Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02683303 2009-10-22
VEHICLE TIRE PRESSURE MONITOR
CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS
This application is a continuation-in-part of Application No. 11/449,340,
filed
June 8, 2006, which is a continuation of Application No. 10/706,828, filed on
November
12, 2003, now U.S. Patent No. 7,145,445, the disclosures of which are all
incorporated by
reference herein in their entirety.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
1. Field of the Invention:
The present invention relates to automotive electronics, and more particularly
to
tire pressure monitoring.
2. Discussion of Related Art:
Proper tire pressure in automotive tires is important for ensuring safe
handling,
maintaining gas mileage, reducing tread wear, and preventing tire blowouts.
Under-
inflated or over-inflated tires can negatively affect the handling of a
vehicle, resulting in
under-steer, over-steer, and/or an increased tendency to hydroplane in wet
conditions.
Under-inflation is a more common problem as tire pressure typically decreases
over time. Under-inflated tires increase rolling resistance, decreasing gas
mileage and
increasing tire wear. Further, under-inflated tires flex greatly as they roll,
the flexing
1
CA 02683303 2009-10-22
generates heat as different layers of the tire rub against one another. The
heat can reach
temperatures beyond the operating parameters of the tire causing catastrophic
tire failure.
These problems are exacerbated by the increasing use of "run-flat" tires. A
run-
flat tire enables a vehicle to travel an extended distance after a significant
loss of air
pressure within the tire through the use of, for example, stiff tire
sidewalls. Thus, even a
significant loss of air pressure within the tire may go unrecognized by a
vehicle operator
because the loss of air pressure may cause only a small deflection of the
sidewall.
Because the sidewall is capable of maintaining the shape of an under-inflated
tire, the
handling characteristics of the vehicle during typical operation may not be
affected.
However, the under-inflation can seriously affect handling in an emergency
situation
where the stresses placed on the tire can be much greater than during typical
operation.
For these and other reasons, proper air pressure is important to the safe and
efficient
operation of a motor vehicle.
Since air pressure is typically overlooked as part of vehicle maintenance,
systems
have been developed to inform vehicle operators of low-pressure situations.
These
systems are typically sold as part of a factory installed package with new
vehicles.
Various tire pressure monitoring systems have been developed to provide
information to a vehicle operator, for example, a tire pressure monitoring
system that
detects when air pressure within a tire drops below a predetermined threshold
pressure
value.
Typically, a tire pressure monitoring system comprises a tire pressure sensor,
a
tire pressure signal transmitter, a tire pressure signal receiver, and an
indicator or display
located on a vehicle instrument panel. The tire pressure sensor and the tire
pressure
2
CA 02683303 2009-10-22
signal transmitter are located inside the tire. The tire pressure sensor may
transmit radio
frequency signals through the transmitter that are received by an antenna
located in the
vehicle.
Tire pressure sensors have been developed with various designs. For example,
tire pressure sensors and transmitters have been attached to air valves.
Another system
utilizes a strap to attach the sensor and transmitter to a rim.
While the tire pressure monitoring systems are useful to vehicle operators,
the
systems are typically standalone systems having dedicated wiring and
interfaces.
Therefore, a need exists for an integrated monitoring system for monitoring
tire
io air pressure and vehicle security.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
A vehicle tire pressure monitoring system comprising of a tire pressure sensor
coupled to a tire of the vehicle, a transmitter coupled to the tire pressure
sensor for
wirelessly transmitting a signal indicative of a tire pressure, a receiver
located in the
vehicle for receiving the signal indicative of the tire pressure, a controller
coupled to the
receiver for processing the signal indicative of the tire pressure, and a
plurality of
displays coupled to the controller via a databus in the vehicle for displaying
on at least
one of the displays the processed signal indicating a tire pressure.
The vehicle tire pressure monitoring system wherein the plurality of displays
are
disposed in any combination of a dashboard, rear view mirror, HVAC, overhead
or
headrest mounted device.
3
CA 02683303 2009-10-22
The system controller generates an alarm condition when the tire pressure
sensed
by the tire pressure sensor decreases by a preset amount. The alarm condition
is
displayed on at least one of the displays located in the vehicle. The
controller
periodically polls the tire pressure sensor.
The system further including a remote keyless entry device for remotely
operating
a security feature of the vehicle, the remote keyless entry device having a
receiver for
receiving the signal indicating tire pressure information and a display for
displaying the
tire pressure information.
The system further comprising a second transceiver coupled to the tire
pressure
sensor, the second transceiver for transmitting a second signal indicating a
tire pressure to
a remote keyless entry device and for receiving a tire pressure request signal
from the
remote keyless entry device.
The system further including a battery for powering the tire pressure sensor.
A
transducer for converting a signal into a current, the transducer provides
power to the tire
pressure sensor
The controller processes the signal indicating tire pressure from each tire of
the
vehicle and the display displays the processed signal indicating tire pressure
numerically
in pounds per square inch.
A vehicle tire pressure monitoring system comprising of a tire pressure sensor
coupled to a tire of the vehicle, a transmitter coupled to the tire pressure
sensor for
wirelessly transmitting a signal indicative of a tire pressure, a receiver of
a remote mobile
device for wirelessly receiving the signal indicative of the tire pressure, a
controller
coupled to the receiver for processing the signal indicative of the tire
pressure, and
4
CA 02683303 2009-10-22
a display located on the remote mobile device for displaying the processed
signal
indicating a tire pressure.
The transmitter transmits signals indicative of the tire pressure in response
to a
variation in tire pressure sensed by the tire pressure sensor. The controller
generates an
alarm condition when the tire pressure sensed by the tire pressure sensor
decreases by a
preset amount. The alarm condition is audibly sounded or displayed on the
display at the
remote mobile device. The display displays the signal indicative of tire
pressure
numerically. The system further includes a battery for powering the remote
mobile
device and a battery for powering the tire pressure sensor.
The system includes a transducer for converting kinetic energy into an
electrical
current, the transducer provides power to the tire pressure sensor. The remote
mobile
device is a keyless entry device configured to operate a security feature of
the vehicle.
The vehicle tire pressure monitoring system comprising of a tire pressure
sensor
coupled to a tire of the vehicle, a transmitter coupled to the tire pressure
sensor for
wirelessly transmitting a signal indicative of a tire pressure, a receiver
located in the
vehicle for receiving the signal indicative of the tire pressure, a controller
coupled to the
receiver for processing the signal indicative of the tire pressure, a display
located in the
vehicle for displaying the processed signal indicating a tire pressure, and a
remote keyless
entry device for remotely operating a security feature of the vehicle, the
remote keyless
entry device having a receiver for receiving the signal indicating a tire
pressure and a
display for displaying the tire pressure.
5
CA 02683303 2009-10-22
The display is disposed in any of a dashboard, rear view mirror, HVAC,
overhead
or headrest mounted device. The receiver of the remote keyless entry device
receives the
signal indicative of the tire pressure from the controller.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described below in more
detail, with reference to the accompanying drawings:
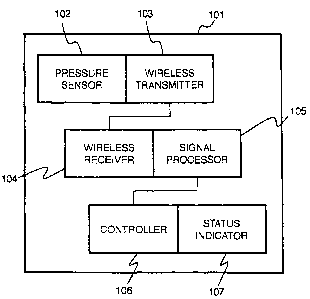
Figure 1 is an illustration of an integrated monitoring system according to an
embodiment of the present invention;
Figure 2 is an illustration of an air pressure sensor according to an
embodiment of
the present invention;
Figure 3 is an illustration of a control system for a vehicle security system
and an
integrated tire pressure monitor according to an embodiment of the present
invention;
Figure 4 is a flow chart of a method according to an embodiment of the present
invention;
Figure 5 is a flow chart of a method according to an embodiment of the present
invention;
Figure 6 is an illustration of an integrated monitoring system according to an
embodiment of the present invention; and
Figure 7 is a flow chart of a method according to an embodiment of the present
invention.
6
CA 02683303 2009-10-22
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
According to an embodiment of the present invention, a vehicle monitoring
system 101 comprises a pressure sensor 102, a wireless transmitter 103, a
wireless
receiver 104, and a signal processor 105, as shown in Figure 1. The air
pressure
monitoring system 101 further comprises a controller 106 and a status
indicator 107. The
wireless transmitter 103 and wireless receiver 104 can operate on a frequency
used by an
integrated vehicle security system. The vehicle security system may comprise a
wireless
key FOB for controlling, for example, the locking and unlocking vehicle doors
and
arming and disarming the security system. The vehicle security system
comprises the
wireless receiver 104, the signal processor 105, and the controller 106 for
operating
security/convenience features.
The pressure sensor 102 can have any form that determines air pressure. For
example, the pressure sensor 102 can be one of a capacitive type sensor, an
inductive
type sensor, and a piezoelectric type sensor. The capacitive type sensor
comprises a plate
is that moves in response to a change in air pressure. The inductive type
sensor comprises a
coil or core that moves in response to a change in air pressure. The
piezoelectric type
sensor comprises a piezo crystal that deforms in response to a change in air
pressure. The
pressure sensor 102 can comprise a sealed vacuum reference to compare against
a current
air pressure as measured by the movement of the plate or coil, or the
deflection of the
piezo crystal.
According to an embodiment of the present invention, the pressure sensor 102
is
coupled to the wireless transmitter 103 for transmitting a signal indicative
of a air
pressure, as shown in Figure 1. Referring to Figure 2, the pressure sensor 102
and
7
CA 02683303 2009-10-22
wireless transmitter 103 are located in or attached to a vehicle tire 201. The
pressure
sensor 102 and wireless transmitter 103 can be, for example, strapped to a rim
or
connected to an air valve stem. A power source 202 is coupled to the pressure
sensor 102
and wireless transmitter 103. The power source 202 comprises a battery and/or
a
transducer for converting a signal, for example, as transmitted by the
wireless key FOB
of the vehicle security system, into a current. The power source 202 provides
power to
the pressure sensor 102 and the wireless transmitter 103. It is contemplated
that the
battery can be a rechargeable type. A transducer which converts kinetic energy
produced
by the motion of the tire to electrical current can be used to charge the
battery.
A wireless system comprises the wireless transmitter 103 mounted in or
attached
to the tire, and the receiver 104 located outside of the tire. The transmitted
signal is
received by a receiver/controller in the vehicle or in a key FOB. The
transmitter 103
transmits signals indicative of tire pressure to the receiver 104. The signal
indicative of
tire pressure can be decoded by the signal processor 105 and handled by the
controller
is 106. The controller outputs a signal to the status indicator 107 based on a
decoded signal
for display to a vehicle operator. The receiver 104, signal processor 105,
controller 106
and status indicator 107 can be located in the vehicle and/or in a key fob.
According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the status
indicator 107 is a display, such as a LED, LCD, or OLED, disposed on one or a
combination of displays disposed anywhere in a vehicle viewable by the driver
or the
passenger. For example, the display can be disposed on the dashboard, rear
view mirror,
HVAC, overhead or headrest mounted auxiliary device. It is contemplated that
the status
indicator 107 is connected to the controller 106 via a databus (not shown). It
is also
8
CA 02683303 2009-10-22
contemplated that there is more than one display connected to the databus
within the
vehicle.
The wireless transmitter 103 comprises an antenna and a circuit for generating
a
signal of a desired frequency. A transmission of the wireless transmitter 103
occurs in
response to a variation in tire air pressure. The transmission can be on a
licensed
frequency or an unlicensed frequency. The frequency is shared between the
vehicle
security system and the tire pressure monitoring system. A separate frequency
can be
used by the tire pressure monitoring system. However, the receiver 104 is
shared
between the security system and the tire pressure monitoring system.
Figure 3 is an illustration of a vehicle monitoring system according to an
embodiment of the present invention. A transmitter 301, comprises controls,
for
example, buttons 302 and 303. Activation of a button or a combination of
buttons
produces a pulse code modulated (PCM) signal, e.g., of 16 bits in the 275-310
MH range.
While the PCM signal is described having 16 bits, other length signals and
coding may be
used.
The wireless receiver 104 is located in a vehicle 304 and receives the PCM
signal
from the wireless transmitter 103. The signal processor 105, also located in
the vehicle
304, amplifies the received PCM signal, demodulates the PCM signal, and passes
the
signal to the controller 106. The controller 106 receives the incoming signal
from the
signal processor 105 and compares or verifies the signal with a code stored in
a memory
305, which may be an E 2 PROM (not shown) in the controller unit 106. If the
code is
verified, then an output signal is provided on an output terminal of the
controller 106.
The output signal can control, for example, vehicle door looks, a status
indicator 107, and
9
CA 02683303 2009-10-22
vehicle windows. The controller 106 further includes a transmitter (not shown)
for
transmitting signals including tire pressure information to the wireless
transmitter 103.
According to an alternative embodiment of the present invention, the wireless
system 103 or the controller 106 wirelessly communicate with any electronic
device
equipped with a wireless receiver, such as a cellular phone, PDA, or a mobile
device, to
receive the air pressure or status information via the wireless transmitter
103 or controller
106. Other wireless communication protocols including Bluetooth or cellular
technologies, e.g. CDMA, TDMA, or 3G are contemplated.
A 12-volt DC power source (not shown), which may be an automobile battery,
supplies power to a voltage regulator, which is connected to and powers the
wireless
receiver 104, the signal processor 105, the controller unit 106, and the
status indicator
107.
Referring to Figure 4, a signal is transmitted 401 from the wireless
transmitter and
received 402 by the wireless receiver. The signal is decoded 403 and an
indication of the
pressure signal is generated 404. The indication is controlled by the
controller 106 and
communicated by the status indicator. The indication can be, for example, a
numerical
display in pounds per square inch, an audio warning, or discrete light
emitting diodes
corresponding to different pressures. Referring to Figure 5, if a decoded
signal is
determined to be below a predetermined threshold 501 by the controller, a
warning can
be issued 502. The warning can be, for example, a visual and/or aural
indication that the
pressure is below a predetermined threshold. In this case, where the pressure
is above the
threshold, no action is taken 503.
CA 02683303 2009-10-22
The air pressure can be determined periodically while the vehicle is being
operated, for example, once every 15 seconds. The controller includes a timer
for
controlling the period of tire pressure sensor polling. The air pressure can
also be
determined upon the happening of an event, for example, upon disarming the
vehicle
security system.
Referring to Figure 6, the pressure sensor 102 is coupled to a second wireless
receiver 601. The second wireless receiver 601 is located in the tire and
receives
transmissions from a second wireless transmitter 602, e.g., the key fob. Upon
receiving
the signal, the air pressure is determined and the wireless transmitter 103
transmits a
io signal to the wireless receiver 104. Further, a second signal processor 603
can be
provided, coupled to the second wireless receiver 601, the pressure sensor
102, and the
wireless transmitter 103, for decoding/encoding signals.
Referring to Figure 7, a vehicle monitoring method comprises receiving the
signal
for controlling a vehicle security system at a tire pressure monitor 701. The
signal can be
i 5 generate by a remote keyless entry device 702 or by a controller 703. The
method
comprises generating a tire pressure signal in response to the signal 704, and
receiving
the tire pressure signal at a controller 705. An indication of tire pressure
is generated
706.
Having described embodiments for tire pressure monitoring, it is noted that
20 modifications and variations can be made by persons skilled in the art in
light of the
above teachings. It is therefore to be understood that changes may be made in
the
particular embodiments of the invention disclosed which are within the scope
and spirit
of the invention as defined by the appended claims. Having thus described the
invention
11
CA 02683303 2009-10-22
with the details and particularity required by the patent laws, what is
claimed and desired
protected by Letters Patent is set forth in the appended claims.
12