Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
1
Rivet element
The invention relates to a rivet element, to a component assembly of a rivet
element and a component of fiber composite material, to a die button for
the attachment of rivet elements and also to a method for the attachment
of rivet elements in components of fiber composite material.
For the attachment of fastener elements, such as in particular rivet
elements to components of sheet metal or fiber composite materials, one
previously assumed that it is necessary to form an opening in the
component for the fastener element. For components of fiber composite
materials in particular, a procedure of this kind is however associated with
considerable disadvantages because discontinuities arise at openings in
the material, which considerably weaken the material and indeed at
positions where, as a result of the fastener elements, a particularly high
material strength is actually required.
The object of the invention is thus to provide a possibility of attaching
fastener elements, such as in particular rivet elements, to components in
such a way that the components do not have to be weakened in a
disadvantageous manner and indeed it should in particular be possible to
attach fastener elements to components of fiber composite materials.
This object is satisfied by the invention by a rivet element having a rivet
section and a fastener section which is provided with a thread, wherein the
rivet section and the fastener section are integrally formed, and wherein
the rivet element tapers in the direction towards a tip which is formed at
least regionally as a spike which tapers in the direction towards the tip and
which can be dilated by means of a die button, wherein the rivet element is
adapted to be mounted to an unprepared component and wherein the
CA 2788797 2019-02-21
la
spike has an introduction aid for the die button at its tip, wherein the rivet
section has a plurality of segments which jointly form the spike and can be
moved apart from one another during the dilation of the spike and wherein
the rivet element segments are adapted to be folded to form a rivet bead at
the lower side of the component. The object is further satisfied by the
invention by a component assembly having the features of the rivet
element described above, by a die button having the features of the rivet
element described above and also by a method for the attachment of rivet
elements having the features of the rivet element described above, in
.. components of fiber composite materials in which a rivet element and a die
button are each pressed with a section formed as a spike into a
component, which is unprepared and which is provided without an
opening for the rivet element and the spike of the rivet element is dilated by
means of the spike of the die button to establish a rivet connection.
CA 2788797 2019-02-21
CA 02788797 2012-09-05
2
The rivet element in accordance with the invention includes a rivet section
which is formed as a spike tapering in the direction of a tip and which can
be at least regionally dilated by means of a die button.
.. By the formation of the rivet section as a dilatable spike it is possible
to
press the rivet element with the spike into the respective material, where-
upon the spike can be dilated by means of a suitably shaped die button
for the formation of a rivet connection.
For components which are manufactured of a material which enables a
pressing in of the rivet section of this kind, at least in certain states of
the
material, it is consequently possible to dispense with the manufacturing of
an opening for the rivet element. The rivet element of the invention is con-
sequently particularly suitable for components of fiber composite materi-
als which are at least for a time in a condition in which the material is
sufficiently soft and/or "pasty". This will be explained in more detail in the
following. A further advantage of the invention lies in the fact that it is
not
necessary to adhesively bond the fastener element to the component.
In a preferred design of the rivet element the rivet section has a plurality
of segments, in particular of tongue-like shape, which jointly form the
spike and which can be moved apart from one another during the dilation
of the spike.
The segments can be connected together with an intentional material
weakening being provided at the connection position points of intended
fracture, for example by use of a smaller wall thickness. The dilation of the
spike is in this case associated with a breaking apart of the spike in order
to move segments apart from one another. As an alternative, the segments
can be at least regionally unconnected and in this respect lie on one an-
CA 02788797 2012-09-05
3
other, or be fractionally spaced from one another, so that in the starting
condition they jointly form a spike serving for pressing into the component
and can be subsequently be moved apart by means of the die button with-
out the breaking open of material.
The component assembly in accordance with the invention includes a rivet
element in accordance with the invention and also a component of fiber
composite material. In particular, the component assembly is character-
ized in that the rivet section of the rivet element engages behind the com-
ponent with a region which is folded at least once. In this way, a particu-
larly good security can be achieved against relatively high press-out forc-
es.
The attachment of rivet element in the component preferably takes place
in such way that in the finished component excess material of the compo-
nent surrounds the rivet element at the side opposite to the rivet section.
The die button in accordance with the invention serves for the attachment
of rivet elements in accordance with the invention and includes a dilating
section for the dilation of the spike of the rivet element, with the dilation
section being itself at least regionally formed as a spike.
In this way the die button can first be pressed with its spike into the com-
ponent before the cooperation of the rivet section and the die button be-
gins, i.e. before the spike of the rivet section is dilated by means of the
spike of the die button to manufacture the desired rivet connection.
In a particularly preferred embodiment of the method, provision is made
that the pressing in of the rivet element and of the die button into the
component takes place during the manufacture of the component. In this
CA 02788797 2012-09-05
=
4
way, on the one hand, the attachment of the rivet element can take place
in the context of the manufacture of the component. In this way it is in
particular possible to simultaneously use the tools used for the manufac-
ture of the component to bring about the pressing in of the rivet elements
and of the die button and also to apply the forces required for the coopera-
tion of the rivet element and the die button. On the other hand, the fact
can be exploited that during the manufacture of components of fiber com-
posite materials the material has, as a result of the process, at least for a
period of time, a consistency which permits the pressing in of the spikes of
the rivet element and of the die button and also permits the displacement
of material required for the manufacture of the rivet connection.
The invention can advantageously be used both in connection with fiber
composite materials with relatively short fibers and also with materials
with relatively long fibers. Components with short fibers can be manufac-
tured in an injection molding process. In this connection the material
mixture can readily be molded so that the tools used for the manufacture
of these components can simultaneously be used for the attachment of
rivet elements. Fiber composite materials with long fibers can be manufac-
tured by laminating, i.e. by the cross-wise application of individual plies
with directional fibers. For many plastic materials it is then possible, in a
similar manner to the deep-drawing of sheet metal parts, to press the
laminated parts under the action of heat by means of a tool into a specific
shape. The presses that are used for this can then simultaneously be ex-
ploited to introduce the rivet element and the die button into the ade-
quately soft composite material.
In both cases, i.e. both with short fiber material and also with long fiber
material the circumstances is thus exploited that the rivet element of the
invention and the die button of the invention can be pressed into the ma-
5
terial which is adequately soft for at least a period of time as a result of
the
process.
Preferred further developments of the invention are set forth in the
description and also in the drawing.
The invention will be described in the following by way of example and with
reference to the drawing, Figs. 1 to 7 of which show different views on the
rivet element in accordance with the invention and of the die button in
accordance with the invention and also the course of a possible attachment
of a rivet element in accordance with the invention to a component.
Figs. 1 to 3 show different views of an embodiment of the rivet element in
accordance with the invention.
The rivet element has a flange section 21 which extends radially with re-
spect to a central axis 15 of the element. On the one side of the flange
section 21 there is a fastener section 27 which is provided with an internal
thread 29 which extends up to and into the flange portion 21.
In this embodiment the rivet element is consequently formed as a nut
element. This is however not compulsory. In an alternative embodiment the
rivet element in accordance with the invention can, for example, also be
formed as a bolt element, which has a shaft is formed with an external
thread as a fastener section.
The underside of the flange portion 21 remote from the fastener section 27
serves as a contact surface 23 for a component 51 (see in particular Fig. 6)
to which the rivet element is to be attached. The contact surface 23 is
CA 2788797 2019-02-21
CA 02788797 2012-09-05
6
provided with a plurality of projecting ribs 25 which extend in the radial
direction and which serve as a security against rotation.
A rivet section 11 extends at the side of the flange portion 21 remote from
the fastener section 27 and the outer diameter of the rivet section corre-
sponds in the region of the contact surface 23 at least substantially to the
outer diameter of the cylindrical fastener section 27.
Starting from flange portion 21, the rivet section 11 first has a substan-
tially cylindrical portion 19 which merges into a spike tapering in the di-
rection towards a tip or apex. At the tip of the spike there is funnel-shaped
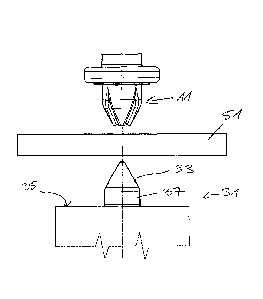
introduction aid 17 for a die button 31 (see in particular Fig. 5).
The rivet section 11 is formed by a plurality of tongue-like segments 13
which start from the flange section 21 and form the tapering spike of the
rivet section 11 in the manner of a closed bud. The four segments 13 in
this embodiment are consequently designed in such a way that they be-
come narrower along the central axis 15 in the direction of the tip starting
from the flange portion 21.
As mentioned in the introductory part the segments 13 can be connected
to one another or for example can simply be unconnected while contacting
one another.
.. The spike of the rivet element makes it possible to press the rivet element
into an adequately soft component to which the rivet element is to be at-
tached without it being necessary to (first) form an opening for the rivet
element in the component.
CA 02788797 2012-09-05
,
7
A possible sequence for the attachment of a rivet element to a component
51 by means of a correspondingly shaped die button is shown in Figs. 4 to
7.
The die button 31 includes a portion 33 for the dilation of the spike of the
rivet element, with this portion 33 of the die button likewise having a por-
tion forming a spike, which in this embodiment is of circular conical
shape. As a consequence, the die button 31 in accordance with the inven-
tion is able to be pressed with its spike into the component.
A cylindrical section 37 is formed between a flat surface 35 of the die but-
ton 31 extending perpendicular to the central axis of the spike and the
spike.
Fig. 5 shows a state in which both the spike of the rivet elements and also
the spike of the die button 31 are pressed into the component 51, the
dilation section 33 of the die button 31 has however not yet started to
dilate the spike of the rivet element.
In total, the die button is shaped, in particular with respect to the diame-
ter and angular relationships in correspondence with the rivet section of
the rivet element in such a way that the end state shown in Fig. 6 results.
Through the collaboration with the die button the spike of the rivet section
11 of the rivet element is dilated whereby the segments 13, on the one
hand, move apart from one another and, on the other hand, are folded, so
that a folded rivet bead 30 results at the lower side of the component. In
the illustrated embodiment this rivet bead lies flush with the underside of
the component 51. This is, however, not essential, the rivet bead can, as
an alternative, also project at the underside of the component 51.
CA 02788797 2012-09-05
8
As Fig. 6 shows, the material of the component 51 is displaced in such a
way that excess material 53 projects circularly at the top side of the com-
ponent 51 around the flange portion 21.
While the folded rivet 30 secures the rivet element against the press-out
forces the flange portion 21 provides security against pull-out forces.
As already mentioned in the introductory part, the pressing in of the rivet
element and of the die button 31 is, in particular, carried out with the aid
of a tool which is used for the manufacture of the respective component
51. The introduction of the rivet elements in accordance with the inven-
tion can consequently take place in the context of the manufacturing pro-
cess which is in any event taking place. This manufacturing process in
particular requires the material to be at least hot and thus soft for a peri-
od of time so that the rivet element and the die button 31 can be pressed
into the material.
The invention also makes it possible to attach rivet elements to compo-
nents of fiber composite materials, also termed "organo sheets" without
openings having been (previously) formed in the material for the rivet ele-
ments. Disadvantageous weakening of the material is hereby avoided in
advantageous manner.
CA 02788797 2012-09-05
9
Reference numeral list
11 rivet section
13 segment
15 central axis
17 introduction aid
19 cylindrical section
21 flange portion
23 contact surface
25 means for providing security against rotation, rib
27 fastener section
29 internal thread
30 folded rivet bead
31 die button
33 dilation section
35 flat surface
37 cylindrical section
51 component
53 excess material