Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02581228 2007-03-20
WO 2006/082600 PCT/IT2005/000049
APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING THE CONSISTENCY OF A FLOW OF STOCK
SOLUTION
IN A PAPERMAKING MACHINE
DESCRIPTION
Background of the invention.
-Field of the invention.
The present invention relates to an apparatus for controlling the consistency
of a
flow of stock solution flowing from a header to a slice lip of a headbox of a
papermaking
machine. More specifically, the present invention relates to an apparatus and
a method
for controlling the consistency of a flow of stock solution flowing from a
header to a
slice lip of a headbox of a papermaking machine so that the cross machine
direction
profile of a resultant web is controlled.
Background information.
In the papermaking industry, a solution of paper stock is supplied to a
headbox of
a papermaking machine. The pressurized stock is guided through a plurality of
headbox
flow channels into a slice chamber of the headbox. The stock is then ejected
as a thin
ribbon through a slice lip defined by the downstream end of the headbox. The
ejected
stock is received onto a moving Fourdrinier screen where water drains from the
stock
solution to provide a formed web.
One of the more important quality parameters in the paper making process is
the
evenness of the cross machine direction basis weight profile. Even if the
cross machine
profile of the concentration of the stock ejected from the headbox slice is
fairly even, the
final basis weight profile is normally altered due to several defects produced
along the
process in the machine. These defects include an uneven flow profile of the
stock ejected
from the headbox, uneven retention of the fibers on the fourdrinier, uneven
pick up of
solids in the size press or in the coating station. The usual way to control
the
aforementioned defects is to compensate for them by controlling the
consistency profile
of the stock before it is ejected from the headbox.
The headbox is divided into several discrete cross machine sections of a
certain
width and in each of these sections the consistency of the stock is
individually controlled
according to the measure of the basis weight of the final sheet in the
corresponding cross
machine section.
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for controlling the
consistency profile in a headbox and for providing a web having a more uniform
cross
machine direction basis weight profile.
CA 02581228 2007-03-20
WO 2006/082600 PCT/IT2005/000049
-2-
Many prior art arrangements have been devised in an attempt to provide a
relatively uniform grammage or basis weight in a cross machine direction of
the web.
Early attempts at controlling the aforementioned characteristic of the web
included the
provision of a plurality of slice lip screw jacks spaced a few inches from
each other in a
cross machine direction. Such jacks were connected to a movable slice lip of
the slice
opening. Controlled movement of the jacks would warp the slice lip in such a
way that a
relatively uniform ribbon of stock would be ejected through the slice opening.
Nevertheless, such arrangements were complex. Also, the adjustment of one of
the jacks
had the tendency to alter the basis weight of stock flowing past an adjacent
jack.
A further development included the provision of uniformly spaced slice lips
while controlling the consistency or dilution of the stock in a cross machine
direction
upstream relative to the slice lips. More particularly, immediately upstream
from the
tube bank, a flow of diluting white water or the like was selectively
introduced into one
or more of the headbox tubes of the tube bank so that the consistency of the
stock
flowing through that particular tube would be changed or diluted relative to
the
consistency of stock flowing through an adjacent tube.
More particularly, in the prior art dilution arrangement, by controlling the
injected suspension flow in the vicinity of the tube bank, it was possible to
a large extent
to control the concentration of the resultant suspension downstream from the
injection
point. Such an injection arrangement has the disadvantage that the correction
of
suspension concentration requires the adding of an extraneous means to the
suspension
itself which can generate technological problems into the paper making
process. Such an
arrangement also necessitates the provision of additional circuitry for the
dilution water
and the provision of additional pumping apparatus. The need of the addition of
a
secondary suspension to control the concentration of the main suspension makes
it
almost impossible to selectively change the suspended particles without
interacting with
the hosting liquid phase.
The present invention provides a unique means for achieving a uniform basis
weight or grammage in a cross machine direction by the application of
ultrasonic waves
for controlling in a cross machine direction, the grammage of the resultant
web.
According to the present invention, when ultrasonic waves are applied to a
liquid
suspension, such ultrasonic waves have the capability of moving the suspended
particles.
In particular, particles suspended in a stationary suspension and contained
within a
reservoir are located in between an ultrasound generator and a ultrasound
absorber
CA 02581228 2007-03-20
WO 2006/082600 PCT/IT2005/000049
-3-
device. When ultrasonic waves are applied to the particles, such particles are
moved by
the ultrasound waves in a direction extending from the generator to the
absorber.
Similarly, the same effect occurs when ultrasonic waves are applied to a
moving
suspension of particles. For example, when a flow of the suspension is moving
in a
generic direction at a generic speed and the suspension flow crosses a region
between the
ultrasound generator and the absorber, then the suspended particles will be
deviated from
the flow direction by a motion component which is parallel to the line going
from the
generator to the absorber.
The result is that downstream from the ultrasonic device, the suspension will
not
have the same homogeneity as the homogeneity of the suspension upstream
relative to
the ultrasonic device. This is so because the suspended particles will tend to
migrate
toward the absorber. As a consequence of such migration downstream from the
ultrasonic device, the suspension flow will have been concentrated on the
absorber side
and diluted on the generator side.
The object of the present invention is the application of the aforementioned
physical principle to control the concentration of a paper making fibrous
material
suspension or stock solution through a head box.
In a paper machine head box, according to the present invention, the control
of
fiber suspension concentration or consistency in any specific cross machine
section of
the headbox is used to control the final paper sheet cross machine grammage
profile.
Applying the above-mentioned effect of ultrasonic waves on fluid suspensions
in
a specific cross machine section of the headbox by the use of an ultrasonic
device
dedicated that specific headbox cross machine section, it is possible to exert
a force on
any single solid particle suspended in the region corresponding to the same
specific cross
machine section of the headbox and move it inside the liquid hosting phase. As
a
consequence, it is possible to locally concentrate or dilute the suspension.
More
specifically, by applying energy in the form of ultrasound waves, it is
possible to create a
degree of dis-homogeneity into the suspension. By controlling the amount of
energy
supplied to the generator, or the capacity of the absorber, it is possible to
control the state
of dis-homogeneity of the suspension in the specific section and as a
consequence, to
control local concentration of the suspension.
As an example, in the system of the present invention, the effect is applied
to a
suspension such as paper stock flowing into a channel from left to right.
CA 02581228 2007-03-20
WO 2006/082600 PCT/IT2005/000049
-4-
Ultrasound waves cross the channel from the top to the bottom. Such waves push
suspended particles or fibers toward the bottom side of the channel.
Downstream from
the ultrasonic device, the channel is split into secondary channels, that is a
supply
channel and a recirculation channel. It is evident that the average
concentration of the
suspension received by the supply channel is in this case lower than the
average
concentration of the suspension received by the recirculation channel. The
difference
between the two concentrations is in some way related to the power delivered
by the
ultrasonic device. In particular, the higher the power, of the generator or
the capacity of
the absorber, the bigger is the difference in concentration between the supply
channel
and the recirculation channel. By controlling the ultrasonic device, it is
possible to
control the concentration in at least one of the two secondary channels.
By controlling the power delivered by the ultrasonic device, it is possible to
control the concentration in at least one of the two secondary channels.
In a paper machine headbox according to the present invention, the fiber
suspension of the stock solution enters the headbox from a supply header and
is
transferred to a tube bank through a bank of flow channels. The adjacent
channels
forming the flow channels can be either physically separated one from the
other by
sidewalls or not. The principle of two secondary channels is applied to each
single flow
channel. Each flow channel is equipped with its own ultrasonic device. Also,
each
ultrasonic device includes an independent control. Each flow channel is split
into two
secondary channels, one top. channel and one bottom channel. One of the two
secondary
channels is a supply channel of a corresponding cross machine direction
section of the
headbox tube bank. The other secondary channel or recirculation channel of
each flow
channel permits recirculation to the supply system of the headbox. A
recirculation header
collects the flow from each of the recirculation channels of all the flow
channels. The
stock collected by the recirculation header is simply recirculated into the
stock approach
system with no need for any extra equipment.
Applying the principle of the present invention, it is evident that it is
possible to
individually control the concentration of the suspension in any secondary
supply channel
covering a specific respective headbox cross machine section by controlling
its
respective ultrasonic generator. From previous knowledge of paper machine
technology,
it is known that if one is able to control independently the stock
concentration into each
specific cross machine section of a headbox, then it is possible to control
the cross
machine grammage profile of the finished paper.
CA 02581228 2007-03-20
WO 2006/082600 PCT/IT2005/000049
-5-
Therefore, it is a primary feature of the present invention to provide an
apparatus
and method for controlling the cross machine consistency profile of a stock
solution
within a headbox of a papermaking machine that overcomes the problems
associated
with the prior art arrangements.
Another feature of the present invention is the provision of an apparatus for
controlling the cross machine consistency profile of a stock solution within a
headbox of
a papermaking machine so that the grammage profile of the resultant web can be
controlled.
Other features and advantages of the present invention will be readily
apparent to
those skilled in the art by a consideration of the detailed description of a
preferred
embodiment of the present invention contained herein.
Summary of the invention.
The present invention relates to an apparatus for controlling the cross
machine
consistency profile of a flow of stock solution flowing from a header to a
slice lip of a
headbox of a papermaking machine so that the cross machine direction
consistency
profile of a resultant web is controlled. The apparatus includes a flow
channel which is
disposed within the headbox between the header and the slice lip. The flow
channel has
an upstream and a downstream end such that the flow of the stock solution is
in a flow
direction from the upstream end towards the downstream end of the flow
channel. The
flow channel includes a primary channel having a first and a second extremity
such that
the flow of the stock solution is through the primary channel from the first
extremity to
the second extremity of the primary channel. A supply channel has a first and
a second
end and is disposed downstream relative to the primary channel for the flow
therethrough of a supply portion of the flow of the stock solution. The second
end of the
supply channel is connected to the slice lip so that the supply portion of the
flow of the
stock solution flows to the slice lip. A recirculation channel has a first and
a second
termination, the recirculation channel being disposed downstream relative to
the primary
channel for the flow therethrough of a recirculation portion of the flow of
the stock
solution. The second termination of the recirculation channel is connected to
the header
so that the recirculation portion of the flow of the stock solution flows to
the header. A
generator is disposed adjacent to the primary channel for generating
ultrasonic waves
within the flow of the stock solution flowing through the primary channel. The
ultrasonic
waves move fiber particles suspended within the stock solution for controlling
the
consistency of the stock solution flowing through the primary channel. Also,
an
CA 02581228 2007-03-20
WO 2006/082600 PCT/IT2005/000049
-6-
ultrasound absorber is disposed adjacent to the primary channel such that the
flow of the
stock solution flows in the flow direction within a region disposed between
the generator
and the absorber so that in operation of the apparatus, when the stock
solution is flowing
within the region, the fiber particles suspended within the stock solution are
deviated
from the flow direction. The arrangement is such that the consistency of the
stock
solution flowing from the primary channel through the supply channel is
different from
the consistency of the stock solution flowing from the primary channel through
the
recirculation channel so that the consistency of the supply portion of the
stock solution
flowing through the slice lip is controlled thereby controlling the cross
machine direction
profile of the resultant web.
In a more specific embodiment of the present invention, the apparatus includes
a
further generator which is disposed adjacent to the primary channel and
laterally relative
to the generator for generating ultrasonic waves within the flow of the stock
solution
flowing through the primary channel. The ultrasonic waves move fiber particles
suspended within the stock solution for controlling the consistency of the
stock solution
flowing through the primary channel.
Furthermore, a further ultrasound absorber is disposed adjacent to the primary
channel and laterally relative o the absorber such that the flow of the stock
solution
flows in the flow direction within a further region disposed between the
further generator
and the further absorber such that in operation of the apparatus, when the
stock solution
is flowing within the further region, the fiber particles suspended within the
stock
solution are deviated from the flow direction so that the consistency of the
stock solution
flowing from the primary channel downstream from the further region through
the
supply channel is different from the consistency of the stock solution flowing
from the
primary channel downstream from the further region through the recirculation
channel.
The arrangement is such that the consistency of a further supply portion of
the stock
solution flowing through the slice lip downstream from the further region is
controlled
relative to the supply portion of the stock solution flowing downstream from
the region
through the slice lip thereby controlling the cross machine direction
consistency profile
of the resultant web.
In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the flow direction is
approximately parallel to a direction from the header to the slice lip.
CA 02581228 2007-03-20
WO 2006/082600 PCT/IT2005/000049
-7-
Also, the primary channel defines a primary conduit of rectangular cross
sectional configuration, the primary conduit extending from the first
extremity to the
second extremity of the primary channel.
More particularly, the first end of the supply channel extends from the second
extremity of the primary channel and the supply channel is disposed above the
recirculation channel.
However, in another embodiment of the present invention, the supply channel is
disposed below the recirculation channel.
Additionally, the first termination of the recirculation channel extends from
the
second extremity of the primary channel such that the flow of the stock
solution flowing
through the primary channel is split into the supply portion and the
recirculation portion
adjacent to the second extremity of the primary channel.
In one embodiment of the present invention, the apparatus further includes a
control device which is electrically connected to the generator for
controllably altering
the generation of the ultrasonic waves by the generator.
However, in an alternative embodiment of the present invention, a device is
mechanically connected to the generator for controllably altering a location
of the
generator relative to the primary channel so that generation of the ultrasonic
waves
within the region by the generator is altered.
In another embodiment of the present invention, a controller is electrically
connected to the ultrasound absorber for controllably altering absorption of
the
ultrasonic waves by the absorber.
Alternatively, a control device is mechanically connected to the absorber for
controllably altering a disposition of the absorber relative to the primary
channel so that
absorption of the ultrasonic waves by the absorber is altered.
In each of the alternative embodiments of the present invention, the flow
direction within the region is disposed non parallel to a direction from the
generator to
the absorber.
However, more specifically, the flow direction within the region is disposed
substantially normal to a direction from the generator to the absorber.
Moreover, the direction from the generator to the absorber is substantially
normal
to the flow direction within the region such that in use of the apparatus, the
ultrasonic
waves deviate movement of the fiber particles in a component direction which
is
CA 02581228 2007-03-20
WO 2006/082600 PCT/IT2005/000049
-8-
disposed angularly between the flow direction and the direction from the
generator to the
absorber.
The present invention also includes a method for controlling the consistency
of a
flow of stock solution flowing from a header to a slice lip of a headbox of a
papermaking
machine so that the cross machine direction consistency profile of a resultant
web is
controlled. The method includes the steps of guiding the flow of the stock
solution
through a flow channel which is disposed within the headbox between the header
and the
slice lip. The flow channel includes a primary channel which has a first and a
second
extremity. A supply channel has a first and a second end, the supply channel
being
disposed downstream relative to the primary channel for the flow therethrough
of a
supply portion of the flow of the stock solution. The second end of the supply
channel is
connected to the slice lip so that the supply portion of the flow of the stock
solution
flows to the slice lip. A recirculation channel has a first and a second
termination, the
recirculation channel being disposed downstream relative to the primary
channel for the
flow therethrough of a recirculation portion of the flow of the stock
solution. The second
termination of the recirculation channel is connected to the header so that
the
recirculation portion of the flow of the stock solution flows to the header.
The method also includes the steps of generating ultrasonic waves within the
flow of the stock solution flowing through the primary channel by an
ultrasonic
generator. The ultrasonic waves move fiber particles suspended within the
stock solution
for controlling the consistency of the stock solution flowing through the
primary
channel.
Additionally, the method includes absorbing the ultrasonic waves by an
ultrasound absorber disposed adjacent to the primary channel such that the
flow of the
stock solution flows in the flow direction within a region which is disposed
between the
generator and the absorber. The arrangement is such that when the stock
solution is
flowing within the region, the fiber particles suspended within the stock
solution are
deviated from the flow direction so that the consistency of the stock solution
flowing
from the primary channel through the supply channel is different from the
consistency of
the stock solution flowing from the primary channel through the recirculation
channel.
The method is such that that the consistency of the supply portion of the
stock solution
flowing through the slice lip is controlled thereby controlling the cross
machine direction
consistency profile of the resultant web.
CA 02581228 2007-03-20
WO 2006/082600 PCT/IT2005/000049
-9-
Many modifications and variations of the present invention will be readily
apparent to those skilled in the art by a consideration of the detailed
description
contained hereinafter taken in conjunction with the annexed drawings which
show a
preferred embodiment of the present invention. However, such modifications and
variations fall within the spirit and scope of the present invention as
defined by the
appended claims.
Brief description of the drawings.
Fig. 1 is a schematic to demonstrate the effect of the application of
ultrasonic
waves on a stock solution according to the present invention;
Fig. 2 is a similar view to that shown in Fig. 1 but shows the generator
energized;
Fig. 3 is a similar view to that shown in Fig. 2 but shows the fiber
suspension or
stock solution in motion;
Fig. 4 is a diagrammatic representation of an apparatus according to the
present
invention for controlling the consistency of stock solution within a headbox
of a
papermaking machine;
Fig. 5 a side elevatiorial view of an apparatus for controlling the
consistency of a
flow of stock solution flowing from a header to a slice lip of a headbox of a
papermaking
machine;
Fig. 6 is a sectional view taken on the line 6-6 of Fig. 5;
Fig 7 is a similar view to that shown in Fig. 6 but shows another embodiment
of
the present invention;
Fig. 8 is a sectional view taken on the line 8-8 of Fig. 7;
Fig. 9 is a side elevational view of another embodiment of the present
invention;
Fig. 10 is a similar view to that shown in Fig. 6 but shows a further
embodiment
of the present invention;
Fig. 11 is a similar view to that shown in Fig. 10 but shows a further
embodiment
of the present invention;
Fig.12 is a similar view to that shown in Fig. 10 but shows another embodiment
of the present invention; and
Fig. 13 is a similar view to that shown in Fig. 11 but shows a further
embodiment
of the present invention.
Similar reference characters refer to similar parts throughout the various
views
and embodiments of the drawings.
Detailed description of the drawings.
CA 02581228 2007-03-20
WO 2006/082600 PCT/IT2005/000049
-10-
Fig. 1 is a schematic to demonstrate the effect of the application of
ultrasonic
waves on a stock solution according to the present invention. As shown in Fig.
1, a
generator 10 is disposed adjacent to a first side of a container 16 and an
absorber 24 is
disposed on the opposite side of the container 16. The container 16 is filled
with a
suspension of fiber particles 18, 19 and 20 randomly dispersed throughout the
host liquid
such as water.
Fig. 2 is a similar view to that shown in Fig. 1. However, as shown in Fig. 2,
the
generator 10 is energized so that the generator 10 emits ultrasonic waves 12,
13 and 14
through the container 16 containing the fiber particles 18, 19 and 20
suspended in water.
Accordingly, the ultrasonic waves 12-14 cause the particles 18-20 to move
through the
water in a direction as indicated by the arrow 22 from the generator 10
towards the
absorber 24.
Fig. 3 is a similar view to that shown in Fig. 2 but shows the fiber
suspension or
stock solution in motion. As shown in Fig. 3, the stock solution which
includes the fibers
18-20 is moving through the container 16 in a flow direction as indicated by
the arrow
26. As shown in Fig. 3, the flow direction 26 is normal to the direction 22.
In this case,
the fiber particles 18-20 will move in a component direction which is
indicated by the
arrow 28. The component direction 28 is disposed angularly between the
directions 22
and 26. Consequently, in a downstream location relative to the generator 10,
the
suspension or stock solution will be more concentrated or will have a higher
consistency
on the side 30 of the container 16 nearest to the absorber 24. Similarly, the
stock solution
will be diluted or will be of a lower consistency on a further side 32 of the
container 16
nearest to the generator 10 as shown in Fig. 3.
Fig. 4 is a diagrammatic representation of an apparatus according to the
present
invention for controlling the consistency of the stock solution 34 which
includes the
fibers 18-20, within a headbox generally designated 36 of a papermaking
machine. As
shown in Fig. 4, when the generator 10 is activated, ultrasonic waves 12-14
are emitted
through the stock solution 34 flowing in the flow direction 26 through the
headbox 36.
The ultrasonic waves 12-14 move in the direction 22 from the generator 10
across the
flow direction 26 of the stock solution 34 towards the absorber 24.
Consequently, the
consistency or concentration of the fibers within the stock solution 34 is
greater on the
side 30 of the headbox 36 which is nearest to the absorber 24. Such
concentrated stock is
diverted through a downstream recirculation channel 38. However, on the
further side 32
of the headbox 36 nearest to the generator 10, the stock solution 34 is
diluted because
CA 02581228 2007-03-20
WO 2006/082600 PCT/IT2005/000049
-11-
many of the fibers 18-20 have migrated towards the side 30 under the influence
of the
applied ultrasonic waves 12-14. Such diluted stock is guided through a
downstream
supply channel 40.
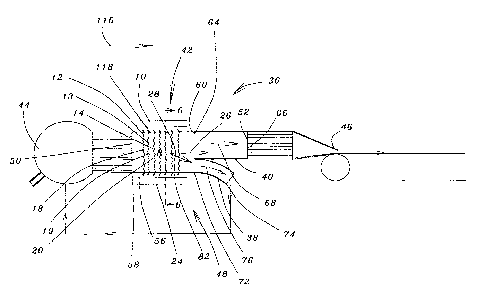
Fig. 5 a side elevational view of an apparatus generally designated 42
according
to the present invention for controlling the consistency of a flow of stock
solution
flowing from a header 44 to a slice lip 46 of a headbox generally designated
36 of a
papermaking machine so that the cross machine direction consistency profile of
a
resultant web is controlled. The apparatus 42 includes a flow channel
generally
designated 48 which is disposed within the headbox 36 between the header 44
and the
slice lip 46. The flow channel 48 has an upstream and a downstream end 50 and
52
respectively such that the flow of the stock solution is in a flow direction
26 from the
upstream end 50 towards the downstream end 52 of the flow channel 48. The flow
channel 48 includes a primary channel 56 having a first and a second extremity
58 and
60 respectively such that the flow of the stock solution is through the
primary channel 56
from the first extremity 58 to the second extremity 60 of the primary channel
56. A
supply channel 40 has a first and a second end 64 and 66 respectively and is
disposed
downstream relative to the primary channel 56 for the flow therethrough of a
supply
portion as indicated by the arrow 68 of the flow of the stock solution. The
second end 66
of the supply channel 40 is connected to the slice lip 46 so that the supply
portion 68 of
the flow of the stock solution flows to the slice lip 46. A recirculation
channel 38 has a
first and a second termination 72 and 74 respectively, the recirculation
channel 38 being
disposed downstream relative to the primary channel 56 for the flow
therethrough of a
recirculation portion as indicated by the arrow 76 of the flow of the stock
solution. The
second termination 74 of the recirculation channel 38 is connected to the
header 44 so
that the recirculation portion 76 of the flow of the stock solution flows to
the header 44.
A generator 10 is disposed adjacent to the primary channel 56 for generating
ultrasonic
waves 12-14 within the flow of the stock solution flowing through the primary
channel
56. The ultrasonic waves. 12-14 move fiber particles 18-20 suspended within
the stock
solution for controlling the consistency of the stock solution flowing through
the primary
channel 56. Also, an ultrasound absorber 24 is disposed adjacent to the
primary channel
56 such that the flow of the stock solution flows in the flow direction 26
within a region
R disposed between the generator 10 and the absorber 24 so that in operation
of the
apparatus 42, when the stock solution is flowing within the region R, the
fiber particles
18-20 suspended within the stock solution are deviated as indicated by the
arrow 28 from
CA 02581228 2007-03-20
WO 2006/082600 PCT/IT2005/000049
-12-
the flow direction 26. The arrangement is such that the consistency of the
stock solution
flowing from the primary channel 56 through the supply channel 40 is different
from the
consistency of the stock solution flowing from the primary channel 56 through
the
recirculation channel 38 so that the consistency of the supply portion 68 of
the stock
solution flowing through the slice lip 46 is controlled thereby controlling
the cross
machine direction consistency profile of the resultant web.
Fig. 6 is a sectional view taken on the line 6-6 of Fig. 5. As shown in Fig.
6, the
flow channel 48 extends across most of the cross machine width of the headbox
36.
Also, the supply channel 40 is shown leading to the slice lip. Furthermore,
the
recirculation channel 38 is shown for returning concentrated stock solution to
the header.
Fig 7 is a similar view to that shown in Fig. 6 but shows another embodiment
of
the present invention. As shown in Fig. 7, an apparatus 42a includes a further
generator
84 disposed adjacent to the primary channel 56 for generating ultrasonic waves
within
the flow of the stock solution flowing through the primary channel 56. The
ultrasonic
waves move fiber particles suspended within the stock solution for controlling
the
consistency of the stock solution flowing through the primary channel 56.
Fig. 8 is a sectional view taken on the line 8-8 of Fig. 7. As shown in Figs.
7 and
8, a further ultrasound absorber 86 is disposed adjacent to the primary
channel 56 such
that the flow of the stock solution flows in the flow direction 26 within a
further region r
disposed between the further generator 84 and the further absorber 86. The
arrangements
is structured such that in operation of the apparatus 42a, when the stock
solution is
flowing within the further region r, the fiber particles suspended within the
stock
solution are deviated from the flow direction 26 so that the consistency of
the stock
solution flowing from the primary channel 56 through the supply channel 62
downstream from the region r is different from the consistency of the stock
solution
flowing from the primary channel 56 downstream from the region r through the
recirculation channel 38. The arrangement is such that the consistency of a
further supply
portion 88 of the stock solution flowing downstream from the region r through
the slice
lip 46 is controlled relative to the supply portion 68 of the stock solution
as shown in
Fig. 5, flowing downstream from the region R through the slice lip 46 thereby
controlling the cross machine direction consistency profile of the resultant
web.
In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the flow direction 26 is
approximately parallel to a direction as indicated by the arrow 116 from the
header 44 to
the slice lip 46.
CA 02581228 2007-03-20
WO 2006/082600 PCT/IT2005/000049
-13-
Also, as shown in Fig. 5, the primary channel 56 defines a primary conduit 118
of rectangular cross sectional configuration. As shown in Fig. 6, the primary
conduit 118
extends from the first extremity 58 to the second extremity 60 of the primary
channel 56.
More particularly, as shown in Fig. 5, the first end of the supply channel 40
extends from the second extremity 60 of the primary channel 56 and the supply
channel
40 is disposed above the recirculation channel 38.
Fig. 9 is a side elevational view of another embodiment of the present
invention.
As shown in Fig. 9, the supply channel 40b is disposed below the recirculation
channel
38b.
Additionally, as shown in Fig. 5, the first termination 72 of the
recirculation
channel 38 extends from the second extremity 60 of the primary channel 56 such
that the
flow of the stock solution flowing through the primary channel 56 is split
into the supply
portion 68 and the recirculation portion 76 adjacent to the second extremity
60 of the
primary channel 56.
Fig. 10 is a similar view to that shown in Fig. 6 but shows a further
embodiment
of the present invention. As shown in Fig. 10, the apparatus further includes
a control
device 120 which is electrically connected to the generator lOc for
controllably altering
the generation of the ultrasonic waves by the generator l Oc.
Fig. 11 is a similar view to that shown in Fig. 10 but shows a further
embodiment
of the present invention. As shown in Fig. 11, a device 122 such as a
hydraulic or a
pneumatic ram is mechanically connected to the generator lOd for controllably
altering a
location of the generator lOd relative to the primary channel 56 as indicated
by the arrow
123 so that generation of the ultrasonic waves within the region R by the
generator l0d
is altered.
Fig. 12 is a similar view to that shown in Fig. 10 but shows a further
embodiment
of the present invention. As shown in Fig. 12, a controller 124 is
electrically connected
to the ultrasound absorber 24e for controllably altering absorption of the
ultrasonic
waves by the absorber 24e.
Fig. 13 is a similar view to that shown in Fig. 11 but shows a further
embodiment
of the present invention. As shown in Fig. 13, a control device 126 such as a
hydraulic or
pneumatic ram is mechanically connected to the absorber 24f for controllably
altering a
disposition of the absorber 24f relative to the primary channel 56 as
indicated by the
arrow 127 so that absorption of the ultrasonic waves by the absorber 24f is
altered.
CA 02581228 2007-03-20
WO 2006/082600 PCT/IT2005/000049
-14-
In each of the alternative embodiments of the present invention, the flow
direction 26 within the region R and r is disposed non parallel to a direction
22 from the
generator 10 to the absorber 24.
However, more specifically, the flow direction 26 within the region R is
disposed
substantially normal to the direction 22 from the generator 10 to the absorber
24.
Moreover, the direction 22 from the generator 10 to the absorber 24 is
substantially normal to the flow direction 26 within the region R such that in
use of the
apparatus, the ultrasonic waves deviate movement of the fiber particles in a
component
direction 28 shown in Fig. 5 which is disposed angularly between the flow
direction 26
and the direction 22 from the generator 10 to the absorber 24.
The present invention also includes a method for controlling the cross machine
consistency profile of a flow of stock solution flowing from a header 44 to a
slice lip 46
of a headbox 36 of a papermaking machine so that the cross machine direction
profile of
a resultant web is controlled. The method includes the steps of guiding the
flow of the
stock solution through a flow channel 48 which is disposed within the headbox
36
between the header 44 and the slice lip 46. The flow channel 48 includes a
primary
channel 56 which has a first and a second extremity 58 and 60. A supply
channel 40 has
a first and a second end 64 and 66, the supply channel 40 being disposed
downstream
relative to the primary channel 56 for the flow therethrough of a supply
portion 68 of the
flow of the stock solution. The second end 66 of the supply channel 40 is
connected to
the slice lip 46 so that the supply portion 68 of the flow of the stock
solution flows to the
slice lip 46. A recirculation channel 38 has a first and a second termination
72 and 74,
the recirculation channel 38 being disposed downstream relative to the primary
channel
56 for the flow therethrough of a recirculation portion 76 of the flow of the
stock
solution. The second termination 74 of the recirculation channel 38 is
connected to the
header 44 so that the recirculation portion 76 of the flow of the stock
solution flows to
the header 44.
The method also includes the steps of generating ultrasonic waves within the
flow of the stock solution flowing through the primary channel 56 by an
ultrasonic
generator 10. The ultrasonic waves move fiber particles suspended within the
stock
solution for controlling the consistency of the stock solution flowing through
the primary
channel 56.
Additionally, the method includes absorbing the ultrasonic waves by an
ultrasound absorber 24 disposed adjacent to the primary channel 56 such that
the flow of
CA 02581228 2007-03-20
WO 2006/082600 PCT/IT2005/000049
-15-
the stock solution flows in the flow direction 26 within a region R which is
disposed
between the generator 10 and the absorber 24. The arrangement is such that
when the
stock solution is flowing within the region R, the fiber particles suspended
within the
stock solution are deviated from the flow direction 26 so that the consistency
of the stock
solution flowing from the primary channel 56 through the supply channel 40 is
different
from the consistency of the stock solution flowing from the primary channel 56
through
the recirculation channel 38..The method is such that that the consistency of
the supply
portion 68 of the stock solution flowing through the slice lip 46 is
controlled thereby
controlling the cross machine direction consistency profile of the resultant
web.
In operation of the apparatus according to the present invention, a stock
solution
is supplied to the header under pressure. The stock flows through the flow
channel 48 so
that when the generator and absorber 10 and 24 respectively are activated,
diluted stock
flows from the region R through the downstream supply channel 40 to the slice
lip 46.
However, in a lateral disposition in a cross machine direction as shown in
Fig. 8, the
further generator and further absorber 84 and 86 respectively act upon the
region r which
is disposed laterally relative to the region R as shown in Fig. 7.
Consequently, the
dilution of the stock flowing downstream from the region r through the supply
channel
40 can be controlled or altered relative to the dilution of the laterally
disposed flow of
stock flowing downstream from the region R. In this manner, by the provision a
number
of generators and corresponding absorbers, the cross machine directional
consistency
profile of the resultant web can be controlled. Such control can be achieved
as shown in
Figs. 10-13 by either controlling the electrical supply to the generator or to
the absorber
or by mechanically moving the disposition of the generator or the absorber or
both the
generator and the absorber relative to the primary channel 56.
According to the present invention, the generation capacity of the generator
can
be changed by increasing or decreasing the electrical input or by moving the
generator
towards or away from the primary channel.
Similarly, the absorption factor of the absorber can be changed by increasing
or
decreasing the electrical input to the absorber or by moving the absorber
towards or
away from the primary channel. Any combination of the above can be used for
controlling the ultrasonic waves within the primary channel.
By altering the power to all of the generators such as 10 and 84 and/or the
corresponding absorbers 24 and 86 to the same power level would have a similar
effect
to altering the grammage valve on a conventional headbox. Typically, in a
conventional
CA 02581228 2007-03-20
WO 2006/082600 PCT/IT2005/000049
-16-
headbox, when the grammage valve is altered, there would be a delay of two
minutes
before such change would take effect downstream on the grammage of the
resultant web.
One of the advantages of the arrangement according to the present invention
when using an electrical control for the generator and/or absorber is that the
consistency
control is accomplished by entirely an electrical device rather than a
mechanical device
in the case of slice lip control.
Although the present invention describes the recirculation portion of the
stock as
returning to the header, it will be apparent to those skilled in the art that
in fact, the
recirculation portion will usually be returned to the header via the stock
supply silo.
The present invention provides a unique apparatus and method for controlling
the
cross machine direction profile of a web.