Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02836756 2013-12-12
s
,
MOVEABLE LED ARRAY FLAPS IN IR LED CAMERA
FIELD
[0001] The field of the invention relates to security cameras and
more
particularly to cameras that operate in low-light conditions.
BACKGROUND
[0002] Security systems are generally known. Such systems are
typically
used to protect a secured area against intruders. In most cases, the secured
area is
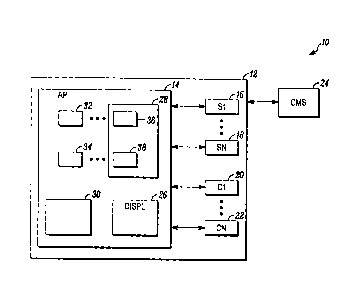
surrounded by a physical barrier (e.g., a fence, the walls of a building,
etc.). One or
more portals (e.g., doors, windows, etc.) through the physical barrier may
provide
access points for authorized persons.
[0003] One or more sensors may be located around the secured area
in order
to detect intruders. The sensors may be coupled to an alarm panel within the
secured area. Upon the detection of an intruder, the alarm panel may sound a
local
audible alarm to alert authorized persons within the area of the presence of
an
intruder.
[0004] The alarm panel may also send an alarm message to a central
monitoring station. The central monitoring station may respond by summoning
the
police.
[0005] The alarm system may include one or more security cameras.
The
cameras may be located along the periphery of the secured area or may be
located
inside to detect intruders that have been able to defeat the physical barrier.
[0006] Well cameras work well, they often rely upon ambient
lighting in order
to detect intruders. In dark areas they may not function properly.
Accordingly, a
need exists for better methods of providing illumination for the operation of
security
cameras.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0007] FIG. 1 is a block diagram of a security system under on
illustrated
embodiment;
- 1 -
CA 02836756 2013-12-12
-,
,
[0008] FIG. 2 is a side, perspective view of a camera of the
security system of
FIG. 1;
[0009] FIG. 3 is a cut-away view of the camera of FIG. 2;
[0010] FIGs. 4A-4B depict details of the camera of FIG. 2;
[0011] FIG. 5 depicts details of a light source of the camera
of FIG. 2; and
[0012] FIGs. 6A-6B show details of the operation of the camera
of FIG. 2.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF AN ILLUSTRATED EMBODIMENT
[0013] While embodiments can take many different forms,
specific
embodiments thereof are shown in the drawings and will be described herein in
detail with the understanding that the present disclosure is to be considered
as an
exemplification of the principles hereof, as well as the best mode of
practicing
same. No limitation to the specific embodiment illustrated is intended.
[0014] FIG. 1 is a block diagram of a security system 10 shown
generally in
accordance with an illustrated embodiment. The security system 10 may include
an
alarm panel 14 located within a secured area 12.
[0015] The security system 10 may include a number of sensors
16, 18 for
the detection of intruders. The sensors 16, 18 may be coupled to the alarm
panel
via a set of conductors or may be coupled to the alarm panel wirelessly. The
sensors 16, 18 may be limit switches located on doors or windows of the
secured
area. Alternatively, the sensors 16, 18 may be motion sensors (e.g., PIR
detectors)
that sense intruders within the protected area 12.
[0016] The security system 10 may also include a number of
cameras 20, 22.
As with the sensors 16, 18, the cameras 20, 22 may be coupled to the alarm
panel
14 via wires or may be coupled to the alarm panel 14 wirelessly.
[0017] Images from the cameras 20, 22 may be coupled to a
display on the
alarm panel or control console 26 associated with the alarm panel 14.
Associated
with the display may be a user interface (e.g., a keyboard) that may be used
for
control of the cameras 20, 22.
[0018] Included within the alarm panel 14 may be a number of
processor
apparatus (processors) 32, 34, operating under control of one or more computer
programs 36, 38 loaded from a non-transitory computer readable medium (memory)
28. As used herein, reference to a program step of programs 36, 38 is also a
reference to the processor 34, 36 that executed that step.
- 2 -
CA 02836756 2013-12-12
..
,
[0019] FIG. 2 is a side perspective view of a camera 20, 22
of the system 10.
As shown in FIG. 2, the camera 20, 22 may include a number of housings 40, 42.
The first housing 42 may provide overall support for the camera assembly. The
second housing 40 may move relative to the first housing 42 under control of a
pan
actuator 50 and a tilt actuator 52.
[0020] FIG. 3 is a simplified cut-away view of the camera of
FIG. 2. A sensor
board 44 and lens 42 are located adjacent an aperture 68 in the housing 40.
The
sensor board 44 includes the image sensing device (e.g., a CCD camera) and
associated circuitry.
[0021] The lens 42 may be supported by the sensor board 44. A
zoom
actuator 54 coupled to the lens 42 may provide a zoom capability that allows
the
camera 20, 22 to change a field of view of the camera 20, 22 by zooming in on
distance objects by increasing a magnification of the image detected by the
image
sensing device. As the camera 20, 22 zooms in on an object, the field of view
is
reduced. As the camera 20, 22 zooms out, the field of view is increased.
[0022] In general, the lens 42 operates to collimate and
focus light on the
image sensing device. The lens 42 defines an imaging axis 64 of the camera 20,
22
located in the center of the field of view.
[0023] Also included within the camera 20, 23 is an
adjustable light source 58
located in an annular space 62 between the camera and a periphery 70 of the
aperture 68 of the housing 40. The adjustable light source may include a
number of
light generating devices (e.g., light emitting diodes (LEDs)) 48 and a number
of
board flaps 46. The board flaps 46 are coupled between a portion 60 of the
camera
or lens 42 and the housing 40.
[0024] FIGs. 4A-B show details of the construction of the
board flaps 46
under one illustrated embodiment. As shown in FIG. 4A, an annulus of circuit
board
material may be provided in a first step. In a second step (as shown in FIG.
4B), the
annulus of circuit board material has been cut into a number of board flaps
46.
[0025] FIG. 5 shows details of the light sources 48 mounted
on the board
flaps 46. As shown in FIG. 5, each of the light sources 48 may have a
relatively
wide angle over which light is emitted. However, the light is predominantly
emitted
by the light source 48 along an axis of illumination 66.
[0026] Under illustrated embodiments, the light control
actuator 56 may be
used to adjust a light distribution to conform with a field of view of the
camera. In
this regard, when the zoom actuator 54 zooms out, the camera 20, 22 captures
- 3 -
CA 02836756 2013-12-12
images from a much larger field of view including a much larger area. In this
regard,
when the zoom actuator 54 zooms in on a distant object, it would be desirable
to
concentrate the light directed to the distant object over a much smaller area.
[0027] In order to adjust the lighting distribution of the light source
58, the
lighting control actuator 56 operates to move the camera or the portion 60 of
the
camera in a direction that is parallel to the imaging axis 64 of the camera
towards or
away from the aperture 68. This movement operates to tilt each of the board
flaps
46 relative to the imaging axis 64 of the camera 20, 22.
[0028] For example, a first end of each of the board flaps 46 is
pivotally
attached to the camera. As shown in FIG. 3, a hinge joint 72 attaches the
first end
to the camera or portion 60 of the camera. The second end of the board flap 46
may be located in a slot 74 between portions 40A and 40B of the periphery 70
of the
housing 40.
[0029] As the actuator 56 moves the camera or portion 60 of the camera
towards the aperture 68 (as shown in FIG. 6A), the board flaps 46 (and
illumination
axis 66) tilt away from the imaging axis 64. Similarly, as the actuator 56
moves the
camera or portion 60 of the camera backwards and away from the aperture 68 (as
shown in FIG. 66), the board flaps 46 (and illumination axis 66) tilt towards
the
imaging axis 64. The direct result of this movement by the light control
actuator is
that the area of illumination directly in front of the camera can be adjusted
to the
surveillance needs of the camera 20, 22.
[0030] Control of the light control actuator 56 (and size of the area of
illumination in the field of view) may be accomplished under any of a number
of
different methodologies. For example, a keyboard 30 on the control console 26
may
be used by a security guard to manually adjust the area of illumination in the
field of
view of the camera 20, 22.
[0031] Alternatively, an illumination processor 32, 34 may monitor a zoom
level of the camera via the zoom actuator 54. In this regard, a look up table
in
memory 28 may be used to retrieve an setting for the illumination actuator 56
that
corresponds to each position of the zoom actuator 54. In this way, the size of
the
area of illumination can be automatically matched to the field of view of the
camera.
[0032] It should be noted in this regard that when the zoom is increased,
the
size of the field of view is reduced, but the area viewed may be much further
away.
However, if the light sources 48 are tilted inwards to concentrate the light
on a
smaller area, the average illumination in lumens per square foot may be kept
- 4 -
CA 02836756 2013-12-12
constant by concentrating the total light output over a smaller area. This may
significantly improve the usefulness of the cameras 20, 22 at night or in
areas with
poor illumination.
[0033] Alternatively, a pan, tilt and zoom processor may activate the
appropriate actuators 50, 52, 54 to cause the camera 20, 22 to sweep through a
predetermined route within the secure area 12. The pan, tilt and zoom
processor
may also coordinate the area of illumination with the pan, tilt and zoom
positions via
the look up table.
[0034] In general, the system 10 includes a number of cameras 20, 22.
Each
of the cameras includes a housing having an aperture. The camera has an
imaging
axis. The camera is disposed in the housing with a lens of the camera disposed
adjacent the aperture providing a field of view extending outwards from the
housing
through the aperture, around the imaging axis of the camera, at least one
light
source having an axis of illumination that illuminates the field of view of
the camera,
the at least one light source is disposed in an annular space between the lens
and
periphery of the aperture, at least one flap that supports the at least one
light source
disposed in the annular space, the flap extends at least partially around the
annular
space, the flap is pivotally attached on a first end to the camera and on a
second,
opposing end to the periphery of the aperture and an actuator that moves the
camera along the imaging axis, the actuator alternatively extends the camera
outwards from the housing through the aperture and retracts the camera into
the
housing, where movement of the camera causes the at least one flap to tilt
relative
to the imaging axis, where movement of the camera outwards causes the axis of
illumination to tilt away from the imaging axis thereby enlarging an
illuminated
portion of the field of view and retraction causes the axis of illumination to
tilt
towards the imaging axis thereby reducing an illuminated portion of the field
of view.
[0035] In another embodiment, the camera has a lens and an imaging axis,
with the lens of the camera providing a field of view extending outwards from
the
camera, around the imaging axis of the camera, at least one light source
having a predominant axis of illumination that illuminates the field of view
of the
camera, the at least one light source is pivotally attached on a first end to
the
camera and on a second, opposing end to a support that is stationary relative
to the
camera and an actuator that moves the camera along the imaging axis, the
actuator
alternatively extends the camera outwards relative to the stationary support
and
retracts the camera back towards the stationary support, where movement of the
- 5 -
CA 02836756 2013-12-12
camera causes the at least one light source to tilt relative to the imaging
axis, where
movement of the camera outwards causes the axis of illumination to tilt away
from
the imaging axis thereby enlarging an illuminated portion of the field of view
and
retraction causes the axis of illumination to tilt towards the imaging axis
thereby
reducing an illuminated portion of the field of view.
[0036] In another embodiment, the camera has a housing with an aperture.
The camera is disposed in the aperture of the housing with a lens of the
camera
disposed adjacent the aperture providing a field of view extending outwards
from the
housing through the aperture, around the imaging axis of the camera. The
camera
includes a plurality of light sources having an predominant field of
illumination that
illuminates the field of view of the camera, the plurality of light sources
equally
spaced around an annulus between the lens and periphery of the aperture, a
plurality of flaps, each of the plurality of flaps supports at least one of
the plurality of
light sources disposed in the annular space, each of the plurality of flaps
extends at
least partially around the annular space, the flap is pivotally attached on a
first end
to the camera and on a second, opposing end to the periphery of the aperture
and a
lighting control actuator that moves the camera along the imaging axis, the
actuator
alternatively extends the camera outwards from the housing through the
aperture
and retracts the camera into the housing, where movement of the camera causes
the plurality of flaps to tilt relative to the imaging axis, where movement of
the
camera outwards causes the field of illumination to expand outwards and away
from
the imaging axis thereby enlarging an illuminated portion of the field of view
and
retraction causes the field of illumination to contract towards the imaging
axis
thereby reducing an illuminated portion of the field of view.
[0037] From the foregoing, it will be observed that numerous variations
and
modifications may be effected without departing from the spirit and scope
hereof. It
is to be understood that no limitation with respect to the specific apparatus
illustrated herein is intended or should be inferred. It is, of course,
intended to cover
by the appended claims all such modifications as fall within the scope of the
claims.
- 6 -