Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02708124 2010-06-04
WO 2009/080882 PCT/F12008/050758
METHOD IN PNEUMATIC MATERIAL CONVEYING SYSTEM AND A
PNEUMATIC MATERIAL CONVEYING SYSTEM
Background of invention
The invention relates to a method according to the preamble of claim 1.
The invention further relates to a pneumatic material conveying system
according
to claim 15.
The invention relates generally to pneumatic conveying systems, such as vacuum
conveying systems, particularly to collecting and conveying waste, such as
conveying household waste.
Systems are known in which waste is conveyed in a piping by means of suction.
In
these, waste is conveyed for long distances in the piping by suction.
Apparatuses
are utilised, inter alia, for conveying waste in different institutions.
Typical for them
is that a vacuum apparatus is used for achieving a pressure difference, in
which
apparatus underpressure in the conveying pipe is provided with vacuum
generators, such as vacuum pumps or an ejector apparatus. In the conveying
pipe, there is typically at least one valve element by opening and closing of
which
make-up air coming in the conveying pipe is regulated. The vacuum conveying
systems typically contain, inter alia, the following problems: high energy
consumption, high air flow in the piping, problems with noise, dust and fine
particles in the outlet pipe. Furthermore, prior-art apparatuses can have
moisture
problems. In rainy weather, the prior-art apparatuses can suck even e.g. 1,000
litres of water per suction from outdoor air. This causes problems with
corrosion
and blockages. For example, waste paper etc. sticks to the piping when moist.
Furthermore, large systems have required arranging several separate make-up
air
valves, which increases the complexity and costs of the systems.
An object of this invention is to achieve a totally novel arrangement into
connection
with material conveying systems by means of which the disadvantages of known
arrangements are avoided. A second object of the invention is to provide an
arrangement applicable for vacuum conveying systems by means of which the
noise problems of material feed can be decreased. A third object of the
invention
is to decrease the production of moisture in the piping. An additional object
of the
CA 02708124 2010-06-04
WO 2009/080882 PCT/F12008/050758
2
invention is to provide an arrangement by means of which the number of make-up
air valves required in the system can be minimised. A further object is to
provide
an arrangement by means of which the volume of outlet air of the system and,
at
the same time, emissions of dust and fine particles and possible odour
nuisances
can be decreased.
Brief description of invention
The method according to the invention is mainly characterised in that at least
a
part of the conveying piping is connectable as a section of a circuit in which
conveying air is circulated at least during the conveyance of the material
with at
least one first pump device, such as a vacuum unit, and with at least one
second
pump device, such as a blower unit.
In addition, the method according to the invention is characterised by what is
stated in claims 2-14.
The material conveying system according to the invention is mainly
characterised
in that at least a part of the conveying piping is connectable as a section of
a
circuit in which conveying air is circulated at least during the conveyance of
the
material with at least one first pump device, such as a vacuum unit, and with
at
least one second pump device, such as a blower unit.
Furthermore, the material conveying system according to the invention is
characterised by what is stated in claims 16-26.
The arrangement according to the invention has numerous significant
advantages.
By opening and closing the feed points of the system according to the
invention,
the material is provided with an effective transfer into and conveyance in the
conveying pipe when, at the same time, the noise effect caused by the
operation
of the system can be minimised. By arranging the conveying pipe of the
material
conveying system to consist of operating areas i.e. partial circuits, it is
possible to
effectively arrange the conveyance of the material in the conveying piping and
emptying the feed points into the conveying pipe. By arranging the piping of
the
system to comprise a circuit where at least part of conveying air circulates,
the
volume of outlet air can be decreased. At the same time, the energy
consumption
of the system is minimised. By maintaining underpressure and simultaneously
CA 02708124 2010-06-04
WO 2009/080882 PCT/F12008/050758
3
blowing, it is possible to provide an effective circulation of conveying air
in the
circuit and conveyance of material in the conveying pipe. With the arrangement
according to the invention, it is possible to decrease the volume of outlet
air
substantially and simultaneously to decrease possible problems with dust and
fine
particles in the outlet pipe. The arrangement according to the invention also
substantially decreases the noise problem caused by prior art. Moisture
accumulated in the piping is minimised and the piping can be dried by
circulating
air in the piping. As the volume of air being sucked inside decreases, also
energy
consumption decreases. By arranging the conveying air circulation in the
reverse
direction, an effective removal of blockings is provided. In a circular
piping, it is
easily possible to arrange the change of the conveying air circulation in the
reverse direction.
Brief description of figures
In the following, the invention will be described in detail by means of an
example
with reference to the accompanying drawings in which
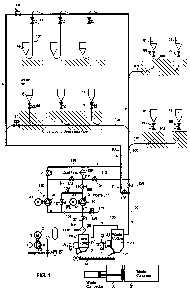
Fig. 1 schematically shows a system according to an embodiment of the
invention,
Fig. 2 schematically shows a system according to a second embodiment of the
invention,
Fig. 3 schematically shows a part of a system according to a third embodiment
of
the invention in a first operating mode,
Fig. 4 schematically shows a part of the system according to the third
embodiment
of the invention in a second operating mode,
Fig. 5 schematically shows a part of the system according to the third
embodiment
of the invention in a third operating mode,
Fig. 6 schematically shows a part of the system according to the third
embodiment
of the invention in a fourth operating mode, and
Fig. 7 schematically shows a part of the system according to the third
embodiment
of the invention in a fifth operating mode.
CA 02708124 2010-06-04
WO 2009/080882 PCT/F12008/050758
4
Detailed description of invention
In Fig. 1, reference number 61, 66 designates a feed station of materials,
particularly of waste material, intended to be conveyed, from which station
material, particularly waste material, such as household waste, intended to be
conveyed is fed to the conveying system. The system can comprise several feed
stations 61, 66 from which the material intended to be conveyed is fed to a
conveying piping 100, 101, 102, 103, 104. Typically, the conveying piping
comprises a main conveying pipe 100 into which several branch conveying pipes
101, 102 can have been connected and into which again several feed stations
61,
66 can have been connected via feed pipes 103, 104. The fed material is
conveyed along the conveying piping 100, 101, 102, 103, 104 to a separator
device 20 in which the material being conveyed is separated, e.g. due to
dropping
rate and centrifugal force, from conveying air. The separated material is
removed,
e.g. when required, from the separator device 20 to a material container, such
as a
waste container 51, or to further treatment. The material container can
comprise,
as in the embodiment of the figures, a waste compactor 50 from which the
material
is further conveyed to the waste container 51. In the embodiment of Fig. 1,
the
separator device 20 is provided with material outlet elements 21, 24. From the
separating device 20, a pipe 105 leads to means 3 for generating underpressure
in
the conveying pipe. In the embodiment of Fig. 1, the means for generating
underpressure comprise a vacuum pump unit 3. With the means for generating
underpressure, underpressure required for conveying the material is provided
in
the conveying piping 100, 101, 102, 103, 104. The vacuum pump unit 3 comprises
a pump 30 which is operated by an actuator 31.
According to the invention, the system further comprises a blower unit 4 which
is
connected in the embodiment of the figure from the blowing side to the
conveying
pipe 100. The conveying pipe 100 is a section of a circuit which in the
embodiment
of the figure consists of the main conveying pipe 100, the separator element
20
and the pipes 105 and 106. The blower unit 4 comprises a blower 40 and its
actuator 41. The blower 40 of the blower unit 4 is arranged from the suction
side to
the pipe 105, 106 coming from the separating device 20. The conveying pipe 100
is thus connected to the blower 40 on its blowing side. In the main conveying
pipe
is arranged at least one valve element 69 typically between the blower 40 of
the
blower unit 4 and the feed pipes 103 and/or branch conveying pipes 101, 102 in
CA 02708124 2010-06-04
WO 2009/080882 PCT/F12008/050758
the blowing direction of the blower 40. The blower also generates
underpressure
together with the vacuum generator.
The valve element 64 and 69 being in the closed position, the blower 40 raises
5 pressure to a section between the blower and the valve element 69 in the
conveying pipe 100. Equivalently in a section of the circuit on the suction
side of
the vacuum generator 3 and/or the blower 40, when travelling against the
conveying direction and/or the air flow direction, which comprises in the
embodiment of the figure the pipes 105, 106, at least one separator device 20,
20'
and a section of the main conveying pipe 100 from the separating device as far
as
the valves 69, underpressure prevails when the valves 69, 64 and the valves
60,
65 of the feed stations 61, 66 to the conveying pipe are closed.
In the embodiment of Fig. 1, the branch conveying pipe 102 extends from the
pressure side of the main conveying pipe 100 to the suction side of the main
conveying pipe i.e. forms a section of a smaller circuit. In the branch
conveying
pipe 102, at its end on the side of the pressure side of the main conveying
pipe, is
arranged the valve 64. The valve 64 of the branch conveying pipe being open
and
the valve 69 of the main conveying pipe being closed, a smaller circuit is
formed in
the embodiment of the figure in which air circulates from the blower 40 from
the
pressure side of the main conveying pipe via the branch conveying pipe 102 to
the
suction side of the main conveying pipe and further via the separator device
to the
pipe 105 and 106. When the vacuum pump unit runs, part of air circulating in
the
circuit is led to an outlet 34.
In the embodiment according to Fig. 1, into the main conveying pipe 100 are
connected two first branch conveying pipes 101. In the figure, into both first
branch
conveying pipes 101 are connected two feed stations 61. Into the second branch
conveying pipe 102 are connected three feed stations 61 by means of feed pipes
103. However, there can be more of them, e.g. 20. They can be opened and the
material conveyed to the conveying pipe stepwise, first the one closest in
relation
to the separator element 20, then the next closest etc.
In the upper part of the figure, there are further three feed stations 66
connected
directly to the main conveying pipe via feed pipes 104.
CA 02708124 2010-06-04
WO 2009/080882 PCT/F12008/050758
6
The sum of suctions provided by the vacuum unit 3 and the blower unit 4 to the
conveying pipe 100, in the figure from the side of the separator element, is
advantageously greater than the blowing provided by the blower unit, whereby
conveyance takes place in underpressure. With the blower 40, it is typically
possible to provide pressure which is e.g. in the range of 0.1-0.5 bar. With
the
vacuum generators, it is again typically possible to provide underpressure
which is
e.g. in the range of 0.1-0.5 bar. The blowing stores energy (i.e.
overpressure) in
the section of the conveying pipe 100 between the blower 40 and the valve 69
(and the valve 64) along with the rise of pressure, when the valves 69, 64 are
closed, e.g. +0.5 bar. The suction of the vacuum unit 3 stores on the other
side i.e.
to the section of the valve 69 and the separator element 20 (and the pipe 105)
underpressure which is e.g. -0.5 bar. When at least one of the valves 69, 64
opens, the pressure difference can then be even 1 bar. The suction being
greater
than blowing, underpressure is provided in the piping, whereby waste can be
sucked inside the piping from a funnel of the feed station 61.
The suction being greater than the blowing, which is the target in the system
according to the invention, material fed to the conveying pipe, particularly
waste
material, will not be compressed and compacted, but will be able to travel
"freely"
in the pipe conveyed by conveying air. Then, the potential of the material
being
conveyed to form blockages is considerably lower than in a situation in which
the
blowing is greater than the suction, whereby there is a risk that the material
being
conveyed will accumulate and block the conveying pipe. Furthermore,
underpressure decreases the power required to convey the material, because
even partial underpressure in relation to the material portion being conveyed
on
the side of the conveying direction considerably decreases air drag, among
others.
In the figure, arrows designate the direction of motion of air in the piping
in the
operating mode.
In conveying material, such as conveying waste material, when the material of
the
feed point is first conveyed by suction via the feed pipe 101, 103 or 104 to
the
conveying pipe, extremely fast acceleration and conveyance are provided for
the
material.
The conveying power provided by the pressure difference can then be e.g. in a
pipe of a diameter of 400 mm about in the range of 12.32 kN (1,256 kp). The
pressure side of the conveying pipe 100, i.e. in the example of the figure the
CA 02708124 2010-06-04
WO 2009/080882 PCT/F12008/050758
7
section between the blower 40 and the valve 69, 64, can be substantially
smaller
of its diameter than the suction side of the conveying pipe, i.e. typically at
least the
section between the valve 69, 64 and the separator element 20. The pressure
side
can then be formed more advantageous of its diameter and costs.
In the embodiment of the figure, in the pipe 106 on the suction side of the
blower is
formed a fitting 107 in which there is a valve 128 by opening of which extra
air can
be brought on the suction side of the vacuum unit and/or the blower from
outside
the circuit. By opening the valve 128, it is possible to raise the pressure of
air in
the conveying pipe if required and to provide an increased conveying rate for
conveying the material.
To the feed pipes 103, 104 is arranged the outlet valve 60, 65 which is opened
and closed so that material portions of suitable size are conveyed from the
feed
point 61, 66 to the branch conveying pipe 101, 102 or directly to the main
conveying pipe 100. Material is fed from the feed point 61, 66, such as a
waste
container, when after the container is full, the outlet valve 60, 65 is opened
either
automatically or manually.
The system typically operates as follows: An outlet hatch 21 of the separator
device 20 is closed and a valve 26 between the main conveying pipe 100 and the
separator device 20 is open. The vacuum pump unit 3 and/or the blower unit 4
maintains underpressure in the main conveying pipe 100. A suction effect
provided
by the vacuum unit 3 and the blower unit 4 together via the separator device
20 to
the conveying pipe 100 is greater than a pressure effect provided by the
blower
unit 4 to the conveying pipe 100 at its one end i.e. to the blowing side, to
the
section between the blower 40 and the valve 69 or the valve 64.
All outlet valves 60, 65 in the vicinity of the feed points i.e. waste
containers are
closed. In the start situation, the area valve 64 of the branch conveying pipe
102
and the line valve 69 of the main conveying pipe 100 are closed.
Let us assume that a waste container of the feed point 61 belonging to the
area of
the first branch conveying pipe 101 is to be emptied. Based on an emptying
signal,
the outlet valve 60 is momentarily opened, e.g. for 2-10 seconds, whereby the
material being conveyed, such as waste material, conveys from the effect of
underpressure to the branch conveying pipe and further to the main conveying
CA 02708124 2010-06-04
WO 2009/080882 PCT/F12008/050758
8
pipe 100. The outlet valve 60 is typically closed after a few seconds after
the start
situation. The vacuum pump unit 3 maintains desired underpressure and the
blower unit 4 starts unless not already running. The valve 69 is opened,
whereby
in the piping is provided blowing i.e. an intensified pressure effect and
suction
effect which conveys the material portion being conveyed along the piping to
the
separator device 20.
When the separator device 20 is full, the valve 26 of the conveying pipe 100
closes and a control valve 23 opens, whereby the actuator 24 of the outlet
hatch
21 of the separator device opens the outlet hatch 21 and the material
accumulated
in the separator device is emptied in the compactor device 50 and further in
the
waste container 51. The outlet hatch 21 of the separator device 20 is closed
and
the valve 26 opened.
After this, the start situation is reverted and the emptying process can be
repeated
or the emptying of some other feed point/feed points can be implemented.
The waste container 51, such as a waste freight container, is replaced or
emptied
when it is full.
In waste conveyance, it is possible to optimise air circulation and blowing so
that
the blowing is always directed as close as possible to the material portion
being
conveyed. If a material portion fed directly via the feed point 66 is being
conveyed,
first is opened the valve 69 in the main conveying pipe 100. After the
material
portion has passed the connecting point of the branch conveying pipe 102 and
the
main conveying pipe 100 in the case of the figure, the valve 64 of the branch
conveying pipe is opened and the valve 69 of the main conveying pipe is
closed,
whereby the blowing effect directs at the material portion being conveyed as
close
as possible and the motion of the material portion can be best maintained in
the
conveying pipe.
Fig. 2 shows an advantageous embodiment of a system according to the
invention. In the figure, the feed stations or feed points 61 and gate
elements 60 in
connection with them are diagrammatically designated along the conveying
piping
100 with one circle. The feed point 61 typically comprises a feed container,
such
as a funnel, and the valve element 60 by which a connection from the feed
point to
the conveying pipe 100 is closed and opened. The system conveying piping 100
CA 02708124 2010-06-04
WO 2009/080882 PCT/F12008/050758
9
and the feed points 61 along with it are dividable by area valves VA, VAB,
VBC, VBE,
VBE.... etc. arranged in the conveying piping to operating areas A, B, C, D,
E, F, G,
H, I. In the figure, each part of the conveying piping 100 of the operating
area is
designated with the letter of the corresponding operating area, whereby at the
point of the operating area A the conveying pipe is designated with 100A and
at
the point of operating area B the conveying pipe is designated with 100B. A
corresponding designation is used for the other operating areas. The operation
of
the system is controlled so that, for emptying the feed points of a desired
operating
area, at least one valve is open in the material conveying direction in
relation to
the operating area of the conveying pipe 100 and on the supply side of the
conveying air i.e. on the side of suction, whereby the suction is able to
affect the
conveying pipe of the operating area. Let us assume that, in the arrangement
according to the figure, the feed points 61 of the area A are to be emptied.
Then,
all area valves between the separator element 20 and the operating area A in
the
conveying pipe 100 (the sections 1008, 1000, 100D of the conveying pipe in the
figure) in the conveying direction are open (the valves VAB, VBC, VCD, VD in
the
figure). Then, suction provided by at least one vacuum generator 3 prevails in
the
conveying piping 100A in the operating area A. At least one valve VA on the
blowing side of the conveying pipe 100A is closed, whereby only suction
prevails
in the operating area A. The feed points 61 of the operating area or at least
part of
them are emptied so that the connection of the feed point 61 (I) closest to
the
delivery end in the conveying direction of the conveying pipe, i.e. in the
embodiment according to the figure closest to the separator device 20, to the
conveying pipe 100A is opened first, whereby the material is able to convey
from
the first feed point to the conveying pipe, and before the connection of the
first
feed point (I) to the conveying pipe closes, the connection of the next feed
point 61
(II) to the conveying pipe is opened. In the embodiment of the figure, this
is, when
travelling against the material conveying direction, the next feed point 61
(II)
intended to be emptied. After this, the connection of the first feed point 61
(I) is
closed to the conveying pipe. Equivalently, the connection of the third feed
point
61 (III) intended to be emptied to the conveying pipe is opened before the
connection of the second feed point 61 (II) to the conveying pipe is closed.
This
operation is repeated until all desired feed points have been emptied. In the
figure,
it has been considered emptying all the feed points 61 of the area A, whereby
their
emptying sequence to the conveying pipe 100, 100A is designated in the figure
by
numerals within parentheses: (I), (II), (III), (IV), (V), (VI), (VII), (VIII),
(IX), (X), and
(XI). When the passage of the last feed point 61 (XI) intended to be emptied
in the
CA 02708124 2010-06-04
WO 2009/080882 PCT/F12008/050758
operating area A to the conveying pipe 100 has been opened, the material has
conveyed to the conveying pipe 100, 100A and the passage of the feed point to
the conveying pipe is closed, a connection is opened in the conveying pipe
100A
of the operating area A from the blowing side i.e. the blower 4 by opening at
least
5 one valve element VA which is between the operating area A and the blower
device 4 blowing to the conveying pipe 100. Then, an intensified conveying
effect
(suction and blowing together) is provided for the material being conveyed
transferred in the conveying pipe 100, 100A, 1008, 1000, 100D. The conveying
air
circulates on a route designated with arrows in the figure, whereby material
10 portions conveyed from the feed points to the conveying pipe convey in the
conveying piping on the route, in the example of the figure, which passes the
areas B, C and D, and further to the separator device 20 in which the material
being conveyed is separated from conveying air. In the figure, the area valves
VBE
and VED of the conveying pipe 100E of the operating area E are closed, whereby
conveying air and material being conveyed are not able to access the conveying
pipe 100E of the operating area E but circulate via the conveying pipe 1000 of
the
area C. In connection with the emptying of different operating areas, the
material
conveying route from the operating area to a delivery station, such as to the
separator element 20, can be optimised by keeping the area valves open along
the desired conveying route.
Material is conveyed in the conveying pipe to the separator device 20. The
separator device 20 is emptied when required, e.g. to the material container
51, in
connection with which there can be the compactor device 50. In the system
according to the figure, a second separator device 20' is further arranged in
the
conveying air channel 105 after the separator element for separating smaller
particles from conveying air. The particles separated by the second separator
element 20' can be conveyed e.g. by a conveyor 27 to the material container
51.
The second separator element 20' is followed in the conveying air channel 105
in
the air circulation direction by a filter element 25 for removing small
particles from
conveying air. The air channel 105 is connected on the suction side of the
vacuum
generator 3 and the conveying air channel 105 branches before the vacuum
generator 3 to a second conveying air channel 106 which is connected on the
suction side of the blower device 4. The blowing side of the blower device is
connected directly or via the air channel 110 to the conveying pipe 100. The
conveying piping 100 comprises at least one circuit in which conveying air can
be
circulated from the blowing side of the blower via the separator element 20 on
the
CA 02708124 2010-06-04
WO 2009/080882 PCT/F12008/050758
11
suction side. It is possible to regulate with the valves which one or ones of
the
operating areas A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I are connected to the active
conveying
circuit of the conveying pipe 100.
Fig. 3 schematically shows a part of a pneumatic material conveying system,
particularly a waste material conveying system. The figure shows an actuating
unit
of the system and a delivery end of material of the conveying system i.e. a
part of
the system in which the material being conveyed is separated from conveying
air.
In the system according to the figure, the main conveying pipe 100 is
connected in
the normal conveying mode from the supply side to the separator device 20. The
system comprises at least one vacuum generator 3 the suction side of which is
connectable to the separator device 20 or to the conveying air channel 105
coming
from the separator device so that, with the vacuum generator 3, it is possible
to
provide underpressure at least to a section of the conveying pipe 100. The
system
comprises at least one blower unit 4. An embodiment of the actuating unit
according to the invention, which comprises at least one vacuum unit 3 and at
least one blower unit 4, has several operating modes. The embodiment of Fig. 3
shows an operating mode in which the suction sides of both the vacuum unit 3
and
the blower unit 4 are connected to the separator element or to the conveying
air
channel 105, 106 coming from the separator device 20, 20'. Then, suction as
high
as possible is providable in the conveying pipe 100. The suction side of the
pump
device 30 of the vacuum unit 3 and the suction side of the blower 40 of the
blower
unit 4 are connected in parallel in the operating mode in question, whereby a
suction effect as high as possible is provided in the conveying pipe 100. In
the
embodiment of the figure, the blowing side of the vacuum unit 3 and the
blowing
side of the blower unit 4 are arranged in the operating mode in question to
blow to
an outlet channel 112, in which at least one filter device 129 for filtering
outlet air is
typically arranged, such as in the embodiment of the figure. This operating
mode
can be particularly utilised in a situation in which material being conveyed,
such as
waste material, is conveyed from one or more feed points 61 or equivalents to
the
conveying pipe 100. Then, an extremely effective feed of waste material is
provided in the conveying pipe.
Fig. 4 shows a second operating mode of the actuating unit of the system
according to the invention in which the blowing side of the vacuum generator 3
is
connected to the suction side of the blowing unit 4 so that at least part of
air on the
blowing side of the vacuum generator is circulated on the suction side of the
CA 02708124 2010-06-04
WO 2009/080882 PCT/F12008/050758
12
blowing unit. In the embodiment of Fig. 3, a conveying air channel 109 is
arranged
from the conveying air channel 108 of the blowing side of the vacuum unit 3
and
conveyed to the medium channel 106 leading to the suction side of the blower
unit. In the conveying air channel 109 is arranged a valve element 121 which
is
open in the operating mode of Fig. 3. The blower unit 4 is in the operating
mode of
Fig. 3 arranged to blow in the air channel 110 which leads to the conveying
pipe
100 on its supply side. Then, in the conveying pipe at least on its return
side is
provided underpressure and a suction effect and in the conveying pipe on the
supply side equivalently a blowing effect. In this operating mode, it is thus
possible
to provide in the circuit, a section of which is formed by at least a part of
the
conveying pipe 100, a maximal conveying air flow, because the vacuum unit 3
sucks from the delivery end of the conveying pipe and the blower unit blows
from
the supply end of the conveying pipe. In the operating mode, the volume of
outlet
air can be kept minimal or nonexistent, because the conveying air is
circulated in
the circuit, a section of which is formed by a part of the conveying pipe 100,
and
the blowing air of the vacuum unit is conveyed on the suction side of the
blowing
unit and further to the conveying pipe 100 and in the circulation back via the
separator device 20 on the suction side of the vacuum unit. The vacuum unit
and
the blower unit are connected "in series". In this operating mode, an
extremely
efficient conveying effect is provided for materials being conveyed in the
conveying pipe. This operating mode is used when conveying material in the
conveying pipe to the delivery end, particularly to the separator device.
Combining
blowing with suction is extremely efficient, because the blowing effect i.e.
the
production of pressure is clearly more cost-effective than the production of
underpressure.
Fig. 5 shows a third operating mode of the actuating unit of the system, in
which
the blowing side of the vacuum unit 3 is connected to the air channel 110
connected on the supply side of the conveying pipe 100 and the blowing side of
the blower unit 4 is connected to the air channel 110 connected on the supply
side
of the conveying pipe 100. The suction side of the vacuum generator is
connected
to the separator device 20 or the air channel 105 coming from it. The suction
side
of the blower unit 4 is connected to the separator device 20 or to the
conveying air
channel 105 coming from it with the air channel 106. Due to a possible
requirement for extra air, there is arranged an inlet air channel 107 the
valve of
which is open in the embodiment of the figure, whereby on the suction side of
the
vacuum generator 3 and/or the blower 4 is led extra air. In the operating mode
of
CA 02708124 2010-06-04
WO 2009/080882 PCT/F12008/050758
13
this embodiment, a maximal air flow is provided in the piping, because both
the
vacuum generator and the blower unit are arranged to blow in the conveying
piping and suck from the conveying piping. This operating mode can be utilised
for
the air flushing of the conveying piping 100 and/or for the drying of the
conveying
piping. In the vacuum unit 3 and/or the blower unit 4, the air is compressed
and
heats up. This facilitates and speeds up the drying operation.
Fig. 6 shows an additional operating mode of the actuating unit in which it is
possible to reverse the circulation direction of conveying air at least in a
section of
the conveying pipe 100. In the conveying pipe is arranged on the supply side
at a
distance from the separator device a valve element 126, at the reverse side of
which in relation to the separator element is arranged an air channel 113 in
which
the blowing side of the vacuum unit is connectable. Equivalently, in the air
channel
110 of the blowing side is arranged the valve element 122 which, when closed,
prevents a connection of at least the blowing side of the blowing unit and/or
the
vacuum generator to the usual supply side of the conveying pipe. From the
blowing side of the vacuum unit is arranged a medium passage 110, 111, 113 to
the conveying piping 100 on its reversed supply side. Equivalently, from the
blowing side of the vacuum unit 3 can be arranged a medium passage 108, 113 to
the conveying piping 100 on its reversed supply side. In the embodiment of the
figure, a suction flow as effective as possible can be provided in the
conveying
pipe 100 with the vacuum generator and the blower connected in parallel. The
reversed circulation direction can be used e.g. in removing a blockage from
the
conveying pipe.
Fig. 7 additionally shows a further embodiment in which the blowing side of
the
vacuum unit 3 is connected on the suction side of the blower unit 4 and the
blowing side of the blower unit 4 is connected via the conveying air channels
110,
111, 113 on the reversed supply side of the conveying pipe 100. The arrows
designate the circulation direction of air in the system. In this embodiment,
an
effective combined suction and pressure effect is provided in the conveying
pipe.
In a case according to the invention, the conveying pipe 100 is at least a
section of
a suction/blowing circuit, the output end and inlet end of which are
advantageously
arranged into connection with the waste station and in which the output end of
the
suction/blowing circuit is on the blowing side of the blower 40 and the inlet
end on
the suction side of the blower 40. The blower can then, the valve 69 being
open,
CA 02708124 2010-06-04
WO 2009/080882 PCT/F12008/050758
14
circulate air in the suction/blowing circuit a section of which is formed by
the
conveying pipe 100. The feed points 61, 66 can be located decentralised along
the
system pipings distributedly. In connection with the waste conveying system,
the
feed points can be e.g. waste bins or waste chutes.
In a case according to the invention, the conveying pipe 100 is at least a
section of
a suction/blowing circuit, the output end and inlet end of which are
advantageously
arranged into connection with the waste station and in which the output end of
the
suction/blowing circuit is on the blowing side of the vacuum generator and/or
blower 40 and the inlet end on the suction side of the vacuum generator and/or
blower 40. The vacuum generator and/or blower can circulate air in the
suction/blowing circuit a section of which is formed by the conveying pipe
100. The
feed points 61, 66 can be located decentralised along the system pipings
distributedly. In connection with the waste conveying system, the feed points
can
be e.g. waste bins or waste chutes.
The invention thus relates to a method in a pneumatic material conveying
system,
such as a waste conveying system, which conveying system comprises at least
one feed point 61 of material, particularly of waste material, a material
conveying
pipe 100 which is connectable to the feed point 61, a separator device 20 in
which
the material being conveyed is separated from conveying air, and means 3, 4
for
providing a pressure difference in the conveying pipe 100 at least during the
conveyance of the material. At least a part of the conveying piping 100 is
connectable as a section of a circuit in which conveying air is circulated at
least
during the conveyance of the material with at least one first pump device,
such as
a vacuum unit 3, and with at least one second pump device, such as a blower
unit
4.
According to an embodiment of a method according to the invention, the
circulation of air in the circuit, which comprises at least a part of the
conveying
piping 100, is regulated and/or controlled and/or opened or closed by
gate/regulating elements, such as valve elements 120, 121, 122, 123, 124, 125,
126, 127, VA, VB, VC, VD, which are arranged in the circuit.
In the first operating mode of an embodiment of the method according to the
invention, underpressure is provided in the circuit with at least one first
pump
device, such as the vacuum generator 3, and/or one second pump device, such as
CA 02708124 2010-06-04
WO 2009/080882 PCT/F12008/050758
the blower unit 4, the suction side of which is connected to the separator
element
or to the conveying pipe 100 via an air channel 105, 106 leading to it.
In the first operating mode of an embodiment of the method according to the
5 invention, the blowing side of at least one first pump device, such as the
vacuum
unit 3, and/or one second pump device, such as the blower unit 4, is connected
to
an outlet channel 112 or equivalent.
In the second operating mode of an embodiment of the method according to the
10 invention, the blowing side of at least one first pump device, such as the
vacuum
unit 3, is connected to the suction side of at least one second pump device,
such
as the blower unit 4, so that at least part of air of the blowing side of the
first pump
device is circulated on the suction side of the second pump device.
15 In an embodiment of the method according to the invention, pressure is
provided
in the circuit with at least one pump device, such as the vacuum generator 3
and/or the blower 4, the blowing side of which is connected to blow in the
circuit.
In an embodiment of the method according to the invention, in the circuit is
20 brought make-up air via at least one air inlet 107, 112 which
advantageously
comprises a valve element 128, 120.
In an embodiment of the method according to the invention, air is removed from
the circuit via at least one air outlet 112 which advantageously comprises a
gate/regulating element, such as the valve element 120.
In an embodiment of the method according to the invention, the conveying air
circulation is connected in the reverse direction at least in a section of the
circuit,
which section is formed by at least a part of the conveying pipe 100,
advantageously for removing a blockage.
In another embodiment of the method according to the invention, at least a
part of
the conveying piping is flushed and/or dried with air by circulating conveying
air in
the circuit, particularly by blowing in the circuit with at least one first
pump device,
such as the vacuum generator 3, and/or one second pump device, such as the
blower 4.
CA 02708124 2010-06-04
WO 2009/080882 PCT/F12008/050758
16
In an embodiment of the method according to the invention, material is fed
from
the material feed points 61 which are waste feed points, such as waste bins or
waste chutes.
In an embodiment of the method according to the invention, between the
material
feed point 61 and the conveying pipe 100, there is at least one valve element
60
by opening and closing of which the feed of material and/or make-up air to the
conveying pipe is regulated.
According to an advantageous embodiment, the valve element 60 between the
material feed point 61 and the conveying pipe 100 is closed advantageously
after
a certain time from opening so that the valve 60 of the previous feed point is
still
open when the valve of the next feed point 61 is opened.
According to another advantageous embodiment, underpressure is provided in the
conveying pipe 100 at least at the point of the feed point 61 intended to be
emptied, the feed points are emptied to the conveying pipe 100 using an
emptying
sequence in which first is emptied a feed point located closer to the
separator
device 20 in the material conveying direction and next a feed point 61 located
substantially farther from the separator device 20 in the material conveying
direction.
The invention also relates to a pneumatic material conveying system, such as a
waste conveying system, which comprises at least one feed point 61 of
material,
particularly of waste material, a material conveying pipe 100 which is
connectable
to the feed point 61, a separator device 20 in which the material being
conveyed is
separated from conveying air, and means 3, 4 for providing a pressure
difference
in the conveying pipe 100 at least during the conveyance of the material. At
least a
part of the conveying piping 100 is connectable as a section of a circuit in
which
conveying air is circulated at least during the conveyance of the material
with at
least one first pump device, such as a vacuum unit 3, and with at least one
second
pump device, such as a blower unit 4.
According to an advantageous embodiment, in the circuit, which comprises at
least a part of the conveying piping 100, are arranged gate/regulating
elements,
such as valve elements 120, 121, 122, 123, 124, 125, 126, 127, VA, VB, VC, VD,
by
CA 02708124 2010-06-04
WO 2009/080882 PCT/F12008/050758
17
means of which the circulation of conveying air can be regulated and/or
controlled
and/or opened or closed.
The means for generating a pressure difference comprise at least one first
pump
device, such as the vacuum generator 3, and/or one second pump device, such as
the blower unit 4, the suction side of which is connected to the separator
element
20 or to the conveying pipe 100 via an air channel 105, 106 leading to it.
According to another advantageous embodiment, in the first operating mode, the
blowing side of at least one first pump device, such as the vacuum unit 3,
and/or
one second pump device, such as the blower unit 4, is connected to an outlet
channel 112 or equivalent.
In the second operating mode of an embodiment, the blowing side of at least
one
first pump device, such as the vacuum unit 3, is connected to the suction side
of at
least one second pump device, such as the blower unit 4, so that at least part
of
air of the blowing side of the first pump device is circulated on the suction
side of
the second pump device.
According to an embodiment, the system is arranged to provide pressure in the
circuit with at least one pump device, such as the vacuum generator 3 and/or
the
blower 4, the blowing side of which is connected to blow in the circuit.
According to a typical embodiment, the system comprises at least one air inlet
107, 112 which advantageously comprises the valve element 128, 120 for
bringing
make-up air in the circuit.
According to another typical embodiment, the system comprises at least one air
outlet 112 which advantageously comprises a gate/regulating element, such as a
valve element 120, for removing at least part of air from the circuit.
According to an advantageous embodiment, the system comprises means for
connecting the conveying air circulation in the reverse direction in at least
a
section of the circuit, which section is formed by at least a part of the
conveying
pipe 100.
CA 02708124 2010-06-04
WO 2009/080882 PCT/F12008/050758
18
According to an advantageous embodiment, the system comprises means for
flushing at least a part of the conveying piping 100 with air and/or for
drying by
circulating the conveying air in the circuit, particularly by blowing in the
circuit with
at least one first pump device, such as the vacuum generator 3, and/one second
pump device, such as the blower 4.
According to a further embodiment, the material feed points 61 are waste feed
points, such as waste bins or waste chutes.
Between the feed point 61 and the conveying pipe 100, there is at least one
valve
element 60 by opening and closing of which the feed of material and/or make-up
air to the conveying pipe is regulated.
It is obvious to those skilled in the art that the invention is not limited to
the
embodiments described above, but it may be varied within the scope of the
enclosed claims. When necessary, the features possibly described in this
specification together with other features may also be used separately from
each
other.