Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02767946 2012-01-12
WO 2011/007123 PCT/GB2010/001325
PROCESS FOR PREPARING LEVOSIMENDAN AND INTERMEDIATES FOR
USE IN THE PROCESS
Field of Invention
The present invention relates to a process for preparing the levo isomer of
[[4-(1,4,5,6-
tetra hyd ro-4-methyl-6-oxo-3-pyridazi nyl) p henyl]hyd razono] pro pa ned in
itri le
(levosimendan), which is represented by the following structure.
NC\ H
}_N N-N
NC NH O
H3C
Formula I
Background and Prior Art
Levosimendan is a highly potent cardiotonic that increases the sensitivity of
the heart to
calcium without causing a rise in intracellular calcium. The drug is marketed
by Abbott
under the trade name Simdax. It was first disclosed in US5569657.
The prior art indicates that pure levosimendan can be obtained by passing the
racemic
mixture over a chiral phase chromatography column. But the process becomes
tedious
and industrially unacceptable when a large quantity of material is involved.
One prior art technique involves using the optically-pure (-)-enantiomer of 6-
(4-
aminophenyl)-5-methylpyridazin-3-(2H)-one as starting material. The method of
obtaining (-)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-5-methylpyridazin-3-(2H)-one is given in
EP208518,
which describes the separation of pure enantiomers of 6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-
dihydro-5-
methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone using a chiral HPLC column.
CA 02767946 2012-01-12
WO 2011/007123 PCT/GB2010/001325
2
CN1616437 describes treating (+)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-
pyridazinone with 50% alkali or 50% acid.
JP10109977 discloses the use of 1-propanol/ethyl acetate as resolving solvent
and L-
or D-tartaric acid as resolving agent.
US5569657 discloses the preparation of levosimendan and its salts. ( )-6-(4-
aminophenyl)-5-methylpyridazin-3-(2H)-one is dissolved in 2-propanol on
heating. L-
tartaric acid is gradually added to the solution and stirred on heating to
obtain a clear
solution. The solution is cooled slowly to room temperature and then stirred
overnight at
C to obtain a crystalline product. On filtering, the wet salt is dissolved in
water and to
it potassium carbonate solution is added with stirring. The free base obtained
is filtered,
washed with water and dried. The product is further dissolved in dioxane on
heating and
allowed to cool to room temperature. The contents are filtered and dried under
vacuum
15 to obtain (-)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-5-methylpyridazin-3-(2H)-one crystalline
solid. The pure
(-)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-5-methylpyridazin-3-(2H)-one compound is then treated
with
sodium nitrite and malononitrile under acidic condition to obtain
levosimendan. A
disadvantage of the resolution process disclosed is that to obtain a high
optical purity
(99.5%) of the pyridazinone compound, recrystallisation with dioxane is
required. Also
20 the process involves multiple steps and is time consuming.
US6180789 describes the preparation of levosimendan by treating the (-)-
enantiomer of
6-(4-amino phenyl)-5-methyl pyridazin-3-(2H)-one, resolved using D- or L-
tartaric acid in
aqueous ethyl acetate, with sodium nitrite and malononitrile and further
crystallizing with
aqueous acetone. The patent also discloses other resolving agents such as
benzoic
acid, sulphuric acid, and resolving solvents such as isopropanol, isobutanol,
isopropyl
acetate, butyl acetate, acetone and acetonitrile. These conditions are said to
cause
partial resolution only.
There are certain drawbacks of the process disclosed in US6180789 -
When D-tartaric acid is the resolving agent -
. Excess amount of resolving agent is required to achieve complete resolution.
CA 02767946 2012-01-12
WO 2011/007123 PCT/GB2010/001325
3
= Seeding with D-tartaric acid salt of (-)-6-(4-amino phenyl)-5-methyl
pyridazin-3-
(2H)-one is also needed in the process.
= Hot filtration of the precipitate is to be done; which is not at all
workable when
dealing with large batches at industrial scale.
= The temperature of reaction is to be maintained at 0 C.
= The enantiomeric purity of the product is low, even after giving a number of
washings.
= In order to obtain the desired enantiomeric excess, it is necessary to
perform
recrystallisation with acetonitrile in the presence of absorbent followed by
washing with excess acetonitrile. Treatment with a large amount of solvent
increases the cost of process and also reduces the yield due to wastage.
When L-tartaric acid is the resolving agent -
= For the precipitation of salt, cooling upto -10 C is required.
= The enantiomeric purity of the desired (-)-6-(4-amino phenyl)-5-methyl
pyridazin-
3-(2H)-one product is quite low (78.7%).
Due to the problems with the prior art there is felt a need to develop a new
process for
resolving levosimendan that is simple, economical, eco-friendly and high-
yielding.
Summary of the Invention
According to a first aspect of the present invention, there is provided a
process for
preparing (-)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-5-methylpyridazin-3-(2H)-one, which process
comprises: a) reacting racemic 6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-
pyridazinone with a resolving agent, preferably a chiral tartaric acid
derivative, typically
in the presence of a solvent; and b) isolating the (-)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-
dihydro-5-
methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazi none.
In an embodiment, step a) results in a diastereomeric salt which is a salt of
(-)-6-(4-
aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone and the chiral tartaric
acid
derivative. The (+)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone
is
present in the mother liquor of the reaction mass, whereas the salt
precipitates
CA 02767946 2012-01-12
WO 2011/007123 PCT/GB2010/001325
4
therefrom. In this embodiment, the process comprises: a) reacting racemic 6-(4-
aminophenyl)-4,5-d ihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone of formula II with the
chiral
tartaric acid derivative to obtain the diastereomeric salt of (-)-6-(4-
aminophenyl)-4,5-
dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone and the chiral tartaric acid derivative;
and b)
reacting the diastereomeric salt with a base to obtain (-)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-
4,5-dihydro-
5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone. In this embodiment, the chiral acid derivative
may be di-
p-anisoyl-D-tartaric acid.
In an alternative embodiment, step a) results in a diastereomeric salt which
is a salt of
(+)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone and the chiral
tartaric
acid derivative. The (-)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-
pyridazinone is
present in the mother liquor of the reaction mass, whereas the salt
precipitates
therefrom. In this embodiment, the process comprises: a) reacting racemic 6-(4-
aminophenyl)-4, 5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone of formula 11 with the
chiral
tartaric acid derivative to obtain the diastereomeric salt of (-)-6-(4-
aminophenyl)-4,5-
dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone and the chiral tartaric acid derivative;
and b)
isolating the (-)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone
from the
mother liquor. In this embodiment, the chiral acid derivative may be di-p-
anisoyl-L-
tartaric acid.
In an embodiment, the chiral tartaric acid derivative is selected from the D-
or L- isomer
of di-p-anisoyl-tartaric acid, di-p-tolyl-tartaric acid or 0, O'-dibenzoyl-
tartaric acid.
Preferably, the chiral acid is the D-isomer of the tartaric acid derivative.
Preferably, the
chiral tartaric acid derivative is di-p-anisoyl-D-tartaric acid. Most
preferably, the chiral
tartaric acid derivative is di-p-anisoyl-D-tartaric acid.
In an embodiment, the solvent employed for resolution, i.e. in step (a), is a
mixture of
water and a polar solvent. The polar solvent may be selected from methanol,
ethanol,
isopropanol, n-butanol, acetone and acetonitrile. Preferably, a mixture of
water and
ethanol is used.
The above process may further comprise converting the (-)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-5-
methylpyridazin-3-(2H)-one to levosimendan. The conversion may comprise
reacting (-)
CA 02767946 2012-01-12
WO 2011/007123 PCT/GB2010/001325
-6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone with sodium
nitrite and
malononitrile. In an embodiment, the process of the present invention yields
levosimendan in substantially-pure enantiomeric form. Preferably, the ratio of
the levo-
isomer : dextro-isomer prepared by the process of present invention is about
99:1.
5 Preferably, the levosimendan prepared from the present process has a purity
of about
99.9%, as determined by chiral HPLC.
According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided the
salt of (-)-6-
(4-aminophenyl)-5-methylpyridazin-3-(2H)-one and di-p-anisoyi-D-tartaric acid.
This
compound has the formula VI shown below.
OH HO
0 0
CH3
O O
0- NH2
O 0-
N-N
H
MeO OMe
Formula VI
According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided the
salt of (+)-6-
(4-aminophenyl)-5-methylpyridazin-3-(2H)-one and di-p-anisoyl-L-tartaric acid.
This
compound has the formula VII as shown below.
OH HO
`CH3 O 0
O O
O Z/Y NH20 HN--\ / -
0
MeO OMe
Formula VII
CA 02767946 2012-01-12
WO 2011/007123 PCT/GB2010/001325
6
A preferred chiral tartaric acid derivative for use in the process of the
present invention
is di-p-anisoyl-tartaric acid, and compounds of formula VI and VII are the
corresponding
preferred products of step a) of the process of the present invention when di-
p-anisoyl-
tartaric acid is the resolving agent. Compounds VI and VII are, therefore,
highly-
advantageous intermediates for use in the process of the present invention.
According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a
process for
preparing a compound of formula VI, which process comprises reacting racemic 6-
(4-
aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone with di-p-anisoyl-D-
tartaric acid.
According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a
process which
comprises: (i) reacting racemic 6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-
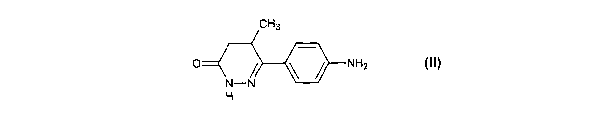
pyridazinone of formula II
CH3
O NH2
N-N
H
Formula II
with a chiral tartaric acid derivative to obtain the diastereomeric salt of (-
)-6-(4-
aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone and the chiral tartaric
acid
derivative and a mother liquor enriched in (+)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-
methyl-
3-(2H)-pyridazinone; (ii) converting (+)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-
methyl-3-(2H)-
pyridazinone obtained from step (i) to racemic 6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-
methyl-
3-(2H)-pyridazinone; and (iii) employing racemic 6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-
5-
methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone obtained from step (ii) in a process as described
above.
According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided (-)-6-
(4-
aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone prepared according to
any one
of the processes described above.
According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided.
levosimendan
prepared according to any one of the processes described above.
CA 02767946 2012-01-12
WO 2011/007123 PCT/GB2010/001325
7
According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a
pharmaceutical
composition comprising levosimendan prepared according to any one of the
processes
described above together with one or more pharmaceutically acceptable
excipients.
Detailed Description of the Invention
The invention will now be described in detail in connection with certain
preferred and
optional embodiments, so that various aspects thereof may be more fully
understood
and appreciated.
The process of present invention relates to the preparation of levosimendan in
high
optical purity without any recrystallisation or purification.
In an embodiment, there is provided a process for preparing levosimendan by
resolving
racemic 6-(4-am ino phenyl)-4,5-d i hyd ro-5-methyl-3-(2 H)-pyridazi none with
a resolving
agent to obtain the diastereomeric salt of (-)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-
methyl-3-
(2H)-pyridazinone and the resolving agent, converting the salt into (-)-6-(4-
aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone and then treating the
free base
with sodium nitrite and malononitrile.
In an embodiment, the process of the present invention comprises resolution of
racemic
6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone of formula II with
a
resolving agent which is a chiral tartaric acid derivative, preferably of
formula III, in the
presence of a solvent to obtain the corresponding diastereomeric salt of
formula IV.
CH3 CH3
Tartaric acid
derivative (III)
0 NH2 Solvent 0 NH2 Tartaric acid
N-N N-N derivative
H H
II IV
The chiral tartaric acid derivative is selected from the D- or L- isomer of di-
p-anisoyl-
tartaric acid, di-p-tolyl-tartaric acid or 0, O'-dibenzoyl-tartaric acid.
Preferably, the chiral
CA 02767946 2012-01-12
WO 2011/007123 PCT/GB2010/001325
8
acid for the process of present invention is the D-isomer of the tartaric acid
derivative.
Most preferably, di-p-anisoyl-D-tartaric acid of formula III is used.
OH OH
O 0
0 0
O O
H3C-O O-CH3
Formula III
The solvent employed for the preparation of the diastereomeric salt in the
process of
present invention is preferably a mixture of water and a polar solvent. The
polar solvent
may be selected from the group consisting of methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, n-
butanol,
acetone and acetonitrile. Most preferably, the solvent used in the resolution
step is a
mixture of water and ethanol.
In another embodiment, the process of the present invention further involves
treating
the diastereomeric salt of formula IV with a base to obtain (-)-6-(4-
aminophenyl)-4,5-
dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone of formula V.
O CH3 \ ! NH2 Tartaric acid Base O CH3
NH2
N-N derivative Solvent N-N
H H
N V
The base used may be an organic or inorganic base, for example selected from
ammonia, sodium methoxide, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, sodium
carbonate, potassium bicarbonate, potassium carbonate or sodium bicarbonate.
CA 02767946 2012-01-12
WO 2011/007123 PCT/GB2010/001325
9
In another aspect of the present invention, (-)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-
5-methyl-
3-(2H)-pyridazinone (V), suitably as prepared by the above process, is treated
with
sodium nitrite and malononitrile to obtain levosimendan (I).
In an embodiment, the particularly preferred process of present invention for
preparing
levosimendan (formula I) comprises:
(a) resolving racemic 6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-
pyridazinone of
Formula II,
CH3
0==~ NH2
N-N
H
Formula 11
with di-p-anisoyl-D-tartaric acid of formula III in the presence of a mixture
of water and
ethanol to form the diastereomeric (-)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-
3-(2H)-
pyridazinone di-p-anisoyl-D-tartaric acid salt of formula VI,
OH HO
O 0
CH3
O O
O O
NH2
NN
H
MeO OMe
Formula VI
typically at a temperature ranging from 55 C to 70 C;
(b) treating the diastereomeric salt of formula VI with an organic or
inorganic base
selected from ammonia, sodium methoxide, sodium hydroxide, potassium
hydroxide,
sodium carbonate, potassium bicarbonate, potassium carbonate or sodium
bicarbonate
CA 02767946 2012-01-12
WO 2011/007123 PCT/GB2010/001325
to obtain the (-)-isomer of 6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-
pyridazinone
of formula V;
CH3
C NHZ
N^N
H
Formula V
5
(c) reacting (-)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone of
formula
V with sodium nitrite and malononitrile under acidic conditions to obtain
levosimendan of
formula I.
10 The salt formed in step (a) may further be optionally recrystallised using
a water and
ethanol solvent mixture.
The mother liquor from the resolution step (a) is enriched with (+)-6-(4-
aminophenyl)-
4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone and may be converted into ( )-6-(4-
aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone and used again in the
process
of the present invention.
The process of present invention yields levosimendan in highly-pure
enantiomeric form.
The ratio of levosimendan : dextrosimendan as prepared by the process of
present
invention is typically about 99:1, as compared to the 96:4 ratio obtained by
prior art
processes. Also the levosimendan prepared from the present process typically
has a
purity of about 99.9%, as determined by chiral HPLC.
In another embodiment, the L-isomer of di-p-anisoyl-tartaric acid may be used.
For
example, racemic 6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone is
reacted with di-p-anisoyl-L-tartaric acid in the presence of a water and
ethanol solvent
mixture to form the diastereomeric (+)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-
3-(2H)-
pyridazinone di-p-anisoyl-L-tartaric acid salt. The mother liquor obtained on
resolution
contains (-)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone which
may act
as starting material for the preparation of levosimendan. The precipitated
product may
CA 02767946 2012-01-12
WO 2011/007123 PCT/GB2010/001325
11
be used in the process of the present invention for recycling the In the
process of the
present invention, highly-pure (-)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-
(2H)-
pyridazinone is obtained without any recrystallisation or purification. Thus,
preventing
the wastage of solvent and corresponding decrease in yield of product; in turn
making
the process economical, high-yielding and industrially-viable. Also, the
preferred use of
di-p-anisoyl-D-tartaric acid as resolving agent causes rapid precipitation of
the
diastereomeric salt which in turn in a single step gives levosimendan in high
yield. The
solvent employed in the process of present invention is preferably a mixture
with water
which makes the process environmentally-friendly.
The details of the invention are given in the examples which are provided
below for
illustration only and therefore these examples should not be construed to
limit the scope
of the invention.
Examples
Example 1 -
Step 1: 50 g of racemic 6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-
pyridazinone
and 500 ml ethanol were added to a flask and stirred at 65 C for 30 minutes.
Further di-
p-anisoyl-D-tartaric acid (113.3 g) and 500 ml water were added and stirring
was
continued for 1 hour. The reaction mass was cooled to 150C and stirred for
another 30
minutes. Then the mass was filtered, washed with water and dried under vacuum
at
55 C to obtain the corresponding diastereomeric salt (yield - 110 g, purity -
99.5%).
Step 2: The obtained salt and water (500 ml) were added to a reaction vessel
and
stirred at 25 - 30 C for 30 minutes. The pH of the resulting solution was
adjusted to 8-9
by adding ammonia solution and stirring was continued for 30 minutes. After
completion
of reaction, the contents were filtered and dried under vacuum at 550C to
obtain solid (-)
-6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone (yield - 24 g,
purity -
99.6%).
Step 3: To a solution of (-)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-
pyridazinone
(20 g) and dilute hydrochloric acid (52 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid
in 789 ml of
CA 02767946 2012-01-12
WO 2011/007123 PCT/GB2010/001325
12
water), 8 g of dilute sodium nitrite (8 g of sodium nitrite in 52 ml of water)
was added
and stirred. After 10 minutes, malononitrile solution (6.3 g malononitrile in
52 ml of
water) was added. The solution was stirred for 1 hour at room temperature. The
pH of
the suspension was adjusted to 6.0 with sodium acetate solution. The
suspension was
filtered, washed with water followed by ethanol and then dried to obtain solid
levosimendan (yield - 22 g, purity - 99.9%).
Example 2 -
g of racemic 6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone and
100
10 ml ethanol were added and stirred at 65 C for 30 minutes. Di-p-anisoyl-L-
tartaric acid
(22.6 g) and 100 ml water were added and stirring continued for 1 hour. After
completion of reaction, the mass was cooled to 15 C to obtain a solid and then
filtered.
The mother liquor obtained was concentrated to remove ethanol then basified
with
ammonia. The precipitated solid was filtered and treated with sodium nitrite
and
malononitrile as described above to obtain solid levosimendan (yield - 4 g,
purity -
99.6%).
Example 3 -
25g of (+)-6-(4-aminophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(2H)-pyridazinone,
obtained from
step 1 of Example 1, and 50% sodium hydroxide solution were heated at 90 C.
The
reaction mass was cooled to room temperature, filtered and washed with water.
The
solid obtained was charged in a flask along with 250 ml ethanol and stirred at
65 C for
minutes. Di-p-anisoyl-D-tartaric acid (56.6 g) and 250 ml water were added and
stirring was continued for 1 hour. The reaction mass was cooled to 15 C and
stirred for
25 another 30 minutes. The reaction mass was filtered and washed with water.
The wet
solid diastereomeric salt was charged in a round bottom flask along with water
and the
contents stirred at 25 C. To this mixture, 10% potassium carbonate was added
and the
pH was adjusted to 8-9. The reaction mass was stirred for 30 minutes and then
filtered.
The solid obtained was treated with sodium nitrite and malononitrile solution
in presence
30 of dilute hydrochloric acid to obtain levosimendan ((yield -10.5 g, purity -
99.5%).
It will be appreciated that the invention may be modified within the scope of
the
appended claims.