Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
PHARMACOLOGICAL ADJUNCTIVE TREATMENT ASSOCIATED WITH
GLAUCOMA FILTRATION SURGERY
BACKGROUND
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for
pharmacological adjunctive treatment associated with glaucoma filtration
surgery. In
particular, the present invention relates to such compositions comprising
dissociated
glucocorticoid receptor agonists ("DIGRAs") and such methods for reducing the
risk of
poorly functioning filtering bleb following glaucoma filtration surgery.
Glaucoma is a group of diseases that are characterized by the death of retinal
ganglion cells ("RGCs"), specific visual field loss, and optic nerve atrophy.
Glaucoma is
the second leading cause of blindness worldwide. Although there are many
individuals
with high intraocular pressure ("IOP") who do not have glaucomatous loss of
vision, an
IOP that is high compared to the population mean is a risk factor for the
development of
glaucoma. Conversely, there are glaucoma patients with normal IOP (normal-
tension
glaucoma). Lowering IOP via pharmaceuticals or surgery is currently the
mainstay of
glaucoma treatment. Even in normal-tension glaucoma patients, it can
significantly
delay glaucomatous changes.
In a normal subject's eye, a fluid, known as the aqueous humor, circulates
freely through the anterior chamber of the eye. This fluid, which is
continuously
produced by the eye's ciliary body, is drained from the eye, through the
trabecular
meshwork, back into the bloodstream. When the fluid drains properly, an
appropriate
fluid pressure is maintained in the anterior chamber, maintaining the shape of
the cornea.
Elevated IOP develops when the filtration mechanism of the trabecular meshwork
is no
longer adequate, leading to an increase in fluid within the anterior chamber.
This
increase in fluid, in turn, leads to an increase in the IOP. It is this
increase in IOP that
subsequently causes pressure on the optic nerve at the level of the optic
nerve head. This
causes damage to the optic nerve, which, in turn, may lead to blindness.
Presently, glaucoma is not curable by any available treatment method.
However, a variety of different treatment options are available to control,
and, perhaps,
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
to slow, the progression of the disease. Possible treatment options include
pharmaceutical therapy, laser eye surgery, and/or conventional surgical
methods.
Although many different surgical techniques have been employed in the past,
glaucoma
filtration surgery (or also known as filtering surgery or trabeculectomy), is
principally
performed today for the surgical (i.e., non-laser) management of glaucoma.
Filtration surgery lowers the IOP by creating a fistula between the anterior
chamber and the subconjunctival space, creating a filtering bleb. The aqueous
humor
that percolates through the bleb can then either be absorbed through veins or
conjunctival
lymphatics or, in some cases where the conjunctiva is thin, pass directly into
the tear
film. A major determinant of glaucoma filtration surgery ("GFS") success is
the
conjunctival wound healing response, with excessive post-operative scarring
leading to
filtration failure.
The filtration surgery technique is designed to provide an alternative
pathway for the aqueous humor fluid to leave the eye. More specifically,
during
filtration surgery the filtering or conjunctival bleb is created which serves
as an auxiliary
"drain" on the outside of the eyeball, and which has direct communication to
the inside
of the eyeball. This alternate pathway has a lower resistance to fluid outflow
than that of
the failing, or irreversibly obstructed, trabecular meshwork found in the
glaucoma
patient. The desired result of this technique is to achieve a lower IOP that
is compatible
with normal optic nerve function.
Because the basic early events of GFS wound healing have not been well
described in humans, animal models have been used to delineate the initial
stages of
wound healing process. Despite a number of studies using animal models and
human
tissues, however, the early events of wound healing after GFS are still not
clearly
understood. In the context of general wound healing, observations in animal
models and
after GFS in humans suggest a sequence of events in GFS wound healing that
occur in
early bleb failure due to non- or poorly functioning bleb. Wound healing has
been
shown to involve an orderly series of events, including extracellular matrix
("ECM")
degradation, cell migration, matrix synthesis, and tissue remodeling. After
surgical
trauma to the conjunctiva, episclera, and iris, blood vessels constrict, and
leakage of
2
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
plasma proteins (including fibrinogen, fibronectin, and plasminogen) and blood
cells
occurs. Fibroblasts proliferate and migrate from the wound edges after GFS and
subsequently synthesize fibronectin, interstitial collagens, and
glycosaminoglycans to
form fibrovascular tissue, and later this tissue is remodeled to form a dense
collagenous
subconjunctival scar with scattered fibroblasts and blood vessels leading to
wound
scarring and filtration failure. Even if the surgery is initially successful,
scarring may
close the drainage channels at the bleb surface layers in the course of months
or years.
GFS differs from most surgical procedures in that inhibition of wound
healing (in the sense of excessive scarring tissue formation) is desirable to
achieve
surgical success. Successful filtration surgery is generally characterized by
formation of
a filtering bleb, which is a subconjunctival accumulation of the aqueous
humor.
Histopathological examinations of functioning blebs demonstrate the appearance
of
loosely arranged connective tissue beneath the conjunctival epithelium. Early
failed
blebs demonstrate abnormally thickened, dense collagenous connective tissue
beneath
the conjunctival epithelium. In contrast, late failing blebs are often thin,
and avascular.
Thus, the long-term maintenance of a well-functioning filtering bleb is
critical for the
success of the procedure.
Although administration of anti-scarring agents such as mitomycin-C
("MMC") and 5-fluorouracil ("5-FU"), during or after surgery, help prevent
postsurgical
scarring and improve glaucoma surgical outcome, they do so by causing
widespread
fibroblast cell death and apoptosis. A small fraction (on the order of a few
percent) of
the cases with postsurgical complication, manifested as late-onset bleb
leakage, is
associated with the use of antiscarring agents. See; e.g., D.S. Greenfield et
al., Arch.
Ophthalmol., Vol. 116, 443 (1998).
Glucocorticosteroids (also referred to herein as "corticosteroids" or "GCs")
have been administered postoperatively, topically and/or orally, to prevent
excessive
scarring and have shown beneficial effects in controlling the glaucomatous
condition.
S.V. Araujo et at., Ophthalmol., Vol. 102, 1753 (1995). GCs are known to have
antifibrotic action. A. Shukla et al., Wound Repair & Regen., Vol. 7, 133
(1999). For
3
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
example, dexamethasone was shown to block TGF-13 (transforming growth factor-
(3)-
induced collagen synthesis. C. Boxall et al., Eur. Respir. J., Vol. 27, 208
(2006).
However, steroidal drugs can have side effects that threaten the overall
health of the patient. Chronic administration of glucocorticoids can lead to
drug-induced
osteoporosis by suppressing intestinal calcium absorption and inhibiting bone
formation.
Other adverse side effects of chronic administration of glucocorticoids
include
hypertension, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia (increased levels of
triglycerides) and
hypercholesterolemia (increased levels of cholesterol) because of the effects
of these
drugs on the body metabolic processes.
In addition, it is known that certain glucocorticoids have a greater potential
for elevating IOP than other compounds in this class. For example, it is known
that
prednisolone, which is a very potent ocular anti-inflammatory agent, has a
greater
tendency to elevate IOP than fluorometholone, which has moderate ocular anti-
inflammatory activity. It is also known that the risk of IOP elevation
associated with the
topical ophthalmic use of glucocorticoids increases over time. In other words,
the
chronic (i.e., long-term) use of these agents increases the risk of
significant IOP
elevation. Therefore, the long-term use of GCs to improve the outcome of GFS
may
exacerbate the condition they are intended to treat.
Therefore, improved alternatives to current pharmacological therapy
adjunctive to GFS are needed.
SUMMARY
In general, the present invention provides compounds, compositions, and
methods for pharmacological adjunctive treatment associated with glaucoma
filtration
surgery.
In one aspect, the present invention provides compounds, compositions, and
methods for reducing the risk of non-functioning, poorly functioning, or
failing
glaucoma filtering bleb.
4
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
In another aspect, the present invention provides compounds, compositions,
and methods for ensuring a functioning filtering bleb after filtration surgery
to control or
prevent the progression of a glaucoma condition.
In still another aspect, such glaucoma condition is selected from the group
consisting of primary open-angle glaucoma, primary angle-closure glaucoma,
secondary
open-angle glaucoma, secondary angle-closure glaucoma, pigmentary glaucoma,
neovascular glaucoma, pseudophakic glaucoma, malignant glaucoma, uveitic
glaucoma,
glaucoma due to peripheral anterior synechia, and combinations thereof.
In yet another aspect, the present invention provides compounds,
compositions, and methods for controlling or preventing an increase in IOP or
adverse
effects thereof.
In yet another aspect, the compounds or compositions comprise at least a
mimetic of a glucocorticoid for controlling or preventing the progression of
such a
glaucoma condition.
In a further aspect, a compound or composition for controlling or preventing
the progression of such a glaucoma condition comprises at least a dissociated
glucocorticoid receptor agonist ("DIGRA"), a prodrug, a pharmaceutically
acceptable
salt thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable ester thereof.
In still another aspect, a composition of the present invention further
comprises an antagonist to TGF-(3. In one embodiment, such an antagonist to
TGF-(3
comprises an antibody to TGF-(3.
In yet another aspect, a composition of the present invention comprises a
topical formulation; injectable formulation; or implantable formulation,
system, or
device.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a method for
pharmacological adjunctive treatment associated with glaucoma filtration
surgery. The
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
method comprises administering a composition comprising at least a DIGRA, a
prodrug
thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a pharmaceutically
acceptable
ester thereof into a subject in need of such treatment.
Other features and advantages of the present invention will become apparent
from the appended figures and the following detailed description and claims.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FIGURES
Figures lA-IF show the effects of BOL-303242-X and dexamethasone on
the IL-I (3-stimulated production of 11-6, IL-7, TGF-a, TNF-a, VGEF, and MCP-
I in
human corneal epithelium cells ("HCECs") at p < 0.05.
Figure 2 shows the effects of BOL-303242-X and dexamethasone on the IL-
I (3-stimulated production of G-CSF in HCECs at p < 0.05.
Figures 3A-3C show the effects of BOL-303242-X and dexamethasone on
the IL-I(3-stimulated production of GM-CSF, 1L-8, and RANTES in HCECs at p <
0.05.
In these figures, "*" denotes comparison to control, and "**" to IL-1(3.
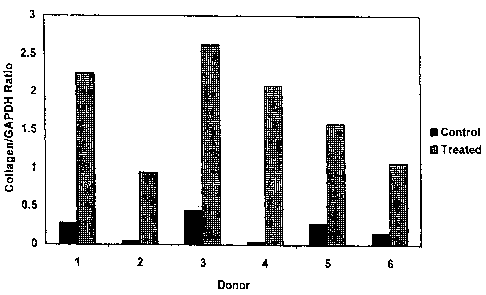
Figure 4 shows the effect of TGF-(3 treatment on collagen level produced by
human Tenon's fibroblasts.
Figure 5 shows the effect of TGF-0 treatment on level of a-smooth muscle
actin produced by human Tenon's fibroblasts.
Figure 6 shows the effect of TGF-(3 treatment on level of tissue
transglutaminase produced by human Tenon's fibroblasts.
Figure 7 shows the inhibitory effect of BOL-303242-X on the expression of
collagen by human Tenon's fibroblasts.
6
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Figure 8 shows the inhibitory effect of BOL-303242-X on the expression of
a-smooth muscle actin by human Tenon's fibroblasts.
Figure 9 shows the inhibitory effect of BOL-303242-X on the expression of
tisuue transglutaminase by human Tenon's fibroblasts.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
As used herein, the term "control" also includes reduction, amelioration, and
alleviation.
As used herein, the term "antagonist to TGF-(3" also includes compounds or
materials that inhibit or impede the activity, transcription, expression, or
signaling
cascade of one or more TGF-(3 isoforms. The term "antagonist to TGF-(3" also
includes a
prodrug, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, hydrate, or ester thereof.
As used herein, a dissociated glucocorticoid receptor agonist ("DIGRA") is a
compound that is capable of binding to the glucocorticoid receptor (which is a
polypeptide) and, upon binding, is capable of producing differentiated levels
of
transrepression and transactivation of gene expression. A compound that binds
to a
polypeptide is sometimes herein referred to as a ligand.
As used herein, the term "alkyl" or "alkyl group" means a linear- or
branched-chain saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon monovalent group, which may be
unsubstituted or substituted. The group may be partially or completely
substituted with
halogen atoms (F, Cl, Br, or I). Non-limiting examples of alkyl groups include
methyl,
ethyl, n-propyl, 1-methylethyl(isopropyl), n-butyl, n-pentyl, l ,1-
dimethylethyl (t-butyl),
and the like. It may be abbreviated as "Alk".
As used herein, the term "alkenyl" or "alkenyl group" means a linear- or
branched-chain aliphatic hydrocarbon monovalent radical containing at least
one carbon-
carbon double bond. This term is exemplified by groups such as ethenyl,
propenyl, n-
7
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
butenyl, isobutenyl, 3-methylbut-2-enyl, n-pentenyl, heptenyl, octenyl,
decenyl, and the
like.
As used herein, the term "alkynyl" or "alkynyl group" means a linear- or
branched-chain aliphatic hydrocarbon monovalent radical containing at least
one carbon-
carbon triple bond. This term is exemplified by groups such as ethynyl,
propynyl, n-
butynyl, 2-butynyl, 3-methylbutynyl, n-pentynyl, heptynyl, octynyl, decynyl,
and the
like.
As used herein, the term "alkylene" or "alkylene group" means a linear- or
branched-chain saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon divalent radical having the
specified
number of carbon atoms. This term is exemplified by groups such as methylene,
ethylene, propylene, n-butylene, and the like, and may alternatively and
equivalently be
denoted herein as "-(alkyl)-".
The term "alkenylene" or "alkenylene group" means a linear- or branched-
chain aliphatic hydrocarbon divalent radical having the specified number of
carbon
atoms and at least one carbon-carbon double bond. This term is exemplified by
groups
such as ethenylene, propenylene, n-butenylene, and the like, and may
alternatively and
equivalently be denoted herein as "-(alkylenyl)-".
The term "alkynylene" or "alkynylene group" means a linear- or branched-
chain aliphatic hydrocarbon divalent radical containing at least one carbon-
carbon triple
bond. This term is exemplified by groups such as ethynylene, propynylene, n-
butynylene, 2-butynylene, 3-methylbutynylene, n-pentynylene, heptynylene,
octynylene,
decynylene, and the like, and may alternatively and equivalently be denoted
herein as "-
(alkynyl)-".
As used herein, the term "aryl" or "aryl group" means an aromatic
carbocyclic monovalent or divalent radical of from 5 to 14 carbon atoms having
a single
ring (e.g., phenyl or phenylene), multiple condensed rings (e.g., naphthyl or
anthranyl),
or multiple bridged rings (e.g., biphenyl). Unless otherwise specified, the
aryl ring may
be attached at any suitable carbon atom which results in a stable structure
and, if
8
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
substituted, may be substituted at any suitable carbon atom which results in a
stable
structure. Non-limiting examples of aryl groups include phenyl, naphthyl,
anthryl,
phenanthryl, indanyl, indenyl, biphenyl, and the like. It may be abbreviated
as "Ar".
The term "heteroaryl" or "heteroaryl group" means a stable aromatic 5- to
14-membered, monocyclic or polycyclic monovalent or divalent radical, which
may
comprise one or more fused or bridged ring(s), preferably a 5- to 7-membered
monocyclic or 7- to 10-membered bicyclic radical, having from one to four
heteroatoms
in the ring(s) independently selected from nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur,
wherein any
sulfur heteroatoms may optionally be oxidized and any nitrogen heteroatom may
optionally be oxidized or be quaternized. Unless otherwise specified, the
heteroaryl ring
may be attached at any suitable heteroatom or carbon atom which results in a
stable
structure and, if substituted, may be substituted at any suitable heteroatom
or carbon
atom which results in a stable structure. Non-limiting examples of heteroaryls
include
furanyl, thienyl, pyrrolyl, oxazolyl, thiazolyl, imidazolyl, pyrazolyl,
isoxazolyl,
isothiazolyl, oxadiazolyl, triazolyl, tetrazolyl, thiadiazolyl, pyridinyl,
pyridazinyl,
pyrimidinyl, pyrazinyl, triazinyl, indolizinyl, azaindolizinyl, indolyl,
azaindolyl,
diazaindolyl, dihydroindolyl, dihydroazaindoyl, isoindolyl, azaisoindolyl,
benzofuranyl,
furanopyridinyl, furanopyrimidinyl, furanopyrazinyl, furanopyridazinyl,
dihydrobenzofuranyl, dihydrofuranopyridinyl, dihydrofuranopyrimidinyl,
benzothienyl,
thienopyridinyl, thienopyrimidinyl, thienopyrazinyl, thienopyridazinyl,
dihydrobenzothienyl, dihydrothienopyridinyl, dihydrothienopyrimidinyl,
indazolyl,
azaindazolyl, diazaindazolyl, benzimidazolyl, imidazopyridinyl, benzthiazolyl,
thiazolopyridinyl, thiazolopyrimidinyl, benzoxazolyl, benzoxazinyl,
benzoxazinonyl,
oxazolopyridinyl, oxazolopyrimidinyl, benzisoxazolyl, purinyl, chromanyl,
azachromanyl, quinolizinyl, quinolinyl, dihydroquinolinyl,
tetrahydroquinolinyl,
isoquinolinyl, dihydroisoquinolinyl, tetrahydroisoquinolinyl, cinnolinyl,
azacinnolinyl,
phthalazinyl, azaphthalazinyl, quinazolinyl, azaquinazolinyl, quinoxalinyl,
azaquinoxalinyl, naphthyridinyl, dihydronaphthyridinyl,
tetrahydronaphthyridinyl,
pteridinyl, carbazolyl, acridinyl, phenazinyl, phenothiazinyl, and
phenoxazinyl, and the
like.
9
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
The term "heterocycle", "heterocycle group", "heterocyclyl", "heterocyclyl
group", "heterocyclic", or "heterocyclic group" means a stable non-aromatic 5-
to 14-
membered monocyclic or polycyclic, monovalent or divalent, ring which may
comprise
one or more fused or bridged ring(s), preferably a 5- to 7-membered monocyclic
or 7- to
10-membered bicyclic ring, having from one to three heteroatoms in at least
one ring
independently selected from nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur, wherein any sulfur
heteroatoms may optionally be oxidized and any nitrogen heteroatom may
optionally be
oxidized or be quaternized. As used herein, a heterocyclyl group excludes
heterocycloalkyl, heterocycloalkenyl, and heterocycloalkynyl groups. Unless
otherwise
specified, the heterocyclyl ring may be attached at any suitable heteroatom or
carbon
atom which results in a stable structure and, if substituted, may be
substituted at any
suitable heteroatom or carbon atom which results in a stable structure. Non-
limiting
examples of heterocycles include pyrrolinyl, pyrrolidinyl, pyrazolinyt,
pyrazolidinyl,
piperidinyl, morpholinyl, thiomorpholinyl, piperazinyl, tetrahydropyranyl,
tetrahydrothiopyranyl, tetrahydrofuranyl, hexahydropyrimidinyl,
hexahydropyridazinyl,
and the like.
The term "cycloalkyl" or "cycloalkyl group" means a stable aliphatic
saturated 3- to 15-membered monocyclic or polycyclic monovalent radical
consisting
solely of carbon and hydrogen atoms which may comprise one or more fused or
bridged
ring(s), preferably a 5- to 7-membered monocyclic or 7- to 10-membered
bicyclic ring.
Unless otherwise specified, the cycloalkyl ring may be attached at any carbon
atom
which results in a stable structure and, if substituted, may be substituted at
any suitable
carbon atom which results in a stable structure. Exemplary cycloalkyl groups
include
cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, cycloheptyl, cyclooctyl,
cyclononyl,
cyclodecyl, norbornyl, adamantyl, tetrahydronaphthyl (tetralin), 1-decalinyl,
bicyclo[2.2.2]octanyl, 1-methylcyclopropyl, 2-methylcyclopentyl, 2-
methylcyclooctyl,
and the like.
The term "cycloalkenyl" or "cycloalkenyl group" means a stable aliphatic 5-
to 15-membered monocyclic or polycyclic monovalent radical having at least one
carbon-carbon double bond and consisting solely of carbon and hydrogen atoms
which
may comprise one or more fused or bridged ring(s), preferably a 5- to 7-
membered
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
monocyclic or 7- to 10-membered bicyclic ring. Unless otherwise specified, the
cycloalkenyl ring may be attached at any carbon atom which results in a stable
structure
and, if substituted, may be substituted at any suitable carbon atom which
results in a
stable structure. Exemplary cycloalkenyl groups include cyclopentenyl,
cyclohexenyl,
cycloheptenyl, cyclooctenyl, cyclononenyl, cyclodecenyl, norbornenyl, 2-
methylcyclopentenyl, 2-methylcyclooctenyl, and the like.
The term "cycloalkynyl" or "cycloalkynyl group" means a stable aliphatic 8-
to 15-membered monocyclic or polycyclic monovalent radical having at least one
carbon-carbon triple bond and consisting solely of carbon and hydrogen atoms
which
may comprise one or more fused or bridged ring(s), preferably a 8- to 10-
membered
monocyclic or 12- to 15-membered bicyclic ring. Unless otherwise specified,
the
cycloalkynyl ring may be attached at any carbon atom which results in a stable
structure
and, if substituted, may be substituted at any suitable carbon atom which
results in a
stable structure. Exemplary cycloalkynyl groups include cyclooctynyl,
cyclononynyl,
cyclodecynyl, 2-methylcyclooctynyl, and the like.
The term "carbocycle" or "carbocyclic group" means a stable aliphatic 3- to
15-membered monocyclic or polycyclic monovalent or divalent radical consisting
solely
of carbon and hydrogen atoms which may comprise one or more fused or bridged
rings,
preferably a 5- to 7-membered monocyclic or 7- to 10-membered bicyclic ring.
Unless
otherwise specified, the carbocycle may be attached at any carbon atom which
results in
a stable structure and, if substituted, may be substituted at any suitable
carbon atom
which results in a stable structure. The term comprises cycloalkyl (including
Spiro
cycloalkyl), cycloalkylene, cycloalkenyl, cycloalkenylene, cycloalkynyl, and
cycloalkynylene, and the like.
The terms "heterocycloalkyl", "heterocycloalkenyl", and
"heterocycloalkynyl" mean cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, and cycloalkynyl group,
respectively, having at least a heteroatom in at least one ring, respectively.
Glucocorticoids ("GCs") are among the most potent drugs used for the
treatment of many diseases, including allergic and chronic inflammatory
diseases or of
11
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
inflammation resulting from infections. However, as mentioned above, long-term
treatment with GCs is often associated with numerous adverse side effects,
such as
diabetes, osteoporosis, hypertension, glaucoma, or cataract. These side
effects, like other
physiological manifestations, are results of aberrant expression of genes
responsible for
such diseases. Research in the last decade has provided important insights
into the
molecular basis of GC-mediated actions on the expression of GC-responsive
genes. GCs
exert most of their genomic effects by binding to the cytoplasmic GC receptor
("GR").
The binding of GC to GR induces the translocation of the GC-GR complex to the
cell
nucleus where it modulates gene transcription either by a positive
(transactivation) or
negative (transrepression) mode of regulation. There has been growing evidence
that
both beneficial and undesirable effects of GC treatment are the results of
undifferentiated
levels of expression of these two mechanisms; in other words, they proceed at
similar
levels of effectiveness.
GCs markedly affect most aspects of wound healing. When administered
sufficiently early after injury, high GC levels delay the appearance of
inflammatory cells,
fibroblasts, the deposition of ground substance, collagen, regenerating
capillaries, tissue
contraction, and epithelial cell migration through effecting a reduction of
TGF-f3 and
IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor-1) production in wounds and a reduction of
collagen
deposition therein. C. Wicke et al., Arch. Surg., Vol. 135, 1265 (2000).
Dexamethasone
can significantly inhibit human Tenon's capsule fibroblasts growth in cell
cultures.
These cells are a source of collagen production and deposition in the wound
repair
process. R. Sun et al., Ophthalmic Surg. Laser, Vol. 30, 382 (1999). It was
also
demonstrated that GC treatment of rat skin fibroblasts decreased the binding
of GC
receptor ("GCR") to the GC response element ("GRE") and of TGF-(3 activator
protein
to the TGF-(3 response element of the type-I procollagen genes proa 1(I) and
proa2(I).
Thus, GCs coordinately regulate procollagen gene expression through both the
GRE and
TGF-P response element. N. Meister et al., J. Cell. Biochem., Vol. 59, 376
(1995); K.R.
Cutroneo et al., J. Cell. Biochem., Vol. 92, 6 (2004). Moreover, GCs can down-
regulate
the expression of TGF-(31, TGF-02, and TGF-(33 isoforms in hepatic stellate
cells, and
thus the TGF-P signaling pathway. U. Bolkenius et al., Biochem. Biophys. Res.
Comm.,
Vol. 325, 1264 (2004). Since TGF-(3 isoforms are expressed and secreted from a
wide
variety of cells, GCs can have the same effect in cells other than hepatic
stellate cells as
12
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
well. The present invention provides GC mimetics, compositions comprising the
same,
and methods of using the same to achieve such effects of GCs without or with
lower
levels of undesired side effects mentioned above.
Studies have demonstrated that peptide growth factors and their receptors are
key modulators of the wound healing process, participating in a well
coordinated process
that involves inflammation, cell proliferation, matrix deposition, and tissue
remodeling.
One of the most important modulators of wound repair is the family of TGF-(3
isoforms,
which are found in large amounts in, and upon degranulation released from,
platelets.
Furthermore, they are produced by several cell types that are present in
wounds, including
activated macrophages, neutrophils, eosinophils, and fibroblasts. TGF-(3s,
acting in an
autocrine manner, regulate fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis
during wound
repair. TGF-01, TGF-(32, and TGF-03 have been found in various parts of the
anterior
segment of the human eye. L.R. Pasquale et al., Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci.,
Vol. 34, No.
1, 23 (1993). TGF-(32 has been found at an increased level in the aqueous
humor of
patients suffering from primary open angle glaucoma ("POAG"). R.C. Tripathi et
al., Exp.
Eye Res., Vol. 59, 723 (1994). In one aspect, the present invention provides a
composition
comprising an antagonist to one or more TGF-(3s, and a method of using such a
composition to reduce the risk of having a non- or poorly functioning
filtering bleb
following GFS. In another aspect, the present invention provides a composition
comprising a material that controls, reduces the levels, or reduces or
inhibits the activity of
one or more TGF-(3s.
In still another aspect, the present invention provides a composition
comprising a DIGRA or pharmaceutically acceptable derivative thereof (such as
a
pharmaceutically acceptable prodrug, salt, or ester thereof) that can control,
reduce, or
inhibit the production of at least a cytokine, chemokine or other factor that
can stimulate
fibroblasts and/or immune cells to produce TGF-(3.
Immediately after wounding, such as a result of GFS, TGF-(3l is released in
large amounts from platelets. This initial burst of active TGF-(31 serves as a
chemoattractant for neutrophils, macrophages, and fibroblasts. As well as
active forms,
latent TGF-13s are also produced and sequestered within the wound matrix, and
then
13
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
released in active form over a longer period of time by proteolytic enzymes.
Cells of the
injured tissue synthesize and release macrophage chemoattractant protein-I
("MCP-I"),
which recruits macrophages, neutrophils, T cells, and mast cells during wound
healing.
These cells then produce additional TGF-0 as the body attempts to accelerate
wound
healing. S.N. Iyer et at., J. Pharmacol. & Expt'l Therapeutics, Vol. 291, No.
1, 367
(1999). Thus, MCP-1 indirectly up-regulates matrix deposition in this process.
MCP-1
knock-out mice have significantly delayed wound reepithelization and
angiogenesis, and
collagen synthesis. S. Werner and R. Grose, Physiol. Rev., Vol. 83, 835
(2003).
Polymorphonuclear leukocytes and activated macrophages also produce an
increased
amount of various pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1(3, IL-6, and TNF-a,
which
play an important role in fibroblast proliferation and matrix deposition. For
example,
TNF-a and IL-1(3 (along with TGF-(31 and TGF-32) can stimulate the
proliferation of
human Tenon's capsule fibroblasts. I.A. Cunliffe et al., Br. J. Ophthalmol.,
Vol. 79, 590
(1995); P.O. Denk et at., Curr. Eye Res., Vol. 27, No.1, 35 (2003); S.C.
Thornton et al.,
J. Leukocyte Biol., Vol. 47, 312 (1990). TNF-a and IL-I are also produced by
fibroblasts, and thus, further accelerate matrix deposition and produce the
undesired
scarring aspect of post-surgical wound healing. IL-6 has been shown to be
another
important factor in initiating wound healing and a chemoattractant for
neutrophils. The
expression of IL-6 is prolonged in adult wounds and excessive levels of this
cytokine
have been associated with scarring. S. Werner and R. Grose, supra. Granulocyte-
macrophage colony-stimulating factor ("GM-CSF"), a cytokine also acting as a
growth
factor, can prolong the survival of eosinophils and promote the activation of
eosinophils,
which, in turn, produce TGF-(3s. Thus, a high level of GM-CSF indirectly
accelerates
the matrix deposition process through increasing the availability of TGF-ps.
Other
cytokines or chemokines that also promote fibroblast proliferation and
collagen
deposition, at least in the context of airway fibrosis and remodeling, include
IL-4, IL-9,
IL-1 l , IL- 13, IL- 17, TGF-a, PDGF, and 0-FGF (fibroblast growth factor).
L.C. Borish
and J.W. Steinke, J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., Vol. 111, No. 2, S460 (2003).
Thus, in one aspect, the present invention provides a method for reducing the
risk of having a non- or poorly functioning filtering bleb following GFS,
which method
comprises administering to a subject that has undergone said GFS a composition
that
14
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
comprises a material that reduces or suppresses the production of chemokines
or
cytokines that can stimulate the production of TGF-(3s.
In another aspect, such chemokines or cytokines are selected from the group
consisting of IL- I (3, IL-6, TNF-a, MCP-1, GM-CSF, and combinations thereof.
In still another aspect, the present invention provides a method for reducing
the risk of having a non- or poorly functioning filtering bleb following GFS,
which
method comprises administering to a subject that has undergone said GFS a
composition
that comprises a material that reduces or suppresses the production of
chemokines or
cytokines that can promote fibrosis or collagen deposition, said chemokines or
cytokines
being selected from the group consisting of IL-1(3, IL-4, IL-6, IL-9, IL-11,
IL- 13, IL- 17,
TNF-a, TGF-a, MCP- 1, GM-CSF, PDGF (platelet derived growth factor), 0-FGF,
CTGF
(connective tissue growth factor), and combinations thereof.
In general, the present invention provides compounds, compositions, and
methods for pharmacological adjunctive treatment associated with glaucoma
filtration
surgery.
In one aspect, the present invention provides compounds, compositions, and
methods for reducing the risk of non-functioning, poorly functioning, or
failing
glaucoma filtering bleb. As used herein, the term "non-functioning, poorly
functioning,
or failing filtering bleb" means a filtering bleb that does not provide
adequate control of
IOP after GFS for bringing such IOP to a normal or near normal level.
In another aspect, the present invention provides compounds, compositions,
and methods for ensuring a functioning filtering bleb after filtration surgery
to control or
prevent the progression of a glaucoma condition.
In still another aspect, such glaucoma condition is selected from the group
consisting of primary open-angle glaucoma, primary angle-closure glaucoma,
secondary
open-angle glaucoma, secondary angle-closure glaucoma, pigmentary glaucoma,
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
neovascular glaucoma, pseudophakic glaucoma, malignant glaucoma, uveitic
glaucoma,
glaucoma due to peripheral anterior synechia, and combinations thereof.
In yet another aspect, the present invention provides compounds,
compositions, and methods for controlling or preventing an increase in IOP or
adverse
effects thereof.
In yet another aspect, the compounds or compositions comprise at least a
mimetic of a glucocorticoid for controlling or preventing the progression of
such a
glaucoma condition. As used herein, a mimetic of a glucocorticoid is or
comprises a
compound that exhibits or produces a beneficial physiological effect similar
to a
glucocorticoid.
In a further aspect, a compound or composition for controlling or preventing
the progression of such a glaucoma condition comprises at least a dissociated
glucocorticoid receptor agonist ("DIGRA"), a prodrug, a pharmaceutically
acceptable
salt thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable ester thereof.
In still another aspect, a composition of the present invention further
comprises an antagonist to TGF-(3. In one embodiment, such an antagonist to
TGF-(3
comprises an antibody to TGF-(3.
Non-limiting examples of antibodies to TGF-(3 include the compounds
disclosed in M.F. Cordeiro, Clin. Sci., Vol. 104, 181 (2003) or A.L. Meade et
at., Invest.
Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci., Vol. 44, 3394 (2003). Other antibodies to TGF-13 are
available,
for example, from Abcam, Inc., Cambridge, Massachusetts.
In one aspect, such an antibody to TGF-(3 is produced by the well-known
recombinant technique.
In another aspect, such an antibody comprises a humanized antibody. In still
another aspect, such a humanized antibody comprises Fv domains of murine anti-
TGF-(3
monoclonal antibody and Fc domains of a human immunoglobulin molecule. In
still
16
CA 02699599 2012-02-07
another aspect, such a humanized antibody comprises CDRs (complementary
determining regions) from the heavy- and light-chain variable domains of
murine
monoclonal anti-TGF-f antibody grafted into the appropriate framework regions
of
human variable domains and Fc domains of a human immunoglobulin molecule.
Processes for humanization of non-human antibodies are known, such as that
disclosed
by S.L. Morrison et al., PNAS, Vol. 81, 6851 (1984). In addition, human
immunoglobulin transgenic mice provide an alternative technique for generation
of
monoclonal antibodies that are well tolerated in human. See; e.g., D.M.
Fishwild et al.,
Nat. Biotech., Vol. 14, 845 (1996). Still another method for obtaining
humanized murine
monoclonal antibodies is disclosed in U.S. Patent 7,087,409 .
In still another aspect, the antagonist to at least one TGF-13 isoform
comprises a soluble extracellular domain of a TGF receptor type I or II
("sTGFRI" or
"sTGFRII" ). Such sTGFRI or sTGFRII can bind to TGF-R isoforms and prevent
them
from initiating a TGF-¾ signaling cascade that upregulates the expression of
gene under
its control, such as the proa1(I) and proa2(I) genes.
In yet another aspect, the antagonist to at least one TGF-(3 isoform comprises
a compound known as SB-431542, which is a TGF-Q I inhibitor. SB-431542 has a
formula shown below and is available from Sigma Aldrich.
0 \ I \ / \ 0
\ N NHZ
H
N
SB-431542
In a further aspect, the antagonist to at least one TGF-1i isoform comprises
an
anti-TGF-R2 antisense oligonucleotide known as AP 12009, which was developed
by
Antisense Pharma GmBH, Regensburg, Germany.
17
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
In yet another aspect, the antagonist to at least one TGF-(3 isoform comprises
prolactin. See European Patent Application EP 0921809. Prolactin also has been
shown
to inhibit the chemotaxis of fibroblasts. Such inhibition would be
advantageous in
preventing excessive tissue scarring after GFS.
In still another aspect, a composition of the present invention comprises: (a)
a DIGRA, a prodrug thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a
pharmaceutically acceptable ester thereof; (b) an antagonist to at least one
of TGF-(31
and TGF-02; and (c) a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug ("NSAID") other
than said
DIGRA, said prodrug thereof, said pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof,
and said
pharmaceutically acceptable ester thereof. Non-limiting examples of such
NSAIDs are
disclosed herein below.
In still another aspect, said at least a DIGRA has Formula I.
R~ R2 R3
/D~ (I)
A B Q
E
wherein A and Q are independently selected from the group consisting of
unsubstituted
and substituted aryl and heteroaryl groups, unsubstituted and substituted
cycloalkyl and
heterocycloalkyl groups, unsubstituted and substituted cycloalkenyl and
heterocycloalkenyl groups, unsubstituted and substituted cycloalkynyl and
heterocycloalkynyl groups, and unsubstituted and substituted heterocyclic
groups; R' and
R1) are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen,
unsubstituted C1-
C15 (alternatively, C1-C1o, orC1-C5, or C1-C3) linear or branched alkyl
groups, substituted
C1-C15 (alternatively, C1-Clo, or C1-C5, or C1-C3) linear or branched alkyl
groups,
unsubstituted C3-C15 cycloalkyl groups, and substituted C3-C15 (alternatively,
C3-C6, or
C3-C5) cycloalkyl groups; R3 is selected from the group consisting of
hydrogen,
unsubstituted C1-C15 (alternatively, C1-Clo, orC1-C5, or C1-C3) linear or
branched alkyl
groups, substituted C1-C15 (alternatively, C1-Clo, orC1-C5, or C1-C3) linear
or branched
alkyl groups, unsubstituted C3-C15 (alternatively, C3-C6, orC3-C5) cycloalkyl
and
heterocycloalkyl groups, substituted C3-C15 (alternatively, C3-C6, orC3-C5)
cycloalkyl
18
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
and heterocycloalkyl groups, aryl groups, heteroaryl groups, and
heterocyclylic groups;
B comprises a carbonyl, amino, divalent hydrocarbon, or heterohydrocarbon
group; E is
hydroxy or amino group; and D is absent or comprises a carbonyl group, -NH-,
or-NR'-
, wherein R' comprises an unsubstituted or substituted C1-C15 (alternatively,
C1-C10, or
C1-C5, or C1-C3) linear or branched alkyl group; and wherein R' and R2
together may
form an unsubstituted or substituted C3-C15 cycloalkyl group.
In one embodiment, B can comprise one or more unsaturated carbon-carbon
bonds.
In another embodiment, B can comprise an alkylenecarbonyl,
alkyleneoxycarbonyl, alkylenecarbonyloxy, alkyleneoxycarbonylamino,
alkyleneamino,
alkenylenecarbonyl, alkenyleneoxycarbonyl, alkenylenecarbonyloxy,
alkenyleneoxycarbonylamino, alkenyleneamino, alkynylenecarbonyl,
alkynyleneoxycarbonyl, alkynylenecarbonyloxy, alkynyleneoxycarbonylamino,
alkynyleneamino, arylcarbonyloxy, aryloxycarbonyl, or ureido group.
In still another embodiment, A and Q are independently selected from the
group consisting of aryl and heteroaryl groups substituted with at least a
halogen atom,
cyano group, hydroxy group, or C1-C10 alkoxy group (alternatively, C1-C5
alkoxy group,
or C1-C3 alkoxy group); R', R2, and R3 are independently selected from the
group
consisting of unsubstituted and substituted C1-C5 alkyl groups (preferably, C1-
C3 alkyl
groups); B is a C1-C5 alkylene group (alternatively, C1-C3 alkyl groups); D is
the -NH-
or -NR'- group, wherein R' is a C1-C5 alkyl group (preferably, C1-C3 alkyl
group); and E
is the hydroxy group.
In yet another embodiment, A comprises a dihydrobenzofuranyl group
substituted with a halogen atom; Q comprises a quinolinyl or isoquinolinyl
group
substituted with a C1-C10 alkyl group; R' and R2 are independently selected
from the
group consisting of unsubstituted and substituted C1-C5 alkyl groups
(preferably, C1-C3
alkyl groups); B is a C1-C3 alkylene group; D is the -NH- group; E is the
hydroxy group;
and R3 comprises a completely halogenated C1-C10 alkyl group (preferably,
completely
19
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
halogenated C1-C5 alkyl group; more preferably, completely halogenated C1-C3
alkyl
group).
In still another embodiment, A comprises a dihydrobenzofuranyl group
substituted with a fluorine atom; Q comprises a quinolinyl or isoquinolinyl
group
substituted with a methyl group; R1 and R2 are independently selected from the
group
consisting of unsubstituted and substituted C1-C5 alkyl groups; B is a C1-C3
alkylene
group; D is the -NH- group; E is the hydroxy group; and R3 comprises a
trifluoromethyl
group.
In a further embodiment, said at least a DIGRA has Formula II or III.
R4
O
H3C CH3 CF3 11
N N (II)
HO
R5
F
R4
O
H3C CH3 CF3
H
N ~ (III)
HO
R5
wherein R4 and R5 are independently selected from the group consisting of
hydrogen,
halogen, cyano, hydroxy, C1-C10 (alternatively, C1-C5 or CI-C3) alkoxy groups,
unsubstituted C1-Clo (alternatively, C1-C5 or C1-C3) linear or branched alkyl
groups,
substituted C1-C10 (alternatively, C1-C5 or C1-C3) linear or branched alkyl
groups,
CA 02699599 2012-02-07
unsubstituted C3-Cio (alternatively, C3-C6 or C3-C5) cyclic alkyl groups, and
substituted
C3-C10 (alternatively, C3-C6 or C3-C5) cyclic alkyl groups.
In still another embodiment, said at least a DIGRA has Formula IV.
CH3
CF3 I
H3C C'H3
\ N \ N (IV)
HO
F
Methods for preparing compounds of Formula 1, II, III, or IV are disclosed,
for example, in U.S. Patents 6,897,224; 6,903,215; 6,960,581
Still other methods for preparing such compounds
also can be found in U.S. Patent Application Publication 2006/0 1 1 6396,
or PCT Patent Application WO 2006/050998 Al.
Non-limiting examples of compounds having Formula I include 5-[4-(5-
fluoro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethyl-
pentyl amino]-2-methylquinoline, 5-[4-(5-fluoro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-
hydroxy-
4-methyl-2-trifluoromethyl-pentylamino]-1-methylisoquinoline, 5-[4-(5-fluoro-
2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethyl-pentylamino]
isoquinol-
](2H)-one, 5-[4-(5-fluoro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethyl-pentylamino]-2,6-dimethylquinoline, 5-[4-(5-fluoro-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-y l)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethyl-pentyl amino] -6-
ch loro-
2-methylquinoline, 5-[4-(5-fluoro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-
trifluoromethyl-pentylamino]isoquinoline, 5-[4-(5-fluoro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-
7-yl)-2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethyl-pentylamino]quinoline, 5-[4-(2,3-dihydro-5-
fluoro-
7-benzofuranyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethyl-pentylamino]quinolin-2[ 1
H]-
one, 6-fluro-5-[4-(5-fluoro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethyl-pentylamino]-2-methylquinoline, 8-fluoro-,5-[4-(5-fluoro-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydrox y-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethyl-pentylamino]-2-
21
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
methylquinoline, 5-[4-(5-fluoro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-
2-
trifl uoromethyl-pentylamino] -2-methylisoquinol-1-[2h]-one, and enantiomers
thereof.
In yet another embodiment, said at least a DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl group optionally independently substituted with one to three
substituent groups, which are independently selected from the group consisting
of C1-C5
alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C1-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl,
heterocyclyl, aryl,
heteroaryl, CI-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl,
CI-C5
alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl,
dialkylaminocarbonyl,
aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy,
CI-
C5 alkanoylamino, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, CI-C5 alkylsulfonyl amino,
aminosulfonyl, CI-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen,
hydroxy,
carboxy, cyano, trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the
nitrogen
atom is optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by Ci-C5 alkyl or
aryl, ureido
wherein either nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with CI-
C5 alkyl,
CI-C5 alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide
or sulfone;
(b) R' and R2 are each independently hydrogen or CI-C5 alkyl;
(c) R3 is the trifluoromethyl group;
(d) B is C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, or C2-C5 alkynyl, each optionally
independently substituted with one to three substituent groups, wherein each
substituent
group of B is independently CI-C3 alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, amino, or oxo;
(e) D is absent;
(f) E is the hydroxy group; and
(g) Q is an azaindolyl group optionally independently substituted with one to
three substituent groups, wherein each substituent group of Q is independently
C1-C5
alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-Cs cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl,
heteroaryl, CI-
C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5
alkoxycarbonyl,
22
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
CI-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl,
aminocarbonyloxy, Ci-Cs alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C.5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy,
C1-
C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino,
aminosulfonyl, C,-Cs alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaminosulfonyl, halogen,
hydroxy, carboxy, cyano, trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy,
trifluoromethylthio, nitro, or
amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally independently mono- or di-
substituted by
CI-C5 alkyl, ureido wherein either nitrogen atom is optionally independently
substituted
with C1-C5 alkyl, CI-C5 alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally
oxidized to a
sulfoxide or sulfone, wherein each substituent group of Q is optionally
independently
substituted with one to three substituent groups selected from the group
consisting of C1-
C3 alkyl, CI-C3 alkoxy, halogen, hydroxy, oxo, cyan, amino, and
trifluoromethyl.
Non-limiting examples of these compounds include 1, 1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-
fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(1H-pyrrolo[2,3-c] pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)pentan-2-
ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(1 H-pyrrolo[3,2-
c] pyridin-
2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-methyl-4-phenyl-2-(I H-pyrrolo[2,3-
c]pyridin-
2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-(4-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-
methyl-2-(I H-
pyrrolo[2,3-c] pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-methyl-4-
phenyl-2-(IH-
pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(4-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(1H-pyrrolo[3,2-c) pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 5-
fluoro-2-[4,4,4-trifluoro-3-hydroxy-1,1-dimethyl-3-(1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-
2-
ylmethyl)butyl] phenol; 4-fluoro-2-[4,4,4-trifluoro-3-hydroxy-1,1-dimethyl-3-
(1 H-
pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)butyl]phenol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(IH-pyrrolo[3,2-c] pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol;
1,1,1-
trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(3-methyl-I H-pyrrolo[2,3-
c]pyridin-
2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; and 4-fluoro-2-[4,4,4-trifluoro-3-hydroxy-1,1-dimethyl-
3-(1 H-
pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)butyl]phenol.
In still another embodiment, said at least a DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl or heteroaryl group, each optionally independently
substituted
with one to three substituent groups, which are independently selected from
the group
consisting of C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, CI-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8
23
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-
C5
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, CI-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, Cl-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, C1-CS
alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by Ci-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl, CI-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R' and R2 are each independently hydrogen or C I -C5 alkyl, or R' and R2
together with the carbon atom they are commonly attached to form a C3-C8 Spiro
cycloalkyl ring;
(c) B is the methylene or carbonyl group;
(d) R3 is a carbocycle, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle-C1-C8
alkyl,
aryl-C1-C5 alkyl, aryl-C,-Cs haloalkyl, heterocyclyl-Cl-C8 alkyl, heteroaryl-
Ci-C8 alkyl,
carbocycle-C2-C8 alkenyl, aryl-C2-C8 alkenyl, heterocyclyl-C2-C8 alkenyl, or
heteroaryl-
C2-C8 alkenyl, each optionally independently substituted with one to three
substituent
groups;
(e) D is the -NH- group;
(f) E is the hydroxy group; and
(g) Q comprises a methylated benzoxazinone.
Non-limiting examples of these compounds include 2-benzyl-4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid(4-methyl-I-oxo-1H-
benzo[d][1,2]oxazin-6-yl)amide; 2-benzyl-4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-
methylpentanoic acid(4-methyl-I-oxo-lH-benzo[d][1,2]oxazin-6-yl)amide; 2-
24
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
cyclohexylmethyl-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic
acid(4-
methyl-l-oxo-IH-benzo[d][1,2]oxazin-6-yl)amide; 2-cyclohexylmethyl-4-(5-fluoro-
2-
hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid(4-methyl- I -oxo- I H-
benzo[d] [ 1,2]oxazin-6-yl)amide; 2-benzyl-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-4-
methylpentanoic
acid(4-methyl-l-oxo-IH-benzo[d][I,2]oxazin-6-yl)amide; and 2-cyclohexylmethyl-
2-
hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid(4-methyl- l-oxo- I H-benzo[d] [ I ,2]oxazin-6-
yl)amide.
In still another embodiment, said at least a DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl or heteroaryl group, each optionally independently
substituted
with one to three substituent groups, which are independently selected from
the group
consisting of Ci-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, CI-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-
C5
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, Ci-C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1 -C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C,-C5 alkanoylamino, Cs-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, C1-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by Ci-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with Ci-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R' and R2 are each independently hydrogen or Ci-C5 alkyl, or R1 and R2
together with the carbon atom they are commonly attached to form a C3-C8 spiro
cycloalkyl ring;
(c) R3 is the trifluoromethyl group;
(d) B is C,-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, or C2-C5 alkynyl, each optionally
independently substituted with one to three substituent groups, wherein each
substituent
group of B is independently C1-C3 alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, amino, or oxo;
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
(e) D is absent;
(f) E is the hydroxy group; and
(g) Q is an aryl or heteroaryl group one to three substituent groups, which
are
independently selected from the group consisting of Ci-Cs alkyl, C2-C5
alkenyl, C2-C5
alkynyl, C1-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, Ci-
Cs alkoxy,
C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl,
aroyl,
aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, CI-
C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkanoylamino, CI-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-CS alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, CI-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-CS dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by Ci-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl, CI-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone,
wherein each
substituent group of Q is optionally independently substituted with one to
three
substituent groups selected from the group consisting of CI-C3 alkyl, C,-C3
alkoxy, acyl,
C1-C3 silanyloxy, Cl-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, carboxy, halogen, hydroxy, oxo, cyano,
heteroaryl, heterocyclyl, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally
independently
mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein either nitrogen
atom is
optionally independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl, and trifluoromethyl.
Non-limiting examples of these compounds include 2-(3,5-difluorobenzyl)-
1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 2-
biphenyl-4-
ylmethyl- 1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol;
2-(3,5-
dime thy lbenzyl)- 1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-
methylpentan-2-ol; 2-
(3-bromobenzyl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methylpentan-2-
ol; 2-
(3,5-dichlorobenzyl)- 1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-
methylpentan-2-ol;
2-(3,5-bis-trifluoromethylbenzyl)- 1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-
methylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-(3-fluoro-5-
trifluoromethylbenzyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 2-(3-chloro-2-fluoro-5-
trifluoromethylbenzyl- )- 1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-
methylpentan-
26
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
2-ol; 4-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]benzonitrile; 2-(3,5-dibromobenzyl)- 1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-
4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-
(2-fluoro-3-trifl uoromethylbenzyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-
fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-(2-fluoro-5-trifluoromethylbenzyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol.
In still another embodiment, said at least a DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl, heteroaryl, or C5-C15 cycloalkyl group, each optionally
independently substituted with one to three substituent groups, which are
independently
selected from the group consisting of CI-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5
alkynyl, CI-C3
alkanoyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, CI-C5 alkoxy, C2-
C5
alkenyloxy, C1--C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl,
aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, CI-
C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkanoylamino, CI-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, CI-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, CI-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl, CI-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R1 and R2 are each independently hydrogen, CI-C5 alkyl, C5-C15 arylalkyl,
or R1 and R2 together with the carbon atom they are commonly attached to form
a C3-C8
spiro cycloalkyl ring;
(c) R3 is the trifluoromethyl group;
(d) B is the carbonyl group or methylene group, which is optionally
independently substituted with one or two substituent groups selected from CI-
C5 alkyl,
hydroxy, and halogen;
(e) D is absent;
27
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
(f) E is the hydroxy group or amino group wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl; and
(g) Q comprises a pyrrolidine, morpholine, thiomorpholine, piperazine,
piperidine, 1H-pyridin-4-one, 1H-pyridin-2-one, IH-pyridin-4-ylideneamine, IH-
quinolin-4-ylideneamine, pyran, tetrahydropyran, 1,4-diazepane, 2,5-
diazabicyclo[2.2. I ]heptane, 2,3,4,5-tetrahydrobenzo[b][I,4]diazepine,
dihydroquinoline,
tetrahydroquinoline, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-lH-quinolin-4-one,
tetrahydroisoquinoline,
decahydroisoquinoline, 2,3-dihydro- I H-isoindole, 2,3-dihydro- I H-indole,
chroman,
1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoxaline, 1,2-dihydroindazol-3-one, 3,4-dihydro-2H-
benzo[1,4]oxazine, 4H-benzo[1,4]thiazine, 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[I,4]thiazine,
1,2-
dihydrobenzo[d] [1,3]oxazin4-one, 3,4-dihydrobenzo[1,4]oxazin4-one, 3H-
quinazolin4-
one, 3,4-dihydro- I H-quinoxalin-2-one, I H-quinnolin-4-one, 1H-quinazolin4-
one, I H-
[ 1,5]naphthyridin-4-one, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro- I H-[ 1,- 5]naphthyridin-4-one,
2,3-dihydro-
IH-[1,5]naphthyridin-4-one, 1,2-dihydropyrido[3,2-d][1,3]oxazin-4-one,
pyrrolo[3,4-
c]pyridine- 1,3-dione, 1,2-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-clpyridin-3 -one, or
tetrahydro[b] [ I ,4]diazepinone group, each optionally independently
substituted with one
to three substituent groups, wherein each substituent group of Q is
independently C1-C5
alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl,
heteroaryl, C-
C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5
alkoxycarbonyl,
CI-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl,
aminocarbonyloxy, C,-C5 alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy,
C1-
C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, CI-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaminosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
oxo, cyan,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, trifluoromethylthio, nitro, amino wherein
the nitrogen
atom is optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl,
ureido wherein
either nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl,
or CI-CS
alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or
sulfone,
wherein each substituent group of Q is optionally independently substituted
with one to
three substituent groups selected from C1-C3 alkyl, C1-C3 alkoxy, C1-C3
alkoxycarbonyl,
acyl, aryl, benzyl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl, halogen, hydroxy, oxo, cyano,
amino wherein
the nitrogen atom is optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5
alkyl, or
28
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
ureido wherein either nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted
with C i -CS
alkyl.
Non-limiting examples of these compounds include 2-(2,6-
dimethylmorpholin-4-ylmethyl)- 1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-
4-
methylpentan-2-ol; 1-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-
4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-3,5-dimethylpiperidin-4-one; I-[4-(5-fluoro-
2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-3-methyl-IH-
quinolin-4-
one; 1-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-2,3-
dihydro-1H-quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(3-fluorophenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(4-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-
4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-quinolin-4-one; I-[4-phenyl-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-
-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(5-fluoro-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-
yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-quinolin-4-one; I-[4-(5-
bromo-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-
quinolin-4-
one; 1-[4-(5-methyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-y- 1)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifl uoromethylpentyl]-1H-quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(5-chloro-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-
2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-
quinolin-4-
one; 1-[4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-
[1,5]naphthyridin-4-one; 1-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-2,4-
dimethylpentyl]-3,5-dimethyl-IH-pyridin-4-one; 1-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-methoxy-5-
thiophen-2-ylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-
(6-
bromobenzo[ 1,3]dioxol-4-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-I H-
quinolin-4-one; I -[4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-3-methyl-1H-quinolin-4-one; 1-[2-hydroxy-4-(4-
hydroxybiphenyl-3-yl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-quinolin-4-one; 1-
{4-[5-
(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)-2-hydroxyphenyl]-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl }-]H-quinolin-4-one;; 1-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-hydroxy-5-
thiophen-3-
ylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-quinolin-4-one; 1-{4-[5-(3,5-
dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)-2-methoxyphenyl]-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
29
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
trifluoromethylpentyl } -1 H-quinolin-4-one; 1-[2-hydroxy-4-methyl-4-(3-
pyridin-3-
ylphenyl)-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-quinolin-4-one; 4-methoxy-3-[4,4,4-
trifluoro-3-
hydroxy-1,1-dimethyl-3-(4-oxo-4H-quinolin-1-ylmethyl)butyl]benzaldehyde; 1-[2-
hydroxy-4-(2-methoxy-5-thiophen-3-ylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-
1 H-
quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(5-furan-3-yl-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-I H-quinolin-4-one; I -[2-hydroxy-4-(4-methoxybiphenyl-
3-yl)-4-
methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(5-acetyl-2-
hydroxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-quinolin-4-one; I-[3,3,3-
trifluoro-2-(6-
fluoro-4-methylchroman-4-ylmethyl)-2-hydroxypropyl]-IH-quinolin-4-one; 1-(4-{3-
[1-
(benzyloxyimino)ethyl] phenyl }-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl)- I
H-
quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(5-acetyl-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]- I H-quinolin-4-one; 1-(2-hydroxy-4- (3-[ 1-
(methoxyimino)ethyl]phenyl}-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl)-1H-quinolin-4-
one; 1-
[4-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-
quinolin-4-one; 1-(2-hydroxy-4-{3-[1-(hydroxyimino)ethyl]phenyl}-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl)-IH-quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(5-bromo-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-
4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-]H-quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(3,5-difluorophenyl)-
2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(3,5-
dimethylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-quinolin-4-one;
1-{2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-4-[3-(2-methyl-[ 1,3]dioxolan-2-yl)phenyl]-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl }-
IH-quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-[1,5]naphthyridin-4-one; 1-[4-(3-[ 1,3]dioxan-2-
ylphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-quinolin-4-one; 1-{4-[3-(3,5-
dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl]-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl }-I H-
quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-3,5-dimethyl-IH-pyridin-4-one; 1-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-2-hydroxymethyl-3,5-
dimethyl-IH-pyridin-4-one; 1-[4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-
2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-3-hydroxymethyl-IH-quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(3-bromophenyl)-
2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-quinolin-4-one; I-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-6-methyl-IH-
quinolin-4-
one; 6-chloro-l-[4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-quinolin-4-one; I-[-4-(2-difluoromethoxy-5-
fluorophenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]- I H-quinolin-4-one; I -(4-biphenyl-
3-yi-2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl)-IH-quinolin-4-one; 1-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-
hydroxy-5-methylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-quinolin-4-one; 1-
[2-
hydroxy-4-(3-isopropoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]- I H-quinolin-
4-one;
1-[4-(3-ethoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]- I H-
quinolin-4-one;
I -[2-hydroxy-4-(2-methoxy-5-methylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-
I H-
quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-quinolin-4-one; 1-[2-hydroxy-4-(3-methoxyphenyl)-4-
methyl-
2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1,2-dihydroindazol-3-one; 7-fluoro-
I -[4-(5-
fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-
quinolin-4-
one; 1-[4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-3,5-
dimethyl-IH-pyridin-4-one; 7-fluoro-1-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-
4-
methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-quinolin-4-one; 1-(2-hydroxy-4-methyl-4-
phenyl-2-
trifluoromethylhexyl)-1 H-quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-H-quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-quinolin-4-one; 8-fluoro-l-[4-(5-
fluoro-
2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-quinolin-4-
one; 6-
fluoro-I -[4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-
1 H-quinolin-4-one; 7-chloro-1-[4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(5-fluoro-2-isopropoxyphenyl)-
2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-H-quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(2-ethoxy-5-
fluorophenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-quinolin-4-one; 8-
fluoro- I -[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-
IH-quinolin-4-one; 6-fluoro-1-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-
2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-quinolin-4-one; 1-[2-hydroxy-4-(5-methanesulfonyl-
2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-quinolin-4-one; 1-
[2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-4-(5-methylsulfanyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-quinolin-4-one; 7-chloro-I-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-quinolin-4-one; 3-chloro-1-[4-(5-
fluoro-
2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-5-trifluoromethyl-
I H-
31
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
pyridin-2-one; 1-[2-hydroxy-4-(5-methanesulfonyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-4-
methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-3-methyl-I H-quinolin-4-one; ]-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-
methoxy-5-pyridin-3-ylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-quinolin-4-
one; 1-
[2-hydroxy-4-(2-hydroxy-3,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-
H-
quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(3-[1,3]dioxan-2-yl-4-fluorophenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-I H-quinolin-4-one; 2-( 1,1-dioxo-2,3-dihydro-I H-I 6-
benzo[ 1,4]thiazin-4-ylmethyl)- 1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-
methylpentan-2-ol; 2-(2,3-dihydrobenzo[ I ,4]oxazin4-ylmethyl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-
4-(5-
fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 1-[4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-H-quinolin-4-one; ]-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-H-[ I
,5]naphthyridin-4-
one; 1-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-H-
quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(4-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-
4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-H-quinolin-4-one; 1-[4-(3-fluoro-4-
methoxyphenyl)-
2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-quinolin-4-one; 1-(4-benzo[1,3]
dioxol-
4-yl-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl)-1 H-quinolin-4-one; I -[4-(5-
fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1,2-dihydroindazol-
3-
one; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(1-oxo-2,3-
dihydro-I H-
W-benzo[1,4- ]thiazin-4-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-
2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-2-hydroxymethyl-3,5-dimethyl- I H-
pyridin-
-4-one; 1-[4-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-3-methyl-iH-quinolin-4-one; 1-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-methoxy-
3,5-
dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-quinolin-4-one; 1-[2-
hydroxy-4-
(2-hydroxy-5-pyridin-3-ylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-
quinolin-4-one;
and 1-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-hydroxy-5-pyridin-5-ylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-quinolin-4-one.
In still another embodiment, said at least a DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
A, R', R2, B, D, E, and Q have the meanings disclosed immediately above, and
R3 is
hydrogen, CI-C8 alkyl, C2-C8 alkenyl, C2-Cg alkynyl, carbocycle, heterocyclyl,
aryl,
heteroaryl, carbocycle-Ci-Cg alkyl, carboxy, alkoxycarbonyl, aryl-Cl-Cg alkyl,
aryl-Ci-
C3 haloalkyl, heterocyclyl-Ci-Cs alkyl, heteroaryl-C1-Cs alkyl, carbocycle-C2-
Cs alkenyl,
32
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
aryl-C2-Cg alkenyl, heterocyclyl-C2-Cs alkenyl, or heteroaryl-C2-Cs alkenyl,
each
optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent groups,
wherein each
substituent group of R3 is independently C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5
alkynyl, C3-
Cs cycloalkyl, phenyl, C1-C5 alkoxy, phenoxy, C1-C5 alkanoyl, aroyl, C1-C5
alkoxycarbonyl, C1-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-CS
alkylaminocarbonyloxy,
C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, aminocarbonyl, C1-C5 alkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C5
dialkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5
alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaminosulfonyl,
halogen,
hydroxy, carboxy, cyano, oxo, trifluoromethyl, nitro, amino wherein the
nitrogen atom is
optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl, ureido
wherein either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone,
wherein R3
cannot be trifluoromethyl.
In still another embodiment, said at least a DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl, heteroaryl, or C5-C15 cycloalkyl group, each optionally
independently substituted with one to three substituent groups, which are
independently
selected from the group consisting of C1-C5 alkyl, C2-Cs alkenyl, C2-C5
alkynyl, C1-C3
alkanoyl, C3-C9 cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C2-
C5
alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl,
aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-
C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, C1-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R' and R2 are each independently hydrogen or C1-C5 alkyl, or R1 and R2
together with the carbon atom they are commonly attached to form a C3-C9 spiro
cycloalkyl ring;
33
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
(c) R3 is the trifluoromethyl group;
(d) B is the carbonyl group;
(e) D is the -NH- group;
(f) E is the hydroxy group; and
(g) Q comprises an optionally substituted phenyl group having the formula
X,
X2
X4 H
X3
wherein X1, X2, X3 and X4 are each independently selected from the group
consisting of
hydrogen, halogen, hydroxy, trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, C1-C5 alkyl, C2-
C5
alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C1-C5 alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom
is
optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone, C1-C5 alkanoyl, C1-C5
alkoxycarbonyl, C1-
C5 acyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5 carbamoyloxy, urea, aryl, and amino
wherein
the nitrogen atom may be independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl,
and
wherein said aryl group is optionally substituted by one or more hydroxy or C1-
C5
alkoxy groups, and wherein either nitrogen atom of the urea group may be
independently
substituted by C1-C5 alkyl; or Q is an aromatic 5- to 7-membered monocyclic
ring having
from one to four heteroatoms in the ring independently selected from nitrogen,
oxygen,
and sulfur, optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent
groups
selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, hydroxy,
trifluoromethyl,
trifluoromethoxy, C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C1-
C5
alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or
sulfone, C1-C5
alkanoyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, C1-C5 acyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5
carbamoyloxy, urea, aryl optionally substituted by one or more hydroxy or C1-
C5 alkoxy
34
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
groups, and amino wherein the nitrogen atom may be independently mono- or di-
substituted by CI-C5 alkyl, and wherein either nitrogen atom of the urea group
may be
independently substituted by CI-C5 alkyl.
Non-limiting examples of these compounds include 4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxy-
phenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethyl-pentanoic acid (3,5-dichloro-
phenyl)-
amide; 4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxy-phenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethyl-
pentanoic
acid (3-chloro-phenyl)-amide; 4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxy-phenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-
2-
trifluoromethyl-pentanoic acid (2-chloro-phenyl)-amide; 4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxy-
phenyl)-
2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethyl-pentanoic acid (2,6-dichloro-pyrimidin-4-
yl)-
amide; 4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxy-phenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethyl-
pentanoic
acid (2,6-dichloro-pyridin-4-yl)-amide; 4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxy-phenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-trifluoromethyl-pentanoic acid (2,3-dichloro-phenyl)-amide; 4-(5-
fluoro-2-
hydroxy-phenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethyl-pentanoic acid (3,5-
dimethyl-
phenyl)-amide; 4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxy-phenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethyl-
pentanoic acid (3,5-bis-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-amide; 4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxy-
phenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethyl-pentanoic acid (2,5-dichloro-phenyl)-amide;
4-(5-
fluoro-2-hydroxy-phenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethyl-pentanoic acid
(3-
bromo-phenyl)-amide; 4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxy-phenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethyl-pentanoic acid (3,5-difluoro-phenyl)-amide; 4-(5-fluoro-2-
hydroxy-
phenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethyl-pentanoic acid (3,5-dibromo-
phenyl)-
amide.
In still another embodiment, said at least a DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl or heteroaryl group, each optionally independently
substituted
with one to three substituent groups, which are independently selected from
the group
consisting of CI-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, CI_-C5 alkynyl, CI-C3 alkanoyl, C3-
Cg
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, CI-C5 alkoxy, C2-G alkenyloxy, C2-
C5
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-Cs dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkanoylamino, CI-
Cs
alkoxycarbonylamino, CI-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, CI-C5
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R and R2 are each independently hydrogen or C1-C5 alkyl;
(c) R3 is C1-C8 alkyl, C2-C8 alkenyl, C2-C8 alkynyl, carbocycle, heterocyclyl,
aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle-C1-C8 alkyl, aryl-C1-C8 alkyl, aryl-C1-C8
haloalkyl,
heterocyclyl-C1-C8 alkyl, heteroaryl-C1-C8 alkyl, carbocycle-C2-C8 alkenyl,
aryl-C2-C8
alkenyl, heterocyclyl-C2-C8 alkenyl, or heteroaryl-C2-C8 alkenyl, each
optionally
independently substituted with one to three substituent groups, wherein each
substituent
group of R3 is independently C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, phenyl, C1-C5 alkoxy, phenoxy, C1-C5 alkanoyl, aroyl, C1-C5
alkoxycarbonyl,
C1-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5
dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, aminocarbonyl, C1-C5 alkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C5
dialkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5
alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaminosulfonyl,
halogen,
hydroxy, carboxy, cyano, oxo, trifluoromethyl, nitro, amino wherein the
nitrogen atom is
optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl, ureido
wherein either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, or C1-
C5
alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or
sulfone,
wherein R3 cannot be trifluoromethyl;
(d) B is C1-C5 alkylene, C2-C5 alkenylene, or C2-C5 alkynylene, each
optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent groups,
wherein each
substituent group of B is independently C1-C3 alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, amino,
or oxo;
(e) D is absent;
(f) E is the hydroxy group; and
36
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
(g) Q comprises an azaindolyl group optionally independently substituted
with one to three substituent groups, wherein each substituent group of Q is
independently C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl,
heterocyclyl,
aryl, heteroaryl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy,
acyl, C1-C5
alkoxycarbonyl, C1-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl,
dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-CS
dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5
alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, C1-Cs alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5
dialkylaminosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy, cyano, trifluoromethyl,
trifluoromethoxy, trifluoromethylthio, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom
is
optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl, ureido
wherein either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, or C1-
C5
alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or
sulfone,
wherein each substituent group of Q is optionally independently substituted
with one to
three substituent groups selected from C1-C3 alkyl, C1-C3 alkoxy, halogen,
hydroxy, oxo,
cyano, amino, or trifluoromethyl.
Non-limiting examples of these compounds include 1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-(5-
fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol;
1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-
b]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1, 1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
(I H-
pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(1H-pyrrolo[3,2-b]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 4-
fluoro-2-[4,4,4-trifluoro-3-hydroxy-1,1-dimethyl-3-(1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-
2-
ylmethyl)butyl]phenol; 4-fluoro-2-[4,4,4-trifluoro-3-hydroxy-1,1-dimethyl-3-(I
H-
pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)butyl]phenol; 4-fluoro-2-[4,4,4-trifluoro-3-
hydroxy-
l,l-dimethyl-3-(IH-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)butyl]phenol; 4-fluoro-2-
[4,4,4-
trifluoro-3-hydroxy-1,l-dimethyl-3-(1H-pyrrolo[3,2-b]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)butyl]phenol;
1, 1,1-trifluoro-4-(3-fluorophenyl)-4-methyl-2-(I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-methyl-2-(IH-
pyrrolo[2,3-
c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 4-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-1,1,1-
trifluoro-4-
methyl-2-(IH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-yelmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 4-(2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-
7-yl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-4-methyl-2-(1 H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-yelmethyl)pentan-
2-ol;
37
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-methyl-4-phenyl-2-(I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridine-2-
ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol;
1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-(4-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(I H-pyrrolo[2,3-
c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-(4-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-
2-(I H-
pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-methyl-4-
phenyl-2-(1H-
pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(4-
fluorophenyl)-4-
methyl-2-(IH-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 5-fluoro-2-[4,4,4-
trifluoro-
3-hydroxy-1,1-dimethyl-3-(1H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)butyl]phenol;
1,1,1-
trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1,1, l-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
(3-
methyl-IH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 4-fluoro-2-[4,4,4-
trifluoro-3-
hydroxy-], l-dimethyl-3-(3-methyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)butyl]phenol;
5-fluoro-2-[4,4,4-trifluoro-3-hydroxy-1,1-dimethyl-3-(1 H-pyrrolo[3,2-
c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)butyl]pentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-
7-yl)-4-
methyl-2-(1H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridine-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 4-fluoro-2-[4,4,4-
trifluoro-
3-hydroxy-1, l-dimethyl-3-(IH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]-[3-methylpyridin]-2-
ylmethyl)butyl] phenol; 4-fluoro-2-[4,4,4-trifluoro-3-hydroxy- 1, 1 -dimethyl-
3-(l H-
pyrrolo[2,3-c]-[2-fluoropyridin]-2-ylmethyl)butyl]phetol; and 4-fluoro-2-
[4,4,4-
trifluoro-3-hydroxy-1,1-dimethyl-3-(1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]-[2-
trifluoromethylpyridin]-2-
ylmethyl)buty1]phenol.
In still another embodiment, said at least a DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl or heteroaryl group, each optionally independently
substituted
with one to three substituent groups, which are independently selected from
the group
consisting of CI-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, CI-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, CI-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-
C5
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-Cs dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkanoylamino, CI-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, CI-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, CI-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
38
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R' and R2 are each independently hydrogen or CI-C5 alkyl, or R' and R2
together with the carbon atom they are commonly attached to form a C3-C8 spiro
cycloalkyl ring;
(c) R3 is the trifluoromethyl group;
(d) B is C1-C5 alkylene, C2-C5 alkenylene, or C2-C5 alkynylene, each
optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent groups,
wherein each
substituent group of B is independently C1-C3 alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, amino,
or oxo;
(e) D is absent;
(f) E is the hydroxy group; and
(g) Q comprises a heteroaryl group optionally independently substituted with
one to three substituent groups, which are independently selected from the
group
consisting of Cl-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C1-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, CI-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-
C5
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, CI-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, CI-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone,
wherein each
substituent group of Q is optionally independently substituted with one to
three
substituent groups selected from the group consisting of C1-C3 alkyl, CI-C3
alkoxy, acyl,
C1-C3 silanyloxy, Cl-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, carboxy, halogen, hydroxy, oxo, cyan,
39
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
heteroaryl, heterocyclyl, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally
independently
mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein either nitrogen
atom is
optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, or trifluoromethyl.
Non-limiting examples of these compounds include 4-cyclohexyl-1,1,1-
trifluoro-4-methyl-2-quinolin-4-ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 4-pyrimidin-5-yi-2-[4,4,4-
trifluoro-3-hydroxy-1, l -dimethyl-3-(1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)butyl]phenol;
4-pyrimidin-5-y1-2-[4,4,4-trifluoro-3-hydroxy-l, l -dimethyl-3-(I H-
pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-
2-ylmethyl)butyl] phenol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-
methyl-2-(3-
methyl-lH-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-
fluoro-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-4-methyl-2-(1 H-pyrrolo[3,2-c] pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol;
1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(3-methyl-I H-
pyrrolo[2,3-
c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 2-(4,6-dimethyl-IH-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 2-
(5,7-
dimethyl-I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)- 1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-
2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-
4-
methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-pyrrolo[3,2-b]pyridine-5-carbonitrile;
1,1,1-
trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(6-methyl- I H-pyrrolo[3,2-
c]pyridin-
2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-
2-(4-
methyl- I H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-4-methyl-1 H-
pyrrolo[3,2-
c]pyridine-6-carbonitrile; 2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-
2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carbonitrile; 2-[4-(5-
fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-I H-pyrrolo[3,2-
c]pyridine-4-carbonitrile; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-
methyl-2-(5H-
pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidin-6-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-thieno[2,3-d]pyridazin-2-ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-
trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(5H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridazin-
6-
ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1, I ,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-
2-(2-
methyl-5H-pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidin-6-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-
fluoro-
2-methylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(I H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyridazin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-
ol; 2-
(4,6-dimethyl-H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-
2-
methylphenyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 4-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-
(4,6-
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
dimethyl- I H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-4-methylpentan-
2-ol; 2-
[4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]- I H-
pyrrolo[3,2-b]pyridine-5-carbonitrile; 4-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-
1,1,1-
trifluoro-4-methyl-2-(3-methyl-1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-
ol; 1 ,1,1-
trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(5H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]- pyridazin-
6-
yl me thyl)pentan-2-ol; 4-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-1,1,1-
trifluoro-4-methyl-
2-(5H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridazin-6-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 4-(5-chloro-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-4-methyl-2-(1-H-pyrrolo[2,3-
d]pyridazin-2-
ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-(7-fluoro-
IH-
pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2ylmethyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-
fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(4-methyl- I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)pentan-2-
ol; 2-(5,7-dichloro-IH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-
fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-
methyl-2-(5-trifluoromethyl-1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol;
1,1,1-
trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-(5-methoxy-I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-
2-
ylmethyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-4-
methyl-2-
(4-methyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-
(5-fluoro-
2-methylphenyl)-2-(5-isopropoxy-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-4-
methylpentan-
2-0l; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-(5-methoxy-IH-pyrrolo[2,3-
c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 4-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-
yl)-
1, 1, 1-trifluoro-2-(5-methoxy-I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-4-
methylpentan-2-ol;
1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-(7-fluoro-1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]
pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 4-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)- I -
trifluoro-4-
methyl-2-(5-trifluoromethyl-IH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol;
1,1,1-
trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(5-trifluoromethyl-I H-
pyrrolo[2,3-
c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 4-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-
1,1,1-
trifluoro-2-(5-isopropoxy-IH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-4-methylpentan-
2-ol; 4-
(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)- 1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-2-(7-fluoro- I H-
pyrrolo[2,3-
c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 4-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-
yl)-2-
(5-dimethylamino-I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-4-
methylpentan-
2-oi; 4-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-4-methyl-2-(5-
piperidin- I -
yl- I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 4-(5-chloro-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-
41
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
7-yl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-4-methyl-2-(5-morpholin-4-yl-1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
(5-
piperidin- l -yl-1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 4-(5-chloro-
2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-(5-ethoxy-I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)- 1,
1, 1 -
trifluoro-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 2-(5-benzyloxy-IH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)-
1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 2-(5-
benzyloxy- I H-
pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-4-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofiran-7-yl)-
1,1,1-
trifluoro-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-
(5-chloro-
1H-pyrrolo[2,3-c- ]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-
(5-fluoro-
2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2- [5 -(methy I amino)- I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl]pentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
(5-
amino-IH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-
fluoro-2-
methylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(6-amino-IH-pyrrol- o[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-
2-ol;
4-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-2-(5-amino-1 H-
pyrrolo[2,3-
c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 4-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-
yl)-
1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4- methyl- 2-(5 -methyl amino- I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)pentan-
2-01; 7-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-
1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-7-ium chloride; 6-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-
4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-2-methyl-IH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-6-ium
chloride; 4-
(5-bromo-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-4-methyl-2-(I H-
pyrrolo[2,3-
c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-methyl-4-(5-methyl-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-(1H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1
,1 ,1 1 ,1-trifluoro-4-methyl-2-(1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-
c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-
4-
methyl-2-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-l-ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-
fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(6-oxy-1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-
ol;
1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-pyrrolo[2,3-
c]pyridin- l -
ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 2-benzo[b]thiophen-2-ylmethyl-1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-
2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-
methyl-2-thieno[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-
fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-indazol-I -ylmethyl-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-
fluoro-
2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-pyrazolo[ I ,5-a]pyridin-2-ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 4-
(5-
42
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2,4-dimethyl- I -thieno[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
ylpentan-2-
ol; 4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2,4-dimethyl-l-thieno[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylpentan-
2-ol;
1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-furo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethy-
1-4-
methylpentan-2-ol; 4-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)- I -furo[2,3-
c]pyridin-2-yl-
2,4-dimethylpentan-2-ol; 4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)- I -furo-[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
yI-2,4-
dimethylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
(IH-
pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol- ; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-methyl-4-(5-
methyl-
2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-(1H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-
ol; 4-(5-
chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-y l)-1, 1 ,1-trifluoro-4-methyl-2-(I H-
pyrrolo[3,2-
c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 4-(5-bromo-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-1,1,1-
trifluoro-4-methyl-2-(IH-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 2-(3-
dimethylaminomethyl- I H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-4-
(5-fluoro-
2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-
methyl-2-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-1-ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-
fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-pyrrolo[3,2-b]pyridin-1-ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 1, 1,1-
trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-furo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl-4-
methylpentan-2-ol; 4-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-4-
methyl-2-
pyrrolo[3,2-b]pyridin-1-ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-thieno[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 4-(5-
chloro-
2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-4-methyl-2-thieno[3,2-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
pyrrolo[3,2-b]pyridin-l-ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-
methylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-thieno[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 4-fluoro-
2-
(4,4,4-trifluoro-3-hydroxy- l , l -dimethyl-3-thieno[3,2-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethylbutyl)phenol;
4-fluoro-2-(4,4,4-trifluoro-3-furo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl-3-hydroxy-1,1-
dimethylbutyl)phenol; 4-fluoro-2-(4,4,4-trifluoro-3-hydroxy-1,1-dimethyl-3-
pyrrolo[3,2-
b]pyridin-1-ylmethylbutyl)phenol; 2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-indole-6-carboxylic acid; 2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]- I H-indole-6-
carboxylic
acid dimethylamide; {2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-indol-6-yl}morpholin-4-ylmethanone; 2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyI I- I H-indole-6-
carboxylic
43
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
acid dimethylamide; {2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-indol-6-yl}morpholin-4-ylmethanone; 2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-indole-6-
carboxylic
acid amide; 2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-indole-6-carboxylic acid amide; 4-fluoro-2-[4,4,4-
trifluoro-3-
hydroxy- 1, 1 -dimethyl-3-(5-nitro- I H-indol-2-ylmethyl)butyl ]phenol; 2-[4-
(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-indole-6-
carbonitrile;
2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1
H-
indole-6-carbonitrile; N-{2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-indol-5-yl}acetamide; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(4-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-(7-fluoro-4-methyl-lH-indo- I-2-ylmethyl)-4-methylpentan-2-
ol; 5-
fluoro-2-[4,4,4-trifluoro-3-(7-fluoro-4-methyl-1 H-indol-2-ylmethyl)-3-hydroxy-
1,1-
dimethylbutyt]phenol; 2-[4-(3-[1,3 ]dioxolan-2-ylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-indole-5-carbonitrile; 2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-indole-5-carboxylic acid-2-
trimethylsilanylethyl ester; 2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-indole-5-carboxylic acid; 2-[4-(4-fluoro-2-
hydroxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpenty-1]-4-methyl-IH-indole-6-carbonitrile;
{2-[4-
(5-Fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-
indol-5-
yl }piperidin- I -ylmethanone; 2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-indole-5-carboxylic acid methylamide; {2-[4-(5-
fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]- I H-indol-5-yl }
pyrrolidin-
1-ylmethanone; 1-{2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]IH-indole-5-carbonyl}piperidin-4-one; 2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]- I H-indole-5-
carboxylic
acid (2-hydroxyethyl)amide; {2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-indol-5-yl}(4-hydroxypiperidin-l-yl)methanone; {2-[4-
(5-
fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-I H-indol-
5-
yl }(3-hydroxypyrrolidin- I -yl)methanone; 2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-
4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]- I H-indole-5-carboxylic acid
cyanomethylamide; 2-[4-
(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-I H-
indole-5-
carboxylic acid (2-dimethylaminoethyl)amide; {2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-
2-
44
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl] -1 H-indol-5-yl } (4-methylpiperazin-
l -
yl)methanone; ({ 2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-indole-5-carbonyl}amino)acetic acid methyl ester; 2-
[4-(5-
fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-I H-indole-
5-
carboxylic acid carbamoylmethylamide; 4-({2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-indole-5-carbonyl}amino)butyric
acid
methyl ester; ({2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-indole-5-carbonyl}amino)acetic acid; 4-({2-[4-(5-
fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-indole-5-
carbonyl}amino)butyric acid; 2-[4-(3-dimethylaminomethylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-indole-5-carbonitrile; 4-fluoro-2-[4,4,4-
trifluoro-3-
hydroxy-1,1-dimethyl-3-(5-trifluoromethyl-lH-indol-2-ylmethyl)butyl]phenol; 2-
[4-(5-
bromo-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-
4-
methyl- I H-indole-6-carbonitrile; 2-[2-hydroxy-4-(5-methanesulfonyl-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-4-methyl-I H-indole-
6-
carbonitrile; 2-[4-(5-bromo-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-indole-5-carboxylic acid; 2-[4-(5-bromo-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-indole-
5-
carboxylic acid amide; 2-[4-(5-bromo-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-
2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-indole-5-carboxylic acid dimethylamide; 2-[4-(5-
Bromo-
2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]- I H-
indole-5-
carboxylic acid cyanomethylamide; {2-[4-(5-bromo-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-indol-5-yl }pyrrolidin-l-
ylmethanone;
{ 2-[4-(5-bromo-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoro-
methylpentyl]-IH-indol-5-yl}morpholin-4-ylmethanone; 2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]- I H-indole-5-
carboxylic
acid amide; {2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-indol-5-yl}morpholin-4-ylmethanone; 2-(4-
benzo[1,3]dioxol-
4-yl-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl)-4-methyl- I H-indole-6-
carbonitrile;
1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-methyl-4-phenyl-2-quinolin-4-ylmethylhexan-2-ol; 2-[2-
hydroxy-4-
methyl-4-(5-methylsulfanyl-2- ,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]- l H-
indole-3-carbonitrile; 7-(4,4,4-trifluoro-3-hydroxy-1,1-dimethyl-3-quinolin-4-
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
ylmethylbutyl)-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-5-carbonitrile; 2-[2-hydroxy-4-(5-
methanesulfonyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-
I H-
indole-3-carbonitrile; 2-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-hydroxy-5-methylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
trifluoro-
methylpentyl]-4-methyl-I H-indole-6-carbonitrile; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-
2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-4-methyl-2-(5-methylsulfanyl-I H-indol-2-
ylmethyl)pentan-2-
ol; 2-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-methoxy-5-methylsulfanylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-indole-3-carbonitrile; 2-[2-Hydroxy-4-(5-
methanesulfonyl-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-I H-indole-3-carbonitrile; 2-
[4-(5-
fluoro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-
IH-
indole-5-sulfonic acid dimethylamide; 1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-y- 1)-4-methyl-2-(5-phenyl-I H-indol-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-
ol; 2-[4-
(5-tert-butyl-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl] -1
H-indole-
3-carbonitrile; 2-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-hydroxy-5-isopropylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-indole-3-carbonitrile; 2-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-hydroxy-
3,5-
dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-indole-3-carbonitrile; 2-
[2-
hydroxy-4-(5-hydroxy-2,4-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-
indole-3-carbonitrile; 2-[4-(5-tert-butyl-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-
2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-indole-3-carbonitrile; 2-[4-(5-tert-butyl-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1-methyl-iH-indole-3-carbonitrile; 2-
[2-
hydroxy-4-(5-isopropyl-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-
indole-3-carbonitrile; 2-[2-hydroxy-4-(5-isopropyl-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1-methyl-iH-indole-3-carbonitrile; 2-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-
hydroxy-5-
methanesulfonylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-indole-3-
carbonitrile; 2-
[2-hydroxy-4-(2-methoxy-5-methylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-4-
methyl-
IH-indole-6-carbonitrile; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-methyl-2-quinolin-4-ylmethyl-4-o-
tolylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-methyl-2-quinolin-4-ylmethyl-4-m-
tolylpentan-2-ol;
1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-(I H-indol-2-ylmethyl)-4-methylpentan-
2-ol; 1,1,1-
trifluoro-4-(2-fluorophenyl)-4-methyl-2-quinolin-4-ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-
trifluoro-
4-(3-fluorophenyl)-2-(1 H-indol-2-ylmethyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-
trifluoro-4-(3-
fluorophenyl)-4-methyl-2-quinolin-4-ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(4-
fluorophenyl)-2-(IH-indol-2-ylmethyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-
(4-
fluorophenyl)-4-methyl-2-quinolin-4-ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 3-(4,4,4-trifluoro-3-
hydroxy-
46
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
1,1-dimethyl-3-quinolin-4-ylmethylbutyl)phenol; 1,1, 1 -trifluoro-4-methyl-2-
quinolin-4-
ylmethyl-4-(2-trifluoromethylphenyl)pentan-2-ol; 1,1,1 -trifluoro-2-(I H-indol-
2-
yImethyl)-4-methyl-4-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)pentan-2-o1; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-
methyl-2-
quinolin-4-ylmethyl-4-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)pentan-2-ol; 4-(3-chlorophenyl)-
1,1,1-
trifluoro-2-(1 H-indol-2-ylmethyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 4-(3-chlorophenyl)-
1,1,1,-
trifluoro-4-methyl-2-quinolin-4-ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 4-(4-dimethylaminophenyl)-
1,1,1-
trifluoro-2-(1 H-indol-2-ylmethyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 4-biphenyl-3-yl- 1, 1,
1 -trifluoro-
4-methyl-2-quinolin-4-ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 4-(3-bromophenyl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-2-
(1H-
indol-2-ylmethyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 4-(2-difluoromethoxy-5-fluorophenyl)-
1,1,1-
trifluoro-2-(1 H-indol-2-ylmethyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 4-biphenyl-3-yl-1,1,1-
trifluoro-
2-(1H-indol-2-ylmethyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 4-(4-dimethylaminophenyl)-1,1,1-
trifluoro-4-methyl-2-quinolin-4-ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
methylphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1,6-dihydropyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-5-
one; 2-
[4-(5-Fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-6-
methyl-
1,6-dihydropyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-5-one; 2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methyl- phenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-4-methyl-1,4-dihydropyrrolo[3,2-b]pyridin-5-
one;
1 ,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-(6-methoxy-1 H-pyrrolo[3,2-
c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-5-methyl-1,5-dihydropyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-6-one; 2-[4-
(5-fluoro-
2-methyl- phenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1,3a-
dihydropyrrolo[3,-
2-c]pyridin-6-one; 2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1,7-dihydropyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridine-4,6-dione; 6-[4-(5-
fluoro-2-
methylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trfluoromethylpentyl]-3-methyl- I ,7-
dihydropyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine-2,4-dione; 2-[4-(5-chloro-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-
2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoro- methylpentyl]-1,6-dihydropyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-
5-one;
2-[4-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-6-methyl-1,6-dihydropyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-5-one; 2-[4-
(5-chloro-
2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1,4-
dihydropyrrolo[ 3,2-b]pyridin-5-one; 2-[4-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofiran-7-
yl)-2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-4-methyl- I ,4-dihydropyrrolo[3,2-
b]pyridin-
5-one; 2-[4-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoro-
methylpentyl]-1,5-dihydropyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-6-one; 2-[4-(5-chloro-2,3-
47
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-5-methyl-
1,5-
dihydropyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-6-one; 4-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-
1,1,1-
trifluoro-2-(6-methoxy-5,6-dihydro-I H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-4-
methylpentan-2-ol; 2-{4-(5-chi oro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yI)-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1,7-dihydropyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridine-4,6-dione; 6-[4-(5-
chloro-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-3-methyl-
1,7-
dihydropyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine-2,4-dione; 2-[4-(3-dimethylaminomethylphenyl)-
2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]- I H-indole-5-carbonitrile; 1,1, I -
trifluoro-2-
(1H-indol-2-ylmethyl)-4-methyl-4-(3-morpholin-4-ylmethylphenyl)pentan-2-ol;
1,1,1-
trifluoro-4-methyl-4-(3-morpholin-4-ylmethylphenyl)-2-(IH-pyrrolo[2- ,3-
d]pyridazin-
2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
(5-
morpholin-4-ylmethyl-I H-indol-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-
fluoro-2-
methylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(5-morpholin-4-ylmethyl-1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; {2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl -2-
trifuoromethylpentyl]-IH-indol-5-yl}phenylmethanone; {2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
methylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpenty-1]-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-
c]pyridin-
5-yl } phenylmethanone; {2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-indol-5-yl}furan-2-ylmethanone; {2-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
methylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]- I H-pyrrolo[2,3-
c]pyridin-
5-yl}furan-2-ylmethanone; 1,1,1-trifluoro-2-(1H-indol-2-ylmethyl)-4-methyl-4-
pyridin-
2-ylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-methyl-4-pyridin-4-y1-2-quinolin-4-
ylmethylpentan-2-
ol; 2-(2,6-dimethylpyridin-4-ylmethyl)- 1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-
methylpentan-2-ol; 2-[3-(2,6-dimethylpyridin-4-ylmethyl)-4,4,4-trifluoro-3-
hydroxy-1,1-
dimethylbutyl]-4-fluorophenol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4,4-dimethyl-5-phenyl-2-
quinolin-4-
ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
pyridin-
4-ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 4-fluoro-2-[4,4,4-trifluoro-3-(2-fluoropyridin-4-
ylmethyl)-3-
hydroxy- 1,1-dimethylbutyl]phenol; 2-[3-(2-bromopyridin-4-ylmethyl)-4,4,4-
trifluoro-3-
hydroxy-1,l-dimethylbutyl]-4-fluorophenol; 2-(6,8-dimethylquinolin-4-ylmethyl)-
1,1,1-
trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxy- phenyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 4-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]pyridine-2-
carbonitrile;
2,6-dichloro-4-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]nicotinonitrile; 4-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-
48
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]quinolin-2-ol; 2,6-dichloro-4-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]nicotinonitrile; 2-
(2-
chloro-8-methylquinolin-4-ylmethyl)- 1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-
methylpentan-2-ol; 2-(2,6-dichloroquinolin-4-ylmethyl)- 1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-
(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 2-[3-(2-chloro-8-methylquinolin-4-
ylmethyl)-
4,4,4-trifluoro-3-hydroxy-1,1-dimethylbutyl]-4-fluorophenol; 2-[3-(2,6-
dichloroquinolin-
4-ylmethyl)-4,4,4-trifluoro-3-hydroxy-1,1-dimethylbutyl]-4-fluorophenol; 4-
(2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-(2,6-dimethylpyridin-4-ylmethyl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-4-
methylpentan-2-ol; 2-(2,6-dimethylpyridin-4-ylmethyl)- 1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-(3-
fluorophenyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 2-(2,6-dimethylpyridin-4-ylmethyl)- 1, 1, 1
-trifluoro-
4-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-
methylphenyl)-4-
methyl-2-quinolin-4-ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 2-(2,6-dimethylpyridin-4-ylmethyl)-
1,1,1-
trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 2-(2,6-
dimethylpyridin-4-
ylmethyl)- 1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-methyl-4-m-tolylpentan-2-ol; 1, 1, 1 -
trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(2-methylquinolin-4-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 4-fluoro-2-
(4,4,4-trifluoro-3-hydroxy-1,1,1-dimethyl-3-quinolin-4-ylmethylbutyl)phenol; 4-
fluoro-
2-[4,4,4-trifluoro-3-hydroxy-1,1-dimethyl-3-(2-methylquinolin-4-
ylmethyl)butyl]phenol;
2-(2,6-dimethylpyridin-4-ylmethyl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(4-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-
methylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(7-
methylquinolin-4-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 2-[3-(2,6-dimethylpyridin-4-ylmethyl)-
4,4,4-
trifluoro-3-hydroxy-1,1-dimethylbutyl]-5-fluorophenol; and 2-(5,7-
dimethylquinolin-4-
ylmethyl)- 1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methylpentan-2-
ol.
In still another embodiment, said at least a DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl or heteroaryl group, each optionally independently
substituted
with one to three substituent groups, which are independently selected from
the group
consisting of C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, CI-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, Cz-
Cs
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, CI-C5
49
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl, CI-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R' and R2 are each independently hydrogen or CI-C5 alkyl;
(c) R3 is hydrogen, CI-C8 alkyl, C2-C8 alkenyl, C2-C8 alkynyl, carbocycle,
heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle-CI-C8 alkyl, carboxy,
alkoxycarbonyl, aryl-Cl-
C8 alkyl, aryl-Ci-C8 haloalkyl, heterocyclyl-CI-C8 alkyl, heteroaryl-CI-Cg
alkyl,
carbocycle-C2-C8 alkenyl, aryl-C2-C8 alkenyl, heterocyclyl-C2-C8 alkenyl, or
heteroaryl-
C2-C8 alkenyl, each optionally independently substituted with one to three
substituent
groups, wherein each substituent group of R3 is independently CI-C5 alkyl, C2-
C5
alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, phenyl, CI-C5 alkoxy, phenoxy, CI-C5
alkanoyl, aroyl, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, CI-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyloxy, CI-
C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, aminocarbonyl, CI-C5
alkylaminocarbonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyl, CI-C5 alkanoylamino, CI-C5
alkoxycarbony I amino, CI-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, CI-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-
C5
dialkylaminosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy, cyano, oxo, trifluoromethyl,
nitro,
amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally independently mono- or di-
substituted by
CI-C5 alkyl, ureido wherein either nitrogen atom is optionally independently
substituted
with CI-C5 alkyl, CI-C5 alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally
oxidized to a
sulfoxide or sulfone, wherein R3 cannot be trifluoromethyl;
(d) B is CI-C5 alkylene, C2-C5 alkenylene, or C2-C5 alkynylene, each
optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent groups,
wherein each
substituent group of B is independently CI-C3 alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, amino,
or oxo;
(e) D is absent;
(f) E is the hydroxy group; and
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
(g) Q comprises a heteroaryl group optionally independently substituted with
one to three substituent groups, which are independently selected from the
group
consisting of C1-C5 alkyl, C-1-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, CI -C3 alkanoyl, C3-
C8
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, CI-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-
C5
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1 -C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, C1-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, CI-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone,
wherein each
substituent group of Q is optionally independently substituted with one to
three
substituent groups selected from the group consisting of Ci-C3 alkyl, Ci-C3
alkoxy, acyl,
CI-C3 silanyloxy, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, carboxy, halogen, hydroxy, oxo, cyano,
heteroaryl, heterocyclyl, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally
independently
mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein either nitrogen
atom is
optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, or trifluoromethyl.
Non-limiting examples of these compounds include 2-cyclopropyl-4-(5-
fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-l-(IH-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-yl)pentan-2-ol;
4-(5-
fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-(I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)pentanoic acid; 4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-(IH-
pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentanoic acid methyl ester; 2-cyclopropyl-4-
(5-fluoro-
2-methylphenyl)-4-methyl- I -(IH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-yl)pentan-2-ol; 4-(5-
chloro-
2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-cyclopropyl-4-methyl- I -(I H-pyrrolo[2,3-
c]pyridin-2-
yl)pentan-2-ol; 2-cyclopropyl-4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-4-methyl-I-(IH-
pyrrolo[3,2-
c]pyridin-2-yl)pentan-2-ol; 4-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-
cyclopropyl-4-
methyl- I -(I H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-yl)pentan-2-ol; 4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-
2,4-dimethyl-l -(1H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-yl)pentan-2-ol; 5-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2,5-dimethyl-3-(1H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol;
5-(5-
fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
51
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol; 2-cyclohexyl-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-l-(IH-
pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-yl)pentan-2-ol; 2-cyclopentyl-4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-
methyl-I-(IH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-yl)pentan-2-ol; 5-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-5-
methyl-3-(I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol; 2-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-4-(IH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)heptan-4-
ol; 2-(5-
fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2,5,5-trimethyl-4-(I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
yl methyl)heptan-4-ol; 1,1-difluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methy1 -2-
(IH-
pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 1-cyclohexyl-4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(IH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 5-
(5-
fl uoro-2-methylphenyl)-2,5-dimethyl-3-(1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)hexan-3-
ol; 5-(5-fuoro-2-methylphenyl- )-2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(IH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol; 5-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2,5-dimethyl-3-(I
H-
pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol; 2-cyclobutyl-4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl- I -(IH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-yl)pentan-2-ol; 2-(5-
fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2,6,6-trimethyl-4-(I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)heptan-
4-ol; 5-
(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-3-(I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)hex- l-en-
3-ol; 5-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-3-(1H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)hex-1-yn-3-ol; I -fluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(1 H-
pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 2,2-difluoro-5-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-3-(IH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol; 2-
fluoro-
5-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2,5-dimethyl-3-(1H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol; 2-fluoro-5-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-3-(IH-
pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol; 5-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2,5-
dimethyl-3-(I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)hex-l -en-3-ol; 1, 1,1-
trifluoro-5-(5-
fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-3-(1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)hexan-
3-ol;
4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-phenyl-l-(1H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
yl)pentan-2-ol; 5-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(I H-
pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol; 5-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2,2,5-
trimethyl-3-thieno[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethylhexan-3-ol; 1,1-difluoro-4-(5-
fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-(I H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 5-
(5-
fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2,5-dimethyl-3-(I H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)hexan-
3-ol; 5-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(1H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-
2-
52
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol; 2-(1-fluorocyclopropyl)-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-
methyl-
1-(1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-yl)pentan-2-ol; 2-(I -fluorocyclopropyl)-4-(4-
fluorophenyl)-4-methyl- I -quinolin-4-ylpentan-2-ol; 2-[4,4-difluoro-3-hydroxy-
1,1-
dimethyl-3-(IH-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)butyl]-4-fluorophenol; 5-(5-
chloro-
2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2,5-dimethyl-3-(IH-pyrrolo [3,2-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol; 5-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2,5-dimethyl-3-(IH-
pyrrolo[3,2-
c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol; 5-(5-fluoro-2-methylpheny1)-2,2,5-trimethyl-3-
(1H-
pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol; 4-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-
7-yl)-
1,1-difluoro-4-methyl-2-(IH-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 4-(5-
chloro-
2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-1,1-difluoro-4-methyl-2-pyrrolo[3,2-b]pyridin- I -
ylmethylpentan-2-ol; 5-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2,2,5-trimethyl-3-
(IH-
pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol; 5-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2,2,5-
trimethyl-3-(3-methyl-iH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol; 5-(5-
chloro-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2,5-dimethyl-3-(3-methyl-IH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol; 5-(5-chi oro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-y1)-2,5-dimethyl-3-
(5-
phenyl-IH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol; 5-(5-fluoro-2-
methylphenyl)-
2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(5-phenyl- I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol;
5-(5-
fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2,5-dimethyl-3-(5-phenyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol; 5-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-5-methyl-3-(5-phenyl- I H-
pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol; 4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2,4-
dimethyl-
1-(5-phenyl- I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-yl)pentan-2-ol; 4-(5-chloro-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)- I ,1-difluoro-4-methyl-2-(6-methyl- I H-pyrrolo[3,2-
c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 5-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2,5-dimethyl-3-(5-pyridin-3-
yl-1H-
pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol; 5-(5-chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-
7-yl)-
5-methyl-3-(5-phenyl- I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol; 4-(5-
chloro-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2,4-dimethyl- l -(5-phenyl-1 H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-
yl)pentan-2-ol; 1,1-difluoro-4-(5-methanesulfonyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-
4-
methyl-2-(IH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)pentan-2-ol; 5-(5-chloro-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2,5-dimethyl-3-(5-pyridin-3-yl- I H-pyrrolo[2,3-
c]pyridin-2-
ylmethyl)hexan-3-ol; 2-(5-bromo- I H-indol-2-ylmethyl)- 1, 1 -difluoro-4-(5-
methanesulfonyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; and 2-[2-
53
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
difluoromethyl-2-hydroxy-4-(5-methanesulfonyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-4-
methylpentyl]-4-methyl- I H-indole-6-carbonitrile.
In still another embodiment, said at least a DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl or heteroaryl group, each optionally independently
substituted
with one to three substituent groups, which are independently selected from
the group
consisting of C1-C5 alkyl, C2-Cs alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C1-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-
C5
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonyl amino, aminosulfonyl, C1-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R' and R2 are each independently C1-C5 alkyl, wherein one or both are
independently substituted with hydroxy, C1-C5 alkoxy, C1-C5 alkylthio wherein
the
sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone, amino wherein
the nitrogen
atom is optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl or
aryl;
(c) R3 is hydrogen, C1-C8 alkyl, C2-C8 alkenyl, C2-C8 alkynyl, carbocycle,
heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle-C1-C8 alkyl, carboxy,
alkoxycarbonyl, aryl-C1-
C8 alkyl, aryl-C1-Cs haloalkyl, heterocyclyl-C1-C8 alkyl, heteroaryl-C1-C8
alkyl,
carbocyele-C2-C8 alkenyl, aryl-C2-C8 alkenyl, heterocyclyl-C2-Cs alkenyl, or
heteroaryl-
C2-C8 alkenyl, each optionally independently substituted with one to three
substituent
groups, wherein each substituent group of R3 is independently C1-C5 alkyl, C2-
C5
alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, phenyl, C1-C5 alkoxy, phenoxy, C1-C5
alkanoyl, aroyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, C1-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-
Cs
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, aminocarbonyl, C1-C5
54
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
alkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-Cs alkylsulfonylamino, C1-Cs alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5
dialkylaminosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy, cyano, oxo, trifluoromethyl,
nitro,
amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally independently mono- or di-
substituted by
C1-C5 alkyl, ureido wherein either nitrogen atom is optionally independently
substituted
with C1-C5 alkyl, C,-C5 alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally
oxidized to a
sulfoxide or sulfone;
(d) B is C1-C5 alkylene, C2-C5 alkenylene, or C2-C5 alkynylene, each
optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent groups,
wherein each
substituent group of B is independently C1-C3 alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, amino,
or oxo;
(e) D is absent;
(f) E is the hydroxy group; and
(g) Q comprises a heteroaryl group optionally independently substituted with
one to three substituent groups, which are independently selected from the
group
consisting of C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C1-C3 alkanoyl, C3-Cg
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-
C5
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-Cs alkanoylamino, CI-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, CI-Cs alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, C1-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone,
wherein each
substituent group of Q is optionally independently substituted with one to
three
substituent groups selected from the group consisting of C1-C3 alkyl, C1-C3
alkoxy, acyl,
C1-C3 silanyloxy, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, carboxy, halogen, hydroxy, oxo, cyano,
heteroaryl, heterocyclyl, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally
independently
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein either nitrogen
atom is
optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, or trifluoromethyl.
In still another embodiment, said at least a DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl, or C3-Cs cycloalkyl group, each
optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent groups,
which are
independently selected from the group consisting of C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5
alkenyl, C2-C5
alkynyl, C1-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C1-
C5 alkoxy,
C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl,
aroyl,
aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-
C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-
CS
alkoxycarbonylamino, CI-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, C1-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R' and R` are each independently hydrogen, C1-C5 alkyl, C5-C15 arylalkyl,
or R' and R2 together with the carbon atom they are commonly attached to form
a C3-Cs
Spiro cycloalkyl ring;
(c) B is the carbonyl group or methylene group, which is optionally
independently substituted with one or two substituent groups selected from the
group
consisting of C1-C3 alkyl, hydroxy, and halogen;
(d) R3 is the trifluoromethyl group;
(e) D is absent;
(f) E is the hydroxy group or amino group wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl; and
56
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
(g) Q comprises a 5- to 7-membered heterocyclyl ring fused to a 5- to 7-
membered heteroaryl or heterocyclyl ring, each optionally independently
substituted
with one to three substituent groups, wherein each substituent group of Q is
independently C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl,
heterocyclyl,
aryl, heteroaryl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy,
acyl, C1-C5
alkoxycarbonyl, C1-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl,
dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1 -C5 alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5
dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1 -
C5
alkylsulfonylamino, CI-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaminosulfonyl,
halogen,
hydroxy, carboxy, oxo, cyano, trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy,
trifluoromethylthio,
nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally independently mono- or di-
substituted by C,-C5 alkyl, ureido wherein either nitrogen atom is optionally
independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl, or CI-C5 alkylthio wherein the
sulfur atom is
optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone, wherein each substituent group
of Q is
optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent groups
selected from
the group consisting of C,-C3 alkyl, Ci-C3 alkoxy, C,-C3 alkoxycarbonyl, acyl,
aryl,
benzyl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl, halogen, hydroxy, oxo, cyano, amino wherein
the
nitrogen atom is optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5
alkyl, and
ureido wherein either nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted
with CI-C5
alkyl or trifluoromethyl, wherein Q cannot be I H-[ 1,5]naphthyridin-4-one.
Non-limiting examples of these compounds include 4-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-thieno[3,2-
b]pyridin-
7-one; 4-[4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpenty- I]-
4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 4-[4-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-
2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 1-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-I H-[ 1,6]
naphthyridin-4-
one; I-[4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]- I H-
[ 1,6]naphthyridin-4-one; 4-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 4-[2-hydroxy-4-(5-
methanesulfonyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-
4H-
thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 1-[2-hydroxy-4-(5-methanesulfonyl-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-
7-yl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-[ I,6]naphthyridin-4-one; 1-[4-(5-
fluoro-2-
57
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
methylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]- I H-[
1,6]naphthyridin-4-
one; 4-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-methoxy-3-methylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-
4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 4-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethyIpentyI]-4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 4-[4-(3-bromo-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-thieno[3,2-
b]pyridin-
7-one; 4-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-hydroxy-3-methylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-
4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 4-[4-(3-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-
trifl uoromethylpentyl] -4H-thieno [3,2-b] pyridi n-7 -one; 3-bromo-l-[4-(5-
chloro-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-
[1,6]naphthyridin-4-one; 6-chloro-4-[4-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-
4-
methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 6-bromo-4-[4-
(2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethy]pentyl]-4H-
thieno[3,2-
b]pyridin-7-one; 3-chloro- 1-[4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-
2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-[1,6]naphthyridin-4-one; 1-[4-(5-chloro-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-3-methyl-1
H-
[1,6]naphthyridin-4-one; 1-[4-(5-Chloro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-
4-
methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-3-methyl-IH-[1,7]naphthyridin-4-one; 1-[2-
hydroxy-4-
(2-methoxy-3,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-3-methyl-1 H-
[1,6]naphthyridin-4-one; 1-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-methoxy-3,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-
methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-3-methyl-lH-[ 1,7]naphthyridin-4-one; 1-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-
hydroxy-3,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-3-methyl-]H-
[1,6]naphthyridin-4-one; 1-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-[I,8]naphthyridin-4-one; 1-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
methylphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-[ 1,7]naphthyridin-4-one; 4-[4-(5-
fluoro-
2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpenty- I]-4H-thiazolo[4,5-
b]pyridin-7-one; 4-[4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-oxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-7-one; 4-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
methylphenyl)-
2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-furo[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 7-[4-
(5-
fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-7H-
thieno[2,3-
b]pyridin-4-one; 4-[4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-oxazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-7-one; 4-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-thiazolo[5,4-
58
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
b]pyridin-7-one; 7-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-7H-furo[2,3-b]pyridin-4-one; 4-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
methylphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-methy1-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1,4-dihydropyrrolo[3,2-b]pyridin-7-
one; I-
[4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-
5,6,7,8-
tetrahydro- I H-[ I ,6]naphthyridin-4-one; 1-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-6-methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro- I H-[
1,6]naphthyridin-4-
one; 1-[4-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-
I H-[ I ,8]naphthyridin-4-one; I- [ 2-hydro xy-4-(5 -methane sul fonyl-2,3 -
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-[
1,7]naphthyridin-4-one;
4-[2-hydroxy-4-(5-methanesulfonyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-4- H-thiazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-7-one; 4-[4-(2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-
7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-oxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-7-
one; 4-
[2-hydroxy-4-(5-methanesulfonyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-furo[3,2-bJpyridin-7-one; 7-[4-(2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-
2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-7H-thieno[2,3-b]pyridin-4-one; 4-
[2-
hydroxy-4-(5-methanesulfonyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-oxazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-7-one; 4-[2-hydroxy-4-(5-
methanesulfonyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-
4H-
thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-7-one; 7-[4-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl.]-7H-furo[2,3-b]pyridin-4-one; 4-[4-(2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-
2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentylJ-1,4-dihydropyrrolo[3,2-b]pyridin-7-
one; I-
[2-hydroxy-4-(5-methanesulfonyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-IH-[ 1,6]naphthyridin-4-one; 1-[4-
(2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl) -6-methyl-
5,6,7, 8-
tetrahydro-]H-[ I ,6]naphthyridin-4-one; 1-[4-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-
hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-5-methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-I H-[
1,5]naphthyridin-4-
one; 1-[4-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-5-
methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-IH-[1,5]naphthyridin-4-one; 4-[2-hydroxy-4-(4-
methoxybiphenyl-3-yl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl1-4H-thieno[3,2-
b]pyridin-7-
one; 4-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-methoxy-5-pyridin-3-ylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethyIpentyl]-4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 4-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-
methoxy-5-
pyrimidin-5-ylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-thieno[3,2-
b]pyridin-7-
59
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
one; 4-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-methoxy-5-thiophen-3-ylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 4-[2-hydroxy-4-(4-
hydroxybiphenyl-3-yl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-thieno[3,2-
b]pyridin-7-
one; 4-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-hydroxy-5-pyridin-3-ylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpenty l]-4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 4-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-
hydroxy-5-
pyrimidin-5-ylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-thieno[3,2-
b]pyridin-7-
one; 4-[2-Hydroxy-4-(2-hydroxy-5-thiophen-3-ylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 1-[2-hydroxy-4-(4-
methoxybiphenyl-3-yl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-[ 1,6]naphthyridin-
4-one;
1-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-methoxy-5-pyridin-3-ylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-
1 H-[ 1,6]naphthyridin-4-one; I -[2-hydroxy-4-(2-methoxy-5-pyrimidin-5-
ylphenyl)-4-
methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-[1,6]naphthyridin-4-one; 1-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-
methoxy-5-thiophen-3-ylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]- I H-
[1,6] naphthyridin-4-one- ; 1-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-methoxy-5-thiophen-3-ylphenyl)-4-
methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-[ 1,6]naphthyridin-4-one; 1-[2-hydroxy-4-
(2-
hydroxy-5-pyridin-3-ylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-I H-[ 1,6]
naphthyridin-
4-one; 1-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-hydroxy-5-pyrimidin-5-ylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-[1,6]naphthyridin-4-one; 1-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-hydroxy-5-
thiophen-3-yphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1H-[1,6]naphthyridin-4-
one; 5-
[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-5H-
pyrido[3,2-d]pyrimidin-8-one; 1-[4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-pyrido[2,3-d]pyridazin-4-one; 5-[4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpenty-1]-5H-pyrido[3,2-
c]pyridazin-8-one; 4-[4-(2-fifluoromethoxy-3-methylphenyl- )-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpenty1]-4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 3-chloro-1-[4-(2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]- I H-
[1,6]naphthyridin-4-one; 4-(4-benzo[I,3]dioxol-4-yl-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl)-6-bromo-4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 4-(4-
benzo[1,3]dioxol-
4-y1-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl)-6-chloro-4H-thieno[3,2-
b]pyridin-7-
one; 6-chloro-4-[2-hydroxy-4-methyl-4-(5-pyridin-3-yl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-
yl)-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; I-(4-benzo[I,3]dioxol-4-
y1-2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl)-3-chloro-IH-[1,6]naphthyridin-4-one;
6-
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
chloro-4-[2-hydroxy-4-methyl-4-(5-pyrimidin-5-yl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 3-chloro-l-[2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-
4-(5-pyrimidin-5-yl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-I H-
[1,6]naphthyridin-4-one; 3-chloro-1-[2-hydroxy-4-methyl-4-(5-pyridin-3-yI-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-[1,6]naphthyridin-4-one; 4-
[2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-4-(5-pyrimidin-5-yl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 1-[2-hydroxy-4-methyl-4-
(5-
pyrimidin-5-yl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-
[1,6]naphthyridin-4-one; 6-chloro-4-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-methoxy-5-pyridin-3-
ylphenyl)-4-
methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 6-chloro-4-[2-
hydroxy-
4-(2-methoxy-5-pyrimidin-5-ylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-
thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 6-chloro-4-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-hydroxy-5-pyridin-3-
ylphenyl)-
4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 6-chloro-4-[2-
hydroxy-4-(- 2-hydroxy-5-pyrimidin-5-ylphenyl)-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-
thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 4-(4-biphenyl-3-yl-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoro-
methylpentyl)-6-chloro-4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 4-(4-biphenyl-3-yl-2-
hydroxy-4-
methy1-2-trifluoromethylpentyl)-4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 3-chloro-l-{4-
[5-(5-
chloropyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl]-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl}-1H-[1,6]naphthyridin-4-one; 6-chloro-4-{4-[5-(2,6-
dimethylpyridin-4-yl)-2-methoxyphenyl]-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl }-
4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one- ; 4-[2-hydroxy-4-(2-hydroxy-5-pyridin-2-
ylphenyl)-4-
methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 6-chloro-4-[2-
hydroxy-
4-methyl-4-(5-pyrazin-2-yl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-
thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 3-chloro-1-[2-hydroxy-4-methyl-4-(5-pyrimidin-2-yI-
2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-[1,6]naphthyridin-4-one; 5-
{7-[3-
(6-chloro-7-oxo-7H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-4-ylmethyl)-4,4,- 4-trifluoro-3-
hydroxy-1,1-
dimethylbutyl]-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-5-yl}nicotinonitrile; 4-{4-Methoxy-3-
[4,4,4-
trifluoro-3-hydroxy- I , I -dimethyl-3-(7-oxo-7H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-4-
ylmethyl)butyl]phenyl}pyridine-2-carbonitrile; 6-chloro-4-{4-[5-(2-fluoro-6-
methylpyridin-4-yl)-2-methoxyphenyl]-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl }-
4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; 3-chloro-l-{2-hydroxy-4-[5-(IH-imidazol-4-yl)-
2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl]-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl } - I H-[ 1,6]
naphthyridin-4-
61
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
one; 6-chloro-4-[2-hydroxy-4-methyl-4-(5-morpholin-4-y1-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-
7-y1)-
2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-4H-thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-one; and 1-[2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-4-
(5-piperidin- l-yl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]- I H-
[1,6]naphthyridin-4-one.
In yet another embodiment, said at least a DIGRA has Formula I, wherein A,
B, D, E, R1, and R2 have the meanings disclosed immediately above, and R3 is
hydrogen,
C1-C8 alkyl, C2-C8 alkenyl, C2-C8 alkynyl, carbocycle, heterocyclyl, aryl,
heteroaryl,
carbocycle-C1-C8 alkyl, carboxy, alkoxycarbonyl, aryl-Cl-C8 alkyl, aryl-Ci-C8
haloalkyl,
heterocyclyl-C1-C8 alkyl, heteroaryl-C1-C8 alkyl, carbocycle-C2-C8 alkenyl,
aryl-C2-C8
alkenyl, heterocyclyl-C2-C8 alkenyl, or heteroaryl-C2-C8 alkenyl, each
optionally
independently substituted with one to three substituent groups, wherein each
substituent
group of R3 is independently C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, phenyl, C1-C5 alkoxy, phenoxy, Ci-C5 alkanoyl, aroyl, C1-C5
alkoxycarbonyl,
C1-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5
dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, aminocarbonyl, C1-C5 alkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C5
dialkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5
alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaminosulfonyl,
halogen,
hydroxy, carboxy, cyano, oxo, trifluoromethyl, nitro, amino wherein the
nitrogen atom is
optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl, ureido
wherein either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, CJ-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone,
wherein R3
cannot be trifluoromethyl.
In yet another embodiment, said at least a DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl, or C3-C8 cycloalkyl group, each
optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent groups,
which are
independently selected from the group consisting of C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5
alkenyl, C2-C5
alkynyl, C1-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C1-
C5 alkoxy,
C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynytoxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl,
aroyl,
aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-
C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-
C5
62
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
alkoxycarbonylamino, CS-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, C1-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-CS alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R' and R 2 are each independently hydrogen or C1-C5 alkyl;
(c) R3 is the trifluoromethyl group;
(d) B is C1-C5 alkylene, C2-C5 alkenylene, or C2-C5 alkynylene, each
optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent groups,
wherein each
substituent group of B is independently C1-C3 alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, amino,
or oxo;
(e) D is absent;
(f) E is the hydroxy group; and
(g) Q comprises an indolyl group optionally substituted with one to three
substituent groups, wherein each substituent group of Q is independently C1-C5
alkyl,
C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl,
heteroaryl, C1-C5
alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5
alkoxycarbonyl, C1-C5
alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl,
aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy,
C1-
C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino,
aminosulfonyl, C1-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaminosulfonyl, halogen,
hydroxy, carboxy, cyano, trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy,
trifluoromethylthio, nitro,
amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally independently mono- or di-
substituted by
C1-C5 alkyl, ureido wherein either nitrogen atom is optionally independently
substituted
with C1-C5 alkyl, or C1-C5 alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally
oxidized to a
sulfoxide or sulfone, wherein each substituent group of Q is optionally
independently
63
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
substituted with one to three substituent groups selected from the group
consisting of Ci-
C3 alkyl, C1-C3 alkoxy, halogen, hydroxy, oxo, cyano, amino, and
trifluoromethyl.
Non-limiting examples of these compounds include 4-(5-bromo-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-2-(I H-indol-2-ylmethyl)-4-
methylpentan-2-ol;
1,1,1-trifluoro-2-(1 H-indol-2-ylmethyl)-4-methyl-4-pyridin-2-ylpentan-2-ol; 4-
(2,3-
dihydro-5-cyanobenzofuran-7-yl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-2-(1 H-indol-2-yi-methyl)-4-
methylpentan-2-ol; 4-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-2-(1H-indol-
2-
y1methyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-(5-fluoro-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-
2-(1 H-indol-2-ylmethyl)-4-methylpentan-2-ol; 1,1,1-trifluoro-2-(1 H-indol-2-
ylmethyl)-
4-methyl-4-(5-methyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)pentan-2-ol; 4-(2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-5-yl)-1,1,1-trifluoro-2-(1 H-indol-2-ylmethyl)-4-
methylpentan-2-ol;
2-[4-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-
1H-
indole-3-carbonitrile; 2-[4-(5-fluoro-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-indole-3-carbonitrile; 2-[4-(5-bromo-2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-
7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-indole-3-carbonitrile; 2-
[4-(2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-4-methyl-
i H-
indole-6-carbonitrile; 2-[4-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-
trifluoromethylpentyl]-IH-indole-5-carbonitrile; 4-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-
yl)-1,1,1-
trifluoro-2-(7-fluoro-lH-indol-2-ylmethyl)4-methylpentan-2-ol; 1-[4-(2,3-
dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethylpentyl]-1 H-indole-
3-
carbonitrile; 4-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)- 1, 1, 1 -trifluoro-4-methyl-2-(5-
trifluoromet-
hyl- I H-indol-2-yimethyl)pentan-2-ol; and 1,1,1-trifluoro-2-(1 H-indol-2-
ylmethyl)-4-
methyl-4-thiophen-3-ylpentan-2-ol.
In a further embodiment, said at least a DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl or heteroaryl group, each optionally independently
substituted
with one to three substituent groups, which are independently selected from
the group
consisting of C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C1-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C, C., alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy,
C2-CS
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5
64
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-CS alkanoylamino, CI-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, CI-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, CI-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl, CI-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R' and R2 are each independently hydrogen or CI-C5 alkyl, or R' and R2
together with the carbon atom they are commonly attached to form a C3-C8 Spiro
cycloalkyl ring;
(c) R3 is carbocycle, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle-CI-Cs alkyl,
carboxy, alkoxycarbonyl, aryl-CI-C8 alkyl, aryl-CI-Cs haloalkyl, heterocyclyl-
CI-C8
alkyl, heteroaryl-Cl-C8 alkyl, carbocycle-C2-C8 alkenyl, aryl-C2-C8 alkenyl,
heterocyclyl-C2-C8 alkenyl, or heteroaryl-C2-C8 alkenyl, each optionally
independently
substituted with one to three substituent groups, wherein each substituent
group of R3 is
independently CI-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl,
phenyl, CI-
CS alkoxy, phenoxy, CI-C5 alkanoyl, aroyl, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, CI-C5
alkanoyloxy,
aminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy,
aminocarbonyl, CI-C5 alkylaminocarbonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyl, CI-C5
alkanoylamino, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, CI-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, CI-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaminosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano, oxo,
trifluoromethyl, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally
independently
mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl, ureido wherein either nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl, CI-C5 alkylthio wherein the sulfur
atom is
optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(d) B is the methylene or carbonyl group;
(e) D is the -NH- group;
(f) E is the hydroxy group; and
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
(g) Q comprises the group
0
0
Non-limiting examples of these compounds include 2-benzyl-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-4-phenylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-
hydroxy-4-methyl-2,4-diphenylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-
yl)amide; 2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-phenethyl-4-phenylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-
dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-hydroxy-2-(3-methoxybenzyl)4-methyl-4-
phenylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-hydroxy-2-
(4-
methoxybenzyl)-4-methyl-4-phenylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-l,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-
5-
yl)amide; 2-hydroxy-2-[2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]4-methyl-4-phenylpentanoic
acid (1-
oxo-l,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-cyclohexylmethyl-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-
4-
phenylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-(4-tert-
butylbenzyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-4-phenylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-
dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-biphenyl-4-ylmethyl-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-4-
phenylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-l,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-naphthalen-2-ylmethyl-4-phenylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-
dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxybenzyl)-4-methyl-4-
phenylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-l,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)-4-phenylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-
dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-benzyl-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-
methylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-
cyclohexylmethyl-
4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-
dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-benzyl-4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-
methylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-
cyclohexylmethyl-
4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-
dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-
(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)pentanoic acid (1-oxo- l ,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-
yl)amide;
66
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
2-(2-chloro-6-fluorobenzyl)-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-l,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-(3-
fluorobenzyl)-
4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-
dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-(2-fluorobenzyl)-4-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-
(3,4-
difluorobenzyl)-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid
(1-
oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-(2-chloro-6-fluorobenzyl)-4-(5-
fluoro-2-
hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-
dihydroisobenzofuran-5-
yl)amide; 2-(3-fluorobenzyl)-4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-l,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-(2-
fluorobenzyl)-
4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-
dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-(3,4-difluorobenzyl)-4-(5-fluoro-2-
hydroxyphenyl)-
2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-
(4-
fluorobenzyl)-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid (1-
oxo-
1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-(3-methylbenzyl)pentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-
yl)amide;
2-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic
acid (1-
oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-(3-methylbenzyl)pentanoic acid (I -oxo- I ,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-
yl)amide;
2-(3,5-difluorophenyl)-4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methylpentanoic acid
(1-oxo- l ,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-
4-methyl-2-(2-methylbenzyl)pentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-
yl)amide; 2-(3,5-dimethylbenzyl)-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-l,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-(2,5-
difluorobenzyl)-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid
(1-
oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-(2,5-difluorobenzyl)-4-(5-fluoro-2-
hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid (I-oxo-I,3-
dihydroisobenzofuran-5-
yl)amide; 4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-(2-
methylbenzyl)pentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-(3,5-
dimethylbenzyl)-4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid
(I-
oxo-I,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-(3-chlorobenzyl)-4-(5-fluoro-2-
hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-I,3-
dihydroisobenzofuran-5-
67
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
yl)amide; 4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-2-[2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]-
4-
methylpentanoic acid (I -oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 4-(5-fluoro-
2-
methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-2-(2-methoxybenzyl)4-methylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-
dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-
phenethylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-(2-
chlorobenzy 1)-4-(5-fl uoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-me thylpentanoic acid
(1-oxo-
1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-2-phenethylpentanoic acid (I -oxo- 1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide;
4-(5-
fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-2-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl]-4-
methylpentanoic
acid (1-oxo-l,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-(2-chlorobenzyl)-4-(5-
fluoro-2-
hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-
dihydroisobenzofuran-5-
yl)amide; 4-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-2-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-4-
methylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-(2-
bromobenzyl)-
4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-
dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-(2-bromobenzyl)-4-(5-fluoro-2-
hydroxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-
(5-
fluoro-2-methoxybenzyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-4-phenylpentanoic acid (I -oxo- 1,3-
dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxybenzyl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-4-
phenylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxybenzyl)-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid
(1-
oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxybenzyl)-4-(5-
fluoro-2-
hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-
dihydroisobenzofuran-5-
yl)amide; 2-(3,5-dimethoxybenzyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-4-phenylpentanoic acid (I-
oxo-
1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-(3,5-dihydroxybenzyl)-2-hydroxy-4-
methyl-4-
phenylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)- amide; 2-hydroxy-2-
(2-
methoxybenzyl)4-methyl-4-phenylpentanoic acid (1-oxo- l ,3-
dihydroisobenzofuran-5-
yl)amide; 12-hydroxy-2-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-4-methyl-4-phenylpentanoic acid (1-
oxo-
1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-hydroxy-2-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl]-4-
methyl-4-phenylpentanoic acid (1-oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 15-
[2-
benzyl-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentylamino]-3H-
isobenzofuran-l-one; 4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-(I-
phenylvinyl)pentanoic acid (1-oxo- l ,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-
hydroxy-4-
68
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
methyl-4-phenyl-2-pyridin-2-ylmethylpentanoic acid(I-oxo-1,3-
dihydroisobenzofuran-5-
yl)amide; 4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-(1-phenylethyl-
)pentanoic acid(1-oxo-l,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 4-(5-fluoro-2-
hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-(I -phenylethyl)pentanoic acid( I -oxo-
1,3-
dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-cyclopentyl-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-
hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid(I -oxo- I ,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-
cyclopentyl-4-(5-fl uoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid(I-
oxo-
1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)amide; 2-cyclopentylmethyl-4-(5-fluoro-2-
hydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid(1-oxo-l,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-
5-
yl)amide; and2-benzyl-2-hydroxy-N-(1-oxo-1,3-dihydroisobenzofuran-5-yl)4-
phenyl-
butyramide.
In still another embodiment, said at least a DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl or heteroaryl group, each optionally independently
substituted
with one to three substituent groups, which are independently selected from
the group
consisting of C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C1-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-
C5
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, C1-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R1 and R2 are each independently hydrogen or C1-C5 alkyl, or R' and R2
together with the carbon atom they are commonly attached to form a C3-C8 Spiro
cycloalkyl ring;
(c) R3 is the trifluoromethyl group;
69
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
(d) B is C1-C5 alkylene, C2-C5 alkenylene, or C2-C5 alkynylene, each
optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent groups,
wherein each
substituent group of B is independently C1-C3 alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, amino,
or oxo;
(e) D is absent;
(f) E is -NR6R7, wherein R6 and R7 are each independently hydrogen, C1-C8
alkyl, C2-C8 alkenyt, C2-C8 alkynyl, C1-C8 alkoxy, C2-C8 alkenyloxy, C2-C8
alkynyloxy,
hydroxy, carbocyclyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, aryloxy, acyl, heteroaryl,
carbocycle-C1-C8
alkyl, aryl-Ci-C8 alkyl, aryl-C1-C8 haloalkyl, heterocyclyl-C1-C8 alkyl,
heteroaryl-C1-C8
alkyl, carbocycle-C2-C8 alkenyl, aryl-C2-C8 alkenyl, heterocyclyl-C2-C8
alkenyl,
heteroaryl-C2-Cs alkenyt, or C1-C5 alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is
oxidized to a
sulfoxide or sulfone, each optionally independently substituted with one to
three
substituent groups, wherein each substituent group of R6 and R7 are
independently C1-C5
alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, phenyl, C1-C5 alkoxy,
phenoxy,
C1-C5 alkanoyl, aroyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, C1-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyl,
C1-C5
alkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, C1-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaminosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano, oxo,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl, ureido wherein either
nitrogen
atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, or C1-C5
alkylthio wherein
the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone; and
(g) Q comprises a heteroaryl group optionally independently substituted with
one to three substituent groups, wherein each substituent group of Q is
independently C1-
C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl,
heteroaryl,
C1-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5
alkoxycarbonyl,
C1-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyl, C1-C5 alkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C5
dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5
dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5
alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, C1-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
dialkylaminosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy, cyano, trifluoromethyl,
trifluoromethoxy, trifluoromethylthio, nitro, or amino wherein the nitrogen
atom is
optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl; or ureido
wherein
either nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl;
or CI-CS
alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or
sulfone,
wherein each substituent group of Q is optionally independently substituted
with one to
three substituent groups selected from CI-C3 alkyl, CI-C3 alkoxy, halogen,
hydroxy, oxo,
cyano, amino, or trifluoromethyl.
Non-limiting examples of these compounds include 3-(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-
phenyl)-3-methyl-l-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-I-trifluoromethyl-butylamine; 3-(5-
fluoro-2-
methoxy-phenyl)-1-(I H-indol-2-ylmethyl)-3-methyl- l -trifluoromethyl-
butylamine; 1-
(2,6-dichloro-pyridin-4-ylmethyl)-3-(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-3-methyl- l-
trifluoromethyl-butylamine; 1-(4,6-dimethyl-pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-3-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxy-phenyl)-3-methyl-l-trifluoromethyl-butylamine; 1-(2-chloro-pyridin-4-
ylmethyl)-3-(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-3-methyl-I-trifluoromethyl-butylamine;
3-(5-
fluoro-2-methyl-phenyl)-3-methyl- I -(3-methyl-1 H-indol-2-ylmethyl)-1-
trifluoromethyl-
butylamine; 3-(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-3-methyl-l-(3-methyl-lH-indol-2-
ylmethyl)-1-trifluoromethyl-butylamine; 1-(6-fluoro-lH-indol-2-ylmethyl)-3-(5-
fluoro-
2-methoxy-phenyl)-3-methyl-I-trifluoromethyl-butylamine; 3-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-3-
methyl- I -(3-methyl- I H-indol-2-ylmethyl)- I -trifluoro-methyl-butylamine; 3-
benzofuran-
7-yl-1-(2,6-dichloro-pyridin-4-ylmethyl)-3-methyl-l-trifluoromethyl-buty
lamine; 3-(2,3-
dihydro-benzofuran-7-yl)- 1-(6-fluoro- I H-indol-2-ylmethyl)-3-methyl- l -
trifluoromethyl-
butylamine; 3-(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-3-methyl-l-quinolin-4-ylmethyl-l-
trifluoromethyl-buty lamine; 1-(2-chloro-quinolin-4-ylmethyl)-3-(5-fluoro-2-
methyl-
phenyl)-3-methyl-l-trifluoromethyl-butylamine; 3-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-3-methyl-l-
quinolin-4-ylmethyl-l-trifluoromethyl-butylamine; 7-[3-amino-3-(IH-
benzoimidazol-2-
ylmethyl)-4,4,4-trifluoro-1,1-dimethyl-butyl]-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-5-
carbonitrile; I-
(6-fluoro-I H-benzoimidazol-2-ylmethyl)-3-(5-fluoro-2-methyl-phenyl)-3-methyl-
l-
trifluoromethyl-butylamine; 2-[3-amino-3-(I H-benzoimidazol-2-ylmethyl)-4,4,4-
trifluoro-],1-dimethyl-butyl]4-fluoro-phenol; 1-(1H-benzoimidazol-2-ylmethyl)-
3-(4-
fluoro-phenyl)-3-methyl-l-trifluoromethyl-butylamine; I-(IH-indol-2-ylmethyl)-
3-meth-
yl-3-pyridin-3-yl-I-trifluoromethyl-butylamine; 1-(1 H-benzoimidazol-2-
ylmethyl)-3-
71
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
methyl-3-pyridin-4-yl-I-trifluoromethyl-butylamine; 3-methyl-l-(3-methyl-IH-
indol-2-
ylmethyl)-3-pyridin-3-yl-I-trifluoromethyl-butylamine; 1-(6-fluoro-IH-indol-2-
ylmethyl)-3-methyl-3-pyridin-3-yl-I-trifluoromethyl-butylamine; 3-(2,3-dihydro-
benzofuran-7-yl)-1-(I H-indol-2-ylmethyl)-3-methyl- I -trifluoromethyl-
butylamine; [3-
(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-3-methyl- I-quinolin-4-ylmethyl- I -
trifluoromethyl-butyl]-
methyl-amine; ethyl-[3-(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-3-methyl-I-quinolin-4-
ylmethyl-l-
trifluoromethyl-butyl]-amine; [3-(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-3-methyl-I-
quinolin-4-
ylmethyl-I-trifluoromethyl-butyl]-propylamine; [3-(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-
3-
methyl-I-quinolin-4-ylmethyl-l-trifluoromethyl-butyl]-isobutylamine; butyl-[3-
(5-
fluoro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-3-methyl- l -quinolin-4-ylmethyl- I -trifluoromethyl-
butyl]-
amine; [3-(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-3-methyl- I -quinolin-4-ylmethyl- I -
trifluoro-
methyl-butyl]-dime thylamine; N-[3-(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-3-methyl-l-
quinolin-
4-ylmethyl-1-trifluoromethyl-butyl]-acetamide; N-[3-(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-
phenyl)-3-
methyl- I -qu inolin-4-yl methyl- I -trifluoromethyl-butyl] -form amide; N-[3-
(5-fluoro-2-
methoxy-phenyl)-3-methyl- I -quinolin-4-ylmethyl- l -trifluoromethyl-butyl]-
methanesulfonamide; ]-(2,6-dimethyl-pyridin-4-ylmethyl)-3-(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-
phenyl)-3-methyl-l-trifluoromethyl-butylamine; 3-(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-3-
methyl-l-(IH-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-I-trifluoromethyl-butylamine; 2-
[2-
amino-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-4-methyl-2-trifluoromethyl-pentyl]-4-
methyl- I H-
indole-6-carbonitrile; N-[3-(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-3-methyl- I -quinolin-
4-
ylmethyl- l-trifluoromethyl-butyl]-hydroxylamine; and 2-(3-amino-4,4,4-
trifluoro- 1, 1 -
dimethyl-3-quinolin-4-ylmethyl-butyl)-4-fluoro-phenol.
In yet another embodiment, said at least a DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
A, B, D, E, R', R2, R6, and R7 have the meanings disclosed immediately above,
and R3 is
CI-C8 alkyl, C2-C8 alkenyl, C2-C8 alkynyl, carbocycle, heterocyclyl, aryl,
heteroaryl,
carbocycle-Ci-Cg alkyl, carboxy, alkoxycarbonyl, aryl-C,-C8 alkyl, aryl-Ci-Cs
haloalkyl,
heterocyclyl-C,-Cg alkyl, heteroaryl-Cl-Cg alkyl, carbocycle-C2-CB alkenyl,
aryl-C2-Cs
alkenyl, heterocyclyl-C2-C8 alkenyl, or heteroaryl-C2-C8 alkenyl, each
optionally
independently substituted with one to three substituent groups, wherein each
substituent
group of R3 is independently C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, phenyl, C[-C5 alkoxy, phenoxy, C1-Cs alkanoyl, aroyl, C1-C5
alkoxycarbonyl,
CI-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5
72
CA 02699599 2012-02-07
dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, aminocarbonyl, C1-C5 alkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C5
dialkylaminocarbonyl, CI-C5 alkanoylamino, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, Cl-C5
alkylsulfonylamino, CI-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, C1 -CS dialkylaminosulfonyl,
halogen,
hydroxy, carboxy, cyano, oxo, trifluoromethyl, nitro, amino wherein the
nitrogen atom is
optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl, ureido
wherein either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone,
wherein R3
cannot be trifluoromethyl.
Non-limiting examples of these compounds include 1-(2,6-dichloro-pyridin-
4-ylmethyl)-3-(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-butylamine; I-ethyl-3-
(5-
fluoro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-3-methyl-l-quinolin-4-ylmethyl-butylamine; 1-
cyclohexylmethyl-3-(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-1-(1H-indol-2-ylmethyl)-3-
methyl-
butylamine; I-(2-chloro-quinolin-4-ylmethyl)-1-cyclopentyl-3-(5-fluoro-2-
methoxy-
phenyl)-3-methyl-butylamine; 1-(2-chloro-pyridin-4-ylmethyl)-1-
cyclopentylmethyl-3-
(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-3-methyl-butylamine; 3-(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-
1,3-
dimethyl-l-quinolin-4-ylmethyl-butylamine; 1-cyclopropyl-3-(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-
phenyl)-3-methyl- I -quinolin-4-ylmethyl-butylamine; 3-(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-
phenyl)-
1,3-dimethyl-I-(1H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-butylamine; I-cyclopropyl-
3-(5-
fluoro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-3-methyl- I -(I H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]-pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-
butylamine; 2-[3-amino-1,1,3-timethyl-4-(lH-pyrrolo[2,3-cJpyridin-2-yl)-butyl]-
4-
fluoro-phenol; 2-[2-amino-4-(5-fluoro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-2,4-dimethyl-pentyl]-4-
methyl-1 H-indole-6-carbonitrile.
Other compounds that can function as DIGRAs and methods for their
manufacture are disclosed, for example, in U.S. Patent Application
Publications
2004/0029932, 2004/0162321, 2004/0224992, 2005/0059714, 2005/0176706,
2005/0203128, 2005/0234091, 2005/0282881, 2006/00 1 47 8 7, 2006/0030561, and
2006/0 1 1 6396
In another aspect, the present invention provides an ophthalmic
pharmaceutical composition for pharmacological adjunctive treatment associated
with
glaucoma filtration surgery. The ophthalmic pharmaceutical composition
comprises at
73
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
least a DIGRA, a prodrug thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof,
or a
pharmaceutically acceptable ester thereof.
In still another aspect, the ophthalmic pharmaceutical composition
comprises: (a) at least a DIGRA, a prodrug thereof, a pharmaceutically
acceptable salt
thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable ester thereof; and (b) an antagonist
to a TGF-(3
isoform. In one embodiment, the TGF-(3 isoform is selected from the group
consisting of
TGF-(31, TGF-(32, and combinations thereof. In another embodiment, the
pharmaceutical
composition further comprises a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. In
another aspect,
said carrier is an ophthalmically acceptable carrier.
The concentration of a DIGRA, a prodrug thereof, a pharmaceutically
acceptable salt thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable ester thereof in
such an
ophthalmic composition can be in the range from about 0.0001 to about 1000
mg/ml (or,
alternatively, from about 0.001 to about 500 mg/ml, or from about 0.001 to
about 300
mg/ml, or from about 0.001 to about 250 mg/ml, or from about 0.001 to about
100
mg/ml, or from about 0.001 to about 50 mg/ml, or from about 0.01 to about 300
mg/ml,
or from about 0.01 to about 250 mg/ml, or from about 0.01 to about 100 mg/ml,
or from
about 0.1 to about 100 mg/ml, or from about 0.1 to about 50 mg/ml).
In one embodiment, an ophthalmic composition of the present invention is in
a form of a suspension or dispersion. In another embodiment, the suspension or
dispersion is based on an aqueous solution. For example, a composition of the
present
invention can comprise sterile saline solution. In still another embodiment,
micrometer-
or manometer-sized particles of a DIGRA, or prodrug thereof, a
pharmaceutically
acceptable salt thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable ester thereof and an
anti-
inflammatory agent can be coated with a physiologically acceptable surfactant
(non-
limiting examples are disclosed below), then the coated particles are
dispersed in a liquid
medium. The coating can keep the particles in a suspension. Such a liquid
medium can
be selected to produce a sustained-release suspension. For example, the liquid
medium
can be one that is sparingly soluble in the ocular environment into which the
suspension
is administered. In still another embodiment, the active ingredient or
ingredients are
suspended or dispersed in a hydrophobic medium, such as an oil.
74
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
The DIGRA and the antagonist to at least a TGF-(3 isoform are present in
amounts effective to reduce the risk of having a non- or poorly functioning
filtering bleb
following GFS, when a composition of the present invention is administered to
a patient,
as a pharmacological treatment associated with said GFS.
In yet another aspect, a composition of the present invention further
comprises an NSAID.
In a further aspect, a composition of the present invention comprises: (a) at
least a DIGRA, a prodrug thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof,
or a
pharmaceutically acceptable ester thereof; and (b) an NSAID.
Non-limiting examples of the NSAIDs are: aminoarylcarboxylic acid
derivatives (e.g., enfenamic acid, etofenamate, flufenamic acid, isonixin,
meclofenamic
acid, mefenamic acid, niflumic acid, talniflumate, terofenamate, tolfenamic
acid),
arylacetic acid derivatives (e.g., aceclofenac, acemetacin, alclofenac,
amfenac,
amtolmetin guacil, bromfenac, bufexamac, cinmetacin, clopirac, diclofenac
sodium,
etodolac, felbinac, fenclozic acid, fentiazac, glucametacin, ibufenac,
indomethacin,
isofezolac, isoxepac, lonazolac, metiazinic acid, mofezolac, oxametacine,
pirazolac,
proglumetacin, sulindac, tiaramide, tolmetin, tropesin, zomepirac),
arylbutyric acid
derivatives (e.g., bumadizon, butibufen, fenbufen, xenbucin), arylcarboxylic
acids (e.g.,
clidanac, ketorolac, tinoridine), arylpropionic acid derivatives (e.g.,
alminoprofen,
benoxaprofen, bermoprofen, bucloxic acid, carprofen, fenoprofen,
flunoxaprofen,
flurbiprofen, ibuprofen, ibuproxam, indoprofen, ketoprofen, loxoprofen,
naproxen,
oxaprozin, piketoprolen, pirprofen, pranoprofen, protizinic acid, suprofen,
tiaprofenic
acid, ximoprofen, zaltoprofen), pyrazoles (e.g., difenamizole, epirizole),
pyrazolones
(e.g., apazone, benzpiperylon, feprazone, mofebutazone, morazone,
oxyphenbutazone,
phenylbutazone, pipebuzone, propyphenazone, ramifenazone, suxibuzone,
thiazolinobutazone), salicylic acid derivatives (e.g., acetaminosalol,
aspirin, benorylate,
bromosaligenin, calcium acetylsalicylate, diflunisal, etersalate, fendosal,
gentisic acid,
glycol salicylate, imidazole salicylate, lysine acetylsalicylate, mesalamine,
morpholine
salicylate, l-naphthyl salicylate, olsalazine, parsalmide, phenyl
acetylsalicylate, phenyl
salicylate, salacetamide, salicylamide o-acetic acid, salicylsulfuric acid,
salsalate,
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
sulfasalazine), thiazinecarboxamides (e.g., ampiroxicam, droxicam, isoxicam,
lornoxicam, piroxicam, tenoxicam), s-acetamidocaproic acid, S-(5'-adenosyl)-L-
methionine, 3-amino-4-hydroxybutyric acid, amixetrine, bendazac, benzydamine,
a-
bisabolol, bucolome, difenpiramide, ditazol, emorfazone, fepradinol,
guaiazulene,
nabumetone, nimesulide, oxaceprol, paranyline, perisoxal, proquazone,
superoxide
dismutase, tenidap, zileuton, their physiologically acceptable salts,
combinations thereof,
and mixtures thereof.
The concentration of such an NSAID in such an ophthalmic composition can
be in the range from about 0.0001 to about 1000 mg/ml (or, alternatively, from
about
0.001 to about 500 mg/ml, or from about 0.001 to about 300 mg/ml, or from
about 0.001
to about 250 mg/ml, or from about 0.001 to about 100 mg/ml, or from about
0.001 to
about 50 mg/m1, or from about 0.01 to about 300 mg/ml, or from about 0.01 to
about 250
mg/ml, or from about 0.01 to about 100 mg/ml, or from about 0.1 to about 100
mg/ml, or
from about 0.1 to about 50 mg/ml).
In a further aspect, a composition of the present invention comprises: (a) at
least a DIGRA, a prodrug thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof,
or a
pharmaceutically acceptable ester thereof; and (b) a PPAR ligand.
In one aspect of the present invention, the PPAR ligand is a PPAR-binding
molecule. In one embodiment, such a PPAR-binding molecule is a PPARa-, PPARB-,
or
PPARy-binding molecule. In another embodiment, such a PPAR-binding molecule is
a
PPARa, PPARB, or PPARy agonist. Such a PPAR ligand binds to and activates PPAR
to
modulate the expression of genes containing the appropriate peroxisome
proliferator
response element in its promoter region.
PPARy agonists can inhibit the production of TNF-a and other inflammatory
cytokines by human macrophages (C-Y. Jiang et al., Nature, Vol. 391, 82-86
(1998)) and
T lymphocytes (A.E. Giorgini et al., Horm. Metab. Res. Vol. 31, 1-4 (1999)).
Such
TNF-a and other inflammatory cytokines are discussed elsewhere herein and
shown to
stimulate the production of, or activate a cascade involving, TGF-(3 isoforms.
More
recently, the natural PPARy agonist 15-deoxy-4-12,14-prostaglandin J2 (or "I5-
deoxy-
76
CA 02699599 2012-02-07
A-12,14-PG J2"), has been shown to inhibit neovascularization and angiogenesis
(X. Xin
et al., J. Biol. Chem. Vol. 274:9116-9121 (1999)) in the rat cornea.
Spiegelman et al., in
U.S. Patent 6,242,196, disclose methods for inhibiting proliferation of PPARy-
responsive hyperproliferative cells by using PPARy agonists; numerous
synthetic PPARy
agonists are disclosed by Spiegelman et al., as well as methods for diagnosing
PPARy-
responsive hyperproliferative cells.
PPARs are differentially expressed in diseased versus normal cells. PPARy is
expressed to different degrees in the various tissues of the eye, such as some
layers of the
retina and the cornea, the choriocapillaris, uveal tract, conjunctival
epidermis, and
intraocular muscles (see, e.g., U.S. Patent 6,316,465).
In one aspect, a PPARy agonist used in a composition or a method of the
present invention is a thiazolidinedione, a derivative thereof, or an analog
thereof. Non-
limiting examples of thiazolidinedione-based PPARy agonists include
pioglitazone,
troglitazone, ciglitazone, englitazone, rosiglitazone, and chemical
derivatives thereof.
Other PPARy agonists include Clofibrate (ethyl 2-(4-chlorophenoxy)-2-
methylpropionate), clofibric acid (2-(4-chlorophenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic
acid), GW
1929 (N-(2-benzoylphenyl)-O-{2-(methyl-2-pyridinylamino)ethyl }-L-tyrosine),
GW
7647 (2-((4-(2-f {(cyclohexylamino)carbonyl}(4-
cyclohexylbutyl)amino}ethyl}phenyl}thio)-2-methylpropanoic acid), and WY 14643
(({4-chloro-6-((2,3-dimethylphenyl)amino}-2-pyrimidinyl)thio}acetic acid). GW
1929,
GW 7647, and WY 14643 are commercially available, for example, from Koma
Biotechnology, Inc. (Seoul, Korea). In one embodiment, the PPARy agonist is 15-
deoxy-A-12, 14-PG 12.
Non-limiting examples of PPAR-a agonists include the fibrates, such as
fenofibrate and gemfibrozil. A non-limiting example of PPAR-6 agonist is
GW501516
(available from Axxora LLC, San Diego, California or EMD Biosciences, Inc.,
San
Diego, California).
In another aspect, a composition of the present invention can further
comprise a non-ionic surfactant, such as polysorbates (such as polysorbate 80
(polyoxyethylene sorbitan monooleate), polysorbate 60 (polyoxyethylene
sorbitan
77
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
monostearate), polysorbate 20 (polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurate), commonly
known by their trade names of Tween 80, Tween R 60, Tween R 20), poloxamers
(synthetic block polymers of ethylene oxide and propylene oxide, such as those
commonly known by their trade names of Pluronic ; e.g., Pluronic F127 or
Pluronic
F108) ), or poloxamines (synthetic block polymers of ethylene oxide and
propylene
oxide attached to ethylene diamine, such as those commonly known by their
trade names
of Tetronic ; e.g., Tetronic 1508 or Tetronic 908, etc., other nonionic
surfactants
such as Brij , Myrj , and long chain fatty alcohols (i.e., oleyl alcohol,
stearyl alcohol,
myristyl alcohol, docosohexanoyl alcohol, etc.) with carbon chains having
about 12 or
more carbon atoms (e.g., such as from about 12 to about 24 carbon atoms). Such
compounds are delineated in Martindale, 34th ed., pp. 1411-1416 (Martindale,
"The
Complete Drug Reference," S. C. Sweetman (Ed.), Pharmaceutical Press, London,
2005)
and in Remington, "The Science and Practice of Pharmacy," 21 Pt Ed., p. 291
and the
contents of chapter 22, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, New York, 2006); the
contents
of these sections are incorporated herein by reference. The concentration of a
non-ionic
surfactant, when present, in a composition of the present invention can be in
the range
from about 0.001 to about 5 weight percent (or alternatively, from about 0.01
to about 4,
or from about 0.01 to about 2, or from about 0.01 to about I, or from about
0.01 to about
0.5 weight percent).
In addition, a composition of the present invention can include additives such
as buffers, diluents, carriers, adjuvants, or other excipients. Any
pharmacologically
acceptable buffer suitable for application to the eye may be used. Other
agents may be
employed in the composition for a variety of purposes. For example, buffering
agents,
preservatives, co-solvents, oils, humectants, emollients, stabilizers, or
antioxidants may
be employed. Water-soluble preservatives which may be employed include sodium
bisulfite, sodium bisulfate, sodium thiosulfate, benzalkonium chloride,
chlorobutanol,
thimerosal, ethyl alcohol, methylparaben, polyvinyl alcohol, benzyl alcohol,
and
phenylethyl alcohol. These agents may be present in individual amounts of from
about
0.001 to about 5% by weight (preferably, about 0.0 1% to about 2% by weight).
Suitable
water-soluble buffering agents that may be employed are sodium carbonate,
sodium
borate, sodium phosphate, sodium acetate, sodium bicarbonate, etc., as
approved by the
United States Food and Drug Administration ("US FDA") for the desired route of
78
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
administration. These agents may be present in amounts sufficient to maintain
a pH of
the system of between about 2 and about 11. As such, the buffering agent may
be as
much as about 5% on a weight to weight basis of the total composition.
Electrolytes
such as, but not limited to, sodium chloride and potassium chloride may also
be included
in the formulation.
In one aspect, the pH of the composition is in the range from about 4 to about
11. Alternatively, the pH of the composition is in the range from about 5 to
about 9,
from about 6 to about 9, or from about 6.5 to about 8. In another aspect, the
composition
comprises a buffer having a pH in one of said pH ranges.
In another aspect, the composition has a pH of about 7. Alternatively, the
composition has a pH in a range from about 7 to about 7.5.
In still another aspect, the composition has a pH of about 7.4.
In yet another aspect, a composition also can comprise a viscosity-modifying
compound designed to facilitate the administration of the composition into the
subject or
to promote the bioavailability in the subject. In still another aspect, the
viscosity-
modifying compound may be chosen so that the composition is not readily
dispersed
after being administered into an environment of an eye. Such compounds may
enhance
the viscosity of the composition, and include, but are not limited to:
monomeric polyols,
such as, glycerol, propylene glycol, ethylene glycol; polymeric polyols, such
as,
polyethylene glycol; various polymers of the cellulose family, such as
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose ("HPMC" ), carboxymethyl cellulose ("CMC")
sodium,
hydroxypropyl cellulose ("HPC"); polysaccharides, such as hyaluronic acid and
its salts,
chondroitin sulfate and its salts, dextrans, such as, dextran 70; water
soluble proteins,
such as gelatin; vinyl polymers, such as, polyvinyl alcohol,
polyvinylpyrrolidone,
povidone; carbomers, such as carbomer 934P, carbomer 941, carbomer 940, or
carbomer
974P; and acrylic acid polymers. In general, a desired viscosity can be in the
range from
about I to about 400 centipoises ("cps") or mPa.s.
79
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
In still another aspect, a method for preparing a composition of the present
invention comprises combining: (i) at least a DIGRA, a prodrug thereof, a
pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable
ester thereof;
and (ii) a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
In yet another aspect, a method for preparing a composition of the present
invention comprises combining: (i) at least a DIGRA, a prodrug thereof, a
pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable
ester thereof;
and (ii) an antagonist to at least a TGF-{3 isoform; and (iii) a
pharmaceutically acceptable
carrier. In one embodiment, such a carrier can be a sterile saline solution or
a
physiologically acceptable buffer. In another embodiment, such a carrier
comprises a
hydrophobic medium, such as a pharmaceutically acceptable oil. In still
another
embodiment, such as carrier comprises an emulsion of a hydrophobic material
and water.
Physiologically acceptable buffers include, but are not limited to, a
phosphate buffer or a Tris-HCI buffer (comprising
tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane
and HCI). For example, a Tris-HCI buffer having pH of 7.4 comprises 3 g/l of
tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane and 0.76 g/l of HCI. In yet another aspect,
the buffer
is l OX phosphate buffer saline ("PBS") or 5X PBS solution.
Other buffers also may be found suitable or desirable in some circumstances,
such as buffers based on HEPES (N-12-hydroxyethyl }peperazine-N'-{2-
ethanesulfonic
acid)) having pKa of 7.5 at 25 C and pH in the range of about 6.8-8.2; BES
(N,N-bis { 2-
hydroxyethyl }2-aminoethanesulfonic acid) having pKa of 7.1 at 25 C and pH in
the
range of about 6.4-7.8; MOPS (3-{N-morpholino}propanesulfonic acid) having pKa
of
7.2 at 25 C and pH in the range of about 6.5-7.9; TES (N-tris{hydroxymethyl}-
methyl-
2-aminoethanesulfonic acid) having pKa of 7.4 at 25 C and pH in the range of
about 6.8-
8.2; MOBS (4-{N-morpholinoIbutanesulfonic acid) having pKa of 7.6 at 25 C and
pH in
the range of about 6.9-8.3; DIPSO (3-(N,N-bis{2-hydroxyethyl}amino)-2-
hydroxypropane) ) having pKa of 7.52 at 25 C and pH in the range of about 7-
8.2;
TAPSO (2-hydroxy-3 { tris(hydroxymethyl)methylamino }-1-propanesulfonic acid)
)
having pKa of 7.61 at 25 C and pH in the range of about 7-8.2; TAPS ({(2-
hydroxy-1,1-
bis(hydroxymethyl)ethyl)amino}- I-propanesulfonic acid)) having pKa of 8.4 at
25 C
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
and pH in the range of about 7.7-9.1; TABS (N-tris(hydroxymethyl)methyl-4-
aminobutanesulfonic acid) having pKa of 8.9 at 25 C and pH in the range of
about 8.2-
9.6; AMPSO (N-(l, I -dimethyl-2-hydroxyethyl)-3-amino-2-hydroxypropanesulfonic
acid)) having pKa of 9.0 at 25 C and pH in the range of about 8.3-9.7; CHES (2-
cyclohexy lamino)ethanesulfonic acid) having pKa of 9.5 at 25 C and pH in the
range of
about 8.6-10.0; CAPSO (3-(cyclohexylamino)-2-hydroxy- I -propane sulfonic
acid)
having pK,a of 9.6 at 25 C and pH in the range of about 8.9-10.3; or CAPS (3-
(cyclohexylamino)- 1-propane sulfonic acid) having pKa of 10.4 at 25 C and pH
in the
range of about 9.7-11.1.
In certain embodiments, a composition of the present invention is formulated
in a buffer having an acidic pH, such as from about 4 to about 6.8, or
alternatively, from
about 5 to about 6.8. In such embodiments, the buffer capacity of the
composition
desirably allows the composition to come rapidly to a physiological pH after
being
administered into the patient.
It should be understood that the proportions of the various components or
mixtures in the following examples may be modified for the appropriate
circumstances.
EXAMPLE 1
Two mixtures I and II are made separately by mixing the ingredients listed in
Table 1. Five parts (by weight) of mixture I are mixed with one part (by
weight) of
mixture II for 15 minutes or more. The pH of the combined mixture is adjusted
to 6.2-
6.4 using I N NaOH or I N HCl to yield a composition of the present invention.
81
CA 02699599 2012-02-07
Table I
Ingredient Amount
Mixture I
Carbopol TM 934P NF 0.25 g
Purified water 99.75 g
Mixture 11
Propylene glycol 5g
EDTA 0.1 mg
Compound of Formula IV HCI 0.5 g
Alternatively, purified water may be substituted with an oil, such as fish-
liver
oil, peanut oil, sesame oil, coconut oil, sunflower oil, corn oil, or olive
oil to produce an
oil-based formulation comprising a compound of Formula IV.
EXAMPLE 2
Two mixtures I and II are made separately by mixing the ingredients listed in
Table 2. Five parts (by weight) of mixture I are mixed with two parts (by
weight) of
mixture II for 15 minutes or more. The pH of the combined mixture is adjusted
to 6.2-
6.4 using 1 N NaOH or 1 N HCI to yield a composition of the present invention.
Table 2
Ingredient Amount
Mixture I
Diclofenac TM 0.3g
Carbopol TM 934P NF 0.25 g
Purified water 99.25 g
Mixture II
Propylene glycol 5g
EDTA 0.1 mg
Compound of Formula IV 0.5 g
82
CA 02699599 2012-02-07
Alternatively, purified water may be substituted with an oil, such as fish-
liver
oil, peanut oil, sesame oil, coconut oil, sunflower oil, corn oil, or olive
oil to produce an
oil-based formulation comprising a compound of Formula IV.
EXAMPLE 3
Two mixtures I and II are made separately by mixing the ingredients listed in
Table 3. Five parts (by weight) of mixture I are mixed with two parts (by
weight) of
mixture II for 15 minutes or more. The pH of the combined mixture is adjusted
to 6.2-
6.4 using 1 N NaOH or 1 N HCl to yield a composition of the present invention.
Table 3
Ingredient Amount
Mixture I
TGF-(3 antibody ab300838 (from 0.2g
Abcam, Inc.)
Carbopol TAI 934P NF 0.25 g
Purified water 99.35 g
Mixture II
Propylene glycol 3 g
Compound of Formula II 0.25 g
EDTA 0.1 mg
EXAMPLE 4:
Two mixtures I and II are made separately by mixing the ingredients listed in
Table 4. Five parts (by weight) of mixture I are mixed with one part (by
weight) of
mixture II for 15 minutes or more. The pH of the combined mixture is adjusted
to 6.2-
6.4 using I N NaOH or I N HCl to yield a composition of the present invention.
83
CA 02699599 2012-02-07
Table 4
Ingredient Amount
Mixture I
CAT-152 TGF-0 antibody (disclosed 0.3g
in A.L. Mead, et al., supra)
Carbopol IM 934P NF 0.25 g
Olive oil 99.15 g
Mixture II
Propylene glycol 7 g
Glycerin 3 g
Compound of Formula III I g
HAP (30%) 0.5 mg
Alexidine 2HC1 1-2 ppm
Note: "HAP" denotes hydroxyalkyl phosphonates, such as those known under the
trade
name Dequest .
EXAMPLE 5:
The ingredients listed in Table 5 are mixed together for at least 15 minutes.
The pH of the mixture is adjusted to 6.2-6.4 using I N NaOH or I N HCl to
yield a
composition of the present invention.
Table 5
Ingredient Amount (% by weight, except where
"ppm" is indicated)
Povidone 1
HAP (30%) 0.05
Glycerin 3
Propylene glycol 3
Compound of Formula IV 0.5
Tyloxapol 0.25
BAK 10-100 ppm
Purified water q.s. to 100
Note: "BAK" denotes benzalkonium chloride.
84
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
EXAMPLE 6:
The ingredients listed in Table 6 are mixed together for at least 15 minutes.
The pH of the mixture is adjusted to 6.2-6.4 using I N NaOH or 1 N HCI to
yield a
composition of the present invention.
Table 6
Ingredient Amount (% by weight, except where
"ppm" is indicated)
Povidone 1.5
HAP (30%) 0.05
Glycerin 3
Propylene glycol 3
Compound of Formula IV 0.75
TGF-(3 antibody ab 18679 (from Abcam, 0.1
Inc., Cambridge, Massachusetts)
Tyloxapol 0.25
Alexidine 2HCI 1-2 ppm
Purified water q.s. to 100
EXAMPLE 7:
The ingredients listed in Table 7 are mixed together for at least 15 minutes.
The pH of the mixture is adjusted to 6.2-6.4 using I N NaOH or I N HCI to
yield a
composition of the present invention.
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Table 7
Ingredient Amount (% by weight, except where
"ppm" is indicated)
CMC (MV) 0.5
HAP (30%) 0.05
Glycerin 3
Propylene glycol 3
Compound of Formula IV 0.25
Ketorolac 0.3
Tyloxapol (a surfactant) 0.25
Alexidine 2HC1 1-2 ppm
Sunflower oil q.s. to 100
EXAMPLE 8:
The ingredients listed in Table 8 are mixed together for at least 15 minutes.
The pH of the mixture is adjusted to 6.2-6.4 using I N NaOH or I N HC1 to
yield a
composition of the present invention.
Table 8
Ingredient Amount (% by weight, except where
"ppm" is indicated)
CMC (MV) 0.5
HAP (30%) 0.05
Glycerin 3
Propylene glycol 3
Compound of Formula IV 0.3
TGF-0 antibody ab49574 (from Abcam, 0.2
Inc., Cambridge, Massachusetts)
Diclofenac sodium 0.3
Tyloxapol (a surfactant) 0.25
Alexidine 2HC1 1-2 ppm
Purified water q.s. to 100
86
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
EXAMPLE 9:
The ingredients listed in Table 9 are mixed together for at least 15 minutes.
The pH of the mixture is adjusted to 6.2-6.4 using I N NaOH or 1 N HCl to
yield a
composition of the present invention.
Table 9
Ingredient Amount (% by weight, except where
"ppm" is indicated)
CMC (MV) 0.5
HAP (30%) 0.05
Glycerin 3
Propylene glycol 3
Compound of Formula IV 0.5
sTGFRI 0.2
sTGFRH 0.2
Tyloxapol (a surfactant) 0.25
Alexidine 2HCI 1-2 ppm
Corn oil q.s. to 100
In another aspect, a DIGRA, a prodrug thereof, a pharmaceutically
acceptable salt thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable ester thereof is
incorporated into
a formulation for topical administration, systemic administration, periocular
injection, or
subconjunctival injection. In still another aspect, an antagonist to TGF-(3
can be included
in the formulation. A formulation can desirably comprise a carrier that
provides a
sustained-release of the active ingredients, such as for a period longer than
about 1 week
(or longer than about 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 months). In certain embodiments, the
sustained-
release formulation desirably comprises a carrier that is insoluble or only
sparingly
soluble in the ocular environment. Such a carrier can be an oil-based liquid,
emulsion,
gel, or semisolid. Non-limiting examples of oil-based liquids include castor
oil, peanut
oil, olive oil, coconut oil, sesame oil, cottonseed oil, corn oil, sunflower
oil, fish-liver oil,
arachis oil, and liquid paraffin.
In one embodiment, a compound or composition of the present invention can
be injected subconjunctivally after GFS to control or prevent the progression
of
87
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
glaucoma, using a fine-gauge needle, such as 25-30 gauge. Typically, an amount
from
about 25 pl to about 100 l of a composition comprising a DIGRA, a prodrug
thereof, a
pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable
ester thereof
is administered into a patient. A concentration of such DIGRA, prodrug
thereof, or
pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof is selected from the ranges disclosed
above.
In still another aspect, a DIGRA, a prodrug thereof, a pharmaceutically
acceptable salt thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable ester thereof is
incorporated into
an ophthalmic device or system that comprises a biodegradable material, and
the device
is injected or implanted into the vicinity of the filtering bleb to provide a
long-term (e.g.,
longer than about 1 week, or longer than about 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 months)
control or
prevention of progression of glaucoma. Such a device or system may be injected
or
implanted by a skilled physician in the subject's subtenon space or periocular
tissue. In
one aspect, such control or prevention is achieved by ensuring a long-term
functioning
filtering bleb.
In still another aspect, a method for controlling or preventing progression of
glaucoma, comprises: (a) providing a composition comprising a DIGRA, a prodrug
thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a pharmaceutically
acceptable
ester thereof; and (b) administering to a subject an effective amount of the
composition
at a frequency sufficient to ensure a functioning filtering bleb, thereby
controlling or
preventing the progression of glaucoma.
In yet another aspect, a method for controlling or preventing progression of
glaucoma in a subject, comprises: (a) performing a GFS procedure on the
subject; (b)
providing a composition comprising a DIGRA, a prodrug thereof, a
pharmaceutically
acceptable salt thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable ester thereof; and
(c)
administering to a subject an effective amount of the composition at a
frequency
sufficient to ensure a functioning filtering bleb, thereby controlling or
preventing the
progression of glaucoma.
In one embodiment, the DIGRA is selected from among those disclosed
above.
88
CA 02699599 2012-02-07
In still another embodiment, the present invention provides a method for
lowering IOP in a subject. The method comprises: (a) performing a GFS
procedure on
the subject; (b) providing a composition comprising a DIGRA, a prodrug
thereof, a
pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable
ester thereof;
and (c) administering to a subject an effective amount of the composition at a
frequency
sufficient to ensure a functioning filtering bleb, thereby lowering said IOP.
In another embodiment, the composition for use in any of the foregoing
method further comprises an antagonist to TGF-(3. Such an antagonist to TGF-(i
is
selected from those disclosed above. The concentrations of the DIGRA, a
prodrug
thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, a pharmaceutically
acceptable ester
thereof, and the antagonist to TGF-1i are selected to be in the ranges
disclosed above.
In another aspect, a composition of the present invention is administered
topically or periocularly. In still another aspect, a composition of the
present invention is
incorporated into an ophthalmic implant system or device, and the implant
system or
device is surgically implanted periocularly in, or in the subtenon space of,
the patient for
the sustained or long-term release of the active ingredient or ingredients. A
typical
implant system or device suitable for use in a method of the present invention
comprises
a biodegradable matrix with the active ingredient or ingredients impregnated
or dispersed
therein. Non-limiting examples of ophthalmic implant systems or devices for
the
sustained-release of an active ingredient are disclosed in U.S. Patents
5,378,475;
5,773,019; 5,902,598; 6,001,386; 6,051,576; and 6,726,918.
In yet another aspect, a composition of the present invention is administered
topically once a day, several (e.g., twice, three, four, or more) times a day,
once a week,
once a month. In another aspect, the composition is implanted in the patient
and is
replaced at a frequency of, for example, once a year, twice a year, four times
a year, or at
a suitable frequency that is determined to be appropriate for controlling or
preventing the
progression of glaucoma.
89
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
COMBINATION THERAPY
A composition or a method of the present invention can be used with other
therapeutic and adjuvant or prophylactic agents commonly used to reduce,
treat, or
prevent (a) an increase of intraocular pressure, (b) a loss of retinal
ganglion cells, or (c)
both, thus providing an enhanced overall treatment or enhancing the effects of
the other
therapeutic agents, prophylactic agents, and adjunctive agents used to treat
and manage
the different types of glaucoma. Therapeutic agents used to treat narrow angle
or acute
congestive glaucoma include, for example, physostigmine salicylate and
pilocarpine
nitrate. Adjunctive therapy used in the management of narrow angle glaucoma
includes,
for example, the intravenous administration of a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor
such as
acetozolamide to reduce the secretion of aqueous humor, or of an osmotic agent
such as
mannitol or glycerin to induce intraocular dehydration. Therapeutic agents
used to
manage wide angle or chronic simple glaucoma and secondary glaucoma include,
for
example, prostaglandin analogs, such as Xalatan and Lumigan , 3-adrenergic
antagonists such as timolol maleate, a-adrenergic agonists, such as
brimonidine and
apraclonidine, muscarinic cholinergic agents (such as pilocarpine or
carbachol), and
carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, such as Dorzolamide (Trusopt or Cosopt ) or
brizolamide (Azopt ). Other therapeutic agents used to manage glaucoma include
the
inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase such as Echothiophate (phospholine iodide).
High doses may be required for some currently used therapeutic agents to
achieve levels to effectuate the target response, but may often be associated
with a
greater frequency of dose-related adverse effects. Thus, combined use of the
compounds
or compositions of the present invention, following GFS, with agents commonly
used to
treat glaucoma allows the use of relatively lower doses of such other agents,
resulting in
a lower frequency of potential adverse side effects associated with long-term
administration of such therapeutic agents. Thus, another indication of the
compounds or
compositions in this invention is to reduce adverse side effects of prior-art
drugs used to
treat glaucoma, such as the development of cataracts with long-acting
anticholinesterase
agents including demecarium, echothiophate, and isoflurophate.
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
COMPARISON OF SIDE EFFECTS OF GLUCOCORTICOIDS AND DIGRAS
Side effects of glucocorticoids and DIGRAs may be compared in their use as
adjunctive therapy following GFS.
In one aspect, a level of at least an adverse side effect is determined in
vivo
or in vitro. For example, a level of said at least an adverse side effect is
determined in
vitro by performing a cell culture and determining the level of a biomarker
associated
with said side effect. Such biomarkers can include proteins (e.g., enzymes),
lipids,
sugars, and derivatives thereof that participate in, or are the products of,
the biochemical
cascade resulting in the adverse side effect. Representative in vitro testing
methods are
further disclosed hereinbelow.
In another embodiment, a level of said at least an adverse side effect is
determined in vivo at about one day after said glucocorticoid or DIGRA (or a
prodrug
thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a pharmaceutically
acceptable
ester thereof) is first administered to, and are present in, said subject. In
another
embodiment, a level of said at least an adverse side effect is determined
about 14 days
after said composition is first administered to, and are present in, said
subject. In still
another embodiment, a level of said at least an adverse side effect is
determined about 30
days after said composition is first administered to, and are present in, said
subject.
Alternatively, a level of said at least an adverse side effect is determined
about 2, 3, 4, 5,
or 6 months after said compounds or compositions are first administered to,
and are
present in, said subject.
In another aspect, said glucocorticoid used to treat said exemplary
inflammation is administered to said subject at a dose and a frequency
sufficient to
produce a beneficial effect on said inflammation equivalent to a compound or
composition of the present invention after about the same elapsed time.
One of the most frequent undesirable actions of a glucocorticoid therapy
(such as anti-inflammation therapy) is steroid diabetes. The reason for this
undesirable
condition is the stimulation of gluconeogenesis in the liver by the induction
of the
91
CA 02699599 2012-02-07
transcription of hepatic enzymes involved in gluconeogenesis and metabolism of
free
amino acids that are produced from the degradation of proteins (catabolic
action of
glucocorticoids). A key enzyme of the catabolic metabolism in the liver is the
tyrosine
aminotransferase ("TAT"). The activity of this enzyme can be determined
photometrically from cell cultures of treated rat hepatoma cells. Thus, the
gluconeogenesis by a glucocorticoid can be compared to that of a DIGRA by
measuring
the activity of this enzyme. For example, in one procedure, the cells are
treated for 24
hours with the test substance (a DIGRA or glucocorticoid), and then the TAT
activity is
measured. The TAT activities for the selected DIGRA and glucocorticoid are
then
compared. Other hepatic enzymes can be used in place of TAT, such as
phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, glucose-6-phosphatase, or fructose-2,6-
biphosphatase. Alternatively, the levels of blood glucose in an animal model
may be
measured directly and compared for individual subjects that are treated with a
glucocorticoid for a selected condition and those that are treated with a
DIGRA for the
same condition.
Another undesirable result of glucocorticoid therapy is GC-induced cataract.
The cataractogenic potential of a compound or composition may be determined by
quantifying the effect of the compound or composition on the flux of potassium
ions
through the membrane of lens cells (such as mammalian lens epithelial cells)
in vitro.
Such an ion flux may be determined by, for example, electrophysiological
techniques or
ion-flux imaging techniques (such as with the use of fluorescent dyes). An
exemplary
in-vitro method for determining the cataractogenic potential of a compound or
composition is disclosed in U.S. Patent Application Publication 200410219512
Still another undesirable result of glucocorticoid therapy is hypertension.
Blood pressure of similarly matched subjects treated with glucocorticoid and
DIGRA
following GFS may be measured directly and compared.
92
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
TESTING 1: Effect of BOL-303242-X (Compound Having Formula IV) on Inhibiting
IL-1(3-Induced Cytokine Expression in Human Corneal Epithelial Cells
1. BACKGROUND/RATIONALE:
Levels of cytokines associated with immune cells are direct indications of
activity of these cells in an inflammatory condition. Reduced levels of these
cytokines
indicate a positive therapeutic effect on inflammation of a test compound.
This study
was designed to determine the effect of BOL-303242-X on IL-IB -induced
cytokine
production in human corneal epithelial cells ("HCECs").
2. PURPOSE
To determine the effects of BOL-303242-X on IL- I Q-stimulated cytokine
expression in primary human corneal epithelial cells using a 30-cytokine
Luminex kit.
Dexamethasone was used as a control.
3. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN
Primary HCECs were seeded in 24-well plates. After 24 h, cells were treated
with vehicle, IL- I B, IL-16 + dexamethasone, or IL- I B + BOL-303242-X in
basic EpiLife
medium for 18 h (Table T-1-1). Each treatment was performed in triplicate.
Media were
collected and used for determination of cytokine content using a 30-cytokine
Luminex
kit. Cell viability was determined by alamarBlue assay (LP06013).
93
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Group* Day I Day 2: cells were treated with the test Day 3
agents in basic EpiLife medium for 18 h
1 Cells Control (0. 1 % DMSO) Media for
2 were 10 ng/ml IL- IB Luminex
3 seeded in 10 ng/ml IL- 113 + 1 nM dexamethasone assays;
4 24-well 10 ng/ml IL-1 B + 10 nM dexamethasone cells for
plates (5 10 ng/ml IL-16 + 100 nM dexamethasone cell
6 X 10 ng/ml IL-1 B + 1 pM dexamethasone viability
7 105/well 10 ng/ml IL-1 B + 10 pM dexamethasone assay
8 in 0.5 ml 10 ng/ml IL-1 B + 1 nM BOL-303242-X
9 medium) 10 ng/ml IL-1B + 10 nM BOL-303242-X
in EpiLife 10 ng/ml IL- I B + 100 nM BOL-303242-X
11 medium 10 ng/ml IL- I B + I p M BOL-303242-X
12 10 ng/ml IL- I B + 10 M BOL-303242-X
*triplicate wells per group
Dexamethasone:
Lot Number: 016K14521
Parent MW: 392.46
Parent:Total MW Ratio = 1.0
BOL-303242-X:
Lot Number: 6286
Parent MW: 462.48
Parent:Total MW Ratio = 1.0
4. DATA ANALYSIS
Median fluorescence intensity (MFI) was used to obtain the concentration of
each cytokines in pg/ml based on the standard curve of each cytokine assayed
by
Luminex. The linear range of the standard curve for each cytokine was used for
determination of cytokine concentration. Duplicate values for each sample were
averaged. Data were expressed as mean SD. Statistical analysis was performed
using
one-way ANOVA-Dunnett's test, and P < 0.05 was considered statistically
significant.
94
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
5. RESULTS
No statistically significant effect on cellular metabolic activity (as
measured
by alamarBlue assay) was observed with the various treatments.
Substantial amounts of 16 out of 30 cytokines tested were detected in this
study and 13 out of 14 cytokines detected were stimulated by 10 ng/ml IL- I S
(Table T- I -
1). IL-1(3 was excluded from analysis because it was the stimulus. IL-lra was
excluded
because the MFI was not within the standard range.
Dexamethasone and BOL-303242-X significantly inhibited IL-16-stimulated
cytokine production with comparable potency on 6 cytokines (IL-6, IL-7, MCP-1,
TGF-
a, TNF-a and VEGF), and a significant inhibitory effect was observed at I nM
on IL-6
and at 10 nM on MCP- 1, TGF-a and TNF-a (Table T-1-1 and Figures 1 A- I F). As
discussed above, these cytokines can induce the production of TGF-(3 by, for
example,
immune cells, leading to excessive matrix deposition and ultimately a non- or
poorly
functioning filtering bleb after GFS. The present data indicate that BOL-
303242-X can
be an effective and improved alternative to GCs that have been used as
pharmacological
adjunctive therapy associated with GFS.
BOL-303242-X also significantly inhibited IL-I B-stimulated G-CSF
production with better potency compared to dexamethasone, and a significant
inhibitory
effect was observed at 10 pg/ml by BOL-303242-X while no significant effect
was
observed by dexamethasone on this cytokine (Fig. 2).
BOL-303242-X also significantly inhibited IL- I f3-stimulated cytokine
production with less potency compared to dexamethasone on 3 cytokines (GM-CSF,
IL-
8, and RANTES). A significant inhibitory effect was observed at 1 nM by
dexamethasone and at 10 nM by BOL-303242-X on GM-CSF. A significant inhibitory
effect was observed at I pM by dexamethasone on RANTES while no significant
effect
was observed by BOL-303242-X on this cytokine (Figures 3A-3C).
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
6. CONCLUSION
BOL-303242-X and dexamethasone have comparable potency for inhibition
of IL- I B-stimulated cytokine production in HCECs for the cases of IL-6, IL-
7, TGF-a,
TNF-a, VGEF, and MCP- 1. BOL-303242-X is more potent than dexamethasone in
inhibiting IL-I6-stimulated production of G-CSF in HCECs. BOL-303242-X is
somewhat less potent than dexamethasone in inhibiting IL-I B-stimulated
production of
GM-CSF, IL-8, and RANTES in HCECs.
Table T-1-1
Inhibition of IL-11 stimulated cytokine production by dexamethasone and BOL-
303242-
X in primary human corneal epithelial cells
Cytokines Stimulated Inhibited by dexamethasone Inhibited by
detected * by IL-113 ( M) BOL-303242-X (pM)
(10 ng/ml) 0.0 0.0 0.1 1 10 0.0 0.0 0.1 1 10
01 1 01 1
G-CSF X X
GM-CSF X X X X X X X X X
IL-la X
IL-6 X X X X X X X X X X X
IL-7 X X X
IL-8 X X X X
113- 10 X
MCP-I X X X X X X X X X
MIP- I a
MIP-I(3 X
RANTES X X X
TGF-a X X X X X X X X X
TNF-a X X X X X X X
VEGF X X X X X
Notes: (*) EGF, Eotaxin, Fractalkine, IFNy, IL- 10, IL-12p40, IL-12p70, IL-13,
IL 15, IL-
17, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, sCD40L were not detected. IL-1 0 was excluded from
analysis
because it was the stimulus. IL-Ira was excluded because the MFI was out of
range of
the standards.
96
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
TESTING 2: Evaluation Of The Effect Of Topical BOL-303242-X,
Administered Unilaterally Four Times Daily, On The Intraocular Pressure in New
Zealand White Rabbits For 33 Days
INTRODUCTION
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of topical BOL-
303242-X on the IOP in New Zealand White rabbits when administered to right
eyes
four times daily for 33 days. Dosing was discontinued after 31 days due to
high mortality
rates and limited supply of test articles.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Test Articles
Three test articles were identified as follows:
mg/g BOL-303242-X (compound having Formula IV) Ophthalmic
Suspension (Lot No. 2676-MLC-270)
5 mg/g BOL-303242-X Ophthalmic Suspension (Lot No. 2676-MLC-270)
1 mg/g BOL-303242-X Ophthalmic Suspension (Lot No. 2676-MLC-270)
A negative control (balanced salt solution (BSS), B. Braun Medical Inc., Lot
No. J6NO11, exp. 10/08), and a positive control (0.1 % dexamethasone
ophthalmic
suspension (MaxidexAlcon Laboratories, Inc., Lot No. I 14619F, exp. 01/09))
were
also provided. The formulations were provided in ready-to-use form and stored
at room
temperature. The suspensions were shaken before dose administrations to re-
suspend
them.
97
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Test System
Animals
Seventy-five female New Zealand White rabbits were obtained from The
Rabbit Source (Ramona, CA). Animals were 6-8 weeks old at the time of IOP-
training
initiation, and they weighed 1.38-2.05 kg at randomization. The protocol
specified that
animals would weigh at least 1.5-2.5 kg; this deviation had no effect on the
outcome of the
study. Animals were identified by ear tags and cage cards.
Animal Husbandry
Upon arrival, animals were examined to ensure that they were healthy and
quarantined for 10 days before placement on study. At the end of the
quarantine period,
animals were again examined for general health parameters and for any
anatomical
ophthalmic abnormalities. Quarantine was conducted according to internal
operating
procedure.
Animals were housed in individual, hanging, stainless steel cages. Housing
and sanitation were performed according to internal operating procedure.
Animals were provided Teklad Certified Global High Fiber Rabbit Diet.
Diet certification and analysis were provided by the vendor, Harlan Teklad. No
analyses
outside those provided by the manufacturer were performed. Animals were
provided tap
water ad libitum. No contaminants were known to exist in the water and no
additional
analyses outside those provided by the local water district and as specified
in internal
operating procedure were performed.
Environmental parameters were monitored according to internal operating
procedure. The study room temperature was 65-72 F with 58-77% relative
humidity
98
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Pre-Treatment Examinations
Prior to placement on study, each animal underwent a pre-treatment
ophthalmic examination (slit lamp and indirect ophthalmoscopy). Observations
were
scored according to the McDonald Shadduck system and recorded using a
standardized
data collection sheet. Acceptance criteria for placement on study were as
follows: Scores
of <_ 1 for conjunctival congestion and swelling; scores of 0 for all other
observation
variables.
IOP Conditioning and Pre-Selection
Seventy-five rabbits underwent two weeks of IOP training to condition them
for IOP measurement. IOP was determined for both eyes of each animal using a
Medtronic Solan, Model 30 classic pneumatonometer. Proparacaine hydrochloride
0.5%
(1 drop) was delivered to each eye prior to IOP measurement. A two-point
diurnal curve
was established: IOP was recorded on Monday, Wednesday, and Friday of each
week, at
8 a.m. and 12 p.m., with a 1 hour range for each of these times. The time of
the
measurements was recorded.
At the end of the two weeks of conditioning, 50 rabbits were selected for
topical dosing based on the consistency of their IOP measurements at each time
point.
The selected rabbits continued to have their IOPs measured for one additional
week.
Randomization
Prior to dosing, 50 animals were weighed and randomly assigned to five
treatment groups. Treatment groups are described in Table T-2- 1. Animals were
randomized to treatment groups according to a modified Latin square.
Topical Dosing Procedure
On Days 1-31, animals received daily topical doses of the appropriate test
article into the right eye. Animals were dosed four times per day, with doses
99
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
administered 2 hours apart. Doses were administered using a calibrated 50-1iL
pipette.
The eyelids were held close for 10 seconds immediately following dosing. The
time of
each dose administration was recorded.
The protocol indicated that animals would be dosed four times daily for 33
days. Per decision of the Sponsor and Study Director, dosing was discontinued
after 31
days due to high mortality rates and limited supply of test articles. This
deviation had no
adverse effect on the outcome of the study.
Mortality/Morbidity
Animals were observed for mortality/morbidity twice daily. Animals
determined to be moribund were euthanized with an intravenous injection of
commercial
euthanasia solution.
Body Weights
Animals were weighed at randomization.
IOP Measurements
IOP was determined for both eyes of each animal on Days 3, 5, 10, 12, 16, 18,
22, 24, 26, 30, and 32. IOP was evaluated with a Medtronic Solan, Model 30
classic
pneumatonometer. Proparacaine hydrochloride 0.5% (1 drop) was delivered to
each eye
prior to IOP measurement. IOP was measured on Monday, Wednesday, and Friday of
each week. A two-point diurnal curve was established: IOP was recorded at 8
a.m. and
12 p.m. on Day 3, and at 8 a.m. and 2 p.m. on later days, with a 1 hour
range for each
of these times. The time of the measurements was recorded.
Ophthalmic Observations
Ophthalmic examinations (slit lamp) were performed prior to the first dosing
on Days 5, 12, 22, 26, and 33. Ocular findings were scored according to the
McDonald
Shadduck system and recorded using a standardized data collection sheet.
100
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Study Completion
Following completion of final ophthalmic observations (Day 33), remaining
animals were returned to the vivarium.
Statistical Analysis
Descriptive statistics were prepared for IOP data of each treatment group
(left and right eyes separately) at each measurement interval. The statistics
included the
number of observations ("N"), mean, standard deviation ("STD"), and standard
error
("SEM"). Statistical analyses were conducted on IOP results using Statistical
Analysis
Systems (SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, V8.0). Parameters were evaluated using
analysis
of variance/GLM Procedure followed by Tukey's Standardized Range Test (Tukey,
1985) for post hoc comparisons of group means. The level of significance was
set at a
probability of p < 0.05 for all statistical procedures. Group IOP means were
compared at
each interval, with left and right eyes compared separately.
IOP data for the following six animals were excluded from group statistics:
Group A, Nos. 3081, 3037, 3068, and 3011; Group C, No. 3034; and Group E, No.
3084.
The excluded Group A animals showed no IOP response to dexamethasone dosing,
and
the excluded Group C and Group E animals had outlying IOP data.
Animal Welfare Statement
This study was performed to develop a hypertensive model of intraocular
pressure in New Zealand White rabbits. Alternatives to performing this study
were
explored; however, to properly develop the model, a whole-body test system was
required. This study complied with all internal animal welfare policies and
was approved
by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
101
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
RESULTS
Mortality
Mortality data are presented in Table T-2-2. Ten rabbits died or were
euthanized between Days I I and 33, as follows: Six of ten rabbits dosed with
dexamethasone, one of ten rabbits dosed with 10 mg/g BOL-303242-X (0.5
mg/dose),
two of ten rabbits dosed with 5 mg/g BOL-303242-X (0.25 mg/dose), and one of
ten
rabbits dosed with I mg/g BOL-303242-X (0.05 mg/dose). Seven rabbits were
noted to
have diarrhea, often described as severe and hemorrhagic, prior to death or
euthanasia.
No signs of poor health were noted for two rabbits that were found dead.
Further
information on observed mortality is shown in the following table.
Group Rabbit Treatment (4 x Daily) Day of Recorded Notes
No. Death"'
A 3011 0.1% Dexamethasone 23 Euthanized due to severe profuse hemorrhagic
diarrhea.
(0.05 mg/dose) Noted to be malnourished and anorexic. 11 A 3016
0.1%Dexamethasone 27 Found dead. No rigor mortis present.
(0 05 mg/dose)
A 3037 0.1% Dexamethasone 25 Euthanized due to severe hemorrhagic diarrhea.
Noted to be
(0.05 mg/dose) dehydrated, lethargic, and cachectic.
A 3038 0.1% Dexamethasone 13 Euthanized due to severe hemorrhagic diarrhea.
(0.05 mg/dose)
--------- ._.. ........... .. _
A 3068 0.1% Dexamethasone 25 Euthanized due to severe hemorrhagic diarrhea.
Noted to be
(0.05 mg/dose) dehydrated, lethargic, and cachectic.
1111-1- A 3086 0.1% Dexamethasone 27 Euthanized. Very sick/poor health; left
(untreated) eye
(0.05 mg/dose) protruding.
B 3008 10 mg/g BOL-303242-X 11 Found dead. Noted on Day 9 to have significant
diarrhea and
dose a yellowish discharge in the dosed eye.
C 3028 5 mg/g BOL-303242-X 17 Euthanized due to severe diarrhea.
(0.25 mg/dose)
C 3074 5 mg/g BOL-303242-X 33 Euthanized prior to final ocular examination due
to a
(0.25 mg/dose) respiratory infection. Diarrhea noted on Day 26.
D 3010 1 mg/g BOL-303242-X 29 Found dead.
(0.05 mg/dose)
Day euthanized or found dead.
Remaining rabbits survived until study completion (Day 33). One surviving
rabbit dosed with 10 mg/g BOL-303242-X (0.5 mg/dose) was noted to have
diarrhea on
Day 18 (Group B, No. 3048).
102
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Ophthalmic Observations
Slit-lamp ophthalmic observations are presented in Table T-2-3. A key to
the ophthalmic observation scores is presented in Table T-2-4. Eyes appeared
normal at
most observations. Mild conjunctival congestion (score = 1) was seen
sporadically,
mostly in treated right eyes, with no consistent association with test or
control article.
The only other findings were a small area of corneal pigmentation in an
untreated left
eye (Group A, No. 3086), a pinpoint corneal scar in a 10 mg/g BOL-303242-X-
dosed
right eye (Group B, No. 3083), and a subconjunctival hemorrhage in a 1 mg/g
BOL-
303242-X-dosed right eye (Group D, No. 3043). The observed corneal lesions
might be
related to the pneumotonometry procedure.
Intraocular Pressure Measurements
Descriptive statistics for IOP data are presented in Table T-2-5 (left eyes,
a.m.), Table T-2-6 (right eyes, p.m.), Table T-2-7 (left eyes, p.m.) and Table
T-2-8 (right
eyes, p.m.).
Mean IOP varied throughout the study for all groups; the variations were
similar for left and right eyes within each group. For all groups (including
the BSS dose
group), mean IOP reached a maximum between Days 5 and 10 for both left and
right
eyes, a.m. and p.m. readings. Diurnal changes in IOP from a.m. to p.m. were
not evident
during the study, possibly due to daily feeding of rabbits prior to p.m.
measurements.
For the dexamethasone group (Group A), mean IOP of both left and right
eyes increased sharply after treatment began. This increase was not seen in
the mean
IOPs of the BOL-303242-X groups (Groups B-D) at any point of the study. On
several
days, the mean IOP in one or both eyes of the dexamethasone group (Group A)
was
significantly higher (p < 0.05) than the mean IOP in the corresponding eyes of
other
groups. This difference was more common in the a.m. than the p.m., and it
occurred at
more timepoints for the untreated left eyes than the treated right eyes. Mean
IOP of
BSS-dosed right eyes (Group E) was generally lower than mean IOP of BOL-303242-
X-
dosed right eyes (Groups B-D) in the a.m. but not in the p.m. No statistically
significant
103
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
(p < 0.05) differences in mean IOP were seen between the BSS group and BOL-
303242-
X groups.
CONCLUSIONS
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of topical BOL-
303242-X on the intraocular pressure (IOP) in New Zealand White rabbits when
administered to right eyes four times daily for 33 days. In conclusion,
unilateral topical
instillation of BOL-303242-X suspension (0.05, 0.25, or 0.5 mg/dose),
dexamethasone
suspension (0.05 mg/dose), or balanced salt solution in rabbit eyes four times
daily up to
31 days was associated with sporadic mild conjunctival congestion. Dosing with
dexamethasone up to 31 days was associated with a higher mortality rate (6
deaths per 10
rabbits) than dosing with BOL-303242-X up to 31 days (per dose level, 1-2
deaths per 10
rabbits). Daily dosing with the BOL-303242-X suspensions did not increase IOP
when
compared to daily dosing with dexamethasone.
Table T-2-1
Treatment Groups
Group No. Treatment (4 x Daily) Dose Location Dose Drug Dose Scheduled Study
(Right Eye) Volume Level Completion')
A 10 0.1% Dexamethasone (Maxidex) Topical 50 tL 0.05 mg/dose Day 33
B 10 10 mg/g BOL-303242-X Topical 50 tL 0.5 mg/dose Day 33
C 10 5 mg/g BOL-303242-X Topical 50 pL 0.25 mg/dose Day 33
D 10 1 mg/g BOL-303242-X Topical 50 pL 0.05 mg/dose Day 33
E 10 Balanced Salt Solution Topical 50 L N/A Day 33
N/A = Not Applicable.
(1) Dosing was performed daily through Day 31. Final ophthalmic examinations
were performed on Day
33.
104
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Table T-2-2
Mortality
Group No. Treatment (4 x Daily) Dose Location Dose Drug Dose Scheduled
Mortality`-'
(Right Eye) Volume Level Study
Completion
(u
A 10 0.1 % Dexamethasone (Maxidex) Topical 50 L 0.05 mg/dose Day 33 6/ 10t3'
B 10 10 mg/g BOL-303242-X Topical 50 L 0.5 mg/dose Day 33 1/10 '
C 10 5 mg/g BOL-303242-X Topical 50 pL 0.25 mg/dose Day 33 2/10Y5'
D 10 1 mg/g BOL-303242-X Topical 50 tL 0.05 mg/dose Day 33 l/10
E 10 Balanced Salt Solution Topical 50 pL N/A Day 33 0/10
N/A = Not Applicable.
(1) Dosing was performed daily through Day 31. Final ophthalmic examinations
were performed on Day
33.
(2) Mortality is expressed as the number of animals found dead or euthanized
prior to study
completion/number of animals in group.
(3) One Group A rabbit was found dead on Day 27. Five Group A rabbits were
euthanized between Days
13 and 27 due to severe diarrhea.
(4) One Group B rabbit was found dead on Day 11; it was observed to have
diarrhea on Day 10.
(5) One Group C rabbit was euthanized on Day 17 due to severe diarrhea. The
other was euthanized on
Day 33 prior to final ophthalmic examinations due to a respiratory infection.
(6) One Group D rabbit was found dead on Day 29.
105
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Table T-2-3
Ophthalmic Observations (Slit-Lamp)
Group Animal No. Treatment (4 x Daily) Eye Day Ophthalmic Observation... Score
A 3016 Untreated Left 5. 12, 22, 26 AN N/A
0.1% Dexamethasone Right 5 Conjunctival Congestion 1
12,22.26 AN N/A
A 3081 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
0.1% Dexamethasone Right 22 Conjunctival Congestion 1
5, 12, 26, 33 AN N/A
A 3086 Untreated Left 26 Cornea 1(2)
5, 12, 22 AN N/A
0.1% Dexamethasone Right 5, 12, 22, 26 AN N/A
---------------- ------
A 3037 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22 AN N/A
0.1% Dexamethasone Right 5, 12, 22 AN N/A
A 3006 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26.33 AN N/A
0.1 % Dexamethasone Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
A 3068 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22 AN N/A
0.1 % Dexamethasone Right 5, 12,22 AN N/A
A 3033 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
0.1% Dexamethasone Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
---------------
A 3029 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
0.1 % Dexamethasone Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
A 3011 Untreated Left 5,12,22 AN N/A
0.1 % Dexamethasone Right 5, 12, 22 AN N/A
A 3038 Untreated Left 5, 12 AN N/A
0.1% Dexamethasone Right 5, 12 AN N/A
AN = Appeared normal. N/A = Not Applicable. See Table T-2-4 for key to
ophthalmic observation scores.
(1) Observations were made prior to the first dose of the day.
(2) Small area of pigmentation in center of cornea.
106
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Table T-2-3 (continued)
Ophthalmic Observations (Slit-Lamp)
Group Animal No. Topical Treatment Eye Day Ophthalmic Observation... Score
B 3083 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26. 33 AN N/A
mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5 Cornea i 2)
5 Surface area of cornea 1
involvement
12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
B 3008 Untreated Left 5 AN N/A
10 mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5 AN N/A
B 3017 Untreated Left 5,12,22,26,33 AN N/A
10 mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5, 12 Conjunctival Congestion 1
22, 26, 33 AN N/A
B 3048 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
10 mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
B 3003 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
10 mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 12 Conjunctival Congestion 1
5, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
B 3042 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
10 mglg BOL-303242-X Right 26 Conjunctival Congestion 1
5, 12, 22, 33 AN N/A
B 3023 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
10 mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
B 3004 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
10 mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
B 3049 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
10 mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
B 3026 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
10 mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5, 12, 22, 26. 33 AN N/A
AN = Appeared normal. N/A = Not Applicable. See Table T-2-4 for key to
ophthalmic observation scores.
(I) Observations were made prior to the first dose of the day.
(2) Pinpoint corneal scar.
107
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Table T-2-3 (continued)
Ophthalmic Observations (Slit-Lamp)
Group Animal No. Topical Treatment Eye Day Ophthalmic Observation... Score
C 3028 Untreated Left 5, 12 AN N/A
mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5, 12 AN N/A
C 3064 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
5 mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5 Conjunctival congestion 1
12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
C 3031 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
5 mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 22 Conjunctival congestion 1
5, 12, 26, 33 AN N/A
C 3032 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
5 mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
C 3041 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
5 mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
C 3034 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
5 mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
C 3035 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
5 mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 22, 26 Conjunctival congestion 1
5,12,33 AN N/A
C 3046 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
5 mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
C 3058 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
5 mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
C 3074 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26 AN N/A
5 mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 26 Conjunctival congestion 1
5.12,22 AN N/A
AN = Appeared normal. N/A = Not Applicable. See Table T-2-4 for key to
ophthalmic observation scores.
(1) Observations were made prior to the first dose of the day.
108
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Table T-2-3 (continued)
Ophthalmic Observations (Slit-Lamp)
Group Animal No. Topical Treatment Eye Day Ophthalmic Observation Score
D 3010 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26 AN N/A
I mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5, 12, 22, 26 AN N/A
---------- - ------ -
D 3039 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
1 mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
D 3043 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN') N/A
1 mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
D 3044 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
1 mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
D 3027 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
I mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
D 3072 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
I mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
D 3040 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
I mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 22 Conjunctival congestion
5, 12, 26, 33 AN N/A
--------- --------------- ------------
D 3020 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
1 mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
D 3063 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
I mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
D 3077 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
I mg/g BOL-303242-X Right 5, 12, 22, 26. 33 AN N/A
AN = Appeared normal. N/A = Not Applicable. See Table T-2-4 for key to
ophthalmic observation scores.
(1) Observations were made prior to the first dose of the day.
(2) Day 12: Subconjunctival hemorrhage observed.
109
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Table T-2-3 (continued)
Ophthalmic Observations (Slit-Lamp)
Group Animal No. Topical Treatment Eye Day Ophthalmic Observation... Score
E 3002 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
Balanced Salt Solution Right 5, 12, 22. 26, 33 AN N/A
E 3084 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
Balanced Salt Solution Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
E 3057 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
Balanced Salt Solution Right 12, 22, 26 Conjunctival Congestion 1
5,33 AN N/A
---------------- ---------------- --- --------
E 3087 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
Balanced Salt Solution Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
E 3018 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
Balanced Salt Solution Right 26 Conjunctival Congestion 1
5,12,22,33 AN N/A
E 3090 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
Balanced Salt Solution Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
E 3047 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
Balanced Salt Solution Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
E 3070 Untreated Left 26 Conjunctival Congestion 1
5, 12, 22, 33 AN N/A
Balanced Salt Solution Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
E 3019 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
Balanced Salt Solution Right 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
E 3007 Untreated Left 5, 12, 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
Balanced Salt Solution Right 5, 12. 22, 26, 33 AN N/A
AN = Appeared normal. N/A = Not Applicable. See Table T-2-4 for key to
ophthalmic observation scores.
(1) Observations were made prior to the first dose of the day.
110
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Table T-2-4
Key to Ophthalmic Observation Scoring System(')
CONJUNCTIVAL CONGESTION
1 = A flushed, reddish color predominantly confined to the palpebral
conjunctiva with
some perilimbal injection but primarily confined to the lower and upper parts
of the
eye from the 4:00 to 7:00 and 11:00 to 1:00 positions.
CORNEA
1 = Some loss of transparency. Only the epithelium and/or the anterior half of
the
stoma are involved. The underlying structures are clearly visible although
some
cloudiness may be readily apparent.
SURFACE AREA OF CORNEA INVOLVEMENT
1 = 1-25% area of stromal cloudiness.
Note (1): Dermatoxicology, F.N. Mazulli and H.I. Maibach, 1997, "Eye
Irritation," T.O.
McDonald and J.A. Shaduck (pages 579-582).
111
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Table T-2-5
Descriptive Statistics for Intraocular Pressure in Untreated Left Eyes (A.M.
Readings)
Intraocular Pressure (mmHg)
Day Statistic 0.1% 10 mg/g 5 mg/g I mg/g Balanced Salt
Dexamethasone BOL-303242-X BOL-303242-X BOL-303242-X Solution
(Group A) (Group B) (Group C) (Group D) (Group E)
Pre-Study MEAN 24.4 23.8 24.2 23.9 23.4
(5/9/07) SEM 0.7 0.6 0.4 0.4 0.5
STD 2.1 1.8 1.2 1.3 1.5
N 10 10 10 10 10
..... _ ----- -_._ . _.-_
3 MEAN 24.3 23.3 23.8 23.5 22.7
SEM 0.5 0.4 0.4 0.6 0.4
STD 1.2 1.2 1.1 1.8 1.3
N 6 10 9 10 9
MEAN 24.3 23.4 24.4 24.4 24.1
SEM 0.8 0.6 0.6 0.5 0.4
STD 2.0 1.9 1.7 1.5 1.3
N 6 10 9 10 9
----._ ---._..
MEAN 269a 24.08 24.6 24.5 25.4
SEM 0.5 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.7
STD 1.2 2.4 1.9 L2 2.1
N 6 10 9 10 9
12 MEAN 26.28 23.8 23.8 22.2a 23.7
SEM 0.6 0.7 0.7 0.7 0.7
STD 1.5 2.0 2.2 2.3 2.0
N 6 9 9 10 9
16 MEAN 25.Oa'b 22.9 23.4 21.68 20.3
SEM 1.0 0.7 0.6 1.1 0.6
STD 2.2 2.1 1.7 3.4 1.9
N 5 9 9 10 9
NOTE: Differences between means with a same superscript (a or b) in the same
row are statistically
significant (p < 0.05).
112
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Table T-2-5 (continued)
Descriptive Statistics for Intraocular Pressure in Untreated Left Eyes (A.M.
Readings)
Intraocular Pressure (mmHg)
Day Statistic 0.1% 10 mg/g 5 mg/g 1 mg/g Balanced Salt
Dexamethasone BOL-303242-X BOL-303242-X BOL-303242-X Solution
(Group A) (Group B) (Group C) (Group D) (Group E)
18 MEAN 24.2a 21.2a 21.9 23.3 22.3
SEM 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.4 0.6
STD 1.0 1.6 1.7 1.4 1.9
N 5 9 8 10 9
22 MEAN 25oa c 21.88 21.6 22.4 22.Oc
SEM 0.5 0.6 1.1 0.3 0.5
STD 1.2 1.8 3.0 1.0 1.6
N 5 9 8 10 9
24 MEAN 23.6a 20.2a 22.1 22.4 20.8
SEM 0.9 0.6 0.6 0.8 0.7
STD 2.1 1.8 1.7 2.5 2.1
N 5 9 8 10 9
26 MEAN 23.7 21.7 21.7 22.9 20.5
SEM 1.0 0.7 1.1 0.6 0.6
STD 2.2 2.0 3.0 2.0 1.7
N 5 9 8 10 9
- ----- --- ----
24.0 22.7 22.6 23.4 22.7
30 MEAN
SEM 1.0 0.6 1.2 0.8 0.5
STD 1.7 1.7 3.4 2.4 1.5
N 3 9 8 9 9
32 MEAN 25.5 22.9 23.1 24.1 22.3
SEM 0.8 0.5 0.7 0.6 0.5
STD 1.3 1.6 2.1 1.8 1.5
N 3 9 8 9 9
NOTE: Differences between means with a same superscript (a, b, or c) in the
same row are statistically
significant (p < 0.05).
113
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Table T-2-6
Descriptive Statistics for Intraocular Pressure in Treated Right Eyes (A.M.
Readings)
Intraocular Pressure (mmHg)
Day Statistic 0.1 % 10 mglg 5 mg/g I mg/g Balanced Salt
Dexamethasone BOL-303242-X BOL-303242-X BOL-303242-X Solution
(Group A) (Group B) (Group C) (Group D) (Group E)
Pre-Study MEAN 24.1 24.0 24.8 24.4 24.1
(5/9/07) SEM 0.7 0.5 0.5 0.6 0.5
STD 2.2 1.7 1.6 1.9 1.6
N 10 10 10 10 10
-- .......... __ .. - -- -_- -___ _ , .......... 3 MEAN 24.3 22.7 23.7 23.0
22.1
SEM 0.8 0.5 0.4 0.6 0.4
STD 2.0 1.5 1.3 2.0 1.3
N 6 10 9 10 9
MEAN 24.7 23.8 24.7 24.7 24.0
SEM 0.8 0.7 0.7 0.5 0.5
STD 1.9 2.3 2.1 1.5 1.5
N 6 10 9 10 9
MEAN 26.9 24.5 25.2 24.8 25.3
SEM 0.3 0.6 0.6 0.5 0.6
STD 0.7 2.0 1.7 1.4 1.8
N 6 10 9 10 9
12 MEAN 26.7 23.9 25.0 23.4 23.2
SEM 0.8 1.1 0.8 0.8 0.5
STD 1.9 3.4 2.3 2.6 1.6
N 6 9 9 10 9
-
16 MEAN 25.8a'b 23.4 24.3 22.1a 20.7
SEM 1.4 0.7 0.6 1.0 0.9
STD 3.2 2.1 1.7 3.0 2.8
N 5 9 9 10 9
NOTE: Differences between means with a same superscript (a or b) in the same
row are statistically
significant (p < 0.05).
114
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Table T-2-6 (continued)
Descriptive Statistics for Intraocular Pressure in Treated Right Eyes (A.M.
Readings)
Intraocular Pressure (mmHg)
Day Statistic 0.1% 10 mg/g 5 mg/g 1 mg/g Balanced Salt
Dexamethasone BOL-303242-X BOL-303242-X BOL-303242-X Solution
(Group A) (Group B) (Group C) (Group D) (Group E)
18 MEAN 24.1 22.3 23.9 23.7 21.9
SEM 0.7 0.8 0.7 0.5 0.8
STD 1.6 2.3 1.9 1.7 2.4
N 5 9 8 10 9
22 MEAN 25.4822.48 22.46 23-.2- 21.4c
SEM 0.4 0.6 0.7 0.4 0.6
STD 0.8 1.9 1.9 1.4 1.8
N 5 9 8 10 9
24 MEAN 24.38 21.2 23.8 22.1 21.18
SEM 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.7 0.9
STD 1.8 2.2 1.7 2.2 2.6
N 5__.._ 9 8 10 9
26 MEAN 23.1 21.8 22.1 23.1 20.4
SEM 0.9 1.0 1.3 0.8 0.5
STD 1.9 3.0 3.7 2.4 1.4
N 5 9 8 10 9
30 MEAN 23.5 22.7 22.9 24.2 22.1
SEM 1.0 0.6 1.3 0.8 0.5
STD 1.8 1.8 3.5 2.4 1.4
N 3 9 8 9 9
---- ----------
32 MEAN 25.5 23.9 23.4 24.9 23.1
SEM 0.6 0.4 0.9 0.6 0.5
STD 1.0 1.2 2.5 1.9 1.4
N 3 9 8 9 9
NOTE: Differences between means with a same superscript (a, b, or c) in the
same row are statistically
significant (p < 0.05).
115
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Table T-2-7
Descriptive Statistics for Intraocular Pressure in Untreated Left Eyes (P.M.
Readings)
Intraocular Pressure (mmHg)
Day Statistic 0.1% 10 mglg 5 mg/g I mg/g Balanced Salt
Dexamethasone BOL-303242-X BOL-303242-X BOL-303242-X Solution
(Group A) (Group B) (Group C) (Group D) (Group E)
Pre-Study MEAN 24.2 23.9 24.4 24.2 24.2
(5/9/07) SEM 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.5 0.4
STD 1.5 1.1 1.1 1.7 1.3
N 10 10 10 10 10
3 MEAN 24.3 23.3 23.9 25.0 23.5
SEM 0.7 0.4 0.5 0.4 0.4
STD 1.7 1.2 1.4 1.3 1.2
N 6 10 9 10 9
S MEAN 25.6 25.2 24.8 24.7 25.1
SEM 0.6 0.6 0.7 0.4 0.4
STD 1.4 2.0 2.0 1.3 1.2
N 6 10 9 10 9
MEAN 26.6 23.5 24.6 24.9 24.9
SEM 0.6 1.5 0.4 0.5 0.4
STD 1.4 4.9 1.1 1.6 1.3
N 6 10 9 10 9
12 MEAN 22.8 24.1 23.3 23.7 24.4
SEM 0.9 0.9 0.5 0.4 0.7
STD 2.2 2.8 1.5 1.4 2.0
N 6 9 9 10 9
16 MEAN 22.6 21.4 20.4 21.9 21.3
SEM 0.6 0.4 0.6 0.4 0.5
STD 1.4 1.2 1.8 1.3 1.5
N 5 9 9 10 9
116
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Table T-2-7 (continued)
Descriptive Statistics for Intraocular Pressure in Untreated Left Eyes (P.M.
Readings)
Intraocular Pressure (mmHg)
Day Statistic 0.1% 10 mg/g 5 mg/g I mg/g Balanced Salt
Dexamethasone BOL-303242-X BOL-303242-X BOL-303242-X Solution
(Group A) (Group B) (Group C) (Group D) (Group E)
18 MEAN 23.6 22.1 21.9 22.7 22.0
SEM 0.7 0.6 0.8 0.4 0.5
STD 1.6 1.9 2.2 1.3 1.5
N 5 9 8 10 9
22 MEAN 23.6 22.6 22.1 22.1 21.1
SEM 0.4 0.5 0.8 0.7 0.8
STD 1.0 1.5 2.2 2.1 2.4
N 5 9 8 10 9
24 MEAN 25.38.6_. 22.8.._. 22.2 a 22.9 22.16
SEM 0.7 0.8 0.8 0.5 0.4
STD 1.5 2.3 2.4 1.6 1.2
N 5 9 8 10 9
26 MEAN 21.9 21.4 22.3 22.1 20.9
SEM 1.2 0.9 1.1 1.0 0.7
STD 2.7 2.6 3.2 3.2 2.0
N 5 9 8 t0 9
30 MEAN 23.3 21.7 20.9 21.3 22.9
SEM 1.1 0.8 1.1 0.4 0.7
STD 1.9 2.4 3.0 1.1 2.0
N 3 9 8 9 9
-------------
32 MEAN 25.2 22.6 21.5 21.9 22.2
SEM 0.3 1.2 1.3 0.3 0.6
STD 0.6 3.5 3.5 1.0 1.7
N 3 9 8 9 9
NOTE: Differences between means with a same superscript (a or b) in the same
row are statistically
significant (p < 0.05).
117
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Table T-2-8
Descriptive Statistics for Intraocular Pressure in Treated Right Eyes (P.M.
Readings)
Intraocular Pressure (mmHg)
Day Statistic 0.1% 10 mg/g 5 mg/g I mg/g Balanced Salt
Dexamethasone BOL-303242-X BOL-303242-X BOL-303242-X Solution
(Group A) (Group B) (Group C) (Group D) (Group E)
Pre-Study MEAN 23.4 24.0 24.5 24.2 24.2
(5/9/07) SEM 0.6 0.4 0.3 0.5 0.5
STD 1.8 1.2 0.9 1.7 1.6
N 10 10 10 10 10
-----
3 MEAN 24.1 23.1 23.6 24.7 23.2
SEM 0.6 0.3 0.5 0.4 0.6
STD 1.4 0.8 1.6 1.2 1.7
N 6 10 9 10 9
MEAN 26.3 25.7 24.8 25.5 25.6
SEM 0.5 0.5 0.6 0.5 0.6
STD 1.2 1.7 1.9 1.6 1.8
N 6 10 9 10 9
MEAN 26.8 24.3 25.6 25.3 24.9
SEM 0.4 1.5 0.5 0.6 0.6
STD 1.0 4.6 1.6 2.0 1.7
N 6 10 9 10 9
12 MEAN 23.4 23.8 23.4 24.0 25.3
----- -- ------
SEM 0.5 0.8 0.6 0.5 0.5
STD 1.3 2.5 1.7 1.5 1.4
N 6 9 9 10 9
16 MEAN 21.5 21.6 21.4 22.0 21.3
SEM 0.9 0.6 0.7 0.5 0.4
STD 2.1 1.9 2.1 1.6 1.1
N 5 9 9 10 9
118
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Table T-2-8 (continued)
Descriptive Statistics for Intraocular Pressure in Treated Right Eyes (P.M.
Readings)
Intraocular Pressure (mmHg)
Day Statistic 0.1% 10 mglg 5 mg/g I mg/g Balanced Salt
Dexamethasone BOL-303242-X BOL-303242-X BOL-303242-X Solution
(Group A) (Group B) (Group C) (Group D) (Group E)
18 MEAN 23.6 22.5 21.6 23.1 21.9
SEM 0.8 0.9 0.9 0.3 0.5
STD 1.8 2.6 2.6 0.9 1.5
N 5 9 8 10 9
------- ---- ----- -------
22 MEAN 23.1 23.1 22.8 22.5 21.2
SEM 1.4 0.5 1.1 0.4 0.8
STD 3.2 1.6 3.0 1.4 2.3
N 5 9 8 10 9
24 MEAN 25.4 22.8 23.4 23.6 22.8
SEM 0.3 0.8 0.9 0.6 0.6
STD 0.7 2.5 2.5 2.0 1.8
N 5 9 8 10 9
26 MEAN 21.2 20.9 22.2 22.6 20.8
SEM 1.1 0.9 1.3 0.7 0.5
STD 2.6 2.6 3.8 2.1 1.5
N 5 9 8 10 9
30 MEAN 22.3 22.4 22.4 21.8 23.5
SEM 1.1 1.1 1.0 0.3 0.5
STD 1.9 3.3 2.7 1.0 1.5
N 3 9 8 9 9
32 MEAN 24.2 23.3 22.7 22.9 22.5
SEM 1.4 1.1 1.2 0.5 0.6
STD 2.4 3.4 3.4 1.5 1.8
N 3 9 8 9 9
TESTING 3: Effect of BOL-303242-X on Inhibiting TGF-(3 Stimulated Cellular
Levels
of Collagen type I, a-Smooth Muscle Actin, and Tissue Transgltaminase in Human
Tenon's Fibroblasts
Purpose: This study was conducted to determine the effect of BOL-303242-X on
proteins (collagen type I, a-smooth muscle actin ("a-SMA"), and tissue
transgitaminase)
that are produced by human Tenon's fibroblasts and that are believed to be
involved in
scarring during post-surgical wound healing.
Methods: Human Tenon's fibroblasts were seeded in 60 mm plates in 10% FBS
MEM (fetal bovine serum/Eagle's minimum essential medium) and grown until
approximately 90% confluency. After the cells were starved in 0.5% FBS MEM for
119
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
approximately 72 hours, the media was changed to fresh 0.5% FBS MEM. Cells
were
then treated with 0.1, 1, 3, 5 or 10 pM BOL-303242-X after which TGF-(3 (5
ng/ml) was
added. Cells were harvested 1, 3 or 5 days later. They were washed twice with
cold IX
PBS and scraped into I x SDS sample buffer. Lysates were assayed for protein
content
using the DC protein assay kit from Bio-Rad. Equal amounts of protein from
each
sample were electrophoresed on a 7.5%Tris-glycine SDS gel. Proteins were
transferred
to a PVDF membrane, blocked and probed with one or more of the following
antibodies:
mouse monoclonal anti-a-smooth muscle actin Clone IA4: (Sigma Aldrich,
#A2547),
mouse monoclonal anti-human GAPDH (6C5) (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., #sc-
32233), goat anti-human collagen alType I (L-19) (Santa Cruz Biotechnology,
Inc., #sc-
8783), or mouse monoclonal anti-transglutaminase II Ab-3 (ClonesCUB7402+TG100)
(NeoMarkers, # MS-300-P). Density of each band was measured densitometrically
and
the ratio to GADPH calculated.
Results and Discussion: Protein levels of collagen type I (Fig. 4), a-smooth
muscle actin (Fig. 5), and tissue transglutaminase (Fig. 6) were found to
increase over
the five-day period following addition of TGF-5 compared to cells incubated
without
TGF-(3. An inhibitory effect that appeared dose-related was observed when
levels of
protein at day 5 from cells treated with TGF-(3 were compared to levels from
TGF-
(3 treated cells incubated with increasing concentrations of BOL-303242-X
(Fig. 4-6).
Collagen deposition is central to wound healing and tissue remodeling. It is
also known
that a-SMA induces contraction of collagen gel, and thus actively participates
in
extracellular matrix remodeling. In addition, transglutaminase aids the
irreversible
cross-linking of extracellular matrix proteins, such as fibronectinand fibrin,
leading to
increased resistance to the outflow of the aqueous humor. Therefore, reducing
the levels
of collagen, a-SMA, and transglutaminase can have a positive effect on the
long-term
functioning of the filtering bleb.
Conclusion: BOL-303242-X was found to inhibit TGF-0-induced increases in
cellular levels of collagen type 1, a-SMA, and tissue transglutaminase. Thus,
administration of BOL-303242-X or a DIGRA to a patient can have a positive
effect on
preserving the long-term functioning of the filtering bleb after GFS.
120
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
Various non-limiting aspects of the present invention are enumerated in the
following section.
1. A composition comprising a dissociated glucocorticoid receptor agonist
("DIGRA"), a prodrug thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a
pharmaceutically acceptable ester thereof in an amount effective to reduce a
risk of
development of a non- or poorly functioning filtering bleb created in glaucoma
filtration
surgery in a subject.
2. The composition of aspect 1, further comprising an antagonist to at least a
TGF-(3
isoform.
3. The composition of aspect 2, wherein said glaucoma is selected from the
group
consisting of primary open-angle glaucoma, primary angle-closure glaucoma,
secondary
open-angle glaucoma, secondary angle-closure glaucoma, pigmentary glaucoma,
neovascular glaucoma, pseudophakic glaucoma, malignant glaucoma, uveitic
glaucoma,
glaucoma due to peripheral anterior synechia, and combinations thereof.
4. The composition of aspect 2, wherein the DIGRA comprises a compound having
Formula I
R~ RZ R3
A B DQ (I)
E
wherein A and Q are independently selected from the group consisting of
unsubstituted
and substituted aryl and heteroaryl groups, unsubstituted and substituted
cycloalkyl and
heterocycloalkyl groups, unsubstituted and substituted cycloalkenyl and
heterocycloalkenyl groups, unsubstituted and substituted cycloalkynyl and
heterocycloalkynyl groups, and unsubstituted and substituted heterocyclic
groups; R' and
R2 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen,
unsubstituted CI-
C15 linear or branched alkyl groups, substituted CI-C15 linear or branched
alkyl groups,
unsubstituted C3-C15 cycloalkyl groups, and substituted C3-C15 cycloalkyl
groups; R3 is
121
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, unsubstituted C1-C15 linear or
branched
alkyl groups, substituted C1-C15 linear or branched alkyl groups,
unsubstituted C3-C15
cycloalkyl and heterocycloalkyl groups, substituted C3-Q5 cycloalkyl and
heterocycloalkyl groups, aryl groups, heteroaryl groups, and heterocyclylic
groups; B
comprises a carbonyl, amino, divalent hydrocarbon, or heterohydrocarbon group;
E is
hydroxy or amino group; and D is absent or comprises a carbonyl group, -NH-,
or -NR'-
, wherein R' comprises an unsubstituted or substituted C1-C15 linear or
branched alkyl
group; and wherein R1 and R2 together may form an unsubstituted or substituted
C3-C15
cycloalkyl group.
5. The composition of aspect 4, wherein the composition causes a lower level
of at
least an adverse side effect in a subject than another composition comprising
at least a
glucocorticoid, wherein both said compositions are used to reduce said risk.
6. The composition of aspect 5, wherein said level of said at least an adverse
side
effect is determined by in vitro testing.
7. The composition of aspect 5, wherein said level of said at least an adverse
side
effect is determined in vivo.
8. The composition of aspect 5, wherein said at least a glucocorticoid is
selected
from the group consisting of dexamethasone, prednisone, prednisolone,
methylprednisolone, medrysone, triamcinolone, triamcinolone acetonide,
fluorometholone, loteprednol etabonate, physiologically acceptable salts
thereof,
combinations thereof, and mixtures thereof.
9. The composition of aspect 5, wherein said at least an adverse side effect
is
selected from the group consisting of ocular hypertension, glaucoma, cataract,
systemic
hypertension, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and hypercholesterolemia.
10. The composition of aspect 5, wherein the level of said at least an adverse
side
effect is determined at a time selected from the group consisting of about 14
days, about
122
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
30 days, about 2 months, about, 3 months, about 4 months, about 5 months, and
about 6
months, after the composition is first administered to, and is present in, a
subject.
11. The composition of aspect 10, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I
R1 R2 R3
A B/ DQ (I)
E
wherein A and Q are independently selected from the group consisting of aryl
and
heteroaryl groups substituted with at least a halogen atom, cyano group,
hydroxy group,
or CI-C10 alkoxy group; R1, R2, and R3 are independently selected from the
group
consisting of unsubstituted and substituted CI-C5 alkyl groups; B is a CI-C5
alkylene
group; D is the -NH- or -NR'- group, wherein R' is a C1-C5 alkyl group; and E
is the
hydroxy group.
12. The composition of aspect 4, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I
R1 R2 R3
A B/DQ (I~
E
wherein A comprises a dihydrobenzofuranyl group substituted with a halogen
atom; Q
comprises a quinolinyl or isoquinolinyl group substituted with a CI-Clo alkyl
group; RI
and R 2 are independently selected from the group consisting of unsubstituted
and
substituted C1-C5 alkyl groups; B is a C1-C3 alkylene group; D is the -NH-
group; E is
the hydroxy group; and R3 comprises a completely halogenated C1-C10 alkyl
group.
13. The composition of aspect 4, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I
R1 R2 R3
A B D'I-, Q (I)
E
123
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
wherein A comprises a dihydrobenzofuranyl group substituted with a fluorine
atom; Q
comprises a quinolinyl or isoquinolinyl group substituted with a methyl group;
R' and R2
are independently selected from the group consisting of unsubstituted and
substituted CI-
C5 alkyl groups; B is a CI-C3 alkylene group; D is the -NH- group; E is the
hydroxy
group; and R3 comprises a trifluoromethyl group.
14. The composition of aspect 4, wherein the DIGRA has Formula II
R4
O
H3C CH3 CF3 II
H
N N
(I1)
HO
R5
F
wherein R4 and R5 are independently selected from the group consisting of
hydrogen,
halogen, cyano, hydroxy, CI-C10 alkoxy groups, unsubstituted C,-C10 linear or
branched
alkyl groups, substituted Ci-Clo linear or branched alkyl groups,
unsubstituted C3-C10
cyclic alkyl groups, and substituted C3-C10 cyclic alkyl groups.
15. The composition of aspect 4, wherein the DIGRA has Formula III
R4
O N
H3C CH3 CF-
N ~ (III)
HO
R5
wherein R4 and R5 are independently selected from the group consisting of
hydrogen,
halogen, cyano, hydroxy, C,-Cio alkoxy groups, unsubstituted C,-Cio linear or
branched
124
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
alkyl groups, substituted CI-C10 linear or branched alkyl groups,
unsubstituted C3-C10
cyclic alkyl groups, and substituted C3-C10 cyclic alkyl groups.
16. The composition of aspect 4, wherein the DIGRA has Formula IV
CH3
O H3C CH3 CF3 / N (IV)
HO
F
17. The composition of aspect 16, further comprising a non-steroidal anti-
inflammatory drug ("NSAID").
18. The composition of aspect 1, further comprising an NSAID.
19. The composition of aspect 4, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl group optionally independently substituted with one to three
substituent groups, which are independently selected from the group consisting
of C1-C5
alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C1-C3 alkanoyl, C3-Cs cycloalkyl,
heterocyclyl, aryl,
heteroaryl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl,
C1-C5
alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl,
dialkylaminocarbonyl,
aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy,
C1-
C5 alkanoylamino, C,-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino,
aminosulfonyl, C1-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen,
hydroxy,
carboxy, cyano, trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the
nitrogen
atom is optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl or
aryl, ureido
wherein either nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-
C5 alkyl,
C1-C5 alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide
or sulfone;
(b) R' and R2 are each independently hydrogen or C1-C5 alkyl;
125
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
(c) R3 is the trifluoromethyl group;
(d) B is C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, or C2-C5 alkynyl, each optionally
independently substituted with one to three substituent groups, wherein each
substituent
group of B is independently C1-C3 alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, amino, or oxo;
(e) D is absent;
(f) E is the hydroxy group; and
(g) Q is an azaindolyl group optionally independently substituted with one to
three substituent groups, wherein each substituent group of Q is independently
C1-C5
alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl,
heteroaryl, C1-
C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5
alkoxycarbonyl,
C1-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl,
aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy,
C1-
C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonyl amino,
aminosulfonyl, C1-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaminosulfonyl, halogen,
hydroxy, carboxy, cyano, trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy,
trifluoromethylthio, nitro, or
amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally independently mono- or di-
substituted by
C1-C5 alkyl, ureido wherein either nitrogen atom is optionally independently
substituted
with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5 alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally
oxidized to a
sulfoxide or sulfone, wherein each substituent group of Q is optionally
independently
substituted with one to three substituent groups selected from the group
consisting of C1-
C3 alkyl, C1-C3 alkoxy, halogen, hydroxy, oxo, cyano, amino, and
trifluoromethyl.
20. The composition of aspect 4, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl or heteroaryl group, each optionally independently
substituted
with one to three substituent groups, which are independently selected from
the group
consisting of C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C1-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-
C5
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
126
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C,-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, Cl-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, CI-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R' and R2 are each independently hydrogen or C1-C5 alkyl, or R' and R2
together with the carbon atom they are commonly attached to form a C3-C8 spiro
cycloalkyl ring;
(c) B is the methylene or carbonyl group;
(d) R3 is a carbocycle, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle-C1-Cg
alkyl,
aryl-C1-Cs alkyl, aryl-C1-C8 haloalkyl, heterocyclyl-C1-C8 alkyl, heteroaryl-
C1-C8 alkyl,
carbocycle-C2-C8 alkenyl, aryl-C2-C8 alkenyl, heterocyclyl-C2-C8 alkenyl, or
heteroaryl-
C2-C8 alkenyl, each optionally independently substituted with one to three
substituent
groups;
(e) D is the -NH- group;
(f) E is the hydroxy group; and
(g) Q comprises a methylated benzoxazinone.
21. The composition of aspect 4, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl or heteroaryl group, each optionally independently
substituted
with one to three substituent groups, which are independently selected from
the group
consisting of C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, CI-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, CI-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-
C5
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
127
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, Ci-Cs
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, CI-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R' and R2 are each independently hydrogen or CI-C5 alkyl, or R' and R2
together with the carbon atom they are commonly attached to form a C3-C8 Spiro
cycloalkyl ring;
(c) R3 is the trifluoromethyl group;
(d) B is CI-C5 alkyl, Cz-C5 alkenyl, or C2-C5 alkynyl, each optionally
independently substituted with one to three substituent groups, wherein each
substituent
group of B is independently CI-C3 alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, amino, or oxo;
(e) D is absent;
(f) E is the hydroxy group; and
(g) Q is an aryl or heteroaryl group one to three substituent groups, which
are
independently selected from the group consisting of C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5
alkenyl, C2-C5
alkynyl, C1-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C1-
C5 alkoxy,
C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C'-'-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonyl,
aroyl,
aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-
C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-Cs dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkanoylamino, CI-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, CI-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, Cl-Cs
alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
128
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone,
wherein each
substituent group of Q is optionally independently substituted with one to
three
substituent groups selected from the group consisting of C1-C3 alkyl, C1-C3
alkoxy, acyl,
C1-C3 silanyloxy, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, carboxy, halogen, hydroxy, oxo, cyano,
heteroaryl, heterocyclyl, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally
independently
mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein either nitrogen
atom is
optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, and trifluoromethyl.
22. The composition of aspect 4, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl, heteroaryl, or C5-C15 cycloalkyl group, each optionally
independently substituted with one to three substituent groups, which are
independently
selected from the group consisting of C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5
alkynyl, C1-C3
alkanoyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C2-
C5
alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl,
aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-
C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-
C5
alkoxycarbonyl amino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, C1-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R' and R2 are each independently hydrogen, C1-C5 alkyl, C5-C15 arylalkyl,
or R' and R2 together with the carbon atom they are commonly attached to form
a C3-C8
spiro cycloalkyl ring;
(c) R3 is the trifluoromethyl group;
129
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
(d) B is the carbonyl group or methylene group, which is optionally
independently substituted with one or two substituent groups selected from C1-
C5 alkyl,
hydroxy, and halogen;
(e) D is absent;
(f) E is the hydroxy group or amino group wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by C,-C5 alkyl; and
(g) Q comprises a pyrrolidine, morpholine, thiomorpholine, piperazine,
piperidine, IH-pyridin-4-one, 1H-pyridin-2-one, 1H-pyridin-4-ylideneamine, 1H-
quinolin-4-ylideneamine, pyran, tetrahydropyran, 1,4-diazepane, 2,5-
diazabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 2,3,4,5-tetrahydrobenzo[b][1,4]diazepine,
dihydroquinoline,
tetrahydroquinoline, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-lH-quinolin-4-one,
tetrahydroisoquinoline,
decahydroisoquinoline, 2,3-dihydro- I H-isoindole, 2,3-dihydro- I H-indole,
chroman,
1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoxaline, 1,2-dihydroindazol-3-one, 3,4-dihydro-2H-
benzo[ 1,4]oxazine, 4H-benzo[ I ,4]thiazine, 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[ I
,4]thiazine, 1,2-
dihydrobenzo[d] [I,3]oxazin4-one, 3,4-dihydrobenzo[1,4]oxazin4-one, 3H-
quinazolin4-
one, 3,4-dihydro-lH-quinoxalin-2-one, 1H-quinnolin-4-one, 1H-quinazolin4-one,
IH-
[ 1,5]naphthyridin-4-one, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro- I H-[ I,- 5]naphthyridin-4-one,
2,3-dihydro-
IH-[1,5]naphthyridin-4-one, 1,2-dihydropyrido[3,2-d][1,3]oxazin-4-one,
pyrrolo[3,4-
c]pyridine-I,3-dione, 1,2-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyridin-3-one, or
tetrahydro[b][1,4]diazepinone group, each optionally independently substituted
with one
to three substituent groups, wherein each substituent group of Q is
independently CI-C5
alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl,
heteroaryl, C-
Cs alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C, -C5
alkoxycarbonyl,
CI-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl,
aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy,
C-
C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaminosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
oxo, cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, trifluoromethylthio, nitro, amino wherein
the nitrogen
atom is optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-Cs alkyl,
ureido wherein
either nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl,
or C1-C5
130
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or
sulfone,
wherein each substituent group of Q is optionally independently substituted
with one to
three substituent groups selected from C1-C3 alkyl, C1-C3 alkoxy, C1-C3
alkoxycarbonyl,
acyl, aryl, benzyl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl, halogen, hydroxy, oxo, cyano,
amino wherein
the nitrogen atom is optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5
alkyl, or
ureido wherein either nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted
with C1-C5
alkyl.
23. The composition of aspect 4, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl, heteroaryl, or C5-C15 cycloalkyl group, each optionally
independently substituted with one to three substituent groups, which are
independently
selected from the group consisting of C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5
alkynyl, C1-C3
alkanoyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C2-
C5
alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl,
aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-
C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, C1-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R1 and R2 are each independently hydrogen, C1-C5 alkyl, C5-C15 arylalkyl,
or R' and R2 together with the carbon atom they are commonly attached to form
a C3-C8
Spiro cycloalkyl ring;
(c) R3 is hydrogen, C1-C8 alkyl, C2-C8 alkenyl, C2-C8 alkynyl, carbocycle,
heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle-C1-C8 alkyl, carboxy,
alkoxycarbonyl, aryl-C1-
C8 alkyl, aryl-C1-C8 haloalkyl, heterocyclyl-C1-Cg alkyl, heteroaryl-C1-Cg
alkyl,
carbocycle-C2-C8 alkenyl, aryl-C2-C8 alkenyl, heterocyclyl-C2-C8 alkenyl, or
heteroaryl-
C2-C8 alkenyl, each optionally independently substituted with one to three
substituent
131
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
groups, wherein each substituent group of R3 is independently CI-C5 alkyl, C2-
C5
alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, phenyl, CI-C5 alkoxy, phenoxy, CI-C5
alkanoyl, aroyl, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, CI-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyloxy, CI-
C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, aminocarbonyl, C1 -C5
alkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, CI-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, CI-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5
dialkylaminosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy, cyano, oxo, trifluoromethyl,
nitro,
amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally independently mono- or di-
substituted by
Ci-C5 alkyl, ureido wherein either nitrogen atom is optionally independently
substituted
with Cl-C5 alkyl, CI-C5 alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally
oxidized to a
sulfoxide or sulfone, wherein R3 cannot be trifluoromethyl;
(d) B is the carbonyl group or methylene group, which is optionally
independently substituted with one or two substituent groups selected from C1-
C5 alkyl,
hydroxy, and halogen;
(e) D is absent;
(f) E is the hydroxy group or amino group wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl; and
(g) Q comprises a pyrrolidine, morpholine, thiomorpholine, piperazine,
piperidine, IH-pyridin-4-one, 1H-pyridin-2-one, IH-pyridin-4-ylideneamine, IH-
quinolin-4-ylideneamine, pyran, tetrahydropyran, 1,4-diazepane, 2,5-
diazabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 2,3,4,5-tetrahydrobenzo[b][1,4]diazepine,
dihydroquinoline,
tetrahydroquinoline, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-]H-quinolin-4-one,
tetrahydroisoquinoline,
decahydroisoquinoline, 2,3-dihydro- I H-isoindole, 2,3-dihydro- I H-indole,
chroman,
1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoxaline, 1,2-dihydroindazol-3-one, 3,4-dihydro-2H-
benzo[ I ,4]oxazine, 4H-benzo[ I ,4]thiazine, 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[ I
,4]thiazine, 1,2-
dihydrobenzo[d] [ I ,3]oxazin4-one, 3,4-dihydrobenzo[ I ,4]oxazin4-one, 3H-
quinazolin4-
one, 3,4-dihydro-IH-quinoxalin-2-one, IH-quinnolin-4-one, IH-quinazolin4-one,
IH-
[1,5]naphthyridin-4-one, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro- I H-[ I,- 5]naphthyridin-4-one,
2,3-dihydro-
IH-[I,5]naphthyridin-4-one, 1,2-dihydropyrido[3,2-d}[I,3]oxazin-4-one,
pyrrolo[3,4-
132
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
c}pyridine-1,3-dione, 1,2-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyridin-3-one, or
tetrahydro[b] [1,4]diazepinone group, each optionally independently
substituted with one
to three substituent groups, wherein each substituent group of Q is
independently C1-C5
alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl,
heteroaryl, C1-
C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C,-C5
alkoxycarbonyl,
C1-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl,
aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy,
C1-
C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, C,-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaminosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
oxo, cyan,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, trifluoromethylthio, nitro, amino wherein
the nitrogen
atom is optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl,
ureido wherein
either nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C,-C5 alkyl,
or C,-C5
alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or
sulfone,
wherein each substituent group of Q is optionally independently substituted
with one to
three substituent groups selected from C1-C3 alkyl, C1-C3 alkoxy, C1-C3
alkoxycarbonyl,
acyl, aryl, benzyl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl, halogen, hydroxy, oxo, cyano,
amino wherein
the nitrogen atom is optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5
alkyl, or
ureido wherein either nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted
with C1-C5
alkyl.
24. The composition of aspect 4, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl, heteroaryl, or C5-C15 cycloalkyl group, each optionally
independently substituted with one to three substituent groups, which are
independently
selected from the group consisting of C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5
alkynyl, C1-C3
alkanoyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C2-
C5
alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl,
aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-
C5
alkyl aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, C1-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
133
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl, CI-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R1 and R2 are each independently hydrogen or CI-C5 alkyl, or R1 and R2
together with the carbon atom they are commonly attached to form a C3-Cs Spiro
cycloalkyl ring;
(c) R3 is the trifluoromethyl group;
(d) B is the carbonyl group;
(e) D is the -NH- group;
(f) E is the hydroxy group; and
(g) Q comprises an optionally substituted phenyl group having the formula
x,
X2
Xq H
X3
wherein X1, X2, X3 and X4 are each independently selected from the group
consisting of
hydrogen, halogen, hydroxy, trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, C1-C5 alkyl, C2-
C5
alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, CI-C5 alkoxy, C1-CS alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom
is
optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone, C1-C5 alkanoyl, C1-C5
alkoxycarbonyl, C1-
C5 acyloxy, CI-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5 carbamoyloxy, urea, aryl, and amino
wherein
the nitrogen atom may be independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl,
and
wherein said aryl group is optionally substituted by one or more hydroxy or CI-
C5
alkoxy groups, and wherein either nitrogen atom of the urea group may be
independently
substituted by C1-C5 alkyl; or Q is an aromatic 5- to 7-membered monocyclic
ring having
from one to four heteroatoms in the ring independently selected from nitrogen,
oxygen,
134
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
and sulfur, optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent
groups
selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, hydroxy,
trifluoromethyl,
trifluoromethoxy, C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C1-
C5
alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or
sulfone, C1-C5
alkanoyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, C1-C5 acyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5
carbamoyloxy, urea, aryl optionally substituted by one or more hydroxy or C1-
C5 alkoxy
groups, and amino wherein the nitrogen atom may be independently mono- or di-
substituted by C1-C5 alkyl, and wherein either nitrogen atom of the urea group
may be
independently substituted by C1-C5 alkyl.
25. The composition of aspect 4, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl or heteroaryl group, each optionally independently
substituted
with one to three substituent groups, which are independently selected from
the group
consisting of C,-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C,-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-
C5
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, C1-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R' and R2 are each independently hydrogen or CI-C5 alkyl;
(c) R3 is C1-C8 alkyl, C2-C8 alkenyl, C2-C8 alkynyl, carbocycle, heterocyclyl,
aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle-C1-Cg alkyl, aryl-C1-C8 alkyl, aryl-C1-C8
haloalkyl,
heterocyclyl-C1-C8 alkyl, heteroaryl-C1-C8 alkyl, carbocycle-C2-C5 alkenyl,
aryl-C2-Cs
alkenyl, heterocyclyl-C2-C8 alkenyl, or heteroaryl-C2-C8 alkenyl, each
optionally
independently substituted with one to three substituent groups, wherein each
substituent
135
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
group of R3 is independently CI-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, phenyl, C1-C5 alkoxy, phenoxy, C1-C5 alkanoyl, aroyl, CI-C5
alkoxycarbonyl,
C1 -C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1 -C5
dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, aminocarbonyl, C1-C5 alkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C5
dialkylaminocarbonyl, C1 -C5 alkanoylamino, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5
alkylsulfonylamino, CI-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaminosulfonyl,
halogen,
hydroxy, carboxy, cyano, oxo, trifluoromethyl, nitro, amino wherein the
nitrogen atom is
optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl, ureido
wherein either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl, or C1-
C5
alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or
sulfone,
wherein R3 cannot be trifluoromethyl;
(d) B is C1-C5 alkylene, C2-C5 alkenylene, or C2-C5 alkynylene, each
optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent groups,
wherein each
substituent group of B is independently CI-C3 alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, amino,
or oxo;
(e) D is absent;
(f) E is the hydroxy group; and
(g) Q comprises an azaindolyl group optionally independently substituted
with one to three substituent groups, wherein each substituent group of Q is
independently CI-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C$ cycloalkyl,
heterocyclyl,
aryl, heteroaryl, CI-Cs alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy,
acyl, CI-C5
alkoxycarbonyl, CI-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl,
dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5
dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkanoylamino, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5
alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, CI-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-Cs
dialkylaminosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy, cyano, trifluoromethyl,
trifluoromethoxy, trifluoromethylthio, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom
is
optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl, ureido
wherein either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl, or CI-
C5
alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or
sulfone,
136
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
wherein each substituent group of Q is optionally independently substituted
with one to
three substituent groups selected from C,-C3 alkyl, C,-C3 alkoxy, halogen,
hydroxy, oxo,
cyano, amino, or trifluoromethyl.
26. The composition of aspect 4, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl or heteroaryl group, each optionally independently
substituted
with one to three substituent groups, which are independently selected from
the group
consisting of C,-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C1-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-
C5
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1 -C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1 -C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, CI-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, CI-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by CI -C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, CI-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R' and R2 are each independently hydrogen or C1-C5 alkyl, or R' and R2
together with the carbon atom they are commonly attached to form a C3-C8 Spiro
cycloalkyl ring;
(c) R3 is the trifluoromethyl group;
(d) B is C1-C5 alkylene, C2-C5 alkenylene, or C2-C5 alkynylene, each
optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent groups,
wherein each
substituent group of B is independently C1-C3 alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, amino,
or oxo;
(e) D is absent;
(f) E is the hydroxy group; and
137
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
(g) Q comprises a heteroaryl group optionally independently substituted with
one to three substituent groups, which are independently selected from the
group
consisting of CI-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-CS alkynyl, CI-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, CI-C5 alkoxy, C2-CS alkenyloxy, C2-
CS
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkanoylamino, CI-
CS
alkoxycarbonylamino, CI-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, CI-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl, CI-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone,
wherein each
substituent group of Q is optionally independently substituted with one to
three
substituent groups selected from the group consisting of CI-C3 alkyl, CI-C3
alkoxy, acyl,
CI-C3 silanyloxy, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, carboxy, halogen, hydroxy, oxo, cyano,
heteroaryl, heterocyclyl, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally
independently
mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein either nitrogen
atom is
optionally independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl, or trifluoromethyl.
27. The composition of aspect 4, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl or heteroaryl group, each optionally independently
substituted
with one to three substituent groups, which are independently selected from
the group
consisting of CI-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, CI-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, CI-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-
C5
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkanoylamino, CI-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, CI-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, CI-CS
alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
138
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R1 and R2 are each independently hydrogen or C1-C5 alkyl;
(c) R3 is hydrogen, C,-C8 alkyl, C2-C8 alkenyl, C2-C8 alkynyl, carbocycle,
heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle-C1-C8 alkyl, carboxy,
alkoxycarbonyl, aryl-C1-
C8 alkyl, aryl-Ci-C8 haloalkyl, heterocyclyl-C1-C8 alkyl, heteroaryl-C1-C8
alkyl,
carbocycle-C2-C8 alkenyl, aryl-C2-C8 alkenyl, heterocyclyl-C2-C8 alkenyl, or
heteroaryl-
C2-C8 alkenyl, each optionally independently substituted with one to three
substituent
groups, wherein each substituent group of R3 is independently C1-C5 alkyl, C2-
C5
alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, phenyl, C1-C5 alkoxy, phenoxy, C1-C5
alkanoyl, aroyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, C1-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-
C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, aminocarbonyl, C1-C5
alkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5
dialkylaminosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy, cyano, oxo, trifluoromethyl,
nitro,
amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally independently mono- or di-
substituted by
C1-C5 alkyl, ureido wherein either nitrogen atom is optionally independently
substituted
with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5 alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally
oxidized to a
sulfoxide or sulfone, wherein R3 cannot be trifluoromethyl;
(d) B is C1-C5 alkylene, C2-C5 alkenylene, or C2-C5 alkynylene, each
optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent groups,
wherein each
substituent group of B is independently C1-C3 alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, amino,
or oxo;
(e) D is absent;
(f) E is the hydroxy group; and
(g) Q comprises a heteroaryl group optionally independently substituted with
one to three substituent groups, which are independently selected from the
group
consisting of C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C1-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8
139
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, CI-CS alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-
CS
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, CI-CS
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-CS dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-CS alkanoylamino, CI-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, CI-CS alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, CI-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl, CI-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone,
wherein each
substituent group of Q is optionally independently substituted with one to
three
substituent groups selected from the group consisting of CI-C3 alkyl, CI-C3
alkoxy, acyl,
CI-C3 silanyloxy, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, carboxy, halogen, hydroxy, oxo, cyano,
heteroaryl, heterocyclyl, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally
independently
mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein either nitrogen
atom is
optionally independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl, or trifluoromethyl.
28. The composition of aspect 4, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl or heteroaryl group, each optionally independently
substituted
with one to three substituent groups, which are independently selected from
the group
consisting of C1 -C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, CI-C3 alkanoyl, C3-
C8
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, CI-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-
C5
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkanoylamino, CI-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, CI-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, CI-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl, CI-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
140
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
(b) R' and R2 are each independently C1-CS alkyl, wherein one or both are
independently substituted with hydroxy, C1-C5 alkoxy, C1-CS alkylthio wherein
the
sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone, amino wherein
the nitrogen
atom is optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl or
aryl;
(c) R3 is hydrogen, C1-C8 alkyl, C2-C8 alkenyl, C2-C8 alkynyl, carbocycle,
heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle-C1-C8 alkyl, carboxy,
alkoxycarbonyl, aryl-Ci-
C8 alkyl, aryl-C1-C8 haloalkyl, heterocyclyl-C1-C8 alkyl, heteroaryl-C1-C8
alkyl,
carbocycle-C2-C8 alkenyl, aryl-C,-C8 alkenyl, heterocyclyl-C2-C8 alkenyl, or
heteroaryl-
C2-C8 alkenyl, each optionally independently substituted with one to three
substituent
groups, wherein each substituent group of R3 is independently C1-C5 alkyl, C2-
C5
alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, phenyl, C1-C5 alkoxy, phenoxy, C1-C5
alkanoyl, aroyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, C1-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-
C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, aminocarbonyl, C1-C5
alkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-Cs alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5
dialkylaminosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy, cyano, oxo, trifluoromethyl,
nitro,
amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally independently mono- or di-
substituted by
C1-C5 alkyl, ureido wherein either nitrogen atom is optionally independently
substituted
with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5 alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally
oxidized to a
sulfoxide or sulfone;
(d) B is C1-C5 alkylene, C2-C5 alkenylene, or C2-C5 alkynylene, each
optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent groups,
wherein each
substituent group of B is independently C1-C3 alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, amino,
or oxo;
(e) D is absent;
(f) E is the hydroxy group; and
(g) Q comprises a heteroaryl group optionally independently substituted with
one to three substituent groups, which are independently selected from the
group
consisting of C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C1-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8
141
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C,-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-
C5
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C,-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C,-C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C,-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C,-C5 alkanoylamino, C,-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, C,-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, C,-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C,-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by C,-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C,-C5 alkyl, C,-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone,
wherein each
substituent group of Q is optionally independently substituted with one to
three
substituent groups selected from the group consisting of C,-C3 alkyl, C,-C3
alkoxy, acyl,
C,-C3 silanyloxy, C,-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, carboxy, halogen, hydroxy, oxo, cyano,
heteroaryl, heterocyclyl, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally
independently
mono- or di-substituted by C,-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein either nitrogen
atom is
optionally independently substituted with C,-C5 alkyl, or trifluoromethyl.
29. The composition of aspect 4, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl, or C3-C8 cycloalkyl group, each
optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent groups,
which are
independently selected from the group consisting of C,-C5 alkyl, C2-C5
alkenyl, C2-C5
alkynyl, C1-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C,-
C5 alkoxy,
C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C,-C5 alkoxycarbonyl,
aroyl,
aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C,-
C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C,-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C,-C5 alkanoylamino, C,-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, C,-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, C,-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C,-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by C,-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C,-C5 alkyl, C,-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
142
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
(b) Ri and R2 are each independently hydrogen, CI-C5 alkyl, C5-C15 arylalkyl,
or RT and R2 together with the carbon atom they are commonly attached to form
a C3-C8
Spiro cycloalkyl ring;
(c) B is the carbonyl group or methylene group, which is optionally
independently substituted with one or two substituent groups selected from the
group
consisting of C1-C3 alkyl, hydroxy, and halogen;
(d) R3 is the trifluoromethyl group;
(e) D is absent;
(f) E is hydroxy group or amino group wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl; and
(g) Q comprises a 5- to 7-membered heterocyclyl ring fused to a 5- to 7-
membered heteroaryl or heterocyclyl ring, each optionally independently
substituted
with one to three substituent groups, wherein each substituent group of Q is
independently C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl,
heterocyclyl,
aryl, heteroaryl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy,
acyl, C1-C5
alkoxycarbonyl, C1-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl,
dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5
dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, CI-C5
alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaminosulfonyl,
halogen,
hydroxy, carboxy, oxo, cyano, trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy,
trifluoromethylthio,
nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally independently mono- or di-
substituted by CI-C5 alkyl, ureido wherein either nitrogen atom is optionally
independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, or C1-C5 alkylthio wherein the
sulfur atom is
optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone, wherein each substituent group
of Q is
optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent groups
selected from
the group consisting of CI-C3 alkyl, Cr-C3 alkoxy, C1-C3 alkoxycarbonyl, acyl,
aryl,
benzyl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl, halogen, hydroxy, oxo, cyano, amino wherein
the
nitrogen atom is optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by CI -C5
alkyl, and
143
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
ureido wherein either nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted
with C,-C5
alkyl or trifluoromethyl, wherein Q cannot be I H-[ 1,5]naphthyridin-4-one.
30. The composition of aspect 4, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl, or C3-C8 cycloalkyl group, each
optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent groups,
which are
independently selected from the group consisting of CI-C5 alkyl, C2-C5
alkenyl, C2-C5
alkynyl, C1-C3 alkanoyl, C3-Cg cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C1-
C5 alkoxy,
C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonyl,
aroyl,
aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, CI-
C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkanoylamino, CI-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, C1-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R' and R2 are each independently hydrogen, Ci-C5 alkyl, C5-Cis arylalkyl,
or R' and R2 together with the carbon atom they are commonly attached to form
a C3-C8
Spiro cycloalkyl ring;
(c) B is the carbonyl group or methylene group, which is optionally
independently substituted with one or two substituent groups selected from the
group
consisting of C,-C3 alkyl, hydroxy, and halogen;
(d) R3 is hydrogen, C1-C8 alkyl, C2-C8 alkenyl, C2-C8 alkynyl, carbocycle,
heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle-C1-C8 alkyl, carboxy,
alkoxycarbonyl, aryl-Ci-
C8 alkyl, aryl-C1-C8 haloalkyl, heterocyclyl-C,-C8 alkyl, heteroaryl-C,-C8
alkyl,
carbocycle-C2-C8 alkenyl, aryl-C2-C8 alkenyl, heterocyclyl-C2-C8 alkenyl, or
heteroaryl-
C2-C8 alkenyl, each optionally independently substituted with one to three
substituent
groups, wherein each substituent group of R3 is independently CI-C5 alkyl, C2-
C5
144
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-Cs cycloalkyl, phenyl, C1-C5 alkoxy, phenoxy, C1-C5
alkanoyl, aroyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, C1-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-
C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, aminocarbonyl, C1-C5
alkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5
dialkylaminosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy, cyano, oxo, trifluoromethyl,
nitro,
amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally independently mono- or di-
substituted by
C1-C5 alkyl, ureido wherein either nitrogen atom is optionally independently
substituted
with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5 alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally
oxidized to a
sulfoxide or sulfone, wherein R3 cannot be trifluoromethyl;
(e) D is absent;
(f) E is hydroxy group or amino group wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl; and
(g) Q comprises a 5- to 7-membered heterocyclyl ring fused to a 5- to 7-
membered heteroaryl or heterocyclyl ring, each optionally independently
substituted
with one to three substituent groups, wherein each substituent group of Q is
independently C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl,
heterocyclyl,
aryl, heteroaryl, C,-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy,
acyl, C1-C5
alkoxycarbonyl, CI-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl,
dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5
dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5
alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaminosulfonyl,
halogen,
hydroxy, carboxy, oxo, cyan, trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy,
trifluoromethylthio,
nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally independently mono- or di-
substituted by C1-C5 alkyl, ureido wherein either nitrogen atom is optionally
independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, or C1-C5 alkylthio wherein the
sulfur atom is
optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone, wherein each substituent group
of Q is
optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent groups
selected from
the group consisting of C1-C3 alkyl, C1-C3 alkoxy, C1-C3 alkoxycarbonyl, acyl,
aryl,
benzyl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl, halogen, hydroxy, oxo, cyano, amino wherein
the
145
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
nitrogen atom is optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5
alkyl, and
ureido wherein either nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted
with CI-C5
alkyl or trifluoromethyl, wherein Q cannot be I H-[ 1,5]naphthyridin-4-one.
31. The composition of aspect 4, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl, or C3-C8 cycloalkyl group, each
optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent groups,
which are
independently selected from the group consisting of CI -C5 alkyl, C2-C5
alkenyl, C2-C5
alkynyl, C1-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C1-
C5 alkoxy,
C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonyl,
aroyl,
aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, CI-
C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkanoylamino, CI-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, C1-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R1 and R2 are each independently hydrogen or C1-C5 alkyl;
(c) R3 is the trifluoromethyl group;
(d) B is C1-C5 alkylene, C2-C5 alkenylene, or C2-C5 alkynylene, each
optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent groups,
wherein each
substituent group of B is independently CI-C3 alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, amino,
or oxo;
(e) D is absent;
(f) E is the hydroxy group; and
(g) Q comprises an indolyl group optionally substituted with one to three
substituent groups, wherein each substituent group of Q is independently CI-C5
alkyl,
146
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-Cs cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl,
heteroaryl, C1-C5
alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5
alkoxycarbonyl, C1-CS
alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl,
aminocarbonyloxy, C1-Cs alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-Cs dialkylaminocarbonyloxy,
C1-
Cs alkanoylamino, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl amino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino,
aminosulfonyl, C1-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaminosulfonyl, halogen,
hydroxy, carboxy, cyano, trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy,
trifluoromethylthio, nitro,
amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally independently mono- or di-
substituted by
C1-C5 alkyl, ureido wherein either nitrogen atom is optionally independently
substituted
with C1-C5 alkyl, or C1-C5 alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally
oxidized to a
sulfoxide or sulfone, wherein each substituent group of Q is optionally
independently
substituted with one to three substituent groups selected from the group
consisting of C1-
C3 alkyl, C1-C3 alkoxy, halogen, hydroxy, oxo, cyano, amino, and
trifluoromethyl.
32. The composition of aspect 4, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl or heteroaryl group, each optionally independently
substituted
with one to three substituent groups, which are independently selected from
the group
consisting of C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C1-C3 alkanoyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-
Cs
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, C1-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkytthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R' and R2 are each independently hydrogen or C1-C5 alkyl, or R' and R2
together with the carbon atom they are commonly attached to form a C3-C8 Spiro
cycloalkyl ring;
147
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
(c) R3 is carbocycle, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle-CI-C8 alkyl,
carboxy, alkoxycarbonyl, aryl-CI-C8 alkyl, aryl-CI-C8 haloalkyl, heterocyclyl-
CI-C8
alkyl, heteroaryl-CI-C8 alkyl, carbocycle-C2-C8 alkenyl, aryl-C2-C8 alkenyl,
heterocyclyl-C2-C8 alkenyl, or heteroaryl-C2-C8 alkenyl, each optionally
independently
substituted with one to three substituent groups, wherein each substituent
group of R3 is
independently CI-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl,
phenyl, CI-
C5 alkoxy, phenoxy, CI-C5 alkanoyl, aroyl, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, CI-C5
alkanoyloxy,
aminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy,
aminocarbonyl, CI-C5 alkylaminocarbonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyl, CI-C5
alkanoylamino, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, CI-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, CI-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaminosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano, oxo,
trifluoromethyl, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is optionally
independently
mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl, ureido wherein either nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl, CI-C5 alkylthio wherein the sulfur
atom is
optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(d) B is the methylene or carbonyl group;
(e) D is the -NH- group;
(f) E is the hydroxy group; and
(g) Q comprises the group
o
0
33. The composition of aspect 4, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
148
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
(a) A is an aryl or heteroaryl group, each optionally independently
substituted with one to three substituent groups, which are independently
selected from
the group consisting of C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-Cs alkynyl, CI-C3
alkanoyl, C3-Cg
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-
C5
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, Ci-Cs alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, CI-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, Ci-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R' and R2 are each independently hydrogen or C,-C5 alkyl, or R' and R2
together with the carbon atom they are commonly attached to form a C3-C8 spiro
cycloalkyl ring;
(c) R3 is the trifluoromethyl group;
(d) B is CI-C5 alkylene, C2-C5 alkenylene, or C2-C5 alkynylene, each
optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent groups,
wherein each
substituent group of B is independently CI-C3 alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, amino,
or oxo;
(e) D is absent;
(f) E is -NR6R7, wherein R6 and R7 are each independently hydrogen, CI-C8
alkyl, C2-C8 alkenyl, C2-C8 alkynyl, C1-C8 alkoxy, C2-C8 alkenyloxy, C2-C8
alkynyloxy,
hydroxy, carbocyclyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, aryloxy, acyl, heteroaryl,
carbocycle-C1-C8
alkyl, aryl-C1-C8 alkyl, aryl-C1-Cg haloalkyl, heterocyclyl-C-C8 alkyl,
heteroaryl-C,-C8
alkyl, carbocycle-C2-C8 alkenyl, aryl-C2-C8 alkenyl, heterocyclyl-C2-C8
alkenyl,
heteroaryl-C2-C8 alkenyl, or C1-C5 alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is
oxidized to a
sulfoxide or sulfone, each optionally independently substituted with one to
three
149
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
substituent groups, wherein each substituent group of R6 and R7 are
independently CI-C5
alkyl, C2-CS alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, phenyl, CI-C5 alkoxy,
phenoxy,
CI-CS alkanoyl, aroyl, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, CI-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyl,
CI-C5
alkylaminocarbonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, CI-Cs
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkanoylamino, CI-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, CI-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, CI-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-C5 dial kylaminosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano, oxo,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl, ureido wherein either
nitrogen
atom is optionally independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl, or C1 -C5
alkylthio wherein
the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone; and
(g) Q comprises a heteroaryl group optionally independently substituted with
one to three substituent groups, wherein each substituent group of Q is
independently CI-
C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl,
heteroaryl,
CI-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, CI-C5
alkoxycarbonyl,
CI-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyl, CI-C5 alkylaminocarbonyl, CI-C5
dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5
dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkanoylamino, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, CI-C5
alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, CI-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-C5
dialkylaminosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy, cyano, trifluoromethyl,
trifluoromethoxy, trifluoromethylthio, nitro, or amino wherein the nitrogen
atom is
optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl; or ureido
wherein
either nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl;
or CI-C5
alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or
sulfone,
wherein each substituent group of Q is optionally independently substituted
with one to
three substituent groups selected from CI-C3 alkyl, CI-C3 alkoxy, halogen,
hydroxy, oxo,
cyano, amino, or trifluoromethyl.
34. The composition of aspect 4, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I, wherein
(a) A is an aryl or heteroaryl group, each optionally independently
substituted with one to three substituent groups, which are independently
selected from
150
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
the group consisting of C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C1-C3
alkanoyl, C3-C8
cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-
C5
alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, aroyl, aminocarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, C1-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaninosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl or aryl, ureido wherein
either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone;
(b) R1 and R2 are each independently hydrogen or C1-C5 alkyl, or R' and R2
together with the carbon atom they are commonly attached to form a C3-C8 spiro
cycloalkyl ring;
(c) R3 is C1-C8 alkyl, C2-C8 alkenyl, C2-C8 alkynyl, carbocycle, heterocyclyl,
aryl, heteroaryl, carbocycle-Cl-CB alkyl, carboxy, alkoxycarbonyl, aryl-C1-C8
alkyl, aryl-
C1-C8 haloalkyl, heterocyclyl-C1-C8 alkyl, heteroaryl-C1-C8 alkyl, carbocycle-
C2-C8
alkenyl, aryl-C2-Cs alkenyl, heterocyclyl-C2-C8 alkenyl, or heteroaryl-C2-C8
alkenyl,
each optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent
groups, wherein
each substituent group of R3 is independently C1-C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-
C5 alkynyl,
C3-C8 cycloalkyl, phenyl, C1-C5 alkoxy, phenoxy, C1-C5 alkanoyl, aroyl, C1-C5
alkoxycarbonyl, C1-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyloxy, C1-C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy,
C1-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, aminocarbonyl, C1-C5 alkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C5
dialkylaminocarbonyl, C1-C5 alkanoylamino, C1-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, C1-C5
alkylsulfonylamino, C1-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, C1-C5 dialkylaminosulfonyl,
halogen,
hydroxy, carboxy, cyano, oxo, trifluoromethyl, nitro, amino wherein the
nitrogen atom is
optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl, ureido
wherein either
nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5
alkylthio
wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone,
wherein R3
cannot be trifluoromethyl;
151
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
(d) B is CI-C5 alkylene, C2-C5 alkenylene, or C2-C5 alkynylene, each
optionally independently substituted with one to three substituent groups,
wherein each
substituent group of B is independently CI-C3 alkyl, hydroxy, halogen, amino,
or oxo;
(e) D is absent;
(f) E is -NR6R7, wherein R6 and R7 are each independently hydrogen, CI-C8
alkyl, C2-C8 alkenyl, C2-C8 alkynyl, CI-C8 alkoxy, C2-C8 alkenyloxy, C2-C8
alkynyloxy,
hydroxy, carbocyclyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, aryloxy, acyl, heteroaryl,
carbocycle-CI-Cs
alkyl, aryl-CI-C8 alkyl, aryl-CI-C8 haloalkyl, heterocyclyl-CI-C8 alkyl,
heteroaryl-CI-Cs
alkyl, carbocycle-C2-Cs alkenyl, aryl-C2-C8 alkenyl, heterocyclyl-C2-C8
alkenyl,
heteroaryl-C2-C8 alkenyl, or CI-C5 alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is
oxidized to a
sulfoxide or sulfone, each optionally independently substituted with one to
three
substituent groups, wherein each substituent group of R6 and R7 are
independently CI-C5
alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, phenyl, CI-C5 alkoxy,
phenoxy,
CI-C5 alkanoyl, aroyl, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonyl, CI-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyl,
CI-C5
alkylaminocarbonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5
alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkanoylamino, CI-
C5
alkoxycarbonylamino, CI-C5 alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, CI-C5
alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-C5 dialkylaminosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy,
cyano, oxo,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, nitro, amino wherein the nitrogen atom is
optionally
independently mono- or di-substituted by CI-C5 alkyl, ureido wherein either
nitrogen
atom is optionally independently substituted with CI-C5 alkyl, or CI-C5
alkylthio wherein
the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone; and
(g) Q comprises a heteroaryl group optionally independently substituted with
one to three substituent groups, wherein each substituent group of Q is
independently CI-
C5 alkyl, C2-C5 alkenyl, C2-C5 alkynyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl,
heteroaryl,
CI-C5 alkoxy, C2-C5 alkenyloxy, C2-C5 alkynyloxy, aryloxy, acyl, CI-C5
alkoxycarbonyl,
CI-C5 alkanoyloxy, aminocarbonyl, CI-C5 alkylaminocarbonyl, CI-C5
dialkylaminocarbonyl, aminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5
dialkylaminocarbonyloxy, CI-C5 alkanoylamino, CI-C5 alkoxycarbonylamino, CI-C5
alkylsulfonylamino, aminosulfonyl, CI-C5 alkylaminosulfonyl, CI-C5
152
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
dialkylaminosulfonyl, halogen, hydroxy, carboxy, cyano, trifluoromethyl,
trifluoromethoxy, trifluoromethylthio, nitro, or amino wherein the nitrogen
atom is
optionally independently mono- or di-substituted by C1-C5 alkyl; or ureido
wherein
either nitrogen atom is optionally independently substituted with C1-C5 alkyl;
or C1-C5
alkylthio wherein the sulfur atom is optionally oxidized to a sulfoxide or
sulfone,
wherein each substituent group of Q is optionally independently substituted
with one to
three substituent groups selected from CI-C3 alkyl, CI-C3 alkoxy, halogen,
hydroxy, oxo,
cyano, amino, or trifluoromethyl.
35. The composition of aspect 4, further comprising an NSAID.
36. A method for pharmacological adjunctive treatment associated with glaucoma
filtration surgery in a subject, the method comprising: (a) providing a
composition
comprising a DIGRA, a prodrug thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt
thereof, or a
pharmaceutically acceptable ester thereof; and (b) administering to said
subject an
effective amount of the composition at a frequency sufficient to provide a
functioning
filtering bleb in said subject.
37. The method of aspect 36, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I
R1 R2 R3
/D (1)
A B
E
wherein A and Q are independently selected from the group consisting of
unsubstituted
and substituted aryl and heteroaryl groups, unsubstituted and substituted
cycloalkyl and
heterocycloalkyl groups, unsubstituted and substituted cycloalkenyl and
heterocycloalkenyl groups, unsubstituted and substituted cycloalkynyl and
heterocycloalkynyl groups, and unsubstituted and substituted heterocyclic
groups; RI and
R2 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen,
unsubstituted C1-
C15 linear or branched alkyl groups, substituted CI-C15 linear or branched
alkyl groups,
unsubstituted C3-C15 cycloalkyl groups, and substituted C3-C15 cycloalkyl
groups; R3 is
selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, unsubstituted C1-C15 linear or
branched
153
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
alkyl groups, substituted C,-Cis linear or branched alkyl groups,
unsubstituted C3-Q5
cycloalkyl and heterocycloalkyl groups, substituted C3-C,5 cycloalkyl and
heterocycloalkyl groups, aryl groups, heteroaryl groups, and heterocyclylic
groups; B
comprises a carbonyl, amino, divalent hydrocarbon, or heterohydrocarbon group;
E is
hydroxy or amino group; and D is absent or comprises a carbonyl group, -NH-,
or -NR'-
, wherein R' comprises an unsubstituted or substituted C1-C15 linear or
branched alkyl
group; and wherein R' and R2 together may form an unsubstituted or substituted
C3-Q5
cycloalkyl group.
38. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition further comprises an
antagonist to TGF-(3.
39. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition further comprises an
NSAID.
40. The method of aspect 38, wherein the composition further comprises an
NSAID.
41. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 5.
42. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 9.
43. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 11.
44. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 12.
45. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 13.
46. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 13.
154
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
47. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 14.
48. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 15.
49. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 16.
50. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 17.
51. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 19.
52. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 20.
53. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 21.
54. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 22.
55. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 23.
56. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 24.
57. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 25.
155
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
58. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 26.
59. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 27.
60. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 28.
61. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 29.
62. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 30.
63. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 31.
64. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 32.
65. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 33.
66. The method of aspect 37, wherein the composition comprises a composition
of
aspect 34.
67. Use of a DIGRA, a prodrug thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt
thereof, or
a pharmaceutically acceptable ester thereof to produce a composition for
pharmacological adjunctive treatment associated with GFS.
68. The use of aspect 67, further including the use of an antagonist to TGF-
(3.
156
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
69. A method for manufacturing a composition for pharmacological adjunctive
treatment associated with GFS, the method comprising:
(a) providing a DIGRA, a prodrug thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt
thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable ester thereof;
(b) providing an antagonist to TGF-j3; and
(c) combining said DIGRA, prodrug thereof, pharmaceutically acceptable salt
thereof, or pharmaceutically acceptable ester thereof with a pharmaceutically
acceptable carrier to produce said composition.
70. The method of aspect 69, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I
R1 R2 R3
A BDQ (1)
E
wherein A and Q are independently selected from the group consisting of
unsubstituted
and substituted aryl and heteroaryl groups, unsubstituted and substituted
cycloalkyl and
heterocycloalkyl groups, unsubstituted and substituted cycloalkenyl and
heterocycloalkenyl groups, unsubstituted and substituted cycloalkynyl and
heterocycloalkynyl groups, and unsubstituted and substituted heterocyclic
groups; R' and
R2 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen,
unsubstituted C1-
C15 linear or branched alkyl groups, substituted C1-C15 linear or branched
alkyl groups,
unsubstituted C3-C15 cycloalkyl groups, and substituted C3-C15 cycloalkyl
groups; R3 is
selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, unsubstituted C1-C15 linear or
branched
alkyl groups, substituted C1-C15 linear or branched alkyl groups,
unsubstituted C3-C15
cycloalkyl and heterocycloalkyl groups, substituted C3-C15 cycloalkyl and
heterocycloalkyl groups, aryl groups, heteroaryl groups, and heterocyclylic
groups; B
comprises a carbonyl, amino, divalent hydrocarbon, or heterohydrocarbon group;
E is
hydroxy or amino group; and D is absent or comprises a carbonyl group, -NH-,
or -NR'-
wherein R' comprises an unsubstituted or substituted C1-C15 linear or branched
alkyl
157
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
group; and wherein R' and R2 together may form an unsubstituted or substituted
C3-CI5
cycloalkyl group.
71. The method of aspect 69, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I
R~ R2 R3
A BI--*- D'-~Q (1)
E
wherein A and Q are independently selected from the group consisting of aryl
and
heteroaryl groups substituted with at least a halogen atom, cyano group,
hydroxy group,
or Ci-C10 alkoxy group; R', R2, and R3 are independently selected from the
group
consisting of unsubstituted and substituted C1-C5 alkyl groups; B is a Cl-C5
alkylene
group; D is the -NH- or -NR'- group, wherein R' is a CI-C5 alkyl group; and E
is the
hydroxy group.
72. The method of aspect 69, wherein the DIGRA has Formula I
R1 R2 R3
A B DQ (l~
E
wherein A comprises a dihydrobenzofuranyl group substituted with a halogen
atom; Q
comprises a quinolinyl or isoquinolinyl group substituted with a Cl-C10 alkyl
group; R'
and R2 are independently selected from the group consisting of unsubstituted
and
substituted C1-C5 alkyl groups; B is a CI-C3 alkylene group; D is the -NH-
group; E is
the hydroxy group; and R3 comprises a completely halogenated C1-Cl0 alkyl
group.
73. The method of aspect 69, wherein the DIGRA has Formula II
158
CA 02699599 2010-03-12
WO 2009/042377 PCT/US2008/075579
R4
O
H3C CH3 CF3 i l
H
N N
\ ~ (II)
HO
R5
wherein R4 and R5 are independently selected from the group consisting of
hydrogen,
halogen, cyano, hydroxy, CI-C10 alkoxy groups, unsubstituted CI-Ci0 linear or
branched
alkyl groups, substituted C1-C10 linear or branched alkyl groups,
unsubstituted C3-C10
cyclic alkyl groups, and substituted C3-C10 cyclic alkyl groups.
74. The method of aspect 69, wherein the DIGRA has Formula III
R4
O N
H3C CH3 CF3
N (III)
HO
R5
wherein R4 and R5 are independently selected from the group consisting of
hydrogen,
halogen, cyano, hydroxy, C1-C10 alkoxy groups, unsubstituted Ci-CIO linear or
branched
alkyl groups, substituted C1-CIO linear or branched alkyl groups,
unsubstituted C3-C10
cyclic alkyl groups, and substituted C3-C10 cyclic alkyl groups.
75. The method of aspect 69, wherein the DIGRA has Formula IV
159
CA 02699599 2012-02-07
CH3
H3C CH3
O CF3
N N (IV)
H
HO
F
76. The method of aspect 36, further comprising administering to the subject
an
effective amount of another therapeutic or prophylactic agent that is used to
treat, reduce,
or prevent (a) increased intraocular pressure, (b) loss of retinal ganglion
cells, or (c) both.
77. The method of aspect 38, further comprising administering to the subject
an
effective amount of another therapeutic or prophylactic agent that is used to
treat, reduce,
or prevent (a) increased intraocular pressure, (b) loss of retinal ganglion
cells, or (c) both.
78. The method of aspect 39, further comprising administering to the subject
an
effective amount of another therapeutic or prophylactic agent that is used to
treat, reduce,
or prevent (a) increased intraocular pressure, (b) loss of retinal ganglion
cells, or (c) both.
79. The method of aspect 76, wherein said another therapeutic or prophylactic
agent
is selected from the group consisting of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors,
muscarinic
cholinergic agonists, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, prostaglandin analogs, (3-
adrenergic
antagonists, a-adrenergic agonists, osmotic agents, and combinations thereof.
80. The method of aspect 77, wherein said another therapeutic or prophylactic
agent
is selected from the group consisting of anti-cholinesterase inhibitors,
muscarinic
cholinergic agonists, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, prostaglandin analogs, (3-
adrenergic
antagonists, a-adrenergic agonists, osmotic agents, and combinations thereof.
While specific embodiments of the present invention have been described in
the foregoing, it will be appreciated by those skilled in the art that many
equivalents,
modifications, substitutions, and variations may be made thereto.
160