Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02592717 2007-06-26
- 1
System and Method for Polymer Distribution to Well Sites
FIELD OF INVENTION
[0001] The present invention relates to oil and gas recovery. More
specifically, the
present invention relates to polymer use in oil and gas recovery.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
[0002] Polymer compounds are used in the oil industry to prevent fingering in
subterranean oil formations. In most cases, polymer solutions are prepared at
each
well site and the resulting formulation is injected into a well. As most oil
fields
comprise several injector-producer wells, there is often a need to inject
polymer into
several wells within the field. Typically, at each injection well, dry polymer
powder is
mixed with an appropriate quantity of water and the resulting solution is
injected into
the well. This approach requires dry polymer to be transported to the various
well
sites. Further, mixing systems, polymer holding tanks and the like must be
stationed at
each well site where polymer is injected. This requires transportation systems
such as
roads and other types of costly infrastructure to be implemented to ensure
that the
proper components and products are present at the appropriate locations and at
the
appropriate times. Further, this type of approach must be monitored closely to
ensure
a continuous supply of dry polymer for injection and also to ensure the
mechanical
components required for injection at each point are working properly.
[0003] There is a need in the art for novel polymer transportation and
distribution
systems in oil and gas fields. Further, there is a need for systems and
methods of
preparing polymer at a central location and transporting the same, potentially
over
large distances to several well sites where the polymer may be diluted if
necessary to a
desired viscosity and pumped down-well.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0004] The present invention relates to oil and gas recovery. More
specifically, the
present invention relates to polymer use in oil and gas recovery.
OTT LAW\ 1510729\5
CA 02592717 2007-06-26
- 2 -
[0005] According to the present invention, there is provided a polymer
transport and
distribution system comprising,
a vessel, pipeline or network of pipes containing polymer mother solution,
and;
one or more pumps for transporting polymer mother solution from a first
location to one or more injection well sites at a second remote location, each
injection well comprising a polymer mother solution input feed line, a water
input feed line, a second pump for controlling mother solution flow rate and
pressure, the second pump upstream of the water input feed line, for
producing polymer daughter solution from polymer mother solution and water,
and injecting the resulting polymer daughter solution into an oil or gas field
well.
[0006] Also according to the present invention, there is provided a polymer
transport
and distribution system comprising,
a vessel, pipeline or network of pipes containing polymer mother solution,
and;
one or more pumps for transporting polymer mother solution from a first
location to one or more injection well sites at a second remote location, each
injection
well comprising a polymer mother solution input feed line, a high pressure
dilution
water input feed line, and a second pump for controlling mother solution flow
rate and
pressure, upstream of the high pressure dilution water input feed line for
producing
polymer daughter solution from polymer mother solution and water, and
injecting the
resulting polymer daughter solution into an oil or gas field well.
[0007] Also provided is a polymer transport and distribution system as defined
above,
further comprising at least one mixer for mixing polymer mother solution with
water.
[0008] The present invention also contemplates a polymer transport and
distribution
system as defined above, wherein the polymer comprises polyacrylamide,
hydrolysed
polyacrylamide, xanthan gum, guar gum, diutan gum, welan gum or a combination
thereof.
OTTI.LAW\ 1510729\5
CA 02592717 2007-06-26
- 3 -
[0009] Also provided is a polymer transport and distribution system as defined
above, wherein the polymer comprises a viscosity in the range of about 1 to
about
25000 cP.
[0010] The present invention further contemplates a polymer transport and
distribution system as defined above, wherein either the polymer mother
solution, the
polymer daughter solution or both comprise less than about 50000 ppm total
dissolved
solids. In an embodiment, which is not meant to be limiting, the polymer
mother
solution, polymer daughter solution or both comprise less than about 25000
ppm,
more preferably less than about 18000 ppm total dissolved solids. In a further
embodiment, which is not meant to be limiting, the polymer mother solution,
polymer
daughter solution or both comprise less than 5000 ppm total dissolved solids.
[0011] Also provided by the present invention is a polymer transport and
distribution
system as defined above, wherein the polymer mother solution, polymer daughter
solution or both comprise a surfactant, biocide, alkaline component,
antifoaming
agent, or a combination thereof.
[0012] The present invention also contemplates a polymer transport and
distribution
system as defmed above, wherein the polymer daughter solution comprises
polymer
mother solution diluted with water.
[0013] Also provided by the present invention is a polymer transport and
distribution
system as defined above, wherein the water is derived from a saline well, a
freshwater
well, a water filtration skid or a combination thereof.
[0014] The present invention also contemplates a polymer transport and
distribution
system further comprising one or more of:
a) a dry polymer holding vessel;
b) a dry polymer transfer system;
c) a water inlet source for hydrating dry polymer;
d) an input source for adding one or more additional components to the dry
polymer, water or polymer mother solution,
OTT _LAW 1510729\5
CA 02592717 2007-06-26
- 4
e) a mixer for preparing polymer mother solution, and;
g) a polymer mother solution holding vessel.
[0015] Also provided by the present invention is a polymer transport and
distribution
system as defined above that comprises a dry polymer polymer transfer system,
wherein the system comprises a calibrated auger or a helix conveyor. Also, the
system
may further comprise a mixer.
[0016] The present invention also contemplates a polymer transport and
distribution
system comprising,
a dry polymer transfer system, a water inlet source, and a first mixer for
preparing a polymer mother solution from said dry polymer and water,
one or more pumps for transporting polymer mother solution through a
pipeline or network of pipes to one or more remote injection pod sites, each
injection
pod site comprising,
one or more injection wells, each injection well comprising a polymer mother
solution input feed line, one or more pumps for controlling mother solution
flow rate
and pressure upstream of a water input feed line, preferably a high pressure
dilution
water input feed line, to produce polymer daughter solution for injection into
a well.
[0017] The present invention also provides a method of distributing polymer to
one
or more injection well sites in an oil or gas field comprising,
a) providing a polymer mother solution;
b) pumping the polymer mother solution through a pipeline or network of
pipes from a first location to one or more remote locations comprising at
least
one injection pod or well site;
c) mixing the polymer mother solution with water and optionally one or more
additional components to form a polymer daughter solution and;
d) injecting the polymer daughter solution into a well.
OTT_LAW\ 1510729\5
CA 02592717 2007-06-26
- 5 -
[0018] The present invention also provides a method of distributing polymer to
one
or more injection well sites in an oil or gas field comprising,
a) storing or producing a polymer mother solution in a polymer processing
station;
b) pumping the polymer mother solution through a pipeline or network of
pipes from the polymer processing station to one or more remote injection
pods or injection well sites;
c) mixing the polymer mother solution with water and optionally one or more
additional components at the injection pod or injection well contained therein
to form a primary polymer daughter solution and;
d) injecting the primary polymer daughter solution into the injection well;
e) extracting oil or gas from a producer well in fluid communication with the
injection well, and;
0 optionally, mixing polymer mother solution with water and if desired, one or
more additional components at the injection pod or injection well site
contained therein to form a secondary polymer daughter solution, wherein the
secondary polymer daughter solution is more dilute in polymer concentration
and less viscous than the primary daughter solution,
g) injecting the secondary daughter polymer solution into the injection well;
h) extracting oil from the producer well in fluid communication with the
injection well, and;
i) optionally repeating steps D-h) using successively more dilute and less
viscous daughter solutions.
[0019] This summary of the invention does not necessarily describe all
features of the
invention.
OTT_LAW\ 1510729\5
CA 02592717 2007-06-26
- 6 -
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0020] These and other features of the invention will become more apparent
from the
following description in which reference is made to the appended drawings
wherein:
FIGURE 1 shows a representative embodiment of a polymer transport and
distribution system according to the present invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
[0021] The following description is of a preferred embodiment.
[0022] The present invention will be further illustrated in the following
examples.
[0023] According to an embodiment of the present invention, there is provided
a
polymer transport and distribution system comprising,
a vessel, pipeline or network of pipes containing polymer mother solution;
one or more pumps for transporting polymer mother solution from a first
location to one or more injection well sites at a second remote location, each
injection well comprising a polymer mother solution input feed line, a water
input feed line, and a second pump for controlling mother solution flow rate
and pressure, preferably at or upstream of the water input feed line, for
producing polymer daughter solution from polymer mother solution and water,
and injecting the resulting polymer daughter solution into an oil or gas field
well.
In a preferred embodiment, the water input feed line is a high pressure
dilution input
feed line.
[0024] In a preferred embodiment, which is not meant to be limiting in any
manner,
there is provided a polymer transport and distribution system comprising,
OTT_LAW\ 1510729\5
CA 02592717 2007-06-26
- 7
a vessel containing a polymer mother solution;
one or more pumps for transporting polymer mother solution from the vessel
through a pipeline or network of pipes to one or more injection pod sites,
each
injection pod site comprising,
a second pump for controlling mother solution flow rate and pressure upstream
of a high pressure dilution water input feed line used to produce polymer
daughter
solution from polymer mother solution and water, the water optionally derived
from a
vessel, pipeline or network of pipes carrying water, and injecting the
resulting
polymer daughter solution into an oil or gas field well.
[0025] It is to be understood that the polymer transport and distribution
system may
further comprise a mixer that mixes the polymer mother solution with water to
produce polymer daughter solution. Inclusion of a mixer is optional as the
combination of polymer mother solution with water to make polymer daughter
solution and the subsequent injecting of the polymer daughter solution into an
oil and
gas field well is usually sufficient to ensure thorough mixing. However, there
are
instances whereby it may be desirable to include a mixer, for example, but not
limited
to, when the viscosity of the polymer mother solution is high compared to that
of
water or in instances when the polymer mother solution is diluted by either a
very
small or very large amount. A person of skill in the art would be able to
determine if a
mixer should be included in the polymer transport and distribution system
having
regard to the information provided herein.
[0026] By the term "polymer mother solution" it is meant an aqueous solution
comprising a polymer, water and optionally one or more additional components.
The
polymer may comprise any polymer known in the art, for example, but not
limited to
polyacrylamide including, but not limited to hydrolyzed polyacrylamide,
xanthan
gum, guar gum, diutan gum, welan gum or a combination thereof. In an
embodiment
of the present invention, which is not meant to be limiting in any manner, the
polymer
mother solution comprises a polyacrylamide polymer. In an alternate
embodiment, the
polymer mother solution comprises xanthan gum. In still a further embodiment,
which
is not meant to be limiting, the polymer mother solution comprises guar gum.
OTT_LAWN 1510729\5
CA 02592717 2015-08-13
- 8 -
However, it is to be understood that other types of polymers, biopolymers,
viscosifying agents or any combination thereof may be employed in the present
invention. Accordingly, the list of polymers provided above is not meant to be
limiting in any manner.
[0027] The polymer mother solution preferably has a viscosity in the range of
about 1
to about 25000 cP, more preferably about 5 to 15000 cP and still more
preferably
about 10 to about 10000 cP. For example, the polymer mother solution may
comprise
a viscosity of about 1,5, 10, 50, 100, 500, 1000, 2000, 5000, 10000, 15000,
20000,
25000 cP or any amount therein between. Further, the viscosity of the polymer
mother
solution may be defined by a range of any two of the values provided above or
any
amounts therein between. However, a polymer mother solution comprising
characteristics outside one or more of these ranges is also contemplated.
[0028] The viscosity of polymer mother solution may be measured according to
known methods in the art, and any such method may be employed to determine the
viscosity of the polymer solutions as defined herein. For example, but not to
be
considered limiting in any manner, viscosity may be measured in accordance
with the
American Petroleum Institute (API) Recommended Practice 63 (RP63), First
Edition,
June 1, 1990.
[0029] In embodiments wherein the polymer mother solution comprises
polyacrylamide polymer, it is preferred that the solution does not comprise
water with
high levels of total dissolved solids, particularly cationic or divalent
species as these
components can inhibit hydrolysis of polymer and/or breakdown the viscosity of
such
polymer solutions. In embodiments wherein polyacrylamide polymer is employed
in
the polymer transport and distribution system, preferably the total dissolved
solids is
less than about 5000 ppm, more preferably less than 2000 ppm.
[0030] By the term "total dissolved solids" it is meant the sum of anions and
cations
from water analysis. Cations may be determined by Inductively Coupled Plasma
(ICP)
using American Public Health Association (APHA) 3120 method. Chloride may be
determined by titration (APHA 4500-Cl:B), sulfate by APHA 3120 and alkalinity
by
CA 02592717 2007-06-26
- 9 -
titration according to APHA 2320:B. Alternatively, other methods to measure
total
dissolved solids as would be known to a person of skill in the art may be
employed.
[0031] As xanthan gum polymers exhibit increased resistance to viscosity
breakdown
in the presence of salts, the use of such polymers is preferred in instances
wherein the
polymer is mixed with water that comprises a high content of total dissolved
solids,
salts, iron, iron-containing species, or a combination thereof. In a preferred
embodiment, which is not meant to be limiting in any manner, xanthan gum
polymers
are employed in polymer compositions wherein the content of total dissolved
solids
(excluding polymer) is greater than about 2000 ppm.
[0032] As described previously, it is also contemplated that the polymer
mother
solution may comprise one or more additional components, for example, but not
limited to a surfactant, biocide, alkaline component such as, but not limited
to caustic
soda, antifoaming agent, or a combination thereof. In the event that a
surfactant or
other component is employed in the polymer mother solution, it preferably
comprises
an amount between about 20 parts per million (ppm) and about 5000 ppm,
preferably
about 500 ppm and about 5000 ppm, for example, but not limited to 20, 50, 100,
200,
500, 1000, 2000, 2500, 3000, 4000, 5000 or any amount therein between.
Further, the
surfactant may be defined by a range of any two of the values listed above or
any
amount therein between. Without wishing to be bound by theory or limiting in
any
manner, a surfactant may lower the interfacial tension of oil deposits and
facilitate
extraction from subterranean formations.
[0033] By the term "polymer daughter solution" it is meant an aqueous solution
comprising the polymer mother solution, water and optionally one or more
additional
components. Typically, the polymer daughter solution comprises a polymer
concentration that is about the same or less than the polymer mother solution.
As
such, the polymer daughter solution usually comprises a lower viscosity than
the
polymer mother solution.
[0034] It is also to be understood that the polymer daughter solution may
comprise
one or more additional components not found in the polymer mother solution.
Similarly, the polymer daughter solution may comprise one or more additional
OTT LAW1 1510729\5
CA 02592717 2007-06-26
- 10 -
components in a different concentration as compared to the polymer mother
solution.
By way of example, but not to be considered limiting in any manner, the
polymer
mother solution may be prepared using a potable water source having low
salinity.
Prior to being injected into a well, the polymer mother solution may be
diluted with
water from a saline well having high salinity. Accordingly, it is apparent
that the
polymer daughter solution may comprise higher levels of dissolved salts, and
potentially other components as compared to the polymer mother solution. In
still a
further embodiment, which is not meant to be considered limiting in any
manner, the
polymer daughter solution may comprise an added surfactant not present in the
polymer mother solution. Other potential differences between the polymer
mother
solution and the polymer daughter solution will be evident to a person of
skill in the
art having regard to the disclosure as provided herein.
[0035] In an embodiment which is not meant to be limiting in any manner, the
polymer daughter solution is polymer mother solution diluted with water. In a
specific
embodiment, but not wishing to be considered limiting in any manner, the
polymer
daughter solution comprises polyacrylamide solution of between about 500 ppm
and
about 2000 ppm, more preferably about 1000 to about 1500 ppm. However, a
polymer
daughter solution outside this range is also contemplated.
[0036] In the embodiments described herein, it is preferred that polymer
mother
solution is sufficiently hydrolysed prior to being diluted to form polymer
daughter
solution and before injection into a well. For example, but not wishing to be
limiting,
the polymer mother solution may remain in a vessel, holding tank, pipeline or
network
of pipes for at least a specified duration in order for the polymer to
hydrolyse to a
desired viscosity. Further, it is contemplated that the extent of hydrolysis
and/or the
viscosity of the solution may be measured and/or monitored at one or more
points
within the polymer transport system including for example, but not limited to
the
vessel, holding tank, pipeline, network of pipes, or injection pod polymer
mother
solution feed line by any method known in the art. Without wishing to be
limiting or
bound by theory in any manner, it is possible that some polymers may require
time to
fully hydrate, unravel and expand to create a viscous solution.
OTT_LAW1 1510729\5
CA 02592717 2007-06-26
- 11
[0037] The polymer mother solution may be provided as a premade solution or
alternatively, the polymer mother solution may be prepared on site, for
example, but
not limited to, by mixing together dry polymer, water and optionally one or
more
additional components. Accordingly, the polymer transport and distribution
system
may comprise a dry polymer holding vessel or container, a dry polymer transfer
system, a water inlet source, an input source for optionally adding one or
more
additional components to the dry polymer, water or polymer mother solution, a
mixer
for preparing the polymer mother solution, a polymer mother solution transport
system, for example, but not limited to one or more pumps, a vessel or
container for
holding polymer mother solution, one or more pipelines or network of pipes or
any
combination thereof. Several or all of these components may be contained in a
polymer processing station (polymer pod) which may be or may not be located
remotely from the injection pod sites and wells.
[0038] The water inlet source providing water for mixing with polymer may be
provided from a well, for example, but not limited to a freshwater or saline
well, water
pipeline, water filtration skid or the like. It is also contemplated that the
water inlet
source may be connected to a water pipeline or network of water pipes that
extends
over the oil/gas field being tapped. In an embodiment, the water is
substantially pure
meaning that it comprises a low amount, for example between 1500 to about 2500
ppm, or lower of total dissolved solids as described herein, particularly
salts as high
levels of salts and are known to inhibit hydrolysis and/or promote breakdown
of
hydrolysed polymers such as polyacrylamides. However, water from a saline well
also may be employed, and may be preferred in instances wherein the polymer is
resistant to viscosity breakdown in the presence of dissolved salts.
[0039] Dry polymer may be fed into a mixer by a dry polymer transfer system
which
may comprise without limitation, a calibrated auger or the like. In a
preferred
embodiment, the dry polymer transfer system comprises a Hapman helix conveyor.
Alternatively, the dry polymer may be transferred by an air transfer system or
both an
air transfer system and a conveyor. Any such system as would be known in the
art
may be employed in the polymer transport and distribution system. Further, one
or
more optional components may be added likewise or they may be added using
other
methods and/or apparatuses known in the art.
OTT LAW\ 1510729\5
CA 02592717 2007-06-26
- 12 -
[0040] The mixing of dry polymer, water and optionally any additional
components
may be performed in any vessel, holding tank or pipeline by a suitable mixer
or
mixing device. In a preferred embodiment, the mixer or mixing device is a
Model
1700 Comitrol Processor made by Urschel Labs. Such a device has been shown to
decrease the time necessary to prepare viscous polymer mother solution. While
such
devices are preferred, other mixing devices can be employed in the present
invention.
As will be evident to a person of skill in the art, it is preferred that
polymer powder is
thoroughly mixed with water and attains the desired viscosity prior to being
diluted to
form polymer daughter solution or injected into a well. In this manner,
polymer
mother solution may be prepared and retained in a vessel or holding tank until
the
polymer mother solution exhibits a desired viscosity. Alternatively, polymer
mother
solution may be prepared and transported in a pipeline or network of pipes to
a second
remote location. In such an embodiment, it is preferred that the polymer
mother
solution attain the desired viscosity while being pumped through the pipeline
or
network of pipes before being diluted to form polymer daughter solution or
injected
into a well.
[0041] The embodiment described above contemplates that that the vessel
containing
the polymer mother solution or the polymer processing station that prepares
the
polymer mother solution can be located remotely from the injection pod or well
sites,
for example, but not limited to about 1, 2, 5, 6, 10 or more km therefrom.
Thus,
polymer mother solution may be prepared and/or stored in a separate area,
building, or
facility from that of the injection pods wherein the daughter polymer solution
is
injected into a well. Polymer mother solution can be pumped from this remote
site
through a pipeline or network of pipes to the injection pod sites wherein the
polymer
mother solution is diluted with water and optionally formulated with other
components to obtain a daughter polymer solution having a desired viscosity
and/or
one or more desired chemical characteristics for injection into a well.
Further, but
without wishing to be limiting in any manner, the water used for mixing with
polymer
mother solution may be provided via a vessel, pipeline or network of pipes
that
parallels or intersects that providing the polymer mother solution at one or
more
points. In an embodiment of the present invention, the polymer transport and
distribution system comprises a plurality of injection pod sites, for example,
two,
OTT_LAW1 1510729\5
CA 02592717 2007-06-26
- 13 -
three, four, five or more injection pod sites. In a preferred embodiment, the
polymer
transport and distribution system comprises five or less sites. Similarly, in
an
embodiment of the present invention, the polymer transport and distribution
system
comprises a plurality of injection wells within each injection pod site, for
example
two, three, four or more injection wells. In a preferred embodiment the
polymer
distribution and transport system comprises four injection wells within each
injection
pod site.
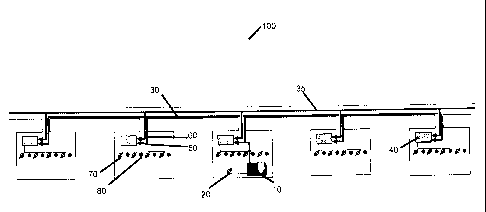
[0042] Referring now to Figure 1, there is shown a representative non-limiting
embodiment of the present invention. Polymer processing station (polymer pod
(10))
receives water from a freshwater source (20) to produce polymer mother
solution
which is pumped through polymer mother solution pipeline network (30) to a
plurality
of injection pods or injection well sites (40). Each injection well site (40)
comprises a
polymer mother solution feed line (50), a water input feed line (60) providing
high
pressure dilution water from water pipeline network (35) and at least a second
pump
for controlling mother solution flow rate and pressure upstream of the water
input feed
line used for producing and injecting polymer daughter solution into an oil or
gas field
well (70). Also shown are producer wells (80) for extracting oil and gas from
subterranean formations in an oil or gas field (100).
[0043] In an alternate embodiment of the present invention which is not meant
to be
limiting in any manner, the polymer transport and distribution system
comprises,
a dry polymer transfer system, a water inlet source, and a first mixer for
preparing a polymer mother solution from dry polymer and water, the resulting
polymer mother solution contained in a vessel;
one or more pumps for transporting polymer mother solution through a
pipeline or network of pipes to one or more remote injection pod sites, each
injection
pod site comprising,
one or more injection wells, each injection well comprising a polymer mother
solution input feed line, a high pressure water input feed line, a second
mixer to
produce polymer daughter solution and a pump for controlling mother solution
flow
OTT_LAW\ 1510729\5
CA 02592717 2007-06-26
- 14 -
=
rate and pressure upstream of a high pressure dilution water input feed line,
for
injecting the resulting polymer daughter solution into a well.
[0044] The present invention also provides a method of distributing polymer to
one or
more injection well sites in an oil or gas field comprising,
a) providing a polymer mother solution;
b) pumping the polymer mother solution through a pipeline or network of
pipes from a first location to one or more remote locations comprising at
least
one injection pod or well site;
c) mixing the polymer mother solution with water and optionally one or more
additional components to form a polymer daughter solution and;
d) injecting the polymer daughter solution into a well.
[0045] In a further embodiment of the present invention there is provided a
method of
distributing polymer to one or more injection well sites in an oil or gas
field
comprising,
a) storing or producing a polymer mother solution in a polymer processing
station;
b) pumping the polymer mother solution through a pipeline or network of
pipes from the polymer processing station to one or more remote injection pod
or well sites;
c) mixing the polymer mother solution with water and optionally one or more
additional components to form a polymer daughter solution and;
d) injecting the polymer daughter solution into a well.
[0046] In an alternate embodiment of the present invention, there is provided
a
method of distributing polymer to one or more injection well sites in an oil
or gas field
comprising,
OTT_LAW\ 1510729\5
CA 02592717 2007-06-26
- 15 -
a) storing or producing a polymer mother solution in a polymer processing
station;
b) pumping the polymer mother solution through a pipeline or network of
pipes from the polymer processing station to one or more remote injection
pods or injection well sites;
c) mixing the polymer mother solution with water and optionally one or more
additional components at the injection pod or injection well contained therein
to form a primary polymer daughter solution and;
d) injecting the primary polymer daughter solution into the injection well;
e) extracting oil from a producer well in fluid communication with the
injection well, and;
0 optionally, mixing polymer mother solution with water and if desired, one or
more additional components at the injection pod or injection well site
contained therein to form a secondary polymer daughter solution, wherein the
secondary polymer daughter solution is more dilute in polymer concentration
and less viscous than the primary daughter solution,
g) injecting the secondary daughter polymer solution into the injection well;
h) extracting oil from the producer well in fluid communication with the
injection well, and;
i) optionally repeating steps 0-h) using successively more dilute and less
viscous daughter solutions.
Examples
[0047] In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, polymer is brought
onto a
skid in 750 kg bags via an overhead crane. The bags of dry polymer are hoisted
over
top and unloaded into a hopper. From the hopper, the polymer is transferred,
for
example via a Hapman helix conveyor/auger to a storage silo. From storage
silo,
polymer powder is augured into a mixer, for example, but not limited to an
Urschel
OTT_LAWN 1510729\5
CA 02592717 2013-10-21
- 16 -
mixer or the like. Water is filtered through a standard bag filter and then
fed into the
mixer at the same time in controlled proportions to created the required
polymer
mother solution. Typically, but not always, the polymer mother solution
comprises
from about 5000 to 15000 ppm depending on particular well injection
requirements.
The polymer mother solution falls out of the bottom of the urschel mixer and
is then
transferred to a tank via a lobe pump where it undergoes hydrolysis prior to
being
diluted to form polymer daughter solution.
[0048] Once the polymer mother solution has sufficiently hydrolysed, it is
pumped
through a pipeline or pipeline network to the injection pod or injection well
sites.
This is accomplished by a progressive cavity pump which draws the polymer off
the
bottom of the tank and pressurizes it up to the pressure required to transport
the
polymer to distant/remote injection pod or well sites. In this example, but
not to be
considered limiting in any manner, the pipeline feeds up to 5 injection pods
which are
up to about 1.6 km away from the polymer processing station. Each injection
pod
comprises a separate pump for each well wherein polymer is injected. The pod
sites
are laid out with 4 injection wells per pod. There is one injection skid per
pod which
has four pumps in it to feed the wells. Polymer mother solution is metered as
it goes
out the building, and then it is blended with water to create polymer daughter
solution
having the required polymer concentration before being injected down the
wells.
Typical polymer concentrations of polymer daughter solution injected down each
well
are about 1000 to about 1500 ppm thus requiring roughly a 9:1 blend of water
to
polymer mother solution.
[0049] The present invention has been described with regard to one or more
embodiments. However, it will be apparent to persons skilled in the art that a
number
of variations and modifications can be made.