Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02686992 2009-11-10
WO 2009/140993 PCT/EP2008/055931
- 1 -
METHOD AND DEVICE FOR REMOVING CONTAMINANTS FROM A CONTAMINATED GAS
STREAM
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to a method for removing
contaminants from a contaminated gas stream, such as a
contaminated natural gas or air stream.
Various processes are known to remove contaminating
components, such as water, hydrates, carbon dioxide
and/or hydrogen sulphide, from a natural gas stream.
The processes may be based on physical and/or
chemical separation techniques.
The physical separation techniques use differences in
boiling, condensation and/or freezing points of the
various contaminating components to selectively remove
one or more of these components in a fractionating
column, or differences in density to separate components
with different densities in a centrifugal or cyclonic
separator.
The chemical techniques may employ selective
absorption or catalytic reactions to convert a
contaminating component into a composition that can be
easily separated.
The standard technique for removing hydrogen sulphide
and carbon dioxide from natural gas is amine treatment,
which is based on solvent absorption. In this process the
contaminating components are bound on a molecule such as
diethanol amine in an aqueous solution. The clean
hydrocarbon gas is not absorbed and emerges in the
product gas stream. The solution with the absorbed
contaminant is recycled and heated by approximately
CA 02686992 2009-11-10
WO 2009/140993 PCT/EP2008/055931
- 2 -
100 C to drive off the gases, which then are collected
in a waste stream. The major cost factors in this process
are the energy requirement for waste gas regeneration,
solvent losses and the fact that the waste gases are
regenerated at near atmospheric pressure - any process
such as reinjection requires compression.
The operating costs for any gas purification process
need to be a relatively small fraction of the value of
the clean gas produced. Amine plants with their extensive
gas-liquid contacting schemes will be fairly large,
expensive and uneconomic if the gas stream contains a
large fraction of contaminants.
Known gas separation centrifuges rotate at about
50,000 revolutions per minute (RPM) to separate gaseous
fractions with only minor differences in density. These
fast rotating centrifuges are known as ultracentrifuges
and have limited separation efficiency and can only
handle a limited flux of gas. If a large gas stream
containing a large fraction of contaminants is to be
purified by means of centrifuges then a large amount of
centrifuges or ultracentrifuges are required, which
renders centrifugal separation uneconomical.
International patent application W02006087332
discloses a method of separating contaminants from a
contaminated gas stream, wherein the contaminated gas
stream is cooled in a nozzle or expansion turbine to such
a temperature that at least some contaminants condense
and the cooled mixture is separated in a channelled
centrifuge into a purified gas stream and a contaminants
enriched side stream.
European patents 1017465, 1438540 and 1140363
disclose cyclonic separators for purifying a contaminated
gas stream, wherein the gas stream is accelerated in a
CA 02686992 2009-11-10
WO 2009/140993 PCT/EP2008/055931
- 3 -
nozzle and thereby cooled such that at least some
contaminants condense and the cooled gas liquid mixture
is induced to swirl in a fluid separation section such
that the liquid components swirl along the outer surface
of the fluid separation section into an annular liquid
outlet and a purified gas stream flows into a central
purified gas outlet conduit.
It is an object of the present invention to provide a
method for removing solid, liquid and/or gaseous
contaminants, such as water, hydrates, carbon dioxide
and/or hydrogen sulphide, from a gas stream in an
efficient and economical manner, even if the gas
comprises a large fraction of contaminants.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
In accordance with the invention there is provided a
method for removing contaminants from a contaminated gas
stream, the method comprising inducing the gas stream to
flow through a conduit having a first and a second
conduit section, which conduit sections each comprise the
following components:
a) a cyclonic fluid separation section in which the gas
stream is induced to swirl such that a solid and/or
liquid contaminants enriched fluid fraction flows to an
outer region of the separation section and a contaminants
depleted gas fraction flows into a central region of the
separation section;
b) a central purified gas outlet tube for discharging
the contaminants depleted gas fraction from the central
region of the centrifugal fluid separation section;
c) an outer discharge tube for discharging the
contaminants enriched fluid fraction from the outer
region of the separation section; and
CA 02686992 2009-11-10
WO 2009/140993 PCT/EP2008/055931
- 4 -
d) a venturi section, which is located upstream of the
centrifugal fluid separation section and in which the gas
stream is induced to flow at a higher axial velocity than
in the centrifugal fluid separation section;
wherein the method further comprises:
- connecting the central purified gas outlet tube of
the second conduit section to the venturi section of the
first conduit section such that a purified gas fraction
is induced to flow from the second conduit section into
the first conduit section;
- injecting a liquid contaminants absorbent into the
venturi section of the first conduit section; and
- connecting the outer discharge tube of the first
conduit section to the venturi section of the second
conduit section, thereby inducing a contaminants and
liquid contaminant absorbent enriched fluid fraction to
flow from the outer discharge tube of the first conduit
section into the venturi section of the second conduit
section.
It will be understood that the acceleration of the
fluid velocity in the venturi section of the second
conduit section will result in a reduction of the static
fluid pressure in particular in the vicinity of a throat
of this venturi section, so that a positive pressure
difference is created between the separated liquid in the
outer discharge tube of the first conduit section and the
fluid flowing through the venturi in the second conduit
section, thereby inducing the separated liquid to flow
from the outer discharge tube of the first conduit
section into the venturi of the second conduit section
without requiring any pumping action.
The conduit may further comprise a third conduit
section, which also comprises the components a),b),c)and
CA 02686992 2009-11-10
WO 2009/140993 PCT/EP2008/055931
- 5 -
d),wherein the method further comprises:
- connecting the central purified gas outlet tube of
the third conduit section to the venturi section of the
second conduit section such that a purified gas fraction
is induced to flow from the third conduit section into
the second conduit section; and
- connecting the outer discharge tube of the second
conduit section to the venturi section of the third
conduit section, thereby inducing a contaminants and
liquid contaminant absorbent enriched fluid fraction to
flow from the outer discharge tube of the second conduit
section into the venturi section of the third conduit
section.
Optionally, the conduit may comprise a series of n
conduit sections, wherein n is in the range from 4 to 40,
which conduit sections each comprise the components
a),b),c)and d) as described in claim 1 and wherein the
method further comprises:
- connecting the central purified gas outlet tube of
the n-th conduit section to the venturi section of the
(n-1)th conduit section such that a purified gas fraction
is induced to flow from the nth conduit section into the
(n-1)th conduit section; and
- connecting the outer discharge tube of the (n-1)th
conduit section to the venturi section of the n-th
conduit section, thereby inducing a contaminants and
liquid contaminant absorbent enriched fluid fraction to
flow from the outer discharge tube of the (n-1)th conduit
section into the venturi section of the n-th conduit
section.
The liquid contaminants absorbent may comprise Mono
Ethylene Glycol (MEG), an amine compound or aqueous amine
compound solution, and/or any other absorbent fluid and
CA 02686992 2009-11-10
WO 2009/140993 PCT/EP2008/055931
- 6 -
be configured to absorb water, hydrogen sulphide, carbon
dioxide and/or other contaminants from the contaminated
gas stream.
The conduit may be located horizontally or vertically
at the bottom of a body of water in the vicinity of the
wellhead of an underwater gas production well and may
form part of an underwater gas processing and
conditioning facility, which receives a contaminated gas
stream from at least one wellhead of at least one
underwater gas production well and which discharges an at
least partially purified gas stream into a downstream
processing facility or into a subsea gas transportation
conduit which may have a length of more than hundred
kilometres Alternatively, the conduit may be located on
an offshore gas production platform or form part of an
onshore gas production and processing facility.
In accordance with the invention there is furthermore
provided a system for removing contaminants from a
contaminated gas stream and a purified gas stream from
which contaminants have been removed by means of the
method according to the invention.
These and other features, embodiments and advantages
of method and system according to the invention are
described in the accompanying claims, abstract and the
following detailed description of a preferred embodiment
in which reference is made to the accompanying drawing.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
FIG.1 is a schematic longitudinal sectional view of a
conduit in which a contaminated gas stream is purified in
accordance with the method according to the invention;
and
FIG.2 is a schematic longitudinal sectional view of
an alternative embodiment of the conduit shown in FIG.1,
CA 02686992 2009-11-10
WO 2009/140993 PCT/EP2008/055931
- 7 -
wherein the conduit sections are not directly connected
to each other, but are interconnected by pipes.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE SHOWN EMBODIMENTS OF THE
INVENTION
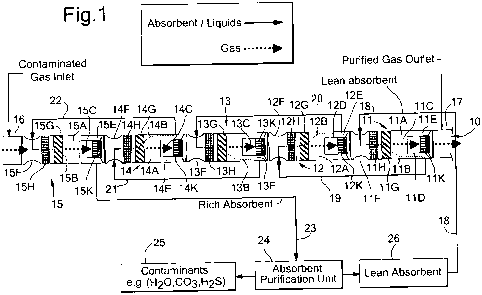
FIG.1 shows a conduit 10, which comprises first,
second third, fourth and fifth conduit sections
11,12,13,14 and 15, respectively, and which is connected
between a contaminated gas inlet conduit 16 and purified
dry gas outlet conduit 17.
Each of the conduit sections 11-15 comprises the
following components:
a) a cyclonic fluid separation section 11A-15A in which
the gas stream is induced to swirl by swirl imparting
vanes 11G-15G such that a solid and/or liquid
contaminants enriched fluid fraction 11B-15B flows to an
outer region of the separation section 11A-15A and a
contaminants depleted gas fraction 11C-15C flows into a
central region of the separation section 11A-15A;
b) a central purified gas outlet tube 11D-15D for
discharging the contaminants depleted gas fraction from
the central region of the centrifugal fluid separation
section 11A-15A;
c) an outer discharge tube 11E-15E for discharging the
contaminants enriched fluid fraction from the outer
region of the separation section 11A-15A; and
d) a venturi section 11F-15F, which is located upstream
of the centrifugal fluid separation section 11A-15A and
in which the gas stream is induced to flow at a higher
axial velocity than in the centrifugal fluid separation
section 11A-15A such that the static pressure of the
accelerated gas stream is reduced in particular in the
vicinity of the throat of the venturi section 11F-15F.
CA 02686992 2009-11-10
WO 2009/140993 PCT/EP2008/055931
- 8 -
In the embodiment shown each of the conduit sections
11-15 furthermore comprises a optional static fluid mixer
11H-15H, which is arranged between the venturi section
11F-15F and the swirl imparting vanes 11G-15G and a
series of anti-swirl flow straightening vanes 11K-15K
arranged in the central purified gas outlet tube 11D-15D.
In accordance with the invention:
- the central purified gas outlet tube 12D of the
second conduit section 12 is directly, as shown in FIG.1,
or indirectly, for example by means of a U-shaped
connection tubular 32 as shown in FIG.2, connected to the
venturi section 11F of the first conduit section such
that a purified gas fraction 12C is induced to flow from
the second conduit section 12 into the first conduit
section 11;
- a liquid contaminants absorbent (e.g. lean MEG) is
injected via a lean absorbent supply conduit 18 into the
venturi section 11F of the first conduit section 11; and
- the outer discharge tube 11E of the first conduit
section 11 is connected to the venturi section 12F of the
second conduit section 12, thereby inducing a
contaminants and contaminant absorbent enriched fluid
fraction 19 to flow from the outer discharge tube 11E of
the first conduit section 11 into the venturi section 12F
of the second conduit section 12.
Furthermore:
- the outer discharge tube 12E of the second conduit
section 12 is connected to the venturi section 13F of the
third conduit section 13, thereby inducing a contaminants
and liquid contaminant absorbent enriched fluid fraction
20 to flow from the outer discharge tube 12E of the
second conduit section 12 into the venturi section 13F of
the third conduit section 13;
CA 02686992 2009-11-10
WO 2009/140993 PCT/EP2008/055931
- 9 -
- the outer discharge tube 13E of the third conduit
section 13 is connected to the venturi section 14F of the
fourth conduit section 14, thereby inducing a
contaminants and liquid contaminant absorbent enriched
fluid fraction 21 to flow from the outer discharge tube
13E of the third conduit section 13 into the venturi
section 14F of the fourth conduit section 14;
- the outer discharge tube 14E of the fourth conduit
section 14 is connected to the venturi section 15F of the
fifth conduit section 15, thereby inducing a contaminants
and liquid contaminant absorbent enriched fluid fraction
22 to flow from the outer discharge tube 14E of the
fourth conduit section 14 into the venturi section 15F of
the fifth conduit section 15; and
- the outer discharge tube 15E of the fifth conduit
section 15 is connected to a contaminants enriched MEG
outlet conduit 23 through which a contaminants enriched
MEG fluid stream is discharged from the conduit 10 and
flows to a MEG purification unit 24 in which the
contaminants enriched MEG fluid stream is separated into
a contaminants enriched and MEG depleted fluid fraction
and a contaminants depleted lean MEG fraction 26,
which is recycled into the lean MEG supply conduit 18.
An advantage of the method according to the invention
25 is that MEG is supplied to the conduit 10 via a single
lean MEG supply conduit 18 into the venturi section 11F
of the first, most downstream, conduit section 11 and is
then automatically recycled into the more upstream
conduit sections 12-15 as a result of the relatively low
static pressure in the throat of each of the venturi
sections 12F-15F of these more upstream sections 12-15
relative to the static pressure in the wider outer
discharge tubes 11E-14E of the downstream sections.
CA 02686992 2009-11-10
WO 2009/140993 PCT/EP2008/055931
- 10 -
FIG.2 shows an alternative embodiment of a conduit
according to the invention, wherein the conduit comprises
four conduit sections 11-14, which are similar to the
conduit sections 11-14 shown in FIG.1 and in which
similar reference numerals are used to identify similar
components, but where the conduit sections 11-14 are not
aligned and are not directly connected to each other, but
are interconnected by U-shaped or other shaped pipes
30,31 and 32, and where the contaminants enriched liquid
absorbent discharged by the fourth conduit section 14 is
fed into an absorbent purification unit (not shown) from
which the lean absorbent is pumped into the venturi
section 11F of the first section.
The outer discharge tube 11E of the first conduit
section 11 is connected to the venturi section 12F of the
second conduit section 12, thereby inducing a
contaminants and contaminant absorbent enriched fluid
fraction 19 to be sucked from the outer discharge tube
11E of the first conduit section 11 into the venturi
section 12F of the second conduit section 12.
The outer discharge tube 12E of the second conduit
section 12 is connected to the venturi section 13F of the
third conduit section 13, thereby inducing a contaminants
and contaminant absorbent enriched fluid fraction 20 to
be sucked from the outer discharge tube 12E of the second
conduit section 12 into the venturi section 13F of the
third conduit section 13.
The outer discharge tube 13E of the third conduit
section 13 is connected to the venturi section 14F of the
fourth conduit section 14, thereby inducing a
contaminants and contaminant absorbent enriched fluid
fraction 21 to be sucked from the outer discharge tube
CA 02686992 2009-11-10
WO 2009/140993 PCT/EP2008/055931
- 11 -
13E of the third conduit section 13 into the venturi
section 14F of the fourth conduit section 14.
It will be understood that the absorbent
recirculation system according to the invention may
operate without any circulation pumps between the conduit
section, which enhances the reliability of the
recirculation since circulation pumps are prone to wear
and require regular maintenance, inspection and
replacement.
It will be understood that in the case that the
conduit comprises n conduit sections, the contaminated
gas stream will first enter the n-th conduit section,
than the purified gas stream from the n-th conduit
section will enter the (n-1)th conduit section, than the
gas stream from the (n-1)th conduit section will enter
the (n-2)th conduit section etc. Finally the purified gas
stream from the first conduit section will leave the
total conduit.
The cyclonic fluid separation sections in the present
invention are especially in-line separation. The gas
stream is flowing through a pipe-line shaped conduit, the
conduit provided with internals as describe above. Thus,
no tangential inflow of the gas stream, the tangential
flow is induced by specific internals as vanes and
swirls.
The contaminated gas stream of the invention is
preferably a natural gas stream, suitably comprising at
least 50 vol% of methane, contaminated with water, carbon
dioxide, hydrogen sulphide and/or mercaptans.