Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
81775406
DEAD FRONT CABLE TERMINAL WITH ISOLATED SHIELD
TECHNICAL FIELD
This invention relates to a dead front cable terminal having an isolated
shield.
The terminal is suitable for cross bonding.
BACKGROUND
A dead front cable termination system typically includes a cable terminated
with a metallic lug (i.e., cable connector), the cable connector and end
portion of the cable
being inserted into the housing of a connecting device, the cable connector
being connected to
a mating device within the confines of the housing. The housing needs to form
a tight seal
around the end portion of the cable to prevent contamination or corrosion of
the connection.
Long distribution underground cable circuits such as those used in wind farm
power collection systems are subject to charge build up in the cable metallic
shield layer on
the cables. The charge build up can become so substantial that the cable has
to be de-rated
(i.e., operated at less than optimum) due to the heat generated by the ground
current through
the metallic shield layer. I-Teat is a contributing factor in cable
degradation.
SUMMARY
At least one embodiment of the present invention seeks to address the issue of
charge build up by employing dead front terminal connectors that can be cross
bonded.
At least one embodiment of the present invention provides an article suitable
for cross bonding or shield isolation comprising a first dead front terminal
comprising a first
connecting device comprising a first housing having an outer semi-conductive
layer and a first
chamber defined by at least one wall wherein the outer semi-conductive layer
comprises a
portion of at least one wall of the first chamber, a first cable assembly
having an exposed
cable insulation shield layer and an exposed cable metallic ground layer, at
least a portion of
the first cable assembly positioned within the first chamber of the first
connecting device,
1
CA 2835889 2018-08-02
=
81775406
wherein the cable insulation shield layer and the cable metallic ground layer
are electrically
insulated, and isolated in an embodiment, from the outer semi-conductive layer
of the
connecting device, and wherein the cable metallic ground layer is electrically
connected to a
first external conductor. One or both of the cable insulation shield and the
cable metallic
ground may be located in the first chamber of the connecting device housing.
At least one embodiment of the present invention provides a system
comprising: nine sections of cable, each having first and second ends, a
first, a second, and a
third cable section each having a second end comprising a cable assembly; a
fourth, a fifth,
and a sixth cable section each having first and second ends comprising a cable
assembly; and
a seventh, an eighth, and a ninth cable section each having a first end
comprising a cable
assembly; twelve connecting devices each comprising a first housing having an
outer semi-
conductive layer and a first chamber defined by at least one wall wherein the
outer semi-
conductive layer comprises a portion of at least one wall of the first
chamber; at least a portion
of each cable assembly residing in a first chamber of a housing of a
connecting device, each
.. cable assembly having an exposed cable insulation shield layer and cable
metallic ground
layer, each cable insulation shield layer and cable metallic ground layer
being electrically
insulated, and isolated in an embodiment, from the outer semi-conductor layer
of the
connecting device; wherein the cable metallic ground layer on the second end
of the first cable
section is electrically connected to the cable metallic ground layer on the
first end of the
fourth cable section; the cable metallic ground layer on the second end of the
second cable
section is electrically connected to the cable metallic ground layer on the
first end of the fifth
cable section; the cable metallic ground layer on the second end of the third
cable section is
electrically connected to the cable metallic ground layer on the first end of
the sixth cable
section; the cable metallic ground layer on the second end of the fourth cable
section is
electrically connected to the cable metallic ground layer on the first end of
the seventh cable
section; the cable metallic ground layer on the second end of the fifth cable
section is
electrically connected to the cable metallic ground layer on the first end of
the eighth cable
section; the cable metallic ground layer on the second end of the sixth cable
section is
electrically connected to the cable metallic ground layer on the first end of
the ninth cable
2
CA 2835889 2018-08-02
81775406
section; wherein the first, fourth, and seventh cable sections are in
different voltage phases of
a three-phase power system, the second, fifth, and eighth cable sections are
in different
voltage phases of a three-phase power system, and the third, sixth, and ninth
cable section are
in different voltage phases of a three-phase power system.
At least one embodiment of the present invention provides a kit for installing
a
dead front cable terminal suitable for cross bonding or shield isolation on a
cable assembly
having an exposed cable shield layer and cable metallic ground layer, the kit
comprising:
a connecting device comprising a housing having an outer semi-conductive
layer and a first chamber defined by at least one wall wherein the outer semi-
conductive layer comprises a portion of at least one wall of the first
chamber; and a
device for electrically insulating, and isolating in an embodiment, one or
both of the
cable insulation shield and the cable metallic ground layer of the cable
assembly from
the outer semi-conductor layer of the connecting device.
2a
CA 2835889 2018-08-02
CA 02835889 2013-11-12
WO 2012/162076 PCT/US2012/038274
At least one embodiment of the present invention provides an article suitable
for cross
bonding comprising: a first dead front terminal comprising a housing having a
first chamber
wherein the walls of the first chamber comprise at least one semi-conductive
layer, a first
cable assembly having a cable insulation shield layer and the cable metallic
ground layer in
the first chamber of the housing, wherein the cable insulation shield layer
and the cable
metallic ground layer are exposed, and wherein the cable insulation shield
layer and the cable
metallic ground layer are electrically insulated from the at least one semi-
conductor layer of
the dead front terminal and are electrically connected to a first external
conductor that
extends outside of the housing.
The above summary of the present invention is not intended to describe each
disclosed embodiment or every implementation of the present invention. The
Figures and
detailed description that follow below more particularly exemplify
illustrative embodiments.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS
Fig. 1 depicts a partial cross-section of an example of a cable assembly of at
least one
embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 2 depicts a cross-section of a connecting device of at least one
embodiment of the
present invention.
Fig. 3 depicts a partial cross-section of a connecting device of at least one
embodiment of the
present invention with a removable support core loaded in the connecting
device.
Figs. 4A-4C depict partial cross-sections of embodiments of dead front
terminals of the
present invention.
Figs. 5 to 8 depict steps in a process of preparing a dead front terminal
according to at least
one embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 9 depicts prior art cross bonded splices.
Fig. 10 depicts a system of cross bonded dead front terminals according to at
least one
embodiment of the present invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
In the following detailed description of the preferred embodiments, reference
is made
to the accompanying drawings that form a part hereof. The accompanying
drawings show,
by way of illustration, specific embodiments in which the invention may be
practiced. It is to
be understood that other embodiments may be used, and structural or logical
changes may be
made without departing from the scope of the present invention. The following
detailed
3
CA 02835889 2013-11-12
WO 2012/162076 PCT/US2012/038274
description, therefore, is not to be taken in a limiting sense, and the scope
of the invention is
defined by the appended claims.
Unless otherwise indicated, all numbers expressing feature sizes, amounts, and
physical properties used in the specification and claims are to be understood
as being
modified in all instances by the term "about." Accordingly, unless indicated
to the contrary,
the numerical parameters set forth in the foregoing specification and attached
claims are
approximations that can vary depending upon the desired properties sought to
be obtained by
those skilled in the art utilizing the teachings disclosed herein. The use of
numerical ranges
by endpoints includes all numbers within that range (e.g. 1 to 5 includes 1,
1.5, 2, 2.75, 3,
3.80, 4, and 5) and any range within that range.
In addition, directional terminology, such as "top," "bottom," "front,"
"back,"
"above," "below," etc., is used with reference to the orientation of the
Figure(s) being
described. Because components of embodiments can be positioned in a number of
different
orientations, the directional terminology is used for purposes of illustration
and is in no way
limiting. In general similar reference numbers are used for similar features
in the various
embodiments. Unless indicated otherwise, these similar features may comprise
the same
materials, have the same attributes, and serve the same or similar functions.
Additional or
optional features described for one embodiment may also be additional or
optional features
for other embodiments, even if not explicitly stated, where appropriate.
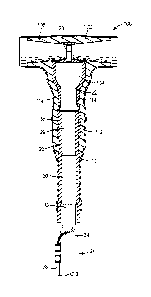
Fig. 1 shows a power cable assembly 20 of the present invention which includes
cable
connector 22 (having aperture 23) attached to a cable 24. Cable 24 includes
cable conductor
26 concentrically surrounded by cable insulation 28, cable insulation shield
30 (typically a
conductive polymer), cable metallic ground 32 (which are shown as conductive
wires, but
may also be equally suitable materials such as conductive tape or solid metal
conductors),
and cable jacket 34. To form cable assembly 20, each of the cable insulation
28, cable
insulation shield 30, cable metallic ground 32, and cable jacket 34 are
stripped back from an
end of cable 24 to expose a portion of the underlying layer, down to cable
conductor 26.
Cable connector 22 is then attached to the exposed portion of cable conductor
26 by any
suitable means, typically by crimping. In the embodiment of Fig. 1, cable
metallic ground
layer 32 comprises metal wires that are folded back, gathered, and attached to
a small
connector, which in turn is attached to an external conductor 38 (a separate
cable). In the
embodiment of Fig. 1, insulating sleeve 36 is applied to cable assembly 20 to
insulate cable
insulation shield 30 and cable metallic ground 32 from the outer semi-
conductor layer of a
connecting device 100 (shown in Fig. 2) when cable assembly 20 is inserted
into connecting
4
CA 02835889 2013-11-12
WO 2012/162076 PCT/US2012/038274
device 100. In the embodiment of Fig. 1, insulating sleeve 36 extends from the
top of cable
insulation layer 28 to, and over, a portion of cable jacket 34. External
conductor 38, and,
optionally, portions of the wires of cable metallic ground 32 extend beyond
the edge of
insulating sleeve 36.
Insulating sleeve 36 may be made from any suitable material. It may comprise
elastomeric material and may further be a cold-shrink sleeve. If it is a cold
shrink sleeve, it
may be made from any material suitable for cold-shrink applications. Most
suitable are
materials such as highly elastic rubber materials that have low permanent
sets, such as
ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), elastomeric silicone, or hybrids
thereof. Any
suitable device that can electrically insulate cable assembly 20 from the semi-
conductive
layers of connecting device 100 may be used in place of insulating sleeve 36.
The connecting device of the present invention may be any connector that is
suited for
use in a dead front terminal, that can accommodate a cable assembly with an
isolated shield,
and that is suitable for cross bonding as described herein. Fig. 2 shows
connecting device
100 which includes housing 102 that generally defines first chamber 104 and
second chamber
106. First chamber 104 and second chamber 106 intersect such that the interior
of first
chamber 104 is in communication with the interior of second chamber 106. First
and second
chambers 104, 106 may intersect to form a general T-shape as shown in Fig. 2
or a general L-
shape (not shown). Housing 102 further includes an outer semi-conductive layer
110, an
intermediate insulating layer 112, and an inner semi-conductive layer 114. A
portion of each
of these layers partially forms the interior wall of first chamber 104.
Housing 102 may be made from any material suitable for cold-shrink
applications.
Most suitable are materials such as highly elastic rubber materials that have
a low permanent
set, such as ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), elastomeric silicone, or
hybrids
thereof. The semi-conductive and insulating materials may be made of the same
or different
types of materials. The semi-conductive and insulating materials may have
differing degrees
of conductivity and insulation based on the inherent properties of the
materials used or based
on additives added to the materials.
To enable cable assembly 20 to be inserted into first chamber 104 of
connecting
device 100, a removable support core 200 may be first loaded into first
chamber 104, as
illustrated in Fig. 3. Once loaded, removable support core 200 typically
extends from the end
of the upper portion of first chamber 104 nearest second chamber 106 to beyond
open end
109 of first chamber 104 through which cable assembly 20 is inserted. When
loaded into first
chamber 104, removable support core 200 radially expands first chamber 104 to
an inner
5
CA 02835889 2013-11-12
WO 2012/162076 PCT/US2012/038274
diameter greater than the outer diameter of the largest portion of cable
assembly 20 that will
be inserted into first chamber 104.
Removable support core 200 may be made of any suitable material and in any
suitable
configuration, but typically consists of an extruded nylon or propylene ribbon
that is helically
wound. Removable support core 200 may be removed from first chamber 104 by
being
unraveled. It is unraveled by pulling on a tab (not shown) extending from one
end of the
removable support core 200 and causing separation of the core along a helical
score line or
joint. Preferably, removable support core 200 is unraveled starting with the
end in the upper
portion of first chamber 104 nearest the second chamber 106 and ending with
the end that
extends beyond the open end 109 of first chamber 104. Unraveling removable
support core
200 in this manner prevents the open end 109 of first chamber 104 from
prematurely
collapsing and obstructing the removal of removable support core 200.
Once the removable support core has been loaded into the first chamber 104,
cable
assembly 20 may be inserted into first chamber 104. Typically, cable connector
22 will
include an aperture 23 at its free end. The free end is positioned in the
intersection of the first
and second chambers, 104, 106 with the remainder of the cable connector
residing in first
chamber 104. Once the cable assembly is correctly positioned, a mating device
is inserted
and holds the cable in place. Removable support core 200 may then be removed
as described
above to cause first chamber 104 to contract and form a tight seal around
cable assembly 20.
In the embodiment of Fig. 4A, when the dead front terminal is assembled, the
portion
of inner semi-conducting layer 114 comprising the interior wall of the first
chamber 104 of
the housing 102 makes intimate contact with the cable connector 22 of cable
assembly 20. A
second portion of the interior wall of first chamber 104 comprises
intermediate insulating
layer 112 and a third portion of the interior wall of first chamber 104
comprises outer semi-
conducting layer 110. To accomplish shield isolation and cross bonding, the
third portion of
the inner wall is prevented from making electrical contact with cable
insulation shield 30 and
with cable metallic ground layer 32. In the embodiment of Fig. 4A, this
electrical contact is
prevented by insulating sleeve 36. The portion of the interior wall of first
chamber 104
comprising outer semi-conducting layer 110 preferably makes intimate contact
with a portion
of insulating sleeve 36 to prevent contaminants and/or moisture from entering
the first
chamber 104. An external conductor 38 is electrically connected to cable
metallic ground
layer 32 so cable metallic ground layer 32, can be cross bonded to the cable
metallic ground
layer 32 of another cable in a second dead front terminal.
6
CA 02835889 2013-11-12
WO 2012/162076 PCT/US2012/038274
To create the device of Fig. 4A, the layers of cable 24 are first removed
generally as
shown in Fig. 1 (and Fig. 4A) so that a portion of each layer is exposed. The
wires of the
cable metallic ground layer 32 are pulled back and connected to the external
conductor 38
with, e.g., a crimp connector. Then insulating sleeve 36 is placed over the
exposed portions
of the cable (except the cable conductor layer 26). In this embodiment, the
insulating sleeve
36 extends from the end of the cable insulation 28 adjacent the conductor 26
all the way to
the cable jacket 34. It covers a portion of the cable jacket, metallic ground
layer 32, and
cable shield 30 to insulate the cable shield 30 and cable metallic ground 32
from outer semi-
conductive layer 110 of connecting device 100.
Fig. 4B shows an alternate embodiment of a dead front terminal of the present
invention. In the embodiment of Fig. 4B, open end 109 of first chamber 104,
which is
formed by outer semi-conductive layer 110, is located adjacent cable
insulation shield 30 of
cable 24 when the dead front temlinal is assembled. Insulating sleeve 36 is
configured to
extend beyond open end 109 of first chamber 104 such that it covers more of
cable insulation
shield layer 30 than does semi-conductive layer 110, but is configured such
that it does not
cover cable metallic ground layer 32 or cable jacket 34. Cable metallic ground
layer 32 may
subsequently be covered by a protective layer, such as tape or an elastomeric
sleeve, to
prevent contact with contaminants and/or moisture.
Fig. 4C shows yet another alternate embodiment of a dead front terminal of the
present invention. The embodiment of 4C is similar to that of 4A except that
insulating
sleeve 36 does not extend from the top of cable insulation layer 28 to, and
over, a portion of
cable jacket 34. Instead, it extends from an intermediate portion of cable
insulation layer 28
to and over, a portion of cable jacket 34.
As can be seen from the embodiments of Figs. 4A-4C, the means by which cable
insulation shield 30 and cable metallic ground 32 arc electrically insulated
from the portion of
first chamber 104 comprising outer semi-conductive layer 110 can be any
suitable means
such as, e.g., tape, mastic, a rigid tube, a crushable tube, a flexible tube,
physical distance,
etc. Cable insulation shield 30 and cable metallic ground 32 may be insulated
by the same or
different insulating means, which means may comprise one or more parts or
sections. Any
suitable combination of insulating means may be used so long as both cable
insulation shield
30 and cable metallic ground layer 32 are adequately electrically insulated
from outer semi-
conductive layer 110.
Figs. 5 to 8 show a more detailed process by which a dead front terminal of
the
present invention is prepared for cross bonding. Fig. 5 shows the connecting
device 100
7
CA 02835889 2013-11-12
WO 2012/162076 PCT/US2012/038274
installed on the cable assembly 20 with an optional mastic ring 120 to create
an
environmental seal once the optional environmental sealing tube (Fig. 7) is
applied. Fig. 6
shows external cable 38 covered by an optional layer of tape 37 and a ground
wire 122 being
attached to the outer semi-conductive layer 110 of the connecting device 100
by tape 39. Fig.
7 shows the application of an optional environmental sealing tube 124, which
is a cold shrink
tube in this case. The optional environmental sealing tube 124 covers a
portion of connecting
device 100, the previously exposed portion of insulating sleeve 36, part of
external connector
38, and part of cable jacket 34. Fig. 8 shows the fully prepared terminal.
External conductor
38 extends from the lower end of environmental sealing tube 124 and ground
wire 122
extends from the upper end (closest to cable connector 22) of environmental
sealing tube 124.
Prior to the present invention, only cross bonding of splices was known.
Typically,
splice cross bonding is done with three equal length sections of cable having
cable metallic
ground layers in different voltage phases wherein the cable sections are
interrupted at one or
more points by a splice connector. When cross bonding is done with splices, it
typically
consists of connecting the metallic ground layer of a cable coming into one
splice connector
to the metallic ground layer of a cable exiting a different splice connector
wherein the
metallic ground layers are in different voltage phases. This is illustrated in
more detail in Fig.
9 in which the metallic ground layer on the first section (to the left of each
splice) of cable A
is connected to the metallic ground layer on the second section (to the right
of each splice) of
cable B; the cable metallic ground layer on the first section of cable B is
connected to the
cable metallic ground layer on the second section of cable C; and the cable
metallic ground
layer on the first section of cable C is connected to the cable metallic
ground layer on the
second section of cable A.
Fig 9 illustrates two sets of cross bonded splices installed along the entire
cable length
in order to create three equal smaller lengths of cables that are required to
complete the phase
shift canceling of the ground currents in the cable metallic ground layers
along the entire
length of cable. These two sets of splices are installed to create 3 equal
lengths of cable so
that the magnitude of the ground currents created in each section are equal
which allows for
phase cancelling when the metallic ground layers of the cables are cross
bonded.
Instead of cable splice connectors, the present invention relates to cross
bonding dead
front cable terminals. For example, as shown in Fig. 10, nine sections of
cable are provided,
1A, 1B, 1C, 2A, 2B, 2C, 3A, 3B, and 3C. Each cable section is terminated at
both ends by a
connecting device. For example, cable 1A is terminated by connecting devices
100A and
100A', cable 2A is terminated by connecting devices 200A and 200A'. At a first
junction
8
CA 02835889 2013-11-12
WO 2012/162076 PCT/US2012/038274
box, the cable metallic ground layer of cable 1A, which is terminated at one
end by
connecting device 100A', is connected to the cable metallic ground layer of
cable 2B, which
is terminated at one end by connecting device 200B; the cable metallic ground
layer of cable
1B, which is terminated at one end by connecting device 100B', is connected to
the cable
metallic ground layer of cable 2C, which is terminated at one end by
connecting device 200C;
and the cable metallic ground layer of cable 1C, which is terminated at one
end by connecting
device 100C', is connected to the cable metallic ground layer of cable 2A,
which is
terminated at one end by connecting device 200A. Similarly, at a second
junction box, the
cable metallic ground layer of cable 2A, which is terminated at one end by
connecting device
200A', is connected to the cable metallic ground layer of cable 3B, which is
terminated at one
end by connecting device 300B; the cable metallic ground layer of cable 2B,
which is
terminated at one end by connecting device 200B', is connected to the cable
metallic ground
layer of cable 3C, which is terminated at one end by connecting device 300C;
and the cable
metallic ground layer of cable 2C, which is terminated at one end by
connecting device
200C', is connected to the cable metallic ground layer of cable 3A, which is
terminated at one
end by connecting device 300A.
As with splices, when cross bonding dead front terminals, it is preferable to
have two
sets of cross bonded terminals installed along the entire cable length in
order to create 3 equal
smaller lengths of cables that are required to complete the phase shift
cancelling of the
ground currents in the cable metallic ground layers along the entire length of
cable. These
two sets of terminals are installed to create 3 equal lengths of cable so that
the magnitude of
the ground currents created in each section are equal with allows for phase
cancelling when
the metallic ground layers of the cables are cross bonded.
Prior to the present invention, in applications such as wind farms, which
require long
distribution cable circuits, typically greater than 1,000 feet, splices were
created in the cables
for the purpose of cross bonding. It was not known to cross bond dead front
terminals. Prior
to the present invention, a significant impediment to cross bonding dead front
terminals was
the inability to electrically isolate the cable metallic ground (and cable
insulation shield layer)
from the outer semi-conductor layer of the connecting devices. At least one
embodiment of
the present invention solves that problem. By cross bonding the cables at the
dead front
terminals, as is done in the present invention, the need to create splices for
cross bonding in
long distribution cable circuits can be eliminated. Cross bonding the dead
front terminals of
the present invention is preferable over the previously used cross bonding
splices because the
connecting devices are above ground whereas the cable splices are below ground
and are
9
CA 02835889 2013-11-12
WO 2012/162076 PCT/US2012/038274
subject to moisture and mechanical damage. Furthermore, it is easier to locate
and repair
dead front terminals because they are above ground. An additional benefit of
at least one
embodiment of the present invention is that the connecting devices are
separable and can
serve as "test points" for very sensitive equipment to be utilized in the
detection of the failed
device(s).
Although specific embodiments have been illustrated and described herein for
purposes of description of the preferred embodiment, it will be appreciated by
those of
ordinary skill in the art that a wide variety of alternate and/or equivalent
implementations
may be substituted for the specific embodiments shown and described without
departing from
the scope of the present invention. This application is intended to cover any
adaptations or
variations of the preferred embodiments discussed herein. Therefore, it is
manifestly
intended that this invention be limited only by the claims and the equivalents
thereof.