Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02674292 2009-07-02
WO 2008/083637 PCT/CZ2008/000009
1
Production method of layered sound absorptive non-woven fabric
Technical field
The invention relates to the production method of layered sound
absorptive non-woven fabric, which comprises a resonance membrane formed
by a layer of nanofibres having diameter to 600 nanometers and basis weight
of 0,1 to 5 gm"2, which is positioned between two layers of the card fibrous
web.
Background art
The CZ PV 2005-226 discloses a layered sound absorptive non-woven
fabric containing a resonance membrane and at least one another layer of
fibrous material. The resonance membrane is formed by a layer of nanofibres
having diameter to 600 nanometers and basis weight of 0,1 to 5 gm 2 and the
resultant fabric is formed by a cross laying to the required thickness and
weight.
In an advantageous embodiment the layer of card fibrous web here
forms the bearing layer on which during electrostatic spinning the layer of
produced nanofibres is being deposited, and consequently both layers join
together in a known manner at the specified temperature in the hot air
chamber.
To increase the efficiency, according to the mentioned document
another layer of card fibrous web may be applied on the fabric, namely from
the originally disposable side of nanofibrous layer. Possibly there may be
another layer, the double or triple one.
Nevertheless the background art for such three- and more layered fabric
requires that at least one fibrous web is prepared separately and the same
after then is joined to the nanofibrous layer of already produced two-layer
fabric. This complicates the production and makes it more expensive.
The goal of the invention is to eliminate the shortcomings of the known
solutions or to restrict them considerably.
CA 02674292 2009-07-02
WO 2008/083637 PCT/CZ2008/000009
2
The principle of invention
The goal of the invention has been reached by a production method of
layered sound absorptive non-woven fabric containing a resonance membrane
formed by a layer of nanofibres, which is positioned between two layers of
card
fibrous web according to the invention, whose principle consists in that, both
layers of card fibrous web are produced simultaneously in carding machine
from which at least one layer of card fibrous web is brought into the device
for
production of nanofibres through electrostatic spinning, in which to the side
of
this layer of card fibrous web adjacent to the remaining layer the layer of
nanofibres is applied, after then after exiting the device for production of
nanofibres through electrostatic spinning, both layers of card fibrous web
near
to one another until their adjacent parts, out of which at least on one there
is
applied a layer of nanofibres forming the resonance membrane, touch one
another.
From the point of view of spatial complexity and arrangement of
individual elements of the device for production of nanofibres through
electrostatic spinning it is advantageous if the layer of nanofibres is being
applied only on one of layers of the card fibrous web, while the lower layer
of
card fibrous web also passes the device for production of nanofibres through
electrostatic spinning, nevertheless outside its spinning compartment.
In case the structure of the device for production of nanofibres does not
enable passage of a layer of card fibrous web on which the layer of nanofibres
is not applied outside the spinning compartment, this layer is guided totally
outside the device for production of nanofibres through electrostatic
spinning,
and to the layer of card fibrous web passing through the spinning
compartment it is nearing only after the device for production of nanofibres
through electrostatic spinning.
According to the claim 3 it is advantageous if both layers of card fibrous
web are guided separately into the device for production of nanofibres
through electrostatic spinning, while at least one layer of the card fibrous
web
passes through the spinning compartment of this device and to the side of this
CA 02674292 2009-07-02
WO 2008/083637 PCT/CZ2008/000009
3
layer of the card fibrous web adjacent to the second layer the layer of
nanofibres is applied.
Guiding of the second layer of the card fibrous web enables its passage
outside the spinning compartment of the device for production of nanofibres
through electrostatic spinning.
In embodiment according to the claim 5 both layers of the card fibrous
web are guided through the spinning compartment of the device for production
of nanofibres through electrostatic spinning, in which one, the upper, layer
of
nanofibres is applied on the side of the first layer of the card fibrous web
adjacent to the second layer of the card fibrous web, and the second, the
lower, layer of nanofibres is applied on the side of the second, the lower,
layer of the card fibrous web reverse to the first, the upper, layer of the
card
fibrous web. This embodiment achieves a higher sound absorption capacity
as it contains two resonance membranes formed by layers of nanofibres, while
each of these membranes may absorb a different range of sound waves.
Another increasing of absorption capacity may be achieved according to
the claim 6 by that, to the layer of nanofibres applied on the side of lower
layer
of the card fibrous web there is joined at least one another layer of the card
fibrous web with a layer of nanofibres applied on the reverse side of this
another layer of the card fibrous web.
At the same time it is advantageous especially from the point of view of
costs, if this further layer of the card fibrous web is produced on the same
carding machine as the upper and lower layer of the card fibrous web.
Or it may be advantageous if this further layer of the card fibrous web is
produced in another carding machine than the upper and lower layer of the
card fibrous web. This embodiment is rather more expensive, but it allows
adding of another one up to three further layers of the card fibrous web.
Especially due to protection of lower layer of nanofibres it is
advantageous if to the layer of nanofibres applied on the outer side of lower
layer of the card fibrous web reverse to the previous layer of the card
fibrous
web an auxiliary layer of the card fibrous web is joined.
CA 02674292 2009-07-02
WO 2008/083637 PCT/CZ2008/000009
4
The auxiliary layer of the card fibrous web may be produced on the
same carding machine as the upper and lower layer of the card fibrous web or
on another carding machine.
The advantage of another variant of solution according to the invention
consists in that both layers of card fibrous web are guided through the
spinning
compartment of the device for production of nanofibres through electrostatic
spinning, in which to the mutually adjacent sides of both layers of the card
fibrous web there is applied always one layer of nanofibres.
In this method it is possible to produce a layered fabric with combination
of nanofibrous layers of a different thickness, possibly of a different
nanofibrous material and so to reach a broader spectra of the sound being
absorbed.
At the same time it is advantageous, if after exiting the device for
production of nanofibres through electrostatic spinning the fabric containing
at
least two layers of the card fibrous web, in between of which there is
arranged
at least one layer of nanofibres is formed by means of cross laying into
layers.
Or according to the claim 14 the fabric containing at least two layers of
the card fibrous web, in between of which there is arranged at least one layer
of nanofibres, after exiting the device for production of nanofibres through
electrostatic spinning may be guided into the laying device in which it is
laid
into layers.
In this manner it is possible to produce a continuous stripe of layered
fabric of a constant composition and specified thickness, which after then, as
the need may be, is divided into panels of desired dimensions.
Further it is advantageous if layers of the fabric are mutually joined by
heating to the temperature of melting the material with the lowest melting
temperature, which is contained in layers of the fabric.
Through this method it is possible to choose between which layers of
the final layered product the joint will be created by means of mutual
smelting
of adjacent surfaces.
CA 02674292 2009-07-02
WO 2008/083637 PCT/CZ2008/000009
Description of the drawing
The embodiments of production lines for performance of the production
method according to the invention are schematically shown on the drawing,
5 where the Fig. 1 represents the production line with passage of one card
fibrous web outside the device for production of nanofibres through
electrostatic spinning, the Fig. 2 a section of the production line with
passage
of both card fibrous webs through the device for production of nanofibres
through electrostatic spinning , while one of them is passing outside the
spinning compartment, the Fig. 3 and 4 a section of the production line, in
which the nanofibres are applied on both layers of the card fibrous web, while
according to the Fig. 3 after exiting the spinning device there is only one
layer
of nanofibres between the two layers of card fibrous web, while according to
the Fig. 4 there are after exiting the spinning device both layers of
nanofibres
positioned together between the two layers of the card fibrous web. The Fig. 5
represents a section of the production line, in which the layers of nanofibres
are applied on four layers of the card fibrous web and the Fig. 6 a section of
the production line according to the Fig. 3, at which on the carding machine
simultaneously three layers of the card fibrous web are being produced, while
the third layer forms the auxiliary covering layer.
Examples of embodiment
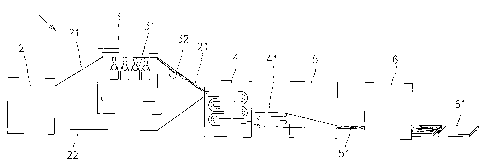
The Fig. 1 schematically represents the production line 1 for
performance of the production method of layered sound absorptive non-woven
fabric, known e.g. from the patent application CZ PV 2005-226, according to
the invention.
At the beginning of the production line 1 there is arranged the known
carding machine 2, which in a known manner prepares the upper layer 21 of
the card fibrous web and the lower layer 22 of the card fibrous web for
production of layered sound absorptive non-woven fabric. The layers 21, 22 of
CA 02674292 2009-07-02
WO 2008/083637 PCT/CZ2008/000009
6
the card fibrous web may be produced from staple bicomponent fibres of the
type core-coating or of another suitable material.
After exiting from the carding machine the upper layer 21 of the card
fibrous web is guided into the device 3 for production of nanofibres through
electrostatic spinning, which is for example the device for production of
nanofibres through electrostatic spinning of polymer solutions according to
the
patent application CZ PV 2005-360. The lower layer 22 of the card fibrous web
is guided outside the device 3 for production of nanofibres through
electrostatic spinning.
The upper layer 21 of the card fibrous web in the device 3 for production
of nanofibres is brought in between the pair of electrodes arranged in the
spinning compartment 31 of the device 3 for production of nanofibres through
electrostatic spinning. After bringing the high voltage of opposite polarity
to
these electrodes an electric field with a high intensity is created, which
through
its action of force to the polymer solution in electrostatic field, e.g. on
surface of
one of the electrodes from this polymer solution creates the polymer
nanofibres. The created polymer nanofibres after their creation are deposited
on the lower side of upper layer 21 of the card fibrous web and they create a
layer 32 of nanofibres, which is adjacent to the lower layer 22 of the card
fibrous web.
After applying the layer 32 of polymer nanofibres of desired thickness
and/or desired basis weight, the upper layer 21 of the card fibrous web with
deposited layer 32 of nanofibres is exiting the device 3 for production of
nanofibres through electrostatic spinning. The upper layer 21 of the card
fibrous web with deposited layer 32 of nanofibres is after then brought to the
lower layer 22 of the card fibrous web passing outside the device 3 for
production of nanofibres through electrostatic spinning and both layers 21, 22
are then together brought into the cross laying device 4 positioned after the
device 3 for production of nanofibres. In the cross laying device 4 there is
performed a known continuous cross laying of layers 21, 22, which contain a
layer 32 of nanofibres, and the non-reinforced layered sound absorptive fabric
41 is produced.
CA 02674292 2009-07-02
WO 2008/083637 PCT/CZ2008/000009
7
The non-reinforced layered sound absorptive fabric 41 is from the cross
laying device 4 brought into the hot-air chamber 5, where through the effect
of
streaming hot air the upper layer 21 containing the card fibrous web and the
nanofibres are joined with the lower layer 22 of the card web, and so the
layered sound absorptive non-woven fabric 51 is produced.
After the hot-air chamber 5 in the production line 1 there is arranged the
cutting device 6, which from the sound absorptive non-woven fabric 51
produces panels 61 of desired dimensions.
The cross laying device 4 may be replaced by any suitable laying
device, which is able to lay the continuously brought layers 21, 22, which
contain a layer 32 of nanofibres one on another and thus to produce the non-
reinforced layered sound absorptive fabric.
Variant of embodiment according to the invention, in which the lower
layer 22 of the card fibrous web is guided through the device 3 for production
of nanofibres through electrostatic spinning outside the spinning
compartment 31 is represented in the Fig. 2. The device 3 for production of
nanofibres through electrostatic spinning here forms a compact unit serving to
guide also the lower layer 22 of the card fibrous web.
In another variants of method according to the invention the layer of
nanofibres 30 is applied not only on the upper layer 21 of the card fibrous
web, but also on the lower layer 22 of the card fibrous web, possibly only on
the lower layer 22 of the card fibrous web.
In the variant according to the invention represented in the Fig. 3 the
device 3 for production of nanofibres through electrostatic spinning comprises
a spinning compartment 31, possibly two separated spinning compartments
311, 312. Upon passage of upper and lower layer 21, 22 of the card fibrous
web the nanofibres are here applied on lower surfaces of both layers 21, 22.
When the layers 21, 22 comprising always the card fibrous web and the layer
32 of nanofibres enter the cross laying device 4, one layer 32 of nanofibres
is
to be found between the layers 21, 22 of the card fibrous web and the second
layer 32 of nanofibres is to be found on the lower surface of the lower layer
22.
CA 02674292 2009-07-02
WO 2008/083637 PCT/CZ2008/000009
8
Exemplary embodiment according to the Fig. 3 may be added by
another layers of the card fibrous web with applied layer of nanofibres. In
embodiment according to the Fig. 5 the device 3 for production of nanofibres
through electrostatic spinning of polymer solutions comprises four spinning
compartments 311, 312, 313, 314, into which there are brought four layers of
the card fibrous web 21, 22, 23, 24 from two carding machines. Upon passage
of layers 21, 22, 23, 24 of the card fibrous web the nanofibres are applied on
the lower surface of layers 21, 22, 23, 24. When the layers 21, 22; 23, 24 of
the card fibrous web containing the layer 32 of nanofibres enter the laying
device 40 the layers 21, 22, 23, 24 are nearing one to another until their
contact occurs, while between the layers 21, 22, 23, 24 of the card fibrous
web
there is always one layer 32 of nanofibres. On the bottom surface of the lower
layer 22 of the card fibrous web there is also a layer of 32 of nanofibres. By
this layer 32 of nanofibres the lower layer 22 of the card fibrous web is laid
in
the laying device on the upper layer 24 of already applied layers of the card
fibrous web 21, 22, 23, 24. The disadvantage of this solution is a fact, that
one
of the outer layers of the resultant layered sound absorptive non-woven fabric
51 is the layer 32 of nanofibres deposited on the utmost lower layer 22 of the
card fibrous web, which is a part of the layered sound absorptive non-woven
fabric 51. This problem is solved by exemplary embodiments according to the
Fig. 4 and 6.
According to the Fig. 6 the carding machine 2 according to the Fig. 3
provided by means for creation of three layers 21, 22, 25 of the card fibrous
web, out of which the layers 21, 22 are brought into the spinning
compartments 311, 312 of the device 3 for production of nanofibres through
electrostatic spinning of polymer solutions, and the layer 25 of the card
fibrous
web is guided outside the spinning compartments or also outside the device 3
for spinning and to the layers 21, 22 on which in the spinning compartments
311, 312 of the device 3 for spinning there were applied layers 32 of
nanofibres, it joins before entering or on entry into the laying device 40 and
so it creates the auxiliary layer 25 of the card fibrous web serving for
protection of nanofibrous layer applied on the lower layer 22 of the card
fibrous web.
CA 02674292 2009-07-02
WO 2008/083637 PCT/CZ2008/000009
9
Also the device according to the Fig. 5 may be provided by an auxiliary
layer 25.
Also in a variant represented in the Fig. 4 the device 3 for production of
nanofibres through electrostatic spinning comprises the spinning compartment
31, possibly two separated spinning compartments 311, 312, as it is described
at the embodiment according to the Fig. 3. Nevertheless the nanofibres are
here applied on layers 21, 22 so that the applied layers 32 of nanofibres are
positioned on mutually adjacent surfaces of layers 21, 22 of the card fibrous
web. The method of application of nanofibres down from top on the upper
surface of the carrying layer is described e.g. in the CZ 294274. Here the
polymer solution is filled into a closed vessel, out of which the polymer
solution
is brought to the surface of the charged electrode, while with the polymer
solution there is wetted e.g. the upper section of circumference of the
cylinder,
which from the vessel carries out on its circumference the necessary quantity
of polymer solution.
In all variants represented in the Fig. 2 to 6 the production procedure of
layered sound absorptive non-woven fabric 51, possibly of it created panels
61 proceeds in a manner shown in the first embodiment variant of the
production line 1 according to the invention, while for the purpose of the
invention it is not important which laying device 40 was applied.
It is obvious, that alternatives of embodiment of the production line I
enable to reach various inner arrangements of the sound absorptive non-
woven fabric 51 and to fulfil in a variable manner the requirements as to
properties of means absorbing the sound. Especially it is possible to each
layer 21, 22, 23, 24 of the card fibrous web to apply a layer 32 of nanofibres
of
different properties, at the same time under the different properties it is
primarily understood the different material, out of which the nanofibres are
produced, the different thickness of the layer 32 of nanofibres, the different
diameter and/or length of nanofibres and other properties influencing
absorbing of the sound.
CA 02674292 2009-07-02
WO 2008/083637 PCT/CZ2008/000009
The described examples of embodiment permit to create further
combinations, which are not described in a detail as they are quite obvious
for
an average specialist.
CA 02674292 2009-07-02
WO 2008/083637 PCT/CZ2008/000009
11
List of referential markings
1 production line
2 carding machine
21 upper layer of the card fibrous web
22 lower layer of the card fibrous web
3 device for production of nanofibres through electrostatic spinning
31 spinning compartment
311 upper section of spinning compartment
312 lower section of spinning compartment
32 layer of nanofibres
4 cross laying device
41 non-reinforced layered sound absorptive fabric
5 hot-air chamber
51 layered sound absorptive non-woven fabric
6 cutting device
61 panel