Some of the information on this Web page has been provided by external sources. The Government of Canada is not responsible for the accuracy, reliability or currency of the information supplied by external sources. Users wishing to rely upon this information should consult directly with the source of the information. Content provided by external sources is not subject to official languages, privacy and accessibility requirements.
Any discrepancies in the text and image of the Claims and Abstract are due to differing posting times. Text of the Claims and Abstract are posted:
| (12) Patent Application: | (11) CA 2798350 |
|---|---|
| (54) English Title: | BENDING MACHINE FOR CREATING BENDS TO THE LEFT AND RIGHT |
| (54) French Title: | CINTREUSE POUR CINTRAGES A GAUCHE ET A DROITE |
| Status: | Deemed Abandoned and Beyond the Period of Reinstatement - Pending Response to Notice of Disregarded Communication |
| (51) International Patent Classification (IPC): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventors : |
|
| (73) Owners : |
|
| (71) Applicants : |
|
| (74) Agent: | SMART & BIGGAR LP |
| (74) Associate agent: | |
| (45) Issued: | |
| (86) PCT Filing Date: | 2011-04-26 |
| (87) Open to Public Inspection: | 2011-11-17 |
| Availability of licence: | N/A |
| Dedicated to the Public: | N/A |
| (25) Language of filing: | English |
| Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT): | Yes |
|---|---|
| (86) PCT Filing Number: | PCT/DE2011/000438 |
| (87) International Publication Number: | WO 2011141015 |
| (85) National Entry: | 2012-11-05 |
| (30) Application Priority Data: | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
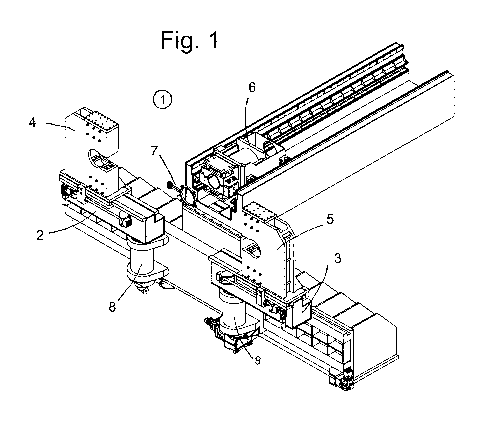
A machine for bending tubes of large diameter in different bending directions, wherein, for bending, in this machine a tube (10) is guided in the axial direction through an inductive heating device (7) enclosing this tube in an annular manner, the tube (10) is secured by a bending lock (4) at the end (11) thereof intended to be bent, at least one bending arm (2), which is mounted rotatably about a vertical axis of rotation (8), is located at the part of the bending machine that is disposed in the advancing direction of the tube (10), the bending lock (4) is indirectly connected to the bending arm (2), the bending lock (4) has a force transmission device between the receiving device for tubes and the bending arm (2), the force transmission device is connected to the bending arm (2) such that it can be set so as to allow the distances between the centre axis of the receiving device for tubes and the vertical axis of rotation (8) to be chosen between the smallest distance and greatest distance, whereby a range between a greatest and a smallest bending radius (12) can be set, the machine has at least one further bending lock (5) with a further bending arm (3), a receiving device for tubes and a force transmission device for bending forces from the receiving device to the further bending arm (3), wherein the direction of rotation of the further bending arm (3) is opposed to the direction of rotation of the first bending arm (2), and each of the two bending arms (2, 3) can be moved parallel to one another and perpendicular to the advancing direction of the tubes to be bent.
L'invention concerne un dispositif pour cintrer des tubes de grand diamètre dans différentes directions de cintrage. Dans ledit dispositif de cintrage, un tube (10) passe dans le sens axial à travers un moyen de chauffage (7) entourant en forme d'anneau ledit tube et agissant par induction ; à son extrémité (11) à cintrer, le tube (10) est immobilisé par un organe de serrage (4) ; au moins un bras de cintrage (2), qui est monté rotatif autour d'un axe de rotation vertical (8), est disposé dans la partie du dispositif de cintrage située dans la direction d'avance du tube (10) ; l'organe de serrage (4) est indirectement relié au bras de cintrage (2) et comporte, entre le moyen de réception des tubes et le bras de cintrage (2), un moyen de transmission de force relié de manière réglable au bras de cintrage (2), de telle sorte que les distances entre l'axe médian du moyen de réception des tubes et l'axe de rotation vertical (8) peuvent être sélectionnées entre une distance minimale et une distance maximale, de manière à pouvoir régler une plage s'étendant entre un rayon de cintrage maximal et un rayon de cintrage minimal (12). Le dispositif comporte au moins un autre organe de serrage (5) avec un autre bras de cintrage (3), un moyen de réception des tubes et un moyen de transmission de force pour transmettre des forces de cintrage du moyen de réception à l'autre bras de cintrage (3), le sens de rotation de l'autre bras de cintrage (3) étant opposé au sens de rotation du premier bras de cintrage (2), et chacun des deux bras de cintrage (2, 3) pouvant être déplacé parallèlement à l'autre bras et perpendiculairement à la direction d'avance des tubes à cintrer.
Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2024-08-01:As part of the Next Generation Patents (NGP) transition, the Canadian Patents Database (CPD) now contains a more detailed Event History, which replicates the Event Log of our new back-office solution.
Please note that "Inactive:" events refers to events no longer in use in our new back-office solution.
For a clearer understanding of the status of the application/patent presented on this page, the site Disclaimer , as well as the definitions for Patent , Event History , Maintenance Fee and Payment History should be consulted.
| Description | Date |
|---|---|
| Time Limit for Reversal Expired | 2017-04-26 |
| Application Not Reinstated by Deadline | 2017-04-26 |
| Inactive: Abandon-RFE+Late fee unpaid-Correspondence sent | 2016-04-26 |
| Deemed Abandoned - Failure to Respond to Maintenance Fee Notice | 2016-04-26 |
| Change of Address or Method of Correspondence Request Received | 2015-01-15 |
| Inactive: Notice - National entry - No RFE | 2013-01-25 |
| Inactive: Acknowledgment of national entry correction | 2013-01-18 |
| Inactive: Cover page published | 2013-01-08 |
| Application Received - PCT | 2012-12-20 |
| Inactive: Notice - National entry - No RFE | 2012-12-20 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2012-12-20 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2012-12-20 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2012-12-20 |
| Inactive: First IPC assigned | 2012-12-20 |
| National Entry Requirements Determined Compliant | 2012-11-05 |
| Application Published (Open to Public Inspection) | 2011-11-17 |
| Abandonment Date | Reason | Reinstatement Date |
|---|---|---|
| 2016-04-26 |
The last payment was received on 2015-03-30
Note : If the full payment has not been received on or before the date indicated, a further fee may be required which may be one of the following
Please refer to the CIPO Patent Fees web page to see all current fee amounts.
| Fee Type | Anniversary Year | Due Date | Paid Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic national fee - standard | 2012-11-05 | ||
| MF (application, 2nd anniv.) - standard | 02 | 2013-04-26 | 2013-04-11 |
| MF (application, 3rd anniv.) - standard | 03 | 2014-04-28 | 2014-04-24 |
| MF (application, 4th anniv.) - standard | 04 | 2015-04-27 | 2015-03-30 |
Note: Records showing the ownership history in alphabetical order.
| Current Owners on Record |
|---|
| AWS SCHAEFER TECHNOLOGIE GMBH |
| Past Owners on Record |
|---|
| AUGUST-WILHELM SCHAEFER |