Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02748824 2013-04-09
74420-505
1
LAUNDRY MACHINE WITH VIBRATION REDUCTION
Technical Field
11] The present invention relates to a laundry machine.
[2] Generally, laundry machines are categorized into washers and dryers.
Such washers
include pulsator type washing machines and drum type washing machines and
washing
machines having washing and drying functions. Here, dryers are electric
appliances
that dry washed washing objects (hereinafter, laundry), using hot air and the
like.
Background Art
[3] Such a washing machine, especially, a drum type washing machine
includes a tub
arranged horizontally therein and also a drum arranged in the tub. Washing
objects
(hereinafter, laundry) are located within the drum and they are tumbled
together with
the rotation of the drum to be washed.
[4] Here, the tub is employed to hold wash water and the drum to have
laundry located
therein only to be washed.
151 The drum is rotatably located in the tub.
[6] A shaft is connected to a rear surface of the drum and the shaft
receives a rotational
force from a predetermined motor. As a result, the motor is rotated to
transmit its ro-
tational force to the drum and the rotational force rotates the drum.
[71 The drum is rotated during rinsing and drying-spinning cycles as well
as a washing
cycle and it is vibrated during its rotation.
[8] The shaft is projected outside the tub, passing through a rear surface
of the tub. The
conventional washing machine would include a bearing housing insert-molded in
the
rear surface of the tub or a bearing housing secured to the rear wall surface
of the tub.
[9] The above bearing housing supports the shaft and the vibration of the
drum is
transmitted to the tub and the bearing housing via the shaft.
[10] Because of that, the tub is vibrated together with the drum and a
damping supporting
material is connected to the tub to dampen such the vibration.
[11] The conventional washing machine includes a plurality of weights
attached to the tub
and the weights are for balancing the mass center of the above vibrating parts
including
the tub and the drum. Typically, the weights are attahced to a front portion
of the tub.
Disclosure of Invention
[12] Embodiments of the present invention may provide a laundry machine
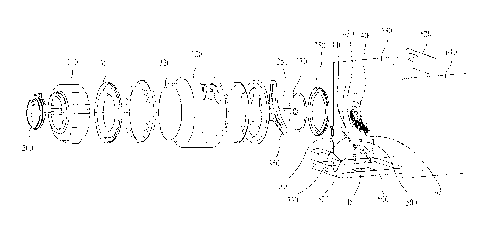
that is different
from the conventional laundry machine in an aspect of weights.
[13] Especially, the laundry machine according to some embodiments of the
present invention
may include
=
CA 02748824 2013-04-09
74420-505
2
weighing means having a different location of an overall gravity weight, by
extension, a
structure of a weight in comparison to the conventional laundry machine. The
change of the
location or structure relating to the weights may stabilize the vibration of
the vibrating system.
[14] One embodiment laundry machine may include a tub to hold water
therein; a
drum rotatbly placed in the tub; a drive assembly comprising a motor; and
means for adding
mass to a vibration system in which the drum is a vibrating system.
[14a] Another embodiment may include a laundry machine comprising: a
cabinet; a
tub fixed to the cabinet to hold water therein; a drum rotatably placed in the
tub; a drive
assembly comprising a shaft connected to the drum, a bearing housing rotatably
supporting
the shaft, and a motor to rotate the shaft; a suspension unit attached to the
bearing housing to
reduce vibration of the drum and separated from the tub; means for adding mass
to any one of
the drive assembly and the suspension unit supporting the drum to reduce
vibrations generated
by the drum, wherein the motor and the overall mass center of the means are
located distant
from a center of the drum in a same axial direction of the shaft.
[15] The motor and the overall mass center of the means are located distant
from a
center of the drum in a same axial direction (longitudinal direction) of the
shaft. The drive
assembly may include a shaft connected to the drum, a bearing housing
rotatably supporting
the shaft and the motor to rotate the shaft.
[16] The laundry machine may further comprises a suspension unit to reduce
vibration of the drum. Here, the motor may be connected with the shaft
directly or indirectly.
[17] The laundry machine may include means for adding mass to the vibration
system in which the drum is a vibrating object.
[18] The means may be a single weight or a plurality of weights.
[19] The overall mass center of the means may be located spaced toward the
motor
apart from a center of the drum in the longitudinal direction. That is, the
overall mass of the
means and the motor may be placed at the same side with respect to the center
of the drum.
CA 02748824 2013-04-09
74420-505
2a
[20] The center of the drum may be a weight center of the drum or a center
of the
longitudinal length of the drum.
[21] In case a door is provided in a front of the drum and the motor is
provided
behind the drum, the overall mass center of the means may be located behind
the center of the
drum.
[22] The overall mass center may be located behind the drum or tub.
[23] The center of the drum may be a longitudinal center of the drum.
Namely, the
center may be at the middle point of the drum in the longitudinal direction
(or the rotational
axis direction).
1 0 [24] The at least one weight of the means may be attached to or
integrally
configured of a bracket included in the suspension unit.
[25] The suspension unit may include a radial bracket or axial bracket.
[26] The radial bracket may be a bracket extended from the bearing housing
toward
the radial direction with respect to the shaft. The axial bracket may be a
bracket extended
from the bearing housing toward the axial direction.
[27] The at least one weight of the means may be located in the bearing
housing.
For
CA 02748824 2011-06-29
WO 2010/077090 PCT/KR2009/007960
3
example, the bearing housing and the at least one weight may be integrally
configured
or the at least one weight may be attached to the bearing housing.
[28] In the laundry machine, the tub may be fixedly supported, or be
supported by a
flexible support structure, such as the suspension unit.
[29] Further, the tub may be supported in an interim state between the
fixed support and
the flexible support.
[30] That is, the tub may be flexibly supported by the suspension unit or
be rigidly
supported. For example, the tub may be supported by the suspensions, be
supported by
rubber bushings to provide less flexible movement than when supported by the
sus-
pensions, or be fixedly supported by being fixed somewhere by screws or so.
[31] For another instance, the cases where the tub is supported more
rigidly than when
supported by the suspension unit are as follows.
[32] Firstly, the tub may be made intergrally with the cabinet.
[33] Next, the tub may be supported by being fastened by screws, ribets,
rubber bushings,
etc. Also, the tub may be welded or bonded to the cabinet. In this cases, the
supporting
or fastening members have larger stiffnesses than a stiffness of the
suspension unit
with respect to the main direction of the vibration of the drum.
[34] The tub may be expanded within the limits of a space in which the tub
is placed. That
is, the tub may be expanded until the circumferential surface thereof
reaches(or almost
reaches) a side wall or a side frame (for example, a left or right plate of a
cabinet) re-
stricting the size of the space at least in the lateral direction (the
direction laterally per-
pendicular to the axial direction of the rotary shaft when the rotary shaft is
horizontally
placed). The tub may be made intergally with the lateral side walls of the
cabinet.
[35] The tub may be formed to be closer in the lateral direction to the
wall or the frame
than the drum. For example, the tub may be spaced away from the wall or the
frame by
an interval of less than 1.5 times an interval with the drum. Under the
condition that
the tub is enlarged in the lateral direction, the drum may also be enlarged in
the lateral
direction. Further, if the lateral interval between the tub and drum is
reduced, the drum
may be expanded in the lateral direction in direct proportion. When the
lateral interval
between the tub and the drum is reduced, the vibration of the drum in the
lateral
direction may be considered. The weaker the vibration of the drum in the
lateral
direction, the more expanded is the diameter of the drum. Therefore, the
suspension
unit to reduce the vibration of the drum may be designed such that rigidity of
the
suspension unit in the lateral direction is greater than rigidities of the
suspension unit in
other directions. For example, the suspension unit may be designed such that
rigidity
of the suspension unit against displacement in the lateral direction is
greatest compared
with rigidities of the suspension unit against displacements in other
directions.
11361 Further, the suspension unit may be directly connected to the bearing
housing
CA 02748824 2011-06-29
WO 2010/077090 PCT/KR2009/007960
4
supporting the rotary shaft. That is, the bearing housing comprises a
supporting portion
to rotatably support the shaft and an extended portion extended from the
supporting
portion, and the suspension unit is attached to the supporting portion of the
bearing
housing or the extended portion of the bearing housing.
[37] The suspension unit may include brackets extended in the axial
direction. In a front
loading type laundry machine, the brackets may be extended forward, namely
towards
a door.
[38] The suspension unit may comprises at least two suspensions which are
arranged
distant from each other in the axial direction of the shaft.
[39] The suspension unit may comprise suspensions placed below the shaft
for standing
support. The supported object(for example, the drum) is supported by the
suspensions
to stand alone.
[40] Alternately, the suspension unit may comprise suspensions placed over
the shaft for
hanging support. In this case, the supported object is supported to be hung.
[41] The mass center of the vibrating object(for example, a combination of
the drum, the
shaft, the bearing housing, and the motor) may be located, with respect to the
center of
the longitudinal length of the drum, at a side where the motor is located. In
a front
loading type laundry machine, the mass center may be located behind the
longitudinal
center of the drum. In this case, at least one suspension may be placed in
front of or
behind the mass center. One suspension may be placed in front of the mass
center and
another suspension behind the mass center.
[42] The tub may be provided with an opening at a rear portion thereof. The
drive
assembly may be connected to the tub by a flexible member. The flexible member
may
seal between the tub and the drive assembly to prevent water from leaking
through the
opening of the rear portion of the tub, and allow the drive assembly to move
relatively
to the tub. The flexible member may be made of a flexible material which can
do the
sealing, for example, a gasket material like a front gasket. In this case, the
flexible
member may be referred to as a rear gasket for convenience. The rear gasket
may be
connected to the drive assembly under the condition that the rotation of the
rear gasket
at least in the rotational direction of the rotary shaft is constrained. In
one embodiment,
the flexible material may be directly connected to the shaft. In another
embodiment,
the flexible material may be connected to a portion of the bearing housing.
[43] Further, a portion of the drive assembly, which is located radially
inside the rear
gasket and thus is likely to be exposed to the water in the tub, may be made
so as no to
be corroded by the water. For example, the portion of the drive assembly may
be
coated, or be surrounded with a separate member made of plastic such as the
tub
back(which will be described below). In a case where the portion of the drive
assembly
is made of metal, the portion may not be directly exposed to water by the
coating or the
CA 02748824 2013-04-09
74420-505
=
separate plastic member, and thus corrosion of the portion may be prevented.
[44] Further, the cabinet may not be necessary. For example, in a
built-in laundry
machine, the laundry machine without the cabinet may be installed within a
space of a
wall structure. However, even in this case, a front plate forming the front
face of the
laundry machine may be required.
[46] The overall weight of the vibrating system provided in the laundry
machine
according to the exemplary embodiment of the present invention may be reduced
and
the vibration of the drum may be stabilized by new means for adding weights.
In
addition, the front of the drum may be prevented from falling downward because
of the
introduction of laundry.
Brief Description of Drawings
[47] The accompanying drawings, which are included to provide further
understanding of
the disclosure and are incorporated in and constitute a part of this
application, illustrate
embodiments of the disclosure and together with the description serve to
explain the
principle of the disclosure.
[48] In the drawings:
[49] FIG. 1 is a perspective view partially illustrating a laundry machine
according to the
present invention;
[50] FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating an exemplary embodiment of the
present invention;
[51] FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating a radial bracket of the laundry
machine shown in FIG.
2;
[52] FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating another embodiment of the present
invention; and
[53] FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating a further embodiment of the present
invention.
Mode for the Invention
[54] FIG. 1 is a partially perspective view illustrating a laundry machine
according to an
exemplary embodiment of the present invention.
[55] The laundry machine includes a tub fixedly supported to a cabinet. The
tub includes
a tub front 100 defining a front portion thereof and a tub rear 120 defining a
rear
portion thereof.
[56] The tub front 100 and the tub rear 120 may be assembled by a screw and
a prede-
termined space is formed inside the assembly of the tub front and rear 100 and
120 to
hold a drum. The tub rear 120 includes an opening formed in a rear portion
thereof and
the opening is connected to a rear gasket 250 that is a flexible member. The
rear gasket
250 may be connected to a tub back 130 in its inner radial portion. A through
hole is
formed in a center of the tub back 130 and a shaft passes through the hole.
The rear
CA 02748824 2011-06-29
WO 2010/077090 PCT/KR2009/007960
6
gasket 250 may be flexible enough not to transmit the vibration of the tub
back 130 to
the tub rear 120.
[57] The rear gasket 250 is sealedly connected with the tub back 130 and
the tub rear 120
such that wash water held in the drum may not leak. The tub back 130 is
vibrating
together with the drum when the drum is rotated and it is spaced apart a
predetermine
distance from the tub rear 120 enough to prevent interference with the tub
rear 120.
Since the rear gasket 120 is transformed flexibly, the tub back 130 is allowed
to
relatively move without interfering with the tub rear 120. The rear gasket 120
may
include a curvature or wrinkle portion 252 extendible to a predetermined
length
enough to allow such the relative motion.
[58] The tub includes an introduction opening formed in a front portion
thereof to
introduce laundry. A front gasket 200 may be installed in the front portion of
the tub in
which the introduction opening is formed to prevent the laundry or foreign
substances
from being stuck between the tub and the drum or to prevent wash water from
leaking
toward the introduction opening or to perform another function.
[59] The drum includes a drum front 300, a drum center 320 and a drum back
340. A ball
balancer may be installed in each of front and rear portions of the drum,
respectively.
The drum back 340 is connected to a spider 350 and the spider 350 is connected
to the
shaft 351. Here, the drum is rotatable within the tub by the rotational force
transmitted
via the shaft 351.
[60] The shaft 351 is connected to a motor, passing through the tub back
130. According
to this embodiment, the motor is connected to the shaft in a concentric
circle. That is,
according to this embodiment, the motor, specifically, a rotor of the motor is
directly
connected to the shaft 351. A bearing housing 400 is secured to a rear surface
128 of
the tub back 130. The bearing housing 400 is provided between the motor and
the tub
back 130 and it rotatably supports the shaft 351.
[61] A stator 80 is fixedly secured to the bearing housing 400 and the
rotor is located
around the stator 80. As mentioned above, the rotor is directly connected to
the shaft
351. Here, the motor is an outer rotor type and it is directly connected to
the shaft 351.
[62] The bearing housing 400 is supported by a base 600 of the cabinet via
a suspension
unit. The suspension unit may include a plurality of brackets connected to the
bearing
housing and the suspension unit may include a plurality of suspensions
connected to
the plurality of the brackets.
[63] According to this embodiment, the suspension may include three
perpendicular
suspension and two oblique suspensions installed oblique with respect to a
forward/
rearward direction. The suspension unit is connected to the cabinet base 600
not
fixedly but flexibly enough to allow the drum to move in forward/rearward and
leftward/rightward directions. That is, the suspension unit is supported by
the cabinet
CA 02748824 2011-06-29
WO 2010/077090 PCT/KR2009/007960
7
base 600, with being flexible enough to allow a predetermined rotation
forward/
rearward and leftward/rightward with respect to the supported location. For
such the
flexible support, the suspension vertically installed may be installed in the
base 600 by
rubber-bushing. Predetermined ones of the suspensions installed vertically are
configured to suspend the vibration of the drum flexibly and the other ones
installed
obliquely may be configured to damp the vibration. That is, in a vibrometer
including a
spring and damping means, the vertically installed ones are employed as spring
and the
obliquely installed ones are employed as damping means.
[64] The tub is fixed to the cabinet and the vibration of the drum is
suspended by the
suspension unit. The front and rear portions of the tub may be fixed to the
cabinet and
the tub is seatedly supported by the cabinet base or fixed to the cabinet
base.
[65] The laundry machine according to this embodiment includes the
supporting structure
of the tub and that of the drum that are substantially independent. In
addition, the
laundry machine has the structure in which the tub is not vibration during the
vibration
of the drum. Here, the quantity of vibration transmitted to the drum may be
variable
according to the rear gasket.
[66] As the vibration of the tub is noticeably small in the laundry machine
according to
the present invention, the space maintained because of the vibration is
unnecessary and
thus an outer surface of the tub may be located close to the cabinet as much
as
possible. This enables the enlarged size of the tub, without the enlarged size
of the
cabinet, and also it enables the capacity of the laundry machine to be
increased, in the
same external size.
[67] Substantially, the distance between a cabinet right 630 or a cabinet
left 640 and the
tub may be only 5mm in the laundry machine according to this embodiment of the
present invention. In contrast, the distance is 300mm to prevent the vibration
of the tub
from interfering with the cabinet in the conventional laundry machine.
Considering a
diameter of the tub, the laundry machine according to this embodiment may
lengthen
the diameter of the tub by 500mm in comparison with the conventional laundry
machine. This results in noticeable difference enabling the capacity of the
laundry
machine to be one-stepped up in the identical external size.
[68] The weight according to this embodiment is located in the suspension
unit and this
technical feature is different from the technical feature of the conventional
laundry
machine that the weight is located in the tub.
[69] The weight may be integrally formed with predetermined elements of the
suspension
unit or it may be secured to the suspension unit. For example, the weight may
be in-
tegrally formed with or secured to a bracket included in the suspension unit.
The
bracket may be an element for connecting the bearing housing with the
suspension.
The bearing housing and one of the suspensions may be spaced apart in a radial
CA 02748824 2011-06-29
WO 2010/077090 PCT/KR2009/007960
8
direction with respect to the shaft as well as in an axial direction of the
shaft. As a
result, the bracket may include a radial bracket extended toward the radial
direction
and an axial bracket extended toward the axial direction.
[70] FIGS. 2 and 3 are diagrams illustrating the weight integrally formed
with the radial
bracket of the suspension unit.
[71] As shown in FIG. 2, the suspension unit includes first second radial
brackets 431 and
430 and first and second axial brackets 450 and 440 and the suspension unit is
secured
to the base 600.
[72] The suspension unit may include a perpendicular suspension for
perpendicular
suspending and a forward/rearward suspension for forward/rearward suspending.
A
single perpendicular suspension may be placed in a rear portion and two
perpendicular
suspensions may be placed in both opposite sides of a front portion with
respect to a
center of the base, respectively. Furthermore, two suspensions may be placed
oblique
from left and right sides in a forward/rearward direction.
[73] As shown in FIG. 2, the suspension unit includes a first suspension
520, a second
suspension 510, a third suspension 500, a first damper 540 and a second damper
530.
[74] The suspension is configured of a cylinder and a piston connected by a
spring
installed there between. The length of the suspension configured of the
cylinder and
piston is stably variable during the suspending. Such the suspension may be
configured
to have a damping effect as well. That is, the suspension may be made of a
spring
damper.
[75] The first damper 540 and the second damper 530 may be made of simple
dampers
and they are not limited thereto. The first and second dampers may be made of
spring
dampers.
[76] The first suspension 520 is connected between the first axial bracket
450 and the base
600. The second suspension is connected between the second axial bracket 440
and the
base 600.
[77] The third suspension 500 is directly connected between the bearing
housing 400 and
the base.
[78] The suspensions are installed vertically and the first and second
dampers are installed
obliquely in a forward/rearward direction.
[79] The third suspension is installed in a center of the rear portion and
the first and
second suspensions are in right and left sides of a front portion,
respectively. The first
and second dampers are installed between the third suspension and the first
and second
suspensions, respectively, symmetrical bilaterally.
[80] The suspensions are connected to the base by rubber-bushing.
[81] FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating the weight more specifically. The
first radial bracket
431 is connected to the left portion of the bearing housing 400 and the second
radial
CA 02748824 2011-06-29
WO 2010/077090 PCT/KR2009/007960
9
bracket 430 is connected to the right portion of the bearing housing 400. The
first and
second radial brackets 431 and 430 are symmetrical to each other with respect
to the
axial direction.
[82] The first and second radial brackets 431 and 430 are formed as weights
and as
bracket connecting the first and second axial brackets 450 and 440 to the
bearing
housing 400, respectively.
[83] The first and second radial brackets 3410 and 430 are extended toward
a radial
direction with respect to the shaft 351 and they are extended toward a forward
reaction.
A coupling hole is formed in an upper portion of each above weight to couple
each
weight is coupled to a corresponding weight coupling part. Four coupling holes
are
formed in each upper portion of the weights.
[84] Position determining grooves 430b and 431b are formed in the radial
brackets 431
and 430, respectively, to be inserted in the bearing housing.
[85] Bracket connecting parts 430c and 431c are formed in the first and
second radial
brackets 431 and 430, respectively, to be connected to the first and second
axial
brackets. The bracket connecting part is heavier than the other parts of the
weight. The
lower the mass center of the weight is, the more stable the vibrating system
is.
[86] Such the first and second radial brackets 431 and 430 may be
fabricated of iron by
casting.
[87] In reference to FIG. 3, the first and second radial brackets 431 and
430 include first
and second coupling parts 431d and 430d formed in the upper portions thereof
to be
connected with the bearing housing 400. The coupling parts 431d and 430d are
fixedly
coupled to first and second extended portions 406a and 406b of the bearing
housing by
coupling members, respectively. Here, when the first and second coupling parts
431d
and 430d are coupled to the first and second extended portion 406a and 406b of
the
bearing housing 400, the angle between the first and second coupling parts
431d and
430d is maintained identical to the angle between the first and second
extended
portions 406a and 406b. For this coupling, the coupling holes are formed in
the
coupling parts 431d and 430d and each of the coupling holes 431d and 430d
includes
four coupling holes to secure the coupling rigidity.
[88] The radial brackets 431 and 430 include middle portions 431e and 430e
extended
from the first and second coupling parts 431d and 430d, respectively. The
middle
portions 431e and 430e are located between the first and second coupling parts
431d
and 430d and the bracket connecting parts 431c and 430c.
[89] The middle portions 431e and 430e are spaced apart a predetermined
distance
rearward from the rear wall of the tub enough not to interfere with the rear
wall
because of the vibration of the drum during the operation of the laundry
machine.
Here, the rear wall of the tub is referenced to as the rear surface connected
by the tub
CA 02748824 2011-06-29
WO 2010/077090 PCT/KR2009/007960
back and the rear gasket. That is, the though hole having a diameter larger
than the
diameter of the tub back is formed in a center of the rear wall of the tub and
an inner
circumference of the rear wall is connected with an outer circumference of the
tub back
by the rear gasket.
[90] The bracket connecting portions 431c and 430c are extended forward
from the
middle portions 431e and 430e. The bracket connecting portions 431c and 430c
are
located in an outer portion of the outer circumferential surface of the tub
with respect
to the radial direction. The bracket connecting portions 431c and 430c may
interfere
with the rear wall of the tub. However, the bracket connection members are
extended
forwardly to be connected with the brackets 440 and 450 and thus they may be
fabricated in consideration of the possibility of interference with the outer
circum-
ferential surface of the side of the tub.
[91] The middle portions 431e and 430e are extended toward the radial
direction, with
maintaining the identical angle to the angle of the first and second coupling
parts 430d
and 431d, and they are curved downward to meet the bracket connecting portions
4301c and 430c.
[92] The mass center of the radial bracket may be located relatively in a
rear portion,
compared with the mass center of the combination of the drum, spider, shaft,
bearing
housing, motor and the like (hereinafter, drum assembly). Once the laundry is
in-
troduced into the drum, rotation displacement may occur, with a front end of
the drum
falling down. Because of that, it is advantageous to locate the mass center of
each
weight in rear of the mass center of the drum such that the front end of the
drum is less
displaced downward.
[93] Each of the weights has the mass of 3kg. If the weights weight too
much, the dis-
placement of the third suspension would increase only to cause falling of a
rear portion
of the drum.
[94] FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating another embodiment of the present
invention.
According to this embodiment, the weight is provided in the radial brackets
1430 and
1431. A first weight 1431a is coupled to a first radial bracket 1431 and a
second
weight 1430a is coupled to a second radial bracket 1430.
[95] In this case, the first and second radial brackets 1431 and 1430 may
be fabricated by
pressing.
[96] The gravity centers of the first and second weights 1431a and 1430a
are located at a
location distant from a center of the drum in a forward/rearward(or
longitudinal)
direction. Further, the gravity centers may be located behind the drum or tub.
[97] Here, the mass center takes the first and second weights 1431a and
1430a into con-
sideration (hereinafter, overall weight center). According to this embodiment,
the first
and second weights 1431a and 1430a are symmetrical with respect to the axial
CA 02748824 2011-06-29
WO 2010/077090 PCT/KR2009/007960
11
direction. As a result, the mass center of each weight and the overall mass
center of the
weights are located in equal positions at least with respect to the axial
direction.
[98] Although not shown in the drawings, the weights may be in the axial
brackets. In this
case, the weights may be integrally formed with or attahced to the axial
brackets. In
addition, the weights may be located in the first and second axial brackets
450 and 440,
respectively, with being symmetrical with respect to the axial direction.
[99] In case the brackets and the weights are formed integrally according
to the above em-
bodiments, the brackets may be fabricated by casting. As metal, especially,
iron has
relatively much weight, the brackets and weights may be made by casting. Iron
may be
typically categorized based on Carbon contents into Armco, Pig Iron and Steel.
[100] FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating a further embodiment.
[101] According to this embodiment, weights 1000 may be provided in the
bearing housing
400. Here, the weight 1000 may be fabricated heavier than the bearing housing
400.
[102] The bearing housing 400 may be made of non-iron metal, for example,
aluminum
and the weight 1000 may be made of iron. Also, the bearing housing 400 may be
made
of a thin steel sheet by pressing.
[103] Although not shown in the drawings, weights may be formed integrally
with the
bearing housing according to a still further embodiment. In this case, the
bearing
housing itself may be made heavy. For example, the bearing housing is made of
iron
by casting to be employed as weight.
Industrial Applicability
[104] The present invention has an industrial applicability. The overall
weight of the
vibrating system of the laundry machine according to the exemplary embodiment
of
the present invention may relatively light and new weighing means presented as
mentioned above may stabilize the vibration of the drum. In addition, rotation
dis-
placement of falling down of the front of the drum may be reduced to a
predetermined
degree.