Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02598110 2007-08-14
- 1. -
"Shaped brick"
The invention relates to a shaped block according to
the preamble of claim 1.
CH 687 394 discloses a shaped block which comprises a
body and wings arranged at two opposite sides thereon.
A disadvantage with this shaped block is that, when
used to construct straight walls, the shaped block only
allows the construction of walls which have openings
toward one side and whose structure is weak in the
region of these openings. A further disadvantage is
that the known shaped block does not permit any length
compensation when used to construct walls or retaining
walls, thereby requiring that shaped blocks have to be
laboriously shortened in order to obtain dimensions
which do not correspond to an integral multiple of the
shaped block unit spacing.
The object on which the invention is based is to
develop a shaped block by means of which stable
straight walls can be constructed and which allows
length or radius compensations during the construction
of walls and retaining walls.
Proceeding from the features of the preamble of claim
1, this object is achieved according to the invention
by the characterizing features of claim 1. Advantageous
and expedient developments are given in the subclaims.
The shaped block according to the invention is equipped
with a left wing and a right wing which are both
arranged in front of, or which are both arranged
behind, a vertical plane, wherein the plane divides the
shaped block at the half shaped block depth into two
halves, and wherein the wings are arranged offset with
respect to one another by at least one wing depth. The
offset arrangement of the wings makes it possible for
CA 02598110 2007-08-14
- 2 -
adjacent shaped blocks to be arranged next to one
another with their wings partially or completely
overlapping. Firstly, this increases the stability of
the wall since the whole wall or at least some of it
has a thickness in the transition region of two
adjacent shaped blocks that corresponds to a double
wing depth. In addition, the offset wings enable
adjacent shaped blocks to be. arranged at different
spacings from one another and the wall length to be
varied as a result. By lining up the shaped blocks such
that they are alternately rotated through 180 about a
vertical axis, it is possible to construct walls in
which the wings of adjacent shaped blocks respectively
lie in front of and behind the vertical dividing plane
and thus stabilize the wall particularly well. The
essence of the invention is a body comprising laterally
arranged wings whose offset arrangement in front of or
behind a mid-plane oriented parallel to the visible
face of the shaped block allows adjacent shaped blocks
a large number of positioning options. These
positioning options include not only the option of
allowing the shaped blocks in a wall layer to follow
one another at various spacings while not having to
accept any losses in terms of the wall quality, but
also the option of joining together the shaped blocks
in various orientations - yawing (rotation about a
vertical axis) through 180 - and of making it possible
thereby to produce walls of different structure and
different appearance.
The invention provides a form-fitting and/or frictional
interaction between the wings of adjacent shaped blocks
so as to impart a high degree of intrinsic stability to
the wall to be formed by virtue of the shaped blocks
actively supporting one another.
Furthermore, the invention provides forming the left
wing and the right wing with identical dimensions.
CA 02598110 2007-08-14
- 3 -
Given the offset provided, this allows optimum
interaction between the wings.
The invention particularly provides forming the left
wing point-symmetrically with respect to the right
wing. This simplifies the construction and leads to the
two wings having comparable loadability.
According to the invention, the shaped block is made of
concrete so that it can be produced cost-effectively in
large quantities.
Furthermore, the invention provides forming a cavity
between the bodies of adjacent shaped blocks and their
wings, for which purpose the two wings are at a
distance from one another or are offset with respect to
one another by more than one wing depth, or have at
least one recess. This cavity results in further
stabilization of the wall and also allows concrete,
mortar or soil to be introduced therein.
The invention provides forming the wing with at least
one projection andJor at least one recess. This makes
possible a form-fitting interaction, such as an
interlocking, for example, between the shaped blocks.
A particular embodiment provides forming the projection
or the recess on a free end of the wing. This allows
force to be introduced deep into the adjacent shaped
block, thereby permitting the transmission of
considerable forces between the adjacent shaped blocks.
Furthermore, the invention provides forming at least
one projection or one recess on the body. This
configuration also allows a form fit between a wing and
a body of an adjacent shaped block and increases the
stability of the wall.
The invention particularly provides an interaction
between the projection or the recess of the wing and
CA 02598110 2007-08-14
- 4 -
the recess or the projection of an adjacent body in
order to increase the stability of the wall.
Likewise, the invention provides an interaction between
the projection or the recess of the wing and the wing
of an adjacent shaped block in order to increase the
stability of the wall.
Provision is made according to the invention for the
body of the shaped block to be formed, in plan view, as
a rectangle or square or triangle or circle or ellipse
or trapezoid. This makes it possible to erect walls of
widely varying appearance that have all the advantages
of the invention.
Furthermore, the invention provides that the shaped
block be provided in the region of its body with at
least one vertical opening extending from an upper side
to a lower side of the shaped block. This makes it
possible for the weight of large shaped blocks to be
kept within limits.
The invention also provides an opening which tapers
toward the lower side of the shaped block. From a
manufacturing point of view, such an opening can be
produced simply using a block-molding machine since
there is a large draft angle.
Furthermore, the invention provides arranging lugs on
an inner face of the opening. As a result, the shaped
block has supports which allow the fastening and
installation of fittings.
The invention provides inserting at least one slab into
the opening so that the opening can be at least
partially closed. This makes it possible, for example
in the case of retaining walls, to direct the roots of
plants into the embankment.
CA 02598110 2007-08-14
- 5 -
The invention provides closing the opening in the
shaped block at an upper side and/or at the lower side
of the shaped block. Closing it at an upper side
permits a simple termination of the uppermost block
layer of a wall. By closing a wall block at the top and
bottom, it is easily possible to provide a region in an
embankment that is selectively free from vegetation.
The invention also provides support ribs which are
formed on the body of the shaped block toward laterally
adjacent shaped blocks. This provides an increased
bearing surface for a shaped block of a wall layer
situated immediately above, this bearing surface
increasing the stability of the wall.
According to the invention, a predetermined breaking
point is provided between the wing and the body so that
corners or wall terminations in which the wing is not
necessary can be formed with little effort.
Finally, the invention provides dimensioning the wing
with a width which lies between 1/3 and 3/4 of the body
width. Such a wing-body ratio also allows considerable
length compensation without having to surrender a
sufficient overlapping of the wings.
For the purposes of the invention, the term "wing" is
to be understood as a continuation whose width (FB) is
greater than its depth (FT) . For the purposes of the
invention, a distinction should be draw between this
and a protrusion in which the width (FB) is less than
the depth (FT). FB > FT applies in principle for the
wings of the shaped blocks according to the invention.
Further details of the invention will be described in
the drawing by way of schematically illustrated
exemplary embodiments.
In the drawing:
CA 02598110 2007-08-14
- 6 -
figures 1-3 show three variant embodiments of a
first shaped block according to the
invention in a perspective
representation,
figure 4 shows a perspective representation of
three shaped blocks arranged next to
one another in a wall layer, these
shaped blocks corresponding to the
shaped block represented in figure 1,
figures 5-6 show plan views of a second and a
third shaped block according to the
invention,
figures 7a-7c show plan views of three different
wall layers which are formed by the
second shaped block known from figure
5,
figures 8a-8c show plan views of three different
wall layers which are formed by the
third shaped block known from figure
6,
figures 9a-9c show plan views of a fourth shaped
block according to the invention and
two wall layers formed therefrom,
figure 10 shows a plan view of a two-layer
retaining wall,
figure 11 shows a plan view of a fifth shaped
block according to the invention with
projections and recesses,
figure 12 shows a plan view of a sixth shaped
block according to the invention, and
CA 02598110 2007-08-14
- 7 -
figure 13 shows a plan view of a further wall
variant.
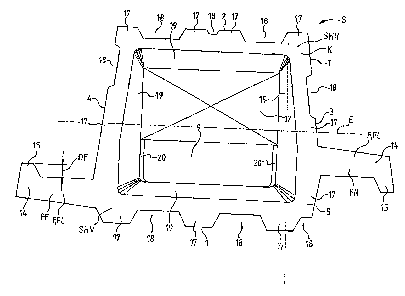
Figures 1 to 3 show three variant embodiments of a
first shaped block S according to the invention in a
perspective representation. The shaped block S
essentially comprises a body K and two wings F, which
are also referred to below as left wing FL and right
wing FR. In plan view the body K has the contour of a
rectangle R. The shaped block S or the body K is
divided by a vertical plane E into a front half SHV and
a rear half SHH. Here, the plane E is arranged
centrally between a first visible side 1 and a second
visible side 2 of the shaped block S. Based on a shaped
block depth ST, the plane E thus has a spacing from
both the front visible side 1 and from the rear visible
side 2 that corresponds to a half shaped block depth
HST = 0.5 x ST. The wings F are arranged on a right
side face 3 and a left side face 4 of the shaped block
S, extend approximately parallel to the plane E and,
since with each having a wing depth FT, a wing width FB
and a wing height FH, have identical dimensions. A
front side 21 of the right wing FR lies together with
the visible side 1 of the shaped block S in a common
plane El, which is parallel to the plane E. A front
side 8 of the left wing FL is set back from this plane
El in the direction of the plane E. The shaped block S
has, apart from the shaped block depth ST, a shaped
block width SB and a shaped block height SH, the shaped
block depth ST corresponding to a body depth KT and the
shaped block height SH corresponding to a body height
KH. Finally, the shaped block width SB is the sum of
the two wing widths FB and a body width KB. The shaped
block S is delimited at the top and bottom by an upper
side 5 and a lower side 6. Wings F or FL and FR
arranged laterally in the front half SHV of the shape S
are characteristic of the shaped block S. These wings
are at a distance DF from one another in the
CA 02598110 2007-08-14
- 8 -
y-direction, the distance DF being measured between a
rear side 7 of the right wing FR and the front side 8
of the left wing FL. The wings FL and FR are
point-symmetrical with respect to a point of symmetry
SP. Optionally, edges K1 and/or K2 at which the wings F
merge into the body K are provided, as predetermined
breaking points Sl, S2, with a notch (not shown here)
so as to make it easier, at the ends of walls, to cut
off a wing F which is not required.
The shaped block S represented in figure 1 is
configured as a solid block. The shaped blocks S
represented in figures 2 and 3, although having
identical dimensions and an identical external shape,
differ therefrom in that they each have a vertical
opening 9 which traverses the shaped block S from the
upper side 5 to the lower side 6. In the variant
embodiment of the shaped block S represented in figure
2, the opening 9 tapers in an arrow direction z' in the
manner of an inverted truncated pyramid.
In the third variant embodiment of the shaped block S
represented in figure 3, the opening 9 is cuboidal in
shape. Four lugs 10 are arranged on inner walls
(without reference signs) of the opening 9 and serve as
supports 11 for a slab 12 which can be inserted into
the opening 9. The positioning chosen for the lugs 10
allows the opening 9 of the shaped block S to be closed
off toward its upper side 5. This is particularly
advantageous in the case of the uppermost layer of a
wall of shaped blocks S, since a relatively neat wall
termination is thus possible with little effort. Of
course, the invention also makes provision to arrange
the lugs close to the lower side 6 of the shaped block
S so as to make it possible to delimit the opening 9 at
the bottom using the slab.
The variant embodiment of the shaped block represented
in figure 2 also allows slabs to be inserted at
CA 02598110 2007-08-14
- 9 -
different heights (z). For this purpose, it is possible
for example to use slabs formed as truncated pyramids.
Analogously to the variant embodiment shown in
figure 3, provision is also made to provide the opening
with lugs or shoulders which can serve as supports for
slabs or other inserts, such as baskets or water
storage means, for example.
Figure 4 shows a left shaped block SL, a central shaped
block S and a right shaped block SR in a perspective
representation. The shaped blocks SL, S, SR are
arranged next to one another and form part of a wall
layer ML of a wall M. The shaped blocks SL, S, SR
represented in figure 4 correspond in terms of their
dimensions to the shaped block known from figure 1. All
three shaped blocks SL, S, SR are arranged in the same
orientation. Consequently, the wings F are situated in
front of the plane E which divides the shaped blocks
SL, S, SR. Figure 4 shows a plane E for each of the
shaped blocks SL, S, SR, these individual planes E of
course forming a common plane when the wall M is formed
straight. The offset arrangement of the wings F means
that the wing FR of the shaped block S and the wing F
of the shaped block SR, and the wing FL of the shaped
block S and the wing F of the shaped block SL, each lie
parallel to one another in front of the plane E. Hence,
the wall M or the wall layer ML is also formed solidly,
and thus stably, between the bodies K by virtue of a
double wing arrangement. In the arrangement of the
shaped blocks SL, S, SR shown in figure 4, the side
faces 3, 4 of the shaped blocks SL, S, SR and the wings
F enclose cavities 13. These have a depth T13 which
corresponds to the distance DF represented in figure 1.
Figure 5 shows a plan view of a second shaped block S.
This is similar in design to the shaped block shown in
figure 1, but here wings F or FL and FR are offset with
respect to one another in the y-direction by only one
wing depth FT and thus, unlike the shaped block known
CA 02598110 2007-08-14
- 10 -
from figure 1, do not have any distance from one
another. Analogously to the shaped blocks represented
in figures 2 and 3, the shaped block S has an opening
9. The two wings F are arranged in front of a plane E
which divides the shaped block S or its body K.
Figure 6 shows a third shaped block S in which wings F
or FL, FR are situated in front of a plane E which
divides a body K. By contrast with the shaped blocks
shown in the preceding figures, the wings F have
projections 15 on free ends 14. The wings FL and FR
have a distance DS from one another.
Figures 7a to 7c are plan views showing different wall
layers ML which are formed by shaped blocks S which
correspond to the shaped block represented in figure 5.
By way of example the individual wall layers ML are
each formed by a left shaped block SL, a central shaped
block S and a right shaped block SR.
The individual wall layers ML have different lengths
L1, L2, L3, where Ll > L2 > L3. These differences are
determined by a different degree of overlapping between
the wings F of adjacent shaped blocks SL, S or S, SR.
In the wall layer ML represented in figure 7a, not
counting tolerances, the wings F overlap one another
virtually completely, so that the degree of overlapping
can be said to be approximately 100%. The shaped blocks
SL, S, SR of the wall layer ML represented in figure 7b
have a degree of overlapping of approximately 50%,
since the wings F are each situated in front of or
behind one another by approximately half a wing width
FB. In the wall layer ML represented in figure 7c, the
degree of overlapping, being approximately 25%, is at a
lower limit.
Figures 8a to 8c again show three different wall layers
ML which are each composed of two shaped blocks SL, S
which correspond to the shaped block described in
CA 02598110 2007-08-14
- 11 -
figure 6. As far as the matter of the lengths of the
wall layers and the degree of overlapping is concerned,
reference should be made to the comments pertaining to
figures 7a to 7c. As figure 8c shows, the projections
15 on the free ends 14 of the wings F prevent the
possibility of falling below a minimum degree of
overlapping, since these projections would only allow a
further parting movement of the shaped blocks S and SL
if one of the shaped blocks S, SL were simultaneously
displaced in the y-direction. Figures 8a and 8b show
how a cavity 13 enclosed between the wings F also
decreases in volume as the degree of overlapping
decreases. In the wall layers ML represented in figures
8a to 8c, the shaped blocks S, SL involved are always
placed in the same orientation next to one another.
Figure 9a shows a plan view of a fourth shaped block S
which is similar in configuration to the shaped block
represented in figure 6. The shaped block S essentially
comprises a body K and wings F or FL and FR arranged
thereon.
In figure 9b, a first wall layer ML comprising three
shaped blocks SL, S, SR is represented. These shaped
blocks SL, S, SR, like the shaped blocks of the wall
layers represented in the preceding figures, are all
laid out with the same orientation so as to generate a
smooth wall pattern at a visible side 1, all the wings
F being situated in front of the plane E in the
y'-direction. At a second visible side 2 which may be
present (free-standing wall), the wall layer ML has
recesses 16 alternating with the bodies K.
Figure 9c shows a further wall layer ML containing four
shaped blocks SL, S, SR, SRR, in which the shaped
blocks S and SRR are arranged with the known
orientation. The remaining shaped blocks SL and SR are
rotated through 180 with respect to the shaped block
S, the rotation taking place about a vertical axis H
CA 02598110 2007-08-14
- 12 -
which emerges vertically from the plane of the drawing.
To make the description of the wings F of the shaped
blocks SL, S, SR, SRR clearer to understand, a
distinction will now be drawn between wings FF which
are remote from the plane E and wings FN which are
situated close to the plane E. The various transitions
between adjacent shaped blocks SL, S or S, SR or SR,
SRR are now defined by the interaction between two
wings FF remote from the plane E or by the interaction
between two wings FN close to the plane E. If two wings
FF interact, the resulting impression is of a recess-
free wall Ml at both visible sides. If two wings FN
interact, the result is a wall section M2 which has
recesses 16 at both visible sides.
The third design variant has already been represented
in figure 9b. This is obtained by the interaction of a
wing FN close to the plane E with a wing FF remote from
the plane E. There results a wall section M3 which has
a recess 16 at only one visible side of the wall.
Depending on the particular system, it is possible
using the shaped block according to the invention to
form either wall layers which are composed continuously
of wall sections M3 or in which wall sections Ml and M2
alternate or in which wall sections Ml, M2 and M3
alternate.
In particular, the formation of a wall which is built
up from wall sections M3 also allows the formation of
arcuate retaining walls.
Figure 10 shows a plan view of a retaining wall M made
up of shaped blocks S, the shaped blocks S
corresponding to the shaped block shown in figure 9a.
The wall M comprises a lower wall layer ML1 and, set
back from this, a wall layer ML2. Adjacent shaped
blocks S of the lower wall layer ML1 are each rotated
with respect to one another through an angle a = 15
CA 02598110 2007-08-14
- 13 -
about a vertical axis rising vertically from the
drawing. When considered in an idealized manner, the
shaped blocks S of the lower wall layer ML1 describe an
arc (not shown) having a radius Rl. On account of the
upper layer ML2 being set back from the lower wall
layer ML1, the upper wall layer ML2 when considered in
an idealized manner describes an arc (not shown) having
a radius R2, where Rl > R2. The shaped blocks S of the
upper wall layer ML2 are each rotated with respect to
one another through an angle (3, it also being the case
in principle, given the smaller radius R2, that a>p.
Such a structure of the retaining wall M is only
possible if the degree of overlapping of interacting
wings F increases from the lower wall layer MLl to the
upper wall layer ML2.
Finally, figure 11 shows a plan view of a fifth shaped
block S which has projections 17 and recesses 18 on
visible sides 1, 2 and on side faces 3, 4 of its body
K. Projections 15 are also formed on free ends 14 of
wings F or FL, FR. The wings F are situated in front of
a plane E which divides the shaped block S in half and
extends perpendicularly into the plane of the drawing.
The shaped block S is divided by the plane E into a
front shaped block half SHV and a rear shaped block
half SHH. The wings FL and FR formed in the front
shaped block half SHV are arranged offset with respect
to one another and have a spacing DT from one another,
the projections 15 arranged on the free ends 14
bridging this distance DT if wings F of adjacent and
identically oriented shaped blocks S interact.
Furthermore, the shaped block S has an opening 9 which
extends from an upper side 5 to a lower side (without
reference sign). Similarly to an inverted truncated
pyramid, the opening 9 has inclined inner faces 19 of
which two merge into a shoulder 20. Onto the shoulders
20 can be deposited a slab 12 which partially closes
the opening. According to a variant embodiment which
has not been represented, provision is made to form
CA 02598110 2007-08-14
- 14 -
further shoulders on the inclined inner faces and thus
make it possible to insert a plurality of slabs at
different levels. Provision is made in particular for
the shaped block to be closed off at its lower side and
at its upper side using a slab. The recesses 18
arranged on the side faces 3, 4 in figure 11 are
dimensioned such that the free ends 14 of shaped blocks
S rotated through 180 with respect to one another
enter these recesses, resulting in a form-fitting
retention of adjacent shaped blocks S. Here, the recess
18 is arranged on the side face 3 alongside the wing FL
or FN close to the plane E, the recess being intended
to accommodate a wing likewise close to the plane E
that belongs to a neighboring block (not shown).
Conversely, the recess 18 is arranged on the side face
4 alongside the wing FR or FF remote from the plane E,
this recess being intended to accommodate a wing
likewise remote from the plane E that belongs to an
adjacent block (not shown). The recesses 18 arranged on
the visible sides 1, 2 make it possible in the case of
right-angled wall runs for the leg of an adjacent
shaped block to be supported in a form-fitting manner.
When considered in an idealized manner, the body K has
the contour of a trapezoid T in plan view.
Figure 12 shows a further shaped block S in plan view.
In this shaped block S the two wings FL, FR are set
back from a visible side 1 of the shaped block S. A
front side 8 of the left wing FL has an offset Vl from
the visible side 1, and a front side 21 of the right
wing FR has an offset V2 from the visible side 1.
Figure 13 shows a plan view of a wall M made up of five
shaped blocks SLL, SL, S, SR and SRR. The shaped blocks
SL and SR are laid by each being rotated through 180
about a vertical axis H with respect to the shaped
blocks S, SLL and SRR, in which arrangement wings FL,
FR of adjacent shaped blocks SLL, SL or SL, S or S, SR
or SR, SRR respectively bear against one another with
CA 02598110 2007-08-14
- 15 -
their front sides 21 or rear sides 22. Provision is
made in particular in such a wall M for the shaped
blocks SLL, SL, S, SR and SRR to be formed as stakes so
as to be able to form a wall run tailored to unevenly
terminating ground.
The invention is not limited to exemplary embodiments
which have been represented or described. Instead, it
covers developments of the invention within the scope
of the claims. In particular, the invention also makes
provision to form the body, in plan view, as a polygon
with straight and/or rounded sides. Furthermore, the
invention makes provision to form the body as a stake.
CA 02598110 2007-08-14
- 16 -
List of reference signs:
1 first visible side of S
2 second visible side of S
3 right side face of S
4 left side face of S
5 upper side of S
6 lower side of S
7 rear side of FR
8 front side of FL
9 vertical opening in K or S
10 lug on 9
11 support for 12
12 slab
13 cavity
14 free end of F
15 projection on F
16 recess in M
17 projection on A
18 recess on K
19 inner face of 6
20 shoulder
21 front side of FR
22 rear side of FL
DF distance
E vertical plane
El plane of 1
F wing
FL, FR left or right wing
FF wing remote from E
FN wing close to E
FB wing width
FH wing height
FT wing depth
H vertical axis of S
HST half shaped block depth
K body
KB body width
CA 02598110 2007-08-14
- 17 -
KH body height
KT body depth
K1, K2 edge between F and K
Ll - L3 length of ML
M wall
ML wall layer
ML1 lower wall layer
ML2 upper wall layer
M1 recess-free wall section
M2 wall section with recess on both sides
M3 wall section with single recess
R rectangle
Rl radius of ML1
R2 radius of ML2
S shaped block
SL left shaped block
SR right shaped block
SLL further shaped block
SRR further shaped block
SB shaped block width
SH shaped block height
ST shaped block depth
SHV front half of S
SHH rear half of S
SP point of symmetry for F
S1, S2 predetermined breaking points
T trapezoid
V1, V2 offset between 1 and 8 or 1 and 21
a angle between adjacent shaped blocks in MLl
0 angle between adjacent shaped blocks in ML2
x, y, z spatial directions