Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02804518 2013-01-31
METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FABRICATING STRETCH FILM ROLLS
Field of the Invention
[0001] The present invention relates generally to stretch film and in
particular,
to a method and apparatus for fabricating stretch film rolls.
Background of the Invention
[0002] Stretch film is widely used for wrapping and securing pallet loads
for
shipping. This is due to the fact that stretch film exhibits a "memory", or a
tendency
to shrink, upon stretching. For example, stretch film that is stretched by an
amount of
10% will shrink nearly 10% of its stretched length. This "memory" assists in
securing
wrapped palletized articles together under compression.
[0003] Stretch film is fabricated in the form of stretch film rolls. Each
stretch
film roll may be used to manually wrap a pallet load, or may be loaded into an
automated wrapping machine.
[0004] An issue with conventional stretch film rolls is that the stretch
film
wound within the roll can become damaged if the stretch film roll is dropped
or
otherwise mishandled. For example, dropping the stretch film roll on its edge
can
result in tearing of the stretch film during wrapping of a pallet load.
[0005] One approach to avoiding such tearing involves folding the
longitudinal edges of the stretch film prior to winding, so as to provide a
stretch film
having reinforced longitudinal edges within the stretch film roll. Methods of
folding
the longitudinal edges of stretch film prior to winding have been described.
For
example, U.S. Patent No. 5,520,872 to Scherer discloses a strip of stretch-
wrap
material having flat, double thickness hems at opposite margins thereof The
hemmed
strip is formed on an apparatus including a first roller having a width less
than the
width of stock material, whereby opposite margins of the stock material
project
beyond opposite ends of the roller, and a second roller for guiding the strip
at an acute
angle from the first roller for causing opposite marginal portions to fold.
The strip is
maintained under tension by a take-up roller or other means, and guide bars
are
provided for further folding the marginal portions past 90 degree angles so
that they
continue to be folded inwardly against the main body of the strip.
CA 02804518 2013-01-31
- 2 -
[0006] Another approach to avoiding tearing involves oscillating the
stretch
film during winding, so as to prevent formation of hard edges within the
stretch film
roll. Methods of oscillating stretch film during winding have been described.
For
example, U.S. Patent No. 5,967,437 to Martin-Cocher et al. discloses a method
of
manufacturing rolls of pre-stretched film that comprises importing oscillation
to the
film with a component perpendicular to the film axis. During pre-stretching
and
winding of the film on a take-up roll, a feed roll, namely a spool from which
the
stretchable film for stretching is taken, is caused to oscillate, and/or the
take-up core is
caused to oscillate.
[0007] Improvements are generally desired. It is therefore an object at
least to
provide a novel method and apparatus for fabricating stretch film rolls.
Summary of the Invention
[0008] In one aspect, there is provided an apparatus for fabricating
stretch film
rolls, comprising: a plurality of cutting blades for cutting a stretch film
web into one
or more stretch film web sections, the plurality of cutting blades being
configured to
be oscillated; and a driven winding shaft for winding the one or more stretch
film web
sections.
[0009] Each stretch film web section may have non-linear longitudinal
edges.
[00010] Each stretch film web section may be wound onto a core supported
by
the winding shaft.
[00011] The plurality of cutting blades may be configured to be oscillated
along an axis that is generally orthogonal to a direction of travel of the
stretch film
web.
[00012] The plurality of cutting blades may be configured to be oscillated
over
a fixed distance. The plurality of cutting blades may be configured to be
oscillated
over a variable distance.
[00013] The plurality of cutting blades may be configured to be oscillated
at a
fixed frequency. The plurality of cutting blades may be configured to be
oscillated at
a variable frequency.
[00014] The apparatus may further comprise a roller positioned adjacent
the
winding shaft, a wound surface of the one or more stretch film web sections
being in
CA 02804518 2013-01-31
-3 -
contact with a surface of the roller. The roller may be configured as a driven
roller.
The roller may be configured as an idler roller.
[00015] In another aspect, there is provided a method for fabricating
stretch
film rolls, comprising: providing a stretch film web; cutting the stretch film
web using
a plurality of cutting blades into one or more stretch film web sections, the
plurality of
cutting blades being oscillated during the cutting; and winding the one or
more stretch
film web sections.
[00016] The cutting may further comprise forming non-linear longitudinal
edges within each stretch film web section.
[00017] The winding may further comprise winding each stretch film web
section onto a core.
[00018] The plurality of cutting blades may be configured to be oscillated
along an axis that is generally orthogonal to a direction of travel of the
stretch film
web.
[00019] The plurality of cutting blades may be configured to be oscillated
over
a fixed distance during the cutting. The plurality of cutting blades may be
configured
to be oscillated over a variable distance during the cutting.
[00020] The plurality of cutting blades may be configured to be oscillated
at a
fixed frequency during the cutting. The plurality of cutting blades may be
configured
to be oscillated at a variable frequency during the cutting.
[00021] In still another aspect, there is provided a method for cutting
stretch
film during fabrication of stretch film rolls, comprising: cutting a stretch
film web
using a plurality of cutting blades into one or more stretch film web
sections, the
plurality of cutting blades being oscillated during the cutting.
[00022] The cutting may further comprise forming non-linear longitudinal
edges within each stretch film web section.
[00023] The plurality of cutting blades may be configured to be oscillated
along an axis that is generally orthogonal to a direction of travel of the
stretch film
web.
CA 02804518 2013-01-31
- 4 -
Brief Description of the Drawings
[00024] Embodiments will now be described more fully with reference to the
accompanying drawings in which:
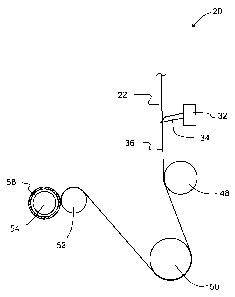
[00025] Figure 1 is a side view of a portion of an apparatus for
fabricating
stretch film rolls, during use;
[00026] Figure 2 is a schematic front view of a cutting station forming
part of
the apparatus of Figure 1, during use; and
[00027] Figure 3 is a side view of a stretch film roll fabricated using
the
apparatus of Figure 1.
Detailed Description of the Embodiments
[00028] Turning now to Figures 1 and 2, a portion of an apparatus for
fabricating stretch film rolls is shown, and is generally indicated by
reference numeral
20. Apparatus 20 comprises an extruder (not shown) that is configured to
dispense a
continuous sheet of plastic film onto a surface of a rotating cast roller (not
shown) so
as to form a stretch film web 22. Apparatus 20 also comprises a set of rollers
(not
shown) configured to receive the stretch film web 22 from the cast roller.
[00029] Apparatus 20 further comprises a cutting station 32 that is
positioned
downstream from the set of rollers. The cutting station 32 comprises a
plurality of
cutting blades 34 that are configured to cut, or "slit", the stretch film web
22 into a
plurality of stretch film web sections 36. At least one assembly (not shown)
is
provided for oscillating the cutting station 32, together with the cutting
blades 34,
along an oscillation axis that is generally orthogonal to the direction of
travel of the
stretch film web 22. In this embodiment, the cutting station 32 is oscillated
at a fixed
frequency and over a fixed distance along the oscillation axis. In this
embodiment,
the fixed frequency is a frequency in the range from 0 cycles per minute to
about 200
cycles per minute, and the fixed distance, and namely the distance travelled
during
one cycle, is a distance in the range from 0 inches to about 4 inches.
[00030] In the embodiment shown, apparatus 20 further comprises a first
intermediate roller 48 that is configured to receive the stretch film web
sections 36
downstream from the cutting station 32, and a second intermediate roller 50
that is
configured to receive the stretch film web sections 36 from the first
intermediate
CA 02804518 2013-01-31
- 5 -
roller 48. In this embodiment, the first intermediate roller 48 and the second
intermediate roller 50 are idler rollers.
[00031] Apparatus 20 further comprises a roller 52 that is configured to
receive
the stretch film web sections 36 from the second intermediate roller 50.
Apparatus 20
further comprises a winding shaft 54 positioned adjacent the roller 52 and
supporting
a plurality of cores 58. The winding shaft 54, with the cores 58 supported
thereon, is
configured to receive the stretch film web sections 36 from the roller 52 for
winding
each stretch film web section 36 onto a respective core 58, so as to form a
plurality of
stretch film rolls. An assembly (not shown) is provided for rotatably driving
the
winding shaft 54. The surface of the stretch film wound onto the cores 58 is
in
contact with the surface of the roller 52, so as to prevent entrapment of air
between
layers of the stretch film during winding. In this embodiment, the roller 52
is
configured as an idler roller.
[00032] During operation, the extruder dispenses a continuous sheet of
plastic
film onto the surface of the rotating cast roller to form the stretch film web
22, which
is then received by the set of rollers. From the set of rollers, the stretch
film web 22
travels downstream to the cutting station 32, where it is engaged by the
plurality of
cutting blades 34 and cut into a plurality of stretch film web sections 36.
The cutting
station 32 and the plurality of cutting blades 34 are being oscillated along
the
oscillation axis. As a result of this oscillation, each stretch film web
section 36 has
longitudinal edges 38 that are defined by cutting lines and that are generally
non-
linear along the length of the stretch film web section 36, as shown
schematically in
Figure 2.
[00033] Downstream from the cutting station 32, the stretch film web
sections
36 are received by the first intermediate roller 48, and in turn by the second
intermediate roller 50. From the intermediate roller 50, the stretch film web
sections
36 are received by the roller 52, and in turn by the winding shaft 54
supporting the
plurality of cores 58, at which each stretch film web section 36 is wound onto
a
respective core 58 so as to form a plurality of stretch film rolls.
[00034] A stretch film roll fabricated by the apparatus 20 is shown in
Figure 3,
and is generally indicated by reference numeral 62. Stretch film roll 62
comprises a
body 64 of stretch film wound onto core 58. The body 64 of stretch film has a
CA 02804518 2013-01-31
. .
,,
- 6 -
generally cylindrical central portion 66 and tapered end portions 68, with the
end
portions 68 being generally softer than the central portion 64. The
configuration of
the stretch film roll 62, and in particular the softness and the tapered shape
of the end
portions 68, results from the oscillation of the cutting blades 34 during
winding onto
the core 58. As will be understood, this oscillation causes the formation of
longitudinal edges 38 that are generally non-linear, which prevents direct
overlap of
the longitudinal edges 38 during winding, and thereby eliminates the formation
of
hard, right-angled corners within the wound film at ends of the roll that
would
otherwise form in absence of oscillation. As will be appreciated, the softness
and the
tapered shape of the end portions 68 advantageously increases the tolerance of
the
stretch film roll 62 to handling errors, such as dropping, which in turn
renders the
stretch film within the stretch film roll 62 less prone to tearing during use.
[00035] For example, although in the embodiment described
above, the cutting
station is oscillated at a fixed frequency, in other embodiments, the cutting
station
may alternatively be oscillated at a variable frequency, such as for example,
a
periodically variable frequency or a random frequency.
[00036] Although in the embodiment described above, the
cutting station is
oscillated over a fixed distance along the oscillation axis, in other
embodiments, the
cutting station may alternatively be oscillated over a variable distance along
the
oscillation axis, such as for example, a periodically variable distance or a
random
distance.
[00037] Although in the embodiment described above, the fixed
frequency is a
frequency in the range from 0 cycles per minute to about 200 cycles per
minute, in
other embodiments, the fixed frequency may alternatively be a frequency that
is
greater than 200 cycles per minute.
[00038] Although in the embodiment described above, the fixed
distance is a
distance in the range from 0 inches to about 4 inches, in other embodiments,
the fixed
frequency may alternatively be a distance that is greater than 4 inches.
[00039] Although in the embodiment described above, the
oscillation axis of
the cutting station and the cutting blades is generally orthogonal to the
direction of
travel of the stretch film web, in other embodiments, the oscillation axis of
the cutting
station and the cutting blades may alternatively be non-orthogonal to the
direction of
CA 02804518 2013-01-31
- 7 -
travel of the stretch film web, provided that each stretch film web section
has
longitudinal edges defined by cutting lines that are generally non-linear
along the
length of the stretch film web section.
[00040] Although in the embodiment described above, the first intermediate
roller and the second intermediate roller are configured as idler rollers, in
other
embodiments, one (1) or both of the first intermediate roller and the second
intermediate roller may alternatively be configured as a driven roller.
[00041] Although in the embodiment described above, the apparatus
comprises
a first intermediate roller and a second intermediate roller, in other
embodiments, the
apparatus may alternatively comprise fewer or more intermediate rollers. In
one
embodiment, the apparatus may alternatively comprise no intermediate rollers.
[00042] Although in the embodiment described above, the cutting station
comprises a plurality of cutting blades that are configured to cut the stretch
film web
into a plurality of stretch film web sections, in other embodiments, the
cutting station
may alternatively comprise two (2) cutting blades that are configured to cut
the stretch
film web into one (1) stretch film web section.
[00043] Although in the embodiment described above, the winding shaft
supports a plurality of cores, in other embodiments, the winding shaft may
alternatively support one (1) core.
[00044] Although in the embodiment described above, the roller adjacent
the
winding shaft is configured as an idler roller, in other embodiments, the
roller
adjacent the winding shaft may alternatively be configured as a driven roller.
In one
such embodiment, the surface speed of the driven roller may be matched to the
surface speed of the wound film on the winding shaft using automated or
computer-
controlled speed matching. In another such embodiment, there may be no
assembly
provided for rotatably driving the winding shaft, and the winding shaft may
alternatively be driven through contact with the surface of the driven roller.
[00045] Although in the embodiment described above, the apparatus
comprises
an extruder and a rotating cast roller for forming the stretch film web, in
other
embodiments, the apparatus may alternatively not comprise an extruder and a
cast
roller for forming the stretch film web, but may alternatively comprise means
for
supporting a supply (e.g. a spool, a roll, etc.) of already-formed stretch
film web, and
CA 02804518 2013-01-31
- 8 -
means for feeding the already-formed stretch film web from the supply to the
set of
rollers, or from the supply to the cutting station if no set of rollers is
provided.
[000461 Although in the embodiment described above, the surface of the
stretch
film wound onto the cores is in contact with the surface of the roller
adjacent the
winding shaft so as to prevent entrapment of air between layers of the stretch
film
during winding, in other embodiments, the winding shaft and any roller
adjacent
thereto may alternatively be configured to enable entrapment of air between
layers of
the stretch film during winding.
[000471 In other embodiments, the cutting station comprising the plurality
of
cutting blades, and the at least one assembly provided for oscillating the
cutting
station together with the cutting blades, may alternatively form part of
another
apparatus used for fabricating stretch film rolls.
[00048] Although embodiments have been described above with reference to
the accompanying drawings, those of skill in the art will appreciate that
variations and
modifications may be made without departing from the scope thereof as defined
by
the appended claims.