Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02579878 2007-03-08
WO 2006/032037 PCT/US2005/033245
-1-
ACTUATOR CAP FOR A CONTAINER
CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS
[0001] This application is a continuation-in-part of U.S. Patent Application
Serial No.
10/810,002, filed March 24, 2004. This application is also a continuation-in-
part of U.S. Patent
Application Serial No. 10/941,791, filed September 15, 2004. This application
is also a
continuation-in-part of U.S. Patent Application Serial No. 11/007,070, filed
December 8, 2004.
This application claims priority to all such previous applications, and such
applications are
hereby incoiporated herein by reference in their entireties.
REFERENCE REGARDING FEDERALLY SPONSORED RESEARCH OR
DEVELOPMENT
[0002] Not applicable
SEQUENTIAL LISTING
[0003] Not applicable
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
1. Field of the Invention
[0004] The present invention relates generally to actuating apparatus, and
more particularly
to actuator caps that are placed on containers and used to dispense product
from the containers.
2. Description of the Background of the Invention
[0005] Various apparatus for dispensing product from a container have been
developed.
One such apparatus has an actuator fitted to a container and has an axially
extending passage
therethrough for discharging product. The actuator has a pair of wings that
extend transversely
from the actuator. The ,container may be moved axially within a device such
that the wings bear
against a surface defining a passage, thereby discharging product through the
passage.
[0006] Another dispensing apparatus has a spray bottle grip used with a nasal
spray bottle.
The grip is coupled to a reciprocating nozzle of the spray bottle, and two
arms extend
CA 02579878 2007-03-08
WO 2006/032037 PCT/US2005/033245
-2-
downwardly along the spray bottle. The arms include finger flanges that
provide an ergonomic
means of reciprocating the nozzle to dispense product from the spray bottle.
Other devices have
a disc-shaped actuator attached to a nozzle of a container. A user depresses
the actuator with a
finger to dispense product from the container.
[0007] One particular type of apparatus has a handle extending along a
container body.
When a user pulls the handle toward the container body, a portion of the
handle pushes
downwardly upon a nozzle portion of the container to dispense product from the
container.
Another type of container has a vertically reciprocating tubular pump. A cap
is fitted to the
container and has an actuator button extending from a sidewall of the cap.
Movement of the
actuator button in a direction toward the sidewall of the cap is translated
into perpendicular
reciprocating movement of the pump.
[0008] Yet other apparatus has a total release actuator that provides a time
delay between
activation of an aerosol valve and discharge of product from an aerosol
container. The actuator
has an upstanding outer wall portion, a base portion terminating in an
inwardly extending
annular lip adapted to snap over and under the perimeter of a mounting cup of
the container to
affix the actuator to the aerosol container. A platform with a valve stem
receiving portion that
attaches to the valve stem is connected to the upstanding wall by a hinge. On
a side opposite the
hinge of the platform is a locking tab. Extending radially outward from the
platform and
through a finger recess in the upstanding outer wall portion is an actuator
lever. When the
actuator lever is depressed the locking tab engages a locking shoulder located
in the wall portion
to prevent movement of the actuator lever.
[0009] Another apparatus for actuating a container has a shoulder cover for an
aerosol
container. The shoulder cover has a hinge in the direction of action of the
shoulder cover fitted
with an aerosol container main body and a locking protrusion and a vertical
groove capable of
separating part of a ring band to the right and left of the hinge on the inner
circumference of the
ring band. The ring band can be torn off from the shoulder cover by holding
the actuator
portion. The actuator of the shoulder cover is a spout or button and once the
ring band is
removed, the actuator can be moved to actuate the container.
[0010] Other apparatuses have a container of product disposed at a first end
of a rod and
having a trigger mechanism at a second end of the rod wherein a user may
actuate the container
CA 02579878 2007-03-08
WO 2006/032037 PCT/US2005/033245
-3-
from a distance. Other devices have an actuating rod with a trigger on a first
end and a
container on a second end. Pulling the trigger moves the actuating rod
longitudinally such that
the second end of the rod moves a bell crank, which in turn, moves an
additional rod that
actuates a valve on the container.
[0011] Another type of apparatus is a cleaning device having a trigger at a
first end of a rod
and a mop cleaning head and a container at a second end of the rod. Pulling
the trigger moves a
pivot link, which in turn actuates a valve of the container, thereby
discharging product from the
container onto the surface to be cleaned by the mop cleaning head.
[0012] Another particular type of container has an air freshener inserted into
a shroud. The
shroud has a nozzle that is fitted over a valve of the container. The
combination of the container
and the shroud is placed within a housing. When a user wishes to spray air
freshener into
ambient air, the user pushes the housing, which in turn pushes the shroud and
the valve to
dispense the air freshener out of the housing.
[0013] In some instances when a user shakes a container while the container is
in a housing,
for example, to shake up the emulsion before spraying, the momentum of the
container can, as
the container is shaken from side to side or if the container is shaken
axially, can shove the can
toward the end of the housing with sufficient force to cause the actuator to
activate the valve of
the containers. The result is an unexpected and undesirable discharge of can
contents.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0014] An actuator cap in one embodiment of the present invention has a base
having an
outer wall with a substantially immovable pillar extending therefrom, and an
actuator member.
The actuator member includes an actuator arm and an engagement member. The
actuator arm
extends from the engagement member and includes a contact surface that extends
outwardly
from the pillar. A flexible web flexibly couples the substantially immovable
pillar to the
actuator member. The flexible web may attach to the actuator member at any
location
including, for example to the engagement member. The flexible web may be
dimensioned so
that movement of the actuator member causes substantially axial movement of
the engagement
member. The flexible web may also be dimensioned such that non-axial movement
of the
engagement member is insufficient to actuate a valve of a container attached
to the actuator cap.
CA 02579878 2007-03-08
WO 2006/032037 PCT/US2005/033245
-4-
The engagement member of the actuator cap is also dimensioned to attach to the
valve of the
container. The substantially immovable pillar may also be dimensioned to
attach to a valve cup
rim of the container.
[0015] In other embodiments, the actuator member includes a plurality of
actuator arms and
the base includes a plurality of substantially immovable pillars where the
actuator arms are
disposed in spaces between the pillars. In some embodiments with a plurality
of actuator arms,
at least two actuator members are separated by substantially the same arcuate
angle. The
actuator cap of the present invention may also have one or more flexible webs
dimensioned so
that when the actuator arms are separated by an arcuate angle of about 180
degrees, movement
of two actuator arms causes substantially axial movement of the engagement
member relative to
an axis of the container; and when the actuator arms are separated by an
arcuate angle of less
than about 180 degrees, movement of at least three actuator members causes
substantially axial
movement of the engagement member relative to an axis of the container.
[0016] The actuator cap of the present invention may also be configured such
that only
substantially axial movement of the engagement member is sufficient to actuate
the valve of the
container when the actuator cap is attached to the container. In one
embodiment, when the
actuator cap is attached to the container, movement of the contact surface in
an axial direction
toward the container actuates the valve of the container.
[0017] The flexible web of the present invention may also be flexibly coupled
to the base of
the actuator cap. The actuator cap may also have one or more guide members
disposed adjacent
the actuator member and configured to guide movement of the engagement member
in, for
example, a substantially linear and/or axial motion. In one embodiment, the
guide member is
disposed on the substantially immovable pillar and/or on the engagement
member.
[0018] Other aspects and advantages of the present invention will become
apparent upon
consideration of the following detailed description.
CA 02579878 2007-03-08
WO 2006/032037 PCT/US2005/033245
-5-
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0019] FIG. 1 is an exploded isometric view of a container and actuator cap;
[0020] FIG. 2 is an exploded isometric view of a housing into which the
container and
actuator cap of FIG. 1 may be placed;
[0021] FIG. 3 is a side elevational view showing a rod and trigger mechanism
in
combination with the housing of FIG. 2;
[0022] FIG. 4 is a sectional view taken generally along the lines 4-4 of FIG.
3 further
illustrating the container of FIG. 1 in elevation and the actuator cap thereof
in section;
[0023] FIG. 5 is an enlarged fragmentary view of FIG. 4;
[0024] FIG. 6 is a view similar to FIG. 5, but showing the actuator cap of
FIG. 1 in an
actuating position;
[0025] FIG. 7 is a plan view of the actuator cap according to the present
invention;
[0026] FIG. 8 is a first side elevational view of the actuator cap of FIG. 7;
[0027] FIG. 9 is a second side elevational view of the actuator cap of FIG. 7;
[0028] FIG. 10 is a third side elevational view of the actuator cap of FIG. 7;
[0029] FIG. 11 is an isometric view of the actuator cap of FIG. 7;
[0030] FIG. 12 is a bottom elevational view of the actuator cap of FIG. 7;
[0031] FIG. 13 is an enlarged fragmentary isometric view of an actuator member
of the
actuator cap of FIG. 7;
[0032] FIG. 14 is a bottom elevational view of the actuator member of FIG. 13;
[0033] FIG. 15 is a plan view of another actuator cap according to the present
invention;
[0034] FIG. 16 is a bottom elevational view of the actuator cap of FIG. 15;
[0035] FIG. 17 is a cross-sectional view of the actuator cap of FIG. 15;
[0036] FIG. 18 is a plan view of yet another actuator cap according to the
present invention;
[0037] FIG. 19 is a bottom elevational view of the actuator cap of FIG. 18;
and
CA 02579878 2007-03-08
WO 2006/032037 PCT/US2005/033245
-6-
[0038] FIG. 20 is a cross-sectional view of the actuator cap of FIG. 18;
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0039] Turning now to the figures, FIG. 1 illustrates a container 50 having a
valve 52 and a
main body 56 containing product (not shown). The valve 52 may be a male or
female valve,
and/or a vertically depressible valve or a tilt valve, for example. As will be
appreciated
hereinafter, if a tilt valve is utilized such valve could also alternatively
be depressed vertically
without tilting to dispense product therethrough. It should be noted that the
valve 52 could be
replaced by any suitable apparatus that may be displaced to release product
from the container
50. An actuator cap 60 is fitted to the container 50.
[0040] FIG. 2 illustrates a housing 70 into which the container 50 and the
actuator cap 60
may be placed. The container 50 and the actuator cap 60 are a product refill
for the housing 70.
It should be noted that the product refill may include additional components
(not shown) besides
the container 50 and the actuator cap 60, such as a sleeve (not shown)
disposed around the
container 50. The actuator cap 60 has a deflectable actuator member 266 in the
forin of actuator
arms 268, 270, 272 and any suitable engagement member 274 attached to the
valve 52. The
housing 70 has a discharge opening 82 through which product stored within the
container 50
may be dispensed.
[0041] Referring to FIGS. 3-6, relatively moving the container 50 and the
housing 70 such
that the container 50 is moved toward the discharge opening 82 deflects the
actuator arms 270,
272, 274, thereby actuating the valve 52 as described herein, causing product
to be released
from the container 50 and dispensed from the housing 70. A rod and trigger
mechanism 84 may
be used to move the container 50 within the housing 70. The mechanism 84
includes a hollow
tube 86 with a handle assembly 88 at a first end 90 of the tube 86, and a
second end 92 of the
tube 86 is secured within a sleeve 94 of the housing 70 in any suitable manner
such as by
welding or appropriately threading the sleeve 94 and the end 92. Pulling a
trigger 96 of the
handle assembly 88 advances a push rod 100 disposed within the tube 86 against
a bottom
surface 102 of the container 50, thereby advancing the container 50 toward the
discharge
opening 82. If necessary or desirable, an end 104 of the push rod 100 may be
shaped and/or
fitted with a plate or other member to distribute'forces more evenly across
the bottom surface
102 of the container 50. Further, if desired, rather than moving the container
50 relative to the
CA 02579878 2007-03-08
WO 2006/032037 PCT/US2005/033245
-7-
housing 70 by using the rod and trigger mechanism 84 one could move the
container 50 and/or
the housing 70 relative to one another by hand to dispense product.
[0042] The housing 70 includes a wall 108 that decreases in cross sectional
size, tapering to
the discharge opening 82. The discharge opening 82 has a cross sectional size
greater than a
radius R (FIG. 1) of the container 50. Referring again to FIG. 2, the housing
70 may include
first and second wall portions 114, 116 that may be joined together to house
the container 50
and the actuator cap 60 fitted thereto. The wall portion 114 may include three
bayonet slots
118a-118c disposed on an end 122 of the wall portion 114 and equally spaced
from one another
by 120 degrees. To join the wall portions 114, 116, a user inserts pins 124
carried by an end
126 of the wall portion 116 into the slots 11 8a- 11 8c and provides a
relative rotation of the wall
portions 114, 116 to seat the pins 124 within recessed regions 130a-130c of
the slots 118.
[0043] Either of the wall portions 114, 116 may include protrusions 136 such
as guide fins
138 having edges 140 that abut the exterior surface of the container 50 to
center the container
within the housing 70. Either of the wall portions 114, 116 may include
elongate openings or
windows 144 that allow a user to see the container 50 when the container is
disposed within the
housing 70. The housing 70 wall portions 114, 116 may include three windows
144 spaced
apart by 120 degrees. The windows 144 may allow a user to see the container 50
including, for
example, written directions or graphics disposed on the container (not shown).
[0044] Referring also now to FIGS. 5 and 6, a main region 150 of the wall
portions 114, 116
may have an inner cross sectional size Cl of about 66 mm (2.6 inches), and
thus the product
refill, comprising the container 50 and the actuator cap 60, may have a cross
sectional size of up
to about 66 mm. In this regard, while a range of sizes is available for the
container 50 one may
wish to provide a container sized at or near maximum to provide a maximum
useful life for the
container 50 given the available space within the housing 70.
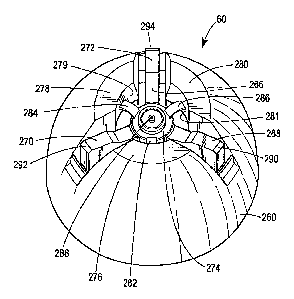
[0045] Also now referring to FIGS. 7-20, the actuator cap 60 has a base 260
that decreases
in cross sectional size along an axial dimension defined between a first end
262 for fitting over
the container 50 and a second end 264 for discharging product from the
container. The actuator
member 266 is disposed in spaces between substantially irnmovable pillars 276,
278, 280 and
includes three actuator arms 268, 270, 272 that are spaced apart by about 120
degrees and
extend transversely to an axial dimension of the cap. The actuator arms 268,
270, 272 each
CA 02579878 2007-03-08
WO 2006/032037 PCT/US2005/033245
-8-
include a contact surface 290, 292, 294 and are attached to an engagement
member 274. The
actuator arms 268, 270, 272 extend from the base 260 and outwardly from
respective pillars
276, 278, 280. The immovable pillars 276, 278, 280 each have a side wall 277,
279, 281, an
interior side wall 277a, 279a, 281a that is dimensioned to attach to a valve
cup rim 296 of the
container 50, and support ribs 276a, 276b, 278a, 278b, 280a, 280b that assist
in resisting
deflection inwardly toward the engagement member 274 or outwardly from the
actuator cap 60.
The support ribs 276a, 276b, 278a, 278b, 280a, 280b may provide resistance to
axial deflection
that assist in increasing crush resistance of the actuator cap. The actuator
member 266 is
flexibly attached to the substantially immovable pillars 276, 278, 280 at the
engagement
member 274 by three flexible webs 282, 284, 286 that are spaced apart by about
120 degrees.
The engagement member 274 is dimensioned to attach to the valve 52 and
includes a
substantially axially oriented discharge orifice 288. The engagement member
274 is secured to
the valve 52 as shown in FIGS. 5 and 6.
[0046] The actuator cap 60 provides a useful centering function in that
peripheral surfaces
156a-156f of the pillars 78a-78f maintain a point of discharge 160 of the
actuator cap 60 in a
centrally located position relative to the discharge opening 82, thereby
minimizing the potential
for product impingement against a surface 164 of the tapered wall 108. The
surfaces 156 may
optionally be tapered. Referring also to FIG. 5, the pillars 78a-78f of the
actuator cap 60 have a
length L defined between a longitudinal centerline C (FIG. 5) of the actuator
cap and a
peripheral surface 168 of the pillars 78a-78f. The length L is selected
relative to the inner
dimensions of the tapered wall 108 such that the peripheral surface 168 is
disposed in interfering
relationship with the tapered wall 108. It should be appreciated that the
actuator cap 60 and/or
the pillars 78a-78f could have any suitable shape so long as the pillars 78a-
78f are dimensioned
to have an interference relationship with the tapered wall 108. The length L
may have any
suitable value such as greater than about one-quarter (25%) a largest diameter
of the product
refill or greater than or equal to about one-third (33%) the largest diameter
of the product refill,
whether the largest diameter is defined by the container 50, the actuator cap
60, or some other
component of the product refill. The length L may be greater than about one-
quarter (25%) of a
largest diameter D of the actuator cap 60, measured at the first end 152. The
length L may be
greater than or equal to about one-third (33%) the largest diameter D. Of
course, the length L
may be alternatively expressed relative to the size of the container 50. In
any event, a largest
CA 02579878 2007-03-08
WO 2006/032037 PCT/US2005/033245
-9-
lateral dimension across the product refill cannot exceed the internal cross
sectional size Cl
(FIG. 6) of the housing 70, and L may have any suitable value such as greater
than about one-
quarter (25%) of this largest lateral dimension Cl. One could select any
suitable cross sectional
size S (FIG. 5) for the discharge opening 82, such as a cross sectional size
of about 34 mm (1.3
inches), and suitable values of L might range between about 18 mm (0.7 inch)
and about 33 mm
(1.3 inches) to provide the above-described interfering relationship. For
example, a value for L
may be about 25 mm (1 inch). It should be noted that while the tapered wall
108 of the housing
70 is illustrated as symmetrical around the longitudinal centerline C of the
housing 70, the wall
108 could be made asymmetrical, greater in cross sectional size in one plane
rather than another,
and the shape of the actuator cap 60 could be made complementary therewith to
serve as a
keying function to orient the container 50 relative to the housing 70 in a
particular angular
orientation. This could be advantageous for various reasons, such as where
product discharges
in an asymmetrical pattern.
[0047] A cover (not shown) may also be fitted to the actuator cap 60 to shield
the contact
surfaces 290, 292, 294 to prevent inadvertent actuation of the valve 52 during
shipment.
[0048] Now referring to FIG. 6, relatively moving the container 50 and the
housing 70 such
that the main body 56 of the container 50 and the discharge opening 82 are
moved toward each
other causes the contact surfaces 290, 292, 294 of the actuator arms 268, 270,
272 to engage the
surface 164 of the tapered wall 108, thereby deflecting the actuator arms.
During such
deflection, the actuator arms 268, 270, 272 and the engagement member 274 move
downwardly
toward the container 50 flexing the flexible webs 282, 284, 286. The flexible
webs 282, 284,
286 may be dimensioned and/or of a stiffness so that movement of the actuator
member 266
causes substantially axial movement of the central engagement member 274
relative to an axis
of the container 50 when the actuator arms 268, 270, 272 are deflected. For
example, a shorter
flexible web 282, 284, 286 may require more force than an otherwise similar
but longer flexible
web before extending to a point that actuates the valve 52 of the container
50. Illustratively,
when the actuator arms 268, 270, 272 are separated by an arcuate angle of less
than about 180
degrees, the flexible webs 282,, 284, 286 are dimensioned such that movement
of at least three
of the actuator members causes substantially linear movement and/or axial
movement, for
example, non-tilting movement, of the engagement member 274. In other
embodiments where
the actuator arms are separated by an arcuate angle of about 180 degrees (not
shown),
CA 02579878 2007-03-08
WO 2006/032037 PCT/US2005/033245
ti
-10-
movement of two actuator arms causes substantially linear movement and/or
axial movement of
the central engagement member 274. Sufficient axial displacement of the
engagement member
274 actuates the valve stem 52 such that product contained in the container 50
dispenses from
the container through the discharge orifice 288 and out of the housing 70.
[0049] The actuator cap 60 disclosed herein may be designed to reduce the
likelihood of
inadvertent dispensing that might result from a user inadvertently shaking or
jostling the
housing 70 with the container 50 disposed therein. For example, where the
valve 52 of the
container 50 is a vertically depressible valve, the flexible webs 282, 284,
286 may be
dimensioned such that non-axial movement of the central engagement member is
insufficient to
actuate the valve stem thereby potentially reducing or minimizing product
discharge from the
container 50. The piIlars 276, 278, 280 of the actuator cap 60 may also be
substantially
immovable having an inherent resistance to movement provided by the support
ribs 276a, 276b,
278a, 278b, 280a, 280b, and the resistance may be increased or decreased as
desired for a
particular actuator cap design. Where the pillars 276, 278, 280 are rigid, a
sufficient amount of
external mechanical force must act upon the contact surfaces 290, 292, 294 of
the actuator arms
268, 270, 272 to overcome resistance provided by the flexible webs 282, 284,
286. In this
regard, the resistance of the flexible webs 282, 284, 286 against movement
provides a reactive
force against forces directing the container 50 toward the discharge opening
82, such that the
reactive force must be overcome before dispensing may occur. This reactive
force is
advantageous in that low force levels may be insufficient to overcome same to
actuate the valve
52 of the container 50 and dispense product from the housing 70.; For example,
such low force
levels may occur from a user jostling the housing 70 while walking or
manipulating the housing
or may arise as a user shakes the housing to mix the contents of the container
50. Such jostling
could cause the actuator cap 60 to be in a condition where one or more of the
contact surfaces
290, 292, 294 are slightly deflected and the engagement member 272 is either
un-deflected or
deflected to a lesser extent than necessary to actuate the valve 52. The
reactive force provided
by the flexible webs 282, 284, 286 reduces inadvertent dispensing until such
time as the user
intentionally applies sufficient force, thereby deflecting the contact
surfaces 290, 292, 294 and
axially deflecting the engagement member 272 to an actuating position thereof.
Thus, the user
can pull the trigger 96 shown in FIG. 3 to intentionally dispense product,
while inadvertent
dispensing is reduced, minimized or avoided.
CA 02579878 2007-03-08
WO 2006/032037 PCT/US2005/033245
-11-
[0050] In other embodiments of the present invention, and now also referring
to FIGS. 15-
20, one or more guide members 400, 402, 404 are provided proximate to or
disposed on the
engagement member 274 to assist in providing linear or axial movement of the
engagement
member w'hen one or more of the actuator arms 268, 270, 272 are depressed in a
direction
toward the first end 262 of the actuator cap 60. The guide members 400, 402,
404 can be
positioned at any location within the actuator cap 60, and as shown in FIGS.
15-17 the guide
inembers may be disposed on the pillars 276, 278, 280 such as on one or more
interior side
walls 277a, 279a, 281a, andlor, as shown in FIGS 18-20, the guide members may
be disposed
on the engagement member 274. The guide members 400, 402, 404 may also be
dimensioned
such that depression of any number of actuator arms creates substantially
axial movement of the
engagement member 274. In FIGS. 15-17 the side walls 408, 410, 412 are tapered
from the
base first end 262 to the base second end 264 to assist in guiding the
engagement member 274
in a substantially linear or axial direction. FIGS 18-20 illustrate guide
members 400, 402, 404
with straight walls 408, 410, 412 that form a cylinder open on three sides
around the
engagement member to allow the actuator arms 268, 270, 272 to pass through the
guide
members if necessary to actuate the valve 52 of the container 50.
[0051] The guide members 400, 402, 404 as shown in FIGS. 15-20 may work in
conjunction
with and/or independently of the flexible webs 282, 284, 286 in guiding the
movement of the
engagement member 274. The guide members 400, 402, 404 may also assist in, for
example,
reducing the number of flexible webs 282, 284, 286 required to attach the
engagement member
274 to the base 260, and/or increasing or decreasing the length, width, and/or
thickness of a
flexible web, and/or reducing the stiffness of a flexible web, to achieve a
desired motion of the
engagement member 274. Also, where the valve 52 is a vertically depressible
valve, the guide
members 400, 402, 404 may be positioned or configured to assist in guiding the
engagement
member 274 in a substantially linear or axial motion. When the valve 52 is a
tilt valve the guide
members 400, 402, 404 may be positioned or configured to assist in guiding the
engagement
member 274 in a direction that actuates the tilt valve, for example, in
direction transverse to an
axial direction of the tilt valve. The guide members 400, 402, 404 may also be
dimensioned,
positioned, and/or configured such that only one actuator arm 268, 270, 272 is
necessary to
create the desired movement of the engagement member 274 independently or in
conjunction
with the flexible webs 282, 284, 286.
CA 02579878 2007-03-08
WO 2006/032037 PCT/US2005/033245
-12-
[0052] The guide members 400, 402, 404 and/or flexible webs 282, 284, 286 may
also assist
in distributing unevenly applied downward force applied to one or more
actuator arms 268, 270,
272 to the remaining actuator arms. In such cases, the force necessary to
depress one actuator
arm 268, 270, 272 independently on a multi-arm actuator member 266, may be
increased due to
the resistance provided by the remaining actuator arms and associated guide
members 400, 402,
404 and/or flexible webs 282, 284, 286. This 'redistribution of force may, for
example, reduce
or minimize the occuiTence of accidental actuation of the valve 52 when fewer
than all actuator
arms 272, 274, 276 are depressed, such as when, for example, a user is
transporting the
container 50 and actuator cap in the housing 70.
INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY
[0053] The foregoing embodiments are useful for dispensing a variety of
products such as
insecticides, cleaning products, air treatment products (for example, air
fresheners), or other
products.
[0054] The invention has been described in an illustrative manner, and it is
to be understood
that the terminology used is intended to be in the nature of description
rather than of limitation.
All patents and other references cited herein are incorporated by reference in
their entirety.
Many modifications, equivalents, and variations of the present invention are
possible in light of
the above teachings, therefore, it is to be understood that within the scope
of the appended
claims, the invention may be practiced other than as specifically described.