame loop, the head tube adapted to be coupled to a pivotable
front fork which
carries a front wheel and handlebars, the top tube, head tube, down tube, and
seat tube each
comprise a tubular member extending about their own longitudinal axis, the
longitudinal axis
each of the top tube, head tube, down tube, and seat tube tubes lying in a
flat longitudinal
central plane, each tubular member having by a circumferential wall about
their longitudinal
axis with the circumferential wall generally symmetrical about the central
plane, selected of
the tubular members being reinforced tubular members, the circumferential wall
of the
reinforced tubular members having portions remote from the central plane
reinforced to
increase the resistance of the reinforced tubular member to lateral out of
plane bending
compared to in plane bending in the vertical direction, the down tube being a
reinforced
tubular member. Such a bicycle frame may have: the pair of chainstays
comprising a left
chainstay and a right chainstay being on opposite sides of the central plane,
the pair of
seatstays comprising a left seatstay and a right seatstay being on opposite
sides of the central
plane, the front end of the right chainstay connected to the main frame loop
proximate the
junction of the seat tube and the down tube on a right side of the central
plane, the front end of
each of the right seatstays connected to the seat tube on a right side of the
central plane spaced
upwardly from the front ends of the chainstays, the rear end of the right
chainstay connected
to the rear end of the right seat stay on the right side of the central plane
rearward of the seat
CA 02558518 2007-12-11
-4-
tube, the front end of the left chainstay connected to the main frame loop
proximate the
junction of the seat tube and the down tube on a left side of the central
plane, the front
end of each of the left seatstays connected to the seat tube on a left side of
the central
plane spaced upwardly from the front ends of the chainstays, the rear end of
the left
chainstay connected to the rear end of the left seat stay on the left side of
the central plane
rearward of the seat tube, the right chainstay, the right seatstay, and the
seat tube
substantially form a closed right rear frame loop, the left chainstay, the
left seatstay, and
the seat tube substantially form a closed left rear frame loop, the rear ends
of the pair of
chainstays adapted to support a rear wheel journalled on an axle extending
therebetween
normal to the central plane, each chainstay and each seatstay comprise a
tubular element
extending about their own longitudinal axis, each reinforced tubular element
having a
circumferential wall about its longitudinal axis with the circumferential wall
generally
symmetrical at each point along the length of the longitudinal axis about a
line of
symmetry through the point normal the longitudinal axis and parallel to the
central plane,
selected of the tubular elements being reinforced tubular elements,
the circumferential wall of the reinforced tubular elements having portions
remote from
the lines of symmetry reinforced to increase the resistance of the reinforced
tubular
element to resisting out of plane bending compared to in plane bending in a
vertical
direction, the chain stays each being a reinforced tubular element.
In a further aspect, the present invention provides a bicycle frame
comprising: a
top tube with a front end and a rear end, a head tube with a top end and a
lower end, a
down tube with a front end and a rear end, a seat tube with a top end and
lower end, a
pair of chainstays each with a front end and rear end, and a pair of seatstays
each with a
CA 02558518 2007-12-11
- 4a-
front end and rear end, the front end of the top tube connected to the top end
of the head
tube, the front end of the down tube connected to the lower end of the head
tube, the top
tube and down tube diverging away from each another as they extend rearwardly
from
the head tube, the rear end of the down tube coupled to the lower end of the
seat tube, the
rear end of the top tube top connected to the top end of the seat tube, the
top tube, the
head tube, the down tube and the seat tube substantially forming a closed main
frame;
loop, the head tube adapted to be coupled to a pivotable front fork which
carries a front
wheel and handlebars, the pair of chainstays comprising a left chainstay and a
right
chainstay being on opposite sides of the central plane, the pair of seatstays
comprising a
left seatstay and a right seatstay being on opposite sides of the central
plane, the front end
of the right chainstay connected to the main frame loop proximate the junction
of the
seat tube and the down tube on a right side of the central plane, the front
end of each of
the right seatstays connected to the seat tube on a right side of the central
plane spaced
upwardly from the front ends of the chainstays, the rear end of the right
chainstay
connected to the rear end of the right seat stay on the right side of the
central plane
rearward of the seat tube, the front end of the left chainstay connected to
the main frame
loop proximate the junction of the seat tube and the down tube on a left side
of the central
plane, the front end of each of the left seatstays connected to the seat tube
on a left side of
the central plane spaced upwardly from the front ends of the chainstays, the
rear end of
the left chainstay connected to the rear end of the left seat stay on the left
side of the
central plane rearward of the seat tube, the right chainstay, the right
seatstay, and the seat
tube substantially form a closed right rear frame loop, the left chainstay,
the left seatstay,
and the seat tube substantially form a closed left rear frame loop, the rear
ends of the pair
CA 02558518 2007-12-11
- 4b -
of chainstays adapted to support a rear wheel journalled on an axle extending
therebetween normal to the central plane, the top tube, the head tube, the
down tube, the
seat tube, the seat stays and the chainstays each comprise a tubular member
extending
about their own longitudinal axis, the longitudinal axis each of the top tube,
the head
tube, the down tube, and the seat tube lying in a flat longitudinal central
plane, each
tubular member having by a circumferential wall about their longitudinal axis
with the
circumferential wall of the top tube, the head tube, the down tube and the
seat tube
generally symmetrical about the central plane, each of the seatstays and
chainstays
having a circumferential wall about their longitudinal axis with the
circumferential wall
generally symmetrical at each point along the length of the longitudinal axis
about a line
of symmetry through the point normal the longitudir-al axis and parallel to
the central
plane, selected of the tubular members being reinforced tubular members, the
circumferential wall of the reinforced tubular members lying in the central
plane having
reinforced portions remote from the central plane reinforced compared to
portions
proximate from the central plane to increase the resistance of the reinforced
tubular
member to lateral out of plane bending compared to in plane bending in the
vertical
direction, the circumferential wall of the reinforced tubular elements outside
the central
plane having reinforced portions remote from the point normal to the
longitudinal axis in
a direction normal the central plane reinforced compared to the portions
normal the
longitudinal axis in a direction parallel to the centra:l plane to increase
the resistance of
the reinforced tubular element to lateral out of plane bending compared to in
plane
banding in a vertical direction, the down tube and the chainstays being
reinforced tubular
members.
CA 02558518 2007-12-11
- 4c -
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Further aspects and advantages of the invention will become apparent upon
reading the following description together with the accompanying drawings in
which:
CA 02558518 2007-12-11
- 5 -
Figure 1 is a side view of a bicycle in accordance with a first embodiment of
the
invention;
Figure 2 is a partial side view of portions of a bicycle in accordance with a
second
embodiment of the invention showing the bicycle frame and the rear wheel;
Figure 3 is a perspective right side view of the bicycle frame shown in Figure
2;
Figure 4 is a right side view of the bicycle frame of Figure 2;
Figurer 5 is a rear view of the bicycle frame shown in Figure 2;
Figure 6 is a top view of the bicycle frame shown in Figure 2;
Figure 7 is an enlarged perspective view of a section of the top tube of the
frame of
Figures 1 or 2;
Figure 8 is a cross-sectional view along section 8-8' in Figure 4;
Figure 9 is a cross-sectional view as in Figure 8 but showing a second
alternate reinforcing
construction;
Figure 10 is a cross-sectional view as in Figure 8 but showing a tube
construction without
reinforcing ;
Figure 11 is a cross-sectional view along section 11-11' in Figure 4;
Figure 12 is a cross-sectional view as in Figure 11 but showing a second
alternate
reinforcing construction;
Figure 13 is a cross-sectional view as in Figure 11 but showing a third.
alternate
reinforcing construction;
Figure 14 is a cross-sectional view as in Figure 11 but showing a fourth
alternate
reinforcing construction;
Figure 15 is a cross-sectional view along section 12-12' in Figure 4;
CA 02558518 2006-08-30
6 -
Figures 16 to 19 are cross-sectional views through other reinforced bicycle
tubes,
chainstays or seatstays;
Figure 20 is a side view of a bicycle frame in accordance with a third
embodiment of the
invention;
Figure 21 is a perspective view of a bicycle frame in accordance with a forth
embodiment
of the invention;
Figure 22 is a side view of the frame of Figure 17;
Figures 23 and 24 are a pictorial view of two frame testing apparatus; and
Figure 25 is a cross-sectional view as in Figure 8 but showing a third
alternate reinforcing
construction.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
Figure 1 is a side view of a bicycle 12 in accordance with a first embodiment
of the
invention. The bicycle 12 has a frame 10 comprising a head tube 20, a top tube
30, a down tube
40 and a seat tube 50. Each of these tubes are connected end-to-end to one
another and form
substantially a closed main frame loop 14. A seat post 73 is supported by an
upper end 51 of the
seat tube 50 carrying a seat 75.
A fork 77 is rotatably coupled to the head tube 20 to extend through the head
tube carr\ i ng.
at an upper end to the handlebars. The fork 77 splits into a pair of arms
supporting the front
wheel 78. A seatstay 65 and a chainstay 67 extend rearwardly from the seat
tube 50 and support
a rear whee179 journalled on a rear axle 83 extending between the rear ends 84
of the chainstays
67. Two pedals 80 are carried on respective pedal crank arms 45 secured to a
pedal axle 46
CA 02558518 2006-08-30
- 7 -
journalled in a pedal crank journal having (not seen in Figure 1) secured
proximate the junction
of seat tube 50 and down tube 40.
Through all of the drawings the same reference numbers are used to refer to
similar
elements.
Reference is made to Figures 2 to 12 which show a bicycle frame 10 in
accordance with a
second embodiment of the invention.
Figure 2 is a right side view of a bicycle however without the seat,
handlebars, front fork
or front wheel. In the second embodiment in Figures 2 to 6 the seat tube 50
comprises an upper
tube section 52 and a lower tube section 56. Figures 3 to 6 show various views
of the bicycle
frame 10 alone.
As in Figure 1, the bicycle frame 10 as best seen in Figures 3 and 4 includes
a head tube
20, a top tube 30, a down tube 40, a seat tube 30, a right hand chainstay 67,
a left hand chainstav
68, a right hand seat stay 65 and a left hand seatstay 66. The head tube 20
has an upper end 21 and
a lower end 22. The top tube 30 has a front end 31 and a rear end 32. The down
tube has a front
end 41 and a rear end 42. The seat tube 50 has an upper end 51 and a lower end
57. The seat
tube has an upper tubular portion 52 which has the upper end 51 and a lower
end 53; and a lower
tubular portion 56 which has an upper end 55 and the lower end 57.
Figure 5 is a rear view of the bicycle frame of Figure 3 and additionally
shows a flat
CA 02558518 2007-12-11
- 8 -
longitudinal central plane 92 that runs through each of the head tube 20, top
tube 30, ciown tube
40 and seat tube 50. In particular, the flat longitudinal central plane 92
runs through a
longitudinal axis 90 centrally of each of the head tube 20, top tube 30, down
tube 40 and seat tube
50.
Figure 6 is a top view of the bicycle frame of Figure 3. Figure 6 also shows
the flat
longitudinal central plane 92.
The front end 31 of the top tube 30 is the top end 21 of the head tube 20. The
front end 41
of the down tube 40 is connected to the lower end 22 of the head tube 20. The
top tube 30 and
down tube 40 diverge away from each other as they extend rearwardly from the
head tube 20.
The rear end 42 of the down tube 40 is coupled to the lower end 57 of the seat
tube 50. The rear
end 32 of the top tube 30 is connected to the top end 51 of the seat tube 51.
The right hand chainstay 67 has a front end 85 and a rear end 84. The left
hand chainstay
68 has a front end 87 and a rear end 86. The right hand seatstay has an upper
end 61 and a lower
end 62. The left hand seatstay 66 has an upper end 63 and a lower end 64. The
front end 85 of the
right chainstay 67 is connected to the lower end 57 of'the seat tube 50 on a
right side thereof. The
upper end 61 of the right seatstay 65 is connected to the seat stay 50 spaced
upwardly from the
front end 85 of the right chainstay 67. The rear end 84 of the right chainstay
67 is connected to
the lower end 62 of the right seatstay 65.
The front end 87 of the left chainstay 68 is connected to the lower end 57 of
the seat tube
CA 02558518 2007-12-11
- 9 -
50 on a left side thereof. The upper end 63 of the left seatstay 66 is
connected to the seat stay 50
spaced upwardly from the front end 87of the left chainstay 68. The rear end 86
of the left
chainstay 68 is connected to the lower end 64 of the left seatstay 66.
Proximate the juncture between the lower enci 57 of the seat tube 50 and the
rear end 42 of
the down tube 40, a pedal crank journal housing 27 is provided adapted to
journal an axle such as
the axle 46 for the pedals shown in Figure 1.
The rear ends 84 and 86 of the chainstays 67 and 68 each carry an axle slotway
71 and 72
adapted to receive a rear axle such as the axle 83 for the rear whee179 shown
in Figure 1.
The head tube 20, top tube 30, down tube 40 and seat tube 50 form a closed
niain frame
loop indicated as 14. The right chainstay 67, right seatstay 65 and the seat
tube 50 between the
front end of the right chainstay 67 and the upper end. of the right seatstay
65 form a closed right
rear frame loop indicated as 15. The left chainstay 68, left seatstay 66 and
the seat tube 50
between the front end of the left chainstay 68 and the upper end of the left
seatstay 66 form a
closed left rear frame loop (not shown).
Each of the head tube 20, top tube 30, down tube 40 and seat tube 50 are
elongate
members disposed about their own longitudinal axis 90. The longitudinal axis
of each of the head
tube 20, top tube 30, down tube 40 and seat tube 501:ie in the same flat
central plane 92 best seen
in the side and top view of Figures 5 and 6. Thus, mainframe loop 14 is
disposed about and lies
centred on the flat central plane 92.
CA 02558518 2006-08-30
- 10 -
Figure 7 illustrates a section of the top tube 30 from either Figure 1 or
Figure 3 in which
the central plane 92 is schematically illustrated in dashed lines. The top
tube 30 is disposed about
its longitudinal axis 90 which extends centrally therethrough.
Figure 8 shows an end view of the section of the top tube 30 in Figure 8 and
also
represents a cross-sectional view through section lines 8-8' in Figure 4.
In accordance with the present invention, the top tube 30 has an annular
circumferential
wall 110 about its longitudinal axis 90. The wall 110 is symmetrical about the
central plane 92,
that is on each side of the main frame loop 14. The wall has side wall
portions 112 which are
remote from the central plane 92 and central wall portions 114 which are
proximate the central
plane 92. The side wall portions 112 remote from the central plane 92 are
reinforced compared to
the central wall portions 114 proximate the central plane 92. Reinforcing of
the side wall portions
112 is illustrated by the side wall portions 112 being increased radial
thickness as contrasted with
the central wall portions 114, on the assumption the nature of the material
forming the wall will
have substantially uniform density and/or strength for the same thickness and
increased stiffness
with increased thickness. Of course if the material forming the walls has
different strengths for
different thickness, as for example, using different materials or the same
material but in different
densities or proportions, the thickness need not necessarily vary. However,
the side wall portions
may be reinforced by adding additional material or stiffer material.
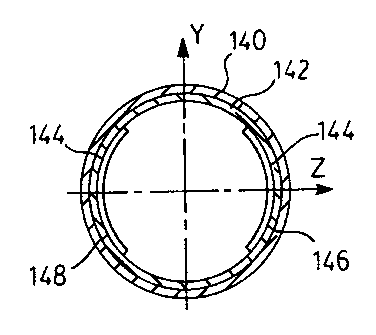
Figure 8 shows the top tube 30 as being constructed from two circumferentially
extending
CA 02558518 2006-08-30
- 11 -
layers of fibre reinforced composite material such as graphite epoxy. The
layers are an outer
circumferential extending layer 140 whose internal surface is fused with an
outer surface of an
inner circumferentially extending layer 142. As reinforcing a reinforcing
layer 144 is provided
however merely on an interior surface of the layer 142 along side wall
portions remote from the
central plane 92 and not over the central wall portions proximate the central
plane 92 at the top
and bottom as seen. The reinforcing layer 144 may comprise two elongate strips
146 and 148 of
the fibre reinforced composite material along the interior sides of the tube
formed by the layers
140 and 142. One or two of more of such cylindrically extending layers 140 and
142 may be
provided. In an alternate embodiment, the reinforcing layer 144 may vary in
width and/or
thickness along the interior of the tubes. A varying width and/or thickness
allows adjustments to
the stiffness of the tubes.
Figure 9 shows an alternate construction for the top tube 30 in which the
reinforcing layer
144 is provided as two stripes 146 and 148 over the side wall portions remote
from the central
plane 92 sandwiched between the inner layer 142 and the outer layer 140. The
sidewall portions
may be reinforced by adding additional material, stiffer material or foam
material. The foam
material may be sandwiched between the inner layer 140 and the outer layer
142.
Figure 10 illustrates an alternate form of the top tube 30 in which the top
tube 30 is not
reinforced but is intended to be a tube having a circumferential wall 110 of
uniform thickness and
material strength throughout its circumference. This is the tube design
commonly in bicycle
frames.
CA 02558518 2006-08-30
- 12 -
Figure 7 schematically illustrates forces or loads that the bicycle frame 10
is subjected to,
namely:
Px being a force in the direction of the longitudinal axis 90,
Py being a force in the central plane 92 normal the longitudinal axis 90,
Pz being a force normal to the central plane,
Mx-x being a torsion load about the longitudinal axis 90,
Mz-z representing in plane bending,
My-y being out of plane bending.
It is appreciated that of these loads the loads My-y out of plane bending and
Mx-x torsion
are typically significant in determining the overall stiffness and resulting
efficiencies of the
bicycle frame 10. These loads are resisted with a bicycle frame tube having
reinforced side ~~al ls
having a construction as illustrated in Figures 7, 8 and 9, while reducing the
overall weight of the
tube compared to a tube of uniform wall thickness. Reducing the weight of the
tubes reduces the
overall weight of the bicycle while attaining the same stiffness as bicycles
with tubes constructed
with reinforcement around the entirety of the tube.
Whereas Figures 7, 8 and 9 each illustrate a reinforced tube for a bike frame,
Figure 10
illustrates a tube which is not reinforced. In any bike frame, incorporating
tubes, one or more of
the tubes is to be reinforced in accordance with the present invention. The
preferred
embodiments show a frame 12 as having the head tube 20, top tube 30, down tube
40, seat tube
50, a pair of chainstays and a pair of seatstays. In accordance with the
invention, one or more of
CA 02558518 2007-12-11
- 13 -
these elements may be a reinforced tube as described,. In one particularly
preferred configuration,
the frame 12 will have both the down tube 40 and the chainstays 67 and 68 as
reinforced tubes.
In another preferred configuration, each of the tubes of the mainframe loop 14
are
reinforced tubes. In another preferred configuration, at least one of the
chainstays and the
seatstays are reinforced tubes. In another preferred configuration, all of the
chainstays and the
seatstays are reinforced tubes.
In one embodiment, the pair of seat stays are symmetrical of each other about
the central
plane 92. The pair of chainstays are also symmetrical of each other about the
central plane 92.
Reference is made to Figure 11 which schematically illustrates a cross-
sectional view along
section line 11-11' in Figure 4 and shows the two chainstays 67 and 68 in
cross-section on either
side of the central plane 92. Each chainstay, as well as each seatstay
although not shown, are
similar to the tubes of the mainframe loop 14 and comprise a hollow tube
extending about its own
longitudinal axis 190 and having a circumferential wall 110. At each point 191
along the
longitudinal axis 190 of each chainstay or seatstay, the tube of the chainstay
or seatstay is
symmetrical about a line of symmetry 193 through such point 191 normal the
longitudinal axis
190 and parallel to the central plane 92. The circumferential wall 110 of the
chainstays is shown
reinforced over side wall portions 112 remote from the line of symmetry 193
compared to central
wall portions 122. As seen in Figure 11, each of the chainstays has a
generally elliptical
circumferential wall 110.
Figure 12 shows an alternate construction for the seatstays. Figure 12
additionally shows
CA 02558518 2006-08-30
- 14 -
an alternate construction for the chainstays. In this embodiment the pair of
seatstays or chainstays
are symmetrical about the central plane 92 but are not symmetrically about
their line of symmetry
193. In particular, in this embodiment the sidewall reinforcement 150 on the
sidewall furthest
from the central plane 92 is thicker than the sidewall closer to the central
plane 92.
Figure 13 shows a further alternate construction similar to that illustrated
in Figure 12 but
where the reinforcement sidewalls 152 furthest from the central plane 92 are
thicker and taller
than the reinforcement in the sidewalls closer to the central plane 92.
Figure 14 shows a still further alternate construction for the seatstays
and/or chainstays
similar to that illustrated in figure 12 but where the reinforcement on the
sidewalls 154 furthest
from the central plane 92 are made of a stiffer material than the
reinforcement on the sidewalls
closer to the central plane.
In a further alternate construction, the seatstays are not symmetrical about
the central plane
92. Furthermore, the chainstays are not symmetrical about the central plane
92.
Figure 15 shows a cross-sectional view through section line 12-12' in Figure 4
and show s
the down tube 40 as tube of a generally airfoil shape as is advantageous with
a forwardly directed
edge 194 to be directed into the air and with the tube taping towards its rear
edge 196. The cross-
section shows the down tube 40 is shown reinforced on its side wall portion
remote from the
central plane 92.
CA 02558518 2006-08-30
- 15 -
Figures 16, 17, 18 and 19show other possible configurations for reinforced
tubes for
bicycle frames including a rectangular in Figure 16, a camber sided rectangle
in Figure 17 a
camber sided triangle on Figure 18 and a diamond in Figure 19, each of which
having reinforced
side wall portions configured to central wall portions, having regard to the
location of the
conceptual central plane 92. Each of the tubes, chainstays or seatstays bay be
shaped as any of
these configurations or may be circular elliptical or airfoil configuration
detailed earlier.
Figures 20, 21 and 22 show two alternate embodiments of bicycle frames in
accordance
with the present invention differing in respect of the relative diameter and
length and cross-
sectional shape of their various tubes and in the location ofjunction of the
tubes with cacli other.
Figure 23 illustrates a first testing apparatus 200 being used to test the
rigidity of a bicycle
frame 10 by holding the rear ends of the chainstay fixed and applying a load
202 to an end of an
extension of the head tube with the head tube received for pivoting on a
curved, upper surface of a
fixed fulcrum post 204.
Figure 24 illustrates a second testing apparatus 220 used to test the rigidity
of a bicycle
frame 10 by holding the rear end of the chainstay fixed holding the head tube
fixed and applying a
load 222 onto a pedal on one side of the frame.
The testing apparatuses of Figures 23 and 24 are common testing apparatuses
used to
determine the overall stiffness in bicycle tubes.
CA 02558518 2006-08-30
- 16 -
The applicant has appreciated that in the frame construction shown in Figures
2 to 22
bending of the frame in a lateral direction outside the central plane is
reduced while in plane
bending in the vertical direction is not reduced.
Figure 25 shows an alternate construction for the tubes, chainstays or
seatstays in which
the reinforcing layer 144 is provided as two stripes 146 and 148 over the side
wall portions
remote from the central plane 92 provided on the exterior of the outer layer
140.
While the invention will be described in conjunction with the illustrated
embodiments, it
is understood that it is not intended to limit the invention to such
embodiments. On the contrary,
it is intended to cover all alternatives, modifications and equivalents as may
be included within
the spirit and scope of the invention as defined by the following claims.