Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02577238 2007-02-15
WO 2006/017928 PCT/CA2005/001247
1
AN OUTFLOW REGULATOR FOR A GRAVITY-FED LIQUID OUTLET
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
This invention relates generally to the control of liquid. More particularly,
it concerns
an outflow regulator for a gravity-fed liquid outlet of a liquid reservoir,
for providing
damping effects on hydraulic events and even distribution of the effluent. The
outflow regulator is suitable for controlling the outflow of any gravity-fed
liquid
outlet. More preferably, it is suitable for regulating the flow rate of a
septic tank
effluent or for regulating the flow rate of multi-compartment reservoirs.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Depending on the intended use of a reservoir containing a liquid, one may wish
to
regulate the flow rate of the reservoir effluent. As for example, one may wish
to
regulate the flow rate of a septic tank effluent, septic tanks being widely
used in
industrialized countries, or the flow rate between the compartments of a multi-
compartment reservoir.
With regards to onsite wastewater systems using septic tanks as primary
treatment
combined with secondary treatment technology, it is interesting to note that,
in
1990 in the USA, 24.7 million houses had an onsite wastewater system including
a
septic tank, which represents 25% of the American population. Recent studies
predict that the number of dwellings using this type of wastewater treatment
will
reach 37 million within 20 years. Moreover, 33% of new constructions will
probably
rely on decentralized wastewater treatment. In France, over 10 million people
depend on onsite systems to treat wastewater and 95% of these systems use a
septic tank as primary treatment. In the province of Quebec (Canada), nearly
650,000 homes have this type of wastewater treatment system, which represents
20% of the provincial population.
Although septic tanks have been widely used in North America and Europe for
decades, they are not very efficient treatment systems and may have
significant
CA 02577238 2007-02-15
WO 2006/017928 PCT/CA2005/001247
2
environmental impact. In fact, the septic tank in its current form can cause
major
problems by ground water contamination. For example, in the USA in 1996, 50%
of
septic tanks contaminated groundwater due to poor design, construction,
maintenance and functioning (Miller and Little, 1996). Moreover, EPA cited
that
regarding the 1995 National Shellfish Register, the third common pollution
source
for shellfish restriction were septic tanks (32%) after urban runoff (40%) and
unidentified upstream sources (39%). Problems were caused by tank leakage and
by overloading the leaching field as a result of poor performance.
Over past decades, septic tank configuration has not changed much and has not
been a source of increases in performance. A few modifications have been
brought
to the inlet and outlet devices (baffle, tees and effluent filters) but these
have not
had a major impact on the hydraulic functioning of septic tanks. For example,
outlet
devices improve scum retention and the effluent filter acts as a fuse when the
septic tank is stressed by a hydraulic event. However, the devices currently
available do not enhance the sedimentation capacity of the septic tank. During
hydraulic events (draining of bath tub, washing machine, etc.), which are the
feeding mode of residential septic tanks, incoming solids do not have
sufficient time
to settie. The sludge accumulated at the bottom of the tank may also be
disturbed,
re-suspended and drawn into the effluent. When such solids are discharged into
the downstream treatment system (leaching field, aerobic treatment unit, etc.)
the
efficiency and/or lifespan of the latter will decrease.
There is still presently an unresolved problem in the field of septic tanks,
which
problem is a consequence of the important flow rate fluctuation of the
influent and
effluent. There is thus presently a need for a flow regulator that will reduce
the
unwished effects of the effluent peak flow.
Generally speaking, it would also be very advantageous to make available on
the
market a simple outflow regulator that is inexpensive to make and use, and
that do
not need any complex hydraulic or electric components.
CA 02577238 2007-02-15
WO 2006/017928 PCT/CA2005/001247
3
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
An object of the present invention is to provide an outflow regulator that
satisfies at
least one of the above-mentioned needs.
Accordingly, the present invention provides an outflow regulator for a gravity-
fed
liquid outlet of a liquid reservoir, the liquid outlet being located in the
reservoir so as
to be crossed by a liquid effluent flowing in a generally horizontal direction
from an
upstream side of the outlet to a downstream side. The outflow regulator
comprises:
- a restriction plate mountable within the liquid outlet for limiting a flow
rate of
the effluent, the restriction device comprising:
a lower orifice allowing a first passage for the effluent when a first
predetermined level of liquid is reached within the liquid reservoir; and
an upper orifice located above the first orifice and allowing a second
passage for the effluent when a second predetermined level of liquid is
reached
within the reservoir; and
- a closure device comprising:
- a flapgate extending on the downstream side of the restriction plate,
the flapgate being pivotable between a closed position where the flapgate
covers
the lower orifice of the restriction device and an opened position away from
the
restriction device, the flapgate including an opening facing the upper orifice
of the
restriction plate when the flapgate is in the closed position; whereby the
flapgate, in
the closed position, closes the first passage and leaves the second passage
free;
and
- a float counterweight operatively connected to the flapgate to urge
the flapgate towards the opened position when the liquid level in the
reservoir is
lower than said second predetermined level and causing the flapgate to move to
the closed position when the liquid level in the reservoir reaches the second
predetermined level.
CA 02577238 2007-02-15
WO 2006/017928 PCT/CA2005/001247
4
Preferably, the float counterweight comprises a lever extending substantially
at
right angle to the flapgate, the lever having a downstream end portion secured
to a
top portion of the flapgate and an upstream end portion provided with a float.
Preferably, the outflow regulator is used in combination with a filter unit
mountable
within the liquid outlet of the reservoir for filtering the effluent.
According to another aspect of the invention, there is also provided a filter
unit for
filtering an effluent in a gravity-fed liquid outlet of a liquid reservoir,
comprising an
outflow regulator as previously defined. More specifically, the filter unit
comprises:
- a liquid inlet for receiving liquid to be filtered;
- a filter chamber in communication with the liquid inlet for filtering the
liquid;
- a liquid outlet in communication with the filter chamber from which the
filtered liquid exit; and
- an outflow regulator as described above, mounted within the liquid outlet.
Still, according to the present invention, there is also provided a method for
regulating a liquid outflow for a gravity-fed liquid outlet of a liquid
reservoir, the
liquid outlet being located in the reservoir so as to be crossed by a liquid
effluent
flowing in a generally horizontal direction from an upstream side of the
outlet to a
downstream side, the method comprising the steps of:
a) mounting a restriction device within the liquid outlet for limiting a flow
rate
of the effluent, the restriction device comprising:
a lower orifice allowing a first passage for the liquid when a first
predetermined level of liquid is reached within the liquid reservoir; and
an upper orifice located above the lower orifice and allowing a second
passage for the effluent when a second predetermined level of liquid is
reached
within the reservoir;
b) allowing the effluent to pass through the first orifice when the liquid
level
in the reservoir is lower than the second predetermined level;
CA 02577238 2007-02-15
WO 2006/017928 PCT/CA2005/001247
c) closing the first orifice when the second predetermined level is reached
within the reservoir and leaving the second passage free; and
d) opening the first orifice when the liquid level in the reservoir is lower
than
second predetermined level.
5 The outflow regulator may be advantageously used for regulating an effluent
oufflowing from a septic tank.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
These and other objects and advantages of the invention will become apparent
upon reading the detailed description and upon referring to the drawings in
which:
Figure 1 is a cross section view of an outflow regulator according to a
preferred
embodiment of the invention comprising a hollow adapter mountable in the
liquid
outlet of a reservoir, the regulator being shown in an opened position.
Figure 2 is the same view as figure 1 showing the regulator in a closed
position.
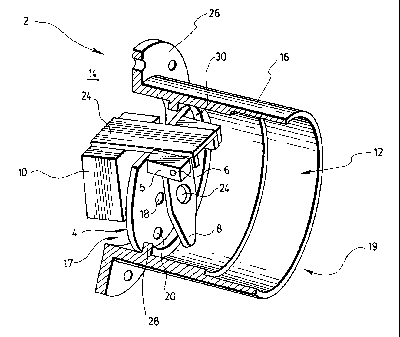
Figure 3 is a perspective view of the regulator shown in figure 1.
Figures 4A to 4F are different cross section views of the regulator of figure
1,
showing its different operating positions when a hydraulic event occurs.
Figure 5 is a graph of the experimental data obtained from a test conducted
using a
flow regulator according to the invention, showing the relationship between
the
level of liquid related to the invert of the lower orifice within the
reservoir and the
flow rate of the effluent outflowing from the liquid outlet.
Figure 6 is a graph showing the fluctuation of the flow rate of the effluent
of a
standard effluent compared with an effluent regulated with a regulator
according to
the invention.
CA 02577238 2007-02-15
WO 2006/017928 PCT/CA2005/001247
6
Figure 7 is an exploded view of the regulator shown in figure 1.
Figure 8 is a schematic cross-sectional perspective view of the upper portion
of a
filter unit in combination with a regulator as shown in figure 1.
While the invention will be described in conjunction with example embodiments,
it
will be understood that it is not intended to limit the scope of the invention
to such
embodiments. On the contrary, it is intended to cover all alternatives,
modifications
and equivalents as may be included as defined by the appended claims.
DESCRIPTION OF PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
Referring to figure 1, the outflow regulator 2 according to the invention is
intended
to be used in a gravity-fed liquid outlet of a liquid reservoir of the type
having its
liquid outlet located in the reservoir so as to be crossed by a liquid
effluent 22
flowing in a generally horizontal direction from an upstream side 14 of the
outlet to
a downstream side 12. The liquid reservoir can be for example the liquid of a
septic
tank. It is worth mentioning that although the liquid reservoir is not
illustrated as
such in the figures, the numeral reference 14 is used to generally identify
the inside
of the reservoir.
Referring to figures 1 to 4, the outflow regulator according to a preferred
embodiment comprises four elements, namely a restriction plate 4, a pivot axis
6, a
flapgate 8 and a float 10. Such a regulator 2 can be mounted directly in the
outlet
of the reservoir such as the outlet of a septic tank or, as shown in figures 1
to 3, it
can be integrated into a rigid adapter 16 sized to snugly fit within the
liquid outlet of
the reservoir. Referring to figure 8, the regulator 2 may also preferably be
integrated into the liquid outlet 42 of an effluent filter 40. Examples of
effluent filters
into which the regulator 2 of the present invention may be integrated can be
found
in US 4,710,295; US 4,439,323; US 5,492,635; US 5,580,453; US 5,382,357;
US 5,482,621; and EP 1,265,686.
CA 02577238 2007-02-15
WO 2006/017928 PCT/CA2005/001247
7
As best shown in figure 3, the adapter 16 is preferably a hollow cylinder that
snugly
fits within the liquid outlet of the reservoir (not illustrated) with the flow
direction of
the effluent being depicted by arrow 22, in figure 1. The adapter 16 has a
first end
17 for receiving the effluent to be regulated, and a second end 19 from which
the
regulated effluent exite. Preferably, the first end 17 of the adapter 16 is
provided
with an outer rim 26 so as to abut against the side wall of the reservoir to
ensure
water tightness. The adapter 16 also has an inner wall provided with a
peripheral
rim 28, for mounting the restriction plate 4 therein. The restriction plate 4
indeed
has a peripheral edge abutting against the peripheral rim 28.
Referring to figures 1 to 4, the restriction plate 4 comprises a lower orifice
20
allowing a first passage for the effluent when a first predetermined level of
liquid is
reached within the liquid reservoir 14. An upper orifice 18 is located on the
restriction plate 4 above the lower orifice 20 to allow a second passage for
the
effluent when a second predetermined level of liquid is reached within the
reservoir
14.
The flapgate 8 extends on the downstream side of the restriction plate 4. The
flapgate 8 has a top portion pivotable about a top edge portion of the
restriction
plate 4 between a closed position (shown in figure 2), where the flapgate 8
covers
the lower orifice 20 of the restriction plate 4, and an open position (shown
in figures
1 and 3) away from the restriction plate 4. The flapgate 8 has an opening 24
positioned so as to face the upper orifice 18 of the restriction plate 4 when
the
flapgate 8 is in the closed position so as to close the first passage and
leave the
second passage free. The flapgate 8 is preferably mounted to the restriction
plate
4, as in the preferred embodiment illustrated. It is howeverworth noting that
without
departing from the scope of the invention, the flapgate 8 can advantageously
be
pivotally mounted to a rod extending over the restriction plate 4. Such rod
could be
connected to the inner wall of the adaptor 16.
The float 10 is operatively connected to the flapgate 8 through a lever 24
extending
substantially at right angle to the flapgate 8. Together, the float 10 and the
lever 24
CA 02577238 2007-02-15
WO 2006/017928 PCT/CA2005/001247
8
form a float counterweight. The lever 24 has a downstream end portion secured
to
the top portion of the flapgate 8 and an upstream end provided with the float
10. By
floating up, when the liquid level in the reservoir 14 reaches the second
predetermined level, the float 10 causes the flapgate 8 to move to the closed
position. By floating down, when the liquid level in the reservoir 14 becomes
lower
than the second predetermined level, the float 10 urges the flapgate 8 towards
the
open position. The float counterweight and the flapgate 8 act as a closure
device
for closing the lower orifice 18 of the restriction plate 4.
Preferably, in order to increase the lever arm effect of the float 10 and,
thus to
improve the stability of the opened position of the flapgate, the pivot axis
is distant
from the longitudinal axis of the flapgate, as best viewed from figure 1. More
particularly, the restriction plate 4 is preferably provided with a pair of
spaced apart
projecting arms 5 projecting from the upper end portion of the restriction
plate 4 on
the downstream side thereof, and the lever 24 has an extension 7 pivotally
connected between the projecting arms by means of the pivot pin 6.
The restriction plate 4 controls the flow of the liquid (effluent) through the
lower and
upper orifices 18, 20, and such depending on the upstream effluent level. An
additional flow rate is obtained in the upper orifice 18 when the lower
orifice 20 is
closed. This phenomenon is achieved by moving the flapgate 8, which pivots
around its pivot axis 6, thus obstructing the lower orifice 20. The flapgate 8
moves
when the upstream effluent level rises, which in turn raises the float
counterweight
10 located at an extremity of the lever 24.
Preferably, the restriction plate 4 is sized so as to leave an overflow
passage 30
over its top edge for the effluent when the liquid level within the reservoir
14 is
higher than the top edge of the restriction plate 4. This overflow passage 30
provides an overflow zone in cases the reservoir capacity is exceeded.
CA 02577238 2007-02-15
WO 2006/017928 PCT/CA2005/001247
9
Mode of operation
Now referring to figures 4A, 4B, 4C, 4D, 4E and 4F, the regulator 2 allows to
obtain
a regulated downstream flow rate (effluent). Thus, the sudden replenishment of
a
considerable amount of liquid in the reservoir would be a typical situation
that the
aforementioned regulator 2 could manage.
The sequence begins with an open flapgate 8 (see figure 4A). This equilibrated
position can be obtained solely by the weight of the float or, according to
the
preferred embodiment illustrated, it can be assured by the retreat of the
pivot axis 6
in respect of the center of mass of the mobile portion of the regulator 2. The
liquid
level is located at the base of the lower orifice 20. No flow of effluent
occurs when
the reservoir is to be replenished.
The sudden replenishment of liquid in the reservoir implies an elevation in
the level
of liquid, and when that liquid is at a certain height, it may freely flow
through the
lower orifice (see figure 4B). If, as mentioned hereinabove, the reservoir is
being
replenished (filled) more quickly than the exit flow rate, then the liquid
level
continuously rises. The effluent flow rate is considered to be free flowing
until the
lower orifice is completely submerged in liquid.
It should be noted that once the level of liquid is above the lower orifice 20
(see
figure 4C), the effluent flow rate is determined by the following equation:
Q=kA(2gh)112 wherein Q = flow rate
k = the orifice coefficient
A = the orifice area
g = gravity
h difference of height between the
liquid level and the center of the orifice.
CA 02577238 2007-02-15
WO 2006/017928 PCT/CA2005/001247
When the inlet (feed) flow rate is superior to the effluent flow rate, the
liquid level in
the reservoir 14 continues to rise. Once the liquid level rises and attains
the float
10, it progressively cancels the float weight, thus activating the flapgate 8.
When the downward thrust generated by the weight of the float 10 and the lever
24
5 is completely nullified by the up thrust buoyancy effect, such buoyancy
provokes
the displacement of the flapgate 8 in the closed position, as shown in figure
4D.
The float 10 rises according to the liquid level and this in turn moves the
flapgate in
such a way so as to obstruct the lower orifice 20 (see figure 4D). Run-off
occurs,
though this time at the upper orifice 18.
10 The elevation of the liquid level is a result of a run-off, which respects
the orifice
equation from the upper orifice 18 (see figure 4E). The design of the device
according to a preferred embodiment of the invention enables the upper portion
of
the rigid adapter to allow run-off (see figure 4F) through the orifice 30. The
regulator 2 was designed in such a way so as to keep in mind the fact that the
reservoir may become too full (i.e. overflow).
The regulator 2 is preferably designed for conduits having a 100 mm diameter
and
for allowing an accumulation of 70 mm of liquid before overflow. The orifices
are
preferably located 30 mm from one another and have a suitable diameter so as
to
have a maximum flow rate of 3L/min before the overflow occurs.
Advantageously, in another preferred embodiment (not illustrated), the
restriction
device comprises more that two orifices, which allow for a better control of
the flow
rate. The present invention can also be used for certain conduits of varying
diameter and of different sections. It is also suitable for use with multi-
compartmental reservoirs. In the latter case, the flow rate can be controlled
in such
a way so as to transfer liquid from one compartment to another.
CA 02577238 2007-02-15
WO 2006/017928 PCT/CA2005/001247
11
Experimental validation
The flow rate graph of figure 5, associated with the regulator provided with
the
lower and upper orifices, comprises three sections. The first two sections
showthe
run-off (flow rate) of the two orifices. The point of inflexion, representing
the closure
of the flapgate 8, is at a height of 35 mm. At liquid levels above 70 mm, the
flow
rate rapidly increases when the reservoir is too full.
Figure 6 represents the quality of the flow rate regulation with a reservoir
of a
conventional septic tank being filled in less than 5 minutes with 100L of
liquid. From
the standard effluent graph (standard 100 mm in diameter outlet device), no
regulation occurs, the curve rapidly increases until a flow rate of 31 L/min
is
achieved. Afterwards, a balanced regime is produced and a flow-rate of
effluent
equivalent to the reservoir fill rate is observed. The hydraulic event
finishes
minutes after the beginning of the filling of the reservoir.
With the present invention, the elevation of the liquid level occurs rapidly.
A slow
15 flow rate (of effluent) is observed in the first minute, and such is due to
the closing
of the flapgate. The reservoir accumulates a liquid which flows toward an
effluent at
a flow rate of about 2,75 L/min or less. Once the hydraulic event terminates,
the
level decreases and causes the flapgate to open in the 21st minute of the
experiment. The waste is expelled through the lower orifice until the level
returns at
its original height, which occurs at the 50th minute. The non-regulated
hydraulic
event which lasted 15 minutes with a peak flow rate of above 31 L/min, became,
when regulated, an event that lasted 50 minutes with a peak flow never
exceeding
2.75 L/min.
Table 1 shows the effect of the outflow regulator on a septic tank suspended
solids
discharge under a 1 00L hydraulic event.
CA 02577238 2007-02-15
WO 2006/017928 PCT/CA2005/001247
12
Table 1: Effect of the outflow regulator on a septic tank suspended solids
discharge under a 100L hydraulic event
N Suspended solids discharge (mg)
Condition (number average Std deviation
of trials)
Without outflow
8 11900 1600
regulator
With outflow
8 8300 1100
regulator
Suspended solids reduction
30% -
(%)
Although preferred embodiments of the present invention have been described in
detail herein and illustrated in the accompanying drawings, it is to be
understood
that the invention is not limited to this precise embodiment and that various
changes and modifications may be effected therein without departing from the
scope or spirit of the present invention.