Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
HETEROCYCLIC BORONIC ACID COMPOUNDS
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
100011 The present invention relates to boronic acid compounds and their use
as
inhibitors of post-proline/alanine cleaving amino-dipeptidases. The invention
also relates to
methods of employing such inhibitors, alone or with another therapeutic agent,
to treating
DPP-N-related diseases, such as Type II diabetes and diabetic complications,
hyperglycemia, Syndrome X, hyperinsulinemia, obesity, atherosclerosis and
related
diseases, as well as various immunomodulatory diseases and chronic
inflammatory bowel
disease. Thus, the invention has applications in the medicinal chemical,
phannacological,
and medical arts.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
[0002] The following background commentary is an aid to in understanding the
present
invention. Inclusion of this commentary is not an admission concerning the
nature or
content of the prior art.
[0003] Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-IV) is a serine protease that belongs to a
group of
post-proline/alanine cleaving amino-dipeptidases. DPP-IV catalyzes the release
of an N-
terminal dipeptide only from proteins with N-terminal penultimate proline or
alanine.
100041 The physiological role of DPP-IV has not been established fully. It is
believed
to play an important role in neuropeptide metabolism, T-cell activation,
gastric ulceration,
functional dyspepsia, obesity, appetite regulation, impaired fasting glucose
(IFG), and
diabetes. In particular, DPP-N has been implicated in the control of glucose
metabolism
because its substrates include the insulinotropic hormones, glucagon like
peptide-1 (GLP-1)
and gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP), which are inactivated by removal of
their two N-
terminal amino acids.
[0005] In vivo administration of synthetic inhibitors of DPP-IV prevents N-
terminal
degradation of GLP-1 and GIP, resulting in higher plasma concentrations of
these
hormones, increased insulin secretion and, therefore, improved glucose
tolerance.
1
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 200-5/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
Therefore, such inhibitors have been proposed for the treatment of patients
with type II
diabetes, a disease characterized by decreased glucose tolerance and insulin
resistance.
[0006) Post-proline/alanine cleaving amino-dipeptidases have been discovered,
including DPP7, DPP8, DPP9, and fibroblast activation protein (FAP), that have
the
substrate- and inhibitor-specificity of DPP-IV. Thus, inhibitors of this sort
may affect
multiple members of the enzyme group. The precise physiological role of each
of these
post-proline/alanine cleaving enzymes is not well defined. Consequently,
inhibiting each of
them separately, a subset of them, or all of them at the same time would have
uncertain
physiological effect(s).
[0007) Diabetic dyslipidemia is characterized by multiple lipoprotein defects,
including
moderately high serum levels of cholesterol and triglycerides, small LDL
particles, and low
levels of HDL cholesterol. The results of recent clinical trials reveal
beneficial effects of
cholesterol-lowering therapy in diabetic and nondiabetic patients, thus
supporting increased
emphasis on treatment of diabetic dyslipidemia. This need for intensive
treatment of
diabetic dyslipidemia was advocated by the National Cholesterol Education
Program's
Adult Treatment Panel III.
[0008] Obesity is a well-known risk factor for the development of many very
common
diseases such as atherosclerosis, hypertension and diabetes. The incidence of
obese people
and thereby also these diseases is increasing throughout the entire
industrialized world.
Except for exercise, diet and food restriction no convincing pharmacological
treatment for
reducing body weight effectively and acceptably currently exist. However, due
to its
indirect but important effect as a risk factor in mortal and common diseases
it will be
important to find treatment for obesity or appetite regulation. Even mild
obesity increases
the risk for premature death, diabetes, hypertension, atherosclerosis,
gallbladder disease and
certain types of cancer. In the industrialized western world the prevalence of
obesity has
increased significantly in the past few decades. Because of the high
prevalence of obesity
and its health consequences, its prevention and treatment should be a high
public health
priority.
2
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
[0009] At present a variety of techniques are available to effect initial
weight loss.
Unfortunately, initial weight loss is not an optimal therapeutic goal. Rather,
the problem is
that most obese patients eventually regain their weight. An effective means to
establish
and/or sustain weight loss is the major challenge in the treatment of obesity
today.
[0010] Accordingly, a need exists for compounds that are useful for inhibiting
DPP-IV
without suppressing the immune system.
100111 Several compounds have been shown to inhibit DPP-[V, but all of these
have
limitations in relation to the potency, stability, selectivity, toxicity,
and/or
pharmacodynamic properties. Such compounds have been disclosed, for example,
in WO
98/19998, WO 00/34241, U.S. patent No. 6,124,305 (Novartis AG), and WO
99/38501
(Trustees of Tufts University).
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0012] The present invention provides DPP-IV inhibitors that are effective in
treating
conditions that may be regulated or normalized by inhibition of DPP-IV. More
particularly,
the invention relates to boronic acid-containing heterocycles and their
derivatives that
inhibit DPP-IV, and to methods for making such compounds. In addition, the
invention
provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising compounds of the invention,
and
combinations thereof including one or more other types of antidiabetic agents;
methods for
inhibiting DPP-IV comprising administering to a patient in need of such
treatment a
therapeutically effective amount thereof; and compounds for use as a
phannaceutical, and
their use in a process for the preparation of a medicament for treating a
condition that are
regulated or normalized via inhibition of DPP-IV.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWING
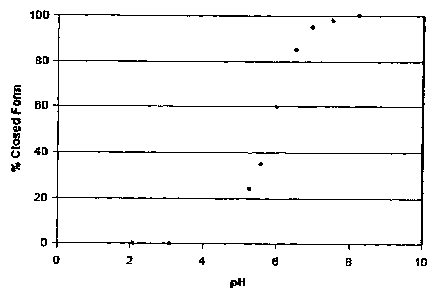
[0013] FIG. I shows the pH dependence of the percentage of linear and cyclic
isomeric
forms present in aqueous solution of a compound of the invention.
3
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
[0014] The present invention provides compounds of formula I:
OR'
R R3 O B-ORZ
R 5~1H N (I) N~~ R" R' 1-/- X "
Z
including all enantiomers, diastereoisomers, solvates, hydrates and
phannaceutically
acceptable salts thereof, wherein:
n is 1 to 3;
X is CH2; S; 0; CF2 or C(CH3)2;
Z is H; halogen; hydroxyl; (C1.6)alkoxy; (CI_12)alkyl; (C3.12)cycloalkyl;
phenyl; or
heteroaryl; where the phenyl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with R7;
optionally, X together with an adjacent ring carbon and Z form a fused
cyclopropyl;
and
optionally, one of the bonds in the ring containing X is a double bond;
R' and R2 independently or together are hydrogen; a boronic acid protecting
group;
or a group capable of being hydrolyzed to a hydroxyl group in an aqueous
solution at
physiological pH or in biological fluids;
CR'R" may be present or absent, wherein if CR'R" is present, then R', R", R3,
R4 and
R5 are selected from (aa), (bb) or (cc):
(aa) R', R", R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and
Rs is
a) hydrogen;
b) (Ci.12)alkyl; (C2.12)alkenyl; (C2_12)alkynyl; (C3.12)
cycloalkyl; or (C3_12)cycloalkenyl; where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl,
cycloalkyl and
cycloalkenyl groups are optionally mono- or independently pluri substituted
with R6, and
where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl portions include linear or branched chains
and may include
cyclic portions;
4
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
R6 is (CI_6)alkyl; (CI.6)alkoicy; cycloalkyl; carboxy;
acetamido; cyano; nitro; halogen; hydroxy; hydroxy(C1_6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl;
trifluoromethyl; trifluoromethoxy; sulfarnoyl; sulfonamido; carbamoyl; aryl;
heteroaryl;
where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or independently
plurisubstituted
with R7; amino, where the amino group is optionally mono- or independently
plurisubstituted with R8; -SOR8; -SO2R8; -CORB; -COZR8, -CONHRB; -CON(R8) 2; -
ORg; or
-S-RB;
R' is halogen; (CI_10)alkyl; (Cl_,0)alkoxy; (C1_10)alkylamino;
(Cl_10) dialkylamino; benzyl; benzyloxy; hydroxyl(C1_6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl;
nitro;
trifluoromethyl; trifluoromethoxy; trifluoromethylthio; N-hydroxyimino; cyano;
carboxy;
acetamido; hydroxy; sulfamoyl; sulfonamido; or carbamoyl;
R8 is (Cl.10)alkyl; (C2_1 )alkenyl; (C2.10)alkynyl; (C3_
10)cycloalkyl; (C5.10)cycloalkenyl; benzyl; phenethyl; aryl; or heteroaryl;
where the alkyl,
alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with aryl or heteroaryl where the aryl and heteroaryl groups
are optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R7 ; and where the aryl and
heteroaryl groups
are optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R7;
c) aryl optionally fused to a(C3_10)cycloalkyl; or heteroaryl
optionally fused to a (C3.10)cycloalkyl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups
are optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R7;
d) indanyl; 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthyl; (CHZ)jadamantyl in
which j is 0-3; or a[2.2.1 ] or [3.1.1 ] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety,
including (4-
pentylbicyclo[2.2.2]oct-1-yl)amine; where the indanyl, 1,2,3,4-
tetrahydronaphthyl, (CH2)j
adamantyl, and [2.2.1] or [3.1.1] bicyclic carbocyclic moieties are optionally
mono- or
independently plurisubstituted with hydroxy, (Ci_$)alkyl, (Ci.$)alkoxy, (C1
_8)alkanoyloxy, or
R9R10N-CO-O-, where R9 and R'0 are independently (CI_8)alkyl, or phenyl, where
the alkyl
and phenyl groups are optionally mono- or independently pluri substituted with
(CI_8)alkyl,
(Ci.8)alkoxy, halogen, or trifluoromethyl, or R9 and R10 together are
(C3_6)alkylene;
e) R"(CHZ)P- where R' 1 is 2-oxopyrrolidinyl; P.6)alkoxy;
phenyl; phenoxy; (CI_$)cycloalkyl; [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety;
pyridinyl; naphthyl;
cyclohexenyl; or adamantyl; where the 2-oxopyrrolidinyl, (CI-6)alkoxy, phenyl,
pyridinyl,
and naphthyl groups are optionally mono- or independently di- or independently
trisubstituted with R12; where the phenoxy group is optionally mono- or
independently
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
disubstituted with (CI.4)alkyl, (Ci.a)alkoxy, or halogen; and where the
[3.3.3] bicyclic
carbocyclic moiety is optionally mono-or independently plurisubstituted with
(C,_g)alkyl;
andpisOto3;
R12 is halogen; trifluoromethyl; cyano; nitro; (Cl-6)alkyl; (Cl.
6)alkoxy; cycloalkyl; carboxy; acetamido; hydroxy; hydroxy(Ci_6)alkyl;
hydroxymethyl;
trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; carbamoyl; sulfonamido; alkylsufonyl;
phenylsulfonyl; aryl;
heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with R';
f) (R13)2CH(CH2)q-, where R13 is phenyl; in which the phenyl
groups are independently optionally mono- or independently disubstituted with
RIZ; and q is
0 to 3;
g) a group of the formula:
R's
I
R14~ (CH2)r__4
where R14 and R'5 are independently hydrogen; (CI_8)alkyl; (C2-
6)alkylcarbonyi; (C3_
12)cycloalkyl ring; (C3_12)cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylamino-carbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the cycloalkyl
ring is
optionally substituted with hydroxy(Cl.6)alkyl, and where the benzyl, benzoyl,
pyridine,
pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R12; or R14 and R15
together form a
(C3.12)cycloalkyl ring; and r is 2 to 6;
h) a group of the formula:
R17
R16"- ~(CHz)s
where R16 and R" are each independently hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl;
(Ci_6)alkylcarbonyl; di-(CI
6)alkylaminocarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine; pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl,
benzoyl,
pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and
phenylsulfonyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R12; or R"
and R17
together form a(C3_12)cycloalkyl ring; and s is I to 6;
6
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
i) a group of the formula:
(CH2)_~
R 19
N--(CH2)t u
R18
where R'g and R19 are independently hydrogen; (C,_8)alkyl; (CI-
6)alkylcarbonyl; di-(Cl-
6)alkylaminocarbonyl; benzyl; benzothiazole; benzoyl; pyridine; pyrimidine;
phenyl;
phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl, or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl,
benzoyl,
benzothiazole, pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl,
alkylsulfonyl, and
phenylsulfonyl groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted
with R1Z; or R18
and R19 together form a(C3.12)cycloalkyl ring; each t is independently 0 to 6;
and u is 0 to 3;
j) a group of the formula:
(phenyl-CH2-C(CH3) 2-),
where the phenyl group is optionally mono- or independently pluri substituted
with R12;
k) a group of the formula:
20 ~ (CH2)1
R ~(CHzs ~ (CH2c~ RYC t
or R2o-N or ~
Ry/ c RY 7
u 20 u
where R20 is hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl; (CI.6)alkylcarbonyl; di-
(CI_6)alkylaminocarbonyl; (C3_
g)cycloalkylcarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl; (CI-6)alkyloxycarbonyl;
arlkyloxycarbonyl, pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl; phenyl substituted thiazole ring; phenylaminocarbonyl;
alkylsulfonyl;
or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl, benzoyl, pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl,
phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl groups are optionally
mono- or
independently di-substituted with R12; RX is hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl; (C3.1Z)
cycloalkyl;
benzyl; phenyl; where the benzyl and phenyl, groups are optionally mono- or
independently
di-substituted on the ring with R12; RY is absent or is halogen, (Ci.g)alkyl,
(CI_8)alkoxy,
0-alkylcarboxylate, 0-aralkylcarboxylate, N-alkylcarboxamido, N-
aralkylcarboxamido; or
phenyl;
7
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
sis 1 to6;tis0to6;anduis0to3;or
1) a group of the formula:
(CH2)i ~
R21-0--(CFi A ~ u
where R21 is hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl; benzyl; or phenyl; in which the benzyl and
phenyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted on the ring with
R12; each t is
independently 0 to 6; and u is 0 to 3;
(bb) R', R", R3, Ra and R5 are independently hydrogen; alkyl; alkenyl;
alkynyl; cycloalkyl; cycloalkylalkyl; bicycloalkyl; tricycloalkyl;
alkylcycloalkyl;
hydroxyalkyl; hydroxyalkylcycloalkyl; hydroxycycloalkyl; hydroxybicycloalkyl;
hydroxytricycloalkyl; bicycloalkylalkyl; alkylbicycloalkyl; alkylthioalkyl;
arylalkylthioalkyl; cycloalkenyl; aryl, aralkyl; heteroaryl; heteroarylalkyl;
cycloheteroalkyl
or cycloheteroalkylalkyl; all optionally mono- or independently
plurisubstituted with
halogen, alkyl, polyhaloalkyl, alkoxy, haloalkoxy, polyhaloalkoxy,
alkoxycarbonyl, alkenyl,
alkynyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl, polycycloalkyl, heteroarylamino,
arylamino,
cycloheteroalkyl, cycloheteroalkylalkyl, hydroxy, hydroxyalkyl, nitro, cyano,
amino,
substituted amino, alkylamino, dialkylamino, thiol, alkylthio, alkylcarbonyl,
acyl,
alkoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl, alkynylamino-carbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl,
alkenylaminocarbonyl, alkylcarbonyloxy, alkylcarbonylamino, arylcarbonylamino,
alkylsulfonylamino, alkylaminocarbonyl-amino, alkoxycarbonylamino,
alkylsulfonyl,
aminosulfinyl, aminosulfonyl, alkylsulfmyl, sulfonamido or sulfonyl; or
R' together with R3 or R4, or R" together with R3 or R4, and the atoms
to which they are attached form a 4 to 8 membered cyclic, polycyclic or
heterocyclic ring
system containing I to 3 heteroatoms selected from N, 0, S, SO or SOZ; and
includes single
rings, fused bicyclic and tricyclic rings, which are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with any of the groups set forth in (aa); or
R 4 and R5 together form -(CR22R23)m where m is 2 to 6, and R22 and
R23 are independently hydrogen; hydroxyl; alkoxy; alkyl; alkenyl; alkynyl;
cycloalkyl; halo;
amino; substituted amino; cycloalkylalkyl; cycloalkenyl; aryl; arylalkyl;
heteroaryl,
heteroarylalkyl; cycloheteroalkyl; cycloheteroalkylalkyl; alkylcarbonylamino;
arylcarbonylamino; alkoxycarbonyl-amino; aryloxycarbonyl-amino;
alkoxycarbonyl;
aryloxycarbonyl; or alkylaminocarbonylamino; or
8
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
R4 and R5 together with the atoms to which they are attached form a 5
to 7 membered ring containing a total of 2 to 4 heteroatoms selected from N,
0, S, SO, or
SO2; or
R4 and R5 together with the atoms to which they are attached form a 4
to 8 membered cycloheteroalkyl ring wherein the cycloheteroalkyl ring
optionally has an
aryl, heteroaryl or 3 to 7 membered cycloalkyl ring fused thereto; or
(cc) R' and R3 are hydrogen; and R" and R4 together form a 4 to 8
membered cyclic, polycyclic or heterocyclic ring system containing 1 to 3
heteroatoms
selected from N, 0, S, SO and SOz, and includes single rings, fused bicyclic
and tricyclic
rings, which are optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with any
of the groups
set forth in (aa) or (bb) and
R5 is any of the groups in (aa) or (bb); and
if CR'R" is absent, then R3, R4 and R5 are selected from (dd), (ee) or (ff):
(dd) R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and
Rs is
a) hydrogen, provided that RS is not hydrogen when n is 1, X
is CH2, and Z is H;
b) (CI_12)alkyl; (C2_12)alkenyl; (C2_12)alkynyl; (C3_12)
cycloalkyl; or (C3_1z)cycloalkenyl; where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl,
cycloalkyl and
cycloalkenyl groups are optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted
with RG, and
where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl portions include linear or branched chains
and may include
cyclic portions;
R 6 is (C1_6)alkyl; (CI_6)alkoxy; cycloalkyl; carboxy;
acetamido; cyano; nitro; halogen; hydroxy; hydroxy(CI_6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl;
trifluoromethyl; trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; sulfonamido; carbamoyl; aryl;
heteroaryl;
where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or independently
pluri substituted
with R7; amino, where the amino group is optionally mono- or independently
plurisubstituted with Rg; -SORg; -SO2R8; -CORa; -CO2Ra, -CONHRB; -CON(R8) 2; -
OR8; or
-S-RB;
R' is halogen; (Cl_lo)alkyl; (CI_Io)alkoxy; (Cl_io)alkylamino;
(Ci_ia) dialkylamino; benzyl; benzyloxy; hydroxyl(C1_6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl;
nitro;
trifluoromethyl; trifluoromethoxy; trifluoromethylthio; N-hydroxyimino; cyano;
carboxy;
acetamido; hydroxy; sulfamoyl; sulfonamido; or carbamoyl;
9
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
R8 is (Cl.I )alkyl; (C2_1 )alkenyl; (C2.10)alkynyl; (C3.
io)cycloalkyl; (C5.1 )cycloalkenyl; benzyl; phenethyl; aryl; or heteroaryl;
where the alkyl,
alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with aryl or heteroaryl where the aryl and heteroaryl groups
are optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R7 ; and where the aryl and
heteroaryl groups
are optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R7;
c) aryl optionally fused to a(C3_10)cycioalkyl; or heteroaryl
optionally fused to a(C3_10)cycloalkyl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups
are optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R7;
d) indanyl; 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthyl; (CHz)jadamantyl in
which j is 0-3; or a[2.2.1 ] or [3.1.1 ] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety,
including (4-
pentylbicyclo[2.2.2]oct-l-yl)arnine; where the indanyl, 1,2,3,4-
tetrahydronaphthyl, (CH2)j
adamantyl, and [2.2.1 ] or [3.1.1 ] bicyclic carbocyclic moieties are
optionally mono- or
independently plurisubstituted with hydroxy, (CI_g)alkyl, (C1_8)alkoxy,
(C1.$)alkanoyloxy, or
R9Ri0N-CO-O-, where R9 and R10 are independently (Ci.8)alkyl, or phenyl, where
the alkyl
and phenyl groups are optionally mono- or independently pluri substituted with
(CI_g)alkyl,
(Ci.g)alkoxy, halogen, or trifluoromethyl, or R9 and R10 together are
(C3.6)alkylene;
e) R"(CHZ)P- where R" is 2-oxopyrrolidinyl; (Ci.6)alkoxy;
phenyl; phenoxy; (C1.8)cycloalkyl; [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety;
pyridinyl; naphthyl;
cyclohexenyl; or adamantyl; where the 2-oxopyrrolidinyl, (CI_6)alkoxy, phenyl,
pyridinyl,
and naphthyl groups are optionally mono- or independently di- or independently
trisubstituted with R'Z; where the phenoxy group is optionally mono- or
independently
disubstituted with (CIA)alkyl, (Ci4)alkoxy, or halogen; and where the [3.3.3]
bicyclic
carbocyclic moiety is optionally mono-or independently plurisubstituted with
(Ci_8)alkyl;
and p is 0 to 3;
R'Z is halogen; trifluoromethyl; cyano; nitro; (Ci.6)alkyl;
(Cl.6)alkoxy; cycloalkyl; carboxy; acetamido; hydroxy; hydroxy(Ci.6)alkyl;
hydroxymethyl;
trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; carbamoyl; sulfonamido; alkylsufonyl;
phenylsulfonyl; aryl;
heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with R7;
f) (R13)2CH(CH2)q-, where R13 is phenyl; in which the phenyl
groups are independently optionally mono- or independently disubstituted with
R1z; and q is
0 to 3;
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
g) a group of the formula:
R15
R14"--
where R 14 and R15 are independently hydrogen; (CI_8)alkyl;
(Ci.6)alkylcarbonyl; (C3_
12)cycloalkyl ring; (C3_12)cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylamino-carbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the cycloalkyl
ring is
optionally substituted with hydroxy(Ci.6)alkyl, and where the benzyl, benzoyl,
pyridine,
pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R12; or R 14 and Rt$
together form a
(C3.12)cycloalkyl ring; and r is 2 to 6;
h) a group of the formula:
R17
(
R16~'N"'(CHz)s s'
where R16 and R" are each independently hydrogen; (Ci_8)alkyl;
(C1.6)alkylcarbonyl; di-(Cl_
6)alkylaminocarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine; pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl,
benzoyl,
pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and
phenylsulfonyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R12; or R' 6
and R"
together form a(C3.12)cycloalkyl ring; and s is I to 6;
i) a group of the formula:
(CHz)i ~
R 19
N-(CH~ u
R~$
where R18 and R19 are independently hydrogen; (C1.$)alkyl;
(Ci.6)alkylcarbonyl; di-(Cl_
6)alkylaminocarbonyl; benzyl; benzothiazole; benzoyl; pyridine; pyrimidine;
phenyl;
phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl,
benzoyl,
benzothiazole, pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl,
alkylsulfonyl, and
phenylsulfonyl groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted
with R'Z; or Ri8
and R19 together form a(C3.iz)cycloalkyl ring; each t is independently 0 to 6;
and u is 0 to 3;
j) a group of the formula:
(phenyl-CH2-C(CH3) 2-),
11
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCTIUS2004/037820
where the phenyl group is optionally mono- or independently pluri substituted
with R12;
k) a group of the formula:
R20 RX(CH2)s~3 ~(CH2)i 1 Ry~ ~(CH2)t I
or R20_N or )
u
Ry/ } N / u Ry ) u R20
where R20 is hydrogen; (CI.8)alkyl; (C1_6)alkylcarbonyl; di-
(CI.6)alkylaminocarbonyl; (C3.
8)cycloalkylcarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl; (CI_6)alkyloxycarbonyl;
arlkyloxycarbonyl, pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl; phenyl substituted thiazole ring; phenylaminocarbonyl;
alkylsulfonyl;
or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl, benzoyl, pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl,
phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl groups are optionally
mono- or
independently di-substituted with R1z; RX is hydrogen; (CI_g)alkyl; (C3.12)
cycloalkyl;
benzyl; phenyl; where the benzyl and phenyl, groups are optionally mono- or
independently
di-substituted on the ring with R12; RY is absent or is halogen, (CI_g)alkyl,
(CI.g)alkoxy,
0-alkylcarboxylate, 0-aralkylcarboxylate, N-alkylcarboxamido, N-
aralkylcarboxamido; or
phenyl;
sis I to6;tisOto6;anduisOto3;or
1) a group of the formula:
(CHZ)-1
R21-O-(CHZi u
where RZ1 is hydrogen; (C1.8)alkyl; benzyl; or phenyl; in which the benzyl and
phenyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted on the ring with
R12; each t is
independently 0 to 6; and u is 0 to 3; or
(ee) R3, R4 and R5 are independently hydrogen; alkyl; alkenyl; alkynyl;
cycloalkyl; cycloalkylaikyl; bicycloalkyl; tricycloalkyl; alkylcycloalkyl;
hydroxyalkyl;
hydroxyalkylcycloalkyl; hydroxycycloalkyl; hydroxybicycloalkyl;
hydroxytricycloalkyl;
bicycloalkylalkyl; alkylbicycloalkyl; alkylthioalkyl; arylalkylthioalkyl;
cycloalkenyl; aryl,
aralkyl; heteroaryl; heteroarylalkyl; cycloheteroalkyl or
cycloheteroalkylalkyl; all optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with halogen, alkyl, polyhaloalkyl,
alkoxy,
haloalkoxy, polyhaloalkoxy, alkoxycarbonyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl,
cycloalkylalkyl,
polycycloalkyl, heteroarylamino, arylamino, cycloheteroalkyl,
cycloheteroalkylalkyl,
hydroxy, hydroxyalkyl, nitro, cyano, amino, substituted amino, alkylamino,
dialkylamino,
thiol, alkylthio, alkylcarbonyl, acyl, alkoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkynylamino-
12
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
carbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, alkenylaminocarbonyl, alkylcarbonyloxy,
alkylcarbonylamino, arylcarbonylamino, alkylsulfonylamino, alkylaminocarbonyl-
amino,
alkoxycarbonylamino, alkylsulfonyl, aminosulfinyl, aminosulfonyl,
alkylsulfinyl,
= sulfonamido or sulfonyl, provided that when n is 1, X is CH2, the ring
containing X is
saturated, and Z, R3 and R5 are H, R4 is not a side chain of a naturally
occurring a-amino
acid, and provided that when n is 1, X is CH2, the ring containing X is
saturated, and Z and
R5 are H, R3 and R4 are not both methyl; or
R4 and R5 together form -(CRZ2R23)rt, - where m is 2 to 6, and R22 and
R23 are independently hydrogen; hydroxyl; alkoxy; alkyl; alkenyl; alkynyl;
cycloalkyl; halo;
amino; substituted amino; cycloalkylalkyl; cycloalkenyl; aryl; arylalkyl;
heteroaryl,
heteroarylalkyl; cycloheteroalkyl; cycloheteroalkylalkyl; alkylcarbonylamino;
arylcarbonylamino; alkoxycarbonyl-amino; aryloxycarbonyl-amino;
alkoxycarbonyl;
aryloxycarbonyl; or alkylaminocarbonylamino; provided that when n is 1, X is
CH2, the ring
containing X is saturated, Z and R3 are H, R4 and R5 together are not -(CH2)2-
or -(CHZ)3-;
or
R4 and R5 together with the atoms to which they are attached form a 5
to 7 membered ring containing a total of 2 to 4 heteroatoms selected from N,
0, S, SO, or
SO2i or
R and R5 together with the atoms to which they are attached form a 4
to 8 membered cycloheteroalkyl ring wherein the cycloheteroalkyl ring
optionally has an
aryl, heteroaryl or 3 to 7 membered cycloalkyl ring fused thereto; or
(ff) R3 is hydrogen; and R4 and RS together with the atoms to
which they are attached form a 4 to 8 member mono- or polycyclic heterocyclic
ring system
containing 1 to 3 heteroatoms selected from N, 0, S, SO and SOZ, wherein the
heterocyclic
ring system is optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with any of
the groups set
forth in (dd) or (ee); provided that when n is 1, X is CH2, the ring
containing X is saturated,
and Z and R3 are H, R4 and R5 together are not -(CH2)2- or -(CH2)3-; and
wherein the bond containing the wavy line signifies the point of attachment.
[0015] In some embodiments of compounds of formula I, R' and R2 independently
or together are the boronic acid protecting group formed from (+)-pinanediol;
pinacol; 1,2-
dicyclohexyl-ethanediol; 1,2-ethanediol; 2,2-diethanolamine; 1,3-propanediol;
2,3-
butanediol, diisopropyl tartrate; 1,4-butanediol; diisopropylethanediol;
(S,S,)-5,6-
decanediol; 1,1,2-triphenyl-1,2-ethanediol; (2R,3R)-1,4-dimethyoxy-1,1,4,4-
tetraphenyl-
13
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
2,3-butanediol; methanol; ethanol; isopropanol; catechol; or 1-butanol. Thus,
it will be
understood by those of skill in the art that R' and R 2 represent a single
protecting group
attached to both boronic ester oxygens when diols such as (+)-pinanediol and
pinacol are
used, whereas R' and R2 represent separate moieties on the boronic ester
oxygens such as
methyl or ethyl when the esters are formed from methanol and ethanol,
respectively. In
other embodiments of compounds of formula I, R' and R 2 independently or
together are a
group capable of being hydrolyzed to a hydroxyl group in an aqueous solution
at
physiological pH or in biological fluids and are formed from 1,2-
dicyclohexylethanediol;
1,2-ethanediol; 1,3-propanediol; 2,3-butanediol, 1,4-butanediol;
diisopropylethanediol;
methanol; ethanol; isopropanol; or 1-butanol. For example, when R' and R 2 are
each
formed from methanol, the resulting R' and R2 groups are methyl. When 2,3-
butanediol is
used, the resulting R' and R2 groups are a single group and the resulting
boronic ester has
the following structure:
B,
,-Zz< o
[0016] Compounds of formula I include those wherein if CR'R" is absent, then
R3, R4
and R5 are selected from (dd), (ee) or (ff):
(dd) R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and
Rs is
a) (C1_12)alkyl; (C2_12)alkenyl; (C2.12)alkynyl; (C3.12)
cycloalkyl; or (C3_12)cycloalkenyl; where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl,
cycloalkyl and
cycloalkenyl groups are optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted
with R6, and
where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl portions include linear or branched chains
and may include
cyclic portions;
R6 is (C1.6)alkyl; (Ci_6)alkoxy; cycloalkyl; carboxy;
acetamido; cyano; nitro; halogen; hydroxy; hydroxy(CI.6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl;
tri fluoromethyl; trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; sulfonamido; carbamoyl; aryl;
heteroaryl;
where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or independently
plurisubstituted
with R'; amino, where the amino group is optionally mono- or independently
14
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
plurisubstituted with Rg; -SORB; -S02R8; -CORg; -C02R8, -CONHRB; -CON(R8) 2; -
ORB; or
-S-RB;
R7 is halogen; (Q-10)alkyl; (C1-io)alkoxy; (CI-10)alkylamino;
(Ci.,o) dialkylamino; benzyl; benzyloxy; hydroxyl(Cl.6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl;
nitro;
trifluoromethyl; trifluoromethoxy; trifluoromethylthio; N-hydroxyimino; cyano;
carboxy;
acetamido; hydroxy; sulfamoyl; sulfonamido; or carbamoyl;
R8 is (CI-io)alkyl; (C2-10)alkenyl; (Ci-1o)alkynyl; (C3-
,o)cycloalkyl; (Cs.lo)cycloalkenyl; benzyl; phenethyl; aryl; or heteroaryl;
where the alkyl,
alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with aryl or heteroaryl where the aryl and heteroaryl groups
are optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R7 ; and where the aryl and
heteroaryl groups
are optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R7;
b) aryl optionally fused to a(C3-, )cycloalkyl; or heteroaryl
optionally fused to a(C3-lo)cycloalkyl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups
are optionally
mono- or independently p luri substituted with R';
c) indanyl; 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthyl; (CHZ)jadamantyl in
which j is 0-3; or a[2.2.1 ] or [3.1.1 ] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety,
including (4-
pentylbicyclo[2.2.2]oct-l-yl)amine; where the indanyl, 1,2,3,4-
tetrahydronaphthyl, (CHZ)j
adamantyl, and [2.2.1] or [3.1.1] bicyclic carbocyclic moieties are optionally
mono- or
independently plurisubstituted with hydroxy, (Cl-g)alkyl, (Cl.B)alkoxy, (CI-
8)alkanoyloxy, or
R9R10N-CO-O-, where R9 and R10 are independently (CI-g)alkyl, or phenyl, where
the alkyl
and phenyl groups are optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with
(C,-8)alkyl,
(C1-8)alkoxy, halogen, or trifluoromethyl, or R9 and R10 together are (C3-
6)alkylene;
d) R't(CHZ)p- where R' 1 is 2-oxopyrrolidinyl; (C1.6)alkoxy;
phenyl; phenoxy; (C1-g)cycloalkyl; [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety;
pyridinyl; naphthyl;
cyclohexenyl; or adamantyl; where the 2-oxopyrrolidinyl, (Cl.6)alkoxy, phenyl,
pyridinyl,
and naphthyl groups are optionally mono- or independently di- or independently
trisubstituted with RT2; where the phenoxy group is optionally mono- or
independently
disubstituted with (Ci-a)alkyl, (Ci4)alkoxy, or halogen; and where the [3.3.3]
bicyclic
carbocyclic moiety is optionally mono-or independently pluri substituted with
(CI_8)alkyl;
and p is 0 to 3;
R'2 is halogen; trifluoromethyl; cyano; nitro; (C1-6)alkyl; (C,_
6)alkoxy; cycloalkyl; carboxy; acetamido; hydroxy; hydroxy(C1_6)alkyl;
hydroxymethyl;
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; carbamoyl; sulfonamido; alkylsufonyl;
phenylsulfonyl; aryl;
heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with R7;
e) (R13)2CH(CH2)q-, where R13 is phenyl; in which the phenyl
groups are independently optionally mono- or independently disubstituted with
R12; and q is
Oto3;
f) a group of the formula:
R's
R14~ (CH2)r-4
where R14 and R15 are independently hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl;
(Ci_6)alkylcarbonyl; (C3_
1Z)cycloalkyl ring; (C3_12)cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylamino-carbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the cycloalkyl
ring is
optionally substituted with hydroxy(C1 -6)alkyl, and where the benzyl,
benzoyl, pyridine,
pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R"; or R14 and R15
together form a
(C3_12)cycloalkyl ring; and r is 2 to 6;
g) a group of the formula:
R17
I
--I(CH2)s
where R16 and R17 are each independently hydrogen; (Ci_8)alkyl; (Ci-
6)alkylcarbonyl; di-(Cl_
6)alkylaminocarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine; pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl,
benzoyl,
pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and
phenylsulfonyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R1Z; or R16
and R"
together form a(C3_i2)cycloalkyl ring; and s is I to 6;
h) a group of the formula:
(CH2)iA
R~N---(CH
R18
where R18 and R19 are independently hydrogen; (C1_8)a1ky1;
(CI.6)alkylcarbonyl; di-(Ci_
6)alkylaminocarbonyl; benzyl; benzothiazole; benzoyl; pyridine; pyrimidine;
phenyl;
16
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenyisulfonyl; where the benzyl,
benzoyl,
benzothiazole, pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl,
alkylsulfonyl, and
phenylsulfonyl groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted
with R12; or R18
and R19 together form a(C3-,Z)cycloalkyl ring; each t is independently 0 to 6;
and u is 0 to 3;
i) a group of the formula:
(phenyl-CH2-C(CH3) Z-),
where the phenyl group is optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted
with R 12;
j) a group of the formula:
R20 Rx (CH2)c~ Ry ~(CH2c~
(CH2}S~ ~
or R2o_N or I,.
u
/ ) Ry u Ry u 20
where R20 is hydrogen; (Cl.8)alkyl; (CI_6)alkylcarbonyl; di-
(Ci.6)alkylaminocarbonyl; (C3.
$)cycloalkylcarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl; (CI .6)alkyloxycarbonyl;
arikyloxycarbonyl, pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl; phenyl substituted thiazole ring; phenylaminocarbonyl;
alkylsulfonyl;
or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl, benzoyl, pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl,
phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl groups are optionally
mono- or
independently di-substituted with R12; R,, is hydrogen; (CI.g)alkyl; (C3_12)
cycloalkyl;
benzyl; phenyl; where the benzyl and phenyl, groups are optionally mono- or
independently
di-substituted on the ring with R12; Ry is absent or is halogen, (CI-8)alkyl,
(C1.8)alkoxy,
0-alkylcarboxylate, O-aralkylcarboxylate, N-alkylcarboxamido, N-
aralkylcarboxamido; or
phenyl;
sisl to6;tisOto6;anduisOto3;or
k) a group of the formula:
(CH2)i I
R21-0-(CH2)t )U
>
where RZ' is hydrogen; (C1.8)alkyl; benzyl; or phenyl; in which the benzyl and
phenyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted on the ring with
R1z; each t is
independently 0 to 6; and u is 0 to 3; or
(ee) R3 and R4 are independently hydrogen, alkyl; alkenyl; alkynyl;
cycloalkyl; cycloalkylalkyl; bicycloalkyl; tricycloalkyl; alkylcycloalkyl;
hydroxyalkyl;
hydroxyalkylcycloalkyl; hydroxycycloalkyl; hydroxybicycloalkyl;
hydroxytricycloalkyl;
bicycloalkylalkyl; alkylbicycloalkyl; alkylthioalkyl; arylalkylthioalkyl;
cycloalkenyl; aryl,
17
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
aralkyl; heteroaryl; heteroarylalkyl; cycloheteroalkyl or
cycloheteroalkylalkyl; all optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with halogen, alkyl, polyhaloalkyl,
alkoxy,
haloalkoxy, polyhaloalkoxy, alkoxycarbonyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl,
cycloalkylalkyl,
polycycloalkyl, heteroarylamino, arylamino, cycloheteroalkyl,
cycloheteroalkylalkyl,
hydroxy, hydroxyalkyl, nitro, cyano, amino, substituted amino, alkylamino,
dialkylamino,
thiol, alkylthio, alkylcarbonyl, acyl, alkoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkynylamino-
carbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, alkenylaminocarbonyl, alkylcarbonyloxy,
alkylcarbonylamino, arylcarbonylamino, alkylsulfonylamino, alkylaminocarbonyl-
amino,
alkoxycarbonylamino, alkylsulfonyl, aminosulfinyl, aminosulfonyl,
alkylsulfinyl,
sulfonamido or sulfonyl;
R5 is alkyl; alkenyl; alkynyl; cycloalkyl; cycloalkylalkyl;
bicycloalkyl; tricycloalkyl; alkylcycloalkyl; hydroxyalkyl;
hydroxyalkylcycloalkyl;
hydroxycycloalkyl; hydroxybicycloalkyl; hydroxytricycloalkyl;
bicycloalkylalkyl;
alkylbicycloalkyl; alkylthioalkyl; arylalkylthioalkyl; cycloalkenyl; aryl,
aralkyl; heteroaryl;
heteroarylalkyl; cycloheteroalkyl or cycloheteroalkylalkyl; all optionally
mono- or
independently plurisubstituted with halogen, alkyl, polyhaloalkyl, alkoxy,
haloalkoxy,
polyhaloalkoxy, alkoxycarbonyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl,
polycycloalkyl, heteroarylamino, arylamino, cycloheteroalkyl,
cycloheteroalkylalkyl,
hydroxy, hydroxyalkyl, nitro, cyano, amino, substituted amino, alkylamino,
dialkylamino,
thiol, alkylthio, alkylcarbonyl, acyl, alkoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkynylamino-
carbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, alkenylaminocarbonyl, alkylcarbonyloxy,
alkylcarbonylamino, arylcarbonylamino, alkylsulfonylamino, alkylaminocarbonyl-
amino,
alkoxycarbonylamino, alkylsulfonyl, aminosulfinyl, aminosulfonyl,
alkylsulfinyl,
sulfonamido or sulfonyl; or
R4 and R5 together form -(CRzZRz3)m - wherein m is 2 to 6, and R22
and R23 are independently hydrogen; hydroxyl; alkoxy; alkyl; alkenyl; alkynyl;
cycloalkyl;
halo; amino; substituted amino; cycloalkylalkyl; cycloalkenyl; aryl;
arylalkyl; heteroaryl,
heteroarylalkyl; cycloheteroalkyl; cycloheteroalkylalkyl; alkylcarbonylamino;
arylcarbonylamino; alkoxycarbonyl-amino; aryloxycarbonyl-amino;
alkoxycarbonyl;
aryloxycarbonyl; or alkylaminocarbonylamino; provided that when n is 1, X is
CH2, and Z
and R3 are H, R4 and R5 together are not -(CH2)2- or -(CHZ)3-; or
18
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
R4 and R5 together with the atoms to which they are attached form a 5
to 7 membered ring containing a total of 2 to 4 heteroatoms selected from N,
0, S, SO, or
SO2; or
R4 and R5 together with the atoms to which they are attached form a 4
to 8 membered cycloheteroalkyl ring wherein the cycloheteroalkyl ring
optionally has an
aryl, heteroaryl or 3 to 7 membered cycloalkyl ring fused thereto; or
(ff) R3 is hydrogen; and R 4 and R5 together with the atoms to
which they are attached form a 4 to 8 member mono- or polycyclic heterocyclic
ring system
containing 1 to 3 heteroatoms selected from N, 0, S, SO and SOz, wherein the
heterocyclic
ring system is optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with any of
the groups set
forth in (dd) or (ee); provided that when n is 1, X is CH2, the ring
containing X is saturated,
and Z and R3 are H, R4 and R5 together are not -(CH2)2- or -(CH2)3-.
[0017] Compounds of formula I also include those wherein X is CH2; the ring
containing
X is saturated; CR'R" is absent, R', R2, R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and R5 is
(CI.12)alkyl; (CZ_
12)alkenyl; (C2_12)alkynyl; (C3.12) cycloalkyl; or (C3_12)cycloalkenyl; where
the alkyl,
alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl and cycloalkenyl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with R6, and where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl portions
include linear or
branched chains and may include cyclic portions. In some such embodiments, R5
is a(Ct_
12)alkyl or (C3_12)cycloalkyl, including, but not limited to, methyl, ethyl, n-
propyl, isopropyl,
n-butyl, isobutyl, sec-butyl, tert-butyl, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl,
cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl,
cyclohexylmethyl, 1-cyclohexylethyl, or adamantyl.
100181 In some embodiments of compounds of formula I, X is CH2; the ring
containing
X is saturated; CR'R" is absent, R', RZ, R3 and RQ are hydrogen; and R5 is
indanyl; 1,2,3,4-
tetrahydronaphthyl; (CH2)j adamantyl in which j is 0-3; or a[2.2.1] or [3.1.1]
bicyclic
carbocyclic moiety, including (4-pentylbicyclo[2.2.2]-oct-l-yl)amine; where
the indanyl,
1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthyl, (CH2)j adamantyl, and [2.2.1] or [3.1.1] bicyclic
carbocyclic
moieties are optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with hydroxy,
(C1.8)alkyl,
(Cl.8)alkoxy, (C1_8)alkanoyloxy, or R9R'(N-CO-O-, where R9 and Rl0 are
independently (C].
g)alkyl, or phenyl, where the alkyl and phenyl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
pluri substituted with (C1.8)alkyl, (CI.g)alkoxy, halogen, or trifluoromethyl,
or R9 and R'0
together are (C3-6)alkylene.
19
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
[0019] In other embodiments of compounds of formula I, X is CH2; the ring
containing
X is saturated; CR'R" is absent, R', Rz, R3 and R 4 are hydrogen; and R5 is
R"(CHZ)P where
R" is 2-oxopyrrolidinyl; (C1_6)alkoxy; phenyl; phenoxy; (Ci_8)cycloalkyl;
[3.3.3] bicyclic
carbocyclic moiety; pyridinyl; naphthyl; cyclohexenyl; or adamantyl; where the
2-
oxopyrrolidinyl, (CI-6)alkoxy, phenyl, pyridinyl, and naphthyl groups are
optionally mono-
or independently di- or independently trisubstituted with R12; where the
phenoxy group is
optionally mono- or independently disubstituted with (C1 .4)alkyl, (Cl
4)alkoxy, or halogen;
and where the [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety is optionally mono-or
independently
plurisubstituted with (CI_g)alkyl; p is 0 to 3; and R12 is halogen;
trifluoromethyl; cyano;
nitro; (CI-6)alkyl; (Ci.6)alkoxy; cycloalkyl; carboxy; acetamido; hydroxy;
hydroxy(Cl_
6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl; trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; carbamoyl; sulfonamido;
alkylsufonyl; phenylsulfonyl; aryl; heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R7.
[0020] In certain embodiments of compounds of formula I, X is CH2; the ring
containing
X is saturated; CR'R" is absent; R', R2, R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and R5 is
(R13)2CH(CH2)Q-,
where R13 is phenyl; in which the phenyl groups are independently optionally
mono- or
independently disubstituted with R12; and q is 0 to 3.
[0021] In some embodiments of compounds of formula I, X is CHZ, the ring
containing
X is saturated; CR'R" is absent, R', R2, R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and R5 is a
group of the
formula:
R's
R14~~\(CH2)r-I'
where R14 and R' 5 are independently hydrogen; (CI .8)alkyl; (CI
_6)alkylcarbonyl; (C3_
12)cycloalkyl ring; (C3_12)cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylamino-carbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the cycloalkyl
ring is
optionally substituted with hydroxy(C1_6)alkyl, and where the benzyl, benzoyl,
pyridine,
pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R'Z; or R14 and R"
together form a
(C3_12)cycloalkyl ring; and r is 2 to 6.
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/1JS2004/037820
100221 Compounds of formula I include those wherein X is CH2; the ring
containing X is
saturated; CR'R" is absent, R', R2, R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and R5 is a group
of the
formula:
R17
R1s1-- (CH)s
where R16 and R" are each independently hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl;
(Ci.(,)alkylcarbonyl; di-(Cl_
6)alkylaminocarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine; pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl,
benzoyl,
pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and
phenylsulfonyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R'Z; or R'6
and R' 7
together form a(C3_1Z)cycloalkyl ring; and s is I to 6.
[0023J Compounds of formula I wherein X is CH2; the ring containing X is
saturated;
CR'R" is absent, R', R2, R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and R5 is a group of the
formula:
(CH2)i ~
R19
N--(CH2 t u
R18
where R18 and R19 are independently hydrogen; (CI_$)alkyl;
(CI_6)alkylcarbonyl; di-(Cl_
6)alkylaminocarbonyl; benzyl; benzothiazole; benzoyl; pyridine; pyrimidine;
phenyl;
phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl,
benzoyl,
benzothiazole, pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl,
alkylsulfonyl, and
phenylsulfonyl groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted
with R12; or R18
and R19 together form a(C3-12)cycloalkyl ring; each t is independently 0 to 6;
and u is 0 to 3.
In some such embodiments, R5 has formula:
(CH2)-~
Rig ",CA or R\
N N
R18 I R18
21
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
[0024] In some embodiments of compounds of formula I, X is CH2; the ring
containing
X is saturated; CR'R" is absent, R', RZ, R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and R5 is a
group of the
formula:
(phenyl-CH2-C(CH3)2-),
where the phenyl group is optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted
with R12
.
[0025] Compounds of Formula I include those having the following structure,
Formula
IA:
,
0 R O\ B~,ORz
H
N -~\~
R5 N )
R4 R3 n
IA
In some such embodiments, R5 is alkyl; alkenyl; alkynyl; cycloalkyl;
cycloalkylalkyl;
bicycloalkyl; tricycloalkyl; alkylcycloalkyl; hydroxyalkyl;
hydroxyalkylcycloalkyl;
hydroxycycloalkyl; hydroxybicycloalkyl; hydroxytricycloalkyl;
bicycloalkylalkyl;
alkylbicycloalkyl; alkylthioalkyl; arylalkylthioalkyl; cycloalkenyl; aryl,
aralkyl; heteroaryl;
heteroarylalkyl; cycloheteroalkyl or cycloheteroalkylalkyl; all optionally
mono- or
independently pluri substituted with halogen, alkyl, polyhaloalkyl, alkoxy,
haloalkoxy,
polyhaloalkoxy, alkoxycarbonyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl,
polycycloalkyl, heteroarylamino, arylamino, cycloheteroalkyl,
cycloheteroalkylalkyl,
hydroxy, hydroxyalkyl, nitro, cyano, amino, substituted amino, alkylamino,
dialkylamino,
thiol, alkylthio, alkylcarbonyl, acyl, alkoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkynylamino-
carbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, alkenylaminocarbonyl, alkylcarbonyloxy,
alkylcarbonylamino, arylcarbonylamino, alkylsulfonylamino, alkylaminocarbonyl-
amino,
alkoxycarbonylamino, alkylsulfonyl, aminosulfinyl, aminosulfonyl,
alkylsulfinyl,
sulfonamido or sulfonyl. In other such embodiments, R5 is alkyl; alkenyl;
cycloalkyl;
cycloalkylalkyl; hydroxyalkyl; cycloalkenyl; aryl, aralkyl; heteroaryl;
heteroarylalkyl;
cycloheteroalkyl or cycloheteroalkylalkyl; all optionally mono- or
independently
pluri substituted as described above (in, e.g., (ee)). In still other such
embodiments, R5 is
alkyl, cycloalkyl or cycloheteroalkyl, optionally mono- or independently pluri
substituted as
described above. In some embodiments of compounds of Formula IA, R3 and R4 are
both
22
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
hydrogen. In other embodiments, n is 1. In some embodiments of compounds of
Formula
IA where n is 1 and R', R2, R3, and R4 are hydrogen, R5 is not methyl.
100261 Compounds of formula I include those wherein X is CH2; the ring
containing X is
saturated; CR'R" is absent, R', R2, R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and R5 is a group
of the
formula:
~
R 20 Rx (CH2) Rx(CH2)t-'_i Ry Rx C (CHz)t
s
or R20-N or
I
Ry/N )u Ry u R2o u
where R20 is hydrogen; (Ct-$)alkyl; (Ci-6)alkylcarbonyl; di-(Ct-
6)alkylaminocarbonyl; (C3_
8)cycloalkylcarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl; (Ct-6)alkyloxycarbonyl;
arlkyloxycarbonyl, pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl; phenyl substituted thiazole ring; phenylaminocarbonyl;
alkylsulfonyl;
or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl, benzoyl, pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl,
phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl groups are optionally
mono- or
independently di-substituted with R12; R,, is hydrogen; (CI_8)alkyl; (C3_12)
cycloalkyl;
benzyl; phenyl; where the benzyl and phenyl, groups are optionally mono- or
independently
di-substituted on the ring with R12; Ry is absent or is halogen, (C1-8)alkyl,
(Ct-8)alkoxy,
0-alkylcarboxylate, 0-aralkylcarboxylate, N-alkylcarboxamido, N-
aralkylcarboxamido; or
phenyl;
s is 1 to 6; t is 0 to 6; and u is 0 to 3. In some such embodiments, R5 has
formula:
R-x (CH2t~
~ (CH2)t~ cY
N
R2o -N
::~ or R2o
100271 In other such embodiments, R5 is
Rx(CH2)t-A
j)NU
R2o
23
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCTIUS2004/037820
including for example, the following structures:
CN N
H or H .
[0028) In still other such embodiments, the compound has the formula
01 B C/~' ,OH B OH
N OH N OH
~O f-~O
HNO..AH HN:~NH
TH C,OH
N B N B
OH OH
H C ~O H3C O
3- NH
' ,,\NH
J7
H<N JT , or HN
[0029] Compounds of formula I wherein X is CH2; the ring containing X is
saturated;
CR'R" is absent, R', RZ, R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and R5 is a group of the
formula:
(CHz)t I
R2'_O_-(CH2)t /u
where R21 is hydrogen; (C1 .8)alkyl; benzyl; or phenyl; in which the benzyl
and phenyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted on the ring with
R12; each t is
independently 0 to 6; and u is 0 to 3. In some such embodiments, R5 has
formula:
(CHZ)-l
or
R21-O R2~-O
24
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
[0030] Compounds of formula I include those wherein R' and R2 are hydrogen; n
is 1; X
together with an adjacent ring carbon and Z form a fused cyclopropyl; CR'R" is
absent;
R3, R4 and R5 are independently hydrogen; alkyl; alkenyl; alkynyl; cycloalkyl;
cycloalkylalkyl; bicycloalkyl; tricycloalkyl; alkylcycloalkyl; hydroxyalkyl;
hydroxyalkylcycloalkyl; hydroxycycloalkyl; hydroxybicycloalkyl;
hydroxytricycloalkyl;
bicycloalkylalkyl; alkylbicycloalkyl; alkylthioalkyl; arylalkylthioalkyl;
cycloalkenyl; aryl,
aralkyl; heteroaryl; heteroarylalkyl; cycloheteroalkyl or
cycloheteroalkylalkyl; all optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with halogen, alkyl, polyhaloalkyl,
alkoxy,
haloalkoxy, polyhaloalkoxy, alkoxycarbonyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl,
cycloalkylalkyl,
polycycloalkyl, heteroarylamino, arylamino, cycloheteroalkyl,
cycloheteroalkylalkyl,
hydroxy, hydroxyalkyl, nitro, cyano, amino, substituted amino, alkylamino,
dialkylamino,
thiol, alkylthio, alkylcarbonyl, acyl, alkoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkynylamino-
carbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, alkenylaminocarbonyl, alkylcarbonyloxy,
alkylcarbonylamino, arylcarbonylamino, alkylsulfonylamino, alkylaminocarbonyI-
amino,
alkoxycarbonylamino, alkylsulfonyl, aminosulfinyl, aminosulfonyl,
alkylsulfinyl,
sulfonamido or sulfonyl; or
R4 and R5 together form -(CR2ZR23)m where m is 2 to 6, and R22 and
R23 are independently hydrogen; hydroxyl; alkoxy; alkyl; alkenyl; alkynyl;
cycloalkyl; halo;
amino; substituted amino; cycloalkylalkyl; cycloalkenyl; aryl; arylalkyl;
heteroaryl,
heteroarylalkyl; cycloheteroalkyl; cycloheteroalkylalkyl; alkylcarbonylamino;
arylcarbonylamino; alkoxycarbonyl-amino; aryloxycarbonyl-amino;
alkoxycarbonyl;
aryloxycarbonyl; or alkylaminocarbonylamino; or
R4 and R5 together with the atoms to which they are attached form a 5
to 7 membered ring containing a total of 2 to 4 heteroatoms selected from N,
0, S, SO, or
SO2; or
R4 and R5 together with the atoms to which they are attached form a 4
to 8 membered cycloheteroalkyl ring wherein the cycloheteroalkyl ring
optionally has an
aryl, heteroaryl or 3 to 7 membered cycloalkyl ring fused thereto.
100311 In some embodiments of compounds of Formula 1, R', R2, R3 and R4 are
hydrogen; n is 1; X is CH2; CR'R" is absent; and RS is aryl or aralkyl.
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCTIUS2004/037820
[0032] In some embodiments, compounds of formula I have the formula:
OR'
0 B-OR2
R5-e N N
100331 In other embodiments, compounds of formula I have the formula:
OR' OR'
O B-OR2 O B-ORZ
H
R5 N R5"1 N N
R4 Rg or R4 R3
[0034] In still other embodiments, compounds of formula I have the formula:
OR'
H O B-OR
R Z
~~ N N
R4 ~
[0035] In still other embodiments, compounds of fonnula I have the formula:
R10 R'O
H O B-OR2 H 0 B-OR2
R5~-N N R5~N N
R4 14
F or OH
[0036] Compounds of formula I include those wherein,
if CR'R" is present, R' and R3 are hydrogen; R" and R4 together form a 4 to 8
membered cyclic, polycyclic or heterocyclic ring system containing 1 to 3
heteroatoms
selected from N, 0, S, SO and SO2, and includes single rings, fused bicyclic
and tricyclic
rings, which are optionally mono- or independently pluri substituted with any
of the groups
set forth in (aa) or (bb) and R5 is any of the groups in (aa) or (bb); or
26
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
if CR'R" is absent, then R3 is hydrogen; and R4 and R5 together with the atoms
to
which they are attached form a 4 to 8 membered cyclic, polycyclic or
heterocyclic ring
system containing I to 3 heteroatoms selected from N, 0, S, SO and SO2, and
includes
single rings, fused bicyclic and tricyclic rings, which are optionally mono-
or independently
plurisubstituted with any of the groups set forth in (dd) or (ee); provided
that when n is 1, X
is CH2, the ring containing X is saturated, and Z and R3 are hydrogen, R4 and
R5 together
are not -(CH2)2- or -(CH2)3-.
[0037] In some such embodiments, compounds of formula I have formula II:
OR'
O BOR2
H
N p t>
R24 4 1 ' )n
Y Jm ~ X
wherein:
Y is 0, S, CHR25 or NR26;
kis 0to3andmis 0to3whenYisCHR25;
k is 2 to 3 and m is 1 to 3 when Y is O or NR26
each R24 is independently:
a) hydrogen;
b) (Cl.12)alkyi; (C2.12)alkenyl; (C2.12)alkynyl; (C3.12) cycloalkyl; or (C3.
12)cycloalkenyl; where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl and
cycloalkenyl groups are
optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R12, and where the
alkyl, alkenyl,
alkynyl portions include linear or branched chains and may include cyclic
portions;
c) aryl; or heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R1Z;
d) R" (CHZ)P where R11 is 2-oxopyrrolidinyl; (C1 -6)alkoxy; phenyl;
phenoxy; (CI_a)cycloalkyl; [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety; pyridinyl;
naphthyl;
cyclohexenyl; (Ci.g)alkylcarbonyl; (C3.1Z)cycloalkylcarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl;
pyrimidinyl;
phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; phenylsulfonyl; or adamantyl; where the
cycloalkyl
ring is optionally substituted with hydroxy(Ci-6)alkyl; where the 2-
oxopyrrolidinyl, (Ci.
6)alkoxy, phenyl, pyridinyl, benzyl, benzoyl, pyrimidinyl,
phenylaminocarbonyl,
alkylsulfonyl, phenylsulfonyl, and naphthyl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
27
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
di- or independently trisubstituted with R12; where the phenoxy group is
optionally mono-
or independently disubstituted with (Ci-4)alkyl, (C,4)alkoxy, or halogen; and
where the
[3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety is optionally mono-or independently
plurisubstituted
with (Ci_$)alkyl; p is 0 to 3; and
R12 is halogen; trifluoromethyl; cyano; nitro; (C1_6)alkyl; (Ci_6)alkoxy;
cycloalkyl; carboxy; acetamido; hydroxy; hydroxy(CI_6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl;
trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; carbamoyl; sulfonamido; alkylsufonyl;
phenylsulfonyl; aryl;
heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with R';
e) (R13)2CH(CH2)y-, where R13 is phenyl; in which the phenyl groups are
independently optionally mono- or independently disubstituted with R12; and q
is 0 to 3;
f) a group of the formula:
Ris
I
R14_~N1_~ (CH2)s__4
where R14 and R15 are independently hydrogen; (CI_8)alkyl;
(CI_6)alkylcarbonyl; (C3_
1Z)cycloalkyl ring; (C3_12)cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylamino-carbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the cycloalkyl
ring is
optionally substituted with hydroxy(C1-6)alkyl, and where the benzyl, benzoyl,
pyridine,
pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R12; or R14 and R15
together form a
(C3_12)cycloalkyl ring; and s is 1 to 6; or
g) a group of the formula:
R21-O'-(CH2)t-~
where R21 is hydrogen; (Ci_g)alkyl; benzyl; or phenyl; in which the benzyl and
phenyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted on the ring with
R12; and t is 1
to 6;
R25 is:
a) hydrogen;
b) (C1_12)alkyl; (C2_12)alkenyl; (C2.12)alkynyl; (C3_12) cycloalkyl; or (C3_
1Z)cycloalkenyl; where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl and
cycloalkenyl groups are
28
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
optionally mono- or independently pluri substituted with R12, and where the
alkyl, alkenyl,
alkynyl portions include linear or branched chains and may include cyclic
portions;
c) aryl; or heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R1Z;
d) R"(CH2)P- where R" is 2-oxopyrrolidinyl; (Cl .6)alkoxy; phenyl;
phenoxy; (CI_8)cycloalkyl; [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety; pyridinyl;
naphthyl;
cyclohexenyl; (C1.8)alkylcarbonyl; (C3.12)cycloalkylcarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl;
pyrimidinyl;
phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; phenylsulfonyl; or adamantyl; where the
cycloalkyl
ring is optionally substituted with hydroxy(C1_6)alkyl; where the 2-
oxopyrrolidinyl, (Ci_
6)alkoxy, phenyl, pyridinyl, benzyl, benzoyl, pyrimidinyl,
phenylarninocarbonyl,
alkylsulfonyl, phenylsulfonyl, and naphthyl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
di- or independently trisubstituted with R12; where the phenoxy group is
optionally mono-
or independently disubstituted with (C i4)alkyl, (C 1 .4)alkoxy, or halogen;
and where the
[3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety is optionally mono-or independently
plurisubstituted
with (CI .g)alkyl; p is 0 to 3; and
R12 is halogen; trifluoromethyl; cyano; nitro; (C1.6)alkyl; (CI.6)alkoxy;
cycloalkyl; carboxy; acetamido; hydroxy; hydroxy(C1.6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl;
trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; carbamoyl; sulfonamido; alkylsufonyl;
phenylsulfonyl; aryl;
heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
pluri substituted with R7;
e) (R13)2CH(CH2)q-, where R13 is phenyl; in which the phenyl groups are
independently optionally mono- or independently disubstituted with R1z; and q
is 0 to 3;
f) a group of the fonmula:
R15
I
R14~ (CHZt ~
where R14 and R'5 are independently hydrogen; (CI _8)alkyl; (C1
.6)alkylcarbonyl; (C3.
12)cycloalkyl ring; (C3.12)cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylamino-carbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the cycloalkyl
ring is
optionally substituted with hydroxy(C1.6)alkyl, and where the benzyl, benzoyl,
pyridine,
pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with RtZ; or R14 and R15
together form a
(C3.12)cycloalkyl ring; and t is 0 to 6; or
29
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/iJS2004/037820
g) a group of the formula:
R21_O-(CN2)t-~
where R21 is hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl; benzyl; or phenyl; in which the benzyl and
phenyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted on the ring with
R12; and t is 0
to 6; and
R26 is:
a) hydrogen;
b) (C1_12)alkyl; (CZ-1z)alkenyl; (C2_12)alkynyl; (C3-iz) cycloalkyl; or (C3_
12)cycloalkenyl; where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl and
cycloalkenyl groups are
optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R12, and where the
alkyl, alkenyl,
alkynyl portions include linear or branched chains and may include cyclic
portions;
c) aryl; or heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with RIZ;
d) R27(CHZ)P-, where R27 is 2-oxopyrrolidinyI; (CI-6)alkoxy; phenyl;
phenoxy; (Ci_8)cycloalkyl; [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety; pyridinyl;
naphthyl;
cyclohexenyl; (CI_S)alkylcarbonyl; (C3_12)cycloalkylcarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl;
pyrimidinyl;
phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; phenylsulfonyl; or adamantyl; where the
cycloalkyl
ring is optionally substituted with hydroxy(C1 -6)alkyl; where the 2-
oxopyrrolidinyl, (C1
6)alkoxy, phenyl, pyridinyl, benzyl, benzoyl, pyrimidinyl,
phenylaminocarbonyl,
alkylsulfonyl, phenyisulfonyl, and naphthyl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
di- or independently trisubstituted with R1z; where the phenoxy group is
optionally mono-
or independently disubstituted with (Ci4)alkyl, (C,4)alkoxy, or halogen; and
where the
[3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety is optionally mono-or independently pluri
substituted
with (CI_g)alkyl; p is 0 to 3; and
R'Z is halogen; trifluoromethyl; cyano; nitro; (CI_6)alkyl; (CI_6)alkoxy;
cycloalkyl; carboxy; acetamido; hydroxy; hydroxy(CI_6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl;
trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; carbamoyl; sulfonamido; alkylsufonyl;
phenylsulfonyl; aryl;
heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with R';
e) (R13)2CH(CH2)q-, where R'3 is phenyl, in which the phenyl groups are
independently optionally mono- or independently disubstituted with R'Z; and q
is 0 to 3;
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
f) a group of the formula:
R15
(
R14~ (CH2)r ~
where R14 and R15 are independently hydrogen; (Ci.s)alkyl;
(C1_6)alkylcarbonyl; (C3.
1Z)cycloalkyl ring; (C3_12)cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylamino-carbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the cycloalkyl
ring is
optionally substituted with hydroxy(Ci-6)alkyl, and where the benzyl, benzoyl,
pyridine,
pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R 12; or R14 and R15
together form a
(C3_12)cycloalkyl ring; and r is 0 or 2 to 6; or
g) a group of the formula:
R21_O-(CH2)i-~
where R21 is hydrogen; (C1 _g)alkyl; benzyl; or phenyl; in which the benzyl
and phenyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted on the ring with
R12; and t is 0
or2to6.
[0038) In some embodiments of compounds of formula II, X is CH2; the ring
containing
X is saturated; and R', R2 and R25 are hydrogen. In other embodiments of
compounds of
formula II, X is CH2; the ring containing X is saturated; Rt, R2 and R 25 are
hydrogen; and
R24 is hydrogen, provided that if k, n, and m are each 1, and Y is CHR25, Z is
not H. In still
other embodiments of compounds of formula II, X is CH2; the ring containing X
is
saturated; R', R 2 and R25are hydrogen; and R24 is (Ci_12)alkyl;
(C2_12)alkenyl; (C2_12)alkynyl;
(C3_12) cycloalkyl; or (C3.12)cycloalkenyl; where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl,
cycloalkyl and
cycloalkenyl groups are optionally mono- or independently pluri substituted
with R12, and
where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl portions include linear or branched chains
and may include
cyclic portions. In some embodiments of compounds of formula II, X is CH2; the
ring
containing X is saturated; R1, R 2 and R25 are hydrogen; and R24 is phenyl
optionally mono-
or independently plurisubstituted with R1 Z
Compounds of formula II include those wherein X is CH2; the ring containing X
is
saturated; R', R 2 and R25 are hydrogen; and R24 is R" (CHZ)P- where Rt 1 is 2-
31
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
oxopyrrolidinyl; (CI.6)alkoxy; phenyl; phenoxy; (CI.8)cycloalkyl; [3.3.3)
bicyclic
carbocyclic moiety; pyridinyl; naphthyl; cyclohexenyl; (Ci.g)alkylcarbonyl;
(C3.
12)cycloalkylcarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl; pyrimidinyl; phenylaminocarbonyl;
alkylsulfonyl;
phenylsulfonyl; or adamantyl; where the cycloalkyl ring is optionally
substituted with
hydroxy(Ci.6)alkyl; where the 2-oxopyrrolidinyl, (C1.6)alkoxy, phenyl,
pyridinyl, benzyl,
benzoyl, pyrimidinyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, phenylsulfonyl, and
naphthyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di- or independently
trisubstituted with R12;
where the phenoxy group is optionally mono- or independently disubstituted
with (Ci.
4)alkyl, (C,-4)alkoxy, or halogen; and where the [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic
moiety is
optionally mono-or independently plurisubstituted with (C1.8)alkyl; p is 0 to
3; and R'Z is
halogen; trifluoromethyl; cyano; nitro; (C1.6)alkyl; (Ci.6)alkoxy; cycloalkyl;
carboxy;
acetamido; hydroxy; hydroxy(CI.6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl; trifluoromethoxy;
sulfamoyl;
carbamoyl; sulfonamido; alkylsufonyl; phenylsulfonyl; aryl; heteroaryl; where
the aryl and
heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with
R7.
[00391 In certain embodiments of compounds of formula II, X is CH2; the ring
containing X is saturated; R', R2 and R25 are hydrogen; and R24 is
(R13)2CH(CH2)q-, where
R13 is phenyl; in which the phenyl groups are independently optionally mono-
or
independently disubstituted with RIZ; and q is 0 to 3.
[00401 In other embodiments of compounds of fonnula H, X is CH2; the ring
containing
X is saturated; R', R2 and R25 are hydrogen; and R24 is a group of the
forrnula:
R15
I
R14""_N\(CH2)s-1'
where R14 and R15 are independently hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl;
(Ci_6)alkylcarbonyl; (C3.
12)cycloalkyl ring; (C3.12)cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylamino-carbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the cycloalkyl
ring is
optionally substituted with hydroxy(C1.6)alkyl, and where the benzyl, benzoyl,
pyridine,
pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R'Z; or R14 and R15
together fonn a
(C3_12)cycloalkyl ring; and s is 1 to 6.
32
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
[0041] In some embodiments of compounds of formula II, X is CH2; the ring
containing
X is saturated; Rl, R2 and R25 are hydrogen; and R24 is a group of the
formula:
R21_0-_(CH2)c-~
where R21 is hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl; benzyl; or phenyl; in which the benzyl and
phenyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted on the ring with
R1Z; and t is 1
to 6.
[00421 Compounds of formula II include those wherein X is CH2; the ring
containing X
is saturated; Rl, R 2 and R 24 are hydrogen. In some embodiments of compounds
of formula
II, X is CH2; the ring containing X is saturated; R', R2, R24 are hydrogen;
and R25 is (Cl_
iZ)alkyl; (C2.12)alkenyl; (CZ.12)alkynyl; (C3_12) cycloalkyl; or
(C3_12)cycloalkenyl; where the
alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl and cycloalkenyl groups are optionally
mono- or
independently pluri substituted with R'Z, and where the alkyl, alkenyl,
alkynyl portions
include linear or branched chains and may include cyclic portions. In other
embodiments of
compounds of formula II, X is CH2; the ring containing X is saturated; R', R2,
R24 are
hydrogen; and R25 is phenyl optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted
with R'Z.
[0043] Compounds of formula II include those wherein X is CH2; the ring
containing X
is saturated; R', R2, R24 are hydrogen; and R25 is R" (CHZ)P where R" is 2-
oxopyrrolidinyl,
(CI.6)alkoxy, phenyl; phenoxy; (C,_8)cycloalkyl; [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic
moiety;
pyridinyl; naphthyl; cyclohexenyl; or adamantyl; where the 2-oxopyrrolidinyl,
(C1.6)alkoxy,
phenyl, pyridinyl, and naphthyl groups are optionally mono- or independently
di- or
independently trisubstituted with R' Z; where the phenoxy group is optionally
mono- or
independently disubstituted with (C1.a)alkyl, (C14)alkoxy, or halogen; and
where the [3.3.3]
bicyclic carbocyclic moiety is optionally mono-or independently
plurisubstituted with (Cl.
g)alkyl; p is 0 to 3; and R12 is halogen; trifluoromethyl; cyano; nitro;
(C1_6)alkyl; (C1.
6)alkoxy; cycloalkyl; carboxy; acetamido; hydroxy; hydroxy(C,_6)alkyl;
hydroxymethyl;
trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; carbamoyl; sulfonamido; alkylsufonyl;
phenylsulfonyl; aryl;
heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with R'.
33
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
[0044] In other embodiments of compounds of formula II, X is CH2; the ring
containing
X is saturated; R', Rz, R 24 are hydrogen; and R25 is (R13)2CH(CH2)q-, where
R13 is phenyl; in
which the phenyl groups are independently optionally mono- or independently
disubstituted
with R1Z; and q is 0 to 3.
[00451 Compounds of formula H include those wherein X is CH2; the ring
containing X
is saturated; R', R2, R24 are hydrogen; and R25 is a group of the formula:
R15
I
R14~N (CH2c ~
where R' and R' 5 are independently hydrogen; (C 1 _8)alkyl; (C 1
_6)alkylcarbonyl; (C3.
1Z)cycloalkyl ring; (C3_12)cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylamino-carbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the cycloalkyl
ring is
optionally substituted with hydroxy(CI_6)alkyl, and where the benzyl, benzoyl,
pyridine,
pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenyisulfonyl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R12; or R14 and R'5
together form a
(C3.12)cycloalkyl ring; and t is 0 to 6.
[0046] In some embodiments of compounds of formula II, X is CH2; the ring
containing
X is saturated; R', R2, R24 are hydrogen; and R25 is a group of the formula:
R21-O-(CH2)--~
where R21 is hydrogen; (CI-8)alkyl; benzyl; or phenyl; in which the benzyl and
phenyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted on the ring with
R'Z; and t is 0
to 6. In other embodiments of compounds of formula II, X is CH2; the ring
containing X is
saturated; R', R2, R24 and R 26 are hydrogen. In still other embodiments of
compounds of
formula II, X is CH2; the ring containing X is saturated; R', R2, R24 are
hydrogen; and R26 is
(Cl.12)alkyl; (C2.12)alkenyl; (C2.i2)alkynyl; (C3_12) cycloalkyl; or
(C3.iZ)cycloalkenyl; where
the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl and cycloalkenyl groups are optionally
mono- or
independently pluri substituted with R12, and where the alkyl, alkenyl,
alkynyl portions
include linear or branched chains and may include cyclic portions. Compounds
of formula
II include those wherein X is CH2; the ring containing X is saturated; R', R2,
R24 are
hydrogen; and R26 is phenyl optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted
with R12.
34
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
[00471 Compounds of formula II wherein X is CH2; the ring containing X is
saturated;
R', R2, R24 are hydrogen; and R26 is RZ'(CHZ)P-, where R 27 is 2-
oxopyrrolidinyl; (Cl_
b)alkoxy; phenyl; phenoxy; (Ci_g)cycloalkyl; [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic
moiety; pyridinyl;
naphthyl; cyclohexenyl; (CI_8)alkylcarbonyl; (C3.12)cycloalkylcarbonyl;
benzyl; benzoyl;
pyrimidinyl; phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; phenylsulfonyl; or adamantyl;
where the
cycloalkyl ring is optionally substituted with hydroxy(Ci-6)alkyl; where the 2-
oxopyrrolidinyl, (CI-6)alkoxy, phenyl, pyridinyl, benzyl, benzoyl,
pyrimidinyl,
phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, phenylsulfonyl, and naphthyl groups are
optionally
mono- or independently di- or independently trisubstituted with R 12; where
the phenoxy
group is optionally mono- or independently disubstituted with (C14)alkyl,
(C14)alkoxy, or
halogen; and where the [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety is optionally mono-
or
independently plurisubstituted with (CI_g)alkyl; p is 0 to 3; and R1Z is
halogen;
tri fluoromethyl; cyano; nitro; (C1_6)alkyl; (CI_6)alkoxy; cycloalkyl;
carboxy; acetamido;
hydroxy; hydroxy(CI-6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl; trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl;
carbamoyl;
sulfonamido; alkylsufonyl; phenylsulfonyl; aryl; heteroaryl; where the aryl
and heteroaryl
groups are optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R7 ; and p
is 0 to 3.
[0048) Compounds of formula II include those wherein X is CH2; the ring
containing X
is saturated; R', RZ, R24 are hydrogen; and R26 is (R13)2CH(CH2)q-; where R13
is phenyl, in
which the phenyl groups are independently optionally mono- or independently
disubstituted
with R12; and q is 0 to 3.
[0049] In some embodiments of compounds of formula II, X is CH2; the ring
containing
X is saturated; R', RZ, R24 are hydrogen; and R26 is a group of the formula:
R15
(
R14--Nll-, (CHz)r ~
where R14 and R15 are independently hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl;
(Ci_6)alkylcarbonyl; (C3.
12)cycloalkyl ring; (C3.12)cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylamino-carbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the cycloalkyl
ring is
optionally substituted with hydroxy(C1_6)alkyl, and where the benzyl, benzoyl,
pyridine,
pynmidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl
groups are
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R1Z; or R14 and R15
together form a
(C3_12)cycloalkyl ring; and r is 0 or 2 to 6.
100501 In other embodiments of compounds of formula H, X is CH2; the ring
containing
X is saturated; R1, R2 , R24 are hydrogen; and R26 is a group of the formula:
R2'-O-1CH2)t-~
where R21 is hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl; benzyl; or phenyl; in which the benzyl and
phenyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted on the ring with
R12; and t is 0
or 2 to 6.
[00511 Compounds of formula II include those that have the formula:
OR'
O B-OR2
H
N
N \
R24 /}
n
m
R25
In some such embodiments, R25 is phenyl optionally mono- or independently
plurisubstituted with R12.
(0052] In other embodiments of compounds of formula II, the compound has the
formula:
OR'
0 B-ORZ
H
N
n
Ll
N
I
R26
36
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
[0053] Compounds of formula II also include those that have the formula:
OR'
O B-ORZ
H
N
N
L
/- X Jn
Z
R29
R28
wherein:
R28 and R29 are each independently hydrogen, hydroxy, alkyl, alkoxy, aryloxy,
or
halogen.
[00541 In some embodiments of compounds of formula I wherein CR'R" is present,
the
compound has formula III:
OR'
H O B-OR1
RN l-~) (III)
R2 k Y Z'X n
~m
ewherein:
Y is 0, S, CHR25 or NR26;
kisOto3andmisOto3whenYisCHRzs;
k is 1 to 3 and m is O to 3 when Y is NRZ6;
kisl to3andmisOto3whenYisO;
R is
a) hydrogen;
b) (C1.12)alkyl; (C2.12)alkenyl; (C2_12)alkynyl; (C3_12) cycloalkyl; or (C3.
1Z)cycloalkenyl; where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl and
cycloalkenyl groups are
optionally mono- or independently pluri substituted with R6, and where the
alkyl, alkenyl,
alkynyl portions include linear or branched chains and may include cyclic
portions;
R6 is (CI.6)alkyl; (C1_6)alkoxy; cycloalkyl; carboxy; acetamido; cyano; nitro;
halogen; hydroxy; hydroxy(Ci.6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl; trifluoromethyl;
trifluoromethoxy;
sulfamoyl; sulfonamido; carbamoyl; aryl; heteroaryl; where the aryl and
heteroaryl groups
37
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
are optionally mono- or independently pluri substituted with R7 ; amino, where
the amino
group is optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R8; -SOR8; -
S02R8; -
CORB; -C02R8, -CONHRB; -CON(R8) 2; -OR8; or -S-R8;
R7 is halogen; (CI_io)alkyl; (Cl.lo)alkoxy; (Cl_io)alkylamino; (Ci_io)
dialkylamino; benzyl; benzyloxy; hydroxyl(C1_6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl; nitro;
trifluoromethyl; trifluoromethoxy; trifluoromethylthio; N-hydroxyimino; cyano;
carboxy;
acetamido; hydroxy; sulfamoyl; sulfonamido; or carbamoyl;
R8 is (C,_1o)alkyl; (C2.1o)alkenyl; (C2_1o)alkynyl; (C3_10)cycloalkyl; (C5_
Io)cycloalkenyl; benzyl; phenethyl; aryl; or heteroaryl; where the alkyl,
alkenyl, alkynyl,
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl groups are optionally mono- or independently
plurisubstituted with
aryl or heteroaryl where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono-
or
independently plurisubstituted with R7 ; and where the aryl and heteroaryl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R7;
c) aryl optionally fused to a(C3_Io)cycloalkyl; or heteroaryl optionally fused
to a(C3_io)cycloalkyl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally
mono- or
independently plurisubstituted with R7;
d) indanyl; 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthyl; (CH2)jadamantyl in which j is 0-3; or
a[2.2.1] or [3.1.1] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety, including (4-
pentylbicyclo[2.2.2]oct-1-
yl)amine; where the indanyl, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthyl, (CHZ)j adamantyl, and
[2.2.1] or
[3.1.1] bicyclic carbocyclic moieties are optionally mono- or independently
plurisubstituted
with hydroxy, (Ci-g)alkyl, (Ci-g)alkoxy, (C1_8)alkanoyloxy, or R9R10N-CO-O-,
where R9 and
R10 are independently (C1 _g)alkyl, or phenyl, where the alkyl and phenyl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with (Ci_g)alkyl,
(C1_8)alkoxy, halogen,
or trifluoromethyl, or R9 and Rlo together are (C3_6)alkylene;
e) R' 1 (CHZ)p- where R" is 2-oxopyrrolidinyl; (CI_6)alkoxy; phenyl;
phenoxy; (Ci.8)cycloalkyl; [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety; pyridinyl;
naphthyl;
cyclohexenyl; or adamantyl; where the 2-oxopyrrolidinyl, (C!_6)alkoxy, phenyl,
pyridinyl,
and naphthyl groups are optionally mono- or independently di- or independently
trisubstituted with R1Z; where the phenoxy group is optionally mono- or
independently
disubstituted with (C1.4)alkyl, (C14)alkoxy, or halogen; and where the [3.3.3]
bicyclic
carbocyclic moiety is optionally mono-or independently pluri substituted with
(Ci_g)alkyl;
and p is 0 to 3;
38
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
R12 is halogen; trifluoromethyl; cyano; nitro; (CI_6)alkyl; (Ci_6)alkoxy;
cycloalkyl; carboxy; acetamido; hydroxy; hydroxy(Ci_6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl;
tnfluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; carbamoyl; sulfonamido; alkylsufonyl;
phenylsulfonyl; aryl;
heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with R7;
f) (R13)2CH(CHZ)y-, where R13 is phenyl; in which the phenyl groups are
independently optionally mono- or independently disubstituted with R1Z; and q
is 0 to 3;
g) a group of the formula:
R15
R14~ (CH2)r_~
where R14 and R15 are independently hydrogen; (CI_g)alkyl; (CI_
6)alkylcarbonyl; (C3_12)cycloalkyl ring; (C3_12)cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl;
benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl; phenylamino-carbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl;
where the
cycloalkyl ring is optionally substituted with hydroxy(Ci_6)alkyl, and where
the benzyl,
benzoyl, pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and
phenylsulfonyl groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted
with R'Z; or R, 4
and R15 together form a(C3_12)cycloalkyl ring; and r is 2 to 6;
h) a group of the formula:
R17
I
R16 ~(CHZ)S
where R16 and R17 are each independently hydrogen; (CI_g)alkyl; (Cl_
6)alkylcarbonyl; di-(Ci_6)alkylaminocarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine;
phenyl; phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the
benzyl, benzoyl,
pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and
phenylsulfonyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R12; or R16
and R'7
together form a(C3_1Z)cycloalkyl ring; and s is I to 6;
39
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
i) a group of the formula:
(CH2)t-~
19
R \
N(CH) )u
R18
where R18 and R19 are independently hydrogen; (CI_8)alkyl; (Ci_
6)alkylcarbonyl; di-(C)_6)alkylaminocarbonyl; benzyl; benzothiazole; benzoyl;
pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl; phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl;
where the
benzyl, benzoyl, benzothiazole, pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl,
phenylaminocarbonyl,
alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl groups are optionally mono- or independently
di-
substituted with R1z; or R18 and R' 9 together form a(C3_iZ)cycloalkyl ring;
each t is
independently 0 to 6; and u is 0 to 3;
j) a group of the formula:
(phenyl-CH2-C(CH3) 2-),
where the phenyl group is optionally mono- or independently
plurisubstituted with R1z;
k) a group of the formula:
R20 ~(CH2)s~3 ~(CH2)t~~ Ry~ ~(CH2)i 1
N or R20_N or ~
Ry~ / u Ry ~ u I20 ~ tJ
R
where R20 is hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl; (CI-6)atkylcarbonyl; di-
(Cl.6)alkylaminocarbonyl; (C3.
g)cycloalkylcarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl; (C1_6)alkyloxycarbonyl;
arlkyloxycarbonyl, pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl; phenyl substituted thiazole ring; phenylaminocarbonyl;
alkylsulfonyl;
or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl, benzoyl, pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl,
phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl groups are optionally
mono- or
independently di-substituted with R'Z; R,, is hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl; (C3_12)
cycloalkyl;
benzyl; phenyl; where the benzyl and phenyl, groups are optionally mono- or
independently
di-substituted on the ring with R12; Ry is absent or is halogen, (C1.8)alkyl,
(CI_$)alkoxy,
0-alkylcarboxylate, 0-aralkylcarboxylate, N-alkylcarboxamido, N-
aralkylcarboxamido; or
phenyl;
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCTIUS2004/037820
sis 1 to6;tisOto6;anduisOto3;or
1) a group of the formula:
(CH2)i ~
R2t_0-(CHP)t )u
where RZ1 is hydrogen; (C,_$)alkyl; benzyl; or phenyl; in which the benzyl
and phenyl groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted on the
ring with
R'Z; each t is independently 0 to 6; and u is 0 to 3;
each R24 is independently:
a) hydrogen;
b) (C1_12)alkyl; (C2.12)alkenyl; (C2_12)alkynyl; (C3_12) cycloalkyl; or (C3_
12)cycloalkenyl; where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl and
cycloalkenyl groups are
optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R'Z, and where the
alkyl, alkenyl,
alkynyl portions include linear or branched chains and may include cyclic
portions;
c) aryl; or heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R1z;
d) R' l(CHZ)p- where R" is 2-oxopyrrolidinyl; (C1_6)alkoxy; phenyl;
phenoxy; (C1_8)cycloalkyl; [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety; pyridinyl;
naphthyl;
cyclohexenyl; (Cj_8)alkylcarbonyl; (C3_12)cycloalkylcarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl;
pyrimidinyl;
phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; phenylsulfonyl; or adamantyl; where the
cycloalkyl
ring is optionally substituted with hydroxy(C1 _6)alkyl; where the 2-
oxopyrrolidinyl, (C,_
6)alkoxy, phenyl, pyridinyl, benzyl, benzoyl, pyrimidinyl,
phenylaminocarbonyl,
alkylsulfonyl, phenylsulfonyl, and naphthyl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
di- or independently trisubstituted with R12; where the phenoxy group is
optionally mono-
or independently disubstituted with (Ci4)alkyl, (CI_4)alkoxy, or halogen; and
where the
[3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety is optionally mono-or independently pluri
substituted
with (C1_8)alkyl; p is 0 to 3; and
R12 is halogen; trifluoromethyl; cyano; nitro; (C1_6)alkyl; (CI-6)alkoxy;
cycloalkyl; carboxy; acetamido; hydroxy; hydroxy(C1_6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl;
trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; carbamoyl; sulfonamido; alkylsufonyl;
phenylsulfonyl; aryl;
heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with R7;
41
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
e) (R13)ZCH(CH2)q-, where R'3 is phenyl; in which the phenyl groups are
independently optionally mono- or independently disubstituted with R12; and q
is 0 to 3;
f) a group of the formula:
R's
I
R14.."1N1,, (CH2)S_~
where R14 and R15 are independently hydrogen; (Cl.B)alkyl;
(Ci_6)alkylcarbonyl; (C3.
1Z)cycloalkyl ring; (C3_12)cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylamino-carbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the cycloalkyl
ring is
optionally substituted with hydroxy(CI.6)alkyl, and where the benzyl, benzoyl,
pyridine,
pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R'Z; or R14 and R'5
together form a
(C3.12)cycloalkyl ring; and s is 0 to 6; or
g) a group of the formula:
R21_O--(CH2)c-~
where R21 is hydrogen; (Ci.8)alkyl; benzyl; or phenyl; in which the benzyl and
phenyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted on the ring with
R1z; and t is 0
to 6;
R25 is:
a) hydrogen;
b) (CI_12)alkyl; (C2_12)alkenyl; (C2.12)alkynyl; (C3.12) cycloalkyl; or (C3_
12)cycloalkenyl; where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl and
cycloalkenyl groups are
optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R'Z, and where the
alkyl, alkenyl,
alkynyl portions include linear or branched chains and may include cyclic
portions;
c) aryl; or heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R12;
d) R" (CHZ)P where R" is 2-oxopyrrolidinyl; (Ci.6)alkoxy; phenyl;
phenoxy; (Ci_B)cycloalkyl; [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety; pyridinyl;
naphthyl;
cyclohexenyl; (C,.B)alkylcarbonyl; (C3_12)cycloalkylcarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl;
pyrimidinyl;
phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; phenylsulfonyl; or adamantyl; where the
cycloalkyl
ring is optionally substituted with hydroxy(C1_6)alkyl; where the 2-
oxopyrrolidinyl, (Cl.
6)alkoxy, phenyl, pyridinyl, benzyl, benzoyl, pyrimidinyl,
phenylaminocarbonyl,
42
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
alkylsulfonyl, phenylsulfonyl, and naphthyl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
di- or independently trisubstituted with R' 2; where the phenoxy group is
optionally mono-
or independently disubstituted with (CI-4)alkyl, (Ci.a)alkoxy, or halogen; and
where the
[3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety is optionally mono-or independently pluri
substituted
with (C1.8)alkyl; p is 0 to 3; and
R'Z is halogen; trifluoromethyl; cyano; nitro; (Ci-6)alkyl; (Ci-6)alkoxy;
cycloalkyl; carboxy; acetamido; hydroxy; hydroxy(C1_6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl;
trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; carbamoyl; sulfonamido; alkylsufonyl;
phenylsulfonyl; aryl;
heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with R7;
e) (R13)2CH(CH2)y-, where R13 is phenyl; in which the phenyl groups are
independently optionally mono- or independently disubstituted with R1z; and q
is 0 to 3;
f j a group of the formula:
R15
I
R~a~ (CH2)t ~
where R14 and R15 are independently hydrogen; (C1 _g)alkyl; (C1 -
6)alkylcarbonyl; (C3.
12)cycloalkyl ring; (C3.12)cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine=,
pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylamino-carbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the cycloalkyl
ring is
optionally substituted with hydroxy(CI -6)alkyl, and where the benzyl,
benzoyl, pyridine,
pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylstilfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R'Z; or R14 and R'S
together form a
(C3.12)cycloalkyl ring; and t is 0 to 6; or
g) a group of the formula:
R27-O-(CHZ),-~
where R21 is hydrogen; (C1.8)alkyl; benzyl; or phenyl; in which the benzyl and
phenyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted on the ring with
R'Z; and t is 0
to 6; and
R26 is:
a) hydrogen;
b) (C,_,Z)alkyl; (C2_12)alkenyl; (C2.12)alkynyl; (C3_12) cycloalkyl; or (C3.
12)cycloalkenyl; where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl and
cycloalkenyl groups are
43
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R12, and where the
alkyl, alkenyl,
alkynyl portions include linear or branched chains and may include cyclic
portions;
c) aryl; or heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R12;
d) R27(CHz)p-, where R27 is 2-oxopyrrolidinyl; (C1.6)alkoxy; phenyl;
phenoxy; (Ct.g)cycloalkyl; [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety; pyridinyl;
naphthyl;
cyclohexenyl; (Cl.8)alkylcarbonyl; (C3_12)cycloalkylcarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl;
pyrimidinyl;
phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; phenylsulfonyl; or adamantyl; where the
cycloalkyl
ring is optionally substituted with hydroxy(CI_6)alkyl; where the 2-
oxopyrrolidinyl, (Ci_
6)alkoxy, phenyl, pyridinyl, benzyl, benzoyl, pyrimidinyl,
phenylaminocarbonyl,
alkylsulfonyl, phenylsulfonyl, and naphthyl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
di- or independently trisubstituted with R12; where the phenoxy group is
optionally mono-
or independently disubstituted with (CI-4)alkyl, (Ci.4)alkoxy, or halogen; and
where the
[3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety is optionally mono-or independently
plurisubstituted
with (C1_8)alkyl; p is 0 to 3; and
R1z is halogen; trifluoromethyl; cyano; nitro; (CI-6)alkyl; (CI .6)alkoxy;
cycloalkyl; carboxy; acetamido; hydroxy; hydroxy(Ci.6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl;
trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; carbamoyl; sulfonamido; alkylsufonyl;
phenylsulfonyl; aryl;
heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with R7;
e) (R' 3)ZCH(CHZ)q-, where R13 is phenyl, in which the phenyl groups are
independently optionally mono- or independently disubstituted with R'Z; and q
is 0 to 3;
f) a group of the formula:
R15
I
R14-- N~(CH2)r ~
where R14 and R15 are independently hydrogen; (Cl.g)alkyl;
(Ci.6)alkylcarbonyl; (C3.
12)cycloalkyl ring; (C3.12)cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylamino-carbonyl; cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylamino-carbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the cycloalkyl
ring is
optionally substituted with hydroxy(C1_6)alkyl, and where the benzyl, benzoyl,
pyridine,
pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl
groups are
44
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R'Z; or R14 and R' 5
together form a
(C3_12)cycloalkyl ring; and r is 0 or 2 to 6; or
g) a group of the formula:
R21-0-(CH2)t-~
where RZ' is hydrogen; (C I _8)alkyl; benzyl; or phenyl; in which the benzyl
and phenyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted on the ring with
R'Z; and t is 0
or 2 to 6.
[0055] Compounds of formula III include those wherein X is CH2; the ring
containing X
is saturated; and R', R2 and R25 are hydrogen; those wherein X is CH2; the
ring containing X
is saturated; R', R 2 and R25 are hydrogen; and R24 is hydrogen; and those
wherein X is CH2;
the ring containing X is saturated; R', R2 and R25 are hydrogen; and R24 is
(CI_12)alkyl; (C2_
lZ)alkenyl; (C2.12)alkynyl; (C3.12) cycloalkyl; or (C3.12)cycloalkenyl; where
the alkyl,
alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl and cycloalkenyl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with R12, and where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl portions
include linear or
branched chains and may include cyclic portions.
[0056] In some embodiments of compounds of formula III, X is CH2; the ring
containing
X is saturated; R', R2 and R25 are hydrogen; and R24 is phenyl optionally mono-
or
independently plurisubstituted with R12. In other embodiments, X is CH2; the
ring
containing X is saturated; R', R2 and R25 are hydrogen; and R24 is R"(CHZ)P-
where Rt I is
2-oxopyrrolidinyl, (CI_6)alkoxy, phenyl; phenoxy; (Ci_8)cycloalkyl; [3.3.3]
bicyclic
carbocyclic moiety; pyridinyl; naphthyl; cyclohexenyl; or adamantyl; where the
2-
oxopyrrolidinyl, (Ct.6)alkoxy, phenyl, pyridinyl, and naphthyl groups are
optionally mono-
or independently di- or independently trisubstituted with R12; where the
phenoxy group is
optionally mono- or independently disubstituted with (CI-0)alkyl, (Ci
A)alkoxy, or halogen;
and where the [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety is optionally mono-or
independently
plurisubstituted with (Ci_8)alkyl; p is 0 to 3; and R12 is halogen;
trifluoromethyl; cyano;
nitro; (CI_6)alkyl; (C1.6)alkoxy; cycloalkyl; carboxy; acetamido; hydroxy;
hydroxy(Ci.
6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl; trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; carbamoyl; sulfonamido;
alkylsufonyl; phenylsulfonyl; aryl; heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R7. In still other
embodiments, X
is CH2; the ring containing X is saturated; R', R 2 and R25 are hydrogen; and
R24 is
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
(R13)2CH(CH2)q-, where R13 is phenyl; in which the phenyl groups are
independently
optionally mono- or independently disubstituted with R'2; and q is 0 to 3.
100571 Compounds of formula III include those wherein X is CH2; the ring
containing X
is saturated; R', R 2 and R25 are hydrogen; and R 24 is a group of the
formula:
R15
I
R1(CH2)s _~-
where R14 and R' 5 are independently hydrogen; (C1_g)alkyl; (Ct-
6)alkylcarbonyl; (C3_
12)cycloalkyl ring; (C3_12)cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylamino-carbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the cycloalkyl
ring is
optionally substituted with hydroxy(Ci-6)alkyl, and where the benzyl, benzoyl,
pyridine,
pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R12; or R14 and R15
together form a
(C3.12)cycloalkyl ring; and s is I to 6.
[00581 Compounds of formula III also include those wherein X is CH2; the ring
containing X is saturated; R1, R2 and R25 are hydrogen; and R24 is a group of
the fonnula:
R2'_O-(CHz)t-~
where R21 is hydrogen; (CI _g)alkyl; benzyl; or phenyl; in which the benzyl
and phenyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted on the ring with
R12; and t is 0
to 6.
[0059] In some embodiments of compounds of formula III, X is CH2; the ring
containing
X is saturated; R', R2 and R24 are hydrogen. In other embodiments, X is CH2i
the ring
containing X is saturated; R1, R2, R 24 are hydrogen; and R25 is (Ct.1Z)alkyl;
(C2.12)alkenyl;
(C2.12)alkynyl; (C3_12) cycloalkyl; or (C3.12)cycloalkenyl; where the alkyl,
alkenyl, alkynyt,
cycloalkyl and cycloalkenyl groups are optionally mono- or independently
plurisubstituted
with R12, and where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl portions include linear or
branched chains
and may include cyclic portions. In still other embodiments, X is CH2; the
ring containing
X is saturated; R', R2, R24 are hydrogen; and R25 is phenyl optionally mono-
or
independently plurisubstituted with R12.
46
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
[0060] In some embodiments of compounds of formula III, X is CH2; the ring
containing
X is saturated; R~, RZ, R24 are hydrogen; and Rz5 is R" (CH2)P- where R' I is
2-
oxopyrrolidinyl, (Ci_6)alkoxy, phenyl; phenoxy; (C1_8)cycloalkyl; [3.3.3]
bicyclic
carbocyclic moiety; pyridinyl; naphthyl; cyclohexenyl; or adamantyl; where the
2-
oxopyrrolidinyl, (C1.6)alkoxy, phenyl, pyridinyl, and naphthyl groups are
optionally mono-
or independently di- or independently trisubstituted with R12; where the
phenoxy group is
optionally mono- or independently disubstituted with (Cl-4)alkyl, (C1
4)alkoxy, or halogen;
and where the [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety is optionally mono-or
independently
plurisubstituted with (C1_8)alkyl; p is 0 to 3; and R 12 is halogen;
trifluoromethyl; cyano;
nitro; (C1_6)alkyl; (CI-6)alkoxy; cycloalkyl; carboxy; acetamido; hydroxy;
hydroxy(Cl_
6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl; trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; carbamoyl; sulfonamido;
alkylsufonyl; phenylsulfonyl; aryl; heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R7.
[0061] In other embodiments of compounds of formula III, X is CH2; the ring
containing
X is saturated; R', R2, R 24 are hydrogen; and R25 is (R13)2CH(CH2)y-, where
R13 is phenyl; in
which the phenyl groups are independently optionally mono- or independently
disubstituted
with R'Z; and q is 0 to 3. In still other embodiments, X is CH2; the ring
containing X is
saturated; R', R2, R24 are hydrogen; and R25 is a group of the fonmula:
R15
(
R14~ (CH2)c ~
where R14 and R15 are independently hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl; (C1
_6)alkylcarbonyl; (C3_
1Z)cycloalkyl ring; (C3.iz)cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylamino-carbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the cycloalkyl
ring is
optionally substituted with hydroxy(Ci_6)alkyl, and where the benzyl, benzoyl,
pyridine,
pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R12; or R14 and R15
together form a
(C3_12)cycloalkyl ring; and t is 0 to 6.
[0062] In certain embodiments of compounds of formula III, X is CH2; the ring
containing X is saturated; R', R2, R24 are hydrogen; and R25 is a group of the
formula:
47
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCTIUS2004/037820
R21-O-'(CH2)t ~
where R21 is hydrogen; (CI.8)alkyl; benzyl; or phenyl; in which the benzyl and
phenyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted on the ring with
R1z; and t is 0
to 6.
[0063] In some embodiments of compounds of formula III, X is CH2; the ring
containing
X is saturated; R', R2, R24 and R26 are hydrogen. In other embodiments, X is
CH2; the ring
containing X is saturated; R', R2, R24 are hydrogen; and R26 is (C1_12)alkyl;
(C2_12)alkenyl;
(C2_12)alkynyl; (C3_12) cycloalkyl; or (C3_12)cycloalkenyl; where the alkyl,
alkenyl, alkynyl,
cycloalkyl and cycloalkenyl groups are optionally mono- or independently
plurisubstituted
with R12, and where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl portions include linear or
branched chains
and may include cyclic portions. In yet other embodiments, X is CH2; the ring
containing X
is saturated; R', R 2, R24 are hydrogen; and R26 is phenyl optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with R12
.
Compounds of formula III include those wherein X is CHi; the ring containing X
is
saturated; R', R2, R24 are hydrogen; and R26 is R27(CH2)P , where R27 is 2-
oxopyrrolidinyl;
(C1.6)alkoxy; phenyl; phenoxy; (Cl.g)cycloalkyl; [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic
moiety;
pyridinyl; naphthyl; cyclohexenyl; (C1.8)alkylcarbonyl;
(C3.12)cycloalkylcarbonyl; benzyl;
benzoyl; pyrimidinyl; phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; phenylsulfonyl; or
adamantyl;
where the cycloalkyl ring is optionally substituted with hydroxy(CI-6)alkyl;
where the 2-
oxopyrrolidinyl, (Ci.6)alkoxy, phenyl, pyridinyl, benzyl, benzoyl,
pyrimidinyl,
phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, phenylsulfonyl, and naphthyl groups are
optionally
mono- or independently di- or independently trisubstituted with R12; where the
phenoxy
group is optionally mono- or independently disubstituted with (C,.4)alkyl,
(CIA)alkoxy, or
halogen; and where the [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety is optionally mono-
or
independently plurisubstituted with (C1_8)alkyl; p is 0 to 3; and R12 is
halogen;
trifluoromethyl; cyano; nitro; (CI-6)alkyl; (Cl.6)alkoxy; cycloalkyl; carboxy;
acetamido;
hydroxy; hydroxy(CI-6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl; trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl;
carbamoyl;
sulfonamido; alkylsufonyl; phenylsulfonyl; aryl; heteroaryl; where the aryl
and heteroaryl
groups are optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R7; and p
is 0 to 3. In
some embodiments of compounds of formula III, X is CH2; the ring containing X
is
saturated; R', R2, R24 are hydrogen; and R26 is (R'3 )2CH(CH2)q-; where Rt3 is
phenyl, in
48
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
which the phenyl groups are independently optionally mono- or independently
disubstituted
withR12;andqisOto3.
[0064] Compounds of formula III include those wherein X is CH2; the ring
containing X
is saturated; R', R2, R24 are hydrogen; and R26 is a group of the formula:
R15
I
R14'N (CH2)r ~
where R14 and R15 are independently hydrogen; (Ci.$)alkyl;
(Ci_6)alkylcarbonyl; (C3.
12)cycloalkyl ring; (C3-1z)cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylamino-carbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the cycloalkyl
ring is
optionally substituted with hydroxy(CI_6)alkyl, and where the benzyl, benzoyl,
pyridine,
pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R12; or R14 and R15
together form a
(C3_12)cycloalkyl ring; and r is 0 or 2 to 6.
[0065] Compounds of formula III also include those wherein X is CH2; the ring
containing X is saturated; Rt, R2, R24 are hydrogen; and R26 is a group of the
formula:
R27-0-(CHZ)t-~
where R21 is hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl; benzyl; or phenyl; in which the benzyl and
phenyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted on the ring with
R12; and t is 0
or 2 to 6.
100661 In some embodiments of compounds of formula I, CR'R" is present. In
other
embodiments of compounds of formula I where CR'R" is present, the compound has
formula IVA or IVB:
R'O R'O
0 B-OR2 0 B-ORZ
H2N H2N
N N
R- R-
z Z
(IVA) (IVB)
49
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
wherein
Ris
a) hydrogen;
b) (CI_12)alkyl; (C2_12)alkenyl; (C2_12)alkynyl; (C3_12) cycloalkyl; or (C3_
i2)cycloalkenyl; where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl and
cycloalkenyl groups are
optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R'Z, and where the
alkyl, alkenyl,
alkynyl portions include linear or branched chains and may include cyclic
portions;
c) aryl; or heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R12;
d) R"(CHZ)P where R" is 2-oxopyrrolidinyl; (Ci-6)alkoxy; phenyl;
phenoxy; (CI _g)cycloalkyl; [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety; pyridinyl;
naphthyl;
cyclohexenyl; or adamantyl; where the 2-oxopyrrolidinyl, (CI.6)alkoxy, phenyl,
pyridinyl,
and naphthyl groups are optionally mono- or independently di- or independently
trisubstituted with R12; where the phenoxy group is optionally mono- or
independently
disubstituted with (Ci.4)alkyl, (C1_4)alkoxy, or halogen; and where the
[3.3.3] bicyclic
carbocyclic moiety is optionally mono-or independently plurisubstituted with
(CI_g)alkyl; p
is 0 to 3; and
R12 is halogen; trifluoromethyl; cyano; nitro; (CI-6)alkyl; (CI-6)alkoxy;
cycloalkyl; carboxy; acetamido; hydroxy; hydroxy(CI-6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl;
trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; carbamoyl; sulfonamido; alkylsufonyl;
phenylsulfonyl; aryl;
heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with R7;
e) (R13)2CH(CH2)q-, where R13 is phenyl; in which the phenyl groups are
independently optionally mono- or independently disubstituted with R12; and q
is 0 to 3;
f) a group of the formula:
R15
I
R14~-N -,, (CH2)s-~'
where R14 and R15 are independently hydrogen; (C1 _8)alkyl; (C1
_6)alkylcarbonyl; (C3.
1Z)cycloalkyl ring; (C3.12)cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylamino-carbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the cycloalkyl
ring is
optionally substituted with hydroxy(Ci.6)alkyl, and where the benzyl, benzoyl,
pyridine,
pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl
groups are
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R1Z; or R14 and R15
together form a
(C3_12)cycloalkyl ring; and s is 0 to 6; or
g) a group of the formula:
R2'_.O-(CHA-~
where RZ1 is hydrogen; (CI_$)alkyl; benzyl; or phenyl; in which the benzyl and
phenyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted on the ring with
R1Z; and t is 0
to 6;
[0067] It has further been discovered that certain boronic acid compounds of
the
invention can exist as either linear or cyclic isomers. Typically, such
compounds form an
equilibrium mixture in aqueous solution. As shown in Figure 1, the
concentration of the
two isomers of such compounds is typically pH dependent. Thus, it is expected
that such
inventive compounds will exist as a mixture of linear and cyclic isomers in
vivo. Moreover,
the cyclic forms of inventive compounds may serve as novel, orally available
prodrugs.
Hence, in this aspect of the invention, there are provided compounds that have
the formula
VA, VB, or a mixture thereof:
R5 H
R3 OR' R3 1/ OR'
R5HN R4 L,.-0R2 R ~ I/ORZ
O N y)n O N )n
L,
X
Z Z
VA VB
including all enantiomers, diastereoisomers, solvates, hydrates and
pharmaceutically
acceptable salts thereof, wherein:
n is l to 3;
X is CHZ; S; 0; CF2 or C(CH3)2;
Z is H; halogen; hydroxyl; (Ci.6)alkoxy; (Cl.iZ)alkyl; (C3_12)cycloalkyl;
phenyl; or
heteroaryl; where the phenyl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
pluri substituted with R7;
51
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCTIUS2004/037820
optionally, X together with an adjacent ring carbon and Z form a fused
cyclopropyl;
and
optionally, one of the bonds in the ring containing X is a double bond;
R' and R2 independently or together are hydrogen; a boronic acid protecting
group;
or a group capable of being hydrolyzed to a hydroxyl group in an aqueous
solution at
physiological pH or in biological fluids;
R3, R4 and R5 are selected from (dd) or (ee):
(dd) R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and
R5 is
a) hydrogen, provided that R5 is not hydrogen when n is 1, X
is CHz, and Z is H;
b) (Ci.12)alkyl; (C2_12)alkenyl; (C2_12)alkynyl; (C3_12)
cycloalkyl; or (C3_12)cycloalkenyl; where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl,
cycloalkyl and
cycloalkenyl groups are optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted
with R6, and
where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl portions include linear or branched chains
and may include
cyclic portions;
R6 is (C1_6)alkyl; (CI-6)alkoxy; cycloalkyl; carboxy;
acetamido; cyano; nitro; halogen; hydroxy; hydroxy(CI-6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl;
trifluoromethyl; trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; sulfonamido; carbamoyl; aryl;
heteroaryl;
where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or independently
pluri substituted
with R'; amino, where the amino group is optionally mono- or independently
plurisubstituted with R8; -SORB; -S02R8; -CORB; -COZRg, -CONHRB; -CON(R8) 2; -
OR 8; or
-S-R8;
R7 is halogen; (CI_Io)alkyl; (CI_1o)alkoxy; (Cl.lo)alkylamino;
(CI_1o) dialkylamino; benzyl; benzyloxy; hydroxyl(CI_6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl;
nitro;
trifluoromethyl; trifluoromethoxy; trifluoromethylthio; N-hydroxyimino; cyano;
carboxy;
acetamido; hydroxy; sulfamoyl; sulfonamido; or carbamoyl;
R8 is (Ct_io)alkyl; (C2.1o)alkenyl; (C2_1o)alkynyl; (C3.
io)cycloalkyl; (C5_10)cycloalkenyl; benzyl; phenethyl; aryl; or heteroaryl;
where the alkyl,
alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with aryl or heteroaryl where the aryl and heteroaryl groups
are optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R7 ; and where the aryl and
heteroaryl groups
are optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R7;
52
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
c) aryl optionally fused to a(C3_10)cycloalkyl; or heteroaryl
optionally fused to a(C3.i )cycloalkyl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups
are optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R7;
d) indanyl; 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthyl; (CHZ)jadamantyl in
which j is 0-3; or a[2.2.1] or [3.1.1] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety, including
(4-
pentylbicyclo[2.2.2]oct-1-yl)amine; where the indanyl, 1,2,3,4-
tetrahydronaphthyl, (CHZ)j
adamantyl, and [2.2.1 ] or [3.1.1 ] bicyclic carbocyclic moieties are
optionally mono- or
independently plurisubstituted with hydroxy, (C1-8)alkyl, (C1.8)alkoxy, (CI
.8)alkanoyloxy, or
R9R10N-CO-O-, where R9 and Rl0 are independently (C1_8)alkyl, or phenyl, where
the alkyl
and phenyl groups are optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with
(CI_8)alkyl,
(C1_8)alkoxy, halogen, or trifluoromethyl, or R9 and R'0 together are
(C3.6)alkylene;
e) R"(CH2)P- where R" is 2-oxopyrrolidinyl; (Ci.6)alkoxy;
phenyl; phenoxy; (C1.8)cycloalkyl; [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety;
pyridinyl; naphthyl;
cyclohexenyl; or adamantyl; where the 2-oxopyrrolidinyl, (CI-6)alkoxy, phenyl,
pyridinyl,
and naphthyl groups are optionally mono- or independently di- or independently
trisubstituted with R12; where the phenoxy group is optionally mono- or
independently
disubstituted with (C,4)alkyl, (Ci4)alkoxy, or halogen; and where the [3.3.3]
bicyclic
carbocyclic moiety is optionally mono-or independently plurisubstituted with
(Ci_8)alkyl;
and p is 0 to 3;
R12 is halogen; trifluoromethyl; cyano; nitro; (CI.6)alkyl;
(Ci.6)alkoxy; cycloalkyl; carboxy; acetamido; hydroxy; hydroxy(Ci-6)alkyl;
hydroxymethyl;
trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; carbamoyl; sulfonamido; alkylsufonyl;
phenylsulfonyl; aryl;
heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with R7;
f) (R13)2CH(CH2)q-, where R'3 is phenyl; in which the phenyl
groups are independently optionally mono- or independently disubstituted with
R12; and q is
O to 3;
g) a group of the formula:
Ris
I
R14~ (CH2)r-~'
where R14 and R15 are independently hydrogen; (CI_g)alkyl; (CI-
6)alkylcarbonyl; (C3.
12)cycloalkyl ring; (C3.12)cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl;
53
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
phenylamino-carbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the cycloalkyl
ring is
optionally substituted with hydroxy(Cl-6)alkyl, and where the benzyl, benzoyl,
pyridine,
pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R1z; or R14 and R15
together form a
(C3_12)cycloalkyl ring; and r is 2 to 6;
h) a group of the fonnula:
R17
R16'N"'(CH'
z)s
where R16 and R" are each independently hydrogen; (C1.8)alkyl; (Ci-
6)alkylcarbonyl; di-(Cl_
6)alkylaminocarbonyI; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine; pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl,
benzoyl,
pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and
phenylsulfonyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R 12; or R16
and R'7
together form a(C3_12)cycloalkyl ring; and s is I to 6;
i) a group of the formula:
(CH2)i ~
R 19
N-(CH2j u
R~$
where R18 and R19 are independently hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl; (CI-
6)alkylcarbonyl; di-(Ci_
6)alkylaminocarbonyl; benzyl; benzothiazole; benzoyl; pyridine; pyrimidine;
phenyl;
phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl;; where the benzyl,
benzoyl,
benzothiazole, pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl,
alkylsulfonyl, and
phenylsulfonyl groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted
with R12; or R18
and R19 together form a(C3_1Z)cycloalkyl ring; each t is independently 0 to 6;
and u is 0 to 3;
j) a group of the formula:
(phenyl-CH2-C(CH3) 2-),
where the phenyl group is optionally mono- or independently pluri substituted
with R12;
k) a group of the formula:
R20 Rx(CHZ)s ~ Rx(CH2)t~ Ry\ Rx(CHZ)t 3
N or R20_N '~r or ~ IN)
1 Ry~ / u Ry ) u 20 u
54
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
where R20 is hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl; (CI_6)alkylcarbonyl; di-
(CI_6)alkylaminocarbonyl; (C3_
g)cycloalkylcarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl; (CI_6)alkyloxycarbonyl;
arlkyloxycarbonyl, pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl; phenyl substituted thiazole ring; phenylaminocarbonyl;
alkylsulfonyl;
or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl, benzoyl, pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl,
phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl groups are optionally
mono- or
independently di-substituted with R'Z; R,, is hydrogen; (CI _$)alkyl; (C3_12)
cycloalkyl;
benzyl; phenyl; where the benzyl and phenyl, groups are optionally mono- or
independently
di-substituted on the ring with R12; Ry is absent or is halogen, (CI_8)alkyl,
(CI_8)alkoxy,
0-alkylcarboxylate, 0-aralkylcarboxylate, N-alkylcarboxamido, N-
aralkylcarboxamido; or
phenyl;
sisl to6;tisOto6;anduisOto3;or
1) a group of the formula:
(CHz)t ~
R21-O-(CH2 t ~ u
where R21 is hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl; benzyl; or phenyl; in which the benzyl and
phenyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted on the ring with
R12; each t is
independently 0 to 6; and u is 0 to 3; or
(ee) R3, R4 and R5 are independently hydrogen; alkyl; alkenyl; alkynyl;
cycloalkyl; cycloalkylalkyl; bicycloalkyl; tricycloalkyl; alkylcycloalkyl;
hydroxyalkyl;
hydroxyalkylcycloalkyl; hydroxycycloalkyl; hydroxybicycloalkyl;
hydroxytricycloalkyl;
bicycloalkylalkyl; alkylbicycloalkyl; alkylthioalkyl; arylalkylthioalkyl;
cycloalkenyl; aryl,
aralkyl; heteroaryl; heteroarylalkyl; cycloheteroalkyl or
cycloheteroalkylalkyl; all optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with halogen, alkyl, polyhaloalkyl,
alkoxy,
haloalkoxy, polyhaloalkoxy, alkoxycarbonyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl,
cycloalkylalkyl,
polycycloalkyl, heteroarylamino, arylamino, cycloheteroalkyl,
cycloheteroalkylalkyl,
hydroxy, hydroxyalkyl, nitro, cyano, amino, substituted amino, alkylamino,
dialkylamino,
thiol, alkylthio, alkylcarbonyl, acyl, alkoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkynylamino-
carbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, alkenylaminocarbonyl, alkylcarbonyloxy,
alkylcarbonylamino, arylcarbonylamino, alkylsulfonylamino, alkylaminocarbonyl-
amino,
alkoxycarbonylamino, alkylsulfonyl, aminosulfinyl, aminosulfonyl,
alkylsulfinyl,
sulfonamido or sulfonyl; provided that when n is 1, X is CH2, the ring
containing X is
saturated, and Z, R3 and R5 are H, R4 is not a side chain of a naturally
occurring a-amino
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
acid; and provided that when n is 1, X is CH2, the ring containing X is
saturated, and Z and
R5 are H, R3 and R4 are not both methyl; and
wherein the bond containing the wavy line signifies the point of attachment.
[0068] In some embodiments of compounds of formula VA and VB, R' and R2
independently or together are the boronic acid protecting group formed from
(+)-pinanediol;
pinacol; 1,2-dicyclohexyl-ethanediol; 1,2-ethanediol; 2,2-diethanolamine; 1,3-
propanediol;
2,3-butanediol, diisopropyl tartrate; 1,4-butanedioI; diisopropylethanediol;
(S,S,)-5,6-
decanediol; 1,1,2-triphenyl-1,2-ethanediol; (2R,3R)-1,4-dimethyoxy-1,1,4,4-
tetraphenyl-
2,3-butanediol; methanol; ethanol; isopropanol; catechol; or 1-butanol. In
other
embodiments, R' and R 2 independently or together are a group capable of being
hydrolyzed
to a hydroxyl group in an aqueous solution at physiological pH or in
biological fluids
formed from 1,2-dicyclohexylethanediol; 1,2-ethanediol; 1,3-propanediol; 2,3-
butanediol,
1,4-butanediol; diisopropylethanediol; methanol; ethanol; isopropanol; or 1-
butanol.
[0069] In some embodiments of compounds of formula VA or VB,
R3 and R4 are independently hydrogen, alkyl; alkenyl; alkynyl; cycloalkyl;
cycloalkylalkyl; bicycloalkyl; tricycloalkyl; alkylcycloalkyl; hydroxyalkyl;
hydroxyalkylcycloalkyl; hydroxycycloalkyl; hydroxybicycloalkyl;
hydroxytricycloalkyl;
bicycloalkylalkyl; alkylbicycloalkyl; alkylthioalkyl; arylalkylthioalkyl;
cycloalkenyl; aryl,
aralkyl; heteroaryl; heteroarylalkyl; cycloheteroalkyl or
cycloheteroalkylalkyl; all optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with halogen, alkyl, polyhaloalkyl,
alkoxy,
haloalkoxy, polyhaloalkoxy, alkoxycarbonyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl,
cycloalkylalkyl,
polycycloalkyl, heteroarylamino, arylamino, cycloheteroalkyl,
cycloheteroalkylalkyl,
hydroxy, hydroxyalkyl, nitro, cyano, amino, substituted amino, alkylamino,
dialkylamino,
thiol, alkylthio, alkylcarbonyl, acyl, alkoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkynylamino-
carbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, alkenylaminocarbonyl, alkylcarbonyloxy,
alkylcarbonylamino, arylcarbonylamino, alkylsulfonylamino, alkylaminocarbonyl-
amino,
alkoxycarbonylamino, alkylsulfonyl, aminosulfinyl, aminosulfonyl,
alkylsulfinyl,
sulfonamido or sulfonyl; and
R5 is alkyl; alkenyl; alkynyl; cycloalkyl; cycloalkylalkyl; bicycloalkyl;
tricycloalkyl; alkylcycloalkyl; hydroxyalkyl; hydroxyalkylcycloalkyl;
hydroxycycloalkyl;
hydroxybicycloalkyl; hydroxytricycloalkyl; bicycloalkylalkyl;
alkylbicycloalkyl;
56
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
alkylthioalkyl; arylalkylthioalkyl; cycloalkenyl; aryl, aralkyl; heteroaryl;
heteroarylalkyl;
cycloheteroalkyl or cycloheteroalkylalkyl; all optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with halogen, alkyl, polyhaloalkyl, alkoxy, haloalkoxy,
polyhaloalkoxy,
alkoxycarbonyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl, polycycloalkyl,
heteroarylamino, arylamino, cycloheteroalkyl, cycloheteroalkylalkyl, hydroxy,
hydroxyalkyl, nitro, cyano, amino, substituted amino, alkylamino,
dialkylamino, thiol,
alkylthio, alkylcarbonyl, acyl, alkoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl, alkynylamino-
carbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, alkenylaminocarbonyl, alkylcarbonyloxy,
alkylcarbonylamino,
arylcarbonylamino, alkylsulfonylamino, alkylaminocarbonyl-amino,
alkoxycarbonylamino,
alkylsulfonyl, aminosulfinyl, aminosulfonyl, alkylsulfinyl, sulfonamido or
sulfonyl.
[0070] In still other embodiments of compounds of formula VA or VB, X is CHZ;
the
ring containing X is saturated; R', Rz, R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and R 5 is
(Ci.12)alkyl; (CZ.
iZ)alkenyl; (C2_12)alkynyl; (C3.12) cycloalkyl; or (C3_12)cycloalkenyl; where
the alkyl,
alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl and cycloalkenyl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
pluri substituted with R6, and where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl portions
include linear or
branched chains and may include cyclic portions. In some such embodiments, R5
is (C3.12)
cycloalkyl such as cyclopentyl.
100711 In some embodiments of compounds of formula VA or VB, X is CH2; the
ring
containing X is saturated; R1, R2, R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and R5 is indanyl;
1,2,3,4-
tetrahydronaphthyl; (CHZ)j adamantyl in which j is 0-3; or a[2.2.1] or [3.1.1]
bicyclic
carbocyclic moiety, including (4-pentylbicyclo[2.2.2]-oct-l-yl)amine; where
the indanyl,
1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthyl, (CHZ)j adamantyl, and [2.2.1 ] or [3.1.1 ]
bicyclic carbocyclic
moieties are optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with hydroxy,
(CI.8)alkyl,
(C1.8)alkoxy, (CI_g)alkanoyloxy, or R9R10N-CO-O-, where R9 and Rl0 are
independently (Cl.
8)alkyl, or phenyl, where the alkyl and phenyl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with (CI_8)alkyl, (CI_g)alkoxy, halogen, or trifluoromethyl,
or R9 and Rlo
together are (C3_6)alkylene.
[0072] Compounds of formula VA or VB include those wherein X is CH2; the ring
containing X is saturated; R1, Rz, R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and R5 is R"(CHZ)P-
where RI I is
2-oxopyrrolidinyl; (Cl.6)alkoxy; phenyl; phenoxy; (CI_8)cycloalkyl; [3.3.3]
bicyclic
carbocyclic moiety; pyridinyl; naphthyl; cyclohexenyl; or adamantyl; where the
2-
57
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
oxopyrrolidinyl, (CI-6)alkoxy, phenyl, pyridinyl, and naphthyl groups are
optionally mono-
or independently di- or independently trisubstituted with R12; where the
phenoxy group is
optionally mono- or independently disubstituted with (Ci4)alkyl, (Ci4)alkoxy,
or halogen;
and where the [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety is optionally mono-or
independently
plurisubstituted with (C1_8)alkyl; p is 0 to 3; and R1Z is halogen;
trifluoromethyl; cyano;
nitro; (CI-6)alkyl; (C1-6)alkoxy; cycloalkyl; carboxy; acetamido; hydroxy;
hydroxy(Cl_
6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl; trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; carbamoyl; sulfonamido;
alkylsufonyl; phenylsulfonyl; aryl; heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R7.
[0073] Compounds of VA or VB further include those wherein X is CH2; the ring
containing X is saturated; R', RZ, R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and R5 is
(Rt3)2CH(CH2)q-,
where R13 is phenyl; in which the phenyl groups are independently optionally
mono- or
independently disubstituted with R12; and q is 0 to 3.
[00741 In some embodiments of compounds of formula VA or VB, X is CH2; the
ring
containing X is saturated; R', Rz, R3 and R 4 are hydrogen; and R5 is a group
of the formula:
R15
Rt4~ (CH2)r__4
where R14 and R15 are independently hydrogen; (Ci.B)alkyl;
(Ci_6)alkylcarbonyl; (C3.
12)cycloalkyl ring; (C3_12)cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylamino-carbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the cycloalkyl
ring is
optionally substituted with hydroxy(Ci-6)alkyl, and where the benzyl, benzoyl,
pyridine,
pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R12; or Rt4 and R'5
together form a
(C3.12)cycloalkyl ring; and r is 2 to 6.
[00751 In other embodiments of compounds of formula VA or VB, X is CH2; the
ring
containing X is saturated; R', R2, R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and R5 is a group
of the formula:
R17
R16~ ~(CHz)s
58
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
where R'6 and R" are each independently hydrogen; (C1.8)alkyl;
(C1.6)alkylcarbonyl; di-(Ci
6)alkylaminocarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine; pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl,
benzoyl,
pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and
phenylsulfonyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R' 2; or R' 6
and R"
together form a(C3_12)cycloalkyl ring; and s is I to 6.
[0076] In certain embodiments of compounds of formula VA or VB, X is CH2; the
ring
containing X is saturated; Rl, R2, R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and R5 is a group
of the formula:
(CH2)c-~
R19N_(CH ~u
R18
where R' 8 and Rt9 are independently hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl; (C1 -
6)alkylcarbonyl; di-(Ci.
6)alkylaminocarbonyl; benzyl; benzothiazole; benzoyl; pyridine; pyrimidine;
phenyl;
phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl,
benzoyl,
benzothiazole, pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl,
alkylsulfonyl, and
phenylsulfonyl groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted
with R12; or R18
and R19 together form a(C3.12)cycloalkyl ring; each t is independently 0 to 6;
and u is 0 to 3.
In some such embodiments, R 5 has formula:
(CHZ)-~
R i 1 9 or Ris
N N
R'B R18
[0077] Compounds of formula VA or VB further include those wherein X is CH2;
the
ring containing X is saturated; R', R2, R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and R5 is a
group of the
formula:
(phenyl-CH2-C(CH3)2-),
where the phenyl group is optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted
with R12
.
59
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 200-5/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
100781 In some embodiments of compounds of formula VA or VB, X is CH2; the
ring
containing X is saturated; R, RZ, R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and R5 is a group of
the formula:
~ ~(CH2)i~ RY Rx(CH2)i ~
R20 R (CH
2)s
or R20__N or CN ~
Ry/ )u RY u R2o e
where R20 is hydrogen; (Ci_8)alkyl; (C1_6)alkylcarbonyl; di-(Ct-
6)alkylaminocarbonyl; (C3_
g)cycloalkylcarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl; (C1_6)alkyloxycarbonyl;
arlkyloxycarbonyl, pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl; phenyl substituted thiazole ring; phenylaminocarbonyl;
alkylsulfonyl;
or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl, benzoyl, pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl,
phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl groups are optionally
mono- or
independently di-substituted with R12; RX is hydrogen; (CI_8)alkyl; (C3_12)
cycloalkyl;
benzyl; phenyl; where the benzyl and phenyl, groups are optionally mono- or
independently
di-substituted on the ring with R'Z; Ry is absent or is halogen, (C1_8)alkyl,
(Ct_8)alkoxy,
0-alkylcarboxylate, O-aralkylcarboxylate, N-alkylcarboxamido, N-
aralkylcarboxamido; or
phenyl;
s is 1 to 6; t is 0 to 6; and u is 0 to 3; or
In some such embodiments, R5 has formula:.
R- (CH2t~
Rx (CH2)t~ ')
N
R2o A or R2o
[0079] In other embodiments of compounds of formula VA or VB, X is CH2; the
ring
containing X is saturated; Rt, R2, R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and R5 is a group
of the formula:
(CH2h-~
R21-O-(CH2)t ~ u
where RZ' is hydrogen; (Cl_$)alkyl; benzyl; or phenyl; in which the benzyl and
phenyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted on the ring with
R12; each t is
independently 0 to 6; and u is 0 to 3. In some such embodiments, R5 has
formula:
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
(CH2)-i
or
R21-O R2i_O
[0080] Compounds of formula VA or VB further include those wherein R' and R 2
are
hydrogen; n is 1; X together with an adjacent ring carbon and Z form a fused
cyclopropyl;
R3, R4 and R5 are independently hydrogen; alkyl; alkenyl; alkynyl; cycloalkyl;
cycloalkylalkyl; bicycloalkyl; tricycloalkyl; alkylcycloalkyl; hydroxyalkyl;
hydroxyalkylcycloalkyl; hydroxycycloalkyl; hydroxybicycloalkyl;
hydroxytricycloalkyl;
bicycloalkylalkyl; alkylbicycloalkyl; alkylthioalkyl; arylalkylthioalkyl;
cycloalkenyl; aryl,
aralkyl; heteroaryl; heteroarylalkyl; cycloheteroalkyl or
cycloheteroalkylalkyl; all optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with halogen, alkyl, polyhaloalkyl,
alkoxy,
haloalkoxy, polyhaloalkoxy, alkoxycarbonyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl,
cycloalkylalkyl,
polycycloalkyl, heteroarylamino, arylamino, cycloheteroalkyl,
cycloheteroalkylalkyl,
hydroxy, hydroxyalkyl, nitro, cyano, amino, substituted amino, alkylamino,
dialkylamino,
thiol, alkylthio, alkylcarbonyl, acyl, alkoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkynylamino-
carbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, alkenylaminocarbonyl, alkylcarbonyloxy,
alkylcarbonylamino, arylcarbonylamino, alkylsulfonylamino, alkylaminocarbonyl-
amino,
alkoxycarbonylamino, alkylsulfonyl, aminosulfinyl, aminosulfonyl,
alkylsulfinyl,
sulfonamido or sulfonyl.
[0081] In certain embodiments of compounds of formula VA or VB, the
compoundshave
the formula:
R5 H
R3 OR' R3 1/ OR'
R5HN R4 I /ORz R4 OR
B
Z
e
O N O N
X
Z Z
or a mixture thereof.
61
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCTIUS2004/037820
[0082] Compounds of fonnula VA or VB include those having the formula:
R5 H
R3 OR' R3 1/ OR1
R5HN R4 B/OR2 R4 ~ B/OR2
e
N N
L S LS
or a mixture thereof.
[0083] In other embodiments, compounds of forniual VA or VB include those
having the
formula:
H
R3 OR' R3 '/ OR1
R5HN R4 I/OR2 R4 N OR2
eB
O N 0 N
or a mixture thereof; or the formula:
R5 H
R3 OR' R3 \ / OR'
B
R5HN R4 L.-OR2 R ~ OR
O N
L O N
,
or a mixture thereof.
62
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCTIUS2004/037820
[0084] Compounds of formula VA or VB further include those having the fonnula:
R5 H
R3 OR' R3 1/ OR'
RSHN R4 B/OR2 R4 NB/OR2
0
O N O N
/ /
,
or a mixture thereof.
[00851 In still other embodiments, compounds of formula VA or VB have the
formula:
R3 OR' R3 1/ OR'
RSHN R B/OR2 R ~ I/ORZ
e
O N O N
F , F
or a mixture thereof.
[0086] In yet other embodiments, compounds of formual VA or VB have the
formula:
R5 H
R3 ORt R3 1/ OR'
RSHN R4 [OR2 R4 ~BOR2
O N O N
OH , OH ,
or a mixture thereof.
63
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
[00871 In still another aspect, the invention provides boronic acid inhibitors
of dipeptidyl
peptidase-IV having an inhibition constant of 10 micromolar or less for
dipeptidyl
peptidase-IV. Such inhibitors comprises a boroproline (including
boropyrrolidines,
boropiperidines, and boroazepanes) attached to an amino acid through an amide
bond. The
amino acid can be a beta-amino acid (including cyclic forms such as , an
N-cycloalkyl-alpha-amino acid, an N-heterocyclyl-alpha amino acid, a cyclic
alpha-amino
acid having at least one substituent on the alpha-amino acid ring or having a
ring other than
pyrrolidine, or N-substituted glycine. In some embodiments, the boronic acid
inhibitor is of
Formula I:
OR '
R4 R3 0 B-ORZ
R ~N N
H
R" R' x "
z
including all enantiomers, diastereoisomers, solvates, hydrates and
pharmaceutically
acceptable salts thereof, wherein:
n is 1 to 2;
X is CH2; S; 0; CF2 or C(CH3)2;
Z is H; halogen; hydroxyl; (C1_6)alkoxy; (CI_12)alkyl; (C3_12)cycloalkyl;
phenyl; or
heteroaryl; where the phenyl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with W;
optionally, X together with an adjacent ring carbon and Z form a fused
cyclopropyl;
and
optionally, one of the bonds in the ring containing X is a double bond;
R' and R2 independently or together are hydrogen; a boronic acid protecting
group;
or a group capable of being hydrolyzed to a hydroxyl group in an aqueous
solution at
physiological pH or in biological fluids;
CR'R" may be present or absent, wherein if CR'R" is present, then R', R", R3,
R4 and
R5 are selected from (aa), (bb) or (cc):
(aa) R', R", R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and
Rs is
a) hydrogen;
64
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
b) (Ct_12)alkyl; (C2_12)alkenyl; (C2_12)alkynyl; (C3_12)
cycloalkyl; or (C3_12)cycloalkenyl; where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl,
cycloalkyl and
cycloalkenyl groups are optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted
with R6, and
where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl portions include linear or branched chains
and may include
cyclic portions;
R6 is (Ci-6)alkyl; (C1 -6)alkoxy; cycloalkyl; carboxy;
acetamido; cyano; nitro; halogen; hydroxy; hydroxy(CI_6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl;
trifluoromethyl; trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; sulfonamido; carbamoyl; aryl;
heteroaryl;
where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or independently
plurisubstituted
with R7 ; amino, where the amino group is optionally mono- or independently
plurisubstituted with R8; -SORB; -S02R8; -COR8; -COZRg, -CONHRg; -CON(R$) 2; -
OR8; or
-S-Rg;
R' is halogen; (C,-,o)alkyl; (Ci.lo)alkoxy; (Cl_-o)alkylamino;
(Cl_lo) dialkylamino; benzyl; benzyloxy; hydroxyl(CI_6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl;
nitro;
trifluoromethyl; trifluoromethoxy; trifluoromethylthio; N-hydroxyimino; cyano;
carboxy;
acetamido; hydroxy; sulfamoyl; sulfonamido; or carbamoyl;
R8 is (Ci_10)alkyl; (C2.1 )alkenyl; (C2_1o)alkynyl; (C3_
1o)cycloalkyl; (CS_jo)cycloalkenyl; benzyl; phenethyl; aryl; or heteroaryl;
where the alkyl,
alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with aryl or heteroaryl where the aryl and heteroaryl groups
are optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R7 ; and where the aryl and
heteroaryl groups
are optionally mono- or independently pluri substituted with R7;
c) aryl optionally fused to a(C3_10)cycloalkyl; or heteroaryl
optionally fused to a(C3_1o)cycloalkyl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups
are optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R';
d) indanyl; 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthyl; (CHZ)jadamantyl in
which j is 0-3; or a[2.2.1] or [3.1.1] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety, including
(4-
pentylbicyclo[2.2.2]oct-l-yl)amine; where the indanyl, 1,2,3,4-
tetrahydronaphthyl, (CH2)j
adamantyl, and [2.2.1] or [3.1.1] bicyclic carbocyclic moieties are optionally
mono- or
independently plurisubstituted with hydroxy, (C1.8)alkyl, (CI_$)alkoxy,
(Ci.8)alkanoyloxy, or
R9R10N-CO-O-, where R9 and Rl0 are independently (CI_8)alkyl, or phenyl, where
the alkyl
and phenyl groups are optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with
(C1.g)alkyl,
(Cl.s)alkoxy, halogen, or trifluoromethyl, or R9 and R10 together are
(C3_6)alkylene;
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
e) R"(CHz)P- where R" is 2-oxopyrrolidinyl; (C1_6)alkoxy;
phenyl; phenoxy; (Ci_$)cycloalkyl; [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety;
pyridinyl; naphthyl;
cyclohexenyl; or adamantyl; where the 2-oxopyrrolidinyl, (C1_6)alkoxy, phenyl,
pyridinyl,
and naphthyl groups are optionally mono- or independently di- or independently
trisubstituted with R12; where the phenoxy group is optionally mono- or
independently
disubstituted with (Ci4)alkyl, (Ci4)alkoxy, or halogen; and where the [3.3.3]
bicyclic
carbocyclic moiety is optionally mono-or independently plurisubstituted with
(C1_8)alkyl;
and p is 0 to 3;
R12 is halogen; trifluoromethyl; cyano; nitro; (C1_6)alkyl; (Cl_
6)alkoxy; cycloalkyl; carboxy; acetamido; hydroxy; hydroxy(Ct-6)alkyl;
hydroxymethyl;
trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; carbamoyl; sulfonamido; alkylsufonyl;
phenylsulfonyl; aryl;
heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with R7;
f) (R13)2CH(CH2)q-, where R13 is phenyl; in which the phenyl
groups are independently optionally mono- or independently disubstituted with
R1z; and q is
Oto3;
g) a group of the fonnula:
R15
I
R141--N1_~ (CH2)r-~_
where R' 4 and R' 5 are independently hydrogen; (C i_8)alkyl; (CI -
6)alkylcarbonyl; (C3_
1Z)cycloalkyl ring; (C3_12)cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylamino-carbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the cycloalkyl
ring is
optionally substituted with hydroxy(C1_6)alkyl, and where the benzyl, benzoyl,
pyridine,
pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with RIZ; or R14 and R15
together form a
(C3_12)cycloalkyl ring; and r is 2 to 6;
h) a group of the formula:
R' 7
~
R16'-N\(CH2)s
where R'b and R17 are each independently hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl; (Ci-
6)alkylcarbonyl; di-(Cl_
6)alkylaminocarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine; pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl,
benzoyl,
66
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and
phenylsulfonyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R12; or R16
and R"
together form a(C3_12)cycloalkyl ring; and s is I to 6;
i) a group of the fon-nula:
(CHz)c-~
R 19
N-(CH2)t u
R18
where R18 and R'9 are independently hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl;
(CI.6)alkylcarbonyl; di-(Cl-
6)alkylaminocarbonyl; benzyl; benzothiazole; benzoyl; pyridine; pyrimidine;
phenyl;
phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl,
benzoyl,
benzothiazole, pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl,
alkylsulfonyl, and
phenylsulfonyl groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted
with R12; or R18
and R19 together form a(C3_12)cycloalkyl ring; each t is independently 0 to 6;
and u is 0 to 3;
j) a group of the formula:
(phenyl-CH2-C(CH3) Z-),
where the phenyl group is optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted
with R12;
k) a group f
R20 f (CHz)s ~ ~tCH2)t Ry ~(CH2)t~3
N or R20_N or )
Ry/ u Ry u R2o u
where R20 is hydrogen; (C1.8)alkyl; (C,.6)alkylcarbonyl; di-
(C1.6)alkylaminocarbonyl; (C3.
.8)cycloalkylcarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl; (Ci.6)alkyloxycarbonyl;
arlkyloxycarbonyl, pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl; phenyl substituted thiazole ring; phenylaminocarbonyl;
alkylsulfonyl;
or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl, benzoyl, pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl,
phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl groups are optionally
mono- or
independently di-substituted with R12; RX is hydrogen; (Cl.B)alkyl; (C3.12)
cycloalkyl;
benzyl; phenyl; where the benzyl and phenyl, groups are optionally mono- or
independently
di-substituted on the ring with R'Z; RY is absent or is halogen, (Ci.$)alkyl,
(C1-8)alkoxy,
0-alkylcarboxylate, 0-aralkylcarboxylate, N-alkylcarboxamido, N-
aralkylcarboxamido; or
phenyl;
67
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
sis 1 to 6; t is 0 to 6; and u is 0 to 3; or
1) a group of the formula:
(CHz~-~
R21-O -(CH2 ! ) u
where R21 is hydrogen; (Ci_$)alkyl; benzyl; or phenyl; in which the benzyl and
phenyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted on the ring with
R12; each t is
independently 0 to 6; and u is 0 to 3;
(bb) R', R", R3, R4 and R5 are independently hydrogen; alkyl; alkenyl;
alkynyl; cycloalkyl; cycloalkylalkyl; bicycloalkyl; tricycloalkyl;
alkylcycloalkyl;
hydroxyalkyl; hydroxyalkylcycloalkyl; hydroxycycloalkyl; hydroxybicycloalkyl;
hydroxytricycloalkyl; bicycloalkylalkyl; alkylbicycloalkyl; alkylthioalkyl;
arylalkylthioalkyl; cycloalkenyl; aryl, aralkyl; heteroaryl; heteroarylalkyl;
cycloheteroalkyl
or cycloheteroalkylatkyl; all optionally mono- or independently
plurisubstituted with
halogen, alkyl, polyhaloalkyl, alkoxy, haloalkoxy, polyhaloalkoxy,
alkoxycarbonyl, alkenyl,
alkynyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl, polycycloalkyl, heteroarylamino,
arylamino,
cycloheteroalkyl, cycloheteroalkylalkyl, hydroxy, hydroxyalkyl, nitro, cyano,
amino,
substituted amino, alkylamino, dialkylamino, thiol, alkylthio, alkylcarbonyl,
acyl,
alkoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl, alkynylamino-carbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl,
alkenylaminocarbonyl, alkylcarbonyloxy, alkylcarbonylamino, arylcarbonylamino,
alkylsulfonylamino, alkylaminocarbonyl-amino, alkoxycarbonylamino,
alkylsulfonyl,
aminosulfinyl, aminosulfonyl, alkylsulfinyl, sulfonamido or sulfonyl; or
R' together with R3 or R4, or R" together with R3 or R4, and the atoms
to which they are attached form a 4 to 8 membered cyclic, polycyclic or
heterocyclic ring
system containing I to 3 heteroatoms selected from N, 0, S, SO or SO2i and
includes single
rings, fused bicyclic and tricyclic rings, which are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with any of the groups set forth in (aa); or
R4 and RS together form -(CRZZR23)m where m is 2 to 6, and RZZ and
R23 are independently hydrogen; hydroxyl; alkoxy; alkyl; alkenyl; alkynyl;
cycloalkyl; halo;
amino; substituted amino; cycloalkylalkyl; cycloalkenyl; aryl; arylalkyl;
heteroaryl,
heteroarylalkyl; cycloheteroalkyl; cycloheteroalkylalkyl; alkylcarbonylamino;
arylcarbonylamino; alkoxycarbonyl-amino; aryloxycarbonyl-amino;
alkoxycarbonyl;
aryloxycarbonyl; or alkylaminocarbonylamino; or
68
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCTIUS2004/037820
R4 and R5 together with the atoms to which they are attached form a 5
to 7 membered ring containing a total of 2 to 4 heteroatoms selected from N,
0, S, SO, or
SO2; or
R4 and R5 together with the atoms to which they are attached form a 4
to 8 membered cycloheteroalkyl ring wherein the cycloheteroalkyl ring
optionally has an
aryl, heteroaryl or 3 to 7 membered cycloalkyl ring fused thereto; or
(cc) R' and R3 are hydrogen; and R" and R4 together form a 4 to 8
membered cyclic, polycyclic or heterocyclic ring system containing 1 to 3
heteroatoms
selected from N, 0, S, SO and SO2i and includes single rings, fused bicyclic
and tricyclic
rings, which are optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with any
of the groups
set forth in (aa) or (bb) and
R5 is any of the groups in (aa) or (bb); and
if CR'R" is absent, then R3, R4 and R5 are selected from (dd), (ee) or (ff):
(dd) R3 and R4 are hydrogen; and
Rs is
a) (CI.12)alkyl; (C2-12)alkenyl; (C2.12)alkynyl; (C3.12)
cycloalkyl; or (C3_12)cycloalkenyl; where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl,
cycloalkyl and
cycloalkenyl groups are optionally mono- or independently pluri substituted
with R6, and
where the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl portions include linear or branched chains
and may include
cyclic portions;
R6 is (CI-6)alkyl; (Ci.6)alkoxy; cycloalkyl; carboxy;
acetamido; cyano; nitro; halogen; hydroxy; hydroxy(Ci-6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl;
trifluoromethyl; trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; sulfonamido; carbamoyl; aryl;
heteroaryl;
where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or independently
plurisubstituted
with R'; amino, where the amino group is optionally mono- or independently
plurisubstituted with R8; -SOR8; -S02R8; -CORB; -C02Rg, -CONHR 8; -CON(R8) 2; -
OR8; or
-S-R8;
R' is halogen; (C1.io)alkyl; (Cl.lo)alkoxy; (CI_1o)alkylamino;
(C,.,o) dialkylamino; benzyl; benzyloxy; hydroxyl(C1.6)alkyl; hydroxymethyl;
nitro;
trifluoromethyl; trifluoromethoxy; trifluoromethylthio; N-hydroxyimino; cyano;
carboxy;
acetamido; hydroxy; sulfamoyl; sulfonamido; or carbamoyl;
R8 is (Ci_io)alkyl; (C24o)alkenyl; (C2_10)alkynyl; (C3.
io)cycloalkyl; (C5.io)cycloalkenyl; benzyl; phenethyl; aryl; or heteroaryl;
where the alkyl,
69
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
plurisubstituted with aryl or heteroaryl where the aryl and heteroaryl groups
are optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R7 ; and where the aryl and
heteroaryl groups
are optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R7;
b) aryl optionally fused to a(C3_,o)cycloalkyl; or heteroaryl
optionally fused to a(C3_lo)cycloalkyl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups
are optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with R7 ;
c) indanyl; 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthyl; (CH2)jadamantyl in
which j is 0-3; or a[2.2.1 ] or [3.1.1 ] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety,
including (4-
pentylbicyclo[2.2.2]oct-1-yl)amine; where the indanyl, 1,2,3,4-
tetrahydronaphthyl, (CHZ)j
adamantyl, and [2.2.1 ] or [3.1.1 ] bicyclic carbocyclic moieties are
optionally mono- or
independently plurisubstituted with hydroxy, (C1 .8)alkyl, (Ci.8)alkoxy,
(Cl_8)alkanoyloxy, or
R9R10N-CO-O-, where R9 and R'0 are independently (CI_8)alkyl, or phenyl, where
the alkyl
and phenyl groups are optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted with
(C1.8)alkyl,
(Ci_S)alkoxy, halogen, or trifluoromethyl, or R9 and R10 together are (C3-
6)alkylene;
d) R"(CH2)p where R" is 2-oxopyrrolidinyl; (C1_6)alkoxy;
phenyl; phenoxy; (CI_$)cycloalkyl; [3.3.3] bicyclic carbocyclic moiety;
pyridinyl; naphthyl;
cyclohexenyl; or adamantyl; where the 2-oxopyrrolidinyl, (CI_6)alkoxy, phenyl,
pyridinyl,
and naphthyl groups are optionally mono- or independently di- or independently
trisubstituted with R12; where the phenoxy group is optionally mono- or
independently
disubstituted with (C,.a)alkyl, (C]4)alkoxy, or halogen; and where the [3.3.3]
bicyclic
carbocyclic moiety is optionally mono-or independently pluri substituted with
(CI_g)alkyl;
and p is 0 to 3;
R'Z is halogen; trifluoromethyl; cyano; nitro; (Ci.6)alkyl; (Cl_
6)alkoxy; cycloalkyl; carboxy; acetamido; hydroxy; hydroxy(Ci.6)alkyl;
hydroxymethyl;
trifluoromethoxy; sulfamoyl; carbamoyl; sulfonamido; alkylsufonyl;
phenylsulfonyl; aryl;
heteroaryl; where the aryl and heteroaryl groups are optionally mono- or
independently
pluri substituted with R';
e) (R13)2CH(CH2)y-, where R'3 is phenyl; in which the phenyl
groups are independently optionally mono- or independently disubstituted with
R12; and q is
O to 3;
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
f) a group of the formula:
Ws
R14~ (CH2)r_~
where R14 and R15 are independently hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl; (CI-
6)alkylcarbonyl; (C3_
iZ)cycloalkyl ring; (C3_12)cycloalkenyl ring; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylamino-carbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the cycloalkyl
ring is
optionally substituted with hydroxy(C1_6)alkyl, and where the benzyl, benzoyl,
pyridine,
pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl
groups are
optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R12; or R14 and R15
together form a
(C3_12)cycloalkyl ring; and r is 2 to 6;
g) a group of the formula:
R17
~
R161_~N,_,(CH2)s
where R16 and R17 are each independently hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl;
(Ci.6)alkylcarbonyl; di-(CI
6)alkylaminocarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl; pyridine; pyrimidine; phenyl;
phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl,
benzoyl,
pyndine, pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and
phenylsulfonyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted with R' Z; or R16
and R' '
together form a(C3.12)cycloalkyl ring; and s is I to 6;
h) a group of the formula:
(CH2)t ~
R 19
N'(CH u
R18
where R18 and R19 are independently hydrogen; (Ci_g)alkyl;
(CI_6)alkylcarbonyl; di-(Cl_
6)alkylaminocarbonyl; benzyl; benzothiazole; benzoyl; pyridine; pyrimidine;
phenyl;
phenylaminocarbonyl; alkylsulfonyl; or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl,
benzoyl,
benzothiazole, pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl, phenylaminocarbonyl,
alkylsulfonyl, and
phenylsulfonyl groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted
with R, Z; or R18
and R19 together form a(C3.12)cycloalkyl ring; each t is independently 0 to 6;
and u is 0 to 3;
i) a group of the formula:
(phenyl-CH2-C(CH3) 2-),
71
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
where the phenyl group is optionally mono- or independently plurisubstituted
with R'Z;
j) a group of the formula:
R20 Rx(CH2)s ~ RX(CH2t~ Ry~ ~(CH2)i ~
or R2oYN or ~
N ~
Ry/ u Ry ~ u R2o u
where R20 is hydrogen; (C1_8)alkyl; (Ci_6)alkylcarbonyl; di-
(Ci.6)alkylaminocarbonyl; (C3_
8)cycloalkylcarbonyl; benzyl; benzoyl; (Ci.6)alkyloxycarbonyl;
arlkyloxycarbonyl, pyridine;
pyrimidine; phenyl; phenyl substituted thiazole ring; phenylaminocarbonyl;
alkylsulfonyl;
or phenylsulfonyl; where the benzyl, benzoyl, pyridine, pyrimidine, phenyl,
phenylaminocarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, and phenylsulfonyl groups are optionally
mono- or
independently di-substituted with R1z; R,, is hydrogen; (Ci_8)alkyl; (C3_12)
cycloalkyl;
benzyl; phenyl; where the benzyl and phenyl, groups are optionally mono- or
independently
di-substituted on the ring with R'Z; RY is absent or is halogen, (Ct_g)alkyl,
(C1_8)alkoxy,
0-alkylcarboxylate, 0-aralkylcarboxylate, N-alkylcarboxamido, N-
aralkylcarboxamido; or
phenyl;
sis 1 to6;tis0to6;anduis0to3;or
k) a group of the formula:
(CH2)t-~
R2'-O-(CH2 , u
where R21 is hydrogen; (Ci.8)alkyl; benzyl; or phenyl; in which the benzyl and
phenyl
groups are optionally mono- or independently di-substituted on the ring with
R'Z; each t is
independently 0 to 6; and u is 0 to 3; or
(ee) R3 and R4 are independently hydrogen, alkyl; alkenyl; alkynyl;
cycloalkyl; cycloalkylalkyl; bicycloalkyl; tricycloalkyl; alkylcycloalkyl;
hydroxyalkyl;
hydroxyalkylcycloalkyl; hydroxycycloalkyl; hydroxybicycloalkyl;
hydroxytricycloalkyl;
bicycloalkylalkyl; alkylbicycloalkyl; alkylthioalkyl; arylalkylthioalkyl;
cycloalkenyl; aryl,
aralkyl; heteroaryl; heteroarylalkyl; cycloheteroalkyl or
cycloheteroalkylalkyl; all optionally
mono- or independently plurisubstituted with halogen, alkyl, polyhaloalkyl,
alkoxy,
haloalkoxy, polyhaloalkoxy, alkoxycarbonyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl,
cycloalkylalkyl,
polycycloalkyl, heteroarylamino, arylamino, cycloheteroalkyl,
cycloheteroalkylalkyl,
hydroxy, hydroxyalkyl, nitro, cyano, amino, substituted amino, alkylamino,
dialkylamino,
thiol, alkylthio, alkylcarbonyl, acyl, alkoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkynylamino-
72
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
carbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, alkenylaminocarbonyl, alkylcarbonyloxy,
alkylcarbonylamino, arylcarbonylamino, alkylsulfonylamino, alkylaminocarbonyl-
amino,
alkoxycarbonylamino, alkylsulfonyl, aminosulfinyl, aminosulfonyl,
alkylsulfinyl,
sulfonamido or sulfonyl;
R5 is alkyl; alkenyl; alkynyl; cycloalkyl; cycloalkylalkyl;
bicycloalkyl; tricycloalkyl; alkylcycloalkyl; hydroxyalkyl;
hydroxyalkylcycloalkyl;
hydroxycycloalkyl; hydroxybicycloalkyl; hydroxytricycloalkyl;
bicycloalkylalkyl;
alkylbicycloalkyl; alkylthioalkyl; arylalkylthioalkyl; cycloalkenyl; aryl,
aralkyl; heteroaryl;
heteroarylalkyl; cycloheteroalkyl or cycloheteroalkylalkyl; all optionally
mono- or
independently plurisubstituted with halogen, alkyl, polyhaloalkyl, alkoxy,
haloalkoxy,
polyhaloalkoxy, alkoxycarbonyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl,
polycycloalkyl, heteroaryl amino, arylamino, cycloheteroalkyl,
cycloheteroalkylalkyl,
hydroxy, hydroxyalkyl, nitro, cyano, amino, substituted amino, alkylamino,
dialkylamino,
thiol, alkylthio, alkylcarbonyl, acyl, alkoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkynylamino-
carbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, alkenylaminocarbonyl, alkylcarbonyloxy,
alkylcarbonylamino, arylcarbonylamino, alkylsulfonylamino, alkylaminocarbonyl-
amino,
alkoxycarbonylamino, alkylsulfonyl, aminosulfinyl, aminosulfonyl,
alkylsulfinyl,
sulfonamido or sulfonyl; or
R4 and R5 together form -(CRzzR23)R, - wherein m is 2 to 6, and R 22
and R23 are independently hydrogen; hydroxyl; alkoxy; alkyl; alkenyl; alkynyl;
cycloalkyl;
halo; amino; substituted amino; cycloalkylalkyl; cycloalkenyl; aryl;
arylalkyl; heteroaryl,
heteroarylalkyl; cycloheteroalkyl; cycloheteroalkylalkyl; alkylcarbonylamino;
arylcarbonylamino; alkoxycarbonyl-amino; aryloxycarbonyl-amino;
alkoxycarbonyl;
aryloxycarbonyl; or alkylaminocarbonylamino; provided that when n is 1, X is
CH2, and Z
and R3 are H, R and R5 together are not -{CHZ)Z- or -(CH2)3-; or
R4 and R5 together with the atoms to which they are attached form a 5
to 7 membered ring containing a total of 2 to 4 heteroatoms selected from N,
0, S, SO, or
SO2; or
R4 and R5 together with the atoms to which they are attached form a 4
to 8 membered cycloheteroalkyl ring wherein the cycloheteroalkyl ring
optionally has an
aryl, heteroaryl or 3 to 7 membered cycloalkyl ring fused thereto; or
(ff) R3 is hydrogen; and R4 and R5 together with the atoms to
which they are attached form a 4 to 8 member mono- or polycyclic heterocyclic
ring system
73
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
containing I to 3 heteroatoms selected from N, 0, S, SO and SOZ, wherein the
heterocyclic
ring system is optionally mono- or independently pluri substituted with any of
the groups set
forth in (dd) or (ee); provided that when n is l, X is CH2, the ring
containing X is saturated,
and Z and R3 are H, R4 and R5 together are not -(CH2)2- or -(CH2)3-; and
wherein a bond containing a wavy line signifies a point of attachment.
[0088] The invention also relates to methods for preparing the above-described
compounds. As shown below and as described in the EXAMPLES, the compounds of
fonnula I and II are prepared by reacting a cyclic amine (e.g., pyrrolidine or
piperidine),
suitably protected with a standard protecting group such as Boc-, Fmoc-, CBz-
or the like,
with sec-BuLi/TMEDA followed by B(OCH3)3, to provide the methyl boronic ester
derivative. Acid hydrolysis of the methyl esters with 2N HCI provides the
boronic acid
intermediate 1. Reaction of 1 with (+) pinanediol, deprotection of the amino
protecting
group, and recrystallization provides the pinanediol ester 2 as an
isomerically pure salt.
[0089] Intermediate 2 is useful for the synthesis of both series A and series
B
compounds. For example, N-acylation of 2 with chloroacetyl chloride provides
the a-
chloro amide 3. Treatment of 3 with Na2CO3 and cyclopentylamine, and
hydrolysis of the
pinanediol boronic ester, provides a compound of formula I, 4. Alternatively,
coupling of
intermediate 2 with N-Boc-5-phenyl-Pro using EDAC/HOBT provides amide 5.
Deprotection of the amino group and hydrolysis of the boronic esters, provides
a compound
of formula II, 6.
74
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
1) s-BuLi, TMEDA -40 C HO'B-OH
CNBoc 2) (MeO)3B 1) (+)-Pinanediol, Et20
3) H3O+ ~NBoc
~VVV 2) HCI, Et20 then re crystallize
(2X) leaving
only R isomer
B-6
O
~'CI jNH.HCI
CI
CI-"Y N 2
B\ N N
O O ~
O 0 O'B-0
O
3
1) Na2CO3
c_NH2 1) HCI, Et20
2) Phenyl Boronic Acid
2) Phenyl Boronic Acid Hexane / H20
Hexane / H20
N N N
H0 HO.B-OH H O HO B-OH
4 6
[0090) This synthetic scheme is adaptable for the preparation of all the
compounds of the
invention, by reacting the appropriate cyclic amine (pyrrollidine, piperidine,
and other
cyclic amines) with sec-BuLi/B(OCH3)3, and coupling the boronic ester
intermediate with
the desired acid chloride or acid via routes A or B, respectively. The
appropriate cyclic
amine may either be commercially available or is easily synthesized through
known
procedures, for example, those procedures disclosed in U.S. Patent Nos.
6,617,340;
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
6,432,969; 6,380,398; 6,172,081; 6,166,063; 6,124,305; 6,110,949; 6,107,317;
6,011,155;
and 6,395,767, which are hereby incorporated by reference in their entirety.
[0091] Thus, another aspect of the invention provides a process for preparing
the
compounds of fon-nula I:
OR'
R4 R3 O B-ORZ
RN. N N (1)
Rii Ri ~/, p
X
z
by coupling a reactive compound of fonnula:
OR'
R R3 0 B-ORZ
L N ,
Rii Ri z I-X n
with an amine of formula: R5-NH2i optionally deprotecting the boronic acid
ester;
and recovering the resultant compound as a free acid or as an acid addition
salt; wherein L
is a leaving group. R', R2, R3, R4, R', R", n, X, and Z are as defined herein.
Preferred
embodiments are those where R3 and R4 are hydrogen, L is halogen, including
but not
limited to Cl, and R5-NH2 is cyclopentylamine.
100921 Still another aspect of the invention provides a process for preparing
the
compounds of formula II:
OR'
H O B-OR2
N
R244 ' )n
Y m 1- X
76
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
by coupling a 2-boroheterocycle having the fonnula:
OR'
B-OR2
HN 1
X I n
z
with the corresponding N-protected cyclic amino acid; optionally deprotecting
the
boronic acid ester; and recovering the resultant compound as a free acid or as
an acid
addition salt. Rland R2 are not hydrogen, and n, X, and Z are as defined
herein. Typically
the 2-boroheterocycle is a 2-boropyrrolidino or 2-boropiperidino. In some such
embodiments, the N-protected cyclic amino acid is N-Boc-4-phenyl-boroPro-OH.
[0093] The compounds of the invention may be prepared in the form of
pharmaceutically acceptable salts, especially acid-addition salts, including
salts of organic
acids and mineral acids. Examples of such salts include salts of organic acids
such as
formic acid, fumaric acid, acetic acid, propionic acid, glycolic acid, lactic
acid, pyruvic
acid, oxalic acid, succinic acid, malic acid, tartaric acid, citric acid,
benzoic acid, salicylic
acid and the like. Suitable inorganic acid-addition salts include salts of
hydrochloric,
hydrobromic, sulphuric and phosphoric acids and the like. Further examples of
pharmaceutically acceptable inorganic or organic acid addition salts include
the
pharmaceutically acceptable salts listed in Journal of Pharmaceutical Science,
66, 2 (1977)
which are known to the skilled artisan.
[0094] The acid addition salts may be obtained as the direct products of
compound
synthesis. In the altemative, the free base may be dissolved in a suitable
solvent containing
the appropriate acid, and the salt isolated by evaporating the solvent or
otherwise separating
the salt and solvent.
100951 The compounds of this invention may form solvates with standard low
molecular
weight solvents, including water to yield hydrates, using methods known to the
skilled
artisan.
[0096] It is to be understood that the invention extends to all of the
stereoisomeric forms
of the claimed compounds, including enantiomers and diastereomers, as well as
the
racemates.
77
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
Methods/Uses
[0097) Another aspect of the invention provides methods and uses for the
compounds of
the invention. In one approach, the invention compounds can be administered to
an
individual suffering from a disease or condition mediated by a post-
proline/alanine cleaving
amino-dipeptidase. In this embodiment, the individual is administered an
amount of the
invention compound effective in reducing the activity of the post-
proline/alanine cleaving
amino-dipeptidase and, thereby, reducing or alleviating symptoms of the
disease or
condition. In some embodiments, the administered compound reduces the
activtity of DPP-
IV. In some embodiments, the disease or condition is selected from the group
consisting of
diabetes, diabetec complications, hyperglycemia, Syndrome X, hyperinsulinemia,
obesity,
atherosclerosis and related diseases. The invention compounds to be
administered may be
one or more of the inventive bronic acid compounds, which may be formulated in
any
manner as described here, including combination with "other type(s) of
therapeutic agents"
identified further below.
[0098] Other exemplary embodiments of the invention methods are represented
by:
[00991 Methods for inhibiting DPP-IV comprising administering to a mammal in
need of
such treatment a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of the
invention, or a
pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salt thereof;
[00100] Methods for treating conditions mediated by DPP-IV comprising
administering to
a mammal in need of such treatment a therapeutically effective amount of a
compound of
the invention, or a pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salt thereof;
[00101] Methods for treating controlling, or preventing diabetes comprising
administering to a patient of an effective amount of a compound of the
invention;
[00102) Methods for treating, controlling, or preventing insulin dependent
(Type I) and/or
non-insulin dependent (Type 2) diabetes mellitus in a mammalian patient in
need of such
treatment, comprising administering to the patient a therapeutically effective
amount of a
compound of the invention;
78
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
[00103] Methods for treating, controlling or preventing hyperglycemia in a
mammalian
patient in need of such treatment, comprising administering to the patient a
therapeutically
effective amount of a compound of the invention;
[00104] Methods for treating, controlling or preventing obesity in a mammalian
patient in
need of such treatment, comprising administering to the patient a
therapeutically effective
amount of a compound of the invention;
[00105] Methods for treating to enhance islet neogenesis, b-cell survival, and
insulin
biosynthesis in a mammalian patient in need of such treatment, comprising
administering to
the patient a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of the invention;
[001061 Methods for treating, controlling or preventing insulin resistance in
a mammalian
patient in need of such treatment, comprising administering to the patient a
therapeutically
effective amount of a compound of the invention;
1001071 Methods for treating, controlling or preventing one or more lipid
disorders
selected from the group consisting of dyslipidemia, hyperlipidemia,
hypertriglyceridemia,
hypercholesterolemia, low HDL, and high LDL in a mammalian patient in need of
such
treatment, comprising administering to the patient a therapeutically effective
amount of a
compound of the invention;
[00108] Methods for treating, controlling or preventing atherosclerosis in a
manunalian
patient in need of such treatment, comprising administering to the patient a
therapeutically
effective amount of a compound of the invention;
1001091 Methods for treating or controlling growth hormone deficiency in a
mammalian
patient in need of such treatment, comprising administering to the patient a
therapeutically
effective amount of a compound of the invention;
1001101 Methods for modulating the immune response in a mammalian patient in
need of
such treatment, comprising administering to the patient a therapeutically
effective amount
of a compound of the invention;
[00111] Methods for treating, or controlling HIV infection in a mammalian
patient in
need of such treatment, comprising administering to the patient a
therapeutically effective
amount of a compound of the invention;
79
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 20051047297 PCT/US2004/037820
[00112] Methods for treating, controlling or preventing in a mammalian patient
in need of
such treatment one or more disorders selected from the group consisting of
neutropenia,
anemia, neuronal disorders, tumor growth and metastasis, benign prostatic
hypertrophy,
gingivitis, hypertension and osteoporosis, comprising administering to the
patient a
therapeutically effective amount of a compound of the invention;
[00113] Methods for reducing sperm motility in a male in a mammalian patient
in need of
such treatment, comprising administering to the patient a therapeutically
effective amount
of a compound of the invention;
[00114] Methods for treating, controlling or preventing in a mammalian patient
in need of
such treatment one or more conditions selected from the group consisting of
(1)
hyperglycemia, (2) low glucose tolerance, (3) insulin resistance, (4) obesity,
(5) lipid
disorders, (6) dyslipidemia, (7) hyperlipidemia, (8) hypertriglyceridemia, (9)
hypercholesterolemia, (10) low HDL levels, (11) high LDL levels, (12)
atherosclerosis and
its sequelae, (13) vascular restenosis, (14) irritable bowel syndrome, (15)
inflammatory
bowel disease, including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, (16)
rheumatoid arthritis,
(17) other inflammatory conditions, (18) pancreatitis, (19) abdominal obesity,
(20)
neurodegenerative disease, (21) multiple sclerosis, (22) retinopathy, (23)
nephropathy, (24)
neuropathy, (25) Syndrome X, (26) ovarian hyperandrogenism, (27) allograft
rejection in
transplantation, and other conditions where insulin resistance is a component,
comprising
administering to the patient a therapeutically effective amount of a compound
of the
invention;
[00115] Methods for treating, controlling or preventing in a mammalian patient
in need of
such treatment one or more conditions selected from the group consisting of
(1)
hyperglycemia, (2) low glucose tolerance, (3) insulin resistance, (4) obesity,
(5) lipid
disorders, (6) dyslipidemia, (7) hyperlipidemia, (8) hypertriglyceridemia, (9)
hypercholesterolemia, (10) low HDL levels, (11) high LDL levels, (12)
atherosclerosis and
its sequelae, (13) vascular restenosis, (14) irritable bowel syndrome, (15)
inflammatory
bowel disease, including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, (16)
rheumatoid arthritis,
(17) other inflammatory conditions, (18) pancreatitis, (19) abdominal obesity,
(20)
neurodegenerative disease, (21) multiple sclerosis, (22) retinopathy, (23)
nephropathy, (24)
neuropathy, (25) Syndrome X, (26) ovarian hyperandrogenism, (27) allograft
rejection in
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US20041037820
transplantation, (28) Type II diabetes, (29) growth hormone deficiency, (30)
neutropenia,
(31) anemia, (32) neuronal disorders, (33) tumor growth and metastasis, (34)
benign
prostatic hypertrophy, (35) gingivitis, (36) hypertension, (37) osteoporosis,
and other
conditions that may be treated by inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV,
comprising
administering to the patient of a therapeutically effective amount of a first
compound of the
invention, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, and one or more
other compounds
selected from the group consisting of:
a) Other dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitors;
b) Insulin sensitizers selected from the group consisting of (i) PPAR
agonists,
(ii) biguanides, and (iii) protein phosphatase-1B inhibitors;
c) Insulin or insulin mimetics;
d) Sulfonylureas or other insulin secretagogues;
e) a-glucosidase inhibitors;
f) glucagons receptor agonists;
g) GLP-1, GLP-1 mimetics, and GLP-1 receptor agonists;
h) GLP-2, GLP-2 mimetics, and GLP-2 receptor agonists;
i) GIP, GIP mimetics, and GIP receptor agonists;
j) PACAP, PACAP mimetics, and PACAP receptor 3 agonists;
k) Cholesterol lowering agents selected from the group consisting of (i) HMG-
CoA reductase inhibitors, (ii) sequestrants, (iii) nicotinyl alcohol,
nicotinic acid or a salt
thereof, (iv) PPARa agonists, (v) PPARa/y dual agonists, (vi) inhibitors of
cholesterol
absorption, (vii) acyl CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase inhibitors, and (viii)
anti-oxidants;
1) PPARS agonists;
m) Anti-obesity compounds;
n) An ileal bile acid transporter inhibitor;
o) Anti-inflammatory agents;
p) G-CSF, G-CSF mimetics, and G-CSF receptor agonists; and
q) EPO, EPO mimetics, and EPO receptor agonists.
[00116] Methods for the treatment, control, or prevention of one or more
conditions
selected from the group consisting of hypercholesterolemia, atherosclerosis,
low HDL
levels, high LDL levels, hyperlipidemia, hypertriglyceridemia, and
dyslipidemia,
comprising administering to a mammalian patient in need of such treatment a
81
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
therapeutically effective amount of a compound of the invention and an HMG-CoA
reductase inhibitor;
1001171 Methods wherein the HMC-CoA reductase inhibitor is a statin;
[00118] Methods wherein the statin is selected from the group consisting of
lovastatin,
simvastatin, pravastatin, fluvastatin, atorvastatin, itavastatin, ZD-4522 and
rivastatin;
[00119] Methods for treating, controlling or preventing atherosclerosis,
comprising
administering to a mammalian patient in need of such treatment a
therapeutically effective
amount of a compound of the invention and an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor;
[00120] Methods for treating, controlling or preventing obesity, comprising
administering
to a mammalian patient in need of such treatment a therapeutically effective
amount of a
compound of the invention and an anti-obesity agent;
[00121] Methods wherein the anti-obesity agent is a beta-3 adrenergic agonist,
a lipase
inhibitor, a serotonin (and dopamine) reuptake inhibitor, a thyroid receptor
beta compound,
an anorectic agent, and/or a fatty acid oxidation upregulator;
[00122] Methods wherein the anti-obesity agent is orlistat, ATL-962, AJ9677,
L750355,
CP331648, sibutramine, topiramate, axokine, dexamphetamine, phentermine,
phenylpropanolamine, famoxin, and/or mazindol;
[00123] Methods for the treatment, control, or prevention of neutropenia
comprising
administering to a mammalian patient in need of such treatment a
therapeutically effective
amount of a compound of the invention and a neutrophilic agent;
[0100] Methods for the treatment, control, or prevention of neutropenia
wherein the
neutrophilic agent is G-CSF, a G-CSF mimetic, or a G-CSF receptor agonist;
101011 Methods for the treatment, control, or prevention of neutropenia
wherein the
neutrophilic agent is pegfilgrastim, filgrastim, lenograstim, or nartograstim;
101021 Methods for the treatment, control, or prevention of anemia, comprising
administering to a mammalian patient in need of such treatment a
therapeutically effective
amount of a compound of the invention and a erythropoietin agonist;
82
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
[0103] Methods for the treatment, control, or prevention of anemia wherein the
erythropoietin agonist is EPO, an EPO mimetic, or an EPO receptor agonist;
[0104] Methods for the treatment, control, or prevention of anemia wherein the
erythropoietin agonist is epoetin alfa, or darbepoetin alfa;
[0105] Methods for treating diabetes, insulin resistance, hyperglycemia,
hyperisulinemia,
or elevated blood levels of free fatty acids or glycerol, obesity, Syndrome X,
dysmetabolic
syndrome, diabetic complications, hypertriglyceridemia, hyperinsulinemia,
atherosclerosis,
impaired glucose homeostasis, impaired glucose tolerance, infertility,
polycystic ovary
syndrome, growth disorders, frailty, arthritis, allograft rejection in
transplantation,
autoimmune diseases, AIDS, intestinal diseases, inflammatory bowel syndrome,
nervosa,
osteoporosis, or an immunomodulatory disease or a chronic inflammatory bowel
disease,
comprising administering to a mammalian species in need of treatment a
therapeutically
effective amount of a compound of the invention;
[0106] Methods for treating type II diabetes and/or obesity;
[0107] A variety of uses of the invention compounds are possible along the
lines of the
various methods of the treating an individual such as a mammal described
above.
Exemplary uses of the invention methods are represented by:
[0108] Use of a compound of the invention for the manufacture of a medicament
for
treating a condition that may be regulated or normalized via inhibition of DPP-
IV;
[0109J Use of a compound of the invention for the manufacture of a medicament
for
treatment of metabolic disorders;
[0110] Use of a compound of the invention for the manufacture of a medicament
for
blood glucose lowering;
[0111] Use of a compound of the invention for the manufacture of a medicament
for
treatment of type II diabetes;
[0112] Use of a compound of the invention for the manufacture of a medicament
for the
treatment of impaired glucose tolerance (IGT);
83
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 20051047297 PCT1US20041037820
[01131 Use of a compound of the invention for the manufacture of a medicament
for the
treatment of impaired fasting glucose (IFG);
101141 Use of a compound of the invention for the manufacture of a medicament
for
prevention of hyperglycemia;
[0115] Use of a compound of the invention for the manufacture of a medicament
for
delaying the progression of impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) to type II
diabetes;
[0116] Use of a compound of the invention for the manufacture of a medicament
for
delaying the progression of non-insulin requiring type II diabetes to insulin
requiring type II
diabetes;
[0117] Use of a compound of the invention for the manufacture of a medicament
for
increasing the number and/or the size of beta cells in a mammalian subject;
[0118] Use of a compound of the invention for the manufacture of a medicament
for
treatment of beta cell degeneration, in particular apoptosis of beta cells.
101191 Use of a compound of the invention for the manufacture of a medicament
for the
treatment of disorders of food intake;
[0120] Use of a compound of the invention for the manufacture of a medicament
for the
treatment of obesity;
101211 Use of a compound of the invention for the manufacture of a medicament
for
appetite regulation or induction of satiety;
[01221 Use of a compound of the invention for the manufacture of a medicament
for the
treatment of dyslipidemia;
[0123) Use of a compound of the invention for the manufacture of a medicament
for
treatment of functional dyspepsia, in particular irritable bowel syndrome; and
[0124] Methods for treating the conditions mentioned above by administering to
a
subject in need thereof an effective amount of a compound of the invention.
84
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
Combination Treatments
[0125] The compounds of the invention may be used in combination with one or
more
other types of antidiabetic agents (employed to treat diabetes and related
diseases) and/or
one or more other types of therapeutic agents which may be administered orally
in the same
dosage form, in a separate oral dosage form or by injection.
[01261 The other type of antidiabetic agent which may be optionally employed
in
combination with the DPP-IV inhibitors of the invention may be 1,2,3 or more
antidiabetic
agents or antihyperglycemic agents including insulin secretagogues or insulin
sensitizers, or
other antidiabetic agents preferably having a mechanism of action different
from DPP-IV
inhibition and may include biguanides, sulfonyl ureas, glucosidase inhibitors,
PPAR y
agonists, such as thiazolidinediones, SGLT2 inhibitors, PPAR al Y dual
agonists, aP2
inhibitors, glycogen phosphorylase inhibitors, advanced glycosylation end
(AGE) products
inhibitors, and/or meglitinides, as well as insulin, and/or glucagon-like
peptide-1 (GLP-1) or
mimetics thereof.
[0127] The use of the compounds of the invention in combination with 1, 2, 3
or more
other antidiabetic agents may produce antihyperglycemic results greater than
that possible
from each of these medicaments alone and greater than the combined additive
antihyperglycemic effects produced by these medicaments.
[0128] The other antidiabetic agent may be an oral antihyperglycemic agent
preferably a
biguanide such as metformin or phenformin or salts thereof, preferably
metformin HCI.
[01291 Where the other antidiabetic agent is a biguanide, the compounds of the
invention
will be employed in a weight ratio to biguanide within the range from about
0.01:1 to about
100:1, preferably from about 0.1:1 to about 5:1.
[0130] Preferably, the other antidiabetic agent can be a sulfonyl urea such as
glyburide
(also known as glibenclamide), glimepiride (disclosed in U.S. patent No.
4,379,785),
glipizide, gliclazide or chlorpropamide, other known sulfonylureas or other
antihyperglycemic agents which act on the ATP-dependent channel of the y-
cells, with
glyburide and glipizide being preferred, which may be administered in the same
or in
separate oral dosage forms.
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
[0131] The compounds of the invention will be employed in a weight ratio to
the
sulfonyl urea in the range from about 0.01:1 to about 100:1, preferably from
about 0.05:1 to
about 5:1.
[0132] The oral antidiabetic agent may also be a glucosidase inhibitor such as
acarbose
(disclosed in U.S. patent No. 4,904,769) or miglitol (disclosed in U.S. patent
No.
4,639,436), which may be administered in the same or in a separate oral dosage
forms.
101331 The compounds of the invention will be employed in a weight ratio to
the
glucosidase inhibitor within the range from about 0.01:1 to about 100:1,
preferably from
about 0.2:1 to about 50:1.
[0134] The compounds of the invention may be employed in combination with a
PPAR y
agonist such as a thiazolidinedione oral anti-diabetic agent or other insulin
sensitizers
(which has an insulin sensitivity effect in NIDDM patients) such as
troglitazone (Warner-
Lambert's Rezulin , disclosed in U.S. patent No. 4,572,912), rosiglitazone
(en),
pioglitazone (Takeda), Mitsubishi MCC-555 (disclosed in U.S. patent No.
5,594,016),
Glaxo-Wellcome's GL-262570, englitazone (CP-68722, Pfizer) or darglitazone (CP-
86325,
Pfizer), isaglitazone (MIT/J&J), JTT-501 (JPNT/P&U), L-895645 (Merck), R-1
19702
(Sankyo/WL), NN-2344 (Dr. Reddy/NN), or YM-440 (Yamanouchi), preferably
rosiglitazone and pioglitazone.
[0135] The compounds of the invention will be employed in a weight ratio to
the
thiazolidinedione in an amount within the range from about 0.01:1 to about
100:1,
preferably from about 0.1:1 to about 10:1.
101361 The sulfonyl urea and thiazolidinedione in amounts of less than about
150 mg
oral antidiabetic agent may be incorporated in a single tablet with the
compounds of the
invention.
[0137] The compounds of the invention may also be employed in combination with
a
antihyperglycemic agent such as insulin or with glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-
1) such as
GLP-1(1-36) amide, GLP-1(7-36) amide, GLP-1(7-36) (as disclosed in U.S. Patent
No.
5,614,492 to Habener, disclosure of which is incorporated herein by
reference), or a GLP-l
mimic such as AC2993 or Exendin-4 (Amylin) and LY-315902 or LY-307167 (Lilly)
and
86
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
NN2211 (Novo-Nordisk), which may be administered via injection, intranasal, or
by
transdenmal or buccal devices.
101381 Where present, metformin, the sulfonyl ureas, such as glyburide,
glimepiride,
glipyride, glipizide, chlorpropamide and gliclazide and the glucosidase
inhibitors acarbose
or miglitol or insulin (injectable, pulmonary, buccal, or oral) may be
employed in
formulations as described above and in amounts and dosing as indicated in the
PHYStCiAN's
DESK REFERENCE (PDR).
[0139] Where present, metformin or salt thereof may be employed in amounts
within the
range from about 500 to about 2000 mg per day which may be administered in
single or
divided doses one to four times daily.
[0140] Where present, the thiazolidinedione anti-diabetic agent may be
employed in
amounts within the range from about 0.01 to about 2000 mg/day which may be
administered in single or divided doses one to four times per day.
[0141] Where present insulin may be employed in formulations, amounts and
dosing as
indicated by the PHYS1CtAN'S DESK REFERENCE.
[0142) Where present GLP-1 peptides may be administered in oral buccal
formulations,
by nasal administration (for example inhalation spray) or parenterally as
described in U.S.
Patent Nos. 5,346,701 (TheraTech), 5,614,492 and 5,631,224 which are
incorporated herein
by reference.
[0143] The other antidiabetic agent may also be a PPAR a/y dual agonist such
as AR-
H039242 (Astra/Zeneca), GW-409544 (Glaxo-Wellcome), KRP297 (Kyorin Merck), as
well as those disclosed by Murakami et al., "A Novel Insulin Sensitizer Acts
As a Coligand
for Peroxisome Proliferation--Activated Receptor Alpha (PPAR alpha) and PPAR
gamma.
Effect on PPAR alpha Activation on Abnonmal Lipid Metabolism in Liver of
Zucker Fatty
Rats," Diabetes 47: 1841-47 (1998), and in U.S. application Ser. No.
09/664,598, filed Sep.
18, 2000, (attorney file LA29NP), the disclosure of which is incorporated
herein by
reference, employing dosages as set out therein, which compounds designated as
preferred
are preferred for use herein.
87
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US20041037820
[0144) The other antidiabetic agent may be an SGLT2 inhibitor, as disclosed in
U.S.
Application Ser. No. 09/679,027, filed Oct. 4, 2000 (attorney file LA49NP),
which is
incorporated herein by reference, employing dosages as set out herein.
Preferred are the
compounds designated as preferred in the above application.
[0145] The other antidiabetic agent, which may be employed in combination with
the
DPP-IV inhibitors in accordance with the present invention, can be an aP2
inhibitor,09/519,079, filed Mar. 6, 2000 (attorney file LA27NP), which are
each
incorporated herein by reference, employing dosages as set out herein.
Preferred
antidiabetic agents to be used in combination with the invention compounds are
those
indicated as preferred in the above cited patents.
[0146) The other antidiabetic agent that may employed with the DPP-IV
inhibitors of the
invention can be a glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor as disclosed, for
instance, in WO
96/39384, WO 96/39385, WO 99/26659, WO 99/43663, WO 2000/47206, EP 978279, EP
1041068, and U.S. patents No. 5,952,322 and No. 5,998,463.
[01471 The meglitinide which may optionally be employed in combination with
the
compound of the invention may be repaglinide, nateglinide (Novartis) or
KAD1229
(PF/Kissei), with repaglinide being preferred.
[0148) The DPP-IV inhibitors of the invention will be employed in a weight
ratio to the
meglitinide, PPAR y agonist, PPAR oJ y dual agonist, SGLT2 inhibitor, aP2
inhibitor, or
glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor within the range from about 0.01:1 to about
100:1,
preferably from about 0.1:1 to about 10:1.
(0149) The hypolipidemic agent or lipid-modulating agent which may be
optionally
employed in combination with the compounds of the invention may include 1,2,3
or more
MTP inhibitors, HMG CoA reductase inhibitors, squalene synthetase inhibitors,
fibric acid
derivatives, ACAT inhibitors, lipoxygenase inhibitors, cholesterol absorption
inhibitors,
ileal Na+/bile acid cotransporter inhibitors, upregulators of LDL receptor
activity, ATP
citrate lyase inhibitors, cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitors, bile
acid sequestrants,
and/or nicotinic acid and derivatives thereof.
[0150) MTP inhibitors employed herein include MTP inhibitors disclosed in U.S.
patents
No. 5,595,872, No. 5,739,135, No. 5,712,279, No. 5,760,246, No. 5,827,875, No.
88
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
5,885,983,-and No. 5,962,440. MTP inihibitors preferred herein are thos
identified as being
preferred in the above referenced patents.
[01511 Most preferred MTP inhibitors, in accordance with the present
invention, are
implitapide (Bayer) and those set out in U.S. patents No. 5,739,135, No.
5,712,279, and No.
5,760,246. A particularly peferred MTP inhibitor in this context is 9-[4-[4-
[[2-(2,2,2-
Trifluoroethoxy)-benzoyl]amino]-1-piperidinyl] butyl]-N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-
9H-
fluorene-9-carboxamide.
[0152] The hypolipidemic agent may be an HMG CoA reductase inhibitor which
includes, but is not limited to, mevastatin and related compounds as disclosed
in U.S. patent
No. 3,983,140, lovastatin (mevinolin) and related compounds disclosed in U.S.
patent
No. 4,231,938, pravastatin and related compounds such as disclosed in U.S.
Patent No.
4,346,227, simvastatin and related compounds as disclosed in U.S. Patent Nos.
4,448,784
and 4,450,171. Other HMG CoA reductase inhibitors which may be employed herein
include, but are not limited to, fluvastatin, disclosed in U.S. Patent No.
5,354,772,
cerivastatin disclosed in U.S. patents No. 5,006,530 and No. 5,177,080,
atorvastatin
disclosed in U.S. patents No. 4,681,893, No. 5,273,995, No. 5,385,929 and No.
5,686,104,
atavastatin (Nissan/Sankyo nisvastatin (NK-104)), disclosed in U.S. patent No.
5,011,930,
and Shionogi-Astra/Zeneca visastatin (ZD-4522), disclosed in U.S. patent No.
5,260,440.
[0153] The squalene synthetase inhibitors suitable for use herein include, but
are not
limited to, a-phosphono-sulfonates disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 5,712,396,
those disclosed
by Biller et a], J. Med. Chem., 1988, Vol. 11, No. 10, pp 1869-1871, including
isoprenoid
(phosphinyl-methyl)phosphonates as well as other known squalene synthetase
inhibitors, for
example, as disclosed in U.S. Patent Nos. 4,871,721 and 4,924,024 and in
Biller, S. A.,
Neuenschwander, K., Ponpipom, M. M., and Poulter, C. D., Current
Pharmaceutical
Design, 2, 1-40 (1996).
[01541 In addition, other squalene synthetase inhibitors suitable for use
herein include
the terpenoid pyrophosphates disclosed by P. Ortiz de Montellano et a], J.
Med. Chem.,
1977, 20, 243-249, the farnesyl diphosphate analog A and presqualene
pyrophosphate
(PSQ-PP) analogs as disclosed by Corey and Volante, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1976,
98, 1291-
1293, phosphinylphosphonates reported by McClard, R. W. et al, J.A.C.S., 1987,
10, 5544
89
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCTIUS2004/037820
and cyclopropanes reported by Capson, T. L., PhD dissertation, June, 1987,
Dept. Med.
Chem. U of Utah, Abstracts Table of Contents, pp 16, 17, 40-43, 48-51,
Summary.
[0155] Other hypolipidemic agents suitable for use herein include, but are not
limited to,
fibric acid derivatives, such as fenofibrate, gemfibrozil, clofibrate,
bezafibrate, ciprofibrate,
clinofibrate, and the like, probucol, and related compounds as disclosed in
U.S. Patent No.
3,674,836, probucol and gemfibrozil being preferred, bile acid sequestrants
such as
cholestyramine, colestipol and DEAE-Sephadex (Secholex , Policexide ), as well
as
lipostabil (Rhone-Poulenc), Eisai E-5050 (an N-substituted ethanolamine
derivative),
imanixil (HOE-402), tetrahydrolipstatin (THL), istigmastanylphos-phorylcholine
(SPC,
Roche), aminocyclodextrin (Tanabe Seiyoku), Ajinomoto AJ-814 (azulene
derivative),
melinamide (Sumitomo), Sandoz 58-035, American Cyanamid CL-277,082 and CL-
283,546 (disubstituted urea derivatives), nicotinic acid, acipimox, acifran,
neomycin, p-
aminosalicylic acid, aspirin, poly(dialiylmethylamine) derivatives such as
disclosed in U.S.
Patent No. 4,759,923, quaternary amine poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride)
and
ionenes such as disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 4,027,009, and other known serum
cholesterol
lowering agents.
[0156] The other hypolipidemic agent may be an ACAT inhibitor such as
disclosed in 24
DRUGS OF THE FuTUttE 9-15 (Avasimibe 1999), "The ACAT inhibitor, Cl-1011 is
effective
in the prevention and regression of aortic fatty streak area in hamsters",
Nicolosi et al,
Atherosclerosis (Shannon, Irel). (1998), 137(1), 77-85; "The pharmacological
profile of
FCE 27677: a novel ACAT inhibitor with potent hypolipidemic activity mediated
by
selective suppression of the hepatic secretion of ApoB 100-containing
lipoprotein", Ghiselli,
Giancarlo, Cardiovasc. Drug Rev. (1998), 16(l), 16-30; "RP 73163: a
bioavailable
alkylsulfinyl-diphenylimidazole ACAT inhibitor", Smith, C., et al, Bioorg.
Med. Chem.
Lett. (1996), 6(1), 47-50; "ACAT inhibitors: physiologic mechanisms for
hypolipidemic
and anti-atherosclerotic activities in experimental animals", Krause et al,
Editor(s): Ruffolo,
Robert R., Jr.; Hollinger, Mannfred A., Inflammation: Mediators Pathways
(1995), 173-98,
Publisher: CRC, Boca Raton, Fla.; "ACAT inhibitors: potential anti-
atherosclerotic agents",
Sliskovic et al, Curr. Med. Chem. (1994), 1(3), 204-25; "Inhibitors of acyl-
CoA:cholesterol
0-acyl transferase (ACAT) as hypocholesterolemic agents. 6. The first water-
soluble ACAT
inhibitor with lipid-regulating activity. Inhibitors of acyl-CoA:cholesterol
acyltransferase
(ACAT). 7. Development of a series of substituted N-phenyl-N'-[(1-
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
phenylcyclopentyl)methyl]ureas with enhanced hypocholesterolemic activity",
Stout et al,
Chemtracts: Org. Chem. (1995), 8(6), 359-62, or TS-962 (Taisho Pharmaceutical
Co. Ltd).
[01571 The hypolipidemic agent may be an upregulator of LD2 receptor activity
such as
MD-700 (Taisho Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd) and LY295427 (Eli Lilly).
[0158] The hypolipidemic agent may be a cholesterol absorption inhibitor
preferably
Schering-Plough's SCH48461 as well as those disclosed in Atherosclerosis 115,
45-63
(1995) and J. Med. Chem. 41, 973 (1998).
[0159] The hypolipidemic agent may be an ileal Na+/bile acid cotransporter
inhibitor
such as disclosed in Drugs of the Future, 24, 425-430 (1999).
[0160] The lipid-modulating agent may be a cholesteryl ester transfer protein
(CETP)
inhibitor such as Pfizer's CP 529,414 (WO/0038722 and EP 818448) and
Pharmacia's SC-
744 and SC-795.
[0161] The ATP citrate lyase inhibitor which may be employed in the
combination of the
invention may include, for example, those disclosed in U.S. patent No.
5,447,954.
[0162] Preferred hypolipidemic agents are pravastatin, lovastatin,
simvastatin,
atorvastatin, fluvastatin, cerivastatin, atavastatin and ZD-4522.
[0163]. The above-mentioned U.S. patents are incorporated herein by reference.
The
amounts and dosages employed will be as indicated in the Physician's Desk
Reference
and/or in the patents set out above.
[0164] The compounds of the invention will be employed in a weight ratio to
the
hypolipidemic agent (where present), within the range from about 500:1 to
about 1:500,
preferably from about 100:1 to about 1:100.
[0165] The dose administered must be carefully adjusted according to age,
weight and
condition of the patient, as well as the route of administration, dosage form
and regimen and
the desired result.
[0166] The dosages and formulations for the hypolipidemic agent will be as
disclosed in
the various patents and applications discussed above.
91
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
[01671 The dosages and fonmulations for the other hypolipidemic agent to be
employed,
where applicable, will be as set out in the latest edition of the Physicians'
Desk Reference.
[0168] For oral administration, a satisfactory result may be obtained
employing the MTP
inhibitor in an amount within the range of from about 0.01 mg/kg to about 500
mg and
preferably from about 0.1 mg to about 100 mg, one to four times daily.
[01691 An oral dosage form, such as tablets or capsules, will contain the MTP
inhibitor
in an amount of from about 1 to about 500 mg, preferably from about 2 to about
400 mg,
and more preferably from about 5 to about 250 mg, one to four times daily.
[0170] For oral administration, a satisfactory result may be obtained
employing an HMG
CoA reductase inhibitor, for example, pravastatin, lovastatin, simvastatin,
atorvastatin,
fluvastatin or cerivastatin in dosages employed as indicated in the PHYS[CwN's
DESK
REFERENCE, such as in an amount within the range of from about 1 to 2000 mg,
and
preferably from about 4 to about 200 mg.
[0171] The squalene synthetase inhibitor may be employed in dosages in an
amount
within the range of from about 10 mg to about 2000 mg and preferably from
about 25 mg to
about 200 mg.
[0172] A preferred oral dosage form, such as tablets or capsules, will contain
the HMG
CoA reductase inhibitor in an amount from about 0.1 to about 100 mg,
preferably from
about 5 to about 80 mg, and more preferably from about 10 to about 40 mg.
[0173] A preferred oral dosage form, such as tablets or capsules will contain
the
squalene synthetase inhibitor in an amount of from about 10 to about 500 mg,
preferably
from about 25 to about 200 mg.
(01741 The other hypolipidemic agent may also be a lipoxygenase inhibitor
including a
15-lipoxygenase (15-LO) inhibitor such as benzimidazole derivatives as
disclosed in WO
97/12615, 15-LO inhibitors as disclosed in WO 97/12613, isothiazolones as
disclosed in
WO 96/38144, and 15-LO inhibitors as disclosed by Sendobry et al "Attenuation
of diet-
induced atherosclerosis in rabbits with a highly selective 15-lipoxygenase
inhibitor lacking
significant antioxidant properties", Brit. J. Pharmacology (1997) 120, 1199-
1206, and
92
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
Cornicelli et al, "15-Lipoxygenase and its Inhibition: A Novel Therapeutic
Target for
Vascular Disease", Current Pharmaceutical Design, 1999, 5, 11-20.
[0175J The compounds of the invention and the hypolipidemic agent may be
employed
together in the same oral dosage form or in separate oral dosage fonms taken
at the same
time.
[01761 The compositions described above may be administered in the dosage
forms as
described above in single or divided doses of one to four times daily. It may
be advisable to
start a patient on a low dose combination and work up gradually to a high dose
combination.
[01771 The preferred hypolipidemic agent is pravastatin, simvastatin,
lovastatin,
atorvastatin, fluvastatin or cerivastatin.
101781 The other type of therapeutic agent which may be optionally employed
with the
DPP-IV inhibitors of the invention may be 1, 2, 3 or more of an anti-obesity
agent including
a beta 3 adrenergic agonist, a lipase inhibitor, a serotonin (and dopamine)
reuptake
inhibitor, a thyroid receptor beta drug, an anorectic agent and/or a fatty
acid oxidation
upregulator.
[0179] The beta 3 adrenergic agonist which may be optionally employed in
combination
with a compound of the invention may be AJ9677 (Takeda/Dainippon), L750355
(Merck),
or CP331648 (Pfizer) or other known beta 3 agonists as disclosed in U.S.
patents No.
5,541,204, No. 5,770,615, No. 5,491,134, No. 5,776,983 and No. 5,488,064, with
AJ9677,
L750,355 and CP331648 being preferred.
101801 The lipase inhibitor which may be optionally employed in combination
with a
compound of the invention may be orlistat or ATL-962 (Alizyme), with orlistat
being
preferred.
101811 The serotonin (and dopamine) reuptake inhibitor which may be optionally
employed in combination with a compound of the invention may be sibutramine,
topiramate
(Johnson & Johnson) or axokine (Regeneron), with sibutramine and topiramate
being
preferred.
[0182J The thyroid receptor beta compound which may be optionally employed in
combination with a compound of the invention may be a thyroid receptor ligand
as
93
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
disclosed in W097/21993 (U. Cal SF), W0099/00353 (KaroBio) and GB98/284425
(KaroBio), with compounds of the KaroBio applications being preferred.
(0183] The anorectic agent which may be optionally employed in combination
with a
compound of the invention may be dexamphetamine, phentermine,
phenylpropanolamine or
mazindol, with dexamphetamine being preferred.
[0184] The fatty acid oxidation upregulator which may be optionally employed
in
combination with the compound of the invention can be famoxin (Genset).
[0185] The various anti-obesity agents described above may be employed in the
same
dosage form with the compound of the invention or in different dosage forms,
in dosages
and regimens as generally known in the art or in the PDR.
[0186] The infertility agent which may be optionally employed in combination
with the
DPP-IV inhibitor of the invention may be 1, 2, or more of clomiphene citrate
(Clomid ,
Aventis), bromocriptine mesylate (Parlodel , Novartis),LHRH analogs, Lupron
(TAP
Pham1.), danazol, Danocrine (Sanofi), progestogens or glucocorticoids, which
may be
employed in amounts specified in the PDR.
[0187] The agent for polycystic ovary syndrome which may be optionally
employed in
combination with the DPP-IV inhibitor of the invention may be 1, 2, or more of
gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH), leuprolide (Lupron ), Clomid , Parlodel
, oral
contraceptives or insulin sensitizers such as PPAR agonists, or other
conventional agents for
such use which may be employed in amounts specified in the PDR.
[0188] The agent for treating growth disorders and/or frailty which may be
optionally
employed in combination with the DPP-IV inhibitor of the invention may be 1,
2, or more
of a growth hormone or growth hormone secretagogue such as MK-677 (Merck), CP-
424,391 (Pfizer), and compounds disclosed in U.S. Ser. No. 09/506,749 filed
Feb. 18, 2000
(attorney docket LA26), as well as selective androgen receptor modulators
(SAR1VIs), which
is incorporated herein by reference, which may be employed in amounts
specified in the
PDR, where applicable.
[01891 The agent for treating arthritis which may be optionally employed in
combination
with the DPP-IV inhibitor of fhe invention may be 1, 2, or more of aspirin,
indomethacin,
94
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
ibuprofen, diclofenac sodium, naproxen, nabumetone (Relafen , SmithKline
Beecham),
tolmetin sodium (Tolectin , Ortho-McNeil), piroxicam (Feldene , Pfizer),
ketorolac
tromethamine (Toradol , Roche), celecoxib (Celebrex , Searle), rofecoxib
(Vioxx ,
Merck) and the like, which may be employed in amounts specified in the PDR.
[0190] Conventional agents for preventing allografft rejection in
transplantation such as
cyclosporin, Sandimmune (Novartis), azathioprine, Immuran (Faro) or
methotrexate may be
optionally employed in combination with the DPP-IV inhibitor of the invention,
which may
be employed in amounts specified in the PDR.
[01911 Conventional agents for treating autoimmune diseases such as multiple
sclerosis
and immunomodulatory diseases such as lupus erythematosis, psoriasis, for
example,
azathioprine, Immuran, cyclophosphamide, NSAIDS such as ibuprofen, cox 2
inhibitors
such as Vioxx and Celebrex, glucocorticoids and hydroxychloroquine, may be
optionally
employed in combination with the DPP-IV inhibitor of the invention, which may
be
employed in amounts specified in the PDR.
[0192] The AIDS agent which may be optionally employed in combination with the
DPP-IV inhibitor of the invention may be a non-nucleoside reverse
transcriptase inhibitor, a
nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, a protease inhibitor and/or an
AIDS adjunct anti-
infective and may be l, 2, or more of dronabinol (Marinol , Roxane Labs),
didanosine
(Videx , Bristol-Myers Squibb), megestrol acetate (Megace(&, Bristol-Myers
Squibb),
stavudine (Zerit , Bristol-Myers Squibb), delavirdine mesylate (Rescriptor ,
Pharmacia),
lamivudine/zidovudine (Combivir.TM., Glaxo), lamivudine (Epivir.TM., Glaxo),
zalcitabine (Hivid , Roche), zidovudine (Retrovir , Glaxo), indinavir sulfate
(Crixivan ,
Merck), saquinavir (Fortovase.TM., Roche), saquinovir mesylate (Invirase ,
Roche),
ritonavir (Norvir , Abbott), nelfinavir (Viracept , Agouron).
[0193] The above anti-AIDS agents may be employed in amounts specified in the
PDR.
101941 The agent for treating inflammatory bowel disease or syndrome which may
be
optionally employed in combination with the DPP-IV inhibitor of the invention
may be 1, 2,
or more of sulfasalazine, salicylates, mesalamine (Asacol(&, P&G) or Zelmac ,
(Bristol-
Myers Squibb), which may be employed in amounts specified in the PDR or
otherwise
known in the art.
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
[0195] Tb.e agent for treating osteoporosis which may be optionally employed
in
combination with the DPP-IV inhibitor of the invention may be 1, 2, or more of
alendronate
sodium (Fosamax , Merck, tiludronate (Skelid , Sanofi), etidronate disodium
(Didronel ,
P&G), raloxifene HC1(Evista , Lilly), which may be employed in amounts
specified in the
PDR.
[01961 In carrying out the methods of the invention, a pharmaceutical
composition may
be employed containing the compounds of the invention, with or without another
antidiabetic agent and/or other type therapeutic agent, in association with a
pharmaceutical
vehicle or diluent. The pharmaceutical composition can be formulated employing
conventional solid or liquid vehicles or diluents and pharmaceutical additives
of a type
appropriate to the mode of desired administration. The compounds can be
administered to
mammalian species including humans, monkeys, dogs, etc. by an oral route, for
example, in
the form of tablets, capsules, granules or powders, or they can be
administered by a
parenteral route in the form of injectable preparations. The dose for adults
is preferably
between 10 and 1,000 mg per day, which can be administered in a single dose or
in the form
of individual doses from 1-4 times per day.
[0197] A typical capsule for oral administration contains compounds of the
invention
(250 mg), lactose (75 mg) and magnesium stearate (15 mg). The mixture is
passed through
a 60 mesh sieve and packed into a No. I gelatin capsule. A typical injectable
preparation is
produced by aseptically placing 250 mg of compounds of the invention into a
vial,
aseptically freeze-drying and sealing. For use, the contents of the vial are
mixed with 2 mL
of physiological saline, to produce an injectable preparation.
[0198) DPP-IV inhibitor activity of the compounds of the invention may be
detennined
by use of an in vitro assay system which measures the potentiation of
inhibition of DPP-IV.
Inhibition constants (Ki values) for the DPP-IV inhibitors of the invention
may be
determined by the method described below.
Pharmaceutical Compositions
[0199] Pharmaceutical compositions containing a compound of the invention of
the
invention may be prepared by conventional techniques, e.g. as described in
Remington: The
Science and Practise of Pharmacy, 19th Ed., 1995. The compositions may appear
in
96
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
conventional forms, for example capsules, tablets, aerosols, solutions,
suspensions or topical
applications.
[0200] Typical compositions include a compound of the invention which inhibits
the
enzymatic activity of DPP-IV or a pharmaceutically acceptable basic addition
salt or
prodrug or hydrate thereof, associated with a pharmaceutically acceptable
excipient which
may be a carrier or a diluent or be diluted by a carrier, or enclosed within a
carrier which
can be in the form of a capsule, sachet, paper or other container. In making
the
compositions, conventional techniques for the preparation of pharmaceutical
compositions
may be used. For example, the active compound will usually be mixed with a
carrier, or
diluted by a carrier, or enclosed within a carrier which may be in the form of
a ampoule,
capsule, sachet, paper, or other container. When the carrier serves as a
diluent, it may be
solid, semi-solid, or liquid material that acts as a vehicle, excipient, or
medium for the
active compound. The active compound can be adsorbed on a granular solid
container for
example in a sachet. Some examples of suitable carriers are water, salt
solutions, alcohols,
polyethylene glycols, polyhydroxyethoxylated castor oil, peanut oil, olive
oil, gelatin,
lactose, terra alba, sucrose, dextrin, magnesium carbonate, sugar,
cyclodextrin, amylose,
magnesium stearate, talc, gelatin, agar, pectin, acacia, stearic acid or lower
alkyl ethers of
cellulose, silicic acid, fatty acids, fatty acid amines, fatty acid
monoglycerides and
diglycerides, pentaerythritol fatty acid esters, polyoxyethylene,
hydroxymethylcellulose and
polyvinylpyrrolidone. Similarly, the carrier or diluent may include any
sustained release
material known in the art, such as glyceryl monostearate or glyceryl
distearate, alone or
mixed with a wax. The formulations may also include wetting agents,
emulsifying and
suspending agents, preserving agents, sweetening agents or flavoring agents.
The
formulations of the invention may be formulated so as to provide quick,
sustained, or
delayed release of the active ingredient after administration to the patient
by employing
procedures well known in the art.
102011 The pharmaceutical compositions can be sterilized and mixed, if
desired, with
auxiliary agents, emulsifiers, salt for influencing osmotic pressure, buffers
and/or coloring
substances and the like, which do not deleteriously react with the active
compounds.
102021 The route of administration may be any route, which effectively
transports the
active compound of the invention which inhibits the enzymatic activity of DPP-
IV to the
97
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCTIUS2004/037820
appropriate or desired site of action, such as oral, nasal, pulmonary, buccal,
subdenmal,
intradermal, transdermal or parenteral, e.g., rectal, depot, subcutaneous,
intravenous,
intraurethral, intramuscular, intranasal, ophthalmic solution or an ointment,
the oral route
being preferred.
[0203] If a solid carrier is used for oral administration, the preparation may
be tabletted,
placed in a hard gelatin capsule in powder or pellet form or it can be in the
form of a troche
or lozenge. If a liquid carrier is used, the preparation may be in the form of
a syrup,
emulsion, soft gelatin capsule or sterile injectable liquid such as an aqueous
or non-aqueous
liquid suspension or solution.
[0204] For nasal administration, the preparation may contain a compound of the
invention which inhibits the enzymatic activity of DPP-IV, dissolved or
suspended in a
liquid carrier, in particular an aqueous carrier, for aerosol application. The
carrier may
contain additives such as solubilizing agents, e.g., propylene glycol,
surfactants, absorption
enhancers such as lecithin (phosphatidylcholine) or cyclodextrin, or
preservatives such as
parabenes.
[02051 For parenteral application, particularly suitable are injectable
solutions or
suspensions, preferably aqueous solutions with the active compound dissolved
in
polyhydroxylated castor oil.
[02061 Tablets, dragees, or capsules having talc and/or a carbohydrate carrier
or binder
or the like are particularly suitable for oral application. Preferable
carriers for tablets,
dragees, or capsules include lactose, corn starch, and/or potato starch. A
syrup or elixir can
be used in cases where a sweetened vehicle can be employed.
[0207) A typical tablet that may be prepared by conventional tabletting
techniques may
contain:
98
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
Core:
Active compound (as free compound or salt thereof) 250 mg
Colloidal silicon dioxide (AerosiI) 1.5 mg
Cellulose, microcryst. (Avicel) 70 mg
Modified cellulose gum (Ac-Di-Sol) 7.5 mg
Magnesium stearate Ad.
Coating:
HPMC approx. 9 mg
*Mywacett 9-40 T approx. 0.9 mg
*Acylated monoglyceride used as plasticizer for film coating.
[0208] The compounds of the invention may be administered to a mammal,
especially a
human in need of such treatment, prevention, elimination, alleviation or
amelioration of the
various diseases as mentioned above, e.g., type II diabetes, IGT, IFG,
obesity, appetite
regulation or as a blood glucose lowering agent, and especially type II
diabetes. Such
mammals include also animals, both domestic animals, e.g. household pets, and
non-
domestic animals such as wildlife.
[0209] The compounds of the invention are effective over a wide dosage range.
For
example, in the treatment of adult humans, dosages from about 0.05 to about
1000 mg,
preferably from about 1 to about 500 mg, per day may be used. A typical dosage
is about 10
mg to about 500 mg per day. In choosing a regimen for patients it may
frequently be
necessary to begin with a higher dosage and when the condition is under
control to reduce
the dosage. The exact dosage will depend upon the mode of administration, on
the therapy
desired, form in which administered, the subject to be treated and the body
weight of the
subject to be treated, and the preference and experience of the physician or
veterinarian in
charge.
[02101 Generally, the compounds of the invention are dispensed in unit dosage
form
comprising from about 0.05 to about 1000 mg of active ingredient together with
a
pharmaceutically acceptable carrier per unit dosage.
99
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
[0211] Usually, dosage forms suitable for oral, nasal, pulmonal or transdermal
administration comprise from about 0.05 mg to about 1000 mg, preferably from
about 0.5
mg to about 250 mg of the compounds admixed with a pharmaceutically acceptable
carrier
or diluent.
[0212) The invention also encompasses prodrugs of a compound of the invention
which
on administration undergo chemical conversion by metabolic processes before
becoming
active pharmacological substances. In general, such prodrugs will be
functional derivatives
of a compound of the invention which are readily convertible in vivo into a
compound of
the invention. Conventional procedures for the selection and preparation of
suitable prodrug
derivatives are described, for example, in "Design of Prodrugs", ed. H.
Bundgaard, Elsevier,
1985.
[02131 The invention also encompasses active metabolites of a compound of the
invention.
[02141 Thus, another aspect of the invention provides pharmaceutical
compositions of
the compounds of the invention, alone or in combination with another type
antidiabetic
agent and/or other type therapeutic agent.
[02151 In one example, the embodiments of the invention are represented by:
[02161 Pharmaceutical compositions comprising, as an active ingredient, at
least one
compound of the invention which inhibits the enzymatic activity of DPP-IV or a
pharmaceutically acceptable salt or prodrug or hydrate thereof together with a
pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or diluent;
[02171 Pharmaceutical compositions comprising a compound of the invention as
described herein, in free form or in pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition
salt form,
together with at least one pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or diluent;
[02181 Pharmaceutical compositions comprising a compound of formula VA, VB, or
a
mixture thereof and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or diluent;
100
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
102191 Pharmaceutical compositions comprising:
a. a substantially pure preparation of a compound of formula VB as described
herein; and
b. a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or diluent;
[02201 Methods of making a pharmaceutical composition comprising mixing a
substantially pure preparation of a compound of formula VB with a
pharmaceutically
acceptable carrier or diluent;
[02211 Methods of making a pharmaceutical composition of a compound described
herein wherein the pharmaceutically acceptable camier or diluent is suitable
for oral
administration;
[02221 Methods of making a pharmaceutical composition of a compound described
herein suitable for for oral administration further comprising the step of
formulating the
composition into a tablet or capsule;
[0223] Methods of making a pharmaceutical composition of a compound described
herein wherein the pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or diluent is suitable
for parenteral
administration;
[02241 Methods of making a pharmaceutical composition of a compound described
herein suitable for parenteral administration further comprising the step of
lyophilizing the
composition to form a lyophilized preparation;
[02251 Pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment, prevention or control of
atherosclerosis, comprising: (1) a compound of the invention, (2) an HMG-CoA
reductase
inhibitor, and (3) a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier;
[02261 Pharmaceutical compositions, comprising:
a) A compound of the invention;
b) One or more compounds selected from the group consisting of:
i) Other dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitors;
ii) Insulin sensitizers selected from the group consisting of (i) PPAR
agonists, (ii) biguanides, and (iii) protein phosphatase-1B inhibitors;
101
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
iii) Insulin or insulin mimetics;
iv) Sulfonylureas or other insulin secretagogues;
v) a-glucosidase inhibitors;
vi) glucagons receptor agonists;
vii) GLP- 1, GLP-1 mimetics, and GLP-1 receptor agonists;
viii) GIP, GIP mimetics, and GIP receptor agonists;
ix) PACAP, PACAP niimetics, and PACAP receptor 3 agonists;
x) GLP-2, GLP-2 mimetics, and GLP-2 receptor agonists;
xi) Cholesterol lowering agents selected from the group consisting of (i)
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, (ii) sequestrants, (iii) nicotinyl alcohol,
nicotinic acid or a salt thereof, (iv) PPARa agonists, (v) PPARo:/y dual
agonists, (vi) inhibitors of cholesterol absorption, (vii) acyl
CoA:cholesterol
acyltransferase inhibitors, and (viii) anti-oxidants;
xii) PPARS agonists;
xiii) Anti-obesity compounds;
xiv) An ileal bile acid transporter inhibitor;
xv) Anti-inflammatory agents;
xvi) G-CSF, G-CSF mimetics, and G-CSF receptor agonists;
xvii) EPO, EPO mimetics, and EPO receptor agonists; and
c) a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
[02271 Pharmaceutical combinations comprising a compound of the invention, an
antidiabetic agent other than a DPP-IV inhibitor for treating diabetes and
related diseases,
and an anti-obesity agent or a lipid-modulating agent or both.
[0228] Pharmaceutical combinations comprising a compound of the invention and
an
antidiabetic agent;
[02291 Pharmaceutical combinations comprising a compound of the invention and
an
antidiabetic agent wherein the antidiabetic agent is 1, 2, 3 or more of a
biguanide, a sulfonyl
urea, a glucosidase inhibitor, a PPAR y agonist, a PPAR a/y dual agonist, an
SGLT2
inhibitor, an aP2 inhibitor, a glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor, an AGE
inhibitor, an insulin
sensitizer, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) or mimetic thereof, insulin
and/or a
meglitinide;
102
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
102301 Phanmaceutical combinations comprising a compound of the invention and
an
antidiabetic agent wherein the antidiabetic agent is 1, 2, 3 or more of
inetformin, glyburide,
glimepiride, glipyride, glipizide, chlorpropamide, gliclazide, acarbose,
miglitol,
pioglitazone, troglitazone, rosiglitazone, insulin, Gl -262570, isaglitazone,
JTT-501, NN-
2344, L895645, YM-440, R-1 19702, AJ9677, repaglinide, nateglinide, KAD1129,
APR-
H039242, GW-409544, KRP297, AC2993, Exendin-4, LY307161, NN221 1, and/or
LY315902;
[0231] Pharmaceutical combinations comprising a compound of the invention and
an
antidiabetic agent wherein the compound is present in a weight ratio to the
antidiabetic
agent within the range from about 0.01 to about 100:1;
[02321 Pharmaceutical combinations comprising a compound of the invention and
an
antidiabetic agent wherein the anti-obesity agent is a beta 3 adrenergic
agonist, a lipase
inhibitor, a serotonin (and dopamine) reuptake inhibitor, a thyroid receptor
beta compound,
an anorectic agent, and/or a fatty acid oxidation upregulator;
[0233] Pharmaceutical combinations comprising a compound of the invention and
an
anti-obesity agent wherein the anti-obesity agent is orlistat, ATL-962,
AJ9677, L750355,
CP331648, sibutramine, topiramate, axokine, dexamphetamine, phentermine,
phenylpropanolamine, famoxin, and/or mazindol;
[0234] Pharmaceutical combinations comprising a compound of the invention and
a
lipid-modulating agent wherein the lipid-modulating agent is an MTP inhibitor,
an HMG
CoA reductase inhibitor, a squalene synthetase inhibitor, a fibric acid
derivative, an
upregulator of LDL receptor activity, a lipoxygenase inhibitor, an ACAT
inhibitor, a
cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitor, or an ATP citrate lyase
inhibitor;
[0235] Pharmaceutical combinations comprising a compound of the invention and
a
lipid-modulating agent wherein the lipid-modulating agent is pravastatin,
lovastatin,
simvastatin, atorvastatin, cerivastatin, fluvastatin, nisvastatin, visastatin,
fenofibrate,
gemfibrozil, clofibrate, implitapide, CP-529,414, avasimibe, TS-962, MD-700,
and/or
LY295427;
103
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCTIUS2004/037820
102361 Pharmaceutical combinations comprising a compound of the invention and
a
lipid-modulating agent wherein the compound is present in a weight ratio to
the lipid-
modulating agent within the range from about 0.01 to about 100:1;
102371 Pharmaceutical combinations comprising a compound of the invention and
an
agent for treating infertility, an agent for treating polycystic ovary
syndrome, an agent for
treating a growth disorder and/or frailty, an anti-arthritis agent, an agent
for preventing
inhibiting allograft rejection in transplantation, an agent for treating
autoimmune disease, an
anti-AIDS agent, an agent for treating inflammatory bowel disease/syndrome, an
agent for
treating anorexia nervosa, an anti-osteoporosis agent and/or an anti-obesity
agent.
Methods For Measuring Activity
[0238] The following methods were used to measure the activities of the
compounds of
the invention which inhibit the enzymatic activity of DPP-IV. The compounds of
the
invention are tested for their ability to inhibit the enzyme activity of
purified DPP-IV.
Briefly, the activity of DPP-IV is measured in vitro by its ability to cleave
the synthetic
substrate Gly-Pro-p-nitroanilide (Gly-Pro-pNA). Cleavage of Gly-Pro-pNA by DPP-
IV
liberates the product p-nitroanilide (pNA), whose rate of appearance is
directly proportional
to the enzyme activity. Inhibition of the enzyme activity by specific enzyme
inhibitors
slows down the generation of pNA. Stronger interaction between an inhibitor
and the
enzyme results in a slower rate of generation of pNA. Thus, the degree of
inhibition of the
rate of accumulation of pNA is a direct measure of the strength of enzyme
inhibition. The
accumulation of pNA is measured spectrophotometrically. The inhibition
constant, Ki, for
each compound is determined by incubating fixed amounts of enzyme with several
different
concentrations of inhibitor and substrate.
[02391 Thus, DPP-IV enzyme activity was determined by a fluorometric assay
with the
substrate Gly-Pro-AMC which is cleaved by DPP-IV to release the fluorescent
AMC
leaving group. Free AMC (7-amino-4-methyl coumarin) was measured using an
excitation
wavelength of 380 nm and an emission wavelength of 460 nm with a Victor-II
fluorescent
reader. Stock solutions of DPP-IV (1 ng/ l, pH 8.0) and Gly-Pro-AMC substrate
(400 M)
in 25 mM Tris buffer (pH 8.0) were prepared separately. Test compounds were
dissolved in
DMSO or in 50 mM glycine buffer (pH 3.0). The assay was performed by diluting
the
DPP-IV stock (10 1) into 25 mM Tris buffer (77.5 41) followed by addition of
test
104
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
compound (2.5 gl) at 26 C. After 10-minutes substrate was added (10 l) and
allowed to
react for 20-minutes at 26 C before free AMC was measured. IC50 values were
determined
in triplicate, using a minimum of six different inhibitor concentrations. IC50
values were
calculated using Nonlinear Regression Analysis (GraphPad, Prism, San Diego,
CA).
102401 To determine the DPP-IV activity in the plasma of mice dosed with test
compounds, plasma (10 l) was diluted into 25 mM Tris buffer (80 41, pH 8.0)
followed by
addition of Gly-Pro-AMC stock solution (10 l) and the free AMC measured after
20-
minutes at 26 C. Analysis was performed as described above.
[02411 The Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) rat model can be used to investigate
the effects
of the compounds of the invention on both the treatment and prevention of
diabetes as rats
of this sub-strain are initially pre-diabetic although they develop severe
type 2 diabetes
characterized by increased HbAI c levels over a period of 6 weeks. The same
strain can be
used to predict the clinical efficacy of other anti-diabetic drug types. For
example, the
model predicts the potency and limited clinical efficacy of thiazolidinedione
insulin
sensitizer compounds.
(0242] The purification of porcine DPP-IV and the enzyme assay under steady
state
conditions are described in (1) Rahfeld, J. Schutkowski, M., Faust, J.,
Neubert., Barth, A.,
and Heins, J. (1991) Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler, 372, 313-318; and (2) Nagatsu,
T., Hino,
M., Fuyamada, H., Hayakawa, T., Sakakibara, S., Nakagawa, Y., and Takemoto, T.
(1976)
Anal. Biochem., 74, 466-476, respectively.
DEFINITIONS
102361 The term "DPP-IV" denotes dipeptidyl peptidase IV (EC 3.4.14.5; DPP-
IV),
also known as "CD-26." DPP-IV cleaves a dipeptide from the N terminus of a
polypeptide
chain containing a proline or alanine residue in the penultimate position.
[0237] The term "diabetes and related diseases" refers to Type II diabetes,
Type I
diabetes, impaired glucose tolerance, obesity, hyperglycemia, Syndrome X,
dysmetabolic
syndrome, diabetic complications, diabetic dyslipidemia, hyperinsulinemia, and
the like.
105
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
102381 The conditions, diseases and maladies collectively referred to as
"diabetic
complications" include retinopathy, neuropathy and nephropathy, and other
known
complications of diabetes.
[0239] The term "other type(s) of therapeutic agents" as employed herein
refers to one
or more antidiabetic agents (other than DPP-IV inhibitors of the invention),
one or more
anti-obesity agents, and/or one or more lipid-modulating agents (including
anti-
atherosclerosis agents), and/or one or more infertility agents, one or more
agents for treating
polycystic ovary syndrome, one or more agents for treating growth disorders,
one or more
agents for treating frailty, one or more agents for treating arthritis, one or
more agents for
preventing allograft rejection in transplantation, one or more agents for
treating autoimmune
diseases, one or more anti-AIDS agents, one or more anti-osteoporosis agents,
one or more
agents for treating immunomodulatory diseases, one or more agents for treating
chronic
inflammatory bowel disease or syndrome and/or one or more agents for treating
anorexia
nervosa.
[02401 The term "lipid-modulating" agent as employed herein refers to agents
which
lower LDL and/or raise HDL and/or lower triglycerides and/or lower total
cholesterol
and/or other known mechanisms for therapeutically treating lipid disorders.
[0241] The term "treatment" is defined as the management and care of a patient
for the
purpose of combating the disease, condition, or disorder and includes
administering a
compound of the present invention to prevent the onset of the symptoms or
complications,
or alleviating the symptoms or complications, or eliminating the disease,
condition, or
disorder.
[0242] The term "beta cell degeneration" is intended to mean loss of beta cell
function,
beta cell dysfunction, and death of beta cells, such as necrosis or apoptosis
of beta cells.
[0243] By "substantially pure" in relation to compounds of the invention such
as, but
not limited to, those of formula VA and VB, it is meant that one isomer or the
other,
including all enantiomers, diastereoisomers, solvates, hydrates, and
pharmaceutically
106
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT1US2004/037820
acceptable salts thereof, represents at least 90% by weight of the
composition. In some
embodiments one isomer represents at least 98% by weight of the composition.
(0244] The term "boronic acid protecting group" as used herein refers to a
moiety
employed to block or protect the boronic acid functionality while reactions
involving other
functional sites of the compound are carried out. Typically, the boronic acid
OH groups are
protected as boronic acid esters derived from alchohols such as (+)-
pinanediol; pinacol; 1,2-
dicyclohexyl-ethanediol; 1,2-ethanediol; 2,2-diethanolamine; 1,3-propanediol;
2,3-
butanediol, diisopropyl tartrate; 1,4-butanediol; diisopropylethanediol;
(S,S,)-5,6-
decanediol; 1,1,2-triphenyl-1,2-ethanediol; (2R,3R)-1,4-dimethyoxy-1,1,4,4-
tetraphenyl-
2,3-butanediol; methanol; ethanol; isopropanol; catechol; 1-butanol; and the
like. As will
be understood by those skilled in the art, alcohols having only a single
hydroxy group, such
as methanol, forni diesters having the structure -B(OR)2 in which R is the
organic moiety
from the alcohol (e.g., -B(OMe)2). By comparison, diols such as pinacol form
cyclic
boronic diesters with -B(OH)2 in which the organic moiety (e.g., -C(Me)2-
C(Me)2-)is
attached to both oxygens.
[0245] The term "N-protecting group" or "N-protected" as used herein refers to
those
groups intended to protect the N-terminus of an amino acid or peptide or to
protect an
amino group against undesirable reactions during synthetic procedures.
Commonly used N-
protecting groups are disclosed in T.W. Greene, P. G. Wuts, "Protective Groups
In Organic
Synthesis, 3~d Ed." (John Wiley & Sons, New York (1999)), which is hereby
incorporated
by reference. N-protecting groups comprise acyl groups such as formyl, acetyl,
propionyl,
pivaloyl, t-butylacetyl, 2-chloroacetyl, 2-bromoacetyl, trifluoroacetyl,
trichloroacetyl,
phthalyl, o-nitrophenoxyacetyl, a-chlorobutyryl, benzoyl, 4-chlorobenzoyl, 4-
bromobenzoyl, 4-nitrobenzoyl, and the like; sulfonyl groups such as
benzenesulfonyl, p-
toluenesulfonyl and the like; carbamate fonming groups such as
benzyloxycarbonyl, p-
chlorobenzyloxycarbonyl, p-methoxybenzyloxycarbonyl, p-nitrobenzyloxycarbonyl,
2-
nitrobenzyloxycarbonyl, p-bromobenzyloxycarbonyl, 3,4-
dimethoxybenzyloxycarbonyl,
3,5-dimethoxybenzyloxycarbonyl, 2,4-dimethoxybenzyloxycarbonyl, 4-
methoxybenzyloxycarbonyl, 2-nitro-4,5-dimethoxybenzyloxycarbonyl, 3,4,5-
trimethoxybenzyloxycarbonyl, 1-(p-biphenylyl)-1-methylethoxycarbonyl, a,a-di
methyl-
3,5-dimethoxybenzyloxycarbonyl, benzhydryloxycarbonyl, t-butyloxycarbonyl,
diisopropylmethoxycarbonyl, isopropyloxycarbonyl, ethoxycarbonyl,
methoxycarbonyl,
107
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
allyloxycarbonyl, 2,2,2,-trichloroethoxycarbonyl, phenoxycarbonyl, 4-
nitrophenoxycarbonyl, fluorenyl-9-methoxycarbonyl, cyclopentyloxycarbonyl,
adamantyloxycarbonyl, cyclohexyloxycarbonyl, phenylthiocarbonyl and the like;
alkyl
groups such as benzyl, triphenylmethyl, benzyloxymethyl and the like; and
silyl groups
such as trimethylsilyl and the like. Preferred N-protecting groups are formyl,
acetyl,
benzoyl, pivaloyl, t-butylacetyl, phenylsulfonyl, benzyl, 9-
fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl
(Fmoc), t-butyloxycarbonyl (Boc) and benzyloxycarbonyl (Cbz).
[0246] The term "alkyl" or "(C1_12)alkyl", alone or in combination, refers to
linear or
branched chains and may include cyclic portions, having from 1-12 (the use of
1-12 herein
implies each of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12) carbon atoms, such
as but not limited
to, e.g. methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, sec-butyl, isobutyl,
tert-butyl, n-pentyl,
2-methylbutyl, 3-methylbutyl, n-hexyl, 4-methylpentyl, neopentyl, 2,2-
dimethylpropyl, and
the like.
[0247] The terms "(Ci.Io)alkyl", "(C1_8)alkyl" and "(CI_6)alkyP", alone or in
combination,'refers to linear or branched chains and may include cyclic
portions, having
from 1-10, 1-8, or 1-6 carbon atoms, respectively, such as but not limited to,
e.g. methyl,
ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, sec-butyl, isobutyl, tert-butyl, n-
pentyl, 2-methylbutyl,
3-methylbutyl, n-hexyl, 4-methylpentyl, neopentyl, 2,2-dimethylpropyl, and the
like.
[0248] The term "(C]4)alkyl", alone or in combination, refers to linear or
branched
chains and may include cyclic portions, having from 1-4 carbon atoms, such as
but not
limited to, e.g. methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, sec-butyl,
isobutyl, tert-butyl, and
the like.
[0249] The terms "(C2_12)alkenyl" and "(C2_io)alkenyl", alone or in
combination, refers
to. a straight or branched, unsaturated hydrocarbon chain having from 2-12 or
2-10 carbon
atoms, respectively, and at least one double bond, such as, but not limited
to, vinyl, 1-
propenyl, allyl, isopropenyl, n-butenyl, n-pentenyl, n-hexenyl, and the like.
[0250] The terms "(C2.12)alkynyl" and "(CZ.io)alkynyl", alone or in
combination, refers
to an unsaturated hydrocarbon chain having from 2-12 or 2-10 carbon atoms,
respectively,
and at least one triple bond, such as but not limited to -C=CH, -C=C-CH3i -
CH2C=CH, -
CH2-CHZ-C=CH, -CH(CH3)C=CH, and the like.
108
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
[0251] The terms "(C3.1Z)cycloalkyl" and "(C3_lo)cycloalkyl" refers to one or
more
saturated cyclic hydrocarbons having from 3-12 or 3-10 carbon atoms,
respectively, such as,
but not limited to, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl,
adamantyl, and the
like.
[0252] The term "(C5_jo)cycloalkenyl" refers to a radical of one or more
cyclic
hydrocarbon having at least one double bond having from 5-10 carbon atoms such
as, but
not limited to, cyclopentenyl, cyclohexenyl, and the like.
[0253] The term "cycloalkylene" refers to a "cycloalkyl" group which has
single bonds
for attachment at two different carbon atoms.
[0254] The terms "(C1_6)alkylaminocarbonyl" and "di-(CI-6)alkylaminocarbonyl"
refer
to straight or branched chain hydrocarbon groups having 1 to 6 carbon atoms
connected to
NC(=O). Exemplary alkyl groups include but are not limited to methyl, ethyl,
propyl,
isopropyl, n-butyl, t-butyl, isobutyl, pentyl, hexyl, and the like.
[0255] The term "(C1_6)alkylcarbonyl" refers to linear or branched chain and
cyclic
hydrocarbon groups having I to 6 carbon atoms connected to C(=0). Exemplary
alkyl
groups include but are not limited to methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, n-
butyl, t-butyl,
isobutyl, pentyl, hexyl, and the like.
[0256] The term (C3_g)cycloalkylcarbonyl refers to cyclic hydrocarbon groups
having 3
to 8 carbon atoms connected to C(=O). Exemplary cycloalkyl groups include but
are not
limited to cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, and the like.
[0257] The terms "(Ci_lo)alkoxy", "(C,_8)alkoxy" and "(CI-6)alkoxy", alone or
in
combination, refers to "0" connected to alkyl, having linear or branched
chains and may
include cyclic portions, having from 1-10, 1-8 or 1-6 carbon atoms,
respectively. Examples
of linear alkoxy groups include but are not limited to methoxy, ethoxy,
propoxy, butoxy,
pentoxy, hexoxy, and the like. Examples of branched alkoxy include but are not
limited to
isoprpoxy, sec-butoxy, tert-butoxy, isopentoxy, isohexoxy, and the like.
Examples of cyclic
109
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
alkoxy include but are not limited to cyclopropyloxy, cyclobutyloxy,
cyclopentyloxy,
cyclohexyloxy, and the like.
[02581 The term "aryloxy" refers to an aryl group bonded to O.
[0259] The term "alkanoyl", alone or as part of another group, refers to alkyl
linked to
a carbonyl group.
[0260] The term "alkylene" refers to alkyl groups which have single bonds for
attachment at two different carbon atoms.
[0261] The term "alkenylene" refers to alkenyl groups which have single bonds
for
attachement at two different carbon atoms.
[0262] The terms "alkynylene" refers to alkynyl groups which have single bonds
for
attachement at two different carbon atoms.
[0263] The term "aryl" refers to monocyclic, bicyclic, or tricyclic
carbocyclic aromatic
ring systems having 6 to 14 carbon atoms in the ring portion. Examples of aryl
groups
include but are not limited to phenyl, naphthyl, biphenyl, anthracenyl,
azulenyl, and the like.
Aryl is also intended to include the partially hydrogenated derivatives of the
carbocyclic
systems including 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-naphthyl, indanyl and the like.
[0264] The term "heteroaryl" as used herein includes heterocyclic unsaturated
ring
systems containing one or more heteroatoms selected from nitrogen, oxygen and
sulphur.
Examples of heteroaryl groups include but are not limited to furyl, thienyl,
pyrrolyl, and the
like. Heteroaryl is also intended to include the partially hydrogenated
derivatives of the
heterocyclic systems enumerated below.
[02651 Examples of "aryl" and "heteroaryl" includes but are not limited to
phenyl,
biphenyl, indenyl, naphthyl (1-naphthyl, 2-naphthyl), N-hydroxytetrazolyl, N-
hydroxytriazolyl, N-hydroxyimidazolyl, anthracenyl (1-anthracenyl, 2-
anthracenyl, 3-
anthracenyl), thiophenyl (2-thienyl, 3-thienyl), furyl (2-furyl, 3-furyl),
indolyl, oxadiazolyl,
110
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
isoxazolyl, quinazolinyl, fluorenyl, xanthenyl, isoindanyl, benzhydryl,
acridinyl, thiazolyl,
pyrrolyl (2-pyrrolyl), pyrazolyl (3-pyrazolyl), imidazolyl (1-imidazolyl, 2-
imidazolyl, 4-
imidazolyl, 5-imidazolyl), triazolyl (1,2,3-triazol-1-yl, 1,2,3-triazol-2-yl
1,2,3-triazol-4-yl,
1,2,4-triazol-3-yl), oxazolyl (2-oxazolyl, 4-oxazolyl, 5-oxazolyl), thiazolyl
(2-thiazolyl, 4-
thiazolyl, 5-thiazolyl), pyridyl (2-pyridyl, 3-pyridyl, 4-pyridyl),
pyrimidinyl (2-pyrimidinyl,
4-pyrimidinyl, 5-pyrimidinyl, 6-pyrimidinyl), pyrazinyl, pyridazinyl (3-
pyridazinyl, 4-
pyridazinyl, 5-pyridazinyl), quinolyl (2-quinolyl, 3-quinolyl, 4-quinolyl, 5-
quinolyl, 6-
quinolyl, 7-quinolyl, 8-quinolyl), isoquinolyl (1-isoquinolyl, 3-isoquinolyl,
4-isoquinolyl, 5-
isoquinolyl, 6-isoquinolyl, 7-isoquinolyl, 8-isoquinolyl), benzo[b]furanyl (2-
benzo[b]furanyl, 3-benzo[b]furanyl, 4-benzo[b]furanyl, 5-benzo[b]furanyl,
6-benzo[b]furanyl, 7-benzo[b]furanyl), 2,3-dihydro-benzo[b]furanyl (2-(2,3-
dihydro-
benzo[b]furanyl), 3-(2,3-dihydro-benzo[b]furanyl), 4-(2,3-dihydro-
benzo[b]furanyl),
5-(2,3-dihydro-benzo[b]furanyl), 6-(2,3-dihydro-benzo[b]furanyI), 7-(2,3-
dihydro-
benzo[b]furanyl), benzo[b]thiophenyl (2-benzo[b]thiophenyl, 3-
benzo[b]thiophenyl,
4-benzo[b]thiophenyl, 5-benzo[b]thiophenyl, 6-benzo[b]thiophenyl, 7-
benzo[b]thiophenyl),
2,3-dihydro-benzo[b]thiophenyl, (2-(2,3-dihydro-benzo[b]thiophenyl), 3-(2,3-
dihydro-
benzo[b]thiophenyl), 4-(2,3-dihydro-benzo[b]thiophenyl), 5-(2,3-dihydro-
benzo[b]thiophenyl), 6-(2,3-dihydro-benzo[b]thiophenyl), 7-(2,3-dihydro-
benzo[b]thiophenyl), indolyl (1-indolyi, 2-indolyl, 3-indolyl, 4-indolyl, 5-
indolyl, 6-indolyl,
7-indolyl), indazole (1-indazolyl, 3-indazolyl, 4-indazolyl, 5-indazolyl, 6-
indazolyl, 7-
indazolyl), benzimidazolyl (1-benzimidazolyl, 2-benzimidazolyl, 4-
benzimidazolyl, 5-
benzimidazolyl, 6-benzimidazolyl, 7-benzimidazolyl, 8-benzimidazolyl),
benzoxazolyl (1-
benzoxazolyl, 2-benzoxazolyl), benzothiazolyl (1-benzothiazolyl, 2-
benzothiazolyl, 4-
benzothiazolyl, 5-benzothiazolyl, 6-benzothiazoly], 7-benzothiazolyl),
carbazolyl (1-
carbazolyl, 2-carbazolyl, 3-carbazolyl, 4-carbazolyl), 5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine
(5H-
dibenz[b,fJazepin-1-yl, 5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine-2-yl, 5H-dibenz[b,flazepine-3-
yl, 5H-
dibenz[b,fJazepine-4-yl, 5H-dibenz[b,fJazepine-5-yl), 10,1 I-dihydro-5H-
dibenz[b,f]azepine
(10,11-dihydro-SH-dibenz[b,fJazepine-l-yl, 10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine-
2-yl,
10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine-3-yl, 10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine-
4-yl,
10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine-5-yl), and the like.
[0266] The terms "arylalkenyl" and "arylalkynyl" alone or as part of another
group
refer to alkenyl and alkynyl groups as described above having an aryl
substituent.
111
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
[02671 The terms "halogen" and "halo" refers to chloro, fluoro, bromo or iodo.
[0268] The term "alkylamino", "arylamino", or "arylalkylamino" alone or as
part of
another group includes any of the above alkyl, aryl or arylalkyl groups linked
to a nitrogen
atom.
[0269] The term "substituted amino" as employed herein alone or as part of
another
group refers to amino substituted with one or two substituents, which may be
the same or
different, such as alkyl, aryl, arylalkyl, heteroaryl, heteroarylalkyl,
cycloheteroalkyl,
cycloheteroalkylalkyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl haloalkyl, hydroxyalkyl,
alkoxyalkyl or
thioalkyl. These substituents may be further substituted with any of the
groups as set out
above. In addition, the amino substituents may be taken together with the
nitrogen atom to
which they are attached to form 1-pyrrolidinyl, 1-piperidinyl, 1-azepinyl, 4-
morpholinyl, 4-
thiamorpholinyl, 1-piperazinyl, 4-alkyl-l-piperazinyl, 4-arylalkyl-l-
piperazinyl, 4-
diarylalkyl-l-piperazinyl, 1-pyrrolidinyl, 1-piperidinyl, or 1-azepinyl,
optionally substituted
with alkyl, alkoxy, alkylthio, halo, trifluoromethyl or hydroxy.
[02701 The terms "alkylthio", "arylthio" or "aralkylthio" alone or as part of
another
group includes any of the above alkyl, aralkyl or aryl groups linked to a
sulfur atom.
[0271] The tenm "acyl" by itself or part of another group refers to an organic
radical
linked to a carbonyl group; examples of acyl groups include any of the groups
attached to a
carbonyl, such as alkanoyl, alkenoyl, aroyl, aralkanoyl, heteroaroyl,
cycloalkanoyl,
cycloheteroalkanoyl, and the like.
102721 The term "cycloheteroalkyl" alone or as part of another group refers to
a 3-, 4-,
5-, 6- or 7-membered saturated or partially unsaturated ring which includes I
to 2 hetero
atoms such as nitrogen, oxygen and/or sulfur, linked through a carbon atom or
a heteroatom,
where possible, optionally via the linker (CHz)g (where g is 1, 2 or 3). The
above groups
may include 1 to 4 substituents such as alkyl, halo, oxo, and the like. In
addition, any of the
cycloheteroalkyl rings can be fused to a cycloalkyl, aryl, heteroaryl or
cycloheteroalkyl ring.
112
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
102731 The term "cycloheteroalkylalkyl" alone or as part of another group
refers
cycloheteroalkyl groups as defined above linked through a carbon atom or
heteroatom to a
(CHZ), chain.
[0274] The term "heteroarylalkyl" or "heteroarylalkenyl" alone or as part of
another
group refers to a heteroaryl group as defined above linked through a C atom or
heteroatom
to a(CHZ), chain, alkylene or alkenylene as defined above.
[0275] The phrase "naturally occurring a-amino acid sidechain" refers to the
moieties
(sidechains) attached to the a-amino carbon in the following naturally
occurring a-amino
acids: glycine, alanine, 2-aminobutyric acid, valine, leucine, isoleucine,
tert-leucine, serine,
threonine, cysteine, asparagine, aspartic acid, glutamine, glutamic acid,
phenylalanine,
histidine, tryptophan, tyrosine, phenylglycine, lysine, methionine, and
arginine. The side
chains of these amino acids are well known in the art. For example, the a-
amino acid
sidechain of alanine is methyl; the sidechain of phenylalanine is benzyl; and
the sidechain
of tert-leucine is tert-butyl.
[0276] The term "polyhaloalkyl" refers to an "alkyl" group as defined above
which
includes from 2 to 9, preferably from 2 to 5, halo substituents, such as F or
Cl, preferably F,
such as CF3CH2, CF3 or CF3CF2CH2.
[0277] The term "polyhaloalkoxy" refers to an "alkoxy" or "alkyloxy" group as
defined
above which includes from 2 to 9, preferably from 2 to 5, halo substituents,
such as F or Cl,
preferably F, such as CF3CH2O, CF3O or CF3CFZCH2O.
[0278] The terms "polycyclic" and "polycycle" refer to two or more rings
(e.g.,
cycloalkyls, cycloalkenyls, aryls, heteroaryls and/or cycloheteroalkyls) in
which two or
more carbons are common to two adjoining rings, e.g., the rings are "fused
rings." Fused
rings that are joined through nonadjacent atoms, are also known as "bridged"
rings. Each of
the rings of the polycycle can be substituted with such substituents as
described above, as
for example, halogen, alkyl, aralkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl, hydroxyl,
amino, nitro,
sulfhydryl, imino, amido, phosphonate, phosphinate, carbonyl, carboxyl, silyl,
ether,
113
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
alkylthio, sulfonyl, ketone, aldehyde, ester, a heterocyclyl, an aromatic or
heteroaromatic
moiety, trifluoromethyl, cyano, or the like.
EXAMPLES
[0279] A further detailed description of the invention is given with reference
to the
following non-limiting examples.
Example 1
Synthesis of (2R)-boroPro-(1S,2S,3R,5S)-pinanediol ester, hydrochloride (2)
[0280] A flame dried round bottom flask equipped with a magnetic stir bar was
charged with N-Boc-pyrrolidine (20 g, 117 mmol, I eq) and dry THF (60 mL)
under a
nitrogen atmosphere. The clear colorless solution was cooled to -78 C and a
solution of s-
BuLi (100 mL of a 1.4 M solution in cyclohexane, 140 mmol) was added slowly
over a 30
minute period. The light orange colored solution was stirred at -78 C for 3
hours followed
by treatment with B(OMe)3 (39 mL, 350 mmol) after which the cooling bath was
removed
and the clear colorless solution slowly warmed to 0 C. Upon reaching 0 C, the
reaction was
quenched with a small amount of water (-2 mL), allowed to wann to room temp
then
extracted into 2 N NaOH (250 mL) and backwashed with additional EtOAc (150
mL). The
aqueous phase was acidified to pH 3 by the addition of 2 N HCl and then
extracted with
EtOAc (3 x 120 mL). The organic extracts were combined and dried over Na2SO4
and
concentrated to produce the free boronic acid (22.08 g, 103 mmol) as a sticky
white solid in
88% yield. Without further purification the boronic acid was dissolved in tert-
butyl methyl
ether (150 mL) and with constant stirring (+)-pinanediol (17.5 g, 103 mmol)
was added at
room temperature. After 18 hr the ether was removed and the (+)-pinanediol
boronic ester
was purified by column chromatography (silica gel, 1:3 hexanes/EtOAc) to give
a clear
thick oil (26.84 g, 76.8 mmol, 76% yield, Rf = 0.6 using a 2:1 hexane/ethyl
acetate eluant,
made visual via 12 and/or PMA stain). Removal of the Boc protecting group was
achieved
by dissolving the oil in dry ether, cooling to 0 C in an ice bath and with
constant stirring dry
HCI (g) was bubbled into the solution for 10 minutes. After 2 hours a white
precipitate
developed in the flask and the ether and excess HCI were removed in vacuo to
afford the
racemic HC1 salt as a white solid. Crystallization and isolation of the
desired isomer was
performed by dissolving the HCI salt in a minimal amount of dichloromethane
(250 mL)
with gentle heating to facilitate a homogenous solution followed by continuous
stirring for 8
114
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
hours to yield a fluffy white precipitate that was collected by vacuum
filtration, dried and
then dissolved in minimal 2-propanol (-200 mL) with gentle heating until
homogenous. The
alcoholic solution was stirred over night and the resulting white precipitate
was collected by
vacuum filtration affording isomerically pure 1 as a white solid. (7.0 g, 27
mmol, 23%
yield). 'H NMR (400 MHz, D20) 8 4.28 (d, J= 8.0 Hz, 1 H), 3.06 (m, 3H), 2.18
(m, 1 H),
1.96 (m, 2H), 1.78 (m, 3 H), 1.62 (m, 2H), 1.21 (s, 3H), 1.05 (m, 5H), 0.84
(d, J=12 Hz,
2H), 0.71 (s, 2H), 0.62 (s, 3H).
Example 2
Synthesis Of Series A Compounds: (2R)-1-(2-Cyclopentylamino-acetyl)-boroPro-OH
m
Step 1: (2R)-1-(2-Chloroacetyl)-boroPro-(1S,2S,3R,5S)-pinanediol ester (3A).
[0281] To a solution of 2 (36.7 g, 129.3 mmol) dissolved in dry CHZCIZ (200
mL)
cooled to 0'C was added chloroacetyl chloride (12.34 mL, 155.2 mmol) under a
blanket of
N2. To this was slowly dripped 4-methylmorpholine (42.4 mL, 182 mmol) to give
an almost
clear light orange solution that was warmed to room temp. After 30 minutes the
solution
was cooled again to 0 C and 200 mL of a 0.2 N solution of HCl was added and
the organic
layers separated, dried and concentrated to give a dark red oil that was a
single spot by TLC
(2:1 hex/EtOAc, Rf = 0.22, made visual via lz and/or PMA stain) and was used
in the next
step without further purification. 'H NMR (400 MHz, CDCI3) 80.80 (s, 3 H),
1.25 (m, 1 H),
1.26 (s, 3 H), 1.42 (s, 3H), 1.75-1.96 (m, 4 H), 1.98-2.10 (m, 3 H), 2.12-2.20
(m, 1 H), 2.29-
2.35 (m, 1 H), 3.12-3.16 (m, 1 H), 3.47-3.53 (m, 1 H), 3.58-3.63 (m, 1 H),
3.97-4.05 (q, 2
H), 4.30-4.32 (d, I H).
Step 2: (2R)-l-(2-Cyclopentylamino-acetyl)-boroPro-(1S,2S,3R,5S)-pinanediol
ester
(3B).
[02821 Compound 3A was dissolved in dry THF (--150 mL) followed by addition of
K2C03 (35 g) and cooled to 0'C before addition of cyclopentylamine (21.93 g,
258 mmol).
The reaction mixture was then allowed to warm to room temperature and stirred
overnight.
TLC indicated all starting material was consumed. The mixture was filtered
through a celite
and silica pad, washed with 5% MeOH in CH2CIZ (200 mL) and concentrated to
yield a
sticky, light orange solid. The red sticky solid was dissolved in CH2CI2 (150
mL) followed
by addition of Et20 (-200 mL) and the solution was stirred overnight. The
resulting milky
white solution was then filtered and the precipitate was washed with cold
EtOAc (2 x 60
115
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
mL) and hexane (2 x 50 mL) and dried to give 3B (28.92 g, 120.5 mmol) as a
fluffy white
solid. The dark red mother liquor filtrate was concentrated and subjected to
the previous
recrystallization conditions to obtain a second crop of 3B (6.17 g, 25.7 mmol)
for a
combined overall yield of 3B (35.09 g, 93.8 mmol) of 73% yield. Rf= 0.45 (10%
MeOH in
CH2ClZ).'H NMR (400 MHz, CDC13) S 4.18 (d, 1H), 3.95 (d, J= 16 Hz, 1H), 3.6
(d, J= 16
Hz, 1H), 3.46 (m, 3H), 2.74 (m, 1H), 2.36 (m, IH), 2.16 (m, 2H), 2.04 (m, 4H),
1.90 (s,
IH), 1.74 (m, 6H), 1.61 (s, IH), 1.46 (m, 2H), 1.34 (s, 3H), 1.30 (s, 3H),
0.88 (s, 3H).
Step 3: (2R)-1-(2-Cyclopentylamino-acetyl)-boroPro-OH (4)
[0283] To a solution of 3B (40.59 g, 108.5 mmol) in HZO (200 mL, adjusted to
pH 2
by addition of 2 N HCl) was added hexane (200 mL) and phenyl boronic acid
(13.37 g,
109.5 mmol) and the bi-phasic mixture was stirred vigorously. The hexane layer
was
periodically removed and replaced with fresh hexane 6 times over a 24-hour
period. The
aqueous layer was separated and applied to a Dowex 50-X2-100 ion exchange
column (H+
form) and eluted with water until the eluate was neutral. Elution with aqueous
animonium
hydroxide (2 wt %) followed by lyophilization of the appropriate fractions
yielded 4 (23.91
g, 99.6 mmol) as a white crystalline solid in a 92% yield. 4=TFA salt 'H NMR
(400 MHz,
D20) S 3_88 (dd, J= 8.0 Hz, 2H), 3.54 (m, 1 H), 3.42 (m, 1 H), 3.28 (m, 1 H),
2.96 (m, 1 H),
1.96 (m, 4H), 1.85 (m, 2H), 1.63 (m, 7H); MS (ESI) m/z 223 (M+H-H20)+.
Example 3
Synthesis of 1-(2-CYclopropylamino-acetvl)-pVrrolidine-(2R)-boronic acid.
(A2):
[0284] The title compound was prepared according to the procedure of Example 2
using appropriate starting materials. 'H NMR (D20) S 4.08 (dd, J = 12 Hz, 2
H), 3.54 (m,
1 H), 3.3 8(m, IH), 3.07 (m, IH), 2.26 (m, 1 H), 2.09 (m, 2H), 1.94 (m, 1 H),
1.71 (m, IH),
0.88 (s, 4H); MS (ESI) m/z 195.13 (MH+-HZO).
Example 4
Synthesis of 1-f2-(3-Hvdroxy-adamantan-l-ylamino)-acetyll-
pyrrolidine-(2R)-boronic acid (A3):
[0285] The title compound was prepared according to the procedure of Example 2
using appropriate starting materials. 'H NMR (DZO) 8 3.94 (d, J= 8 Hz, 2H),
3.54 (m, 1H),
116
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
3.40 (m, 1H), 3.09 (m, 1H), 2.41 (s, 2H), 2.09 (m, 3H), 1.93 (m, 2H), 1.87 (m,
7H), 1.71 (m,
6H), 1.56 (m, 2 H); MS (ESI) m/z 305.21 (MH+-HZO).
Example 5
Synthesis of 1-(5R-Phenyl-pyrrolidine-2S-carbonyl)-pyrrolidine-(2R)-boronic
acid (6):
Step 1: N-Boc-5-phenylPro-(2R)-boroPro-(1S,2S,3R,5S)-pinanediol ester (5):
[0286] To an ice-cooled (0 C) solution of N-Boc-5-phenyl-Pro-OH (0.84 mmol) in
dry
CH2Cl2 was added EDAC (174 mg, 0.91 mmol) and HOBt (105 mg, 0.775 mmol). The
reaction was stirred at 0 C for 15-minutes and then 2 (200 mg, 0.7 mmol) and N-
methyl
morphiline (0.25 mL, 2.1 mmol) was added and the reaction was slowly warmed to
room
temperature and the reaction continued for 8 hours. The coupling reaction was
then
quenched with the addition ofNaHCO3 (10 mL), extracted into EtOAc (2 x 15 mL),
washed
with brine (15 mL), dried over Na2SO4, concentrated and further purified via
column
chromatography (silica gel, eluted with a gradient of EtOAc in hexanes, 30-
50%) to afford 5
(320 mg, 0.62 mmol, 88%) as an off-white solid.
Step 2: 1-(5R-Phenyl-pyrrolidine-2S-carbonyl)-pyrrolidine-(2R)-boronic acid
(6):
[0287] An ice-cooled solution of 5 (320 mg, 0.62 mmol) in dry ether was
saturated
with dry HCI (g) and allowed to stir for 1-hour. The solution was then
concentrated under
vacuum to afford a sticky white solid that was taken up in H20 (10 mL,
adjusted to pH 2 by
addition of 2 N HCI) and hexane (10 mL) and phenyl boronic acid (74 mg, 0.62
mmol) and
the bi-phasic mixture was stirred vigorously. The hexane layer was
periodically removed
and replaced with fresh hexane 6 times over a 24-hour period. The aqueous
layer was
separated and applied to a Dowex 50-X2-100 ion exchange column (H+ form) and
eluted
with water until the eluate was neutral. Elution was continued with aqueous
ammonium
hydroxide (2 wt%) and the appropriate fractions were lyophilized to afford the
free boronic
acid BI (76 mg, 0.26 mmol) as an amorphous white solid. 'H NMR (D20) 8 7.46
(m, 5H),
3.65 (m, 1H), 3.44 (m, IH), 3.04 (m, IH), 2.54 (m, IH), 2.3 8(m, 2H), 2.20 (m,
IH), 2.06
(m, 2H), 1.86 (m, IH), 1.66 (m, 1H); MS (ESI) m/z 271 (MH+-H2O).
117
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 20051047297 PCT/US2004/037820
Example 6
Synthesis of 1-(Piperidine-2S-carbonyl)-avrrolidin42R)-boronic acid (B2):
[0288] The title compound was prepared according to the procedure of Example 5
using appropriate starting materials. 'H NMR (D20) S 4.07 (m, 1H), 3.61 (m,
1H), 3.34 (m,
2H), 2.94 (m, 2H), 2.16 (m, l H), 2.03 (m, 2H), 1.87 (m, 3H), 1.56 (m, 4H); MS
(ESI) m/z
209 (MH+-HZO).
Example 8
Synthesis of 1-(2,3-Dihydro-lH-indole-2S-carbonyl)-nvrrotidine-(2R)-boronic
acid
B3 :
[0289] The title compound was prepared according to the procedure of Example 5
using appropriate starting materials. 'H NMR (DZO) S 4.54 (m, IH), 3.73 (m,
IH), 3.58 (m,
1H), 3.34 (m, IH), 2.48 (m, 1H), 2.37 (m, 1H), 2.06 (m, 3H), 1.83 (m, 3H),
1.58 (m, 4H),
1.32 (m, 4H); MS (ESI) m/z 249 (MH+-HZO).
Example 9
Synthesis of 1-(4S-Phenylõpyrrolidine-2S-carbonyt)-ayrrolidine-(2R)-boronic
acid
JP41,
[0290] The title compound was prepared according to the procedure of Example 5
using appropriate starting materials. 'H NMR (D20) S 7.34 (d, J=13 Hz, 2H),
7.27 (m,
3H), 4.79 (m, IH), 3.83 (m, IH),3.59 (m, IH), 3.34 (m, 2H), 3.06 (m, IH), 2.53
(m, 2H),
2.08 (m, 2H) 1.77 (m, IH), 1.64 (m, 1 H); MS (ESI) m/z 271 (MH+-H2O).
118
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
Example 10
Synthesis of (2R)-1-{2-[(3S)-Pyrrolidin-3-ylamino]-acetyl}-pyrrolidine-2-
boronic acid
(8)
NH2
. _ ~ B
O L N
N O
CI p ~O
NH
O K2CO3, THF 7
N
BOC PhB(OH)2,
H3O+, Hexanes
O H
N OIB/ %
~ OH
O
~~NH
HN 8
Step 1: (2R)-1-{2-[(3S)-l-tert-Butoxycarbonyl-pyrrolidin-3-ylamino]-acetyl}-
pyrrolidine-
2-boronic acid (1S,2S,3R,5S)-pinanediol ester (7)
[0291] The protocol described above for the synthesis of 3B was followed
employing
(3S)-3-amino-pyrrolidine-l-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester in place of
cyclopentylamine.
Compound 7 was obtained as an oil.
(2R)-1-{2-[(3S)-Pyrrolidin-3-ylamino]-acetyl}-pyrrolidine-2-boronic acid (8)
[0292] The protocol described above for the deprotection of the pinanediol
boronic
ester 3B (Example 2, Step 3) was applied to 7. Compound 8 was obtained as a
white solid.
8-TFA salt. 'H-NMR (500 MHz, CD3OD) S 4.12 (m, 3H), 3.76 (m, IH), 3.54 (m,
3H), 3.41
(m, 2H), 3.26 (m, 1H), 2.55 (m, IH), 2.28 (m, IH), 2.05 (m, 3H), 1.74 (m, 1H).
MS m/z (rel
intensity) 241 (M) (27), 224 (100), 209 (73), 155 (47).
119
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
Example 11
Synthesis of (2R)-1-{2-f(3R)-Pyrrolidin-3-ylaminol-acetyll-pyrrolidine-2-
boronic acid
(10)
NH2
- d
~
N B
O = N
~. - 1
g Boc ~O
CI O ~<
~O K2C03, THF N- NH 9
Boc PhB(OH)2,
H30+, Hexanes
OH
N B %
r-~O OH
NH 10
HN
Step 1: (2R)-1-{2-[(3R)-1-tert-Butoxycarbonyl-pyrrolidin-3-ylamino]-acetyl}-
pyrrolidine-
2-boronic acid (1S,2S,3R,5S)-pinanediol ester (9).
[02931 The protocol described above for the synthesis of 3B was followed
employing
(3R)-3-amino-pyrrolidine-l-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester in place of
cyclopentylamine.
Compound 9 was obtained as an oil. MS m/z (rel intensity) 476 (M + 1)+ (100),
376 (74),
239 (38), 224 (67), 155 (55).
Step 2: (2R)-1-{2-[(3R)-Pyrrolidin-3-ylaminoj-acetyl}-pyrrolidine-2-boronic
acid (10)
[02941 The protocol described above for the deprotection of the pinanediol
boronic
ester 3B (Example 2, Step 3) was applied to 9. Compound 10 was obtained as a
white solid.
10-TFA salt. 'H-NMR (500 MHz, CD3OD) S 4.13 (m, IH), 4.08 (bs, 2H), 3.76 (dd,
J=
13.0, 8.0 Hz, 1H), 3.55 (m, 3H), 3.41 (m, 2H), 3.27 (m, 1H), 2.53 (m, 1H),
2.26 (m, 1H),
2.10 (m, 2H), 1.99 (m, 1H), 1.75 (m, 1H). MS m!z (rel intensity) 224 (M-
17)(100), 206
(25), 180 (29), 155 (70).
120
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
Example 12
Synthesis of Series B Compounds: (2R)-1-((2S)-Azetidine-2-carbonyll-boroPro-OH
(12)
Step 1: (2R)-1-[(2S)-1-tert-Butoxycarbonyl-azetidine-2-carbonyl]-boroPro-
(1S,2S,3R,5S)-pinanediol ester (11)
102951 To a solution of (2S)-azetidine-l,2-dicarboxylic acid 1-tert-butyl
ester (169 mg,
0.8 mmol) in CH2Clz (5 mL) was added HOBt (105 mg, 0.8 mmol) and EDC (174 mg,
0.9
mmol). The reaction solution was then cooled to 0 C in an ice bath for 10 min
followed by
sequential addition of 2 (200 mg, 0.7 mmol) and NMM (0.25 mL, 2.1 mmol). The
reaction
solution was allowed to warm up to room temperature and stirred ovemight. The
reaction
mixture was diluted with additional CH2C12 (5 mL), washed with NaHCO3 (2 x 10
mL), 0.1
M aqueous HCI (5 mL) and brine (10 mL). The organic layer was dried over
NazSO4 and
evaporated under reduced pressure. The resulting oily residue was purified by
column
chromatography (silica gel, solvent eluent gradient from 1:4 EtOAc/hexane to
1:2
EtOAc/hexane) to afford 11 as a clear viscous oil.
Step 2: (2R)-1-[(2S)-Azetidine-2-carbonyl]-boroPro-OH (12)
[02961 A solution of compound 11 in 4N HCI in dioxane was stirred at room
temperature for 4 h. The solvent was removed under vacuum and the resulting
residue was
submitted to the pinanediol ester deprotection protocol described above for
the preparation
of boronic acid 4. Compound 12 was obtained as a white solid. 12-TFA salt 'H-
NMR (500
MHz, D20) S 5.23 (m, 1 H), 4.11 (m, 1 H), 3.90 (m, 1 H), 3.42 (m, 1 H), 3.18
(m, 1 H), 2.99
(m, IH), 2.79 (m, IH), 2.55 (m, IH), 1.92 (m, 3H), 1.63 (m, 1H). MS m/z (rel
intensity) 199
(M + 1)+ (7), 181 (M-17) (100), 152 (53).
Example 13
Synthesis of Series C Compounds: (2R)-1-1(2S,4S)-4-Amino-
pyrrolidine-2-carbonyll-boroPro-OH (15)
Step 1: (2R)-1-[(2S,4S)-1-tert-Butoxycarbonyl-4-benzyloxycarbonylamino-
pyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]-boroPro-(1S,2S,3R,5S)-pinanediol ester (13)
. [02971 The protocol described for the synthesis of 11 was followed employing
(2S,4S)-
Fmoc-4-amino-l-boc-pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (628 mg, 2.2 mmol) in place
of
121
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
azetidine-1,2-dicarboxylic acid 1-tert-butyl ester. Compound 13 was obtained
as a clear
colorless oil that was used in the next step without further purification.
Step 2: (2R)-1-[(2S,4S)-1-tert-Butoxycarbonyl-4-amino-pyrrolidine-2-carbonylj-
boroPro-(1S,2S,3R,5S)-pinanediol ester (14)
[02981 To a solution of 13 dissolved in DCM (10 ml) was added diethyl amine (5
ml)
at once and the resulting colorless solution was stirred ovemight at room
temperature. The
reaction was evaporated to dryness and additional DCM was added followed by
evaporation
once again to dryness. The resulting oil was purified by column chromatography
(silica gel,
eluted with a gradient of 2.5 to 5% MeOH in DCM, made visible by I2 and/or
PMA) to give
14 as a clear colorless oil in a 48% yield over 2 steps.
Step 3: (2R)-1-[(2S,4S)-4-Amino-pyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]-boroPro-OH (15)
[02991 The protocol described above for the N-Boc deprotection and pinanediol
ester
hydrolysis in the synthesis of compound 12 was applied to 14. Compound 15 was
obtained
as a white solid. 15-TFA salt 'H-NMR (500 MHz, D20) S 4.42 (dd, 1H), 3.87 (m,
1H), 3.5
(dd, IH), 3.28 (m, 2H), 3.07 (m, IH), 2.73 (m, IH), 2.64 (m, IH), 1.86 (m, 1
H), 1.72 (br m,
2H), 1.55 (br m, 2H), 1.34 (m, 2H). MS m/z (rel intensity) 228 (M + 1) (55),
210 (M + 1-
H20) (95).
Example 14
Synthesis of Series D Compounds: (2R)-1-1(2S)-4-Methanesulfonvl-
aiperazine-2-carbonyil-boroPro-OH (19)
Step 1: (2R)-1-[(2S)-1-tert-Butoxycarbonyl-4-benzyloxycarbonyl-piperazine-2-
carbonyl]-boroPro-(1S,2S,3R,5S)-pinanediol ester (16)
103001 The protocol described above for the synthesis of 11 was followed
employing
(2S')-N-1-Boc-N-4-Cbz-2-piperazine carboxylic acid (1 g, 2.6 mmol) in place of
azetidine-
1,2-dicarboxylic acid 1-tert-butyl ester. Compound 16 (690 mg, 1.5 mrnol) was
obtained in
57% yield as an oil after silica gel column chormatography. MS m/z (rel
intensity) 618 (M +
23)+ (17), 596 (M + 1)+ (100), 496 (38).
Step 2: (2R)-1-[(2S)-I-tert-Butoxycarbonyl-piperazine-2-carbonyl]-boroPro-
(1S,2S,3R,5S)-pinanediol ester (17)
[03011 To a solution of compound 16 (314 mg, 0.53 mmol) in MeOH (6 mL) was
added Pd/C (40 mg). The mixture was stirred under a H2 atmosphere for 2 h.
Upon
122
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
completion of the reaction, it was filtered through a plough of Celite. The
solvents were
removed under reduced pressure and the oily residue used in the next step
without further
purification. MS m/z (rel intensity) 462 (M + 1)+ (100), 406 (12), 362 (11).
Step 3: (2R)-1-[(2S)-1-tert-Butoxycarbonyl-4-methanesulfonyl-piperazine-2-
carbonyl]-boroPro-(1S,2S,3R,5S)-pinanediol ester (18)
[0302] To a solution of compound 17 (214mg, 0.46 mmol) in CH2C12 (5 mL) cooled
to
0 C was sequentially added N-methylmorpholine (204 L, 1.9 mmol) and
methanesulfonyl
chloride (72 L, 0.93 mmol). The reaction mixture was allowed to warm up to
room
temperature and stir for 3 hours. The reaction was then diluted with CH2C12 (6
ml) and
water (6 mL). The organic phase was isolated and dried over MgSO4. After
filtration,
solvents were removed under reduced pressure. The oily residue was purified by
column
chromatography (silica gel) using a mixture of EtOAc/Hexanes as eluent.
Compound 18
(112 mg, 0.21 mmol) was obtained in 45% yield. MS m/z (rel intensity) 562 (M +
23)+ (14),
540 (M + 1) (100), 388 (75).
Step 4: (2R)-1-[(2S)-4-Methanesulfonyl-piperazine-2-carbonyl]-boroPro-OH (19)
[0303] The protocol described above for the N-Boc deprotection and pinanediol
ester
hydrolysis in the synthesis of compound 12 was applied to 18 (112 mg, 0.21
mg).
Compound 19 (32 mg, 0.11 mmol) was obtained in 53% yield. 19=TFA salt 'H-NMR
(500
MHz, D20) S 4.32 (dd, J= 11.0, 3.5 Hz, IH), 4.05 (m, IH), 3.93 (m, 1H), 3.77
(m, 1H),
3.60 (ddd, J= 10.5, 8.0, 2.5 Hz, IH), 3.47 (ddd, J= 12.5, 3.0, 3.0, 1 H), 3.3
5(m, 2H), 3.16
(m, 2H), 3.02 (dd, J=13.8, 11.3 Hz, 1H), 2.93 (s, 3H), 1.96 (m, 2H), 1.81 (m,
1H), 1.72 (m,
1H), 1.56 (m, IH). MS m/z (rel intensity) 575 (12), 328 (M + 23)+ (6), 288 (M -
17) (100).
Example 15
Synthesis of Series F Compounds: (2R)-l-12-1(3S)-Pyrrolidin-3-ylaminol-
acetyl}-boroPro-OH (21)
Step 1: (2R)-1-(2-[(3S)-1-tert-Butoxycarbonyl-pyrrolidin-3-ylamino]-acetyl)-
boroPro-
(1S,2S,3R,5S)-pinanediol ester (20)
[0304] The protocol described above for the synthesis of 3B was followed
employing
(3S)-3-amino-pyrrolidine-l-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester in place of
cyclopentylamine.
Compound 20 was obtained as an oil.
Step 2: (2R)-1-{2-[(3S)-Pyrrolidin-3-ylamino]-acetyl}-boroPro-OH (21)
123
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US20041037820
[0305) The protocol described above for the N-Boc deprotection and pinanediol
ester
deprotection of compound 12 was applied to 20. Compound 21 was obtained as a
white
solid. 21-TFA salt 'H-NMR (500 MHz, CD3OD) S 4.12 (m, 3H), 3.76 (m, 1 H), 3.54
(m,
3H), 3.41 (m, 2H), 3.26 (m, 1 H), 2.55 (m, IH), 2.28 (m, 1 H), 2.05 (m, 3H),
1.74 (m, 1 H).
MS m/z (rel intensity) 241 (M) (27), 224 (100), 209 (73), 155 (47).
Example 16
103061 Using the procedures illustrated above, the following compounds in the
Table
were prepared and characterized using liquid chromatography-mass spectroscopy
(LC-MS).
TABLE
Compound Series Structure LC-MS
No.
22 A ~OH 255 (M+1)(13), 237
(_IIN -..B (100)
%
O
H
N O
23 A OH 227 (M+1)(10), 209
B (100)
H~ OH
~N O
24 A O~Y' OH 229 (M+1 )(18), 211
(100)
H N OH
N.~O
25 A 'OH 215 (M+1)(12), 197
C ~.. B (100)
H L OH
N '/'~ O
26 A C~/ QH 263 (M+1)(5), 245 (100)
B
N~O OH
27 A ,QH 277 (M+1)(4), 259 (100)
B
cyi OH
l0
124
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
Compound Series Structure LC-MS
No.
28 A OH 283 (M+1)(22), 265
~B (100)
0-~ H N-_~ OH
O
29 A /-~ OH 277 (M+1)(5), 259 (100)
'~e
N N O OH
30 A ~ OH 283 (M+1)(21), 265
N 8 (100)
Q,oH
N O
31 A ~OH 269 (M+1)(16), 251
~g (100) %
OH
N
32 A H 0 HO OH 763 (6), 382 (M+1)(100)
N~ ,g_
N
PhS02N
33 A 284 (M+1)(19), 266(100)
~N~ N
0 N
H 0 HO B'OH
34 A 651 (28), 326 (M+1)(57),
N 308(100)
0 N
H 0 HO.B'OH
35 A 691 (22), 346
0 (M+1)(100), 328 (86)
N~ N Q
H 0 HO B-OH
36 A 703 (28), 352 (M+1)(18),
334 (100)
O Na N N
H 0 HO B-OH
37 A BzN 691 (49), 346 (M+1)(14),
Q 328 (100)
H O HO=B'OH
125
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
Compound Series Structure LC-MS
No.
38 A 0 703 (27), 352 (M+1)(3),
ND.,"N ,,( N 334 (100)
H O HO B-OH
39 A 651 (48), 326 (13), 308
NJ " (100)
''N~
H 0 HO B-OH
40 A p 382 (M+1)(100), 364 (7)
%N N N
0
H 0 HO B-OH
41 A 332 (M+1)(100), 314
" N (10)
~
'~
N
2HCI H 0 Hd B'OH
42 A 531 (15), 266 (M-
AcN~D N 17)(100)
"'N~
H O HO.B'OH
43 A HO 271 (M+1)(100), 253
~ N (16)
N
H 0 HO B-OH
44 A H2" 270 (M+1)(100), 252
'a')~ q (17)
N
H 0 H0 B10H
45 A HO 731 (42), 366
N '0 ,g-OH (M+1)(100), 348 (43)
N ,h,
O HCI ~"
46 A HCI Hog-OH 791 (12), 396 (M+1)
N~
O~N ~
~ \ ,0
i
47 A 721 (10), 361
0 (M+1)(100)
'CLN N
H O HO.B'OH
126
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
Compound Series Structure LC-MS
No.
48 A 285 (M+1)(100), 267
O N (12)
N
H p HO B-OH
49 A 0 595 (48), 298
(M+1)(100), 280 (80)
N
ACLN-'-r
CI HHOr B-OH
H
50 A 0 679 (29), 340 (100)
N
N
N
HCf H O HO'B-OH
51 A 719 (92), 360 (M+1)(65),
BzN ..,N N 342 (100)
H~ HO B-OH
HCI
52 A 791 (35), 396
o ~ N (M+1)(100), 378 (14)
C S0 HCI H 0 HO B-OH
53 A 595 (89), 298 (M+1)(44),
~ N 280 (100)
N/ N~ B_
, H 0 H~ OH
O
54 A 719 (72), 360 (M+1)(40),
N 342 (100)
BzN N
H p HO B-OH
55 A OO,'N 731 (100). 366
(M+1)(34), 348 (86)
o N' B-OH
-
HO
HCI
56 A 340 (M+1)(5), 322 (100),
rN--"N"-(N 304 (18)
,~y
H 0 HOiB'OH
O
57 A 731 (100), 366
N'y N (M+1)(52), 348 (94)
H 0 HO=B'OH
0
58 A 773 (33), 396
o\ (N-'N~N (M+1)(100), 378 (16)
~S H 0 HO B-OH
127
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCTIUS2004/037820
Compound Series Structure LC-MS
No.
59 A 595 (93), 298 (M+1)(26),
N N~N 280 (100)
0 H O HO.B'OH
60 A 679 (100), 340 (98), 322
>LyN , N--'-If N (70)
O H 0 HO,B'OH
61 A ~ 346 (M+1)(100),
f._NH N 328 (12)
N ~
B-OH
O HO
62 6 ~ OH 249(M-17)major,
267(M+1)minor
OH
0
NH
63 B OH 289(M+1)minor, 271(M-
N g 17)major
OH
/ ... O
NH
64 B oH 289(M+1)minor, 271(M-
N OH 17)major
O
NH
65 B ~ 'OH 213(M-17), 425(2M+1)
N B
OH
~ ' O
NH
66 B C~-~ 282(M-17) major
B
flH
O
\ NH
N
H
67 257(M-17)major,
t 1 275(M+1)minor
HN-~ - N?
0
HO' S'OH
128
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
Compound Series Structure LC-MS
No.
68 B 0- OH 209(M-17)major,
227(M+1)minor
N B~
O
NH
c0H
69 B 285(M-17)major,
303(M+1)minor
N~
~~"
H 0 HO.s"OH
70 B 209(M-1 7)major,
N 227(M+1)minor
N
H O HO,B'OH
71 B HQ 211(M-17)major,
229(M+1)minor
N
H p HdB-OH
72 B 209(M-17)major,
N 227(M+1)minor
~
H2N O HO B~OH
(cis)
73 B 209(M-1 7)major,
N 227(M+1)minor
-
H2N
B-OH
HO
1R,2R
74 B "c' 257(M-17)major,
NHz 275(M+1)minor
O HO
,<
='~OH
N
0
75 B O 209(M-17)major,
N~ 227(M+1)minor
H2N=.,
,B-OH
HO
1S,2S
129
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
PCTIUS2004/037820
WO 2005/047297
Compound Series Structure LC-MS
No.
76 g 223(M-17)major,
~III;LNIi 241(M+1)minor
NH2 O HO,B'OH
77 B 223(M-17)major,
241(M+1)minor
N ,B'OH
NH2 O HO
78 g 223(M-17)major,
N? 241(M+1)minor
-
HZN 0 ~B,
HO OH
79 B 235(M-17)major,
N 253(M+1)minor
NH2 O HO=B'OH
80 B 235(M-17)major,
e 253(M+1)minor I'll 'f N
NHZ O O B-OH
OH 235(M-17)major,
81 B H0, .
g
O 253(M+1)minor
NH2 No
(1R,2S)
82 B HO, OH 251(M-17)major,
O B 269(M+1)minor
No
NHZ
'OH
83 B 235(M-17)major,
4NO2 OH 253(M+1)minor
N IB'OH
~
84 B 233(M-17)major,
N 251(M+1)minor
NH2 O HO,B-OH
85 B , 233(M-1 7)major,
N 251(M+1)minor
NH2 O ,S-OH
130
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
Compound Series Structure LC-MS
No.
86 B 275(M-17)major,
293(M+1)minor
/ N
NH2 O HO B-OH
87 B oH 311(M-17)major,
HO-B 329(M+1)minor
,D
Nf
NHZ
70% 6-Ph, 30% 5-Ph
Predominate isomer drawn
88 B 209(M-17)major,
N 227(M+1)minor
CINH O ~B-OH
HO
89 B 3 434(M-17) major
0
S
o I~~
Y'" ~(N~
H2N IO' HOB OH
90 B HO,e OH 446 (M+1)(23), 428
(100)
0
HZN, I~Nlo
lNl
O=S=O
/ I
SO Me
91 B HO,B,OH 350(M-17)major,
0 368(M+1)minor
HZN No
N
O=S=O
131
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
Compound Series Structure LC-MS
No.
92 B HO_BP 434(M-17) major
o
H2N N N~
f
0=5=0
OCF3
93 B 346 (M+1)(100), 328
(14)
N~ J_.( N
2HCI H 0 HO g-OH
94 B 511 (9), 256 (M+1)(100),
H141D, N ly N 238(19)
H 0 HOrB OH
2HCI
95 B 201 (M+1)(100), 183
N
A--r N (22)
H 0 HO=B'OH
96 B ~N N 255 (M+1)(100), 237
(100)
H O HO B-OH
97 B OH 187 (M+1)(5), 169 (100)
H OH
/N O
98 B 0~ /OH 243(M+1)(5), 225 (71)
= N B
\~\ OH
.IINH
99 B ~OH 449(5), 243(M+1)(7),
N g 225 (100)
OH
NH
100 B 02 223(M+23)(3), 183(48)
Me
H2NN
# O B'OH
132
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
Compound Series Structure LC-MS
No.
101 B 02H 223(M+23)(4), 183(10)
MeN
NH2 0 HO,B,OH
102 C H2N 228(M+1)(55), 210 (M-
~ 17)(95)
N N
H O HO g_OH
103 C H 210(M-17)major,
C N 228(M+1)minor
N~N
O HO,B,OH
H
104 C H2N, 210(M-17)major,
228(M+1)minor
N
N
H O HO B-OH
105 D C~ ~OH 575 (12), 328 (M+23)(6),
N g 288(100)
0 O%
H
S'NO
~NH.HCI
106 D ~~ QH 452 (M+1)(3), 434 (100)
N~-s
H OH
CNl O
N
O OCF3
107 D C~s,oH 368 (M+1)(2), 350 (100)
H OH
CNf O
N _
p s
0
108 D O\~ ,O ~ 'OH 428 (M-17)(100)
N
OH
ao
N--~O
(,-"NH.HCI
109 D F C)-.lB' OH 386 (M-17)(100)
N I
O OH
N~O
F O LI-INH.HCI
133
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/1JS2004/037820
Compound Series Structure LC-MS
No.
110 D /oH 436 (M+1)(10), 418
s (100)
Cf3 N OH
O
01 N
V--/NH.HCI
111 D 436 (M+1)(4), 418 (100)
F N
OH
OS\N/,''
~NH.HCI
112 D HO 627 (25), 332 (M+1)(10),
B-OH 314 (100)
CN( 0
CIJ]IL "TNH N J J (ormic acid selt
113 D oH 368(M+1)(38), 350 (100)
oO S
OHN 0
NH
HCI
114 D ~ oH 350 (M-17)(100), 332
~.N~e (22)
~ 0 OH
HN~O
NH
115 D 0 332(M+1)(4), 314 (93)
NH
JNQ
HCI H 0 H~ B- OH
116 D 0 338(M+1)(3), 320 (98)
-NH
N
HCI HN 0 iB'OH
HO
117 D 0 332(M+1)(27), 314 (100)
NH
N
HCI H O HO B'OH
118 D 338 (M+1)(21), 320
NH (100)
N
HCI INj O ( B'OH
HO
134
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
Compound Series Structure LC-MS
No.
119 D ,OH 727(8), 364 (M-17)(56)
H2N N OH
~ O
N
/
120 D ~OH 603(24), 302 (M-17)(73)
HZN N OH
0
N
~ 5=0
O
121 F 242 (M+1)(100), 224
H HO g-OH (19)
Nv'' =
HN-' ~
HCi
122 F HNa 242 (M+1)(100), 224 (9)
N N
H 0 Hd g' OH
123 F 0 300 (M+ 1)(11), 282
JO--~~ (100)
HNa N N
H 0 Hd B OH
124 F 371(M-17)major,
389(M+1)minor
NH
O =~
HN\), N
H p Hcr B'OH
125 F 256 (M+1)(100)
HNN ~
H 0 eH'O~,B'OH
126 F 256 (M+1)(100), 238(8)
HN N N
HCI H~ HO,s'OH
127 F 256 (M+1)(100), 238(10)
HN ,N N
H~ .B'OH
HCI HO
135
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCTIUS2004/037820
Compound Series Structure LC-MS
No.
128 F HN 210(M-17)(major), 228
~N-'-r N (M+1)(minor)
H 0 HO-B'OH
129 F ~ 256 (M+1)(100), 238
HN N~y N (28)
H 0 HO B~OH
HC{
130 G H 623 (28), 312 (M+1)
~ N' a N N ( 100), 294 (30)
H 0 HO B-OH
131 G i H 819 (20), 410 (100)
N
~ .. N
Sa O ry
H p~eB'OH
132 G N H (36 j(M+1)(100), 356
0 N ~NH 0 Hd B_OH
133 G H 759 (57), 380
O N (M+1)(100), 362 (64)
H ~ HO,g'OH
Example 17
Dependence of Aminoboronate and Boronic Acid Forms of Inventive Compounds on
P-HI
103071 A 0.4 M stock solution of Na2HPO4 was prepared by dissolving 909 mg of
salt
in 16 mL of D20. pH was adjusted to the desired value by dropwise addition of
either
20% DCI in D20 or 5% DC1 in D20. The pH values were measured with a Fisher
Scientific Accumet AB15 pH meter. Aliquots of the stock solution (4 mL) were
prepared
and 8 mg of compound 4 in the closed form (aminoboronate) were added to each
one.
The scintillation vials were capped, sealed with paraflim and allowed to stand
in the dark
for three days. After this time pH was measured again. The open/closed (i.e.,
linear/cyclic)
ratio of compound 4 isomers at each pH was determined by recording the
corresponding
'H-NMR spectra in a Varian AS 500 MHz instrument and measuring the ratio of
the
136
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
integrals of the peaks at 2.90-2.95 ppm and 2.40-2.50 ppm characteristic of
the open and
closed forms, respectively. FIG. I shows that the closed form predominates at
higher pHs
such as physiological pH, whereas the open fon-n predominates at lower pHs.
Example 18
103081 The final compounds of Examples 1-16 were tested in vitro as described
herein
and each displayed an IC50 or K; of 10 M or less.
[0309] While the invention has been described and exemplified in sufficient
detail for
those skilled in this art to make and use it, various alternatives,
modifications, and
improvements will be apparent to those skilled in the art without departing
from the spirit
and scope of the claims.
[0310] All patents and publications are herein incorporated by reference to
the same
extent as if each individual publication was specifically and individually
indicated to be
incorporated by reference.
[0311] The invention illustratively described herein suitably may be practiced
in the
absence of any element or elements, limitation or limitations which is not
specifically
disclosed herein. Thus, for example, in each instance herein any of the terms
"comprising", "consisting essentially ofl' and "consisting oP' may be replaced
with either
of the other two terms. The terms and expressions which have been employed are
used as
terms of description and not of limitation, and there is no intention that in
the use of such
terms and expressions of excluding any equivalents of the features shown and
described
or portions thereof, but it is recognized that various modifications are
possible within the
scope of the invention claimed. Thus, it should be understood that although
the present
invention has been specifically disclosed by preferred embodiments and
optional features,
modification and variation of the concepts herein disclosed may be resorted to
by those
skilled in the art, and that such modifications and variations are considered
to be within
the scope of this invention as defined by the appended claims.
[0312] In addition, where features or aspects of the invention are described
in terms of
Markush groups, those skilled in the art will recognize that the invention is
also thereby
described in terms of any individual member or subgroup of members of the
Markush
group. For example, if X is described as selected from the group consisting of
bromine,
137
CA 02602772 2007-07-18
WO 2005/047297 PCT/US2004/037820
chlorine, and iodine, claims for X being bromine and claims for X being
bromine and
chlorine are fully described.
[0313] Other embodiments are set forth within the following claims.
138