Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02647331 2013-03-06
1
Assembly for pressing pressing parts, especially those made out of wood
The invention relates to a new arrangement for pressing of pressed parts,
especially
those made out of wood, preferably for pressing of wooden lamellae into large
elements for
timber constructions, with a press unit with a press table to support the
pressed parts to be
connected to each other, and a counter-pressure plate that is arranged above
the press table
which can be moved up and down, where for the application of compressive force
onto the
material to be pressed made with the pressed parts, a plurality of pressure
elements,
particularly arranged side-by-side, such as hoses, bags, balloons, pads or
suchlike, are
arranged underneath the counter-pressure plate, which can particularly be
inflated with
pressure fluid, particularly compressed air, and be pressurized from a
pressure fluid source,
particularly a compressed air source.
When pressure-bonding bulky and/or large-surface press parts with dimensions
from e.g. up to
3 m width and up to 16 m length with a thickness of e.g. 0.1 to 0.5 m, it is
extremely difficult to
apply the necessary compacting pressure evenly and then uniformly maintain
same across the
entire surface of the press parts to be connected to each other, once the
compacting pressure
is reached. Such presses furthermore have a complex design and are actually
still not user-
friendly and energy-efficient.
An object of the invention is to apply uniform pressure onto the entire
surface of the material to
be pressed formed with the press parts, on the one hand, and on the other to
obtain a press
device with low energy consumption with concurrent high operational comfort.
The subject
matter of the invention thus is an arrangement of the type mentioned at the
outset with the
characterizing features described herein.
According to an aspect of the invention, there is provided an arrangement for
pressing of pressed parts, especially those made out of wood, preferably for
pressing of
wooden lamellae into large elements for timber constructions, with a press
unit with a press
table to support the pressed parts to be connected to each other, and a
counter-pressure
plate which can be moved up and down is arranged above the press table, where
for the
application of compressive force onto the pressed parts, a plurality of
pressure elements,
particularly arranged side-by-side, such as hoses, bags, balloons, pads or
suchlike, are
arranged between the counter-pressure plate and the, which can particularly be
inflated
with pressure fluid, particularly compressed air, and be pressurized from a
pressure fluid
source, particularly a compressed air source, characterized in that
- the counter-pressure plate of the press unit designed with preferably side-
by-side
pressure elements, if necessary, laterally, adjacently arranged I-profile
beams, is formed
with a heavy, pressure-absorption plate, which is rigid and torsionally stiff
across its entire
surface area and on the side facing the aforementioned material to be pressed
and/or the
pressed parts forming the same,
CA 02647331 2013-03-06
la
- which along both of their longitudinal sides and/or longitudinal lateral
flanks has carrier
rollers that are preferably arranged and/or supported and horizontal distances
between
each other and can be moved with these carrier rollers on arranged parallel to
each other
guide rails with an upward slope and which are arranged at the same horizontal
distances
between each other, and are tied to the lateral frame members of the press
unit, at an
acute angle of maximums 300 with reference to the main extension of press
table and
material to be processed and/or the pressed parts for the same, and which can
be vertically
moved and adjusted by means of a preferably hydraulic drive on the
aforementioned
sloping guide rails.
With the provided plurality of expandable pressurizing elements pressurized
with compressed
air as taught by the invention, a large surface area can be uniformly
pressurized. High pressure
can be supplied, since the pressure elements used can be made pressure
resistant easily up to
bar and even higher, so that a high uniform pressure across a large surface
can ultimately
be achieved. With a relatively simple design of the arrangement, this high
surface pressure
achieved can be a multiple of the pressure that can be achieved with a vacuum
forming press,
way a maximum surface pressure of approximately 10N/cm2 is achievable.
Furthermore, the new arrangement is also more simply constructed and easier to
operate,
particularly when compared to the arrangement described in AT 406133 B:
CA 02647331 2013-03-06
2
All that is needed is to provide the necessary compressed air for generating
the compacting
pressure and introduce it into the pressure elements. The decompression of the
press is carried
out by venting the compressed air from the pressure elements into the
environment, while
maintaining the height of its counter-pressure plate and/or pressure-
absorption plate. The
necessary compacting pressure can be built-up rapidly and kept constant over
extended periods
of time. It is not necessary to having to absorb the weight of the respective
material to be
pressed with the pressure elements, because the pressure elements are arranged
above the
material to be pressed and press against the material to be pressed from the
pressure-
absorption plate. Because of its mobility on the inclined guide rails, the
pressure-absorption
plate is supported vertically adjustable in the pressing unit at can be lifted
and lowered such that
the pressure elements and an optional pressure plate which seals these towards
the materials
to be pressed s act in a preferably merely slight bearing against the pressed
goods. In order to
apply the necessary compacting pressure, it is then only necessary to
pressurize the pressure
elements and/or their pressure medium with their respective pressure.
While it was previously necessary to provide e.g. tie bars between the
pressing table and the
pressure-absorption plate in order to ensure the position invariance between
these two
components to each other during the press operation, it has now been provided
that a high-
stability location of the pressure-absorption plate is securely assured
through force closure
by means of locking wedges, rails or suchlike, which are arranged on this
pressure-
absorption plate and cooperate through force closure with the top sides on the
bottom side
of the guide rails.
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement
as described herein, characterized in that the pressure-absorption plate is
equipped with
locking wedges that are arranged and respectively assigned at the same
horizontal
distances from each other as the carrier rollers and the guide rails with the
locking surfaces
on the top facing the underside of the guide rails with a wedge angle which at
least
essentially agrees with the ascent angle of the guide rails for a force-closed
wedging of
pressure-absorption plates with the guide rails to prevent the lifting of the
pressure-
absorption plate at the start of and during the pressure application by means
of the
pressure fluid filling the pressure elements.
The pressing table and the pressure-absorption plate are designed
appropriately rigid and
torsionally stiff so that they can absorb the tensile, compressive, and shear
forces that occur
during the pressure application without any negative impact on the material to
be pressed.
Aspects of the invention provide for an advantageous spacing between the
locking wedges,
guide rails and carrier rollers, a preferred range for the ascent angle of the
guide rails, a
particularly favorable ascent angle of the lock surfaces of the locking wedges
for the deadlock of
CA 02647331 2013-03-06
2a
the pressure-absorption plate during application of pressure on the pressure
elements, a
favorable intermediate position for feeding press material to the press unit
between same and
the pressing table, as well as a protective foil which covers the pressure
elements against the
material to be pressed.
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that at each height
adjustment of the
pressure-absorption plate, so long as this lies completely upon its carrier
rollers on the
guide rails, the top face lock surfaces of the locking wedges are arranged at
a small
distance, preferably below 1 cm, from the underside of the guide rails.
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that the guide rails have an
ascent
angle from 10 to 20 , particularly approximately 15 .
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that the ascent angle of the
lock
surfaces of the locking wedges is 0.05 to 0.25 greater than the ascent angle
of the guide
rails.
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that the pressure elements
facing the
press table, which is coated if necessary with Teflon composite or at least
with a metal
plate, and/or the material to be pressed terminate in a pressure plate for
pressure
distribution.
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that the pressure elements
facing the
material to be pressed and/or the pressed parts forming the same, and/or
facing a
pressure plate that may be present, are covered with a shared textile,
composite, or metal
film, preferably with a low residual surface roughness.
Further aspects of the invention provide for a preferred geometrical
arrangement of the pressure
elements below the pressure-absorption plate, how the pressure elements can be
filled with
pressure fluid efficiently, preferred material characteristics of the pressure
element walls,
CA 02647331 2013-03-06
3
preferred tubing for use with same, advantageous sizing for the same, and an
effective
configuration of the pressure elements on the surface.
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that the pressure elements
are formed
with hoses that are preferably mounted or held in the longitudinal dimension
of the
pressure-absorption plate next to one another and above the shared film and/or
above a
pressure plate that may be present, or are affixed suspended or in a similar
fashion on the
pressure-absorption plate.
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that the pressure elements
provided
with a compressor connection are provided with at least one valve for rapid
pressure
release.
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that the pressure elements,
which are
preferably inflatable and are impervious to the pressed medium, have flexible
and/or
deformable wall areas, which are however essentially not elastic or elastic to
only a very
limited extent.
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that fabric-sleeved hoses,
particularly
hoses with a structure similar to fire hoses, are provided as the pressure
elements.
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that the pressure elements
essentially
have the same dimensions as each other, and in particular are formed with the
same
diameters and otherwise have the same dimensions.
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that more than 50% and
particularly
more than 60 to 70%, of the surface of the pressure-absorption plate and/or a
pressure
plate that may be provided is covered by the pressure elements.
Further aspects of the invention provide for the feeding and/or supply of the
pressure fluid
to the pressure elements, in particular compressed air, as well as the labor
and cost-
saving control of introducing the pressure fluid.
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that each or a number of the
pressure
elements can be supplied with a pressure medium, particularly compressed air,
independently of one another in order to adjust a respectively desired
identical pressure in
the individual pressure elements.
CA 02647331 2013-03-06
,
3a
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that all pressure elements
are
connected to a compressed air distributor unit that is supplied by a
compressed air
source, or can be supplied with compressed air from only one compressed air
source.
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that the pressure medium,
particularly
compressed air, supplied for adjusting the pressure elements, has a control
unit with an
input unit for adjusting the duration of pressure application and/or the
pressing duration
and/or pressing pressure.
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that a device for
maintaining constant
pressing pressure is connected to the control unit, by which means the
application of
compressed air can be regulated and any pressure that is set can be fully
maintained for a
predefined period of time.
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that the inlet valves and
outlet valves
provided on the pressure elements and/or connected therewith are similarly
controllable
by means of the control unit.
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that the lift of the
pressure-absorption
plate and/or the pressure plate can be adjusted to approximately 5 to 15% of
the
maximum press clearance and/or the maximum adjustable distance between the
press
table and the pressure-absorption plate.
Further aspects of the invention provide for a favorable adjustment for the
size of the
clearance between the pressing table at the pressure-absorption plate and/or
its pressure
elements of the respective material to be pressed to be pressed, the structure
of the
framework of the press unit, naturals stabilizers for the material to be
pressed in the press
unit and a favorable arrangements of the material to be pressed feed and
discharge
opening of the press unit.
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that the press table and the
pressure-
absorption plate and/or the ride rails supporting the same form are mounted in
and/or on a
number of side-by-side (steel) frames, forming a longitudinal loadbearing
structure
extending transverse to the direction of feed, and/or are supported and/or
received by this
structure.
CA 02647331 2013-03-06
3b
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that at least one pressure
application
device, particularly a pressure pad or similar device, is arranged and/or
mounted on or
along at least one longitudinal side of the press unit and can be brought into
proximity to
and/or placed upon and/or hold together this unit, and which can preferably be
loaded with
compressed air.
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that the feed opening and
the
discharge opening of the press unit are provided on its narrow sides.
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that the press unit has an
upstream
feeding unit and a conveying unit for the material to be pressed, wherein if
necessary the
feeding unit, has a feed and/or joining unit for the pressed parts arranged on
its sides
and/or an adhesive and/or glue application unit to apply adhesive and/or glue
layers to the
pressed parts.
Further aspects of the invention provide for the consolation of the main
components of the press assembly as taught by the invention, on the loading
and
unloading of the material to be pressed within this assembly and on the
movement of the
pressed table itself.
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that the feeding unit and/or
the
conveying unit is or are in the form of a roller conveyor, an air film
conveyor, or a belt
conveyor.
According to another aspect of the invention, there can be provided an
arrangement as described herein, characterized in that the press table can be
slid in and
out of the press unit on rails, and can preferably be slid between a
positioning unit and/or
feeding unit positioned upstream of the press unit and an unloading unit
positioned
downstream from the press unit.
According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided an
arrangement
for pressing of pressed parts, the arrangement comprising:
a press unit with a press table to support a material to be pressed and/or the
pressed parts to be connected to each other; and
a counter-pressure plate, which can be moved up and down, arranged above the
press table, wherein for an application of compressive force onto the material
to be
pressed and/or the pressed parts, a plurality of pressure elements, which can
be
CA 02647331 2013-03-06
3c
pressurized from a pressure fluid source, are arranged between the counter-
pressure
plate and the material to be pressed and/or the pressed parts,
wherein the press unit further comprises guide rails equidistantly arranged
and in
parallel with one another, the guide rails being tied to lateral frame members
of the press
unit at an upward slope with a maximum ascent angle of 300 with respect to a
plane of the
press table and the material to be pressed and/or the pressed parts, and
wherein the counter-pressure plate of the press unit is formed with a heavy,
pressure-absorption plate, which is rigid and torsionally stiff across its
entire surface area
and on a side facing the material to be pressed and/or the pressed parts, and
wherein carrier rollers that are arranged along longitudinal sides and/or
longitudinal
lateral flanks of the pressure-absorption plate, are carrier rollers that can
be moved on the
guide rails to allow the counter-pressure plate to be vertically moved and
adjusted by
means of a drive on the guide rails.
Further advantages of the inventions can be derived from the following
description
and the embodiments of the invention that are described and/or illustrated in
the drawings.
The invention will now be described in greater detail, for example, by means
of the
drawings.
Figure 1 shows a schematic arrangement as taught by the invention;
Figure 2 shows a schematic plan view of the invention;
Figure 3 shows a schematic side elevation of an arrangement as taught by the
invention;
Figure 4 is a detailed view of the press unit;
Figure 5 is a schematic longitudinal/side elevation of the press unit as
taught by
the invention;
Figure 6 is an oblique view of the pressure-absorption plate;
Figure 7 is a detail of the press unit;
Figs. 8a and 8b show different pressure elements schematically; and
Figure 9 is a schematic illustration of an embodiment of an arrangement for
pressing as taught by the invention.
Figure 1 is a schematic illustration of an entire arrangement for pressing of
press parts 1, 4 as
taught by the invention, in which a press unit 6 with successively arranged
frame members 60 is
supplied with press parts, preferably made out of wood, that are to be
connected to each other
into a wall panel or suchlike by means of a feeding unit 5, which are removed
by means of a
conveying unit 7 after the pressing process.
Such pressing arrangements are particularly used for the manufacture of large-
surface
and in particular also bulky material to be pressed. The material to be
pressed can e.g.
CA 02647331 2013-03-06
. .
3d
have dimensions of 16 m long, 3 m wide and 0.5 m high, resulting in a total
weight of 10 to
12 t for the material to be pressed from the wood parts that are to be
pressure-bonded to
each other.
CA 02647331 2008-11-03
WO 2007/124525 PCT/AT2007/000203
4
The wood parts to be pressure-bonded are e.g. longitudinal lamellae 1 and
transverse lamellae
4, which are preferably used in a planed form.
According to Figure 1, the longitudinal lamellae 1 are provided with bonding
and/ r glue
layers in a bonding and/or gluing unit 2 and are loaded onto the feeding unit
5 by means of a
loading unit 3 located on the side of the feeding unit 5, and are then
arranged here on the
same with the traverse lamellae which are advanced from the other side in the
respective
desired form, e.g. as a stack with the reference symbol 36, which is not
directly shown in
Figure 1, which is then moved into the press unit 6 through the opening 33.
The feeding of
same is facilitated, if a roller, air-film or belt conveyor or a similar
conveyor unit is used as the
feeding unit 5, for transferring heavy and bulky loads into the press unit 6
in a suitable manner.
In a similar manner as the feeding unit 5, also the conveying unit 7 with
discharge opening 34
arranged behind the press unit 6, is designed. Conveyor units for the stacked
press parts 1
and 4 into and/or from the press unit 6, which are provided to be pressure-
bonded to material
to be pressed 36, are not represented.
According to a preferred embodiment of the invention, press parts 1, 4 are
respectively loaded
onto a multiplex or steel plate 35 in the desired arrangement, as shown in
Figure 3. This plate
35 rests during the formation of the stack 36 on the feeding unit 5, which can
be a roller table,
for example. After the stack 36 has been formed from press parts 1 the 4,
plate 35 and the
press parts 1 and 4 resting upon it can be pushed or pulled on the pressing
table 13 by sliding,
by means of chain conveyors, for example. Then the press operation is
performed in press unit
6. Thereafter, the bed plate 35 with the material to be pressed 36 resting
upon it can be pulled
out or pushed by means of a conveyor device onto conveying unit 7.
In the arrangement as taught by the invention it is no longer necessary that
in order to obtain a
relatively small lift of the pressure-absorption plate 9, which is not
detailed here but shown in
Figure 3, that the material 1, 4 to be pressure-bonded must be moved on more
or fewer back
plates 35 with stacks 36 and/or pressed parts 1, 4 sandwiched on top of each
other into the
press unit 6 in order to optimally utilize the available clear span of the
press unit 6 in this
manner, which resulted in that the press lift remained small up to this time
in that the height
adjustment of the extremely heavy counter-pressure plate 9 of press unit 6
could be kept within
distances as small as possible, as was the case in the press arrangement known
from AT
406133 B.
Figure 2 shows ¨ with otherwise constant reference number symbols ¨ as a
schematic plan
view in Figure 3 and as a schematic side elevation, the longitudinal parts 1
and the transverse
parts 4 of the press material 36 as well as the loading unit 5 and the
conveying unit 7,
respectively developed as a roller table.
CA 02647331 2008-11-03
WO 2007/124525 PCT/AT2007/000203
From Figure 3, the basic configuration of the new press unit 6 is also
evident: Within a
sequence of frame elements with rising vertical beams 10 on both sides of the
pressing table
13, the pressure-absorption plate 9 is which is resistant to bending and
degradation and formed
with I-Beams 91 welded to each other on the side, which is always arranged
parallel to pressing
table 13. Same is supported on both sides with a plurality of carrier rollers
93 arranged along its
longitudinal lateral flanks on a plurality of guide rails 101 sloping upward
with an ascent angle a.
The pressure-absorption plate 9 is held in position by means of hydraulic
cylinders 96 which are
respectively located above it and be moved on the guide rails 101 parallel to
the I-beams
whether to each other with the pressing table 13 formed with a support plate.
Figure 4 shows ¨ with otherwise constant reference number symbols ¨ a a
schematic part
section diagonal in relation to the direction of conveyance of the stacks 36
of the press unit 6
show in in Figure 11. Each of the frame member 60 is formed from two lateral
frame beams 10,
an upper beam 11 and a lower beam 12, which supports the pressing table 13.
The beams 10,
11, 12 are connected to each other by welding and/or screwing and/or riveting
into rigid
individual frame member 60, which frame member 60 are connected by means of
longitudinal
beams into a rigid support and/or framework of the press unit 6. Along the
length of the press
unit 6, a plurality of such frame member 60 are arranged and the beams 12
carry the pressing
table plate 13, and/or support same, N./or in combination with the support
plate form the
pressing table 13.
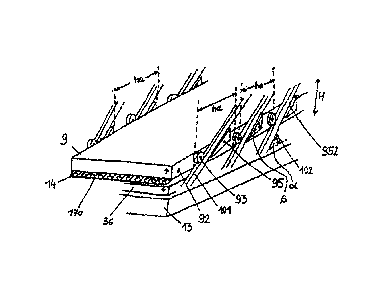
The pressure-absorption plate 9, as particularly shown in Figure 5 ¨ with
otherwise constant
reference number symbols ¨ is formed with a large number of adjacent 1-beams
91 welded to
each other, is very heavy and in spite of its high area propagation is
completely rigid and
torsionally stiff. On both longitudinal lateral flanks 92 carrier and/or
traversing rollers 93 are
mounted with spacing ha between each other. The pressure-absorption plate 9
can be moved
with and/or on same on guide rails 101, which are tied to the upright beams 10
of the frame
member 60, here with an ascent angle a of approximately 150 sloping upward
aligned parallel to
each other. These guide rails 101 have the same horizontal distance ha from
each other as the
roller carriers 93 on the pressure-absorption plate 9. The pressure-absorption
plate 9 serving as
the counter-pressure plate can be moved on the guide rails 101 by means of¨ in
this case four
¨ hydraulic cylinders 96 successively arranged at a distance of each other.
CA 02647331 2008-11-03
WO 2007/124525 PCT/A T2007/000203
6
Looking at Figure 6, where ¨ with otherwise constant reference number symbols
¨ the pressure-
absorption plate 9 with its traversing and/or carrier rollers 93 is shown
resting on the guide rails
101 before the application of pressure, in greater detail. If pressure fluid
is used to fill the above
described pressure elements 14, thus especially compressed air, these pressure
elements 14
push down against the potentially present pressure plate or against its common
sheething 170
and ultimately against the press parts 1, 4 and/or material to be pressed 36,
on the one hand,
and on the other upward against the pressure-absorption plate 9 and lift same
very slightly
upward. At this moment, each of the locking wedges tied, e.g. welded onto
pressure-absorption
plate 9, which are arranged at the same horizontal distances ha in relation to
each other as the
carrier rollers 93, make contact with their top face lock surfaces 952, which
essentially have the
same ascent angles Beta ((I) as the ascent angles a of the guide rails 101,
the undersides 102
of the guide rails 101 and engage with them in force closure, whereby the
pressure-absorption
plate 9 is extremely securely located in exactly this position and acts fully
upon the counter-
pressure plate without any necessity of any other anchorage of same for
position stabilization
e.g. by means of anchor bracing or suchlike during the time when pressure is
introduced into
the pressure elements 14. In addition, the pressure-absorption plate 9 can
respectively be
individually adjusted to the respective height of the material to be pressed
36, 1, 4 and take-up
any height within the support frame 9 of press unit 6, and no longer is ¨ as
previously ¨
restricted to one or only very few height position/s.
Now, back again to Figure 4: Covered on the outside by textile or metal
sheathing 170, the
pressure elements 14 are tied onto the pressure-absorption plate 9, which, can
be moved by
means of the hydraulic cylinders 96 on the inclined guide rails 101, as
already previously
described. These pressure elements 14 are preferably inflatable and push down
in the direction
of the arrow and away from the pressure-absorption plate 9. During an/or after
the completion of
the pressurization, the pressure elements 14 relax and the dropping down
and/or moving down
of the pressure-absorption plate 9 resulting from relieving the force closure
between the also
already previously described locking wedges 95 and the guide rails 101, is
prevented by the
hydraulic cylinders 96 keeping said pressure-absorption plate in its exact
position. The lift of the
pressure-absorption plate 9 is denoted with H.
As can be seen very clearly from Figure 4, the pressure elements 14 are so to
speak
suspended on the pressure-absorption plate 9 and/or are attached to it in a
manner which is not
represented in detail. With 14', the pressure elements 14 are illustrated in
the form in the
unpressurized state before and/or after pressure application. With 14, the
pressure elements
are denoted in their pressurized form; depending on the pressure application,
the pressure
elements 14 and/or an optionally provided pressure plate at its bottom end or
a, as previously
mentioned, e.g. textile sheathing 170, is lowered as needed.
CA 02647331 2008-11-03
WO 2007/124525 PCT/AT2007/000203
7
In order to reduce the compressed air volume required for the expansion of the
pressure
elements 14 and thus the time for pressurization and/or the positioning
stability of the pressure
elements 14, rounded filler bodies 15, e.g. wooden or plastic roads are
arranged around the
edges of the pressure elements 14. In the pressing position, the pressure
elements 14 with the
tubular and/or round cross-section have an elliptical shape because of their
deformation under
pressure.
With respect to their form, the pressure elements 14 have flexible and/or
deformable wall areas.
Advantageously, fiber-reinforced (plastic) hoses are used that are practically
flat and/or nearly
flat without pressure, just as represented with 14', and which adopt a
specified form in each
case and/or insofar as they are squeezed in between the press table 13 and/or
material to be
pressed 14 and pressure-absorption plate 9, attempt to return into the actual
specified form.
Pillow-shaped, pad-shaped, bag-shaped or differently shaped pressure elements
14 can be
used instead of hoses; important is that same are designed appropriately
pressure fluid sealed,
particularly airtight and have adequate pressure resistance.
The pressure elements 14 are advantageously arranged side-by-side in the
longitudinal
direction of the press unit 6. Between the individual pressure elements 14,
advantageously
spaces can run to keep the pressure elements 14 in position. The spaces and/or
the pressure
elements 14 with their filler bodies 15 can have the same height in the
unpressurized position of
the pressure elements 14.
Figure 7 shows ¨ with otherwise constant reference number symbols ¨ a
pressurized pressure
element 14 in a press unit 6 as a longitudinal section. A closure element 25
is provided in the
end area of the pressure elements 14, by means of which decompression is
possible, if
necessary. On the other end of the tubular pressure elements 14 is a
connection 26 for the
supply of compressed air from a compressed air source 27 and/or a compressor.
A control unit
28 regulates the compressed air source 27 and/or the inlet valve on connection
26 of the
pressure element hose 14. If necessary, the control unit 28 can also regulate
the closure 25,
namely for bleeding compressed air when the press operation is completed.
The lift H of the pressure-absorption plate 9 with regard to the clear height
of the pressroom can
advantageously be small; according to an advantageous embodiments version it
is provided
that this lift H is approximately 5 to 15% of the maximum press clearance
and/or the maximum
distance between the press table 13 and the underside of the pressure elements
14.
CA 02647331 2008-11-03
WO 2007/124525 PCT/AT2007/000203
8
The surface of the pressure absorption plate 9 should favorably be occupied
more than 50%
with pressure elements 14, particularly more than 60 to 70%. In this manner, a
particularly
uniform and appropriately high and uniform surface pressure is achievable, the
big advantage of
the new press unit 6 is that the lift H of the pressure-absorption plate 9 is
no longer limited,
since same is essentially movable along the guide rails 101 parallel to the
press table 13. The
advantage thus is that only one dimension of the pressure elements 14 with the
same cross-
section is required. From an economical perspective it is naturally favorable
to provide small
press strokes, such as a lift of approximately 5 cm, for example, which is
also favorable in terms
of operational safety.
The assembly of the press parts 1, 4 to be connected on the feeding unit
and/or on the
bed plate 35 can be facilitated by means of different machines; such devices
have not been
detailed in the drawing, however, and are obvious for a person skilled in the
art.
Fig. 8a and 8b show a plan view of different embodiments of the pressure
elements 14. In the
left area of Fig. 8a U-shaped and the right area snaky pressure elements 14
are arranged,
which are represented with appropriate closures 25 and/or compressed air
connections 26.
Fig. 8b represents a plan view of schematic below-shaped and/or square and
wrecked
angular and/or round or similar formed pressure elements 14; in principle, the
pressure
elements 14 can have any form of cross-section and/or form of volume.
Longitudinal tubular
shapes and hoses with an essentially circular or elliptical cross-section have
proven to be
particularly advantageous, however. Advantageously, fire hoses or those hoses
with a similar
structure are used. As already mentioned above, it is advantageous if the
pressure elements 14
are supported by the pressure-absorption plate 9.
From an operational point of view it is further advantageous if a device for
keeping the
compacting pressure constant is connected to the control unit 28, by means of
which the
pressurization with compressed air can be adjusted over extended press
periods. Depending on
circumstances, in special cases it may be beneficial, if for the adjustment of
a desired, possibly
different pressure in individual pressure elements 14, same are supplied
independently of each
other with compressed air and are respectively provided and/or connected with
a compressed
air source 27, which is controlled from control unit 28.
CA 02647331 2008-11-03
WO 2007/124525 PCT/AT2007/000203
9
The individual pressure elements 14 are advantageously reciprocally
identically sized and/or
designed with the same diameter and/or have the same dimensions. The form and
type of the
embodiment of a stack 36 to be pressure-bonded from longitudinal lamellae 1
and traverse
lamellae 4 is optional; these lamellae can also be supplemented through flat
wooden boards, if
necessary. In principle it is possible to encase the press unit 6 with the
guide rails 101 and
provide cladding for thermal insulation, if necessary, and/or heat the press
interior.
Figure 9 shows an embodiment of an arrangement as taught by the invention, in
which the
press table 13 between the feeding unit 5 and a loading and/or conveying unit
7 connecting to
the press unit 6, can be moved on rails 56, as shown in Figs. 1 to 3. Between
the feeding unit 5
and the press unit 6, a glue application unit 2 is arranged, under which the
press table 13 loaded
with the material to be pressed stack 36 can pass through.
The press table 13 is rigidly designed and can be reinforced by means of
reinforcing braces, or
suchlike, if necessary. It carries the material to be pressed 36. The pressure-
absorption plate 9
along with the pressure elements 14 arranged underneath it can be lowered
along the guide
rails 101, until the pressure elements 14 bear against the material to be
pressed 36 or are
arranged just above the material to be pressed 36. When the pressure-
absorption plate 9 is
adjusted in the respectively desired defined distance to the press table 13
and/or to the material
to be pressed 36, the above described pressure elements 14 are pressurized
with pressure
fluid, whereby the sheathing 170 covering same and/or covering its underside
and or and
optionally provided pressure plate 17, is pushed down against the material to
be pressed 36.
Through the pressurization of the pressure elements 14, the pressure-
absorption plate 9 is
pushed up, the already described carrier rollers 93 are lifted very slightly
above the top side of
the guide rails 101, and in its position the inclined top face lock surfaces
952 of the locking
wedges 95 are force-closed with the undersides 102 of the guide rails 101,
whereby an
extremely stable location on the pressure-absorption plate 9 is totally secure
at any pressure. Of
the completion of the press operation, the pressure elements 14 are
depressurized, the
pressure elements 14 relax, the carrier rollers 93 are supported again on the
guide rails 101 and
the pressure application [sic] plate 9 is held in position by the hydraulic
cylinders. The material
to be pressed 36 is now unloaded and can be conveyed by means of the press
table 13 into the
conveying unit 7.
CA 02647331 2008-11-03
WO 2007/124525 PCT/AT2007/000203
In the outline manner, the machine set-up time has been minimized, and a quick
transport of
the material to be pressed 36 in two and/or from the press unit 6 is assured.
Only the pressure
which is introduced into the pressure elements 14 and exerted by the same
represents the
compacting pressure exerted to the press parts 1, 4 of the material to be
pressed . The control
and the feeding of the already previously described pressure-absorption plates-
hydraulic
cylinders 96 is centrally performed with appropriate hydraulic pressure
fluids, in particular with
compressed air.