Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02822992 2013-08-01
PAPER CONVEYING APPARATUS IN A PRINTING MACHINE
Background of the Invention
Technical Field
[0001] The present invention relates to a paper conveying appa-
ratus for conveying continuous paper in a printing machine for pro-
cessing the continuous paper successively by from printing to ma-
chining such as punching or perforating.
Background Art
[0002] A printing machine for processing continuous paper succes-
sively by from printing to machining has hitherto been known which
is provided with a paper feed section for feeding continuous paper, a
printing section and a machining section in order in a path of con-
tinuous paper conveyance to perform printing, and machining of
various sort on the way of continuous paper conveyance.
In the printing machine, it is important that a proper
amount of tension be generated and imparted to continuous paper
and the tension be unvaried in the printing and machining sections,
to allow continuous paper to be conveyed in a stabilized state. The
conventional paper conveying apparatus as disclosed in JP H10 ¨
17186 A is equipped with a first feed roll unit at an outlet side of
the paper feed section, a second feed roll unit at an outlet side of
the printing section and a third feed roll unit at an outlet side of the
machining section, each having a feed rate (paper feed rate) set the
larger the more downstream it is; for example, if the feed rate of the
first feed roll unit is set at 100, the feed rate of the second feed roll
unit is set at 100.01 and the feed rate of the third feed roll unit is
set at 100.02, so that a proper amount of tension may be generated
and imparted to continuous paper over the entire path of paper con-
veyance, thereby stabilizing the conveyance of paper.
[0003] To wit, due to a long path of continuous paper conveyance, a
total conveyance resistance from the paper feed section to the ma-
chining section if it acts on continuous paper may break the contin-
uous paper. To prevent this, the apparatus is so configured that
¨1¨
CA 02822992 2013-08-01
with each of the first, second and third feed roll units constituted by
a rotating roll and a nip roll made in pressure contact with each
other, continuous paper after it is passed or fed through to each feed
roll unit is caught between the rotating and nip rolls whereupon
continuous paper between the first and second feed roll units has a
conveyance resistance imparted thereto that is based on a difference
in feed rate between them and continuous paper between the second
and third feed roll units has a conveyance resistance imparted
thereto that is based on a difference in feed rate between them,
thereby feeding continuous paper consecutively under respective
forces of conveyance of the feed roll units while preventing continu-
ous paper from undergoing a total conveyance resistance that may
be applied thereto from the paper feed section to the machining sec-
tion.
[0004] In such a paper conveying apparatus of the printing machine
in the prior art as mentioned above, it has been found to be still
possible that with continuous paper being passed or fed through
over the feed roll units when the printing machine starts to be
driven (viz, in the course of initial paper threading), the continuous
paper may be broken at a point on the way of conveyance.
To wit, with continuous paper from its leading end being
then fed or passed successively between the rotating and nip rolls in
pressure contact of the first, second and third feed roll units over
the entire printing machine (all the sections therein), the tension
imparted thereto is prone to be not uniform widthwise thereof (in a
direction transverse to the direction of paper conveyance) at a point
or points on the way of paper threading due to its meandering and
such and consequently be locally larger as generated, causing con-
tinuous paper to be broken.
[0005] If continuous paper is broken on the way of a paper thread-
ing operation in the course of initial paper threading as mentioned
above, the paper threading operation must be started again from the
position of break, giving rise to an unscheduled operating time and
thus lowering the efficiency of paper threading operation.
Especially in the case of printing and machining of continu-
- 2 -
I
CA 02822992 2013-08-01
ous paper that is thin and/or has a line of perforations, the contin-
uous paper is prone to break in the course of initial threading,
making it prone to develop problems of an increased burden of oper-
ation, being time-consuming and wastefulness of paper.
[0006] In view of problems as mentioned above, it is an object of
the present invention to provide a paper conveying apparatus in a
printing machine, which is capable of generating a proper amount of
tension and imparting it to continuous paper in the course of print-
ing and machining, conveying continuous paper as the tension is
held unvaried and stable in printing and machining sections, and
preventing or restraining continuous paper from being broken in the
course of initial paper threading.
Disclosure of the Invention
[0007] In accordance with the present invention in a first aspect
thereof a paper conveying apparatus in a printing machine which is
provided in a path of conveyance of continuous paper with a printing
section, a machining section, and a plurality of feed roll units for
conveying continuous paper by feeding it while it is being caught in
each of them, to successively print on and machine continuous paper
while in conveyance by the feed roll units, characterized in that the
paper conveying apparatus comprises:
a control means for individually controlling respective feed
rates of the feed roll units,
the control means having a printing mode and an initial pa-
per threading mode,
the control means when in the printing mode controlling the
respective feed rates of the feed roll units so that the feed rate of a
feed roll unit at a downstream side is larger than the feed rate of a
feed roll unit at a side upstream thereof so as to generate a proper
amount of tension and impart it to the continuous paper,
the control means when in the initial paper threading mode
controlling the respective feed rates of the feed roll units so that the
feed rate of the feed roll unit at the downstream side is smaller than
the feed rate of the feed roll unit at the side upstream thereof so as
-3--
CA 02822992 2013-08-01
not to generate tension to the continuous paper.
[0008] The present invention provides in an second aspect thereof a
paper conveying apparatus in a printing machine which is provided
in a path of conveyance of continuous paper with a printing section,
a machining section, and a plurality of feed roll units for conveying
continuous paper by feeding it while it is being caught in each of
them, to successively print on and machine continuous paper while
in conveyance by the feed roll units, characterized in that the paper
conveying apparatus comprises:
a control means for individually controlling respective feed
rates of the feed roll units,
the control means having a printing mode and an initial pa-
per threading mode,
the control means when in the printing mode controlling the
respective feed rates of the feed roll units so that the feed rate of a
feed roll unit at a downstream side is larger than the feed rate of a
feed roll unit at a side upstream thereof so as to generate a proper
amount of tension and impart it to the continuous paper,
the control means when in the initial paper threading mode
controlling the respective feed rates of the feed roll units so that the
feed rate of the feed roll unit at the upstream side is identical to the
feed rate of the feed roll unit at the side downstream thereof so as
not to generate tension to the continuous paper.
[0009] The present invention provides in a third aspect thereof a
paper conveying apparatus in a printing machine which is provided
in a path of conveyance of continuous paper with a printing section,
a machining section, and a plurality of feed roll units for conveying
continuous paper by feeding it while it is being caught in each of
them, to successively print on and machine continuous paper while
in conveyance by the feed roll units, characterized in that the paper
conveying apparatus comprises:
a control means for individually controlling respective feed
rates of the feed roll units,
the control means having a printing mode and an initial pa-
per threading mode,
-4-
CA 02822992 2013-08-01
the control means when in the printing mode controlling the
respective feed rates of the feed roll units so that the feed rate of a
feed roll unit at a downstream side is larger by a first rate increase
than the feed rate of a feed roll unit at a side downstream thereof so
as to generate a proper amount of tension and impart it to the con-
tinuous paper,
the control means when in the initial paper threading mode
controlling the respective feed rates of the feed roll units so that the
feed rate of the feed roll unit at the downstream side is larger than
the feed rate of the feed roll unit at the side upstream thereof by a
second rate increase smaller than the first rate increase so as to
generate a tension smaller than the tension to be generated in the
said printing mode to the continuous paper.
[0010] Specifically in the paper conveying apparatus in a printing
machine according to the present invention, each of the feed roll
unit means has a rotating roll and a nip roll between which contin-
uous paper is to be caught and to pass through while the rotating
roll is being rotated, thereby conveying the continuous paper, and
the control means is adapted to control a rotation rate of the
rotating roll of each of the feed roll units independently of those of
others to individually control a feed rate of each of the feed roll
units,
the rotation rate of the rotating roll of the feed roll unit at
the downstream side being controlled with reference to the rotation
rate of the rotating roll of the feed roll unit at the upstream side.
[0011] Consequently, it is ensured that continuous paper as it is
caught between a rotating roll and a nip roll can be fed and con-
veyed.
[0012] Specifically in the paper conveying apparatus in a printing
machine according to the present invention, the rotating roll of each
of the feed roll units is adapted to be rotated by an independent
motor,
the control means has the printing mode in which a rotating
roll has a rotation rate set to correspond to a feed rate set for
printing on and machining continuous paper and the initial paper
-5-
threading mode in which a rotating roll has a rotation rate set to
correspond to a feed rate set for initially feeding continuous paper
through the path,
a rotating roll is rotatable in the printing mode at the rota-
tion rate set for the printing mode, and
a rotating roll is rotatable in the initial paper threading mode
at the rotation rate set for the initial paper threading mode.
[0013] This facilitates controlling the respective feed rates of the
feed roll units.
[0014] According to the present invention in the first, second and
third aspects thereof in which when the control means is in the
printing mode, the feed rate of a feed roll unit at a downstream side is -
made larger than the feed rate of a feed roll unit at an upstream side,
generating a proper amount of tension and imparting it to continuous
paper in the course of printing and machining, it is possible to convey
continuous paper in a stabilized state under the tension that is
proper and held unvaried in the printing and machining sections.
According to the present invention in the first and second
aspects thereof whereby when the control means is in the initial
paper threading mode, tension is not generated to continuous paper,
it is ensured that continuous paper during the course of initial paper
threading can be prevented from being broken.
According to the present invention in the third aspect thereof
whereby a tension as generated and imparted to continuous paper
when the control means is in the initial paper threading mode is
made smaller than a tension to be generated and imparted to con-
tinuous paper when the control means is in the printing mode, it is
possible to restrain continuous paper in the course of initial paper
threading from being broken.
- 6 -
CA 2822992 2017-10-31
_
[0014a]According to another aspect of an embodiment, there is pro-
vided a paper conveying apparatus for conveying continuous paper in
a printing machine which is provided with a printing section, a ma-
chining section, and a plurality of feed roll units for conveying the
continuous paper by feeding the continuous paper in the printing
section and the machining section while the continuous paper is
caught in the feed roll units so as to successively print on and ma-
chine the continuous paper while in conveyance by the feed roll units,
wherein the paper conveying apparatus comprises: a control means
for individually controlling respective feed rates of the feed roll units,
the control means having a printing mode and an initial paper
threading mode, the control means when in the printing mode con-
trolling the respective feed rates of the feed roll units so that the feed
rate of a feed roll unit at a downstream side is larger than the feed
rate of a feed roll unit at a side upstream thereof so as to generate a
proper amount of tension and impart it to the continuous paper, the
control means when in the initial paper threading mode controlling
the respective feed rates of the feed roll units so that the feed rate of
the feed roll unit at the downstream side is smaller than the feed rate
of the feed roll unit at the side upstream thereof so as not to generate
tension to the continuous paper.
Accordingly, the frequency of needs for a wasteful repetitive
paper threading operation from a position of paper at which it may
otherwise be broken is diminished, reducing an operational burden,
avoiding waste of operating time and enhancing the efficiency of op-
erations.
- 6a "
CA 2822992 2017-10-31
CA 02822992 2013-08-01
And, improvements in the efficiency of operation heighten
the productivity. Lesser the broken paper becomes, the lesser the
loss of paper becomes, reducing the production cost.
Especially in the case of printing and machining thin paper
or paper formed with perforations, tremendous improvements can be
achieved in aspects of reducing occurrence of loss of paper and ren-
dering the preparatory operations efficient.
Brief Description of the Drawing
[0015 In the Drawing:
Fig. 1 is an explanatory view of a printing machine which
includes a first form of implementation of the paper conveying ap-
paratus of the present invention;
Fig. 2 is an explanatory view illustrating one control device
for the paper conveying apparatus; and
Fig. 3 is an explanatory view illustrating another control
device for the paper conveying apparatus.
Best Modes for Carrying Out the Invention
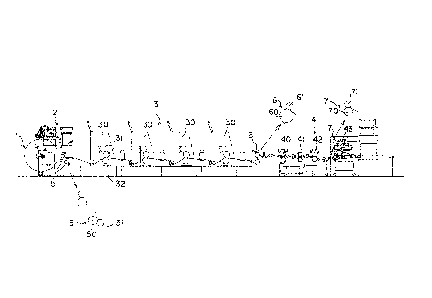
[0016] Fig. 1 illustrates one form of the printing machine which in-
cludes a paper feed section 2 for feeding continuous paper 1 into a
path of conveyance, a printing section 3 and a machining section 4
for processing continuous paper 1 successively by from printing to
machining.
The printing section 3 here has four printing units (printers)
30 with which continuous paper 1 is printed on in four colors.
Each of the printing units 30 has a printing cylinder 31 and
an impression cylinder 32, the printing and impression cylinders 31
and 32 being held in pressure contact with each other in printing on
continuous paper 1 and being spaced from each other when contin-
uous paper 1 is passed or fed through the machine before printing
and machining.
The machining section 4 may comprise a punching unit 40
for punching a hole in continuous paper 1, a longitudinal perforator
41 for forming a series of longitudinal perforations in continuous
¨7¨
CA 02822992 2013-08-01
paper 1 and a transverse perforator 42 for forming a series of
transverse perforations in continuous paper 1, and further a folding
unit (folding machine) 43 for folding continuous paper 1.
The printing machine should not be limited to that described
above. For example, the printing section 3 may comprise three
printing units 30, the machining section 4 may not include the fold-
ing unit 43, and such.
[0017] The printing and impression cylinders 31 and 32 of each
printing unit 30, the punching unit 40, the longitudinal perforator
41, the transverse perforator 42 and the folding unit 43 are syn-
chronously driven and controlled. For example, they may be syn-
chronously driven and controlled by a main motor M as shown in Fig.
2.
[0018] Next, mention is made of a first form of implementation of
the paper conveying apparatus of the present invention.
The paper feed section 2 is provided at its feed-out or outlet
side with a first feed roll unit 5 with which continuous paper 1 is
fed and conveyed towards the printing section 3.
The printing section 3 is provided at its outlet side with a
second feed roll unit 6 with which continuous paper 1 is fed and
conveyed towards the machining section 4.
The machining section 4 is provided midway of the path of
paper conveyance between the transverse perforator 42 and the
folding unit 43 with a third feed roll unit 7 with which continuous
paper 1 is fed and conveyed towards the folding unit 43.
[0019] The first feed roll unit 5 has a rotating roll 50 and a nip roll
51 between which continuous paper 1 is caught and with which it is
fed and conveyed.
The second, third feed roll 6, 7 likewise has a rotating roll
60, 70 and a nip roll, 61, 71 between which continuous paper 1 is
caught and with which it is fed and conveyed.
The first, second and third feed roll units 5, 6 and 7 so ar-
ranged ensures that continuous paper 1 can be fed and conveyed.
[0020] The first, second and third feed roll units 5, 6 and 7 are de-
signed to be driven and controlled independently from each other so
¨8¨
CA 02822992 2013-08-01
that the distances of conveyance of continuous paper 1 that are fed
and conveyed by them per unit time, viz, their feed rates, may each
be controlled individually.
For example, a first, a second and a third motor Ml, M2 and
M3 that can be driven and controlled independently of each other
may be provided and connected as shown in Fig. 2 to directly rotate
the rotating roll 50 of the first feed roll unit 5, to directly rotate the
rotating roll 60 of the second feed roll unit 6 and to directly rotate
the rotating roll 70 of the third feed roll unit 7, respectively, per-
mitting the rotating rolls 50, 60 and 70 to rotate at different rota-
tion rates and thereby the feed rates of the first, second and third
feed roll units 5, 6 and 7 to be individually controlled.
Individually controlling the respective rotating rolls 50, 60
and 70 with the first, second and third motors Ml, M2 and M3 which
are independent of each other facilitates controlling the feed rates
of the first, second and third feed roll units 5, 6 and 7.
[0021] The first, second and third motors Ml, M2 and M3 are driven
each in synchronism with a rotation signal to the main motor M.
For example, with a drive mode selection signal entered from
an operating unit 8 into a control unit 9 as shown in Fig. 2, the con-
trol unit 9 acts to furnish the main motor M and the first, second
and third motors Ml, M2 and M3 with rotation drive control signals,
respectively, to synchronously rotate them.
[0022] The first, second and third feed roll units 5, 6 and 7 are ro-
tation-drive controlled in a mode of printing when printing and ma-
chining are performed and in a mode of initial paper threading when
continuous paper from its leading end is initially passed or fed
through.
In the printing mode, the first, second and third feed roll
units 5, 6 and 7 have their feed rates controlled to increase in the
order of their positions from upstream towards downstream.
For example, with the feed rate of the first feed roll unit 5
set at 100, the feed rate of the second feed roll 6 is set at 100.01 and
the feed rate of the third feed roll unit 7 is set at 100.02. The ten-
sion of continuous paper 1 between the first and second roll units 5
-9-
CA 02822992 2013-08-01
and 6 (in the printing section 3) is set at a magnitude that corre-
sponds to a difference (0.01) between the feed rate (100) of the first
feed roll unit 5 and the feed rate (100.01) of the second feed roll unit
6. And, the tension of continuous paper 1 between the second and
third roll units 6 and 7 is set at a magnitude that corresponds to a
difference (0.01) between the feed rate (100.01) of the first feed roll
unit 6 and the feed rate (100.02) of the third feed roll unit 7.
[0023] This allows generating a proper amount of tension and im-
parting it to continuous paper over the entire path of paper convey-
ance and developing a state of printing operation in which continu-
ous paper 1 can be conveyed stably while the tension is held unvar-
ied in the printing and machining sections 3 and 4.
[0024] In the initial paper threading mode, the first, second and
third feed roll units 5, 6 and 7 have their feed rates controlled to
decrease in the order of their positions from upstream towards
downstream.
For example, if the feed rate of the first feel roll unit 5 is set
at 100, the feed rate of the second feed roll unit 6 is set at 99.99 and
the feed rate of the third feed roll unit 7 is set at 99.98 whereby no
tension is generated to continuous paper between the first and se-
cond feed roll units 5 and 6 and to continuous paper between the
second and third feed roll units 6 and 7, with only a force of feed or
conveyance applied to continuous paper for its conveyance.
To wit, the feed rates of the first, second and third feed roll
units 5, 6 and 7 are set at values such that while a force of feed is
applied to continuous paper 1 for paper conveyance, no tension
thereto is created over the entire path of paper conveyance.
[0025] This ensures that when continuous paper from its leading
end is initially passed or fed through along the path of paper con-
veyance, or through the machine, the continuous paper is prevented
from being broken due to its meandering in the sections on the way
of the path of paper conveyance.
[0026] A form of implementation of controlling the feed rates of the
first, second and third feed roll units 5, 6 and 7 is configured so that
the control unit 9 is provided with the printing mode 9a and the ii-
-10¨
CA 02822992 2013-08-01
tial paper threading mode 9b as shown in Fig. 2 and that the control
unit 9 in response to an initial paper threading signal may select
the initial paper threading mode 9b and in response to a printing
signal may select the printing mode 9a.
And, when the initial paper threading mode 9b is selected,
the first, second and third motors Ml, M2 and M3 are
drive-controlled so as to rotate at pre-established rotation rates for
the respective rotating rolls 50, 60 and 70 to rotate at rotation rates
such as to yield the preset feed rates (100, 99.99 and 99.98).
To wit, with the rotation rate of a rotating roll at an up-
stream side taken as a reference, the rotation rate of a rotating roll
at its downstream side is controlled.
[0027] When the printing mode 9a is selected on the other hand, the
first, second and third motors Ml, M2 and M3 are drive-controlled
so as to rotate at pre-established rotation rates for printing for the
respective rotating rolls 50, 60 and 70 to rotate at rotation rates
such as to yield the preset feed rates (100, 100.01 and 100.02).
To wit, with the rotation rate of a rotating roll at an up-
stream side taken as a reference, the rotation rate of a rotating roll
at its downstream side is controlled.
[0028] For example, with an initial paper threading signal entered
from the operating unit 8 into the control unit 9, let the initial pa-
per threading mode 9b be selected.
And, upon visually confirming that continuous paper 1 has
been passed or fed up to the most downstream of the machining sec-
tion 4, let a printing signal be entered from the operating unit 8 in-
to the control unit 9 to switch to the printing mode 9a. Alternatively,
a sensor upon detecting that continuous paper 1 has been passed or
fed up to the most downstream of the machining section 4 may issue
a signal of the detection that is entered as a printing signal into the
control unit 9.
[0029] Switching from the initial paper threading mode 9b to the
printing mode 9a after the initial paper threading in this manner
facilitates shifting to a state of printing operation that the proper
amount of tension to continuous paper is being generated.
¨11¨
CA 02822992 2013-08-01
[0030] While in the form of implementation mentioned above, the
rotating rolls 50, 60 and 70 of the first, second and third feed roll
units 5, 6 and 7 are drive-controlled by the independent first, second
and third motors Ml, M2 and M3, respectively, to individually con-
trol the feed rates, it should be noted that this is not a limitation of
the present invention.
For example, the main motor M may as shown in Fig. 3 be
connected to the rotating rolls 50, 60 and 70 via differential mecha-
nisms 80 which may be controlled to control rotation rates of the
rotating rolls 50, 60 and 70, thereby individually controlling the
feed rates of the first, second and third feed roll units 5, 6 and 7.
The differential mechanism 80 may comprise a differential
device 81 such as a planet gear or a harmonic drive mechanism and
a motor 82 where the motor 82 is rotation-controlled so that they
may develop differences in rotation rate between the main motor M
and the rotating rolls 50, 60 and 70.
[00311 In this case, by controlling the rotation of the motor 81 de-
pending on the printing mode 9a and the initial paper threading
mode 9b, the feed rates of the first, second and third feed roll units
5, 6 and 7 are individually controlled as mentioned above.
[0032] Next, mention is made of a second form of implementation of
the present invention.
In this form of implementation, the printing machine is like
that shown in Fig. 1, the paper conveyance control apparatus for the
printing machine is like that shown in Fig. 2 or 3, and the control
operation performed by the control unit 9 upon selection of the
printing mode 9a is like as mentioned above but the control opera-
tion by the control unit 9 upon selection of the initial paper thread-
ing mode 9b is performed differently from that mentioned above.
To wit, when the initial paper threading mode 9b is selected,
the feed rates of the first, second and third feed roll units 5, 6 and 7
are made identical to each other so that no tension to continuous
paper 1 may be generated.
For example, by driving the first, second and third motors
Ml, M2 and M3 to rotate at an identical rotation rate and in turn to
-12-
CA 02822992 2013-08-01
rotate the rotating rolls 50, 60 and 70 at an identical rotation rate,
the feed rates of the first, second and third feed roll units 5, 6 and 7
are made identical to each other.
[0033] Next, mention is made of a third form of implementation of
the present invention.
In this form of implementation, the printing machine, the
paper conveyance control apparatus and the control operation per-
formed upon selection of the printing mode are like those in the first
form of implementation mentioned above, but the control operation
upon selection of the initial paper threading mode is performed dif-
ferently from that in the abovementioned first form of implementa-
tion.
To wit, it is set that when the initial paper threading mode
9b is selected, the feed rates of the first, second and third feed roll
units 5, 6 and 7 are increased in the order of their positions from
upstream towards downstream by an increase or increases of feed
rate which are smaller than that or those when the printing mode
9a is selected so that a tension generated to continuous paper is
smaller anywhere than the tension when the printing mode 9a is
selected.
[0034] For example, let it be assumed that when the printing mode
9a is selected, the rotation rate of the first motor MI. is VI., the ro-
tation rate of the second motor M2 is V2 (where Vi < V2), and the
rotation rate of the third motor M3 is V3 (where V2 < V3); and the
feed rate of the first feed roll unit 5 is Li, the feed rate of the se-
cond feed roll unit 6 is L2 (where Li < L2) and the feed rate of the
third feed roll unit 7 is L3 (where L2 < L3). When the initial paper
threading mode 9b is selected, it is set that the rotation rate of the
first motor MI. is V4 (where V4 = VI.), the rotation rate of the second
motor M2 is V5 (where V5 < V2) and the rotation rate of the third
motor M3 is V6 (where V6 < V3); and the feed rate of the first feed
roll unit 5 is L4 (where L4 = Li), the feed rate of the second feed
roll unit 6 is L5 where L5 < L2) and the feed rate of the third feed
roll unit 7 is L6 (where L6 < L3) wherein increases of feed rate (L5 ¨
L4) and (L6 ¨ L5) are smaller than increases of feed rate (L2 ¨ Li)
¨ 13¨
CA 02822992 2013-08-01
and (L3 ¨ L2), respectively, when the printing mode 9a is selected.
[0035] Consequently, it follows that a tension generated and im-
parted to continuous paper between the first feed roll unit 5 and the
second feed roll unit 6 and a tension generated and imparted to con-
tinuous paper between the second feed roll unit 6 and the third feed
roll unit 7 while the continuous paper is initially passed or fed
through the path are made smaller than the tension while the con-
tinuous paper is in the course of printing and machining.
Accordingly, it is ensured that continuous paper in the
course of initial paper threading can be prevented or restrained
from breaking due to a small magnitude of tension thereto as caused
by occurrence of its meandering and such in a section on the way of
its conveyance.
[0036] While in the forms of implementation described above, the
feed roll units are shown provided at three places, they may be pro-
vided at four places. The tension generated and imparted to contin-
uous paper 1 is determined by a value of difference of the feed rates
of adjacent feed roll units. As in the first, second and third forms of
implementation, the feed rates of the feed roll units can be variably
set so that in the course of printing and machining a proper amount
of tension may be generated over the entire path of conveyance to
convey continuous paper stably and in the course of initial paper
threading the continuous paper may be prevented from breaking or
restrained from breaking to reduce the frequency of paper breaks.
-14-