Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
POWER LINE PROXIMITY SENSING AND WARNING SYSTEM
CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS
[0001] This patent application is related to U.S. Provisional Patent
Application No.
61/580,918 filed on December 28, 2011, titled "POWER LINE PROXIMITY SENSING
AND WARNING SYSTEM", and U.S. Provisional Patent Application No. 61/747,187
filed on December 28, 2012, titled "VOLTEK NS SYSTEM".
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
[0002] Field of the Invention: The present invention relates generally to
proximity
sensors. More particularly, this invention relates to power line proximity
sensing and
warning systems, for enhanced safety of operators and their machinery around
high
voltage power lines. The embodiments disclosed herein may be configured as a
standalone power line warning device (PWD) system= or may be used in
conjunction with each other or with other conventional PWD systems.
[0003] Description of Related Art. Conventional power line proximity alarms
are
electronic radio units designed to detect the electromagnetic field that
surround active
high voltage power lines. This electromagnetic field is detected or sensed,
thereby
generating warning sounds to alert the operator of the machinery equipped with
the
power line warning device (PWD), that a high voltage has been detected within
the
vicinity of the machine.
[0004] Currently, the PWD market offers products that are analog based
(fused).
Such systems are purchased individually and perform a simple and single
function of
warning when an equipped piece of machinery is approaching a high voltage
power
line.
1
CA 2846703 2020-03-30
CA 02846703 2014-03-13
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0005] The embodiments of the invention disclosed here provide a user-friendly
approach to power line safety through a full line of completely digital and
highly
technical products that are interactive, collective, supportive of each other,
simple to
operate and ancillary to a base/main unit that can be configured in an array
of
combinations to accommodate any articulating, overhead boomed or extending
mobile
equipment type. The embodiments disclosed herein are believed to be more
accurate,
dependable than conventional systems and include a wider range of options and
features that no other PWD on the market offers.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0006] The following drawings illustrate exemplary embodiments for carrying
out the
invention. Like reference numerals refer to like parts in different views or
embodiments
of the present invention in the drawings.
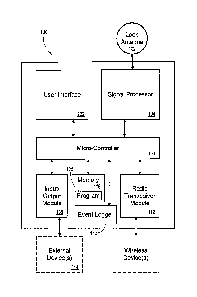
[0007] FIG. 1 is a block diagram of an embodiment of a power line proximity
sensing
and warning system, according to the present invention.
[0008] FIG. 2 is an embodiment of a user interface for use with the power line
proximity sensing and warning system shown in FIG. 1, according to the present
invention.
[0009] FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram of an environment in which the power line
proximity sensing and warning system shown in FIG. 1 might be used, according
to the
present invention.
[0010] FIG. 4 is a flowchart of an embodiment of a method for remotely
alerting an
operator of machinery when an extended structure of the machinery is moved
near high
voltage power lines, according to the present invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
[0011] The invention includes a novel suite of power line proximity sensing
and
warning systems, having a base or general configuration that may be upgraded
with
various enhanced feature embodiments and still other embodiments which may be
incorporated into existing PWD systems. The embodiments disclosed herein may
be
2
CA 02846703 2014-03-13
configured as standalone PWD systems or may be used in conjunction with each
other
or with other conventional PWD systems.
[0012] The various embodiments of the present invention provide a user-
friendly
approach to power line safety by manufacturing a full line of completely
digital and
highly technical products that are interactive, collective, supportive of each
other, simple
to operate and ancillary to a base/main unit that can be configured in an
array of
combinations to accommodate any articulating, overhead boomed or extending
mobile
equipment type. We believe our designs are more accurate, dependable and offer
a
wider range of options and features that no other PWD on the market offers.
The
following is a description of the various embodiments of power line proximity
sensing
devices, accessories and enhancements according to the present invention.
[0013] FIG. 1 is a block diagram of an embodiment of a power line proximity
sensing
and warning system 100 for use by an operator of machinery operating near high-
voltage power lines, according to the present invention. A commercial
embodiment of
system 100 is known as Voltek NSTM is available from United Safety, Inc.,
Kalispell,
Montana. System 100 may include a loop antenna 102 disposed about a structure
(not
shown) of the machinery (not shown). The structure, e.g., a crane boom, is
generally
configured for movement near the power lines. Antenna 102 runs along the boom
of
the machinery. The antenna is a loop of wire with both ends connected to the
signal
processor 104 input. One embodiment of the signal processor 104 processes and
filters the incoming signal and includes the following features, 60 band-pass
filter,
dynamics compression (apply a specific response curve), gain, and read signal
amplitude.
[0014] The loop antenna 102 may be in communication with a signal processor
104.
Signal processor 104 may be a digital signal processor or any other suitable
signal
processor capable of sending test signals through the loop antenna 102 and
receiving
those test signals to confirm proper antenna operation. Signal processor 104
may also
be configured for receiving field strength signals from the loop antenna 102
generated
by an electromagnetic field generated by the power lines (not shown, but see
FIG. 3
and related discussion) proximate to the loop antenna 102.
3
CA 02846703 2014-03-13
[0015] The system periodically performs an antenna self-test: Normally, both
ends of
the antenna wire are connected to the DSP Input For self-test mode, a set of
relays
disconnects one end from the DSP Input and connects it to the DSP Output The
DSP
outputs a 60 Hz sine wave test signal. If the antenna 102 is in working
condition, the
test signal will go through the antenna wire into the DSP Input. If the test
signal can be
detected, the test is Passed.
[0016] System 100 may also include a micro-controller 106 in communication
with the
signal processor configured for interpreting the received field strength
signals from the
loop antenna and comparing the received field strength signals to a user-
adjustable,
sensitivity level. Sensitivity adjustments allow the operator to set a warning
distance
based on the strength of the electromagnetic field surrounding the power line.
Micro-
controller 106 may further be configured for generating a proximity signal
based on the
received field strength signal. Micro-controller 106 may further be configured
for
graphically displaying the proximity signal on a color display, and audibly
warning the
operator when the proximity signal exceeds preset levels of field sensitivity.
[0017] The micro-controller 106 may be configured to read the signal amplitude
and
calculates a value based on the user-adjustable sensitivity level. The reading
is
displayed on a color-coded display meter. The three levels displayed are:
* GREEN - Safe Zone: the equipment is operating in at a safe distance from
power
lines.
* YELLOW - Warning Zone: the equipment is operating closer to power lines than
the
set safe distance. The Warning indicator turns on and the horn emits a pulse
tone,
reminding the operator to back the equipment away from the power lines until
it is in the
Safe Zone.
* RED - Danger Zone: the equipment is dangerously close to power lines. The
shutdown indicator turns on, the horn emits a solid tone, and the equipment is
forced to
shut down by engaging the Emergency Stop system, (e.g., emergency shutdown
button
206, FIG. 2).
[0018] System 100 may further include an input/output (I/O) module 108 in
communication with the micro-controller 106. The I/O module 108 may be
configured
for communicating with external devices, e.g., other computers or computer
peripherals
4
CA 02846703 2014-03-13
for retrieving data from the system 100 or for programming system 100.
Communications through the I/O module 108 may be according to any known serial
or
parallel synchronous or asynchronous interface standard, e.g., universal
serial bus
(USB). Such computer data communications interfaces are well-known to those
skilled
in the art and, thus, will not be further elaborated herein.
[0019] System 100 may further include an event logger 110 in communication
with the
micro-controller 106 for recording user interface button presses, user
interface
sensitivity adjustments, received field strength signals, alerts generated,
alarms
generated, system cable connections, power loss, errors and system status, all
as a
function of time. According to one embodiment, an integrated event logger is
capable of
generating a record of these events. These records can be accessed by any
suitable
computer (external device, shown at dotted box 114) installed with an
appropriately
coded software program, referred to herein as Voltek Systems T" Core T"
software (not
shown). The event logger 110 may include an internal date/time clock with a
battery
power backup to keep it running even when the system 100 is disconnected from
power. Whenever such an external computer running Voltek Systems TM Core TM
software downloads events from system 100, it automatically synchronizes the
event
logger 110 clock with the computer's clock.
[0020] System 100 may further include a radio transceiver module 112 in
communication with the micro-controller 106. The radio transceiver module 112
may be
configured for wireless communication with external wireless devices. System
100 may
further include memory 118 in communication with micro-controller 106. Memory
118
may be configured to store data from the event logger 110 or software
programming
code (program 120) with instructions for operating the micro-controller 106.
According
to one embodiment, a USB wireless adapter allows an external computer running
Voltek
Systems TM Core TM to wirelessly download events and perform other actions
without
having to connect a USB cable directly to system 100, however the option of
doing so is
available through I/O module 108.
[0021] FIG. 2 is an embodiment of a user interface 122 for use with the power
line
proximity sensing and warning system 100 shown in FIG. 1, according to the
present
invention. User interface 122 may include a power button 202 used to turn the
system
100 on and off. User interface 122 may also include a wireless link button 204
for
wirelessly linking the system 100 with one or more remote wireless devices.
According
to one embodiment, a two-way digital messaging system allows communication
with
remote wireless accessories over the radio transceiver module 112. User
interface 122
may also include an emergency shutdown button 206 that stops the machinery
from
further movement. User interface 122 may also include sensitivity adjust up
208A and
down 208B buttons for manually configuring the sensitivity of system 100. User
interface 122 may also include a graphical display using a red-yellow-green
field
strength bar 210. The graphical display may further include "shutdown" and
"warning"
indicators that flash or illuminate, according to the illustrated embodiment.
[0022] The Voltek ShadowTm, available from United Safety, Inc., Kalispell,
Montana
(the assignee of this application) is a remote control (see FIG. 3, 314) for
system 100,
an embodiment known as Voltek NSTM is also available from United Safety, Inc.
The
Voltek ShadowTM is 'a battery-powered remote controller (see FIG. 3, 314) for
system
100, also referred to herein as Voltek NSTM or the Voltek NSTM Powerline
Proximity
Alarm. The Voltek ShadowTM uses two-way radio communication (radio transceiver
112)
to allow remote operation and view the status of the main unit while operating
the
equipment from outside the cab or when a spotter needs to monitor powerline
safety
from an outside viewpoint.
[0023] Unlike many conventional remote control devices, any Voltek Shadow TM
can
be easily linked to any Voltek NS TM (system 100) without the hassle of
connecting a
cable, shipping the units to the manufacturer to be reprogrammed, or entering
codes.
Simply turn on both devices, press the link button on each device, and point
the Voltek
ShadowTm at the Voltek NSTM. The units instantly recognize each other and
establish a
radio link. This is very useful in situations where you have multiple units in
charging
cradles. Simple grab any one of them, take it to the equipment you will be
using for that
day, and link the devices together. According to one embodiment, the Voltek
Shadow TM
has the exact same controls as the Voltek NSTM with the addition of a "panic
button"
= that lets a spotter either warn the operator of a hazard or shutdown the
machine
remotely to prevent an accident. The Voltek ShadowTM also alerts the user when
radio
communication has been lost or the battery is low. Voltek ShadowTM has a
serial
6
CA 2846703 2020-03-30
CA 02846703 2014-03-13
number, so each main unit can establish a link with a specific remote unit
without
interfering with other nearby units. A proprietary messaging system sends
messages
between units to communicate button presses, sensor readings, status changes,
event
log data, etc. The Link button 204 on user interface 122 of system 100 may
include an
Infrared LED under it. The Voltek ShadowTM enclosure may include an Infrared
receiver
under an infrared-passing window in the front of the enclosure.
[0024] The remote unit links to the main unit like this:
* Turn on both units
* press the Link button on each unit
* point the remote at the main unit. The main unit transmits an ID code to the
remote
unit via an Infrared transmitter.
* The remote uses the ID code to establish a digital radio link with the main
unit. The ID
code tells the remote what "address" to send messages to when transmitting
messages
over the radio.
[0025] FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram of an environment in which the power line
proximity sensing and warning system 100 shown in FIG. 1 might be used,
according to
the present invention. As shown in FIG. 3, a machinery 300 operated by an
operator
302 may have an extended structural member, simply structure 304. System 100
once
installed, includes the loop antenna 102 disposed about the surface of the
structure
304, where it can sense invisible electromagnetic fields from power lines
(three shown
generally at arrow 306). In the configuration shown in FIG. 3 the operator 302
has
access to the user interface 122 of system 100, typically in the cab of the
machinery.
From that position, operator 302 can control the system 100 directly.
Alternatively, a
remote user 310 can control system 100 using a wireless remote controller 314,
e.g.,
the Voltek Shadow. Remote user may also be holding a wireless computer 316
running Voltek Systems TM Core TM software.
[0026] FIG. 4 is a flowchart of an embodiment of a method for remotely
alerting an
operator of machinery when an extended structure of the machinery is moved
near high
voltage power lines, according to the present invention.
[0027] An upgraded feature referred to herein as "Voltsense TM " may be added
to the
"Voltek NS TM " embodiment in order to form a wireless antenna sensor PWD
system.
7
Another embodiment, referred to herein as "Voltek ShadowTM" is a hand held
remote for
use with the general "Voltek NSTM" embodiment, with or without the
"VoltsenseTM"
upgrade, for spotters or operators controlling machinery remotely. Another
upgrade
embodiment, referred to herein as "Line Defense WLTm", replaces the wired
sensor
antenna of the "Voltek NSTM" embodiment with access to the load cable as a
wireless
sensor antenna by way of a novel connector referred to herein a "Pour Cap
LinkTm".
Still another upgrade embodiment, referred to herein as "Line Defense WDTm",
extends
the wired sensor antenna of the "Voltek NSTM" embodiment with access to the
load
cable as a sensor antenna by way of the "Pour Cap LinkTM" connector. Yet
another
embodiment, referred to herein as "Voltek ScribeTM" is an upgrade for use with
any of
the above PWD embodiments and may also be used with other conventional PWDs as
an event logger and data recorder. Finally, the "Voltek PDTM" embodiment is
disclosed.
The "Voltek PDTM" is a completely standalone PWD device for use on a single
person,
e.g., first responders, tree trimmers, lineman, etc.
[0028] Voltek NSTM
[0029] A general PWD embodiment, referred to herein as "Voltek NSTM", includes
a
wired antenna sensor. In its most general embodiment, the Voltek NSTM is a PWD
for
heavy machinery and motorized equipment that warns the operator, spotter,
ground
crew and by-standers when the machinery is approaching active high voltage
power
lines. According to one embodiment, the Voltek NSTM detects both 50 Hz and 60
Hz
without re-programming or manual setting. U.S. Provisional Patent Application
No.
61/747,187 filed on December 28, 2012, titled "VOLTEK NS SYSTEM", discloses
engineering drawings, schematics and bills of materials for a presently
preferred
embodiment of a power line proximity sensing and warning system, according to
the
present invention.
[0030] To detect electrostatic, or electromagnetic fields, an antenna wire
must be
connected and placed in or near the field lines emanating from the
electromagnetic field
source, e.g., high voltage power lines. To ensure that the antenna wire is
completely
intact, the antenna is looped. Both ends are connected to a control board so
that a
continuity check can be performed. If there is a break in the wire, an error
indicator on
8
CA 2846703 2020-03-30
CA 02846703 2014-03-13
the control panel alerts the operator. All basic Voltek NSTM units come with
the hard
wire antenna. However, this embodiment is configured to be equipped with
wireless
capability should the owner choose to upgrade to a wireless sensor in the
future.
[0031] Voltek NSTM utilizes the most modern technologies. Digital signal
processors
and microprocessors ensure precise and reliable operation of the Voltek NS TM
.
Updatable firmware allows features and behavior to be modified on-site without
changing hardware, should the need arise. According to one embodiment, the
Voltek
NS TM may be configured to operate on 12V or 24V power systems without any
changes
or need for external converter. Self-resetting circuit protection eliminates
the need to
replace fuses. Modern digital radio transceivers are utilized for wireless
communication
with various accessories.
[0032] The Voltek NSTM is typically mounted inside the cab of the machine
where the
operator can interact with the system. Sensitivity adjustments allow the
operator to set
a warning distance based on the strength of the electrostatic field
surrounding the high
voltage power line. When the equipment moves inside the set distance, audible
and
visual alerts are activated. If the operator continues to move toward the
power line, the
Voltek NSTM can automatically shut down the machinery to prevent contact with
the
power line. A light emitting diode (LED) bar graph on the control panel
indicates the
detected field strength and whether the warning or auto-shutdown thresholds
have been
exceeded.
[0033] All Voltek NS units come equipped with an internal "event logger/data
recorder" (Voltek Scribe TM technology as described below.). Software
implementing the
method embodiments of the present invention through computer instructions for
execution in a microprocessor or other specialized hardware, may be provided
at the
point of purchase. The software may be loaded onto owner computer (e.g.,
Windows
7TM or newer). The computer then, by Voltek NSTM universal serial bus (USB)
connection, downloads the stored data into the pre-loaded software program for
interpretation of the owner as well as view diagnostics, error information,
change
options and/or upload new firmware and upgrades.
[0034] Voltek Shadow 1M
[0035] The Voltek Shadow TM is a wireless hand held remote and alert unit
providing
9
CA 02846703 2014-03-13
the same adjustments and status indicators as the main unit (Voltek NS TM).
The Voltek
ShadowTM is synchronized with the main unit at all times. This wireless remote
is useful
when the operator is remotely controlling the machinery (e.g., concrete pumps,
conveyor s trucks, etc.) or when a spotter needs to observe operation from a
ground
position.
[0036] Voltek Shadow TM has override capabilities to shut down the machinery
before
or when power line contact is eminent or the operator is maneuvering the
machinery
blind (cannot see the load). Voltek ShadowTM uses the latest in advanced
technology
available in wireless, microprocessing and re-chargeable LI battery
technology.
[0037] VoltSense TM
[0038] The VoltSense TM feature incorporates wireless remote sensors to the
system
(Voltek NSTM) in order to ensure complete coverage of the machinery without
the need
of a hard wire antenna. Wireless sensors can be powered by various sources and
may
be provided in various detecting configurations, according to embodiments of
the
present invention.
[0039] Due to the nature of existing wireless antenna sensing, the sensing or
detecting field is typically radial or round in shape. By addition of an
external micro-
antenna to the wireless sensor and continuing it to a given point, the sensing
field
becomes linear or elongated, thus, eliminating the need for additional sensors
to cover
a linear area or object such as a boom or extension.
[0040] According to one embodiment, mounting of VoltSense TM may be achieved
by
magnetic coupling to metallic structure of the machine to which it is
attached. According
to other embodiments, the VoltSense TM may be mechanically mounted to the
machine
structure. According to one embodiment, the power source for VoltSense TM may
be the
latest lithium (LI) battery technology with solar backup and recharge options.
However,
any suitable power source may be used with the embodiments of the invention
described herein.
[0041] To establish a wireless link between the main unit (Voltek NSTM) and
the
wireless remote units and sensors, a link cable is connected between the
units. Once
the link has been established and the units synchronized, the cable is
unplugged and
the devices will communicate with each other within their own wireless network
without
CA 02846703 2014-03-13
interference from other nearby Voltek NSTM systems. If any associated device
loses its
communication link, an error indicator will alert the operator at the Voltek
NS' m and Volt
ShadowTm control panels.
[0042] Line Defense WLTM
[0043] The Line Defense WLTM is a wireless load line sensor. Again, utilizing
the
same wireless technology as with Voltek NSTM, Voltek Shadow TM and VoltSense
TM , this
wireless utility is the first of its kind in the world. Never before has any
PWD
manufacturer been able to protect the load line of a crane or mobile
machinery. By
attaching a proprietary connection (referred to herein as Pour Cap Linkrm and
discussed
further below), wireless sensor, microprocessor and additional hardware to
either end of
the load line (lifting cable) of a crane, the sensor utilizes the load line as
an extension of
itself though that connection by unconventional (never realized) means. Thus
the cable
not only is protected but becomes part of the sensor itself. Line Defense WLTm
is
powered by the latest in LI technology and solar back-up and re-charge.
[0044] Line Defense WDTM
[0045] The Line Defense WDTM is a wired load line sensor. Line Defense WD Tm
is a
method of load line protection that is directly attached to the cable/load
line through the
Pour Cap Link Tm connection at either end of the cable/load line of a crane
with the
Voltek NSTM hard wire antenna. Before now, the load line has been considered a
single
strand conductor (wire) due to way a cable is made. Therefore, a loop cannot
be
obtained to complete the continuity of the antenna. The inventors have
designed a
connection (Pour Cap LinkTM) that allows Voltek NSTM system to utilize the
cable/load
line as an extension of the sensor/antenna. Line Defense WD is a method of
sensing
the electrostatic field through the load line/cable powered by the main unit
Voltek NSTM.
[0046] Voltek Scribe
[0047] The Voltek Scribe TM is an event logger and data recorder. The Voltek
Scribe TM
utilizes the same technology as described above and utilized internally within
Voltek
NS TM . The Voltek Scribe TM may be used to time and date stamp the events of
any
PWD. The Voltek Scribe TM comes with software for Microsoft Windows XPTM and
is
compatible with newer versions of operating systems and computers/laptops.
According to one embodiment, the Voltek Scribe TM may be configured to store
up to
11
CA 02846703 2014-03-13
3500 events. The Voltek Scribe T" may be configured to download events, view
diagnostics, change options and upload new firmware to computer though an
external
USB port. The Voltek Scribe TM may be powered by direct connection to the
battery of
the machine to which it is attached or installed.
[0048] Voltek PD TM
[0049] The Voltek PDT" is smaller personally worn power line sensing and
warning
device. The Voltek PDTM may be thought of as a condensed version of the Voltek
NSTM. The Voltek PDTM may be worn on the body with various carry or attachment
options (clip, pouch, etc.). The Voltek PDTM may be configured with all the
same
features (with exception of "event logger") as Voltek NSTM with the freedom of
Voltek
Shadow. The Voltek PDTM may be configured with the following features: compact
(2
way radio size), audio alert, LED warning and function indicators, back-lit
control panel
(for night/dark conditions), waterproof, impact resistant , re-chargeable LI
battery
technology with charging cradle.
[0050] Pour Cap LinkTm
[0051] The Pour Cap LinkT" is a novel connector that is monolithically
attached to the
end of the machine load cable. Once the Pour Cap LinkT" is attached to the
load line
cable, either one of the Line Defense WLT" or the Line Defense WDTM can then
be
attached to the Pour Cap LinkTM in order to utilize the load cable as part of
the system
sensor. Pour Cap LinkTM is a "hyper-link" that magnifies or amplifies the
system sensor
at the load cable end. The Pour Cap LinkTM is unique in that it amplifies the
signal and
makes a single wire/conductor (the load cable) into a closed loop sensing
system.
[0052] While the foregoing advantages of the present invention are manifested
in the
illustrated embodiments of the invention, a variety of changes can be made to
the
configuration, design and construction of the invention to achieve those
advantages.
Hence, reference herein to specific details of the structure and function of
the present
invention is by way of example only and not by way of limitation.
12