Some of the information on this Web page has been provided by external sources. The Government of Canada is not responsible for the accuracy, reliability or currency of the information supplied by external sources. Users wishing to rely upon this information should consult directly with the source of the information. Content provided by external sources is not subject to official languages, privacy and accessibility requirements.
Any discrepancies in the text and image of the Claims and Abstract are due to differing posting times. Text of the Claims and Abstract are posted:
| (12) Patent: | (11) CA 2620735 |
|---|---|
| (54) English Title: | METHOD FOR COLD FORGING HIGH STRENGTH FASTENER WITH AUSTENITIC 300 SERIES MATERIAL |
| (54) French Title: | METHODE PERMETTANT LE FORGEAGE A FROID DE DISPOSITIF D'ATTACHE HAUTE RESISTANCE AVEC MATERIEL AUSTENITIQUE SERIE 300 |
| Status: | Granted and Issued |
| (51) International Patent Classification (IPC): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventors : |
|
| (73) Owners : |
|
| (71) Applicants : |
|
| (74) Agent: | MACRAE & CO. |
| (74) Associate agent: | |
| (45) Issued: | 2012-03-06 |
| (22) Filed Date: | 2008-02-08 |
| (41) Open to Public Inspection: | 2009-08-08 |
| Examination requested: | 2008-02-08 |
| Availability of licence: | N/A |
| Dedicated to the Public: | N/A |
| (25) Language of filing: | English |
| Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT): | No |
|---|
| (30) Application Priority Data: | None |
|---|
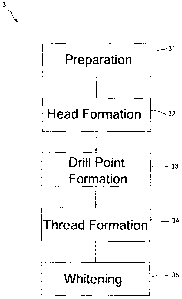
The present invention pertains to a method for cold forging high
strength fastener with austenitic 300 series material comprising the
procedures of initially preparing a raw austenitic shaft and then
proceeding through a cold forging method to reduce its diameter for
thereafter generating a preliminary shank, which can undertake above
1/2 force more than the raw shaft; further passing through the following
formations of the head, the drilling portion and threads in sequence
to build an integral fastener. Thus, the entire cold forging facilitates
to fabricate the fastener with high strength and hardness by lower
manufacturing cost and with effective corrosion resistance, so as to
firmly drill the fastener into objects and increase the screwing
security.
La présente invention se rapporte à une méthode qui permet de forger à froid une pièce de fixation à haute résistance avec un matériau austénitique série 300. Les opérations applicables sont comme suit. La préparation initiale d'une tige austénitique brute et l'application ensuite de la méthode préconisée pour réduire son diamètre, ce qui permet de produire par la suite une queue préliminaire pouvant subir une force égale à plus de la moitié de la force que pourrait subir la tige brute; la réalisation ultérieure successive des formations de la tête, de la partie perçage et des filets, pour fabriquer une fixation intégrale. Par conséquent, le forgeage à froid complet facilite la fabrication de la fixation avec une haute résistance et une dureté élevée, des coûts de fabrication moindres et avec une résistance à la corrosion efficace, de façon à aléser fermement la fixation dans des objets et à accroître la sécurité du vissage.
Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2024-08-01:As part of the Next Generation Patents (NGP) transition, the Canadian Patents Database (CPD) now contains a more detailed Event History, which replicates the Event Log of our new back-office solution.
Please note that "Inactive:" events refers to events no longer in use in our new back-office solution.
For a clearer understanding of the status of the application/patent presented on this page, the site Disclaimer , as well as the definitions for Patent , Event History , Maintenance Fee and Payment History should be consulted.
| Description | Date |
|---|---|
| Common Representative Appointed | 2019-10-30 |
| Common Representative Appointed | 2019-10-30 |
| Grant by Issuance | 2012-03-06 |
| Inactive: Cover page published | 2012-03-05 |
| Inactive: Final fee received | 2011-12-19 |
| Pre-grant | 2011-12-19 |
| Notice of Allowance is Issued | 2011-10-03 |
| Letter Sent | 2011-10-03 |
| Notice of Allowance is Issued | 2011-10-03 |
| Inactive: Approved for allowance (AFA) | 2011-09-29 |
| Amendment Received - Voluntary Amendment | 2011-02-18 |
| Inactive: S.30(2) Rules - Examiner requisition | 2010-11-24 |
| Amendment Received - Voluntary Amendment | 2010-04-14 |
| Inactive: S.30(2) Rules - Examiner requisition | 2009-10-23 |
| Application Published (Open to Public Inspection) | 2009-08-08 |
| Inactive: Cover page published | 2009-08-07 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2009-05-25 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2009-05-25 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2009-05-22 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2009-05-22 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2009-05-22 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2009-05-22 |
| Inactive: First IPC assigned | 2009-05-22 |
| Amendment Received - Voluntary Amendment | 2008-04-15 |
| Inactive: Filing certificate - RFE (English) | 2008-03-14 |
| Filing Requirements Determined Compliant | 2008-03-14 |
| Letter Sent | 2008-03-14 |
| Application Received - Regular National | 2008-03-14 |
| All Requirements for Examination Determined Compliant | 2008-02-08 |
| Request for Examination Requirements Determined Compliant | 2008-02-08 |
| Small Entity Declaration Determined Compliant | 2008-02-08 |
There is no abandonment history.
The last payment was received on 2011-12-15
Note : If the full payment has not been received on or before the date indicated, a further fee may be required which may be one of the following
Please refer to the CIPO Patent Fees web page to see all current fee amounts.
| Fee Type | Anniversary Year | Due Date | Paid Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Application fee - small | 2008-02-08 | ||
| Request for examination - small | 2008-02-08 | ||
| MF (application, 2nd anniv.) - small | 02 | 2010-02-08 | 2010-02-05 |
| MF (application, 3rd anniv.) - small | 03 | 2011-02-08 | 2011-02-02 |
| MF (application, 4th anniv.) - small | 04 | 2012-02-08 | 2011-12-15 |
| Final fee - small | 2011-12-19 | ||
| MF (patent, 5th anniv.) - small | 2013-02-08 | 2013-01-18 | |
| MF (patent, 6th anniv.) - small | 2014-02-10 | 2014-01-29 | |
| MF (patent, 7th anniv.) - small | 2015-02-09 | 2015-01-29 | |
| MF (patent, 8th anniv.) - small | 2016-02-08 | 2016-01-13 | |
| MF (patent, 9th anniv.) - small | 2017-02-08 | 2017-01-17 | |
| MF (patent, 10th anniv.) - small | 2018-02-08 | 2018-01-12 | |
| MF (patent, 11th anniv.) - small | 2019-02-08 | 2018-12-31 | |
| MF (patent, 12th anniv.) - small | 2020-02-10 | 2020-01-15 | |
| MF (patent, 13th anniv.) - small | 2021-02-08 | 2021-01-07 | |
| MF (patent, 14th anniv.) - small | 2022-02-08 | 2022-01-13 | |
| MF (patent, 15th anniv.) - small | 2023-02-08 | 2023-01-09 | |
| MF (patent, 16th anniv.) - small | 2024-02-08 | 2023-12-26 |
Note: Records showing the ownership history in alphabetical order.
| Current Owners on Record |
|---|
| YU-SHENG TSENG |
| JIAN-SHIUN TSENG |
| Past Owners on Record |
|---|
| None |