Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02603454 2007-10-02
WO 2006/111315 PCT/EP2006/003381
PROTECTED CARBON STEEL PIPE FOR FIRE TUBE HEAT
EXCHANGE DEVICES, PARTICULARLY BOILERS
Technical Field
The present invention relates to a protected carbon steel pipe for fire
tube heat exchange devices, particularly boilers.
Background Art
It is known that fire tube heat exchange devices exist which provide
pipes designed to convey flue gases generated by combustion in appropriate
furnaces, such pipes being provided within a vessel which contains the fluid
to be heated; among such devices, boilers for generating hot water or
another heat transfer fluid are particularly important.
The pipes comprised within said devices are made of carbon steel in
order to ensure optimum quality of the welded joints between the pipes and
the structures of the devices, which are also made of carbon steel; however,
in the case of devices, such as for example condensing boilers, in which the
water vapor contained in the flue gases condenses inside the flue gas
conveyance pipes, condensation forms which attacks strongly by corrosion
the wall of the pipes.
Pipes of the described type are not typical only of boilers, but can be
present also in other devices of industrial thermal cycles, such as for
example condensers, economizers and heat exchangers.
Disclosure of the Invention
The aim of the present invention is to provide a carbon steel pipe
adapted to convey flue gases which is entirely protected against the danger
of corrosion caused by condensation and further ensures high efficiency in
the transmission of heat from the flue gases to the fluid, and in particular
to
the water, to be heated.
The proposed aim is achieved by a protected carbon steel pipe for fire
tube heat exchange devices, particularly boilers, according to the invention,
characterized in that it comprises the features disclosed in the appended
CA 02603454 2007-10-02
WO 2006/111315 PCT/EP2006/003381
2
claims
Brief Description of the Drawings
Further characteristics and advantages will become better apparent
from the description of some preferred but not exclusive embodiments of
the protected carbon steel pipe for fire tube heat exchange devices,
particularly boilers according to the invention, illustrated by way of non-
limiting example in the accompanying drawings, wherein:
Figure 1 is a longitudinal sectional view of a fire tube boiler with a
pipe according to the present invention;
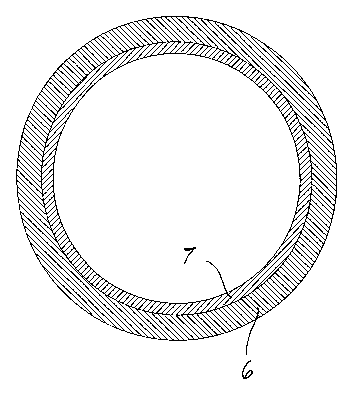
Figure 2 is a partial sectional view, taken along the line II-II of Figure
1;
Figures 3 to 25 show the same sectional view according to variations.
Ways of carrying out the Invention
With reference to the Figures 1 and 2, the reference numeral 1
generally designates a fire tube boiler with a burner 2, a furnace 3, a flue
gas
reversal chamber 4a, a vessel 5 which contains the water to be heated with
couplings 5a, 5b respectively for inflow and outflow, pipes 6 designed to
convey the gases generated by combustion in the furnace which arrive from
the reversal chamber 4a and are sent to the output chamber 4b according to
the arrows shown in figure 1.
The boiler 1 is of the type known as condensing boiler, and therefore
the water vapor contained in the flue gases condenses therein as they flow
within the pipes such as 6; the structure of said boiler is made of carbon
steel.
An important characteristic of the invention consists in that the pipe 6
is made of carbon steel and comprises internally, bonded thereto, a layer 7
made of a corrosion-resistant material, such as aluminum or stainless steel.
In this manner, the dual need to be able to weld the pipe to the carbon
steel structure of the boiler and to protect said pipe against the aggression
of
the condensation generated in the flue gases is achieved in an optimum
CA 02603454 2007-10-02
WO 2006/111315 PCT/EP2006/003381
3
manner.
As can be seen from Figure 1, the layer 7 is present along the entire
length of the pipe 6, but it should be clearly noted that such layer might be
provided only in the part of the pipe toward the outlet of the flue gases.
An embodiment of the pipe according to the invention is shown in
Figure 3: the carbon steel pipe 8 comprises, bonded thereto, a layer 9 made
of corrosion-resistant material and accommodates internally a coaxial sleeve
10, which is closed by at least one plug 10a, likewise made of corrosion-
resistant material.
An interspace 11 for conveying the flue gases in a reduced cross-
section is thus provided: the consequent increase in speed effectively helps
to increase heat exchange between the flue gases and the water to be heated.
A further increased efficiency of said exchange occurs in the variation
of Figure 4, in which a carbon steel pipe 12 has, bonded thereto, a layer 13
of corrosion-resistant material, and a sleeve 14, closed by a plug 14a, has
ribs 14b which extend monolithically from it and which, by entering an
interspace 15 through which the flue gases flow, make contact with the layer
13, transmitting thereto, and ultimately to the water to be heated, heat by
conduction.
An identical situation occurs in the variations of Figures 5, 6, 7, and
8, changing only the shape of the cross-section of the ribs: while the ribs of
the solution of Figure 4 are shaped so as to have a cross-section with a
rounded cusp, the ribs of the variations of said figures respectively have a
rectangular cross-section 16, a triangular cross-section 17 in which the
thickness decreases gradually toward the central region 18, and a
rectangular cross-section with an end face 19.
The variation of Figure 9 provides, bonded to a carbon steel pipe 20,
a first layer 21 made of corrosion-resistant material, and a second layer 22,
also made of corrosion-resistant material, which provides ribs 22a adapted
to make contact, by entering an interspace 23 through which the flue gases
CA 02603454 2007-10-02
WO 2006/111315 PCT/EP2006/003381
4
flow, with a sleeve 24 closed by a plug 24a, thus providing a situation
which is similar to the one described earlier.
Variations of the cross-sections of the ribs identical to the ones shown
in Figures 5, 6, 7, 8 are visible in Figures 10, 11, 12, 13: therefore, there
is
no need to deal with these variations.
The variations of Figures 14 to 18 replicate the constructive
embodiments shown in Figures 9 to 13, with the only difference related to
the fact that there is just one layer made of corrosion-resistant material
bonded to the carbon steel pipe: thus, for example, the variation of Figure
14 provides, bonded to a carbon steel pipe 25, only a layer 26 made of
corrosion-resistant material, which is provided with a ribs 26a which make
contact with a sleeve 27.
Figure 19 illustrates an embodiment in which a first layer 29, made of
corrosion-resistant material, and a second layer 30, also made of corrosion-
resistant material, are bonded to a carbon steel pipe 28; ribs 30a protrude
from said second layer and are alternated with ribs 31 a which protrude from
a sleeve 31, leaving spaces 32 between said ribs for the flow of the flue
gases: ribs 31a extend until they make contact with the layer 30 in the
presence of references 31 b which ensure correct positioning.
A variation of the embodiment of Figure 19 is shown in Figure 20:
the only difference is the absence of the layer 29 bonded to a carbon steel
pipe 33, and therefore only a layer 34 made of corrosion-resistant material
and provided with the ribs as described above, is present.
The variation shown in Figure 21 is now described: it comprises,
bonded to a carbon steel pipe 35, a layer 36 made of corrosion-resistant
material, which is provided with variously shaped ribs 36a arranged
alternately with respect to variously shaped ribs 37a which protrude from a
sleeve 37 and are adapted to make contact in the presence of references 37b
with the wall of the layer 36.
Another variation is described with reference to Figure 22, in which
CA 02603454 2007-10-02
WO 2006/111315 PCT/EP2006/003381
the reference numeral 38 designates a carbon steel pipe, which comprises
internally two flue gas conveyance modules, designated generally by the
reference numerals 39 and 40 respectively, which are delimited by a closed
wall made of corrosion-resistant material.
5 The wall of the module 39 comprises a portion 41, which is bonded to
the wall of the pipe 38 substantially along half of the circumferential
extension thereof, and a straight portion 42, which extends transversely, and
likewise the wall of the module 40 comprises a portion 43 bonded to the
wall of the pipe 38 and a straight portion 44; the straight portions 42 and 44
are in mutual contact.
The described configuration allows to obtain the dual result of
protecting the wall of the pipe 38 against contact with the flue gases, and
this is done by the portions 41 and 43 of the walls of the modules, and of
providing an intense transmission of heat from the flue gases to the water
contained in the boiler which strikes the outer surface of the pipe 38,
determined by the presence of the portions 42 and 44 of said walls which
make contact with the flue gases at the region where said flue gases have a
particularly high temperature.
Figure 23 illustrates another variation of the invention, which
provides, inside the pipe 38, six flue gas conveyance modules which are
substantially shaped like wedges and are designated respectively by the
reference numerals 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50.
The walls of the module, which are made of corrosion-resistant
material, are identical and comprise an arc-like portion, 45a for the module
45, bonded to the wall of the pipe 38, and two straight portions 45b, 45c for
said module, which protrude from the ends of said arc-like portion toward
the axis of said pipe; the straight portions of the individual modules are in
mutual contact.
Of course, this embodiment, too, ensures the functional
characteristics stated with reference to the embodiment shown in Figure 22.
CA 02603454 2007-10-02
WO 2006/111315 PCT/EP2006/003381
6
As regards the variation of Figure 24, it differs from the embodiment
of Figure 23 only in that inside the pipe 38 there are twelve flue gas
conveyance modules 51 instead of the six modules provided in the
embodiment of Figure 23.
The variation shown in Figure 25 provides for the presence, inside the
pipe 38, of a continuous layer 52, provided with protrusions such as 53
which protrude toward the axis of the pipe and thus provide, as in the
previously described variations, optimum conditions both as regards the
protection of the pipe 38 against corrosion and for high efficiency in heat
transfer from the flue gases contained in the pipe 3 8 to the water to be
heated.
The described invention is susceptible of numerous other
modifications and variations, all of which are within the scope of the
appended claims: thus, for example, it is important to stress the fact that
the
various means for protecting the carbon steel pipe made of corrosion-
resistant material may cover different lengths within the described pipes.
The disclosures in Italian Patent Applications No. MN2005A000023
and No. MN2006A000012 from which this application claims priority are
incorporated herein by reference.