Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02795607 2012-10-05
2
MACHINE FOR CLEAVING SLATE
OBJECT OF THE INVENTION
The present invention, as expressed in the statement of this
specification, relates to a machine for cleaving slate which significantly
improves the cleaving process of the slate pieces by achieving a better seal
at
the side faces of the corresponding block to be cleaved, which detail is very
important to obtain a high-quality clean cutting.
The machine of the invention is more versatile, while at the same time it
allows achieving a high productivity with respect to other conventional
machines
for the same purpose.
Basically, the machine is responsible for handling two blocks to be
cleaved to place them in a static position to then proceed to the cleaving by
applying pressure with a cutter to begin an incision and fissure acting at
successive stages on the side faces on cleavage planes parallel to the bases
of
the block where these bases are arranged on vertical planes, such that by said
pressure and subsequent injection of pressurized air by the cleavage plane,
the
corresponding slate pieces will be obtained in successive stages.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
In the present day, the machines for cleaving slate which incorporate
means to statically hold a slate block with its bases arranged in vertical
planes
are known.
In this situation an incision by pressure is subsequently applied on the
upper side face with beginning of fissure by a cutter for obtaining in
successive
stages the various slate pieces with laminar structure as it is evident, in
correspondence with the different cleavage planes of the slate block.
The French invention patent FR 2290051 describes a cleaving method
which is carried out with a beginning of fissure along one of the sides or
side
faces of the block, such that the separation corresponding with the incision
plane of the cutter, is produced by traction using suction cups that are
applied
against the opposite bases of the block, said suction cups being connected to
a
vacuum source.
The invention patent No. 513613 describes a cleaving method which is
characterized in that the beginning of fissure is carried out practically over
the
CA 02795607 2012-10-05
3
entire length of one of the sides of the block joining the bases of the same
and
surrounding a closed chamber, inside of which a pressure higher than the
ambient pressure that prevails on the opposite faces of the block is
temporarily
set.
For example, it is also known the invention patent number 9100276
relating to another cleaving method which is characterized in that it
comprises
the following stages: provision of a cutting cutter equipped with a cutting
edge
that determines a straight alignment; arrangement of the block to be cleaved
such that said side edge will be accessible to said cutter; application of
said
edge to said side edge; operation of said cutter for the introduction of the
edge
in the slate block, causing a brief crack in the same; and injection of a
fluid
under pressure into said crack until the total division of said slate block to
be
cleaved.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The machine for cleaving slate constituting the object of the invention is
characterized in that it comprises two work stations and one movable truck
carrying a cutting cutter that comes into contact with an upper side face of
the
slate block previously placed in a stable and static manner on a central area
of
one of the two work stations.
Another feature of the invention is the incorporation of a clamp which
comprises in a first embodiment two sets of opposing rollers, each of which
has
pairs of support collateral rollers and one central roller made of soft
material that
seals the cleavage plane or shear plane during the process of separation when
the cutting cutter comes into contact with the upper side face of the slate
block
arranged vertically with its bases placed on two vertical planes. In a second
embodiment of the clamp each central roller is replaced by a pneumatic
mattress with a rigid base.
Some conventional machines, instead of using the collateral rollers
mentioned above, use rubber plates that are less accurate and very
damageable.
Both the cutting cutter and the two sets of opposing rollers are supported
by the movable truck superiorly suspended from a pair of transversal guide
bars
to be able to place said truck set in correspondence with one or another work
station arranged in two parallel longitudinal directions.
CA 02795607 2012-10-05
4
In correspondence with each of the work stations there is located a
longitudinal bed of rollers that is interrupted in a central transversal zone
where
there are two tilting support elements to flip and place the block of slate in
the
correct position to then proceed to obtain the various slate sheets through
the
cutting cutter that will come into contact with the upper side face of the
corresponding slate block initially dragged by the rollers to the respective
tilting
support element located in the central transversal zone, in correspondence
with
which is located the movable truck that will run above the slate block that is
driven on the referenced transversal guide bars.
The cutter moves vertically to separate the different slate pieces by a
linear actuator, such as a pneumatic or oil-hydraulic cylinder. In turn, the
block
is held by one of its bases against a seat of the tilting support element,
while on
the other matching base other front linear actuators press in a controlled
manner.
With this described arrangement, a slate block is supported in principle
by one of its bases on the respective longitudinal bed of rollers of one of
the
work stations, dragging it to the respective tilting support element located
in the
central transversal zone of the machine, which tilting support element will
flip
the slate block 90 until placing it in such a position that its bases will
be
arranged on vertical planes, which slate block will be maintained supported on
said tilting support element, while the static position of the slate block is
ensured
by the linear front actuators referred to above.
In this situation, the movable truck is placed on top of the slate block so
that through the cutting cutter it pushes down on the upper side face of the
slate
block in correspondence with a cleavage plane or shear plane parallel to the
bases of the slate block, and then pressurized air is blown into the incision
made to facilitate the cleaving, such that it is important that the air does
not
escape through the sides of the slate block but that it does escape through
the
bottom, once the cleaving has ended. Therefore, the new sealing system is
envisaged based on a central roller with rubber coating the generatrix of
which
L 1. L L with ..2t. .~~. the block 4 creating :...~ the necessary closure,
enters into contact wit I the suf face of U lure,
after pressure from the slate block on said side faces. Said necessary closure
can also be carried out with the pneumatic mattress instead of the central
roller.
Next, in order to facilitate a better understanding of this specification and
forming an integral part thereof, figures are accompanied in which the object
of
CA 02795607 2012-10-05
the invention has been represented with an illustrative character and without
limitation.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
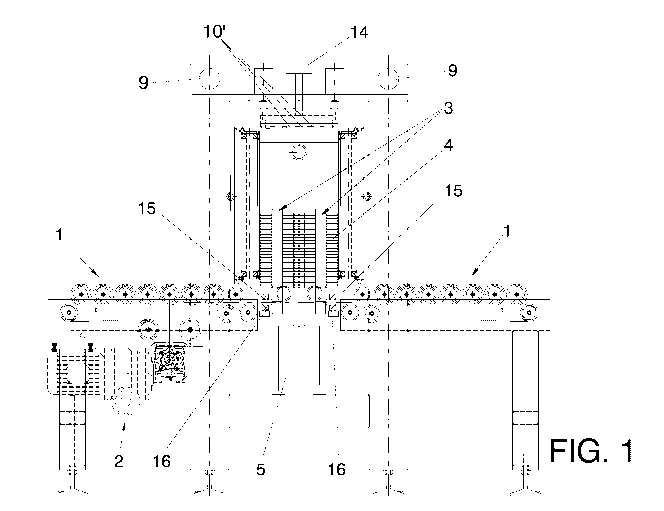
5 Figure 1.- It shows an elevational view of the machine for cleaving slate,
object of the invention. Said slate pieces are obtained from a block using a
cleaving process.
Figure 2.- It shows a profile view of the machine of the invention.
Figure 3.- It shows an elevational view of the cleaving machine.
Figure 4.- It shows a plant view of the machine of the invention.
Figure 5.- It depicts a view of a part of the machine showing essentially a
clamp equipped with a roller made of soft material that seals the shear plane
during the cleaving process of the slate block.
Figure 6.- It depicts a view similar to the previous one where the clamp
incorporates a pneumatic mattress instead of the central roller made of soft
material.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
Considering the numbering adopted in the figures, the machine for
cleaving slate comprises a frame which supports two longitudinal beds of
rollers
1 rotating through two reducing motors 2 while their continuity is interrupted
in a
central transversal zone 2 where there are two tilting support elements 3 with
an
L-shaped angular structure, such that in the initial position, the major
branch of
such tilting support elements 3 is located in the same horizontal plane as the
longitudinal beds of rollers 1, on which the slate blocks 4 are supported in
principle by one of their bases, being drawn until placing them on the
respective
tilting support element 3, and, at such time, it will tilt through a major oil-
hydraulic cylinder 5 until being positioned in a vertical position in which
the
major branch of such tilting support element 3 will be arranged in a vertical
plane as the bases of the slate block 4, on the free base of which a pair of
front
oil-hydraulic cylinders 6 will press to ensure the stability and static
clamping of
the slate block 4.
The minor branch of the tilting support elements 3 forms a height-
adjustable seat base 7 to adjust the height of the slate block 4.
Above the central transversal zone where the two tilting support
CA 02795607 2012-10-05
6
elements 3 are, there is a movable truck 8 coupled and guided on a pair of
transversal guide bars 9 fixed at their ends to the frame of the machine.
This movable truck 8 carries a cutting cutter 10-10' and also a clamp 11 -
11' that in a first embodiment comprises two groups of vertical rollers, each
of
which groups includes a central roller 12 with elastomeric surface and two
pairs
of supporting collateral rollers 13, such that the central roller 12 seals the
shear
plane or separation of the slate block 4. The cutter 10-10' moves through a
vertical cylinder 14.
In a second embodiment, the central roller 12 is replaced by a pneumatic
mattress 12' with a rigid base 18, such that in this case the pneumatic
mattress
12' is the element that seals the shear plane of the slate block 4.
Optionally, an
air pressure system may be included that will introduce pressurized air into
the
pneumatic mattress 12', adapting it better to the irregularities that the
slate block
4 has.
The structure of the cutting cutter may comprise a conventional
configuration convergent structure 10 or comprise a modular structure 10'
formed by several cutter portions arranged in the same vertical plane.
Thus, the machine of the invention has a double work station which
corresponds to the two longitudinal beds of rollers 1, such that the movable
truck 8 which carries the cutter 10-10' performs a cut on the upper side face
of
the respective slate block 4, which movable truck 8 will move alternately to
one
and the other work station.
Once the incision or fissure has been carried out with the cutting cutter
10-10' on the upper side face of the slate block 4, pressurized air is blown
into
the incision made to produce the cleaving, being equally important to achieve
that the air does not escape through the sides of the block, but that it does
it
through the bottom after the cleaving. Therefore, the new sealing system based
on the central roller 12 with rubber coating has been envisaged, the
generatrix
of which contacts the surface of the block, creating the necessary closure,
after
pressure from the slate block 4 on the corresponding opposing side faces.
1-_.._- also L. J out L.. of FL..
c
Jdld necessary closure can In also uC l du ieu O W . uy means UI L 11
pneumatic mattress 12' instead of the central roller 12 made of soft material.
It should be noted that in the case of a modular cutter formed by small
individual portions of cutter, they can be replaced one by one to improve the
incision on the slate block 4.
CA 02795607 2012-10-05
7
The tilting support elements 3 have lateral portions 15 associated to
horizontal guides 16 to control the mobility of said tilting support element 3
during its tilting for flipping the slate blocks 4.
Each group of vertical rollers 11 is coupled to opposing supports 17 with
adjustment to adapt to the width of the slate blocks 4.
Is also important to highlight the management and control that the
electrical components installed have on the mechanics, from the automatic
logic
controller to the ones that provide the accurate readings of the dimensions of
the pieces to be cleaved.
The process to perform the cutting of the pieces is the following.
Initially and after having positioned the slate block, an accurate
measurement of the thickness of the piece to be cut is carried out. The
automatic logic controller makes a precise calculation of the measures at
which
it has to make the cuts (within pre-set tolerances), with the aim of cutting
all the
block into pieces of equal size without leaving the last piece out of measure
as
rejection. It is understood that the measures of the pieces of a block to be
cleaved, shall be equal to the difference of the two blocks divided by the
number of pieces. Also, certain dimensions can be preset, at the front and
rear
parts of the faces of the block as a useless discards due to their
irregularities or
little value, in which case the automatic logic controller will not consider
these
two preset dimensions as part of the block and it will make the subdivisions
without these discards.
On the other hand, the machine of the invention incorporates a
pneumatic reservoir with adjustable pressure (not shown in the figures) to
feed
the pneumatic mattress 12' of the clamp 11, as well as to blow the pressurized
air into the incisions on the slate block 4 to produce the cleaving and in
general
to supply pressurized air to any element or part of the machine that may need
it.