Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02795781 2012-11-20
MOTOR-DOUBLE ALTERNATOR APPARATUS
Field of the Invention
The invention relates to electric power systems, and more particularly to
electric power systems
intended to reduce non-renewable energy source consumption.
Background of the Invention
It is well known in the art of power system design to seek to reduce
consumption of non-
renewable energy sources. In the specific field of electric power systems,
such power systems
require input energy, commonly from a direct current source such as a battery.
Batteries convert
stored chemical energy into electrical energy, but they lose their utility
over time due to
discharge or other factors. requiring a new battery in time.
It is known in the art to use. an energy source to drive a device that itself
can produce power
which can be fed back into the system. For example, it is known to drive
alternators or
generators to produce power by converting mechanical energy to electrical
energy, which energy
can be used to recharge a power source battery.
There have been many attempts to employ alternators to generate energy to help
drive an electric
power system. For example, United States Patent Application No. 12/471,447 to
Chen teaches a
power device comprising a motor connected to a generator by means of a shaft,
where the
generator provides power to the battery powering the motor.
However, it has been determined that some of these prior art attempts fail to
appreciate and
address the problem of friction. Friction occurs within the apparatus, using
up energy and
draining the battery more rapidly than anticipated. A preferred apparatus
would therefore seek to
address the problem of friction by taking into account the extra energy
consumption.
1
CA 02795781 2012-11-20
What is required, therefore, is an apparatus that provides a means to generate
produced energy
that can be used to power the apparatus itself, and preferably energy that can
be used to address
loss due to friction.
Summary of the Invention
The present invention therefore seeks to provide an apparatus that comprises
first and second
alternators, both driven by a single motor.
According to a broad aspect of the present invention there is provided an
apparatus comprising:
an energy storage unit;
a motor operably connected to the energy storage unit and configured to
receive operating energy
therefrom;
a shaft mechanically connecting the motor to first and second alternators,
such that operating the
motor rotates the shaft thereby providing mechanical energy to the first and
second alternators to
produce electrical energy;
the first alternator connected to the energy storage unit to recharge the
energy storage unit; and
the second alternator connected to the motor for providing operating energy.
In exemplary embodiments of the present invention: a fuse. switch and start
capacitor are
preferably positioned in line between the energy storage unit and the motor; a
voltage regulator,
fuse and switch are preferably positioned in line between the first alternator
and the energy
storage unit; and a voltage regulator, fuse and switch are preferably
positioned in line between
the second alternator and the motor. The apparatus preferably further
comprises a power source
for the energy storage unit. The energy storage unit is preferably a battery
and the power source
is preferably a battery charger.
A detailed description of an exemplary embodiment of the present invention is
given in the
following. It is to be understood, however, that the invention is not to be
construed as being
limited to this embodiment.
2
CA 02795781 2012-11-20
Brief Description of the Drawing
In the accompanying drawing, which illustrates an exemplary embodiment of the
present
invention:
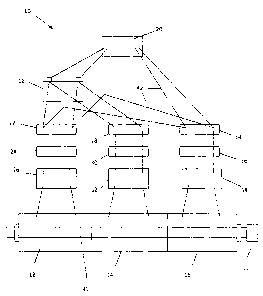
Figure 1 is a simplified schematic of an apparatus according to the present
invention.
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention will now be described with
reference to the
accompanying drawing.
Detailed Description of Exemplar' Embodiment
The present invention relates to a novel motor-alternator arrangement in which
two alternators
are driven by a single motor. Only those parts of the apparatus as are
necessary for description
of the novel arrangement are discussed herein, and the remaining parts and
functions of the
apparatus will not be discussed as they are conventional and well known to
those skilled in the
art. Simplified wiring is shown by means of wiring 42 for ease of
illustration.
The term "switch" when used in this application refers to an electrical
component that can break
an electrical circuit, interrupting the current, moveable from a closed
position (where the
contacts are touching and electricity can [low between them) and an open
position (where the
contacts are separated and the switch is nonconducting). The tern "fuse" when
used in this
application refers to a resistor that acts to provide ovcrcurrent protection
by interrupting the
current. The terns "start capacitor" when used in this application refers to
any type of capacitor
useful for providing desired torque to the motor. The term "voltage regulator"
when used in this
application refers to any device capable of automatically converting varying
input voltage and
producing a constant regulated output voltage. Although the above terms have
been provided
with standard definitions, one skilled in the art would be able to select
appropriate components
for an apparatus according to the present invention for a particular use,
including alternate
components of desirable functionality to those defined above and discussed
herein.
3
CA 02795781 2012-11-20
Turning to Figure 1, an apparatus is illustrated and indicated with the
reference numeral 10. The
apparatus 10 comprises a motor 12, a first alternator 14 and a second
alternator 16, which motor
12 and alternators 14, 16 are operably connected by means of a shaft 40. The
shaft 40 is shown
in the simplified drawing as being a solid length extending through the motor
12 and alternators
14, 16, but it will be clear to those skilled in the art that other forms of
mechanical force
transmission from the motor 12 to the alternators 14, 16 are possible, such as
universal joint
connectors between discrete shaft lengths. The motor 12 and alternators 14, 16
may be of
conventional design. modified as necessary for particular applications, as
would be obvious to
those skilled in the art. The shaft 40 is provided with an end joint 44 which
can be used to drive
peripheral equipment, in a manner well known to those skilled in the art,
although either end of
the shaft 40 could be used to drive peripheral equipment. Also, an increase or
decrease in
voltage for peripheral equipment may be attained using a transformer.
A battery 18 is connected to the motor 12 by means of a fuse 22, switch 24 and
start capacitor 26
in series, all components connected by wiring 42. The battery 18 is preferably
but not
necessarily a 12 volt battery of conventional design. The battery 18 is
powered by means of a
battery charger 20, which is also of conventional design.
The first alternator 14 is connected to the battery 18 by means of a voltage
regulator 32, fuse 30
and switch 28 in series, all components connected by wiring 42.
The second alternator 16 is connected to the battery charger 20 by means of a
voltage regulator
38, fuse 36 and switch 34 in series, all components connected by wiring 42.
The second
alternator 16 is also connected to the motor 12 by wiring 42 that comprises a
connection between
the switch 34 and the fuse 22, as is illustrated in Figure 1.
In operation, all three switches 24, 28, 34 must be in the closed or "on"
position, to allow current
to flow through the wiring 42; alternatively, to stop the current flow all
three switches 24, 28, 34
must be in the open or "off" position. Electricity flows from the battery 18
to the fuse 22 when
the switch 24 is closed, then to the start capacitor 26 and then to the motor
12; this powers the
motor 12, thereby rotating the shaft 40. Rotation of the shaft 40 powers the
first and second
4
CA 02795781 2012-11-20
alternators 14. 16, thereby producing electrical energy. The electricity
produced by the first
alternator 14 flows through the voltage regulator 32 to the fuse 30 and then
to the switch 28,
from which it flows to the battery 18 to recharge the battery 18, thereby
helping to address the
friction problem. The electricity produced by the second alternator 16 flows
through the voltage
regulator 38 to the fuse 36 and then to the switch 34, from which it flows to
both the battery
charger 20 and the fuse 22, thereby helping to power both the battery charger
20 and the motor
12.
An apparatus according to the present invention could be used, for example, to
power a vehicle
block heater or vehicle warmer, although many applications will be clear to
one skilled in the art.
The foregoing is considered as illustrative only of the principles of the
invention. Thus, while
certain aspects and embodiments of the invention have been described, these
have been
presented by way of example only and are not intended to limit the scope of
the invention, The
scope of the claims should not be limited by the exemplary embodiment set
forth in the
foregoing, but should be given the broadest interpretation consistent with the
specification as a
whole.
5