Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02771853 2012-02-20
WO 2011/031248 PCT/US2009/004897
KIT FOR MOUNTING A PHOTOVOLTAIC ASSEMBLY
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The invention disclosed here relates, in general, to the field of photovoltaic
panels, and
more specifically, to a kit used for facilitating the mounting of a
photovoltaic assembly
on to a supporting structure such as, but not limited to, a pole.
BACKGROUND
A photovoltaic panel is a combination of solar cells which converts sunlight
into usable
energy. An arrangement of more than one photovoltaic panel connected to
provide a
cumulative energy output is referred to as a photovoltaic array. The
photovoltaic panel
produces energy in the form of Direct Current (DC) electricity. DC electricity
can be
converted into Alternating Current (AC) electricity and used to operate
various electric
devices, for example, household appliances. The conversion of DC electricity
to AC
electricity is carried out using an inverter. For the purpose of description,
the
combination of a photovoltaic panel and the inverter is called a photovoltaic
module,
and an assembly of elements required to convert sunlight into usable electric
power, for
example AC electricity, is hereinafter referred to as a photovoltaic assembly.
For
example, the photovoltaic assembly includes a photovoltaic module, wires and
other
elements, such as a battery.
In general, the photovoltaic assembly is mounted to a utility grade pole or a
similar
supporting structure. Due to the size and weight of these assemblies, their
installation
can be labor intensive. Multiple installers, in conjunction with a lifting
apparatus, are
required to accurately align the assembly on a pole above the ground level,
and achieve
a safe and efficient installation. Even when the supporting structure is on
ground level,
more than one individual is required to hold the assembly in place and fix it
to the
supporting structure using the appropriate hardware.
In light of the above, there is a need for an arrangement that can facilitate
easy
installation of a photovoltaic assembly by minimizing the number of
individuals
PES-006PCT 1
CA 02771853 2012-02-20
WO 2011/031248 PCT/US2009/004897
necessary to complete the installation, and the amount of time required to
safely attach
the assembly to a pole or a supporting structure using the appropriate
hardware.
SUMMARY
An object of the invention is to enable easy and efficient installation of a
photovoltaic
assembly. In order to achieve this objective, the present invention provides a
kit for
facilitating the installation of a photovoltaic assembly on a supporting
structure. The kit
comprises one or more engagement members and a holding member. The holding
member conforms to the shape of the one or more engagement members and is
configured to be mounted on the supporting structure. The photovoltaic
assembly is
mounted on the holding member using the one or engagement members. Thereafter,
the photovoltaic assembly is secured to the supporting structure using the
appropriate
hardware. The kit may further comprise a channel which is configured to be
attached to
the supporting structure. The holding member and the photovoltaic assembly may
be
attached to the supporting structure via this channel. The kit of the present
invention
reduces the manual effort and time required during the installation of the
photovoltaic
assembly, thereby improving the efficiency of the whole process.
It is further an object of the present invention to provide a method for easy
and efficient
?0 installation of a photovoltaic assembly using the above kit.
It is yet another object of the invention to provide a photovoltaic assembly
configured to
be installed using the above method.
PES-006PCT 2
CA 02771853 2012-02-20
WO 2011/031248 PCT/US2009/004897
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
The preferred embodiments of the invention will hereinafter be described in
conjunction
with the appended drawings provided to illustrate and not to limit the
invention, wherein
like designations denote like elements, and in which:
FIGs. 1(a) and 1(b) illustrate a perspective view of an engagement member and
a
holding member, respectively, in accordance with an embodiment of the present
invention;
FIG. 2 illustrates a perspective view of a channel, in accordance with an
embodiment of
the present invention;
FIG. 3 illustrates a perspective view of a photovoltaic assembly, in
accordance with an
embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 4 is a flow diagram illustrating a method for installation of a
photovoltaic assembly,
in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 5 illustrates a perspective exploded view of the hardware required to
prepare a
supporting structure prior to installation of the photovoltaic assembly on it,
in
accordance with an embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 6 illustrates a perspective view of a supporting structure prepared for
installing the
photovoltaic assembly on it, in accordance with an embodiment of the present
invention;
FIG. 7 illustrates a perspective view of the photovoltaic assembly being
installed on the
supporting structure, in accordance with an embodiment of the present
invention;
FIG. 8 illustrates a perspective view of the photovoltaic assembly installed
on the
supporting structure, in accordance with an embodiment of the present
invention;
PES-006PCT 3
CA 02771853 2012-02-20
WO 2011/031248 PCT/US2009/004897
FIG. 9 illustrates a perspective view of the photovoltaic assembly installed
on the
supporting structure, in accordance with yet another embodiment of the present
invention; and
FIG. 10 illustrates a perspective view of the photovoltaic assembly installed
on the
supporting structure, in accordance with still another embodiment of the
present
invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
While the preferred embodiments of the invention have been illustrated and
described, it
will be clear that the invention is not limited to these embodiments only.
Numerous
modifications, changes, variations, substitutions and equivalents will be
apparent to
those skilled in the art without departing from the spirit and scope of the
invention.
In an embodiment, the invention provides a kit for mounting a photovoltaic
assembly on
a supporting structure such as a grade pole. The kit includes one or more
engagement
members and a holding member. The engagement members can be attached to the
photovoltaic assembly itself and the holding member can be attached to the
supporting
structure. The construction of the holding member is such that it conforms to
the shape
of the engagement members, and the photovoltaic assembly can be held on the
holding
member, which is already attached to the supporting structure, using the
engagement
members. The photovoltaic assembly mounted on the holding member can then be
attached to the supporting structure using the necessary hardware.
The kit may further include a channel which can be attached to the supporting
structure.
In this embodiment the photovoltaic assembly and the holding member can be
attached
to the channel and, hence, to the supporting structure via the channel
The kit of the present invention thus facilitates the alignment and
installation of the
photovoltaic assembly on a supporting structure and improves the overall
efficiency of
the process by reducing the amount of labor and time required for the
installation.
PES-006PCT 4
CA 02771853 2012-02-20
WO 2011/031248 PCT/US2009/004897
FIGs. 1(a) and 1(b) illustrate a perspective view of an engagement member 100
and a
holding member 106, respectively, both of which form parts of a kit that
facilitates the
mounting of a photovoltaic assembly (not shown) on a supporting structure (not
shown),
such as, but not limited to, a grade pole. In an embodiment the engagement
member
100 is of the form of an S-shaped hook as shown in FIG. 1(a). The engagement
member 100 is shown to include holes 102 and 104 that are used to attach the
engagement member 100 to a photovoltaic assembly, as described later in
reference to
FIG 3. This attachment can be achieved using an arrangement such as, but not
limited
to a nut and bolt arrangement. One or more of engagement members similar to
the
engagement member 100 are attached to the photovoltaic assembly in a way that
enables the mounting of the photovoltaic assembly onto a holding member 106
using
these engagement members as shown for example in Fig 8, where the engagement
members are numbered 310 and 312. The shape and structure of the holding
member
106 is such that it conforms to the shape of the engagement member 100 in a
way that
enables the photovoltaic assembly to be hung on to the holding member 106
using
engagement members similar to the engagement member 100. In addition, the said
shape and structure of the holding member 100 is such as to keep the
photovoltaic
assembly desirably aligned on the supporting structure. After mounting the
photovoltaic
assembly onto the holding member 106, which is already mounted onto the
supporting
structure, the photovoltaic assembly is secured to the supporting structure as
shown in
FIGs. 7 and 8 to complete the installation. FIG. 8 depicts an embodiment of
the
invention in which the holding member 106 and the photovoltaic assembly 300
are
attached to the supporting structure via a channel. The channel is described
with
reference to FIG. 2.
In an embodiment, the photovoltaic assembly is mounted onto the holding member
106
using two engagement members, each being similar to the engagement member 100.
The engagement member 100 is manufactured by techniques such as punching,
extrusion, machining, forming, casting or combinations thereof. It will be
readily evident
to a person of ordinary skill in the art that the shape of the engagement
member 100,
PES-006PCT 5
CA 02771853 2012-02-20
WO 2011/031248 PCT/US2009/004897
manufacturing method of the engagement member 100, method of attachment of the
engagement member 100 to the photovoltaic assembly and the number of
engagement
members attached to the photovoltaic assembly can be other than those
mentioned
above.
In an embodiment, the holding member 106 is of the form of a hanger as shown
in FIG.
1(b). The holding member 106 is shown to include a hole 108 that is used to
attach the
holding member 106 to the supporting structure or, in an embodiment, to the
supporting
structure via a channel 200, as shown in FIG. 5 and 6. The holding member 106
is
manufactured by techniques such as punching, extrusion, machining, forming,
casting
or combinations thereof. It will be readily evident to a person of ordinary
skill in the art
that the manufacturing method of the holding member 106, and the method of
attachment of the holding member 106 to the supporting structure can be other
than
those mentioned above.
FIG. 2 illustrates a perspective view of a channel 200 that, according to an
embodiment
of the invention, is used to realize the connection between the holding member
106 and
a supporting structure (not shown) and between a photovoltaic assembly (not
shown)
and the supporting structure. The channel 200 is shown to include holes 202
and 204,
through which bolts can be driven to secure the channel 200 to the supporting
structure.
Further, the hole 204 on the channel 200 is formed such that, when the holding
member
106 is aligned to be secured to the channel 200, a bolt can be driven through
the hole
108 and the hole 204 into the supporting structure to achieve a connection
between the
holding member 106 and the channel 200 and in turn between the holding member
106
and the supporting structure, as shown in FIG. 6. Further, the sets of holes
206 and 208
shown on the channel are meant to receive bolts for securing the photovoltaic
assembly
to the channel as shown in FIG. 7. It will be readily evident to a person of
ordinary skill
in the art that the method and hardware for connecting the channel 200, the
photovoltaic assembly, and the holding member 106 to each other and to the
supporting
structure can be other than those mentioned above. The channel 200 is
manufactured
PES-006PCT 6
CA 02771853 2012-02-20
WO 2011/031248 PCT/US2009/004897
by techniques such as punching, extrusion, machining, casting and forming or
combinations thereof.
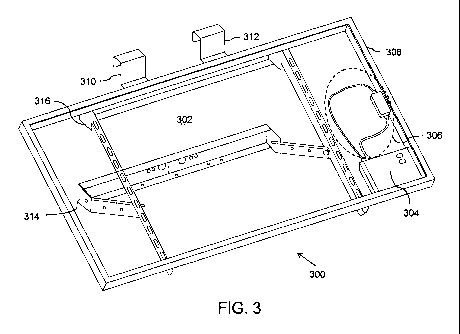
FIG. 3 illustrates a perspective view of a photovoltaic assembly 300, in
accordance with
an embodiment of the present invention. The photovoltaic assembly 300 of the
present
invention is such that it can be installed on a supporting structure (not
shown) using the
kit i.e. the holding member 106, engagement members similar to the engagement
member 100, and the channel 200, as described above. The photovoltaic assembly
300
is shown to include a photovoltaic panel 302 made of solar cells that convert
sunlight
into usable energy. This energy is in the form of Direct Current (DC)
electricity. The DC
electricity thus produced by the photovoltaic panel is converted into
Alternating Current
(AC) electricity to be used to operate various electric devices. The
conversion of DC
electricity to AC electricity is carried out by using the inverter module 304.
For the
purpose of this description, the inverter module 304 and the photovoltaic
panel 302
have been collectively termed as the photovoltaic module. Also shown in the
figure is
the associated electronic circuitry 306 that is used in the process of
conversion of
sunlight into AC electricity. The associated circuitry 306 included in the
photovoltaic
assembly 300 is readily known to a person of ordinary skill in the art. The
photovoltaic
module (302 and 304) and the associated circuitry 306 are mounted on a support
assembly. The support assembly comprises a rectangular frame 308 and rack
components 314 and 316. The frame 308 holds the photovoltaic module 302 and
the
associated circuitry 306 together. Two engagement members 310 and 312, which
are
the same or similar to the engagement member 100 of Fig 1(a), are attached to
the rack
component 316. During installation, the photovoltaic assembly 300 is held on
to the
holding member 106, using the engagement members 310 and 312, as described
above in reference to Fig 1 (a). The engagement members 310 and 312 are
attached to
the rack component 316 by driving bolts through engagement holes that are
similar to
the engagement holes 102 and 104 as defined in FIG. 1(a). Hence, the base of
the
engagement members 310 and 312, containing the engagement holes, is attached
to
the rack component 316 and the rest of the engagement member extends upwards.
Thus, a substantial part of each of the engagement member 310 and 312 lies
above the
PES-006PCT 7
CA 02771853 2012-02-20
WO 2011/031248 PCT/US2009/004897
plane in which the photovoltaic module (302 and 304) lies. This ensures that
the line of
sight of the engagement members 310 and 312 is above the line of sight of the
photovoltaic module (302 and 304). Hence, an operator can easily engage the
engagement members 310 and 312 with the holding member 106, pre-mounted on the
supporting structure, to mount the photovoltaic assembly 300 on the holding
member
106. The same operator can then position himself below the photovoltaic
assembly to
attach it to the channel 200 to complete the installation, as will be
explained below. This,
thereby, eliminates the need of another operator to complete the installation
of the
photovoltaic assembly 300 while the first operator ensures that it is held at
a desired
alignment and position on the supporting structure. The number of engagement
members attached to the frame 308 can be different from that mentioned above.
Thereafter, the rack components 314 and 316 are secured to the supporting
structure
using the necessary hardware, such as, but not limited to, U-bolts. This
completes the
installation of the photovoltaic assembly 300 on the supporting structure.
Further details
of this embodiment are given in FIG. 9 and 10.
In an embodiment, the rack components 314 and 316 are secured to the
supporting
structure via the channel 200. In this embodiment, the rack components 314 and
316
are attached to the channel using bolts driven through the holes 206 and 208.
Further
details of the said attachment have been provided in FIG. 7.
In the above embodiments the hardware used to secure the rack components 314
and
316, and in turn the photovoltaic assembly 300 to the supporting structure
directly or via
the channel 200, can be different from those mentioned above.
FIG. 4 is a flow diagram 400 illustrating a method for installation of the
photovoltaic
assembly 300, using the kit of the present invention, the components of which
have
been described in FIGs. 1(a), 1(b) and FIG. 2. The method starts at 402. At
404, the
holding member 106 is fixed onto the supporting structure. This process has
been
described in detail with reference to FIG 6. Thereafter at 406, the
photovoltaic assembly
PES-006PCT 8
CA 02771853 2012-02-20
WO 2011/031248 PCT/US2009/004897
300 is mounted onto the holding member 106 using the engagement members 310
and
312, as described in FIGs. 1(a), 1(b) and 3. Finally, at 408 the installation
is completed
by securing the photovoltaic assembly 300 to the supporting structure via rack
components 314 and 316 as described with reference to FIGs. 3 and 7. The
method
ends at 410.
In an embodiment, the holding member 106 and the photovoltaic assembly 300 are
fixed to the supporting structure via the channel 200. First, the channel 200
is fixed to
the supporting structure as described with reference to FIG. 2. Thereafter,
the holding
member 106 is attached to the channel 200 and in turn to the supporting
structure.
Then, the photovoltaic assembly 300 is mounted on the holding member 106 as
described in step 406 above. Finally, the rack components 314 and 316 of the
photovoltaic assembly 300 are secured to the channel 200, as described with
reference
to FIGs. 3 and 7 to fix the assembly to the supporting structure.
FIG. 5 illustrates a perspective exploded view of the hardware used to prepare
a
supporting structure 500 prior to installation of the photovoltaic assembly
300 on it in
accordance with an embodiment of the present invention. The supporting
structure
could be made of metal, wood or concrete, and may vary in size and shape. For
the
purpose of description, the supporting structure in this figure is shown to be
a metal
grade pole of circular cross section, and the terms "supporting structure" and
"grade
pole" have been used interchangeably. The grade pole 500 is shown to be
mounted
with a safety line 502. The safety line 502 serves to keep the operator (not
shown) or
the photovoltaic assembly 300 or both lifted in case of emergencies such as
failure of
?5 the lifting apparatus that is being used to lift the operator and the
photovoltaic assembly
300 up along the pole 500. The elements 504 and 506 are called support
channels and
facilitate the fixing of the channel 200 and the holding member 106 to the
pole 500. The
said fixing of the channel 200 and the holding member 106 to the pole 500 is
achieved
in the following manner. The bolt 508 driven through hole 202 of the channel
200 runs
through the predrilled pole 500, through the hole 510 of the support channel
504 and
receives the nut 512 on the face of the support channel 504 that is opposite
to the face
PES-006PCT 9
CA 02771853 2012-02-20
WO 2011/031248 PCT/US2009/004897
towards the pole 500. Similarly, the bolt 514 driven through the hole 108 of
the holding
member 106 runs through the hole 204 of the channel 200, through the pole 500,
further
through the hole 516 of the support channel 506 and finally receives the nut
518 on the
face of the support channel 506 that is opposite to the face towards the pole
500. In an
embodiment, where the pole does not have a predrilled hole, the above-
mentioned
attachments can be made by using hardware such as, but not limited to,
brackets that
wrap around the grade pole to secure the photovoltaic system or U-bolts etc.
It will be readily evident to a person of the ordinary skill in the art that
the above
technique and hardware used for fixing the channel 200 and the holding member
106 to
the pole 500 is merely exemplary, and other techniques and hardware can also
be
used. Moreover, in an embodiment, the holding member 106 and the photovoltaic
assembly 300 are directly attached to the supporting structure 500 without the
use of
the channel 200, as described with reference to FIGs. 3 and 4. Further details
of this
embodiment have been provided with reference to FIGs. 9 and 10.
FIG. 6 illustrates a perspective view of the grade pole 500 prepared for
installing the
photovoltaic assembly 300 on it, in accordance with an embodiment of the
present
invention. It can be seen that the grade pole 500 is mounted with a safety
line 502 and
the holding member 106 and the channel 200 have been attached to the pole 500
using
the technique described with reference to FIG. 5. The photovoltaic assembly
300 can
now be mounted on the holding member 106 using the engagement members 310 and
312, as described with reference to FIGs 1(a), 1(b) and 3. Further, the
installation can
be finished by securing the photovoltaic assembly 300 to the channel 200, as
described
with reference to FIGs. 3 and 7.
FIG. 7 illustrates a perspective view of the photovoltaic assembly 300 mounted
on the
holding member 106 (not visible in the Figure) and being secured to the
channel 200 to
finish its installation on the grade pole 500, in accordance with an
embodiment of the
present invention. The photovoltaic assembly 300 is shown to be secured to the
channel 200, via rack components 314 and 316, using nut and bolt arrangements
700
PES-006PCT 10
CA 02771853 2012-02-20
WO 2011/031248 PCT/US2009/004897
which are known in the art. However, it will be evident to a person of
ordinary skill in the
art that other such arrangements can also be used for securing the
photovoltaic
assembly.
FIG. 8 illustrates a perspective view of the photovoltaic assembly 300
installed on the
grade pole 500 using the kit of the present invention in accordance with the
same
embodiment described in reference to FIG. 7. The photovoltaic assembly 300,
its
engagement members 310 and 312, the holding member 106 and the channel 200 are
as described in the above figures. Further, the installation of the
photovoltaic assembly
300 on the pole 500 is also carried out as described with reference to the
figures above.
FIG. 9 illustrates a perspective view of the photovoltaic assembly 300
installed on the
grade pole 500 using the kit of the present invention, according to another
embodiment
of the present invention. In this embodiment the holding member 106 and the
photovoltaic assembly 300 are fixed to the grade pole 500 without the channel
200. The
exemplary hardware used in this embodiment to achieve the connection of the
holding_
member 106 and the photovoltaic assembly 300 with the grade pole 500 are U-
bolts
902. However, it will be readily evident to a person of ordinary skill in the
art that
hardware other than U-bolts can be used in the above embodiment.
FIG. 10 illustrates a perspective view of the photovoltaic assembly 300
installed on the
grade pole 1002 using the kit of the present invention, according to yet
another
embodiment of the present invention. In this embodiment the grade pole 1002 is
shown
to be a concrete pole with a rectangular cross-section. Additionally, in this
embodiment
the holding member 106 and the photovoltaic assembly 300 are fixed to the
grade pole
1002 without the channel 200. The exemplary hardware used in this embodiment
to
achieve the connection of the holding member 106 and the photovoltaic assembly
300
with the grade pole 1002 are U-bolts 1004. However, it will be readily evident
to a
person of ordinary skill in the art that hardware other than U-bolts can be
used in the
above embodiment.
PES-006PCT 11
CA 02771853 2012-02-20
WO 2011/031248 PCT/US2009/004897
In accordance with the present invention, the kit for mounting a photovoltaic
assembly
on a supporting structure provides various advantages. Some of the advantages
are
discussed below. The Kit of the present invention reduces the manual effort
and time
required during the installation of the photovoltaic assembly, and thereby
improves the
efficiency of the whole process. In turn, the invention enhances the incentive
to utilize
green technology and aids in mass quantity installations of photovoltaic
assemblies due
to its advantages.
PES-006PCT 12