Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02766862 2012-02-01
PATENT
METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MAKING A STEPPED END
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
[0001] The invention relates to a method and apparatus for making a
stepped end on a
tube of flexible material, wherein the stepped end is adapted to be closed to
provide a closed end
on a bag.
BACKGROUND
[0002] US 6,800,051 B2 and US 4,008,850 and US 2009/0159192 A1,
respectively,
disclose a method for making a bag having a staggered end also known as a
stepped end.
[0003] US 2009/0159192 Al discloses a perforation line in a web of
tubular film, along
which perforation line a segment is severed from the web of tubular film to
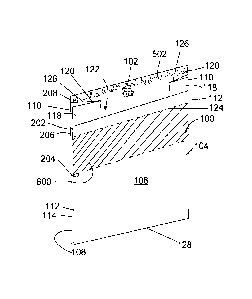
form a staggered end.
The perforation line is formed in a flat web of film, after which the tubular
film is formed by
folding side parts so as to overlap, and then simultaneously inserting the
side folds and affixing a
longitudinal center weld. Scoring apparatus are disclosed in US 4,273,550 and
US 5,840,002 to
make creases in the film for folding the film.
[0004] US 2010/0029455 A1 discloses a fabric having a layer of woven
plastic bands and
at least one additional material layer, and the cutting capacity of a laser
can be adjusted to a
thickness of the material layers to provide a perforation line.
[0005] A perforation line in a flat web of film is unsuited for a
tube. Instead of
manufacturing a flat web of film having a perforation line, a continuous tube
without a
perforation line can be manufactured at a high production speed, followed by
cutting the tube to
a desired length at the high production speed. The tube can be seamless.
Alternatively, the tube
can have one or more longitudinal seams as disclosed by Coating Excellence LLC
in US
20080187695 Al, U.S. Application No. 12/019,407, filed January 24, 2008. Then
it would be
desirable to manufacture a stepped end on the tube, wherein the stepped end is
adapted to be
closed to make a bag. However, a tube does not encompass a flat web of film.
It follows, it
would be desirable to manufacture a staggered end, also known as a stepped
end, on a tube, in
order to take advantage of high speed manufacture of the tube.
1
C:\Users\ dmw009 \ Desktop \Application docx
CA 02766862 2012-02-01
PATENT
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0006] The invention relates to a method and apparatus for making a
stepped end on a
tube of flexible material, wherein the stepped end is adapted to be closed to
provide a closed end
on a bag.
[0007] A method of making a stepped end on a tube of flexible material
includes slitting
the tube adjacent an open end of the tube to provide first slits beside a
first panel of the tube and
to provide second slits beside a second panel of the tube; trimming the first
panel to a first
shortened length adjacent to the open end of the tube while the first slits
separate the first panel
from a remainder of the tube, wherein the remainder of the tube comprises side
gussets and the
second panel; trimming each of side gussets to a second shortened length
adjacent to the open
end of the tube while the second slits separate each of the side gussets from
the second panel,
wherein the second shortened length is longer than the first panel and shorter
than the second
panel; and applying adhesive material on the tube above and below a fold line
across the tube,
wherein the tube is adapted to be folded along the fold line, and the adhesive
material is adapted
to form an adhesive to adhesive seal above and below the fold line while the
tube is folded to
provide a closed stepped end for a bag.
[0008] An apparatus for making a stepped end on a tube of flexible
material includes a
tube slitting station having a slitting tool with double edge slitting blades
penetrating through the
tube to provide respective slits beside a first panel and beside a second
panel, respectively; a first
trimming station trimming a first panel of the tube to a first shortened
length, a second trimming
station trimming the side gussets to a second length, wherein the second
length is longer than the
first shortened length of the first panel; and an adhesive applying station
applying adhesive on
the tube above and below a fold line across the tube, wherein the tube is
adapted to be folded
along the fold line, and the adhesive material is adapted to form an adhesive
to adhesive seal
above and below the fold line while the tube is folded to provide a closed
stepped end for a bag.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0009] Embodiments of the invention will now be described by way of
example with
reference to the accompanying drawings.
Fig. 1 is an isometric view of a tube having a first panel and a second panel,
and
side gussets, wherein the tube is adapted for making a bag.
2
CAUsers \dmw009 \Desktop \Applicatton docx
CA 02766862 2012-04-30
PATENT
Fig. 2 is an isometric view of a tube manufactured with a stepped end.
Fig. 2A is an isometric view of another embodiment of a tube manufactured with
a stepped end.
Fig. 3 is an isometric view of an apparatus for making a stepped end on a
tube,
and further disclosing a tube slitting station of the apparatus.
Fig. 4 is an isometric view of a first panel trimming station of the apparatus
of
Fig. 3.
Fig. 4A is a view similar to Fig. 4, and further disclosing a shortened end of
a first
panel of the tube.
Fig. 5 is an isometric view of a second panel trimming station of the
apparatus of
Fig. 3.
Fig. 5A is a view similar to Fig. 5, and further disclosing a shortened end on
each
of the side gussets of the tube.
Fig. 6 is an isometric view of a creasing station and an adhesive applying
station
of the apparatus of Fig. 3.
Fig. 7 is an isometric view of the stepped end of the tube of Fig. 6 being
folded
and sealed.
Fig. 8 is an isometric view of a slitting station for slitting side gusset
folds on the
tube of Fig. 2A.
Fig. 8A is a view similar to Fig. 8 indicating an operation of the slitting
station of
Fig. 8.
Fig. 8B is a view similar to Fig. 8 indicating another operation of the
slitting
station in Fig. 8.
Fig. 9.
Fig. 9 is a view similar to Fig. 5 indicating a gusset trimming station.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
[0010] Fig. 1 discloses a tube 100 of flexible polymeric material,
wherein the tube 100 is
formed with a first side gusset 110 and a second side gusset 110. Side edges
112, 112 of a first
panel 106 are connected to the first side gusset 110 and the second side
gusset 110, respectively.
Side edges 114, 114 of a second panel 108 are connected to the first side
gusset 110 and the
second side gusset 110, respectively. The first side gusset 110 and the second
side gusset 110
3
C \ Users \dmw009\Desktop \ Application docx
CA 02766862 2012-02-01
PATENT
are foldable inward along longitudinal creases or folds 116, 116 to flatten
the tube. The gussets
110, 110 fold or crease along the side edges 112, 112 and the side edges 114,
114.
[0011] Fig. 1 discloses the tube 100 having an open end 122 encircled
by a first panel
106, a second panel 108 and the side gussets 110, 110. The first panel 106
refers to a front panel
of the bag while the second panel 108 refers to a back panel of the bag.
Alternatively, the first
panel 106 refers to a back panel of the bag while the second panel 108 refers
to a front panel of
the bag.
[0012] In Fig. 2 and Fig. 2A, respective first sections 118, 118 of
the side gussets 110,
110 are adjacent to the first panel 106. Respective second sections 120, 120
of the side gussets
110 are adjacent to the second panel 108. The side gussets 110 are folded
along the folds 116.
The first sections 118 and the second sections 120 fold inwardly along the
folds 116, and are in
an inwardly folded orientation between the first panel 106 and the second
panel 108 while the
tube 100 is flat. Each side gusset 110 is adapted to unfold outwardly from
between the first
panel 106 and the second panel 108 to expand the bag interior. In an
embodiment of Fig. 2A, the
second sections 120, 120 of the side gussets 110, 110 are shorter than the
first sections 118, 118
of the side gussets 110, 110, and are made as described with reference to
Figs. 8 and 9.
[0013] An embodiment of the tube 100 is formed as a laminated tube
100 that has a
woven inner layer 102, a portion of which is illustrated to comprise a tight
basket weave of thin,
flexible, elongated strips of a polymeric material, for example,
polypropylene. The inner layer
102 advantageously comprises a woven seamless tube that is highly flexible due
to the weave.
The laminated tube 100 has at least one outer layer 104 of a printable
nonwoven polymeric
material, for example, polypropylene film that is capable of being printed
with graphics using
water based pigments or solvent based pigments.
[0014] In an embodiment of the invention, the outer layer 104 is
reverse printed on an
inside surface of a first polypropylene film. In another embodiment, a second
layer of
polypropylene film is laminated to the first polypropylene film, with the
printed surface between
the first and second layers of polypropylene film. Alternatively, the second
layer of
polypropylene film can be printed with the graphics.
[0015] After printing, the outer layer 104, and each second layer of
polypropylene film, if
present, and the woven inner layer 102 are laminated, for example, by applying
a solventless
adhesive material or solvent based adhesive material between the layers to be
laminated, and
4
\Users\dmw009\Desktop\Application docx
CA 02766862 2012-02-01
PATENT
applying heat and pressure to laminate each outer layer 104, second layer and
the inner layer 102
and form the continuous laminated tube 100. The woven inner layer 102 can be
seamless
tubular, while the outer layer 104 and each second layer of polypropylene film
can overlap and
form a lengthwise closed seam, that is adhesively sealed shut to form a seamed
tubular
construction, further described by US 20080187695 Al, U.S. Application No.
12/019,407, filed
January 24, 2008.
[0016] Alternative embodiments of the tube 100 are fabricated with
one or more
nonwoven polypropylene films to provide a nonwoven inner layer 102 and a
nonwoven outer
layer 104.
[0017] Further embodiments of the tube 100 comprise, a seamless blown tube,
a seamless
woven tube and a tube manufactured from flat sheets laminated together to form
a seamed
tubular construction. Embodiments of the tube comprise, a seamless blown tube,
a seamless
woven tube and a tube manufactured from flat sheets laminated together to form
a seamed
tubular construction. Further, a particular embodiment of a tube includes a
seamless woven tube
of polypropylene or other polyolefin material, which is desired for its
tensile strength in order to
package and store heavy contents in granular form, such as, dog food, cereals,
grains and
construction materials.
[0018] Fig. 2 discloses the tube 100 wherein the open end 122 of the
bag is pinch closed
by closing the first panel 106 and the second panel 108 against each other at
their end edges
adjacent the open end 122. The tube 100 is made with a stepped, or step cut
construction at the
open end 122, wherein a portion of the first panel 106 is removed by severing,
cutting or hot
knife, and wherein the first panel 106 is made shorter than a longer portion
502 of the second
panel 108 at the open end. Further, a portion of each of the side gussets 110,
110 is removed,
wherein the side gussets are made longer than the first panel 106 and shorter
than the second
panel 108. The longer portion 502 provides a foldable flap portion 502 on the
second panel 108.
As a result, a stepped end 122 is formed on the tube 100. Although the stepped
end 122 is
disclosed on an embodiment of the tube 100 in Fig. 1, the stepped end 122 can
be made on any
embodiment of a tube of flexible polymeric material intended for making a bag.
[0019] First, the tube 100 in Fig. 2 is made with a stepped end 122.
After making the
stepped end 122, a first layer 600 of an adhesive material is provided on the
first panel 106 of the
tube 100 below a fold line 206.
5
C Users \ dinw009 \Desktop \Application docx
CA 02766862 2012-02-01
PATENT
[0020] An apparatus and method will now be described for making the
stepped end 122
of the tube 100. Advantageously the tube 100 eliminates a perforated line to
make the stepped
end. Further, advantageously the apparatus and method applies to any
embodiment of a tube of
flexible polymeric material intended for making a bag, including, but not
limited to an
embodiment of the tube 100 described in Fig. 1.
[0021] Fig. 3 discloses the tube 100 formed with a slit portion 208
of the second panel
108 adjacent to the open end 122 of the tube 100. The second panel 108 has
first corresponding
slits 210, 210 along the side edges 114, 114 thereof. The first corresponding
slits 210, 210 are
adjacent to the open end 122 and extend into the open end 122. The first
corresponding slits 210,
210 separate the slit portion 208 of the second panel 108 from the side
gussets 110, 110.
[0022] Fig. 3 discloses a slit portion 300 of the first panel 106
adjacent to the open end
122. The first panel 106 has second corresponding slits 302, 302 along the
side edges 112, 112
thereof. The second corresponding slits 302, 302 are adjacent to the open end
122 and extend
into the open end 122. The second corresponding slits 302, 302 separate the
slit portion 300
from the side gussets 110, 110. Fig .3 discloses the slits 302, 302 are longer
than the shorter slits
210, 210.
[0023] Fig. 3 discloses the tube 100 in an apparatus 400. The tube
100 is conveyed, for
example, by a continuous or intermittent or segmented belt conveyor 428, and
is indexed into
position in front of a slitting station 402. The slitting station 402 of the
apparatus 400 is
provided with a slitting tool 404 disclosed in its home position. The slitting
tool 404 has spaced
apart, double edge slitting blades 406, 408. Although the slitting blades 406,
408 are disclosed
as fixed flat blades, they can take the form of rotary blades or reciprocating
blades.
[0024] In Fig. 3, the open end 122 of the tube 100 is opened and
maintained open, for
example, by blowing air under pressure into the open end 122 of the tube 100
or by surrounding
the tube 100 in a suction chamber, not shown. While the tube 100 is open, the
slitting tool 404 is
initially in its home position disclosed by Fig. 3. Then, the slitting tool
404 is indexed or
displaced from its home position toward and into the open end 122 of the tube
100, in a direction
disclosed by the arrow 410, to a first tool position to insert the slitting
blades 406, 408 into the
open end 122 of the tube 100.
[0025] Then while the slitting tool 404 is inside the tube 100, the tool
slitting 404 is
indexed or displaced, relative to the tube 100, in a forward direction
indicated by the forward
6
C \Users \ dmw009 \Desktop \ Application docx
CA 02766862 2012-02-01
PATENT
pointing arrow 412. Thereby, the slitting tool 404 is indexed or displaced to
a stationary second
tool position while the slitting blades 406, 408 have forward slitting edges
414, 416 that perform
slitting through a first pair of the side edges 112, 114 of the first panel
106 and the second panel
108, respectively. The forward slitting edges 414, 416 serve to provide a
first pair of forward
respective slits 210, 302 beside the panels 106, 108.
[0026] The tube 100 is conveyed or displaced in a forward direction
indicated by the
arrow 418, provided that the slitting tool 404 is displaced in a forward
direction 412 faster,
relative to forward displacement of the tube 100, while the forward slitting
edges 414, 416
perform slitting through a first pair of the side edges 112, 114 of the first
panel 106 and the
second panel 108, respectively. Alternatively, the tube 100 can be stationary
while the slitting
tool 404 is displaced in a forward direction 412 while the forward slitting
edges 414, 416
perform slitting through a first pair of the side edges 112, 114 of the first
panel 106 and the
second panel 108, respectively.
[0027] Then, while the tube 100 is being conveyed in a forward
direction 418, the slitting
tool 404 while inside the tube 100, and is indexed in a reverse or rearward
direction indicated by
the rearward pointing arrow 420, to return to its first tool position while
inside the tube 100. The
slitting blades 406, 408 have rearward slitting edges 422, 424 that perform
slitting through a
second pair of the side edges 112, 114 of the first panel 106 and the second
panel 108,
respectively. Thereby, the rearward slitting edges 422, 424 provide a second
pair of the
respective slits 302, 210 beside the panels 106, 108. Then the tube 100
continues in the forward
direction 418, while the slitting tool 404 is being indexed in a rearward
direction indicated by the
rearward pointing arrow 426 to its home position shown in Fig. 2. The slitting
tool 404 can bias
the flexible gussets 110, 110 out of the way, as the slitting tool 404 returns
to its home position
disclosed in Fig. 3. The tube 100 continues to be conveyed in the forward
direction 418, and
leaves the slitting tool 404. By repeating the operation of the apparatus 400
as described herein,
multiple tubes 100 in succession are provided with the slits 210 and 302.
[0028] Fig. 4 discloses the apparatus 400 having a first panel
trimming station 500.
The tube 100 continues to be conveyed by the belt conveyor 428 of Fig. 3 in a
forward direction
indicated by the arrow 418 in Fig. 3, such that belt conveyor 428 extends
beyond the slitting
station 402 of Fig. 3 to convey the tube 100 from the slitting station 402 of
Fig. 3 to the first
panel trimming station 500 of Fig. 4. At the first panel trimming station 500,
the tube 100 is
7
C \Users \dmw009 \Desktop \ Application docx
CA 02766862 2012-02-01
PATENT
supported on a table or rotary knife anvil 504, disclosed in exploded
configuration for clarity.
The tube 100 is folded along an edge 506 of the table or anvil 504, which
folds the side gussets
110, 110 and the slit portion 208 of the second panel 108, down and away from
the slit portion
300 of the first panel 106. The slits 302, 302 separate the slit portion 300
of the first panel 106
from a remainder of the tube 100, wherein the remainder of the tube 100
includes the side
gussets 110, 110 and the slit portion 208 of the second panel 108. The first
panel trimming
station 500 includes a cutting blade 508 which cuts through the first panel
106 and performs
trimming. The terminology "trimming" means to shorten in length, by severing,
cutting or hot
knife, which is accomplished, for example, by a knife cutting blade or rotary
cutting blade, pair
of shears, punch press or an equivalent tool or machine.
[0029] Further, Fig. 4 discloses the side gussets 110, 110 being
pivoted away from the
slit portion 300 of the first panel 106. The slitted portion 208 of the second
panel 108 is behind
the pivoting gussets 110, 110. For this reason, the slitted portion 208 of the
second panel 108
pivots and moves away with the side gussets 110, 110. Both the slitted portion
208 of the second
panel 108 and the side gussets 110, 110 are folded downwardly away, while the
first panel 106 is
trimmed.
[0030] Fig. 4A discloses the slit portion 300 of the first panel 106
being removed and
discarded. As a result, the first panel 106 is trimmed to a first shortened
length 124. As
disclosed by Fig. 2, the first shortened length 124 of the first panel 106
will be adjacent to the
open end 122 of the tube 100.
[0031] Fig. 5 discloses the apparatus 400 having a second panel
trimming station 604.
The tube 100 continues to be conveyed by the belt conveyor 428 of Fig. 3 in a
forward direction
indicated by the arrow 418 in Fig. 3, such that belt conveyor extends beyond
the slitting station
402 of Fig. 3 to convey the tube 100 from the slitting station 402 of Fig. 3
to the first panel
trimming station 500 of Fig. 4, and then to the second panel trimming station
604 in consecutive
order. The tube 100 is conveyed by the belt conveyor 428 of Fig. 4 from the
first panel trimming
station 500 of Fig. 4 to the second panel trimming station 604 of Fig. 5. At
the second panel
trimming station 604, the tube 100 is supported on a table or rotary knife
anvil 606. The tube
100 is folded along an edge 608 of the table 604, which folds the slitted
portion 208 of second
panel 108, down and away from the side gussets 110, 110. The slits 210, 210
separate the side
gussets 110, 110 from the remainder of the tube 100, wherein the remainder of
the tube 100
8
C \User \dinw009 \Desktop \Application docx
CA 02766862 2012-02-01
PATENT
includes the second panel 108, and especially the slit portion 208 of the
second panel 108. The
second trimming station 604 includes a cutting blade 610 which cuts through
the side gussets
110, 110, and performs trimming to cut through the side gussets 110, 110 to
cut and remove
sections 612, 612 of the side gussets 110, 110.
[0032] Fig. 5A discloses the sections 612, 612 being removed and discarded.
As a result,
each of the side gussets 110, 110 are trimmed to a second shortened length
126, Fig. 2. As
disclosed by Fig. 2, the second shortened length 126 of each of the side
gussets 110, 110 will be
adjacent to the open end 122 of the tube 100.
[0033] The side gussets 110, 110 become longer than the first panel
106 adjacent to the
open end 122 of the tube 100, and the side gussets 110, 110 become shorter
than the second
panel 108 adjacent to the open end 122 of the tube 100, which comprises a
stepped end 122 of
the tube 100 Fig. 2. The second panel 108 provides a sealing flap portion 502
adjacent to the
stepped end 122 of the tube 100. After formation of the stepped end 122 of the
tube 100, the
tube 100 is flattened by inwardly folding the side gussets 110, 110.
[0034] In Fig. 6, a fold line 206 across the tube 100 indicates a line
along which the tube
100 can be folded. To form the fold line 206 with an optional crease, the
flattened tube 100 is
conveyed through a scoring apparatus 700 of the apparatus 400, which provides
a crease along
the fold line 206 across the tube 100. A scoring apparatus 700 is disclosed in
Fig. 6 in schematic
representation of a commercially available scoring apparatus, for example, as
disclosed in US
4,273,550 and US 5,840,002. As a result, the invention provides a method of
making a stepped
end 122 and a fold line 206 with an optional crease on a tube 100 of flexible
material for a
tubular bag.
[0035] Further, Fig. 6 discloses a method of making a tube 100 of
flexible material with a
stepped end 122 that folds to close the stepped end 122 and form a bag, and
adhesive material
applied as layers 600 for sealing the stepped end 122. Fig. 6 discloses a
process of applying a
layer 600 of adhesive material below the fold line 206. The adhesive material
layer 600 is
applied, while the tube 100 is flat, by an adhesive material applicator 702
including, but not
limited to a roller, brush or spraying apparatus. The adhesive material layer
600 below the fold
line 206 is applied as fluent compositions including emulsions or solutions
constituted in a fluid
including, but not limited to water or a chemical solvent. Then the adhesive
material layer 600 is
9
c \Users\dmw009\Desktop\Application docx
CA 02766862 2012-02-01
PATENT
dried in a heated oven to drive off the fluent substances. The adhesive
material layer 600 is
capable of forming moisture and water resistant, heat activated adhesive-to-
adhesive seals.
[0036] The adhesive-to-adhesive seal is formed by heating the
adhesive material layer
600 below the fold line 206 to a melt flow temperature at which it attains a
melt flow, adhesive
state. The adhesive material layer 600 below the fold line 206 has a
respective melt flow
temperature of about 3000 F. maximum to avoid heating the polymeric material
of the tube 100
to its melt flow temperature above the 3000 F. threshold temperature. The
adhesive material
corresponding to the adhesive layer 600 has a coating weight of at least 5-10
lb./ream on each of
opposing surfaces to form an adhesive-to-adhesive seal between the opposing
surfaces of about
10 lb./ream coating weight to about 20 lb./ream coating weight. The adhesive
material layer 600
is activated to an adhesive state by applying heat at a heat activation
temperature below the heat
activation temperatures of standard or traditional hot melt adhesives or
solvent based adhesives
that can seal traditional paper and polymer laminated bags without damaging
the paper layers,
but which exceed the softening point temperature Tg of polymeric bags 100
fabricated without
paper layers. The standard or traditional hot melt adhesives cannot be
combined with
polypropylene bags 100 because the temperatures needed to activate the
adhesives are
destructive to the PP material structure.
[0037] Polypropylene has a melting point temperature of about 160 C
(320 F), as
determined by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The softening point
temperature of
polypropylene is below its melting point temperature. Thus, a polypropylene
tube 100 can be
heated to a temperature below its softening point temperature without causing
heat damage of the
polypropylene material.
[0038] One suitable adhesive material for heat sealing polyolefin
films of the tube 100
comprises a water based emulsion of triethylamine adhesive commercially
available as
AQUAGRIPO 19566F, manufactured by Bostik, Inc., 11320 Watertown Plank Road,
Wauwatosa, WI 53226 USA. Another embodiment of a hot melt adhesive for heat
sealing
polyolefin films of the tube 100 comprises a hot melt adhesive H9463 available
commercially
from Bostik, Inc. Wauwatosa, WI 53226, USA. Another embodiment of a hot melt
adhesive for
heat sealing polyolefin films of the tube 100 comprises a hot melt adhesive
H9477 Generation II
of H9463, now or soon to be available commercially from Bostik, Inc.,
Wauwatosa, WI 53226,
c \use's \dmw009 \Desktop \Application docx
CA 02766862 2012-02-01
PATENT
USA, wherein the adhesives per se form no part of the present invention
separate from being a
structural component of the tubes disclosed herein.
[0039] Another embodiment of a suitable adhesive material for heat
sealing polyolefin
films of the tube 100 comprises an aqueous based dispersion or emulsion as an
opaque liquid or
fluid of an ethylene copolymer or ethylene copolymers, butyl acetate and
acetaldehyde, which is
commercially available as the product name ROBOND TM HS 37-140 adhesive
material
manufactured by Rohm and Haas Company, 100 Independence Mall West,
Philadelphia, PA
19106-2399 USA. Another embodiment of a suitable adhesive material for heat
sealing
polyolefin films of the tube 100 comprises an aqueous based dispersion or
emulsion as an
opaque liquid or fluid, including an ionomer dispersion in water, based upon
Surlyn ionomer
resin, and which can be diluted or thickened or crosslinked for enhanced
properties, and which is
commercially available as the product name ADCOTETm 37-220 Heat Seal Coating,
manufactured by Rohm and Haas Company, 100 Independence Mall West,
Philadelphia, PA
19106-2399 USA, wherein the adhesives per se form no part of the present
invention separate
from being a structural component of the tubes disclosed herein.
[0040] Another embodiment of a suitable adhesive material for heat
sealing polyolefin
films of the tube 100 comprises an aqueous based dispersion or emulsion as an
opaque liquid or
fluid, including water, acrylic polymer, polyester polyurethane resin,
formaldehyde, ammonium
hydroxide, alumina and further including ammonia as a combustion product,
which is
commercially available as the product name NWC 23526K (and NWC 23526KC) FDA
WATER BASE HEAT SEAL FOR POLYWOVENTM adhesive material, product code 728575,
manufactured by ASHLAND Inc., P.O. Box 2219, Columbus, OH 43216, USA, wherein
the
adhesive per se forms no part of the present invention separate from being a
structural
component of the tubes disclosed herein.
[0041] Another embodiment of a suitable adhesive material for heat sealing
polyolefin
films of the tube 100 comprises a liquid state, acrylated epoxy based adhesive
commercially
available as the product name, VERSA-WELD TM 70-7879, adhesive material
manufactured by
Henkel Corporation, P.O. Box 6500; 10 Finderline Avenue, Bridgewater, NJ 08807
USA,
wherein the adhesive per se forms no part of the present invention separate
from being a
structural component of the tubes disclosed herein.
11
CAUsers \dinw0090esktop\ApplicatIon docx
CA 02766862 2012-02-01
PATENT
[0042] The embodiments of adhesive material 600 as a structural
component of the bags
includes 1.75 grams adhesive material per bag applied wet, solubilized in
water, assuming an 18
inch wide bag and a 3 inches wide stripe of adhesive on the bag, which is
equivalent to 0.6 grams
per bag dry or about 10.6 lbs per ream dry weight coating. Once the adhesive
material 600 is
applied, it must pass under a drying system to evaporate the water and dry the
adhesive layer to a
stable state impervious to water, water vapor and ambient temperatures.
[0043] The tube 100 is adapted to be closed and sealed at one end 122
to make a bag,
according to a process described as follows, a heat source including, but not
limited to heated air
or a hot bar applies heat to activate the adhesive material 600 to its
respective, heat-activatable
adhesive state. While the adhesive material 600 is in an adhesive state, the
source of heat is
removed and the end 122 of the tube 100 is folded on the fold line 206, while
the tube 100 is
pinched closed to close and seal one end 122 of the tube 100 to make a bag
with one closed end
122, while an opposite end 128 is open. According to another embodiment, the
tube 100 is open
at the end 122, and is closed and sealed at the opposite end 128, by any known
means, for
example, stitching or gluing. The foldable tube 100 is flattened by folding
along its gusseted
side panels 110 for shipping and handling, in preparation for shipment to a
location where the
tube 100 is opened at one end 122 and filled with contents. The adhesive
material layer 600 is in
its dry, solidified state during bag filling, and is moisture and water
resistant, by which the
adhesive material layer 600 avoids contamination of the bag contents. After
the tube 100 has
been filled with contents, the tube 100 is closed and sealed at the end 122,
according to a process
described as follows, a heat source including, but not limited to heated air
or a hot bar applies
heat to activate the adhesive material 600 to its respective, heat-activatable
adhesive state. While
the adhesive material 600 is in its adhesive state, the source of heat is
removed and the end 122
of the tube 100 is folded on the fold line 206, while the tube 100 is pinched
closed to hold the
contents in the tube 100.
[0044] Further, with reference to Fig. 7, while the adhesive material
600 is in its adhesive
state, the tube 100 is folded along a fold line 206 across the tube 100, which
folds the bag panel
106 on itself, with the adhesive material layer 600 therebetween. Pressure is
applied until an
adhesive seal forms by the adhesive material, which is below the fold line 206
and which is
between the folded panel 106. The fold line 206 can be free of adhesive
material. The fold line
206 is below a portion 202 of the first panel 106 adjacent the stepped end
122, which is free of
12
C \ Users \ dmw0091Desktop \ Application docx
CA 02766862 2012-02-01
PATENT
adhesive material, such that upon folding along the fold line 206, the
adhesive material on the
first panel 106 below the fold line 206 can form an adhesive seal with the
portion 202 of the first
panel 106 adjacent the end 122. Further, by folding along the fold line 206,
the sealing flap 502
is folded toward the bag section 600 of the panel 106. Pressure is applied
against the sealing flap
502 until that adhesive layer 600 forms an adhesive seal of the sealing flap
502. The adhesive
seal is established to seal the stepped end 122 with the sealing flap portion
502. In one
embodiment of Fig. 6, the fold line 206 is not creased, and the tube 100 is
folded without a
crease. Alternatively, in Fig. 6, the fold line 206 can be formed as a crease.
Then, the flattened
and creased tube 100 is conveyed through the adhesive applicator 702 of the
apparatus 400.
[0045] Fig. 8 discloses an embodiment of the apparatus 100 for making a
stepped end
122, Fig. 2A, and more particularly, a double stepped end 122. Fig. 8
discloses a slitting station
802 of the apparatus 400. The tube 100 is conveyed, for example, by a
continuous or
intermittent or segmented belt conveyor 428, and is indexed into position in
front of the slitting
station 802 for slitting the side gusset folds 116.
[0046] For purposes of illustration, Fig. 8 discloses the tube 100 having
the slits 210 and
302. The slits 210 and 302 were provided previously by the slitting station
402. Alternatively,
the slits 210 and 302 would not be present in Fig. 8, in an embodiment of the
invention wherein
the slitting station 402 is in a sequence following the slitting station 802.
Further, for purposes of
illustration, Fig. 8 discloses the open end 122 of the tube 100 being opened,
in a manner
similarly as in Fig. 3. Alternatively, the open end 122 can be closed, at
least partially, by
folding, at least partially, along the gusset folds 116 of both side gussets
110. The gusset folds
116 become slitted according to the description that follows.
[0047] Fig. 8 discloses the slitting station 802 of the apparatus 400
is provided with a
slitting tool 804 disclosed in its home position. The slitting tool 804 has a
retractable, slitting
blade 806 that retracts into the tool 804, as indicated by the arrow 808, and
alternately, extends to
project from the tool 804 to perform a slitting operation. The slitting blade
806 has a sharpened,
single slitting edge 810. Further, either the slitting blade 806 or the tool
804 is reversely
rotatable 180 as indicated by the arrow 812 to face the slitting edge 810
either in a forward
direction indicated by the arrow 418 or in a rearward direction opposite the
forward direction.
Alternatively, another slitting edge 810 is on the slitting blade 806 to
provide a double edge
blade 806, not shown, in order to eliminate a need for rotation of the blade
806.
13
C \ Users \ dmw009 \Desktop \Application docx
CA 02766862 2012-02-01
PATENT
[0048] In Fig. 8, the tube 100 is being conveyed or displaced in a
forward direction
indicated by the arrow 418, such that a leading edge 814 of the tube is
displaced past the slitting
tool 804 while the slitting edge 810 facing in a rearward direction, projects
from the tool 804 and
slits through the gusset fold 116 to provide a first gusset slit 816 in the
gusset fold 116 at the
leading edge 814. The first gusset slit 816 divides the gusset 110 at the open
end 122 into a first
slitted gusset portion 118 and a slitted gusset portion 120.
[0049] As disclosed by Fig. 8A, after cutting the first gusset slit
816, the slitting blade
806 retracts into the tool 804, while the tube 100 continues to be displaced
in the forward
direction 418 until a trailing edge 818 of the tube 100 is displaced past the
tool 804 having the
retracted slitting blade 806.
[0050] As disclosed by Fig. 8B, after a trailing edge 818 of the tube
100 is displaced past
the tool 804, the slitting blade 806 is extended to project from the tool 804,
and simultaneously,
or in sequence, the slitting blade 806 is reversed in direction to face the
slitting edge 810 in the
forward direction 418. Further, the tool 804 is displaced in a forward
direction indicated by an
arrow 812 faster than the tube 100 is being conveyed in the forward direction
418, while the
slitting edge 810 cuts through the gusset fold 116 at the trailing edge 818 of
the tube 100 to
provide a second gusset slit 816 in the gusset fold 116 at the trailing edge
818. The second
gusset slit 816 divides the gusset 110 at the open end 122 into a first
slitted gusset portion 118
and a slitted gusset portion 120. Thus, both gussets 110 are divided into a
first slitted gusset
portion 118 and a second slitted gusset portion 120. Then the blade 806
retracts, and the tool 804
is displaced rearward, indicated by the arrow 820 to return to its home
position, as disclosed by
Fig. 8. At the returned home position, the blade 806 is extended outward from
the tool 804, and
is reversed in direction to face the slitting edge 810 in a rearward
direction, while another tube
100, in succession to a prior tube 100, is conveyed or displaced in a forward
direction indicated
by the arrow 418, such that a leading edge 814 of said another tube 100 in
succession is
displaced past the slitting tool 804 while the slitting edge 810 facing in a
rearward direction,
projects from the tool 804 and slits through the gusset fold 116 to provide a
first gusset slit 816
in the gusset fold 116 at the leading edge 814. By repeating the operation of
the apparatus 400 as
described herein, multiple tubes 100 in succession are provided with a pair of
gusset slits 816,
816.
14
C `Users\ dmw009\Desktop\Application docx
CA 02766862 2012-02-01
PATENT
[0051] According to the following description, the tube 100 having
the gusset slits 816,
816 is provided with a stepped end, wherein the stepped end is disclosed by
Fig. 2A. First, the
tube 100 is conveyed to the first panel trimming station 500, Fig. 4, wherein
the first panel 106 is
trimmed to a first shortened length 124 disclosed in Fig. 2A. Further, Fig. 2A
discloses that the
first shortened length 124 of the first panel 106 will be adjacent to the open
end 122 of the tube
100. Then the tube 100 is conveyed to the second panel trimming station 604 in
consecutive
order. At the second panel trimming station 604, each of the side gussets 110,
110 is trimmed to
a second shortened length 126, Fig. 2A. Further, Fig. 2A discloses that the
second shortened
length 126 of each of the side gussets 110, 110 will be adjacent to the open
end 122 of the tube
100.
[0052] Then, the embodiment of the tube 100 having the gusset slits
816, 820 is
conveyed from the second panel trimming station 604 to a gusset trimming
station 900, Fig. 9.
At the gusset trimming station 900, Fig. 9, the tube 100 is supported on a
table or rotary knife
anvil 906. The tube 100 is folded along an edge 908 of the table 904, which
folds, down and
away, the slitted portion 208 of second panel 108, which now includes an
additional slitted
portion 208A. Further, such folding additionally folds the slitted portions
120, 120 of the two
gussets 110, 110 down and away from the slitted portions 118, 118 of the two
gussets 110, 110.
Each slitted gusset portion 120 is separated from the slitted gusset portion
118 by having the slits
210, 210 and the gusset slits 116, 116. The gusset trimming station 904
includes a cutting blade
910 which cuts through both slitted gusset sections 118, 118, and performs
trimming to reduce
the height of the gusset sections 118, 118, as disclosed by Fig. 2A, wherein
the gusset sections
118, 118 have a height shorter than the gusset sections 120, 120, and have a
height longer than
the front panel 106 adjacent the end 122 of the tube 100 that becomes a
stepped end 122 of the
tube 100. Further, the stepped end 122 in Fig. 2A becomes a double stepped end
122, because of
the double steps in the gussets 110.
[0053] After formation of the double stepped end 122 of the tube 100,
the tube 100 is
flattened by inwardly folding the side gussets 110, 110. To form a crease
along the fold line 206,
the flattened tube 100 is conveyed through the scoring apparatus 700 of the
apparatus 400, which
provides a crease along the fold line 206 across the tube 100. Further, Fig. 6
discloses a method
of making a tube 100 of flexible material with a stepped end 122 that folds to
close the stepped
end 122 and form a bag, and adhesive material layer 600 for sealing the
stepped end 122. Fig. 6
C \ Users\ dmw009 \ Desktop\ Application docx
CA 02766862 2012-02-01
PATENT
discloses a process of applying an adhesive material layer 600 on the first
panel 106 of the tube
100 below the fold line 206. The adhesive material layer 600 is applied, while
the tube 100 is
flat, by an adhesive material applicator 702. Above the fold line 206 is at
least a portion 202 of
the first panel 106 adjacent the end 124 of the first panel 106 and adjacent
the stepped end 122,
such that upon folding along the fold line 206, the portion 202 of the first
panel 106 adjacent the
end 122 can form an adhesive to adhesive seal with the adhesive material below
the fold line
206.
[0054] The invention provides a method and a system for making an end
122 on a tube of
flexible material into a stepped end 122, wherein the stepped end is adapted
to be closed and
sealed to make a bag. The invention is described in conjunction with a tube
100 having an open
end 122 and an opposite end 128. A stepped end 122 according to the invention
can be provided
on either end 122 or 128. Stepped ends 122, 122 according to the invention can
be provided on
tube ends 122 and 128, respectively.
[0055] This description of the exemplary embodiments is intended to
be read in
connection with the accompanying drawings, which are to be considered part of
the entire
written description. In the description, relative terms such as "lower,"
"upper," "horizontal,"
"vertical,", "above," "below," "up," "down," "top" and "bottom" as well as
derivative thereof
(e.g., "horizontally," "downwardly," "upwardly," etc.) should be construed to
refer to the
orientation as then described or as shown in the drawing under discussion.
These relative terms
are for convenience of description and do not require that the apparatus be
constructed or
operated in a particular orientation. Terms concerning attachments, coupling
and the like, such
as "connected" and "interconnected," refer to a relationship wherein
structures are secured or
attached to one another either directly or indirectly through intervening
structures, as well as
both movable or rigid attachments or relationships, unless expressly described
otherwise.
[0056] Patents and patent applications referred to herein are hereby
incorporated by
reference in their entireties. Although the invention has been described in
terms of exemplary
embodiments, it is not limited thereto. Rather, the appended claims should be
construed broadly,
to include other variants and embodiments of the invention, which may be made
by those skilled
in the art without departing from the scope and range of equivalents of the
invention.
16
C Users \ dmw009 \ Desktop \Application docx